Flight Mechanics - TU Delft
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
108 Terms
Plain Flap,
Split Flap
Slotted Flap
Fowler Flap
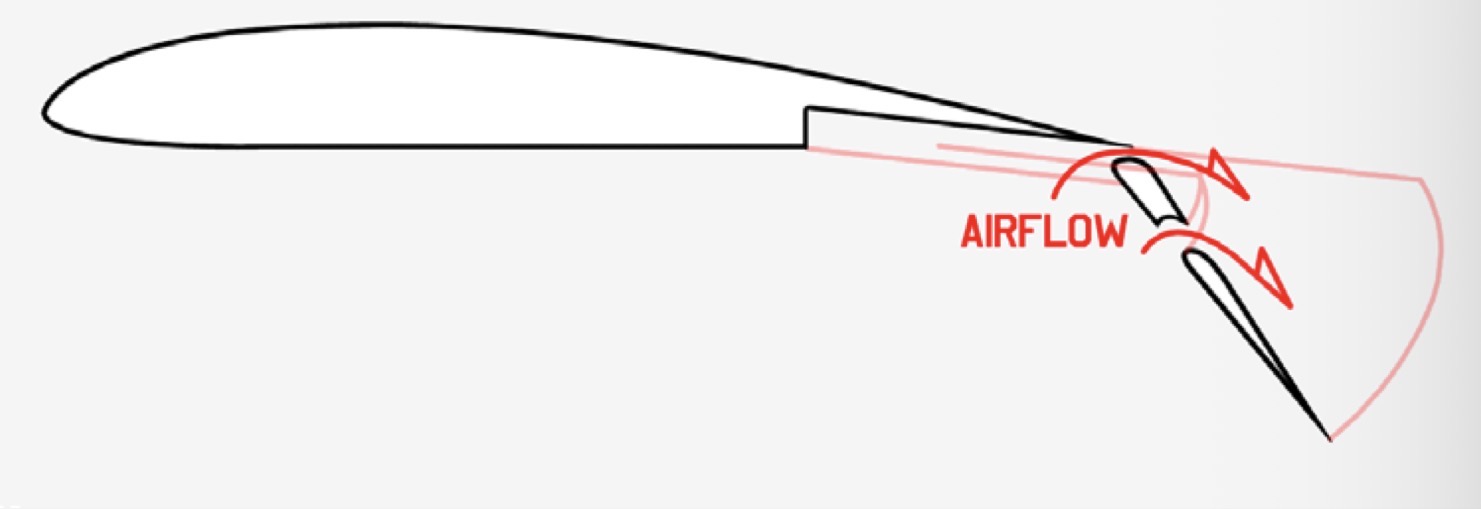
Double-slotted Fowler Flap
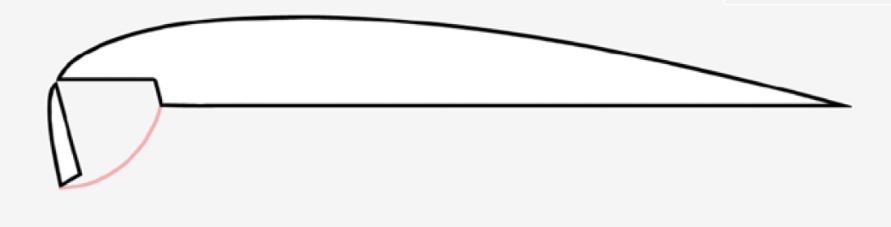
Krueger Flap
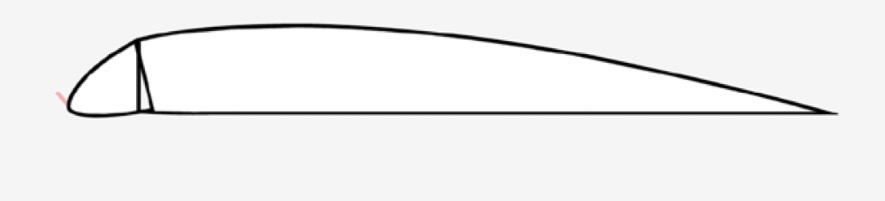
Leading Edge Droop

Handley-Page Slot
What is the mechanism and function of a Plain Flap?
Mechanism: Trailing edge section hinges downward.
Function: Increases the wing’s camber, increases both lift and drag.
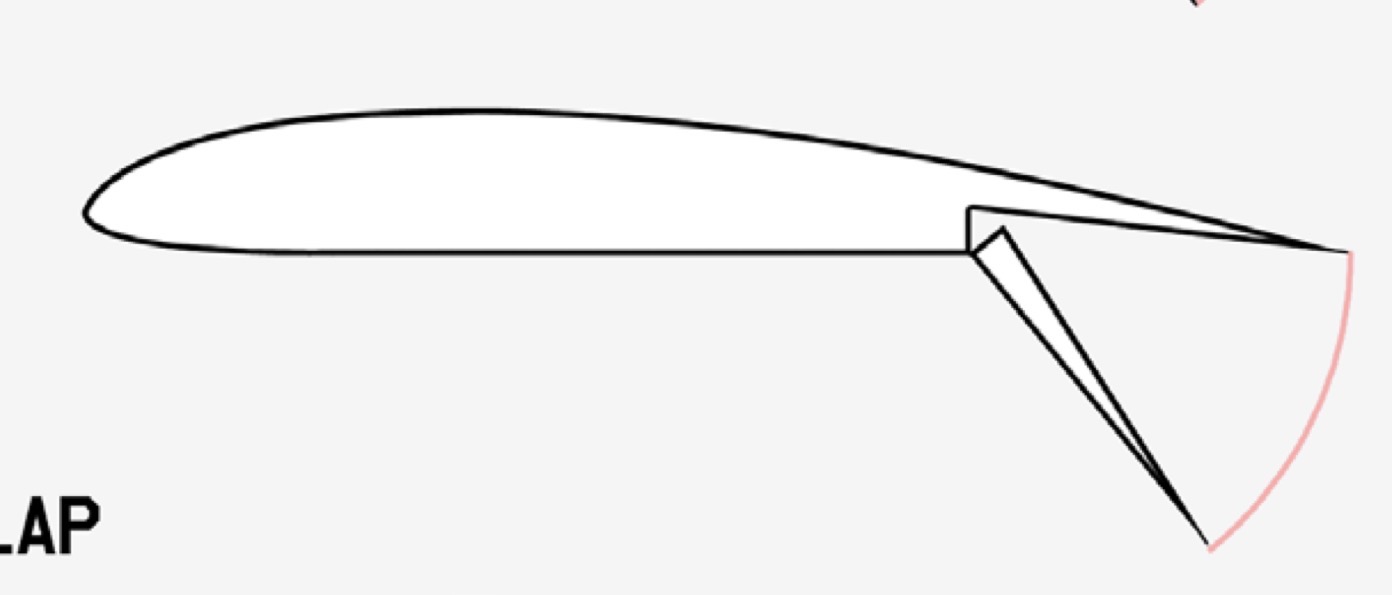
What is the mechanism and function of a Split Flap?
Mechanism: Only the bottom surface of the trailing edge hinges downward.
Function: Increases lift but increases drag a lot.
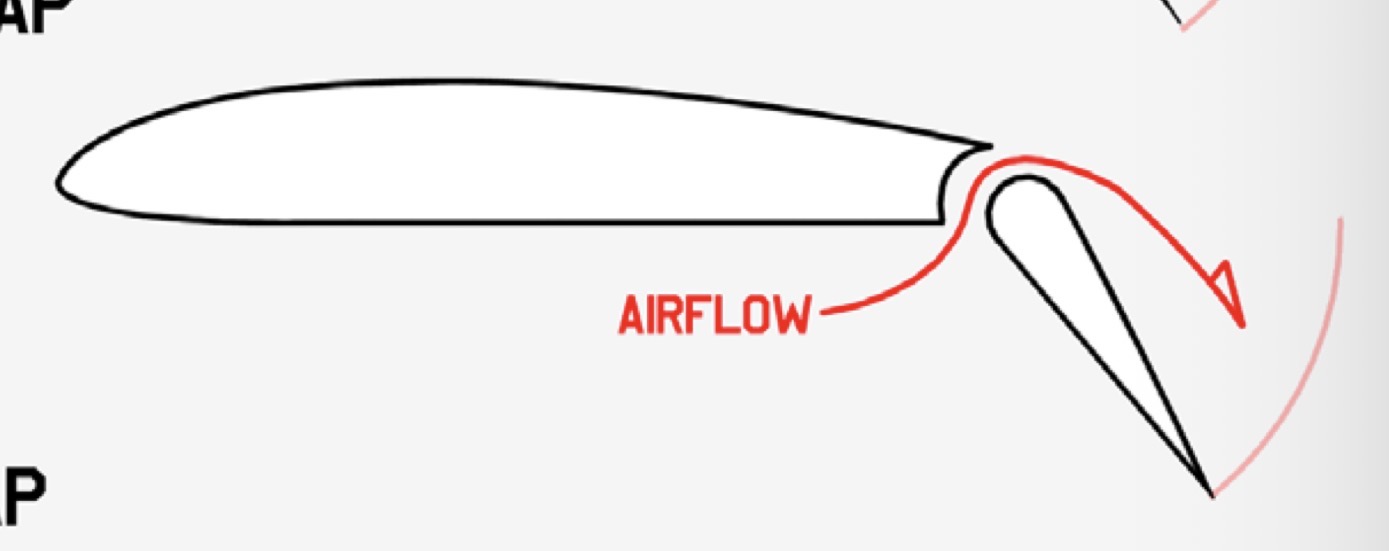
What is the mechanism and function of a Slotted Flap?
Mechanism: A flap hinges down, creating a slot.
Function: The slot reenergizes the air with high pressure air, delaying flow separation (stall)
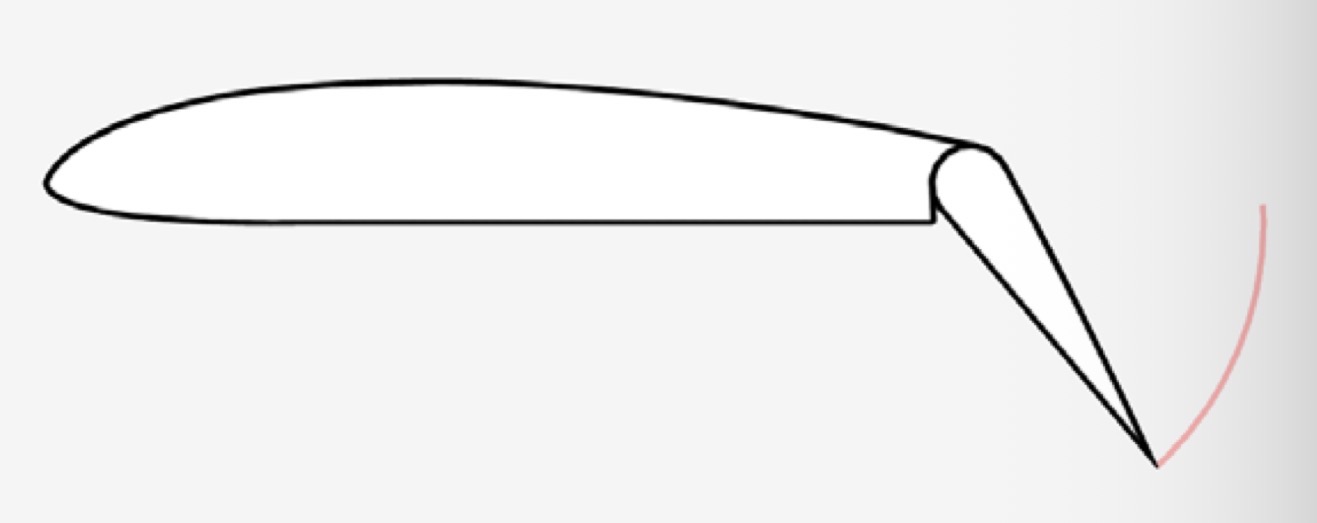
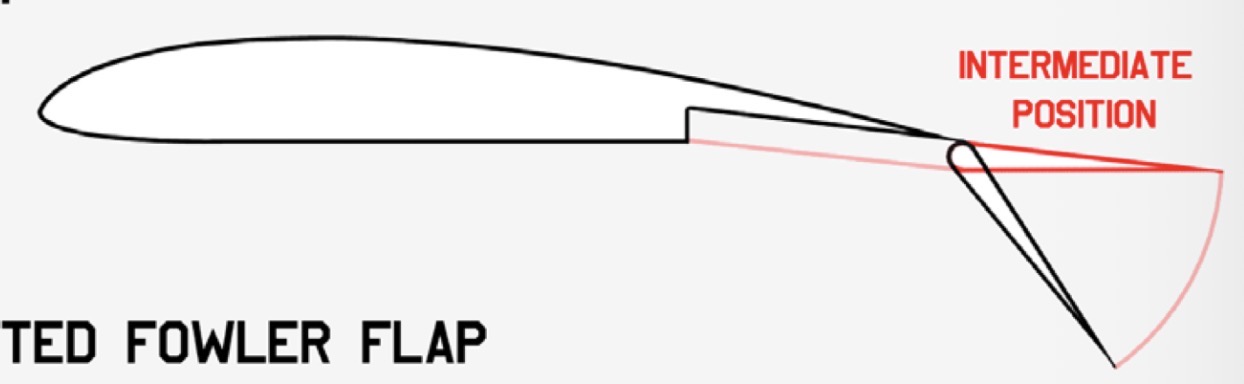
What is the mechanism and function of a Fowler Flap?
Mechanism: Slides backward and then hinges downward.
Function: Increases both surface area and camber, large increase in lift.
What is the mechanism and function of a Double-slotted Fowler Flap?
Mechanism: A Fowler flap which itself splits into two sections (double slots).
Function: Same as a Fowler flap, but at higher AoA from the double slots.
What is the mechanism and function of a Krueger Flap?
Mechanism: Leading edge device which hinges downward and forward.
Function: Increases camber and directs airflow to the top side, delaying stall.
What is the mechanism and function of a Leading Edge Droop?
Mechanism: Leading edge device where the nose section pivots downward.
Function: Increases camber and allows for higher AoA.
What is the mechanism and function of a Handley-Page (Slat)?
Mechanism: Leading edge device where a separate airfoil section (slat) moves forward.
Function: Opens a slot which directs high-energy air over the top, delaying stall.
The Earth Axis System is denoted as ___ and is attached to ___.
Xg, Zg and the ground, stationary
The Moving Earth Axis System is denoted as ___ and is attached to ___.
XE, ZE and the aircraft’s position (not rotated)
The Body Axis System is denoted as ___ and is attached to ___.
XB, ZB and the fuselage
The Air Path Axis System is denoted as ___ and is attached to ___.
