DCAP Ch 7 & Ch 8
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
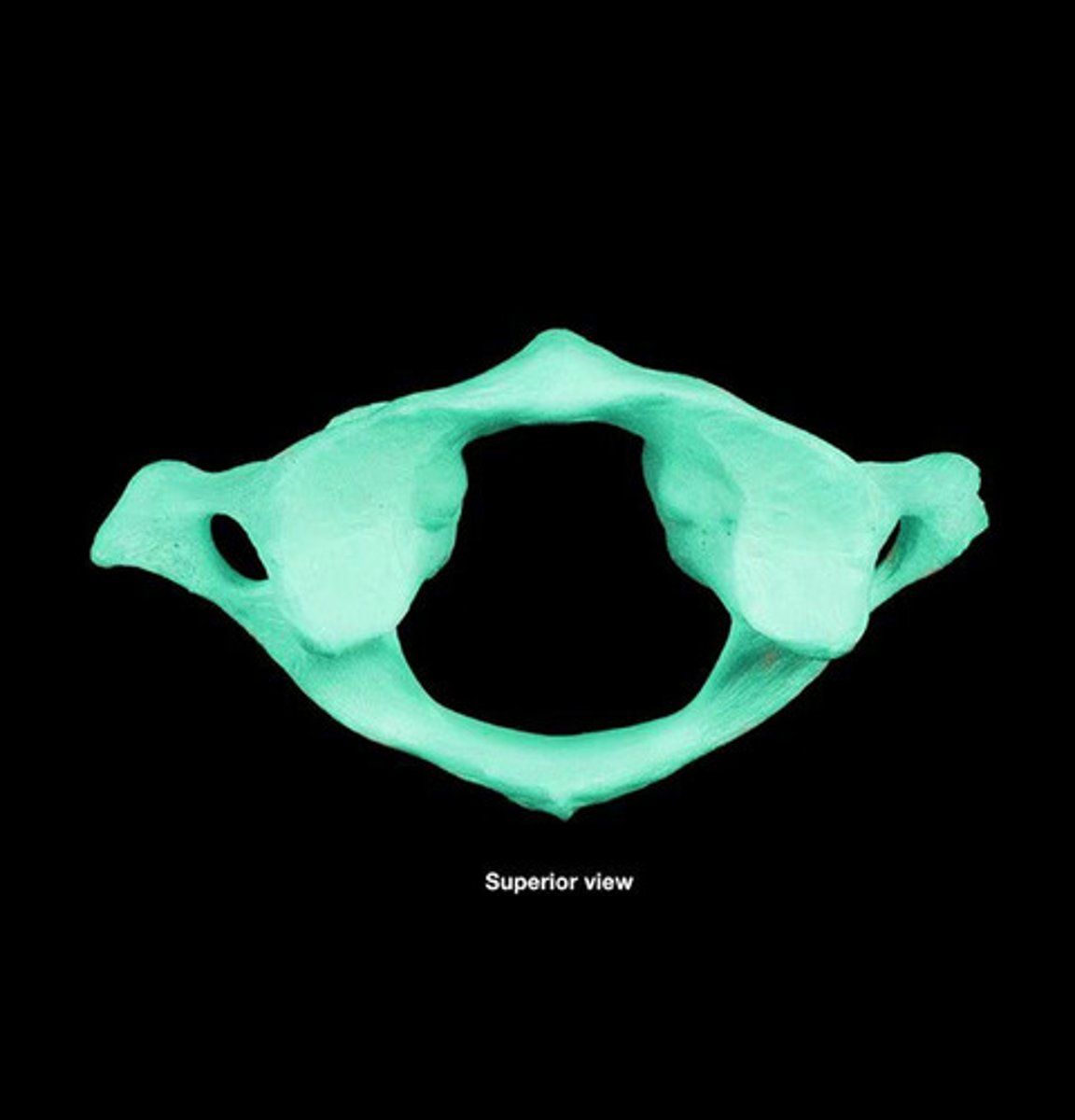
Atlas
C1 bone; allows one to nod; articulates with skull
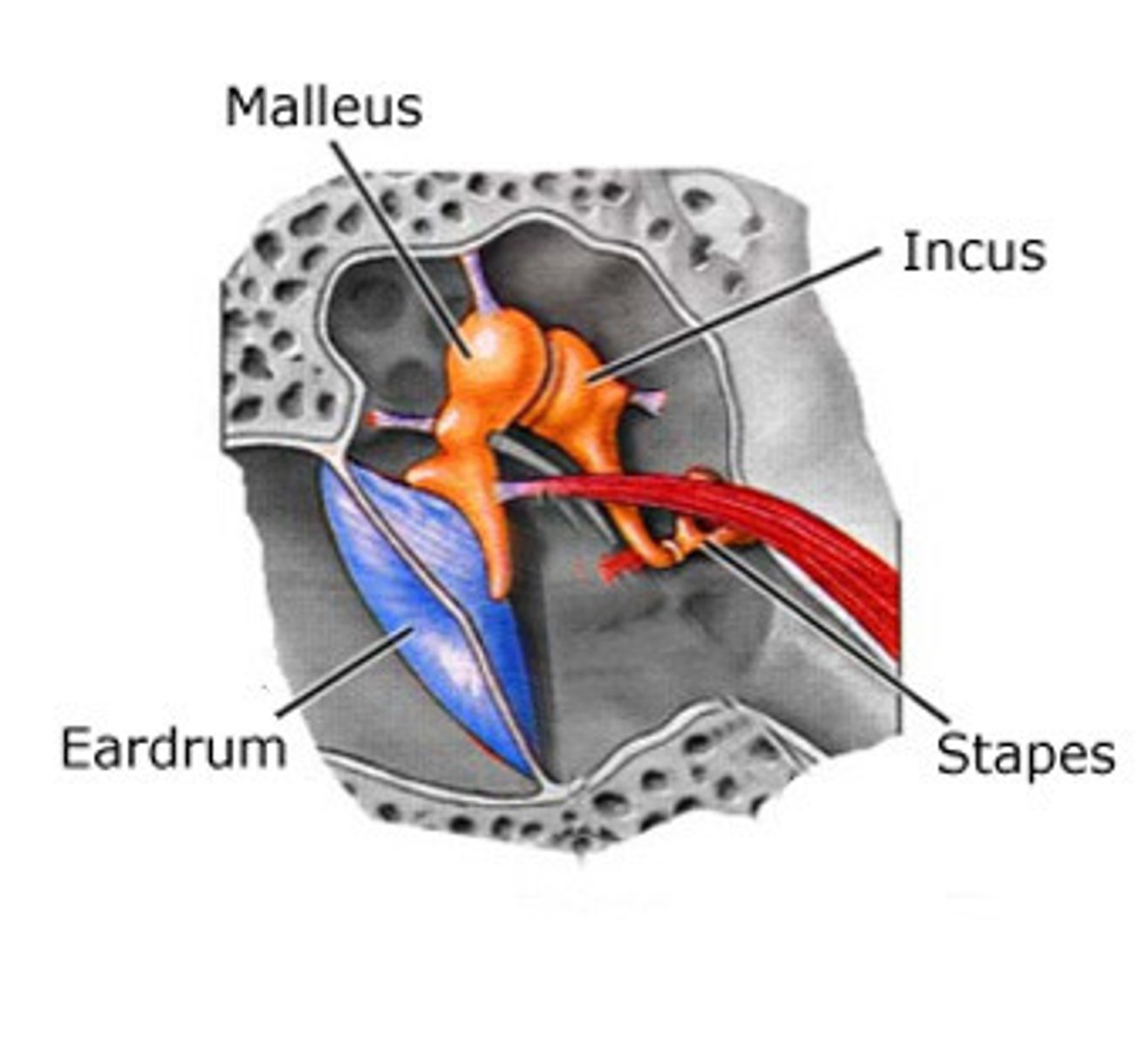
Auditory ossicles
made up of malleus, incus, stapes, found deep in the ear canal
Axial skeleton
Portion of the skeletal system that consists of the skull, rib cage, and vertebral column
Axis
