Ch.3 The Microscope
1/9
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
10 Terms
Types of Microscopes
Compound light microscopes
Commonly used in veterinary in-house laboratories
Electron microscopes
Research setting or large human medical facilities
Fluorescent microscopes
Phase-contrast microscopes
Reference laboratories
Dark field microscopes
Reference laboratories
Compound Light Microscope
Generate image by using a combination of lenses.
Optical tube length
Distance between the objective lens and the eyepiece
160 mm in most
Mechanical stage
Holds slide
The mechanical stage controls move the stage back and forth, and left to right
Coarse and fine focus knobs
Used to focus objects
Substage Condenser
Consists of two lenses that focus light from the light source on the object
Focused by raising or lowering the condenser
Aperture Diaphragm (Iris Diaphragm)
Opens and closes to control the amount of light illuminating the object.
Compound Light Microscope: Two Separate Lens Systems
Ocular
Located in the eyepiece
Usually ×10 magnification
Binocular—two eyepieces
Monocular—one eyepiece
Objective
3 to 4 objective lenses, each with different magnification
×4-scanning
x10-low
x40-high dry
x100-oil immersion
x50-low oil immersion
Magnification
Total magnification is calculated by
multiplying the ocular magnification by the objective magnification power.
Example
×10 (ocular lens) × ×40 (objective lens) = ×400 total magnification
Adjusting the Köhler Illumination
Care and Maintenance
Follow manufacturer guidelines.
Use only high quality lens paper to clean lens.
Solvent is only methanol or specially designed product.
Excessive oil can be removed with xylene.
Can dissolve adhesives that secure lens.
Wipe clean.
Cover when not used.
Annual cleaning and adjustment by a professional
Extra lightbulbs
Proper location in lab
Protect from excessive heat and humidity
Avoid jarring
Carry with both hands!!!

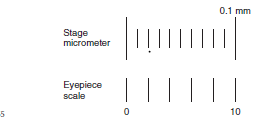
Calibration
Important in identifying objects on the slides.
Parasite ova often look similar, but size helps to identify them.
Should be performed on every microscope in the practice.
Stage micrometer
Ocular micrometer
The stage micrometer is a microscope slide etched with a 2-mm line marked in 0.01-mm (10-μm) divisions.
Operating Microscope
Operating Microscope
Digital Microscopy
Use optics and a camera to capture an image.
Photomicrographs can be added to patient files.
Becoming more affordable.
Evaluate cost, resolution, and quality of images.