XA, ZA and the air speed vector VA
The force perpendicular to the air speed vector in the KD
mV(dγ/dt) (m=W/g)
The force parallel to the air speed vector in the KD
m(dV/dt) (m=W/g)
Climb Angle
γ (between XE and XA)
Thrust Angle
αT (between XA and the thrust vector T)
Angle of Attack (geometric)
α (between XA and XB)
Pitch Angle
θ (between XE and XB)
Relationship between the angles in the FBD and KD
θ = γ + α
The equation of motion parallel to VA
T*cosαT - D - W*sinγ = (W/g)(dV/dt)
The equation of motion perpendicular to VA
L - W*cosγ + TsinαT = (W/g)V(dγ/dt)
Steady Flight means…
The forces and moments acting on the aircraft do not vary in time, neither in magnitude, nor in direction (dV/dt = 0)
Horizontal Flight means…
The aircraft remains at a constant altitude (γ = 0)
Symmetric Flight means…
The angle of sideslip is zero and the plane of symmetry of the aircraft is perpendicular to the earth (β=0 and the aircraft is not turning)
Straight Flight means…
Flight in which the center of gravity of the airplane travels along a straight line (dγ/dt = 0)
Minimum Air Speed is obtained from…
Maximum CL
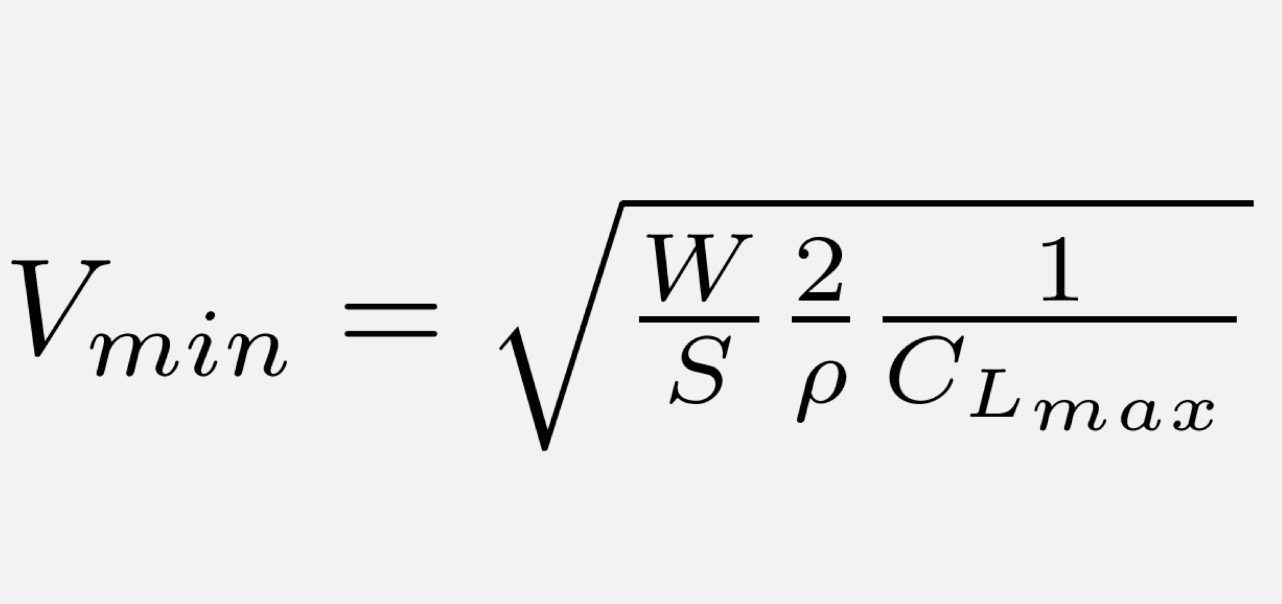
Optimal Air Speed is obtained from…
Optimal CL
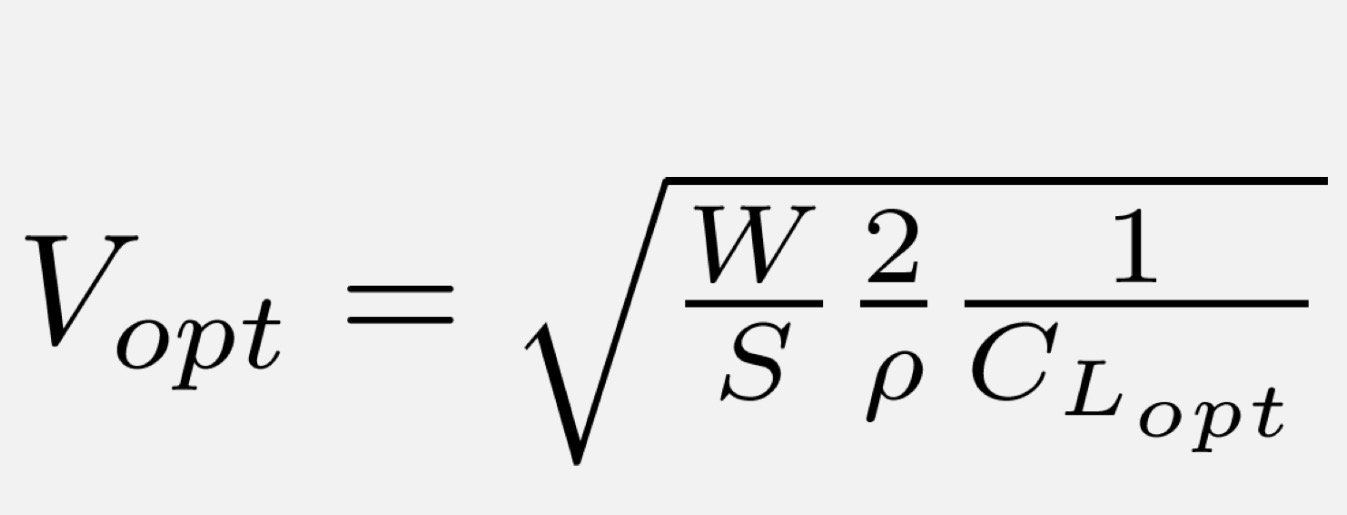
The effect of weight on the performance diagram is…
The curve shifts up and to the right (optimal airspeeds changes)
An aircraft’s speed is stable if…
If its in the frontside of the power curve (i.e. faster than the minimum)
An aircraft’s speed is unstable if…
If its in the backside of the power curve (i.e. slower than the minimum)
CDA is an acronym for…
Continuous Descent Approach
ILS is an acronym for…
Instrument Landing System (guides the aircraft along the flight path)
A Steep Climb means…
Maximum Climb Angle, γ
A Fast Climb means…
Maximum Rate of Climb, ROC
The effect of air density on the glide path angle (negative γ)
Decreases with increasing density (the drag is constant, D=(CD/CL)W, while lift is proportional to ρ)
What is a Hodograph (Polar of a glider)
A graph showing Rate of Descent (ROD) as a function of Air Speed (V = sqrt(V²v + V²h))
Increasing altitude makes the drag curve in the performance diagram…
Shift to the right
Increasing altitude makes the power required curve in the performance diagram…
Scale up and to the right (each point is move along a line directed away from the origin)
How is the thrust from a jet engine affected by increased altitude?
Decreased, since T/T0 = ρ/ρ0
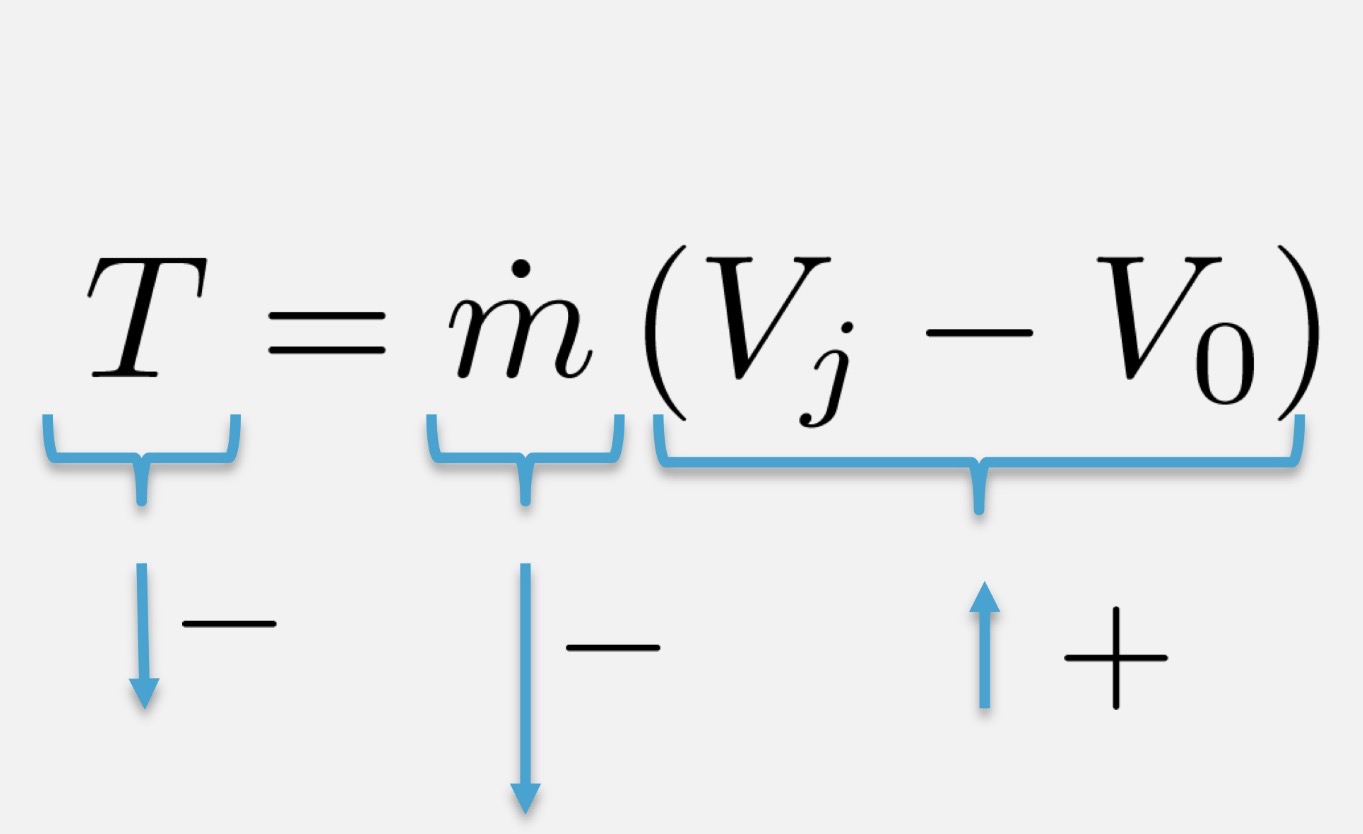
How is the power avaliable from a propeller engine affected by increased altitude?
Decreased, since P/P0 = ρ/ρ0
How is the minimum air speed affected by increased altitude?
Increased
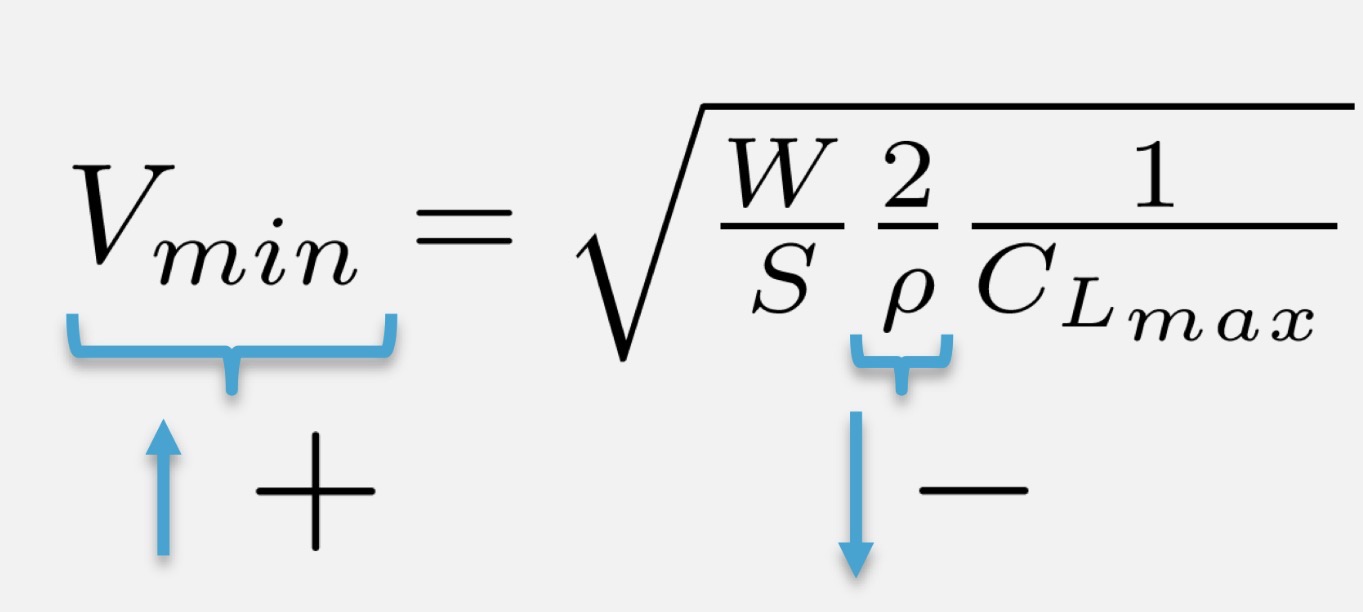
Why does the minimum air speed curve deviate to higher speeds at high altitudes?
The curve deviates when the limits goes from as stall limit to power limit. I.e. when the maximum thrust is lower than the tip of the backside of the power curve.
If, for a certain gain in altitude, the aerodynamics of the aircraft is more affected than the propulsion, how is the maximum airspeed affected?
Increase, since the drag curve shift to the right more than the thrust is shifted down (aerodynamics dominant)
If, for a certain gain in altitude, the propulsion of the aircraft is more affected than the aerodynamics, how is the maximum airspeed affected?
Decreased, since the thrust is shifted down more than the drag curve is shifted to the right (propulsion dominant)
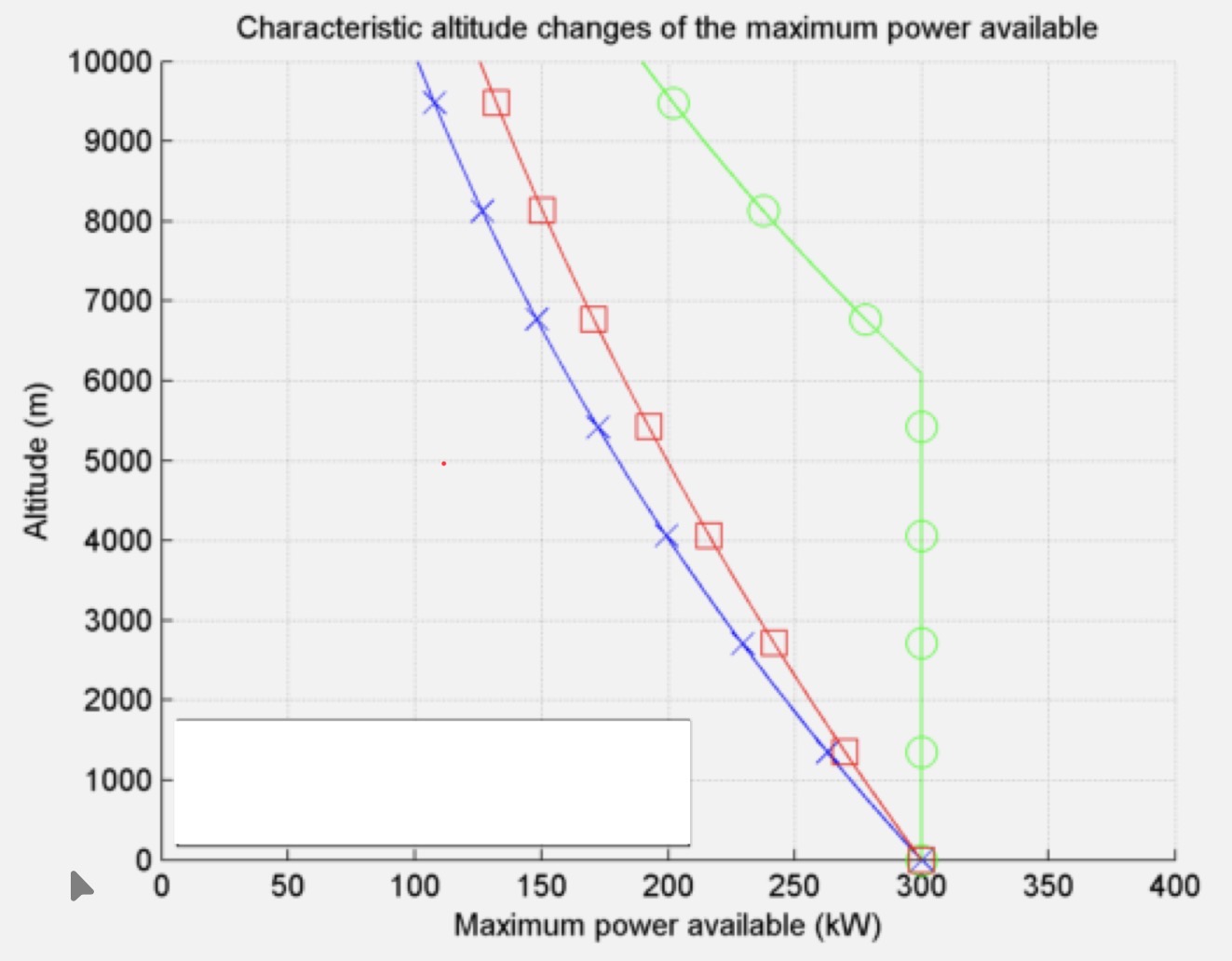
What kind of propulsion produces the performance graph in blue?