C2 bone; allows one to pivot neck
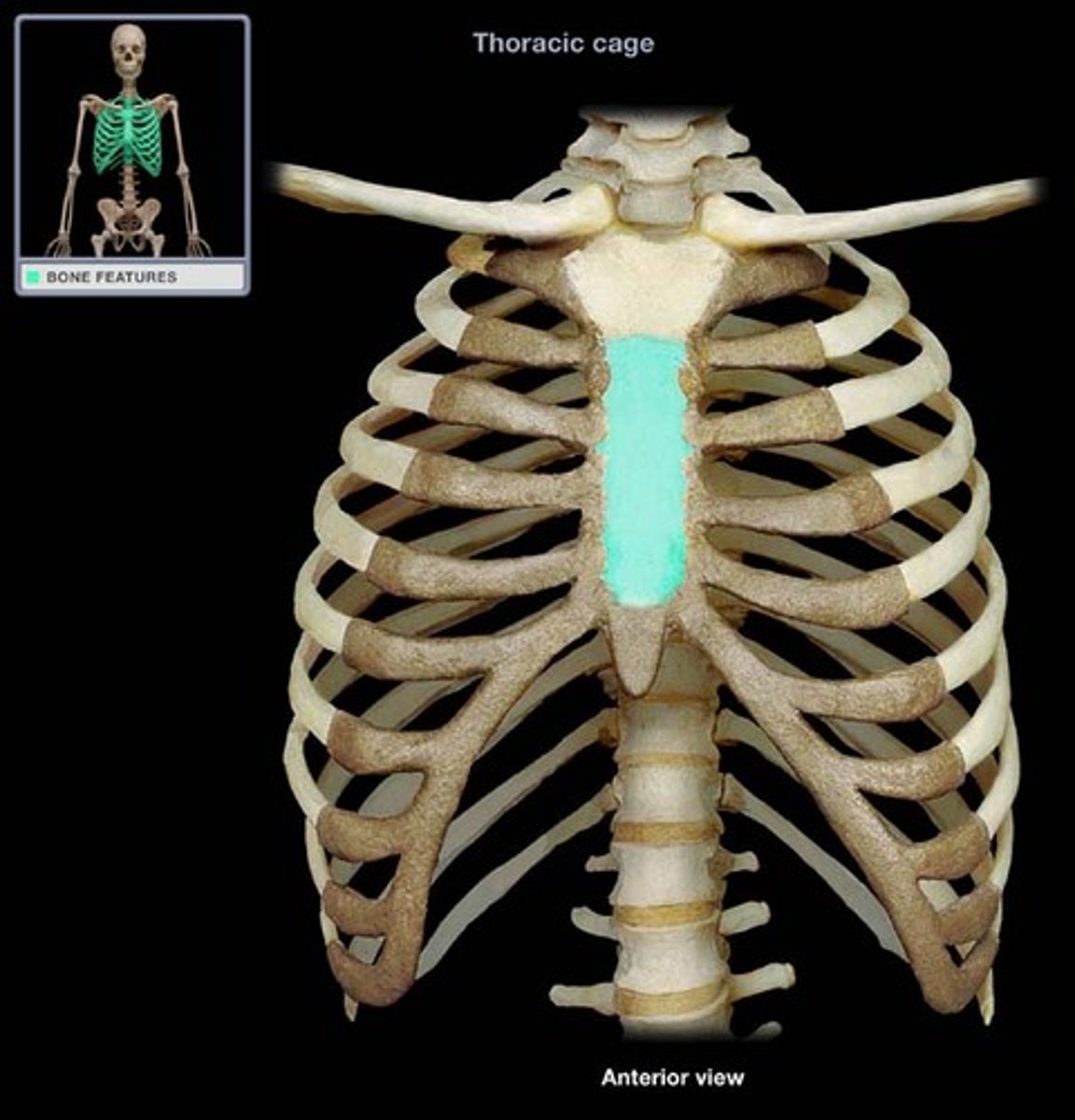
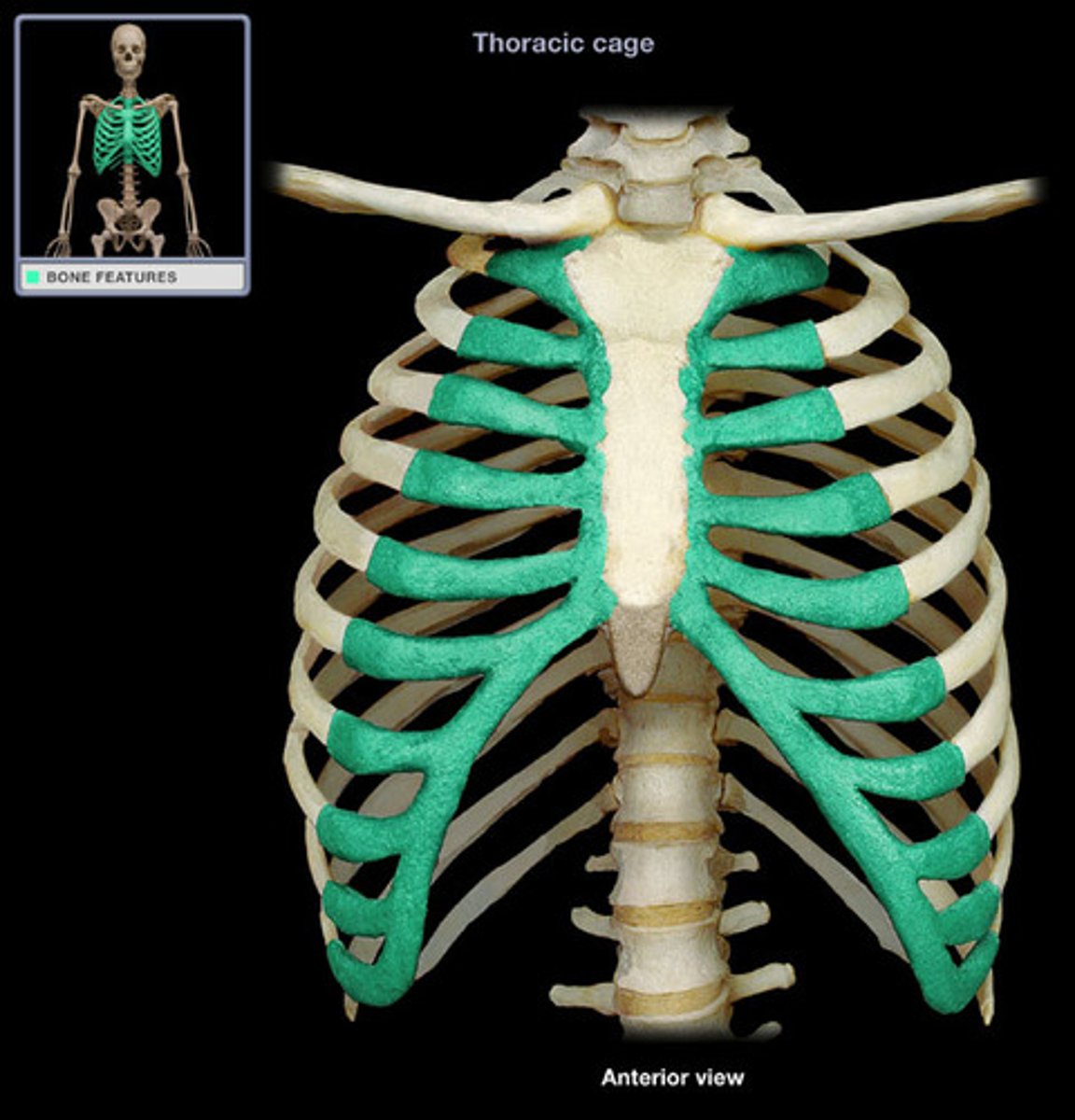
body of sternum
the main portion of the sternum
bone functions
Support the weight of the body, allows for body movements, protect internal organs
ligament functions
Hold bones together at a movable joint; prevent excessive movements that may lead to injury
Calvaria
cranium without the face; skull cap