Piston Engine
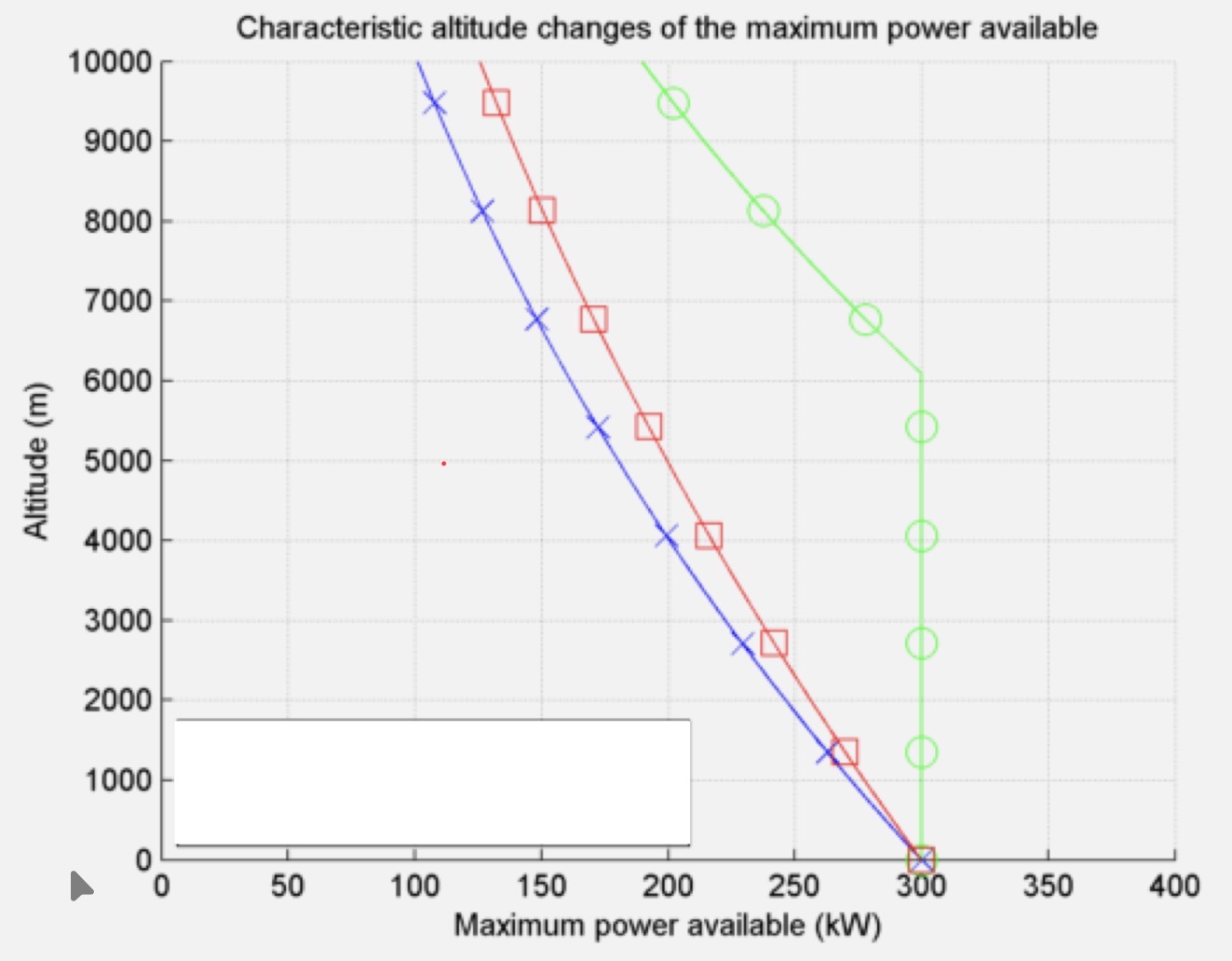
What kind of propulsion produces the performance graph in green?
Supercharged Piston Engine
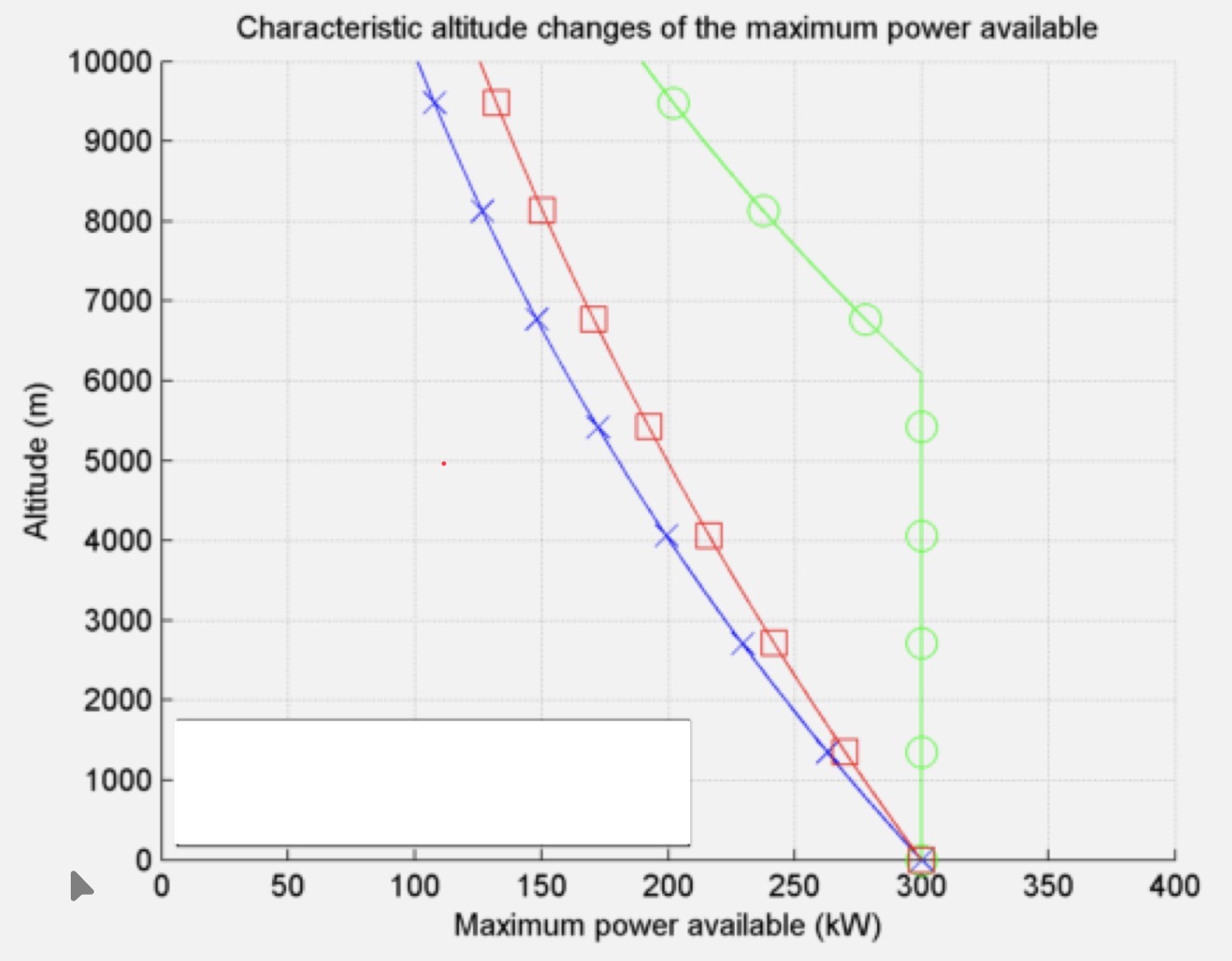
What kind of propulsion produces the performance graph in red?
Turboprop
The place where stall, thrust and maximum rate of climb intersect is called…
Theoretical ceiling or coffin corner
The altitude at which the rate of climb (ROC) is zero is called…
Absolute ceiling (or theoretical ceiling)
The altitude at which the maximum rate of climb (ROCmax) is below minimum rate of climb is called…
Service ceiling (usually at MROC=100 ft/min)
Optimizing for high altitude flight, h max, means…
High aspect ratio
Low zero-lift drag
Propulsion system designed for low density and low temperature
The total drag coefficient, CD, is made up of…
Wing drag coefficient (CDw) and Parasitic drag coefficient (Σ(CDnSn)/S)
The wing drag coefficient, CDw, is made up of…
Profile drag coefficient (CDp) and Induced drag coefficient (CDi)
Jet power
Pj = ½Vj² - 1/2V0²