Cartilage function
Provides flexible strength and support for body structures; unites adjacent bones
Provides cushioning
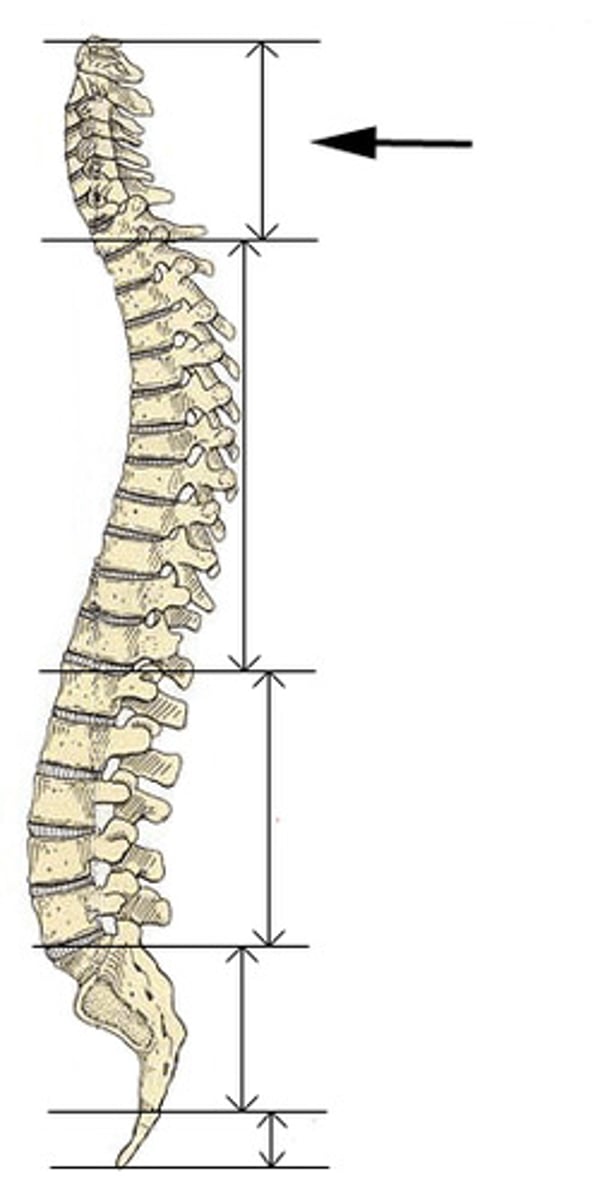
Cervical curve
The first curve of the back, consists of 7 vertebrae (c1-c7), supports the head
Cervical vertebrae
Have a small body with a bifid (y-shaped) process; only vertebrae with transverse foramen
Coccyx
tailbone found distal to the sacrum
Coronal suture
the suture between the parietal and frontal bones of the skull
Costal cartilage
connects ribs to sternum
Cranium
the portion of the skull that encloses the brain
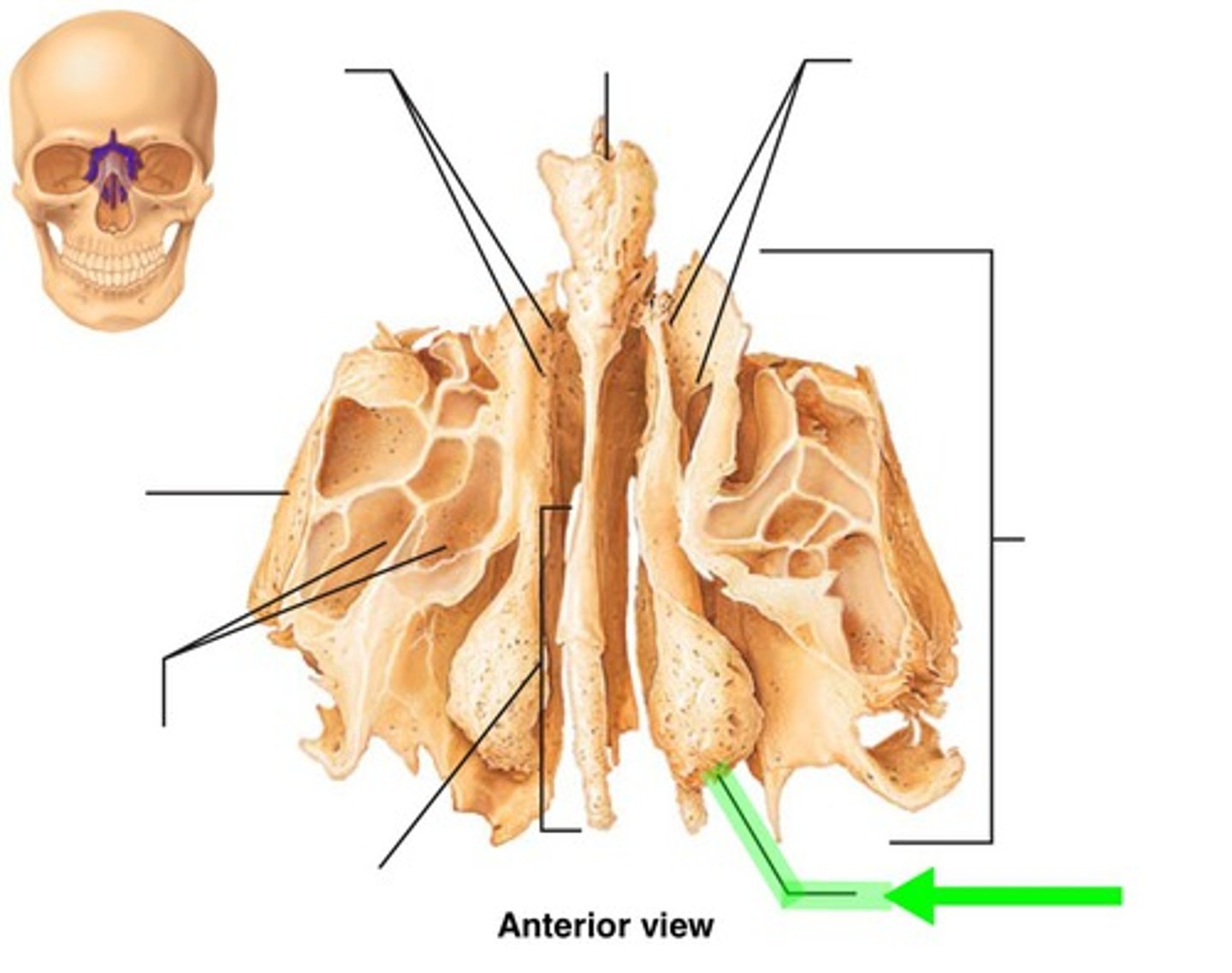
ethmoid bone
found deep in the nasal cavity in front of the sphenoid bone, forms part of the posterior portion of the nose, the orbit, and the floor of the cranium
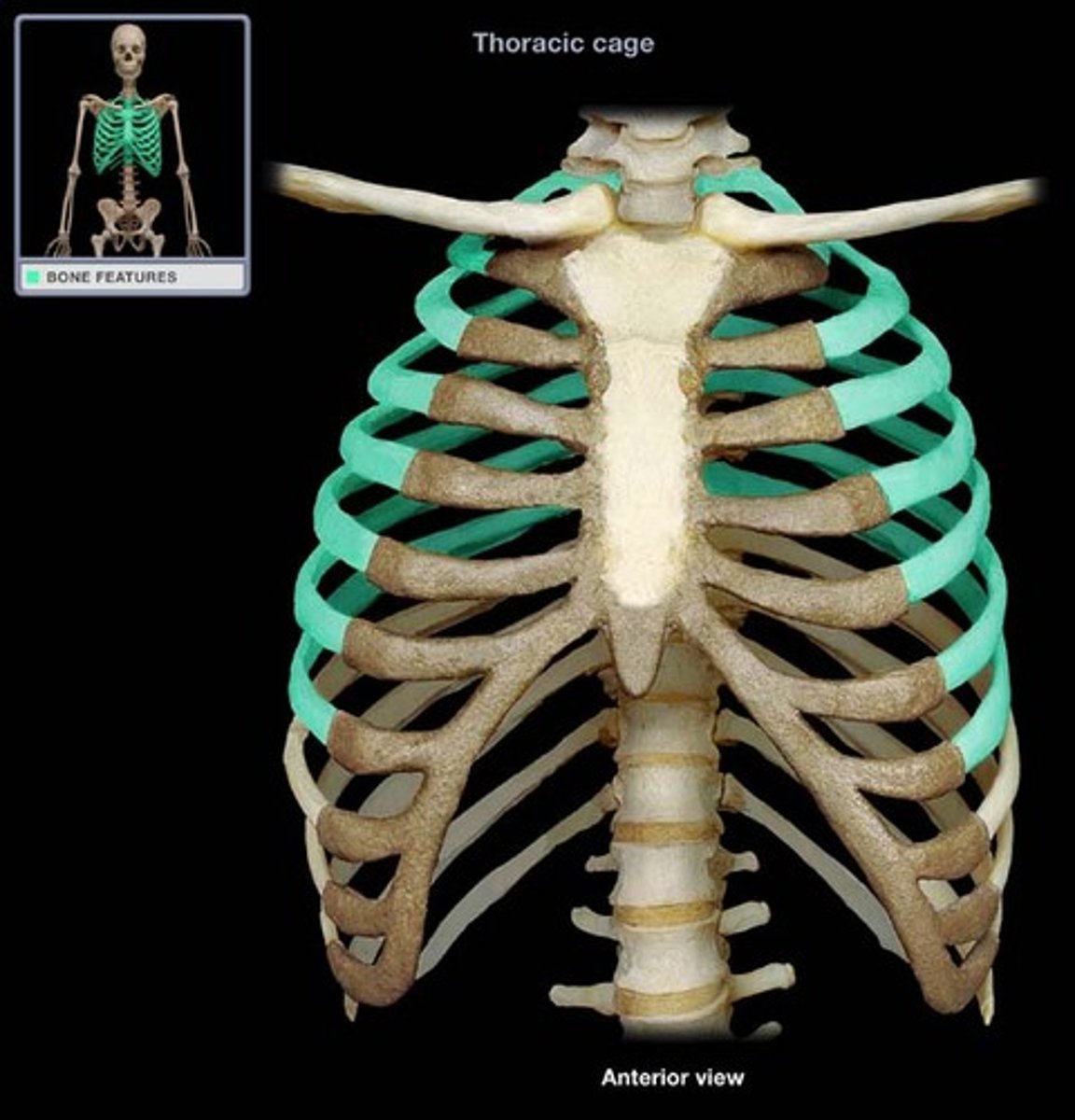