Jet power avaliable
Pa = TV
Jet total efficiency
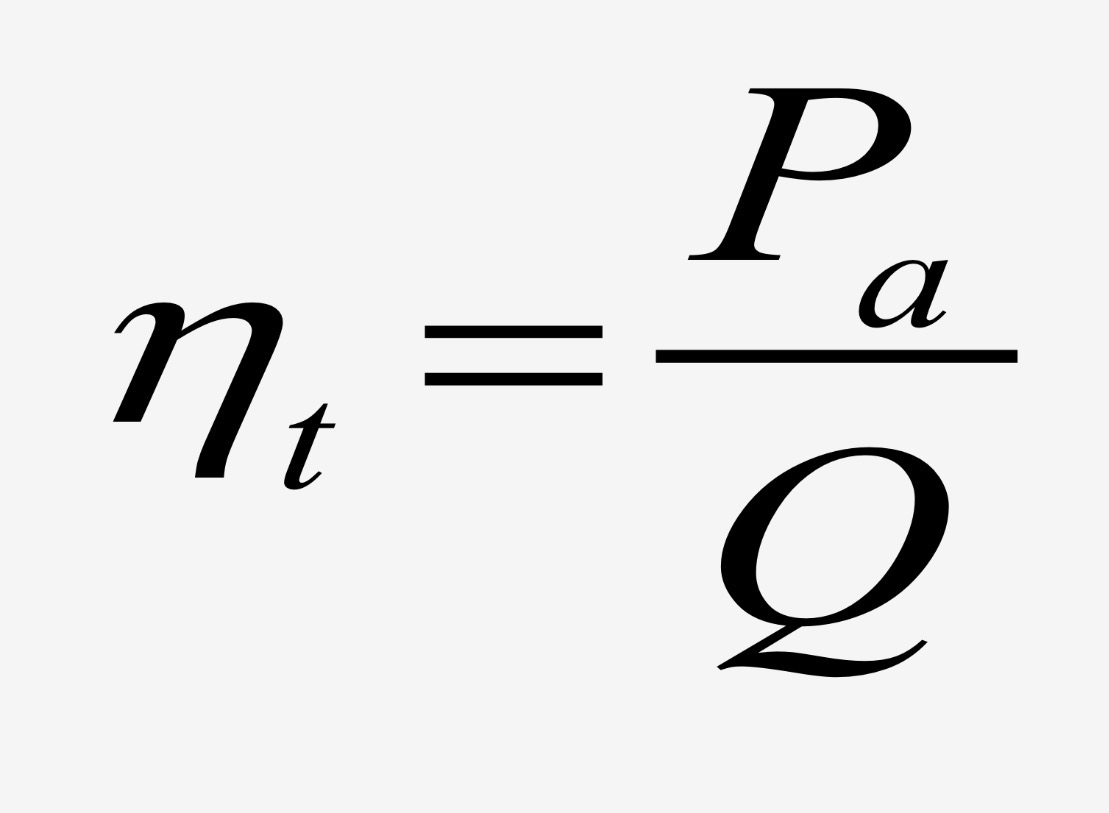
Jet thermal power
H = Amount of energy per unit fuel
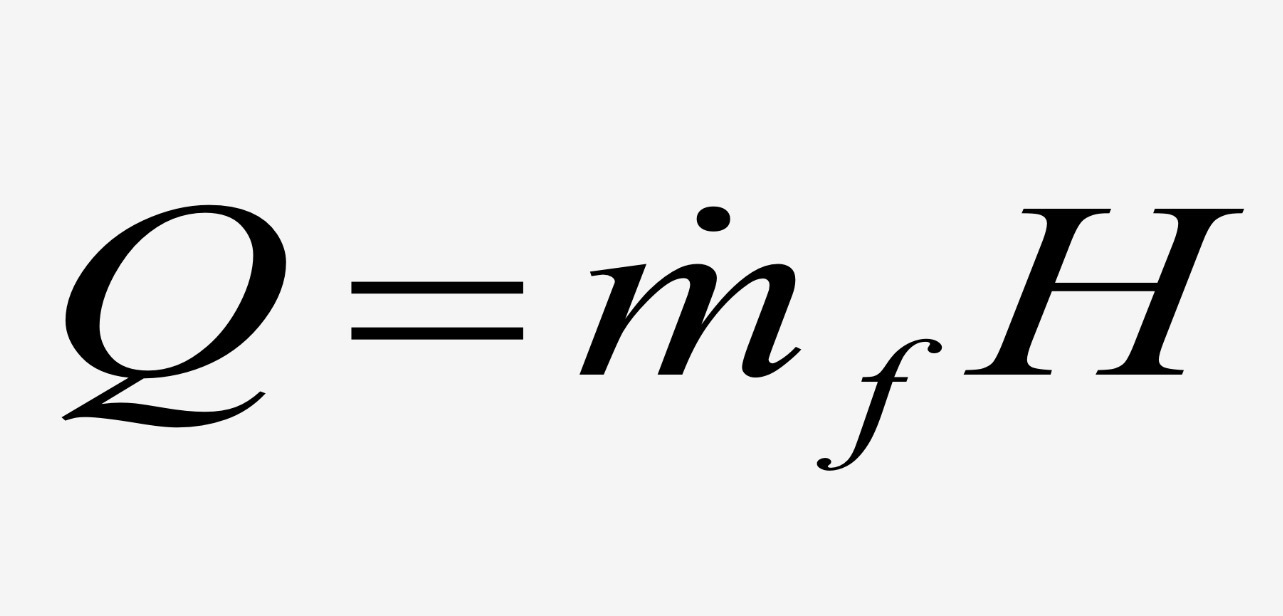
Jet thermal efficiency
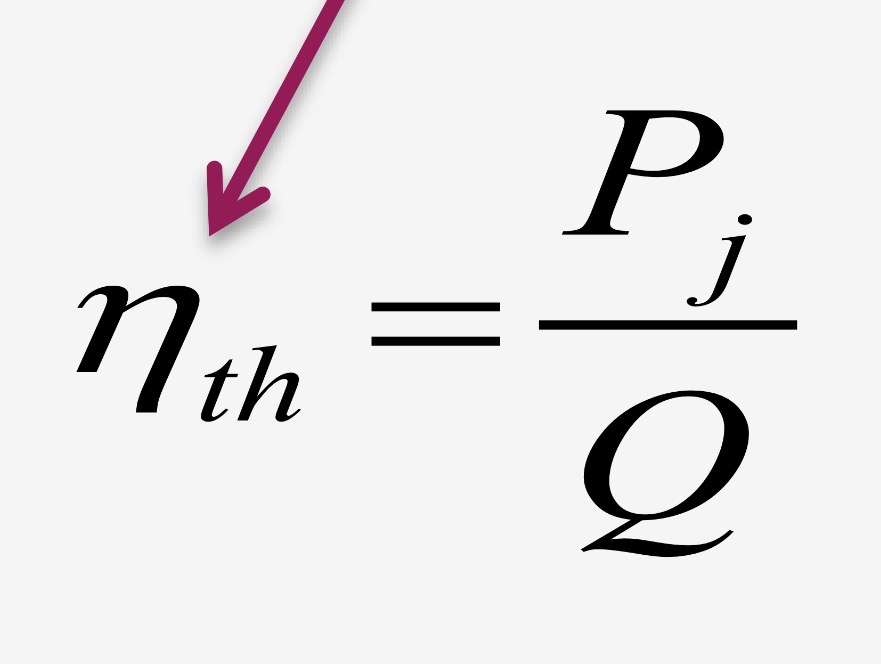
Jet propulsive efficiency
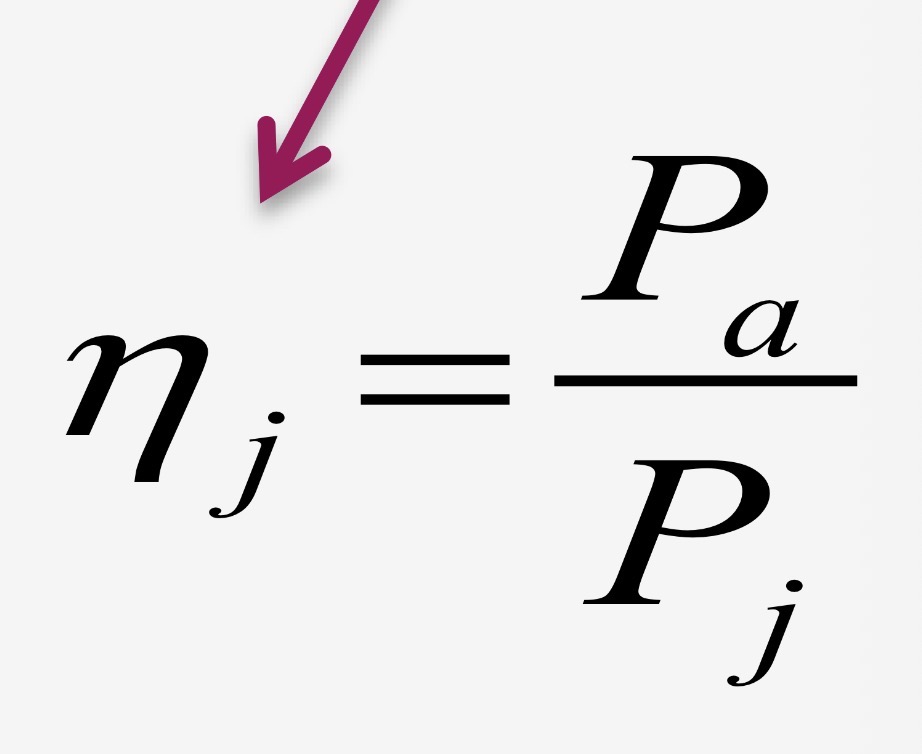
Jet total efficiency is the product of…
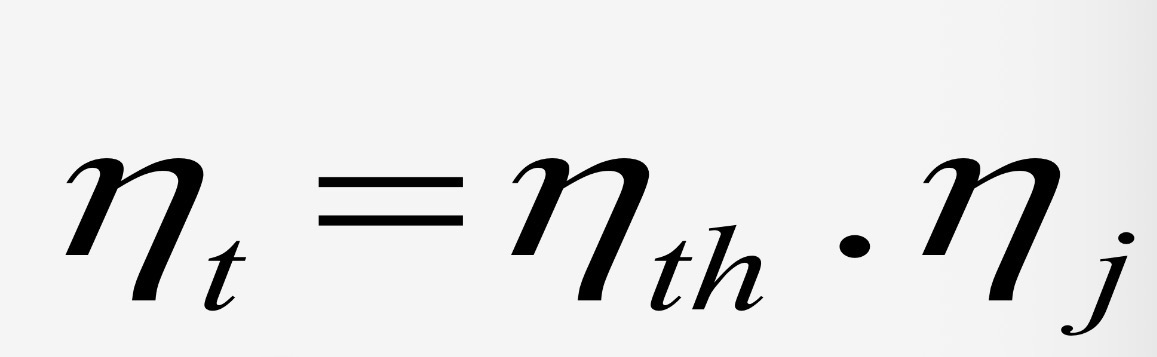
Jet propulsive efficiency as a function of Vj and V0
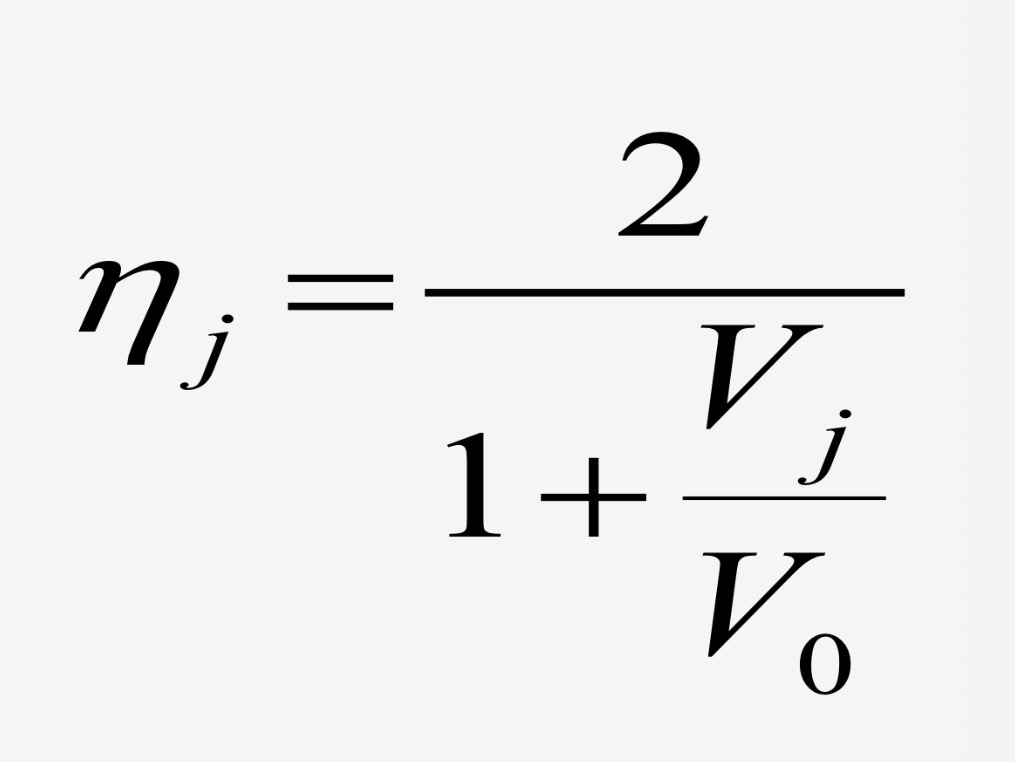
Propeller efficiency
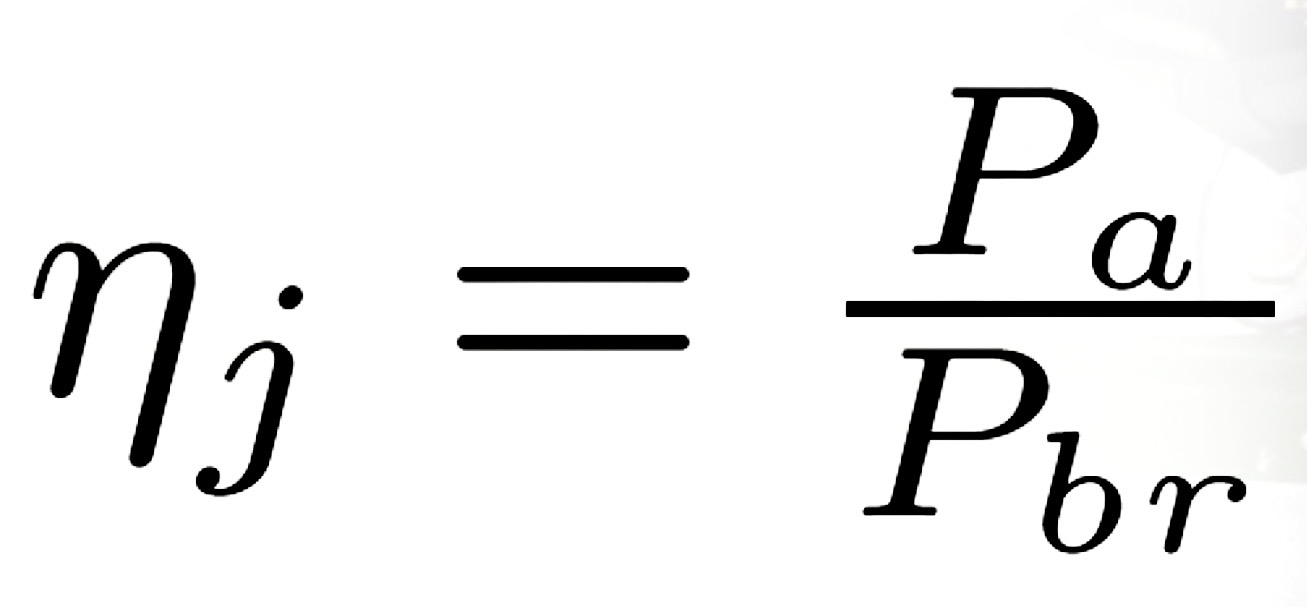
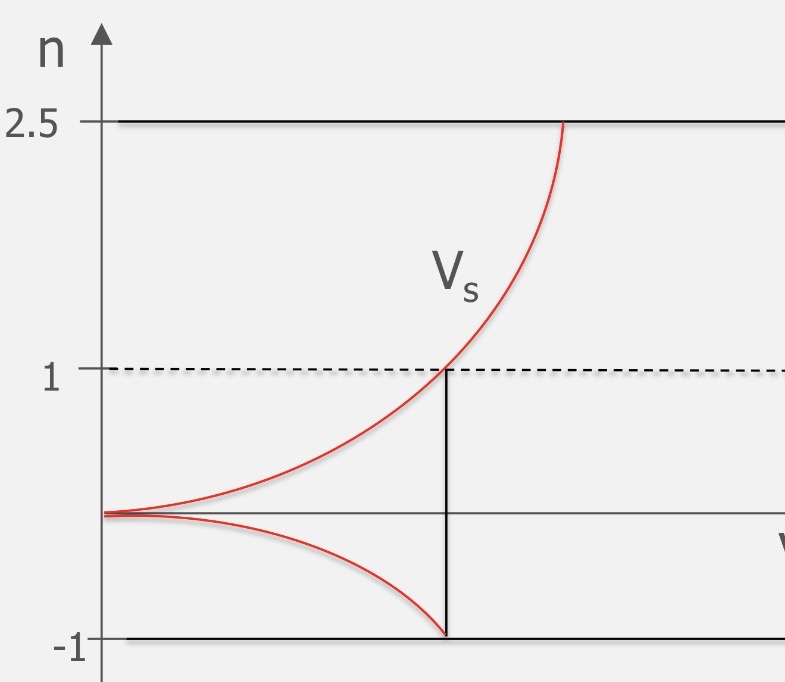
This shape is derived from…
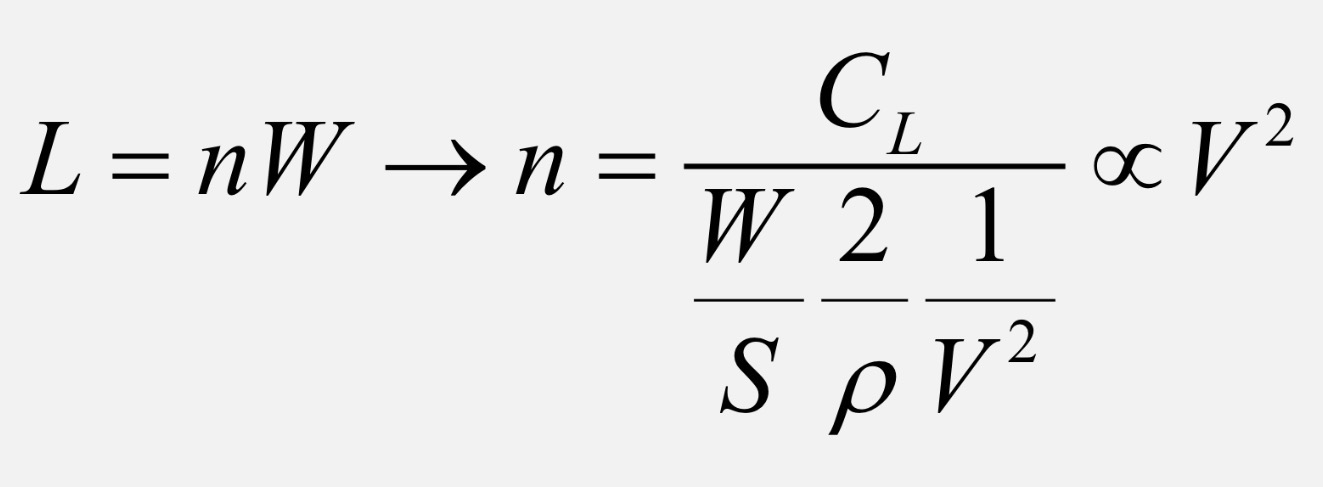
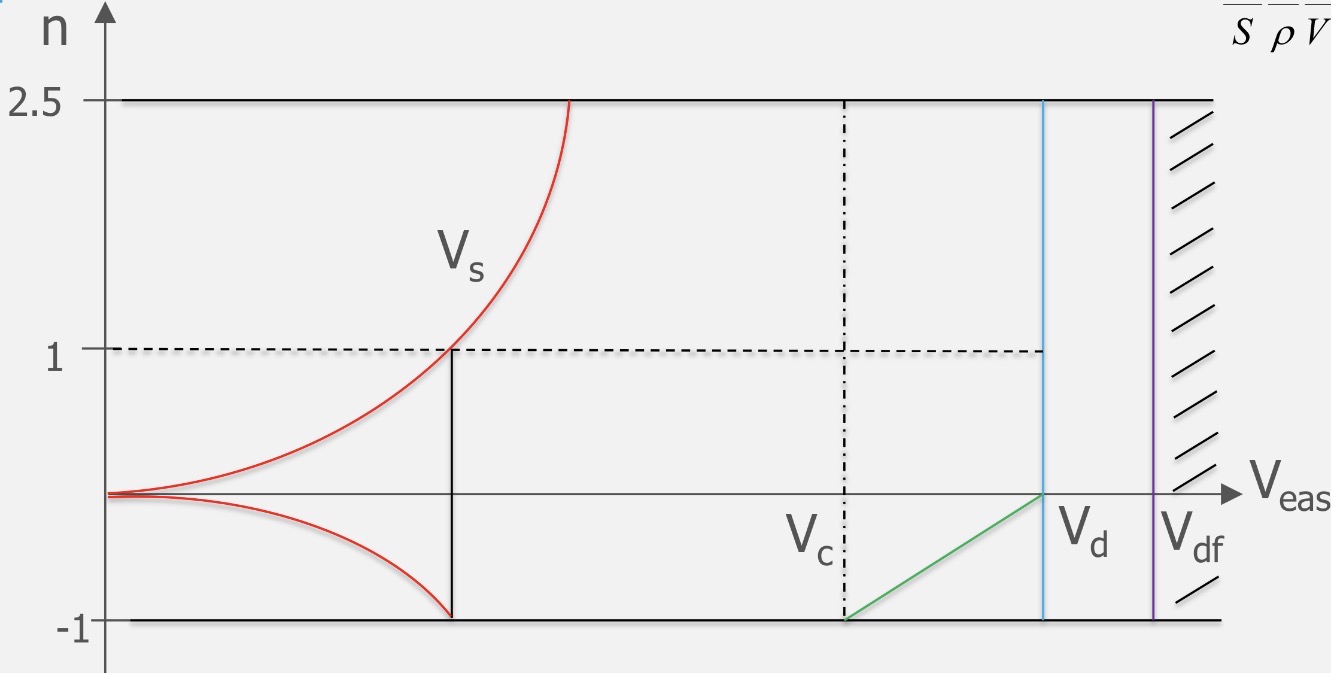
The purple line represents…
EAS for flutter dive speed (aerolastic effect)
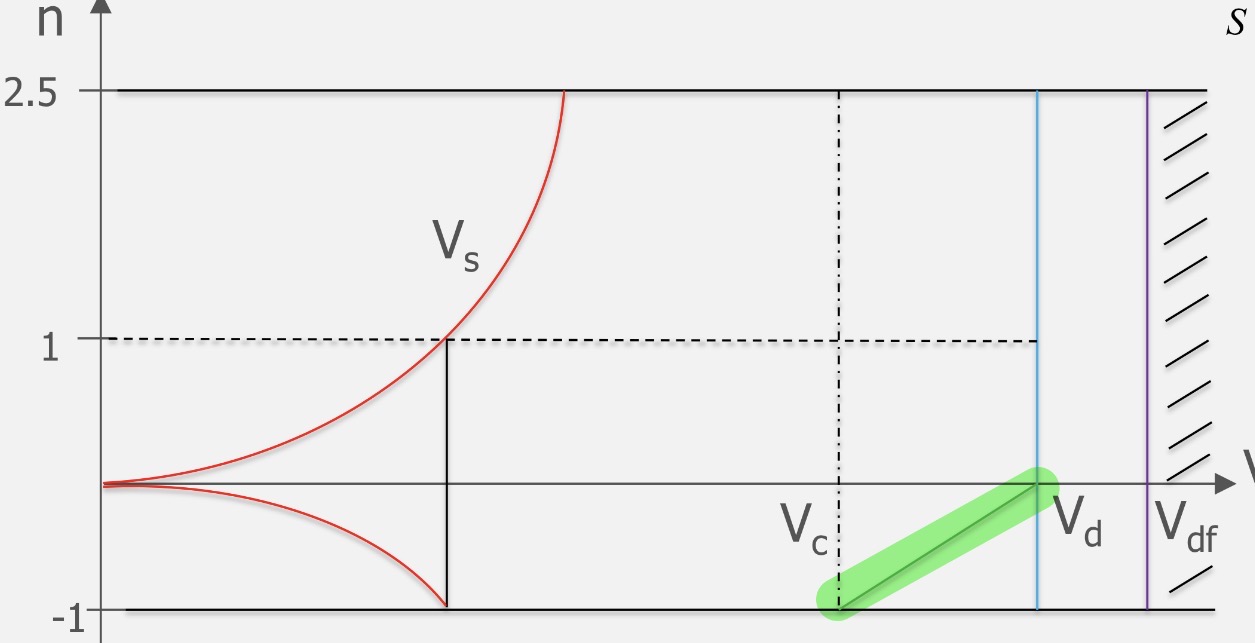
Explain the highlighted limit to the flight envelope
Beyond the line the aircraft is overspeeding, where a combination of negative g’s and speed will lead the aircraft to surpass the design dive speed Vd.