false ribs
last 5 pairs of ribs; attach indirectly to sternum via hyaline cartilage (specifically costal cartilage)
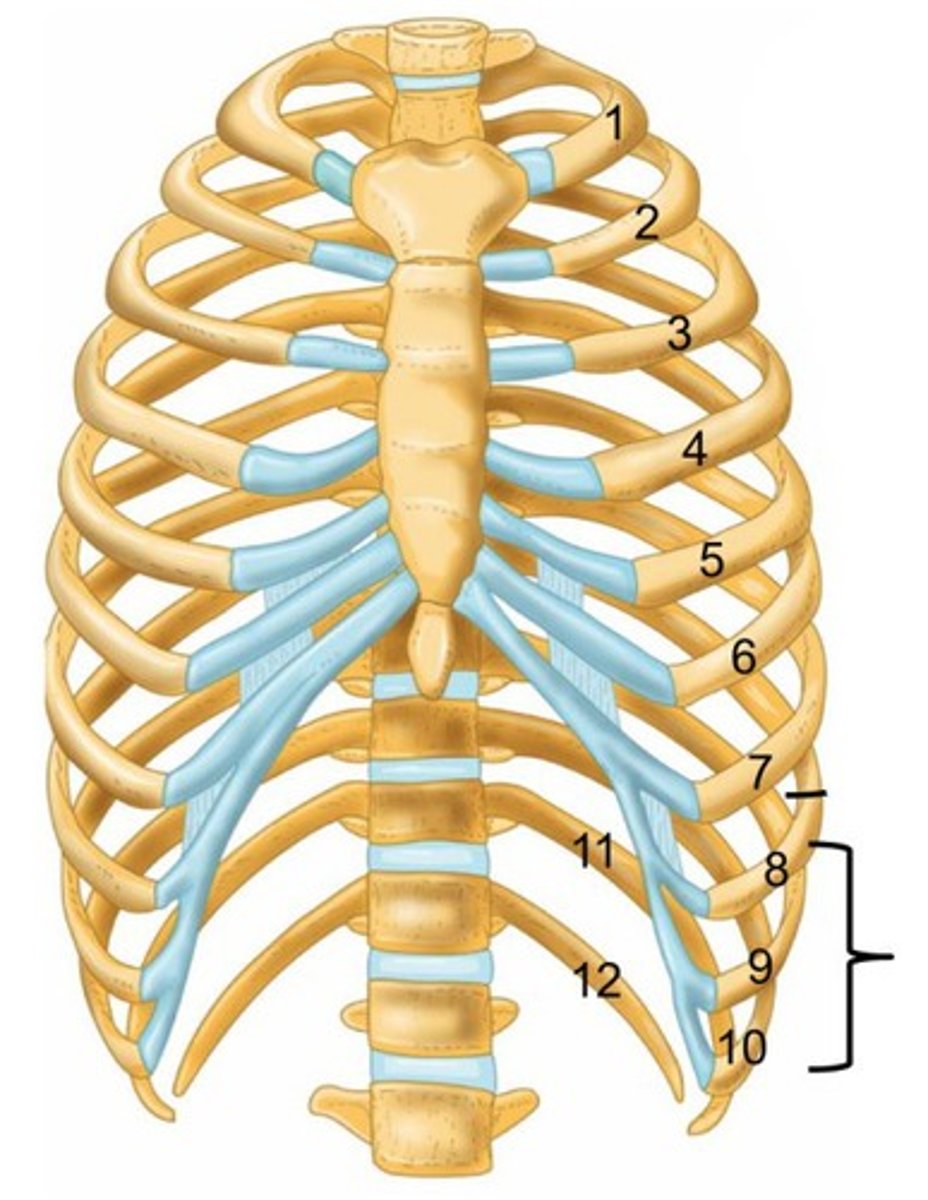
floating ribs
2 false ribs (11-12) that do not connect to the sternum via costal cartilage at all
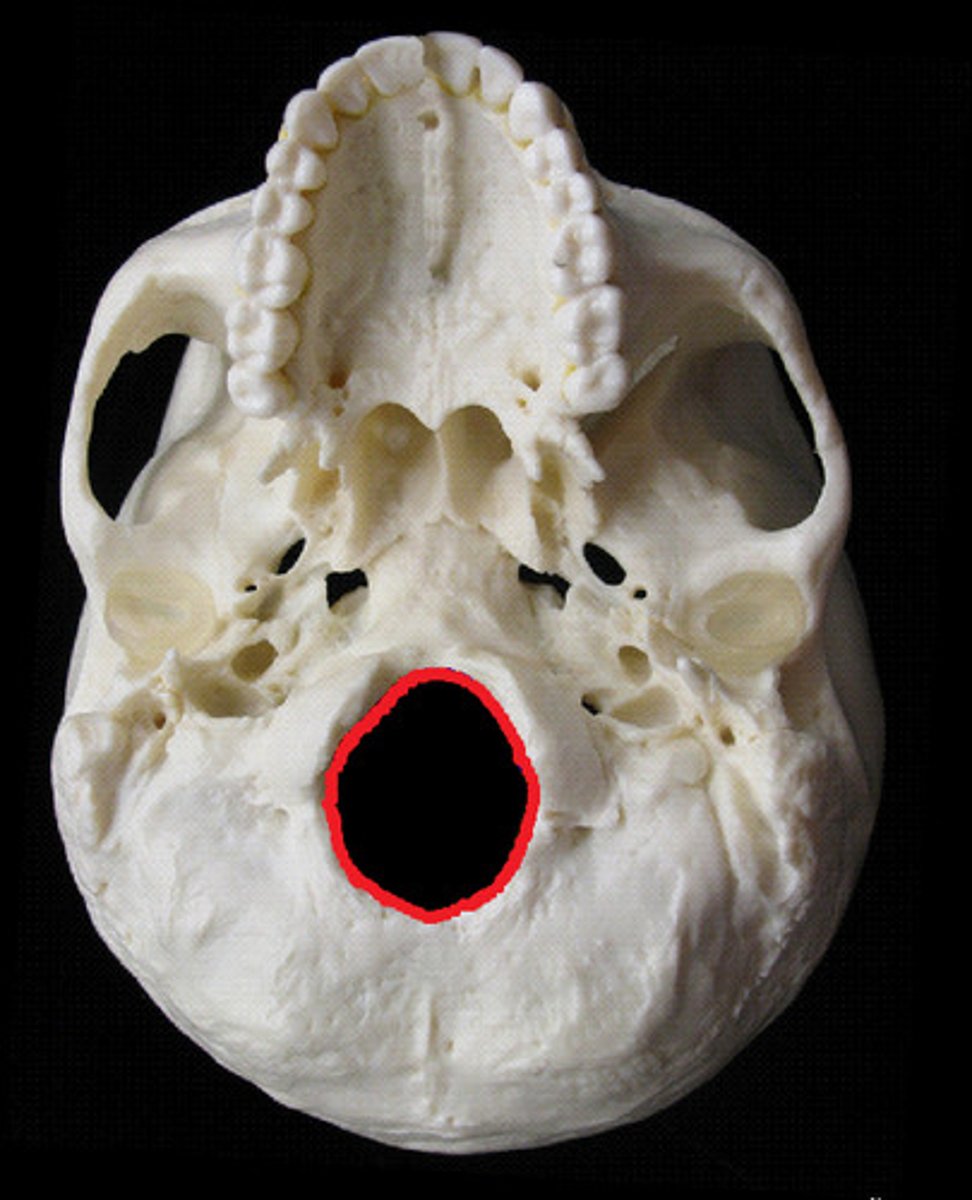
Foramen magnum
A large opening at the base of the skull through which the spinal cord connects to brain.
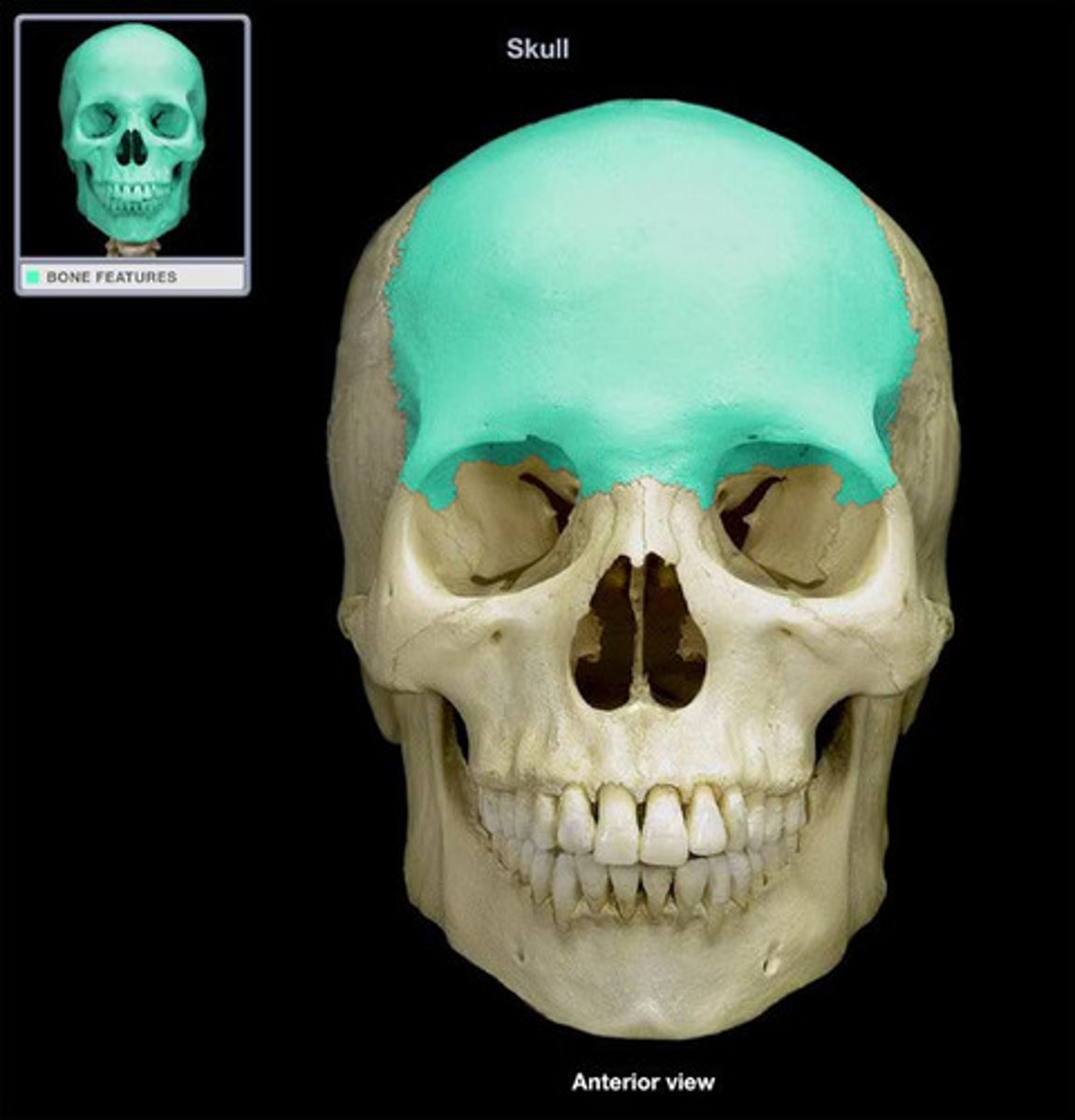
Frontal bone
the anterior cranial bone
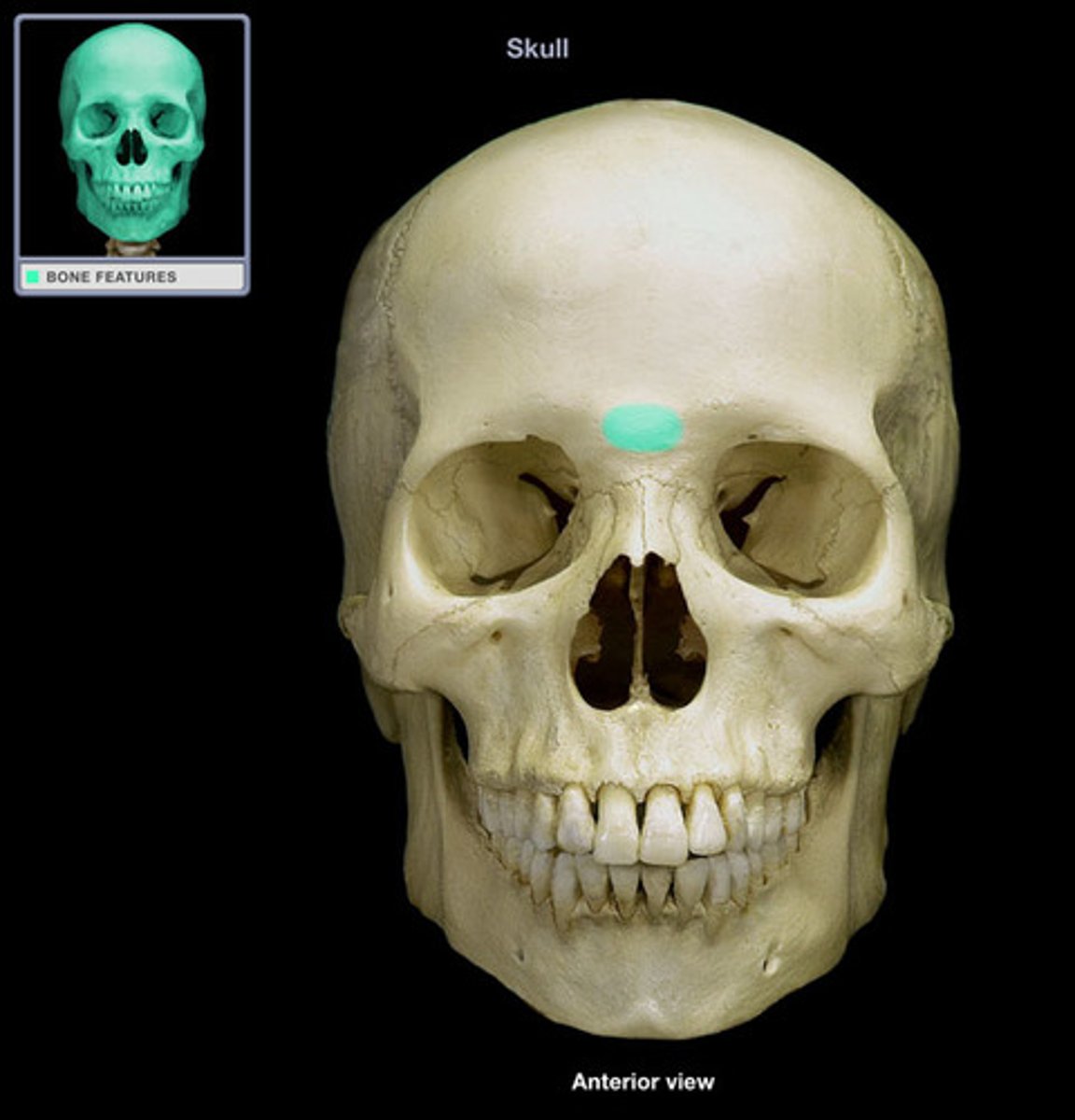
Glabella
the area between the eyebrows
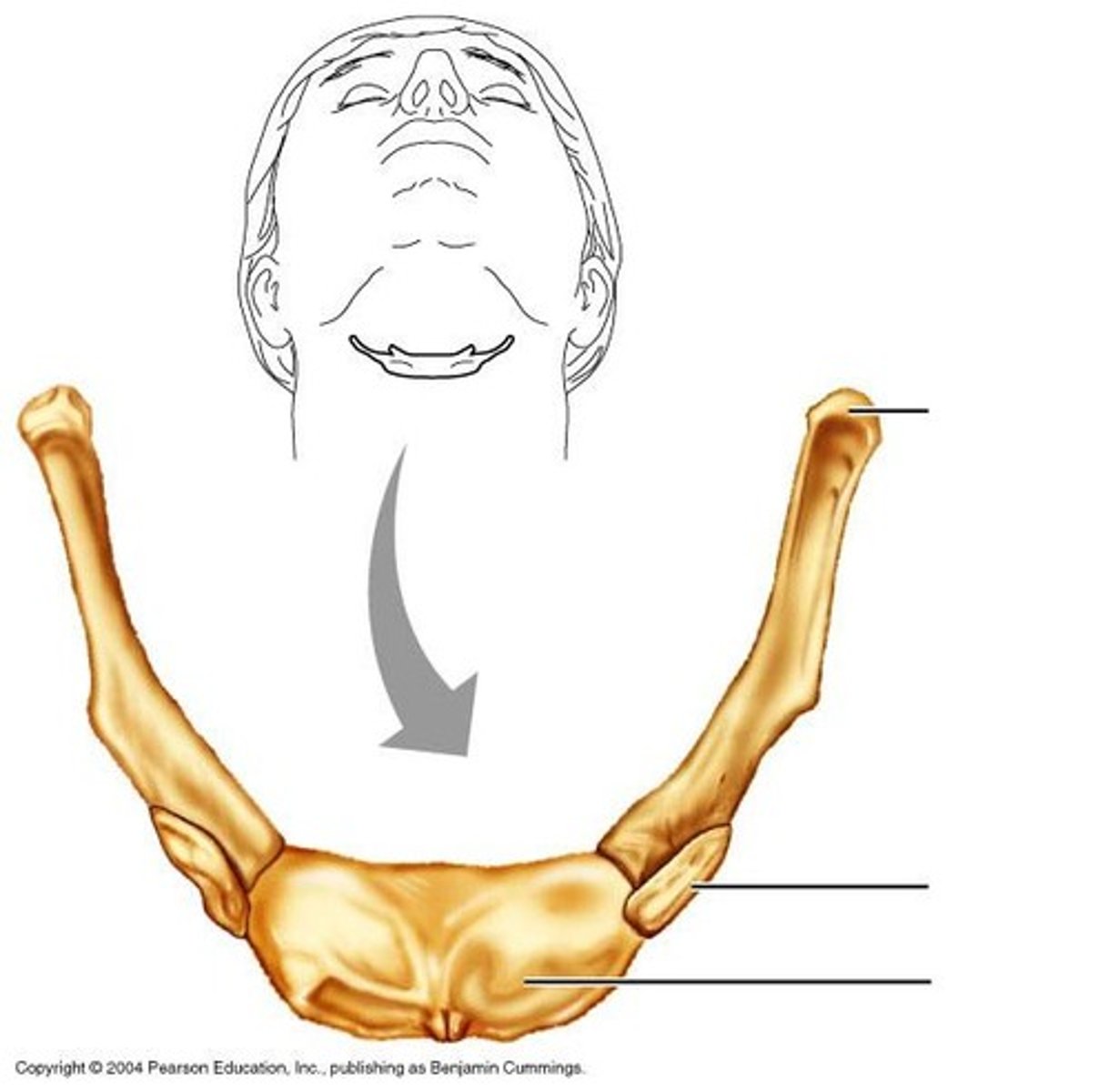
hyoid bone
U-shaped bone at the base of the tongue that supports the tongue and its muscles.
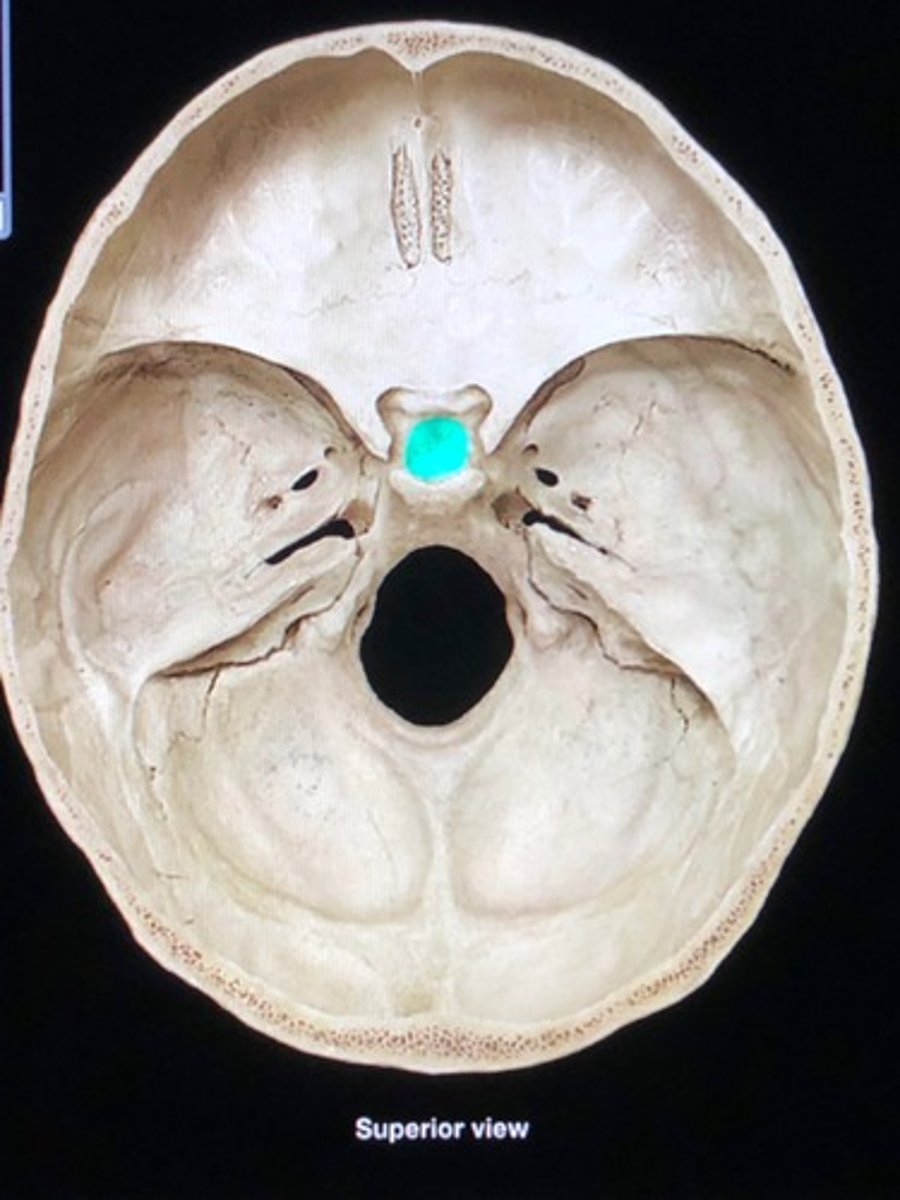
hypopheseal fossa