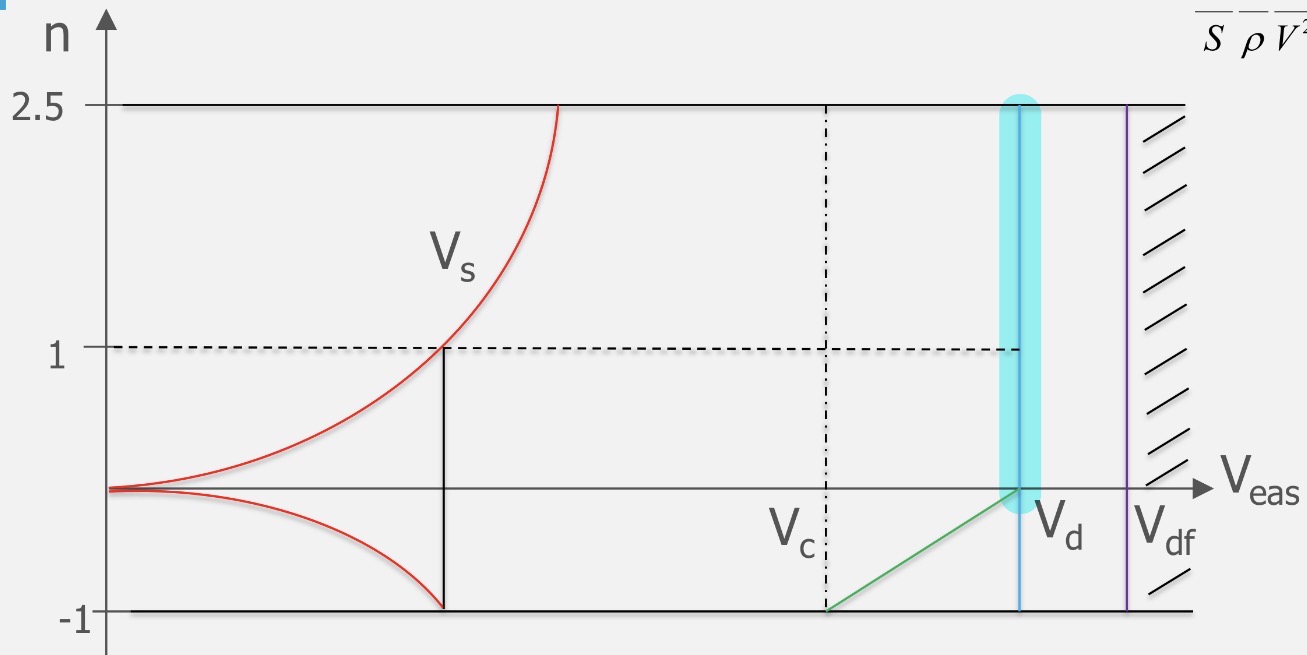
Explain the highlighted limit to the flight envelope
The design dive speed, set by the manufacturer
Gust load equation
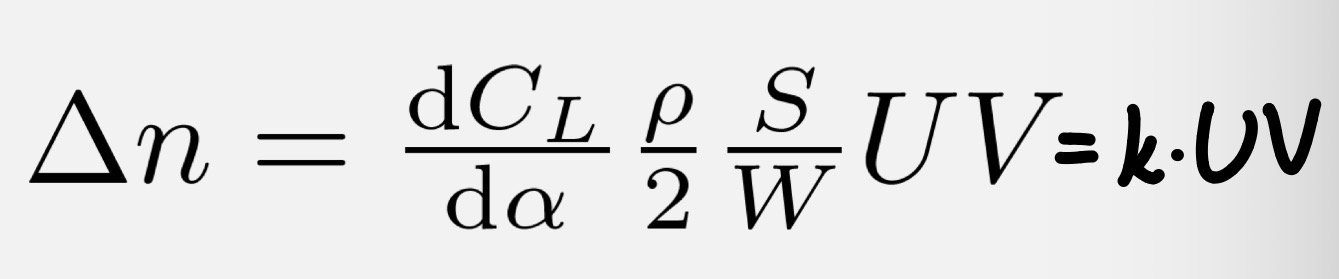
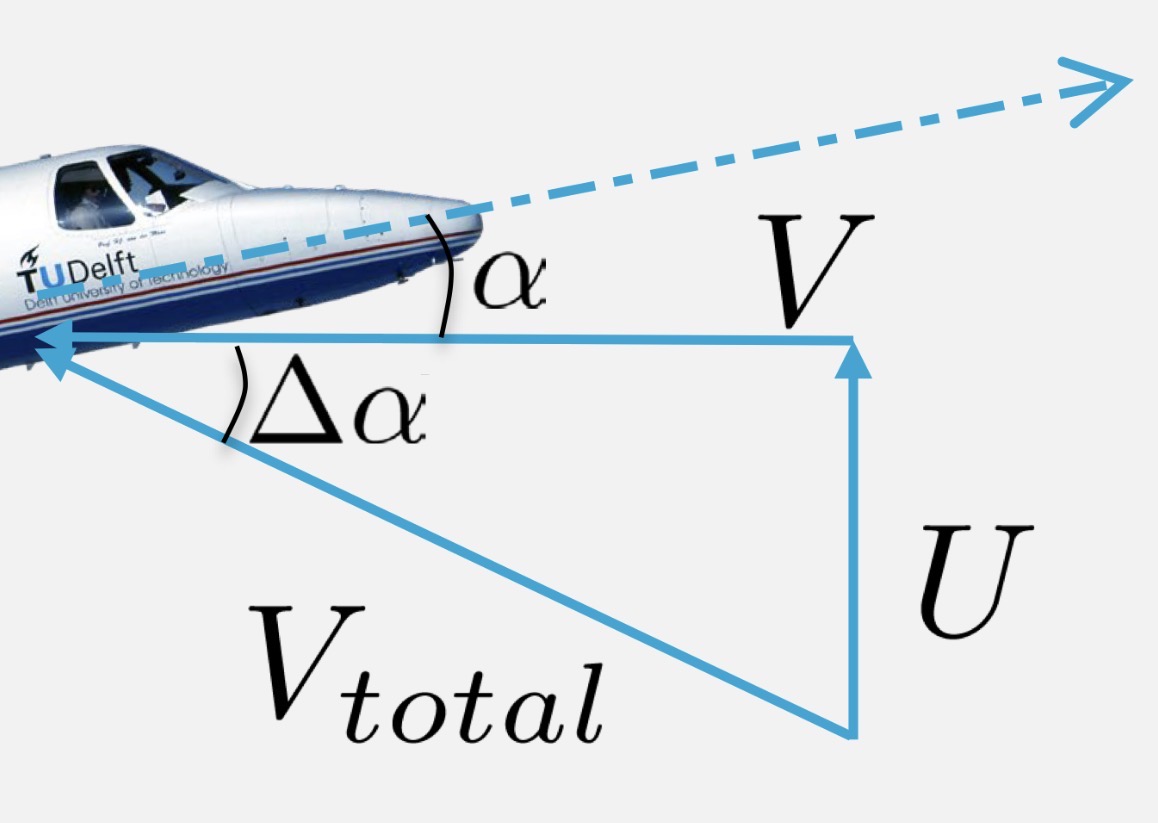
How is the equation for gust loads derived?
From ΔCL = (dCL/dα) and Δα = arctan(U/V), approximated to U/V
The design dive speed minus a safety margin yields…
V(MO), maximum operating air speed, or V(NE), never exceed air speed
The coefficients in the lift-drag polar is a function of what
The Mach number
Supersonic airflow over the wings of an aircraft leads to…
Shock waves, which can cause buffet
The aerodynamic center shifts, can cause severe pitch motion
Aerodynamic control surfaces become less effective
What is buffeting
Vibrations caused by airflow separation or shockwave oscillations
The maximum Mach number minus a safety margin yields…
Maximum operating Mach number M(MO)
How does the pressurized cabin put a operational limit on the aircraft
By limiting the maximum altitude, since Pout decreases with altitude while Pin is constant.
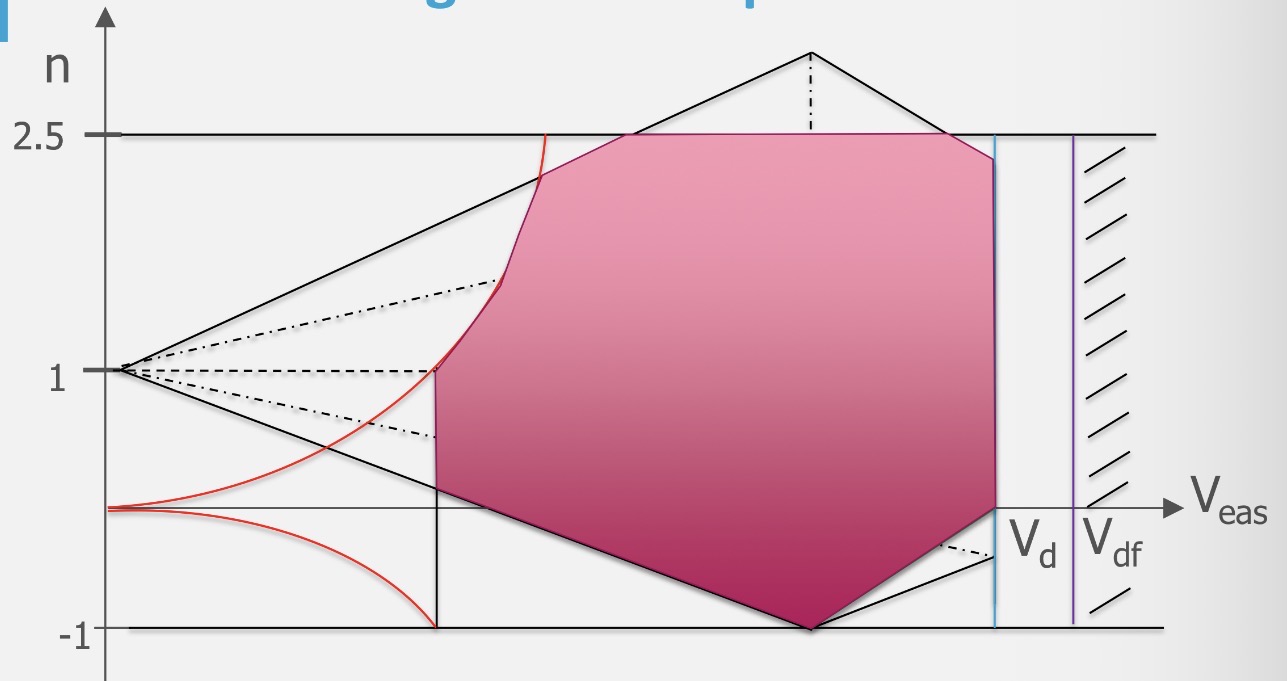
What kind of envelope is this?
Manoeuvre and gust envelope
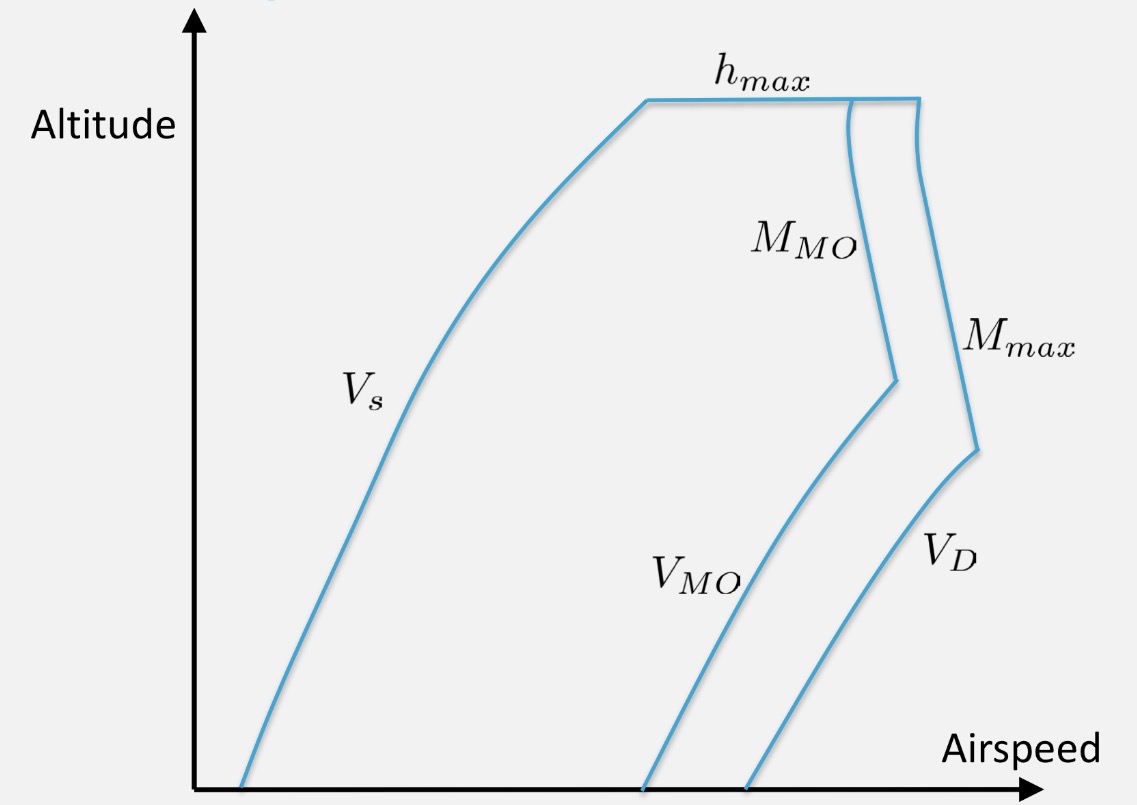
What kind of envelope is this?
Flight envelope
What is the difference between performance and operational limits?
Performance limits: from the aircraft itself
Operational limits: arbitrarily set
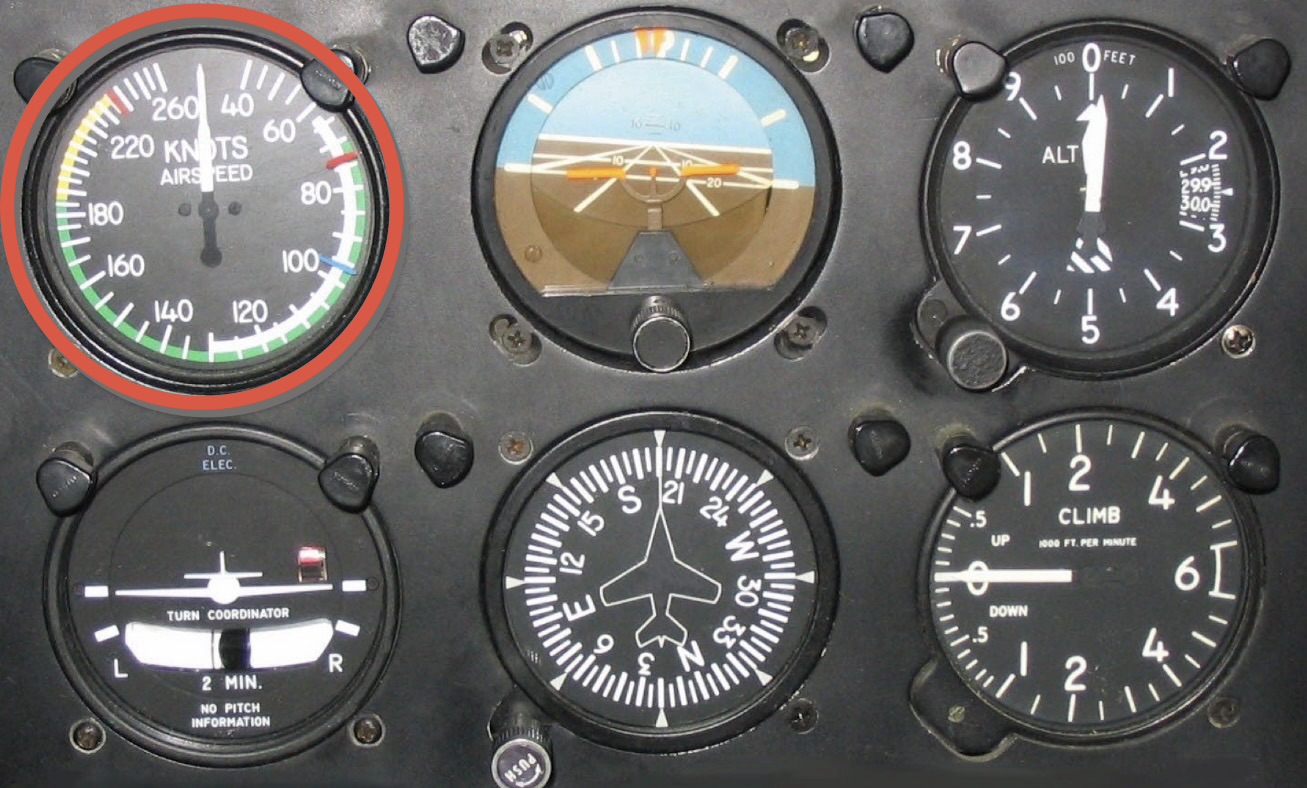

What instrument is this and what is its function?
Air speed indicator: 2 inputs (pitot tube and static port). Green line is good, yellow line requires care (between Vc and Vd), red line indicates V(MO), the white line indicates speed range with flaps.
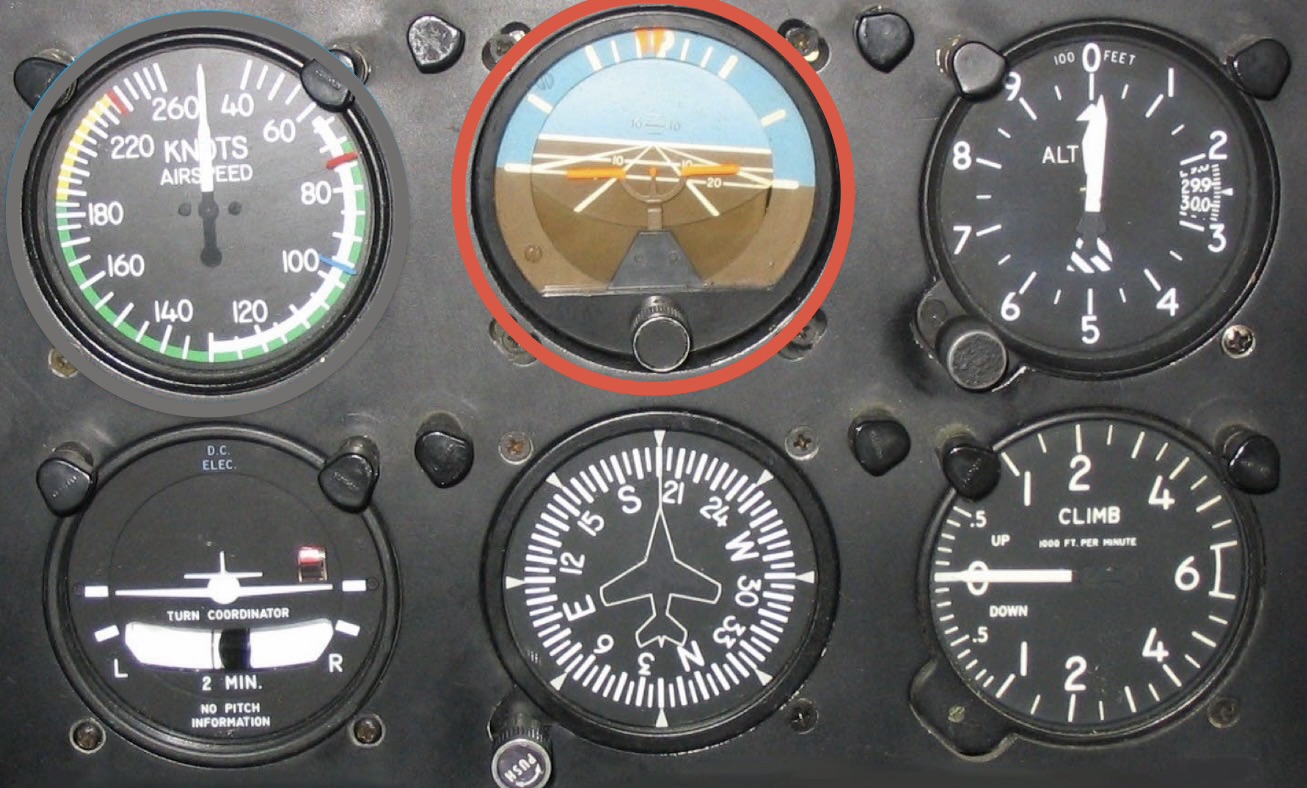

What instrument is this and what is its function?
Artificial horizon: runs off a gyroscope. Indicates attitude towards the ground.
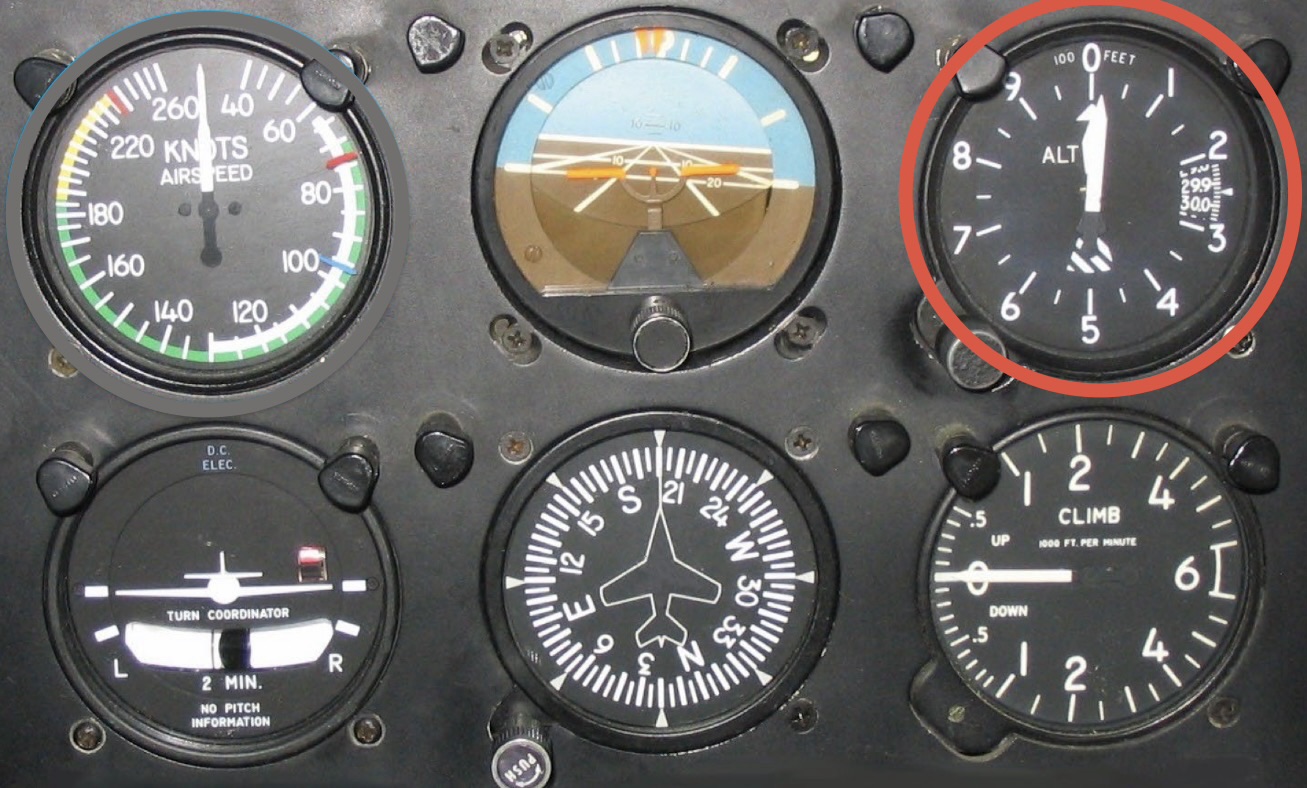

What instrument is this and what is its function?
Altimeter: statics port as input, knob to adjust airfield altitude via QNH
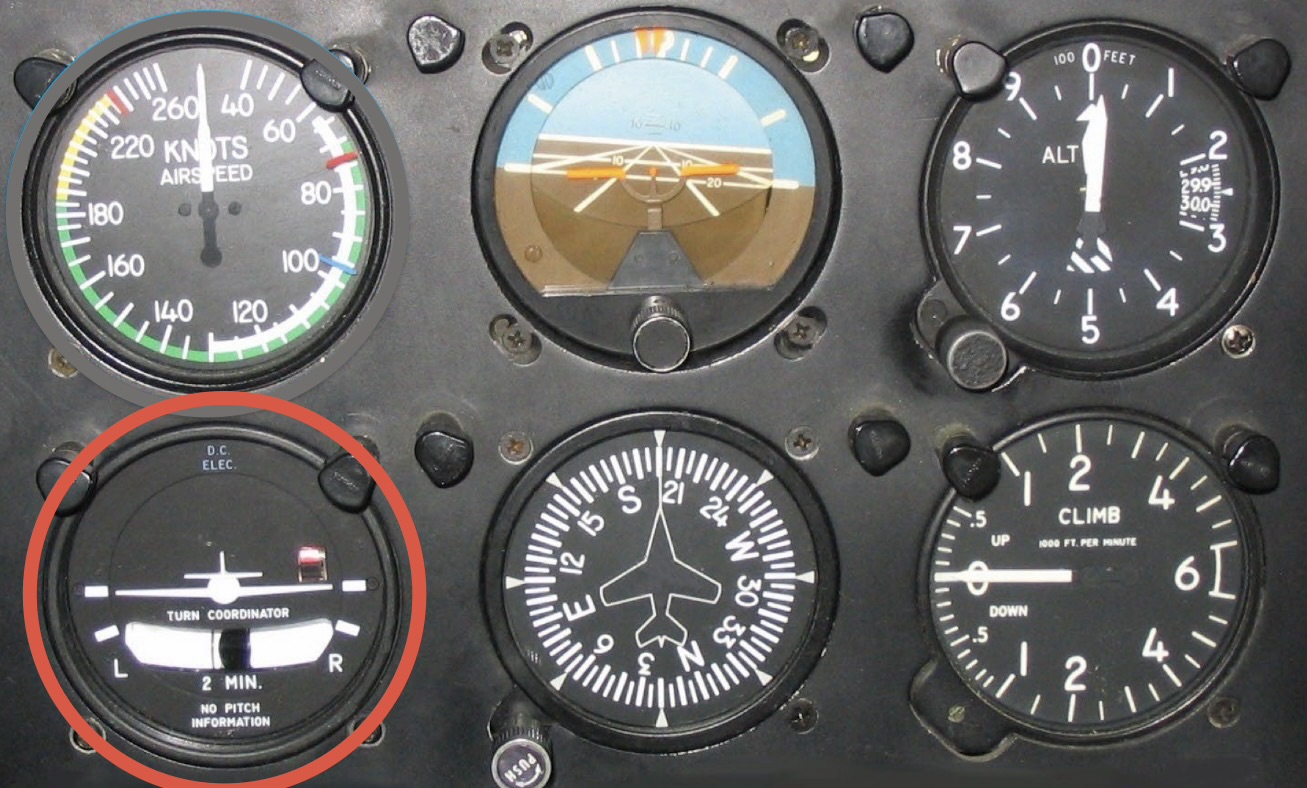

What instrument is this and what is its function?
Turn and bank indicator: uses a gyroscope (turn rate displayed as the planes roll angle) and an inclinometer (the ball in the tube) to indicate if the turn is coordinated.

What instrument is this and what is its function?
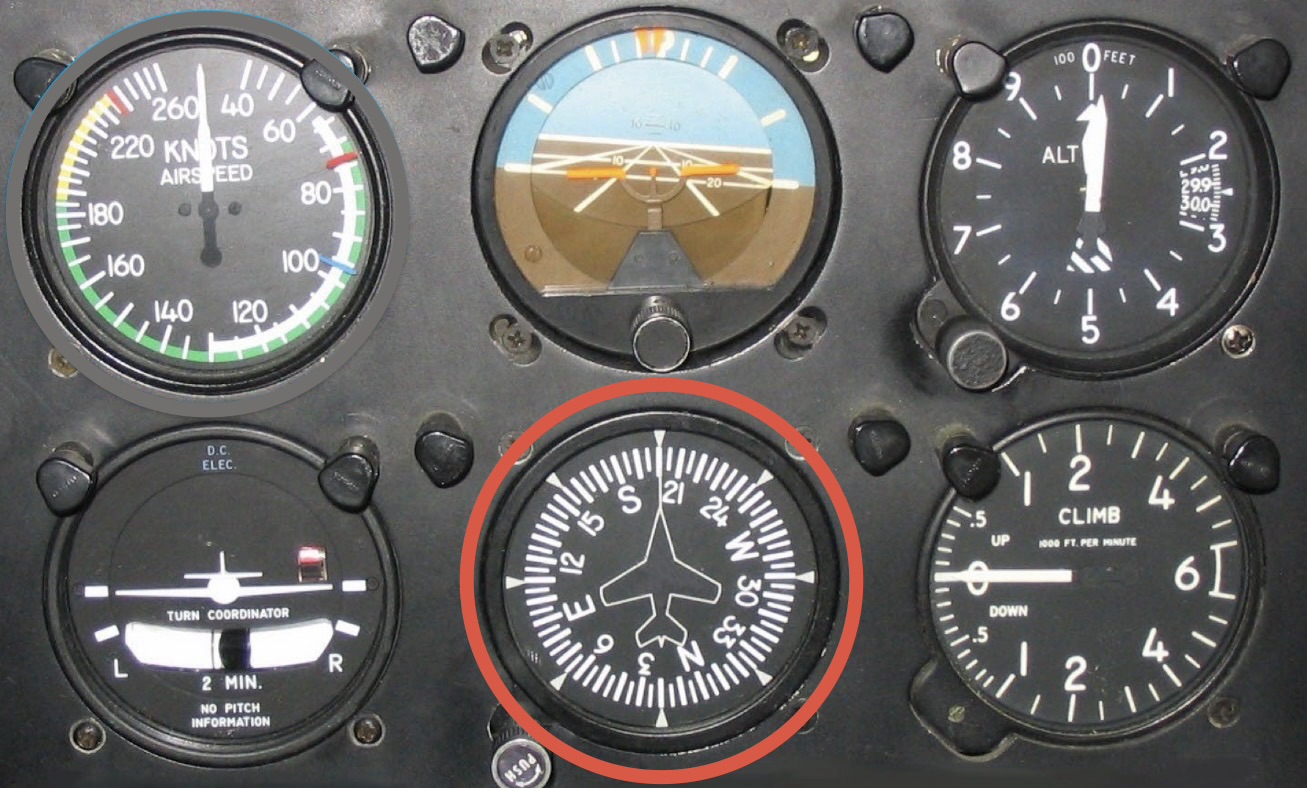
Directional gyro: basically a compass, calibrated to the magnetic compass.

What instrument is this and what is its function?
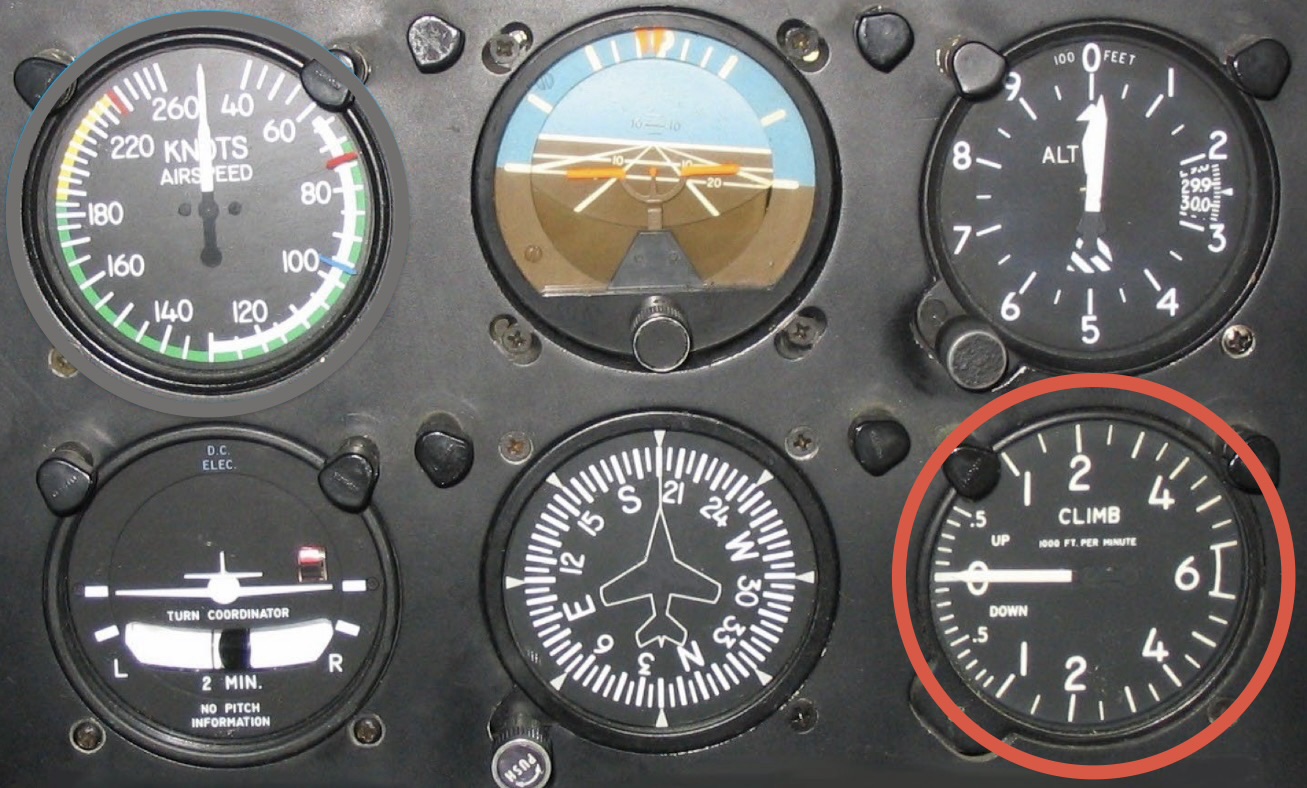
Vertical speed (or climb rate) indicator: measures the difference in pressure between the static port and a container with a small drain port.
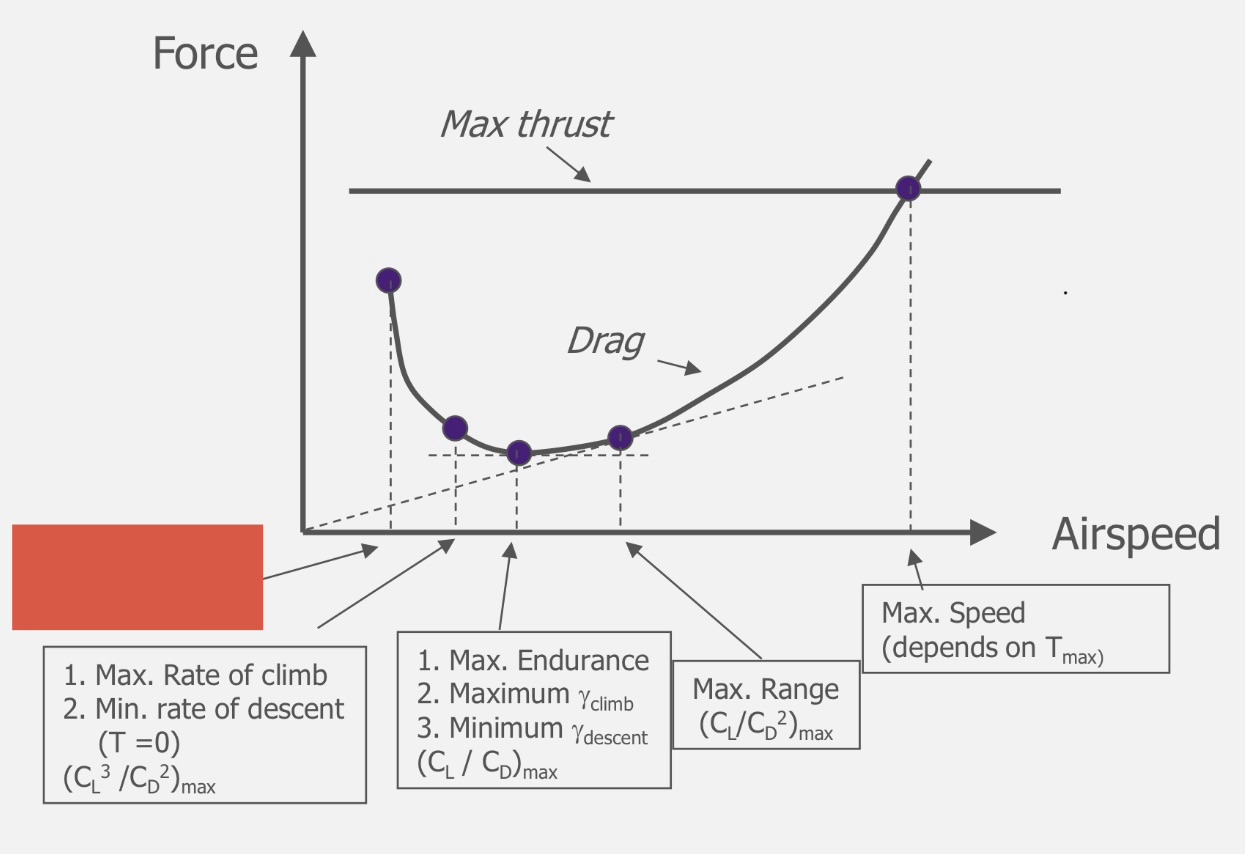
(CL)max
Minimum Speed
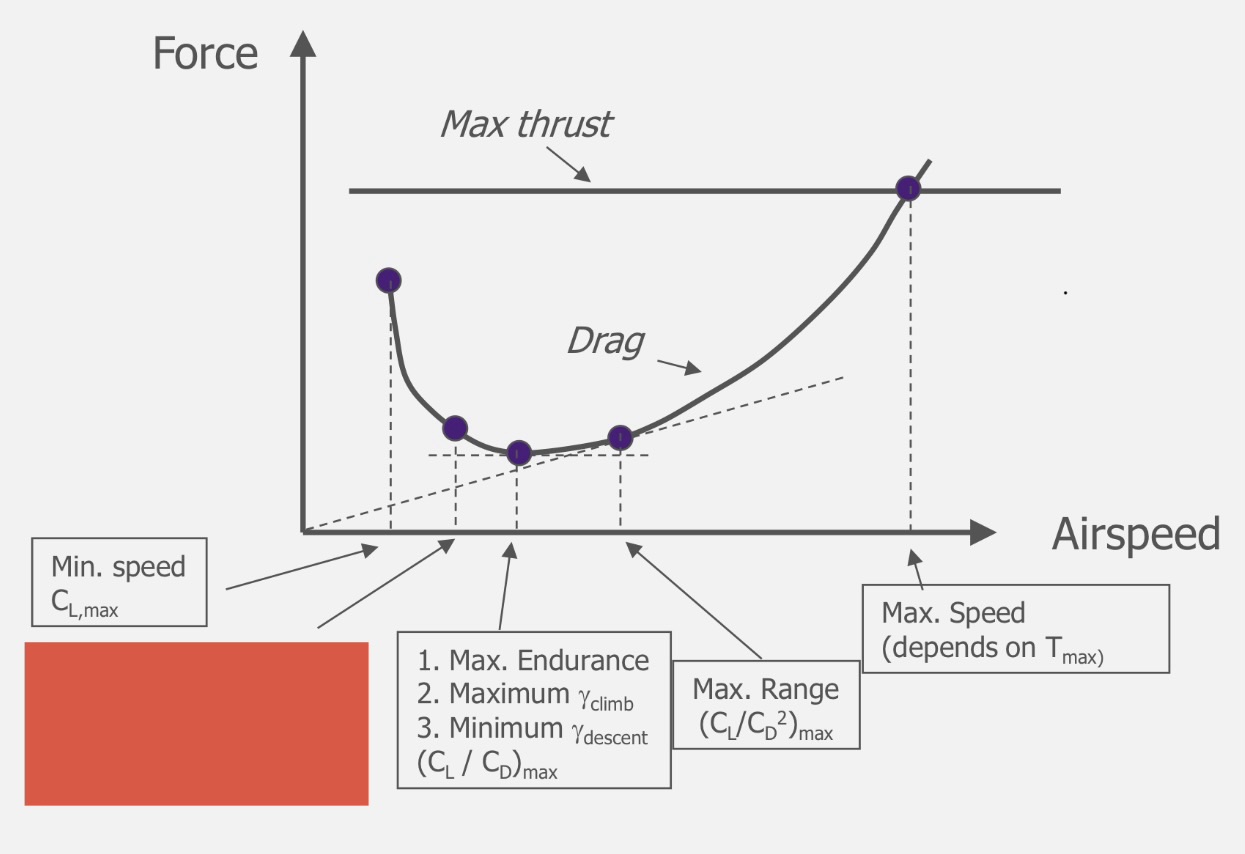
(CL³/CD²)max
Maximum ROC
Minimum ROD (T=0)
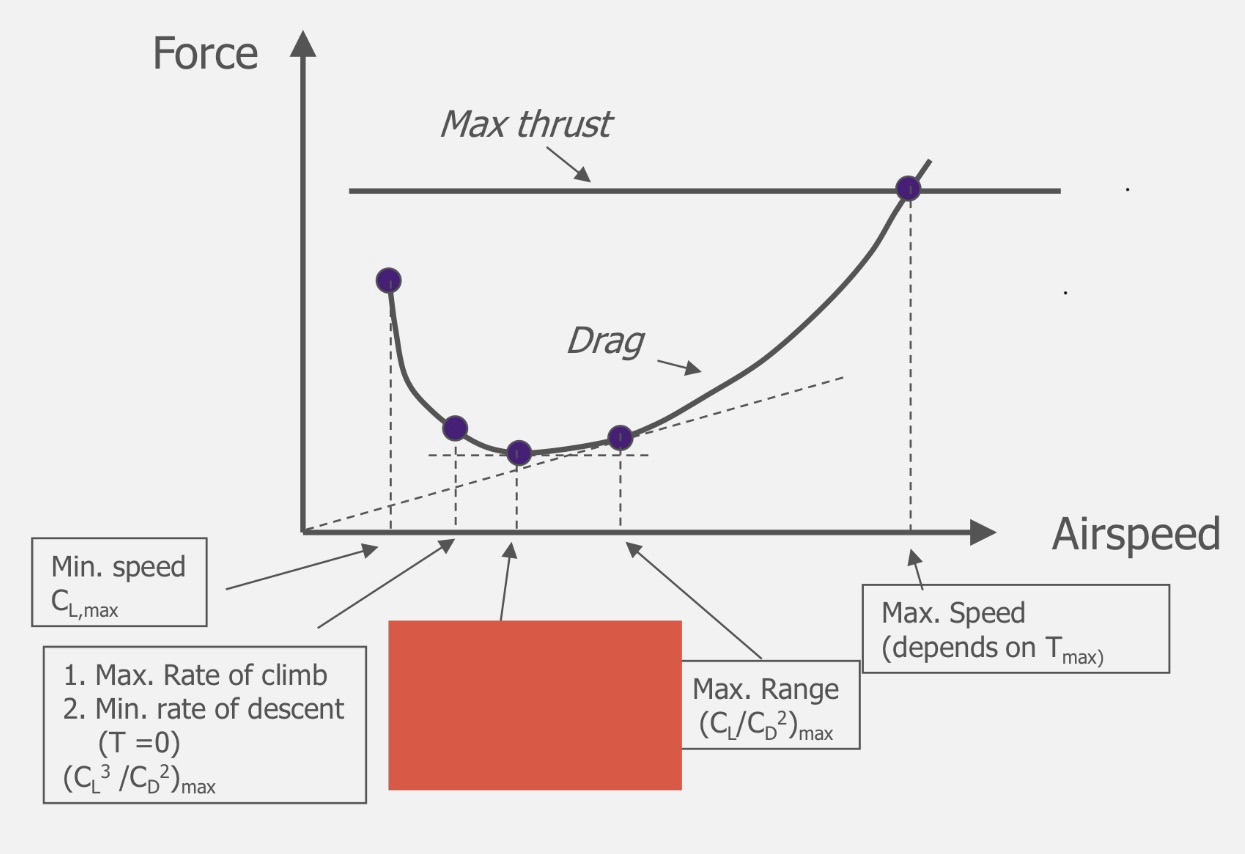
(CL/CD)max
Maximum endurance
Maximum climb angle
Minimum descent angle
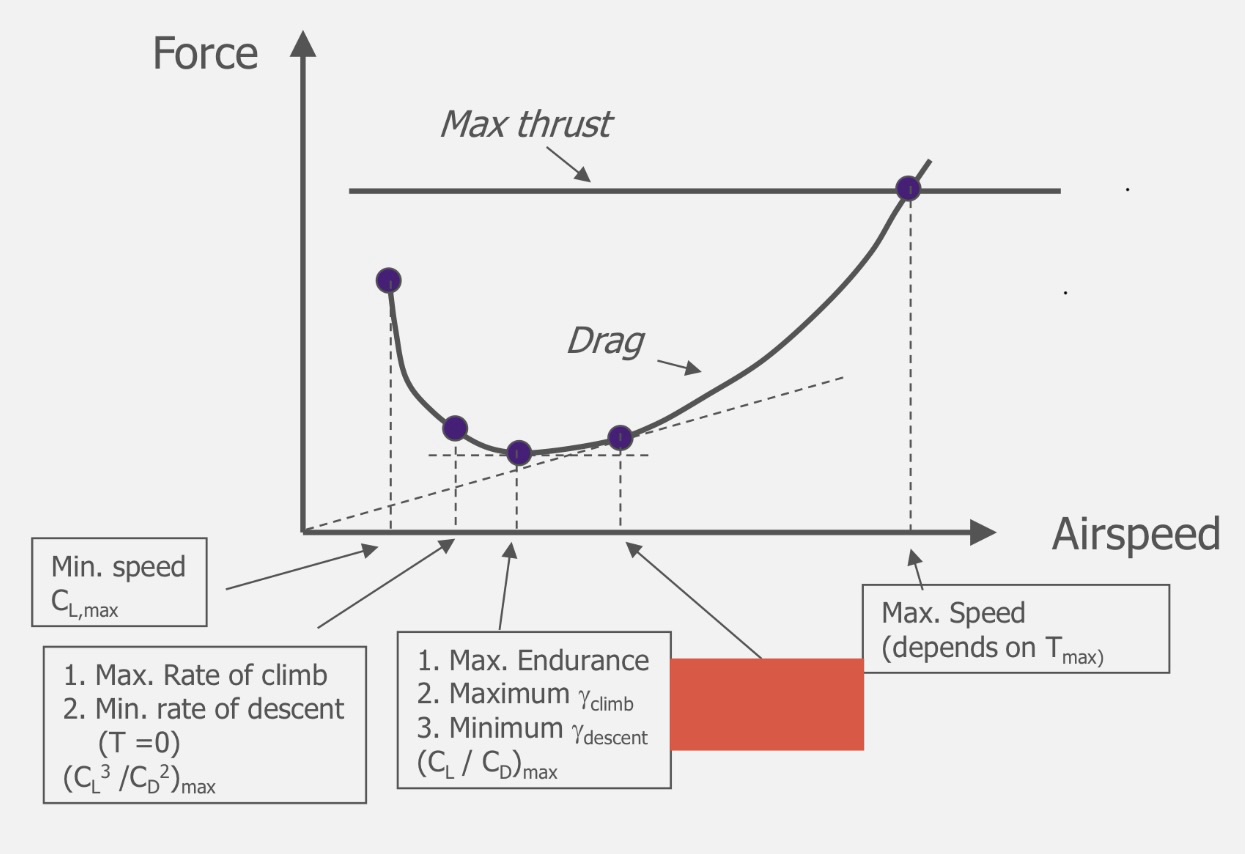
(CL/CD²)max
Maximum range
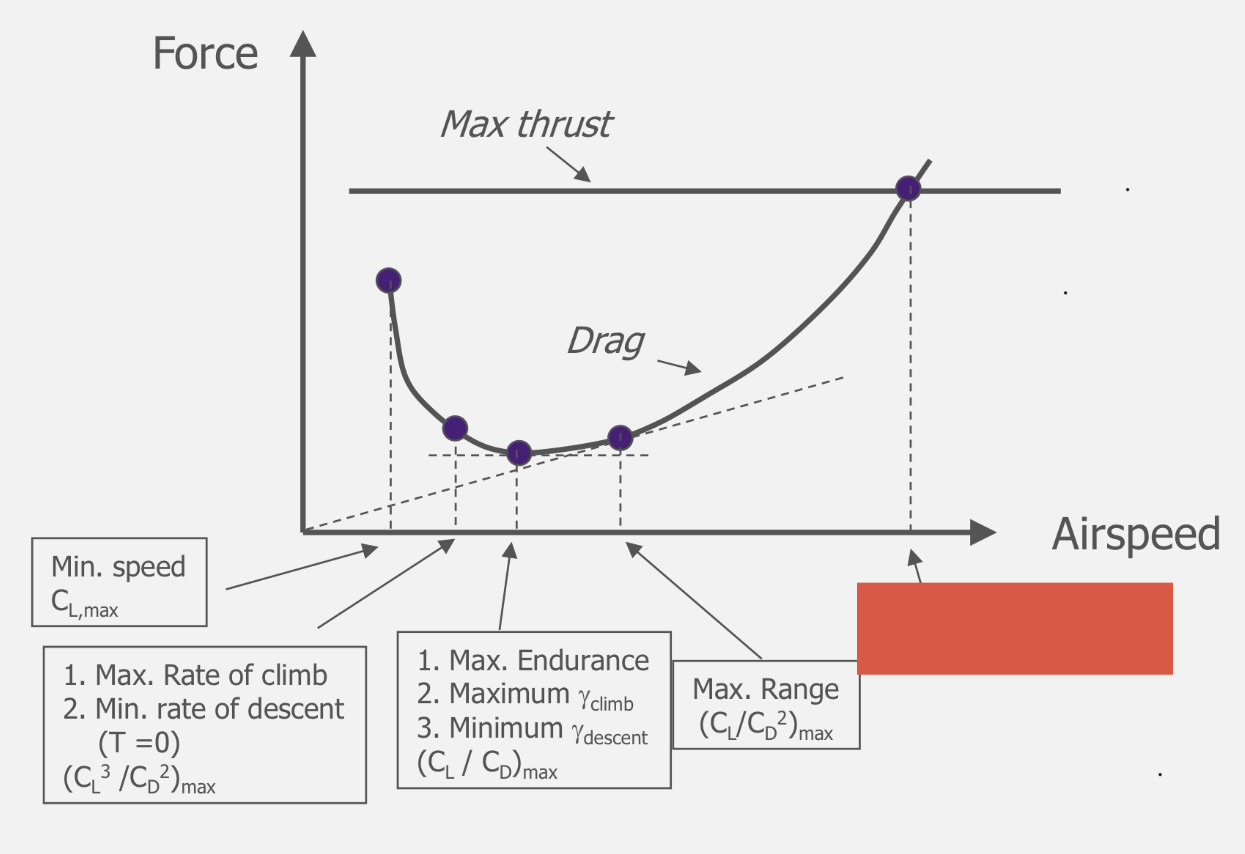
Maximum speed (depends on Tmax)
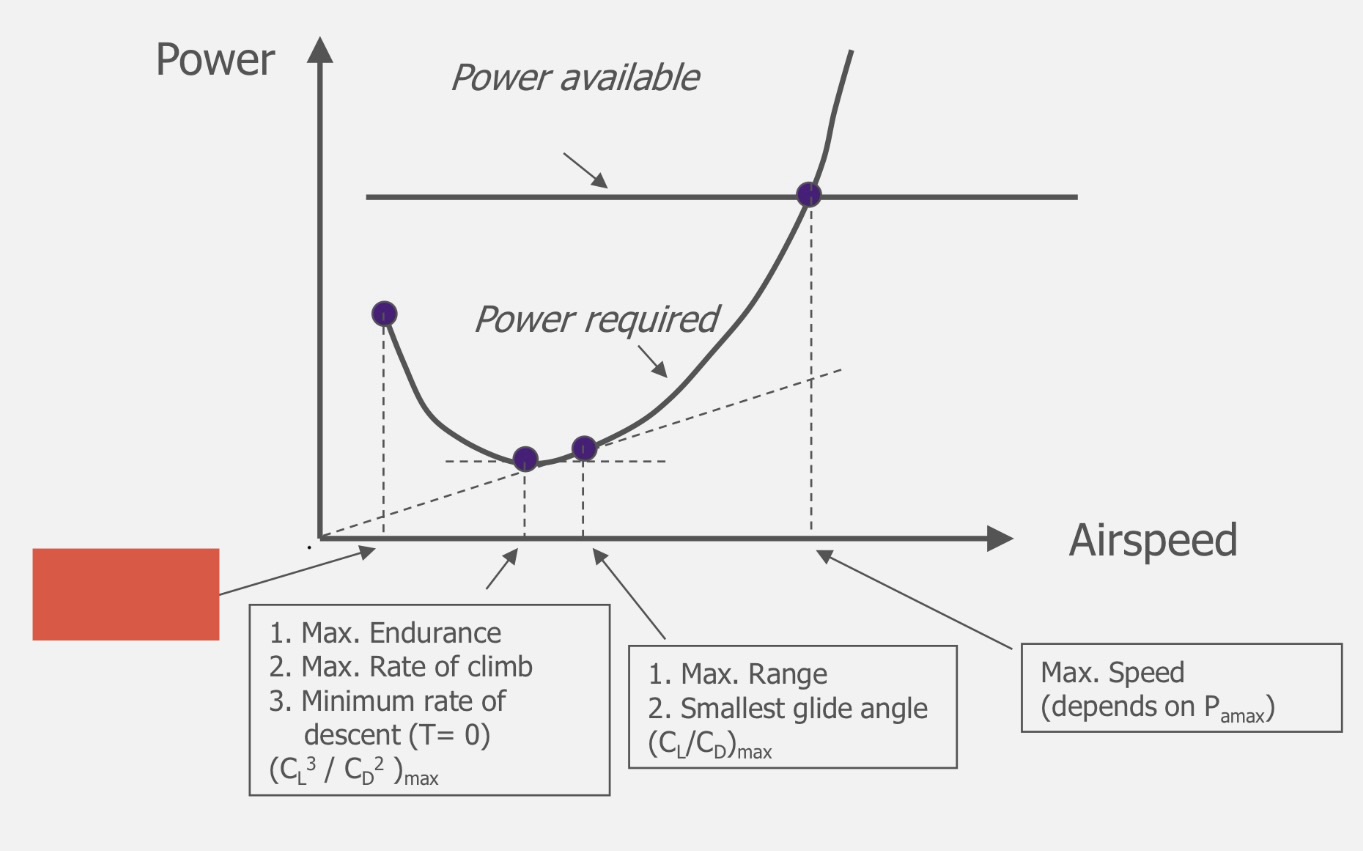
(CL)max
Minimum Speed
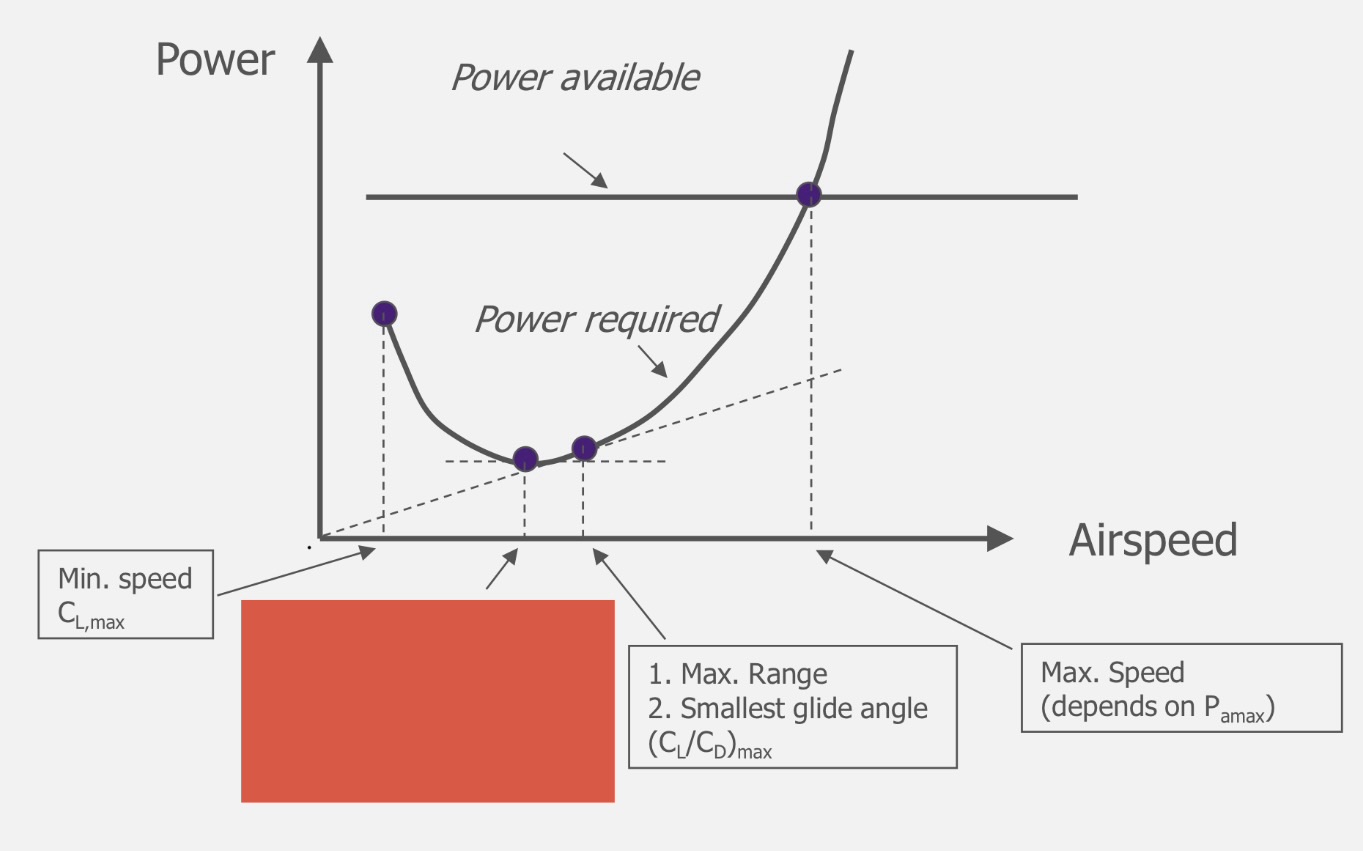
(CL³/CD²)max
Maximum endurance
Maximum ROC
Minimum ROD (T=0)
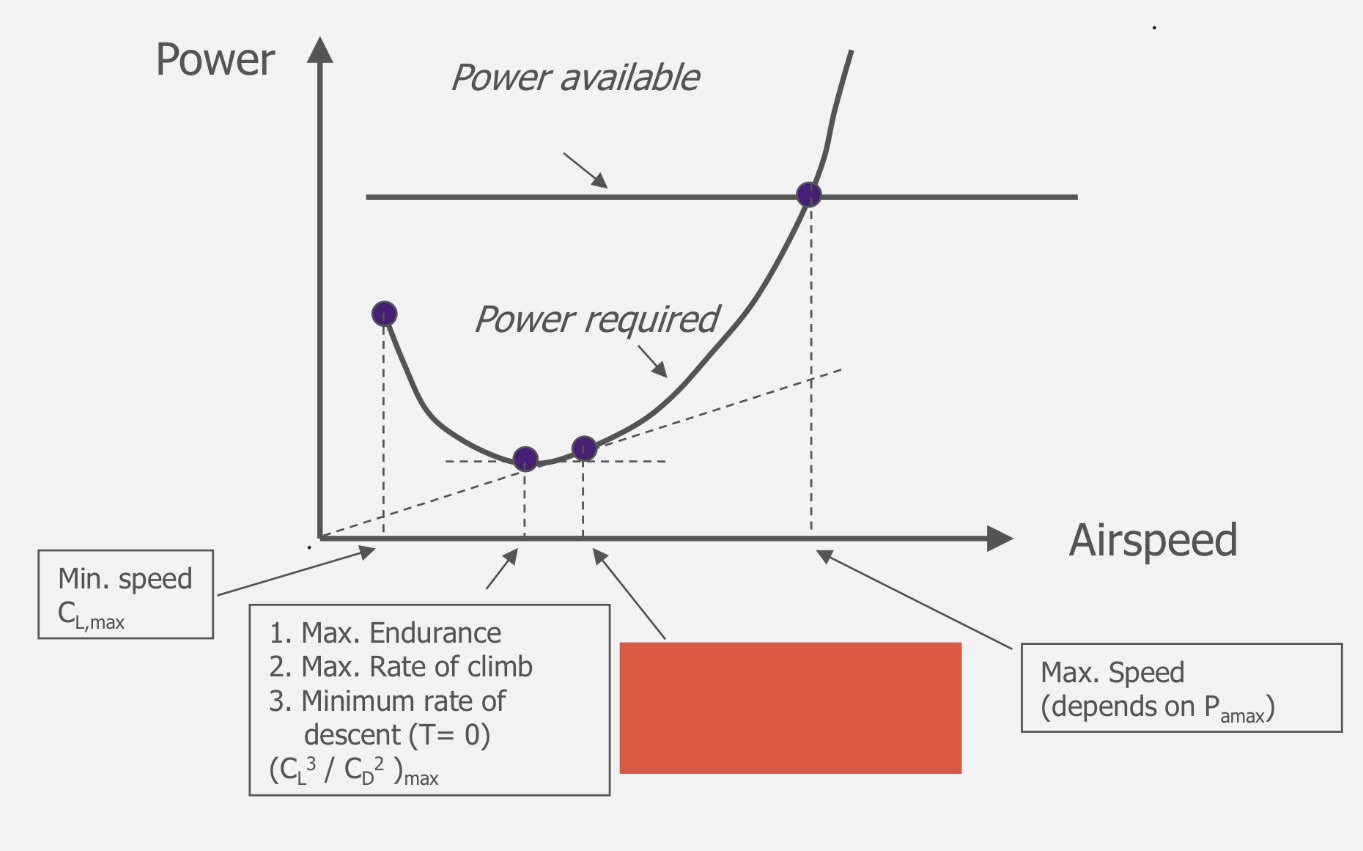
(CL/CD)max
Maximum range
Maximum climb angle
Minimum descent angle