the depression of the sella turcica; home of the pituitary gland
Inferior articular process of vertebrae
downward projecting process that connects the vertebrae to its lower counterpart
Inferior nasal conchae
the lower projections of the nasal cavity
Infratemporal fossa
inferior to the temporal fossa; articulation region for the mandible which allows chewing
Intervertebral discs
fibrocartilage pads that separate and cushion the vertebrae
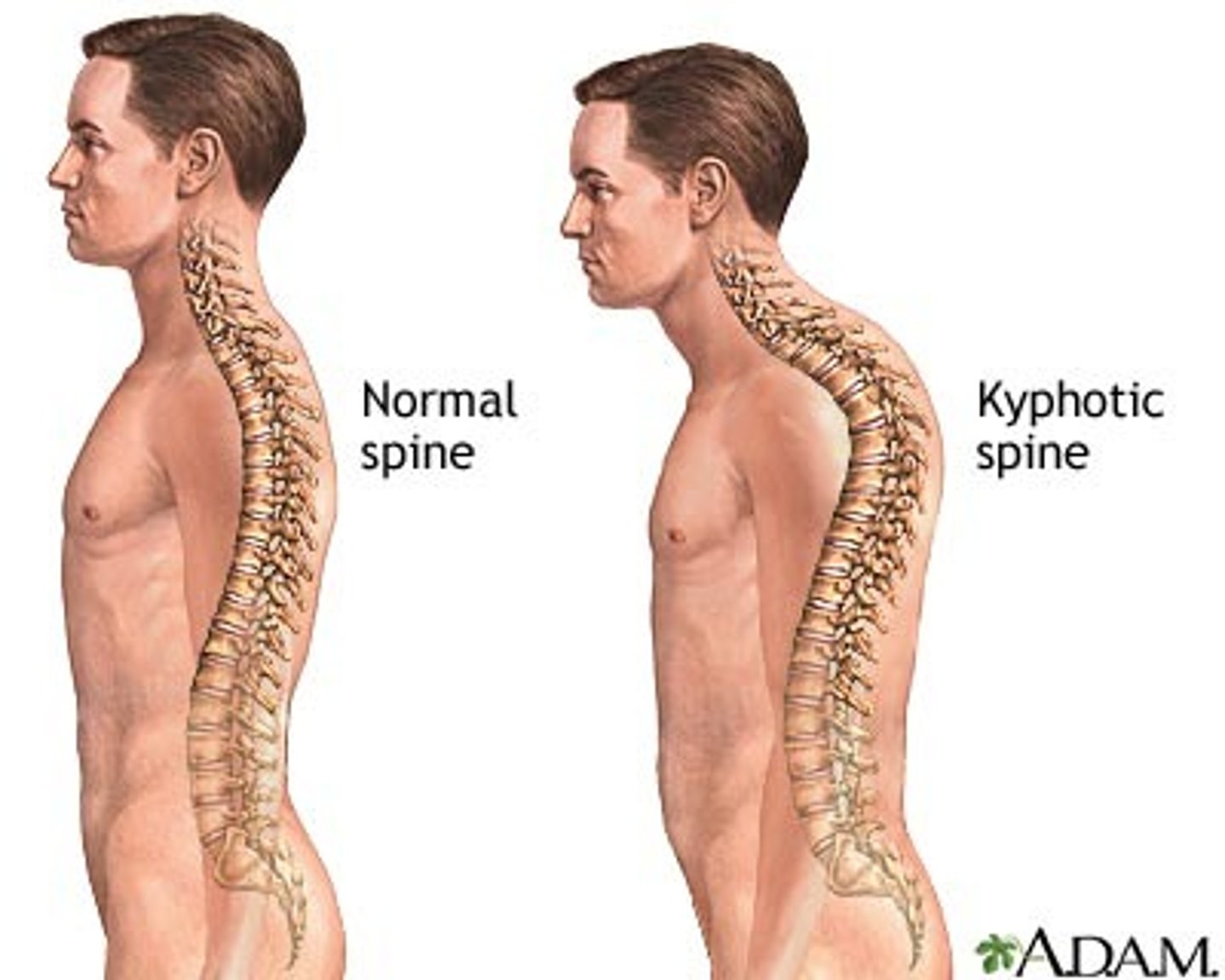
Kyphosis
excessive outward curvature of the thoracic curve
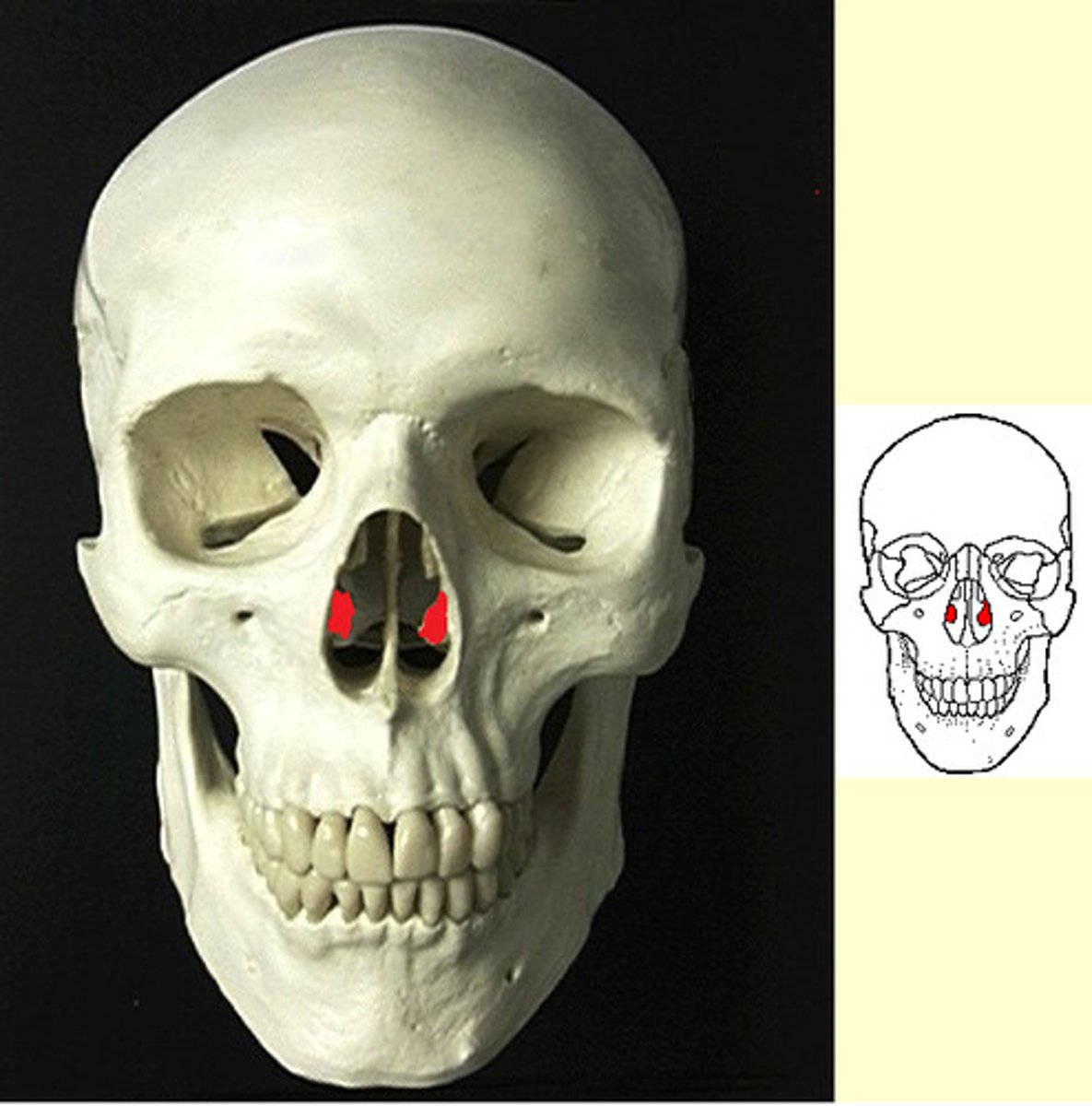
Lacrimal bone
small fragile bone making up part of the front inner walls of each eye socket and providing room for the passage of the lacrimal ducts (tear ducts)
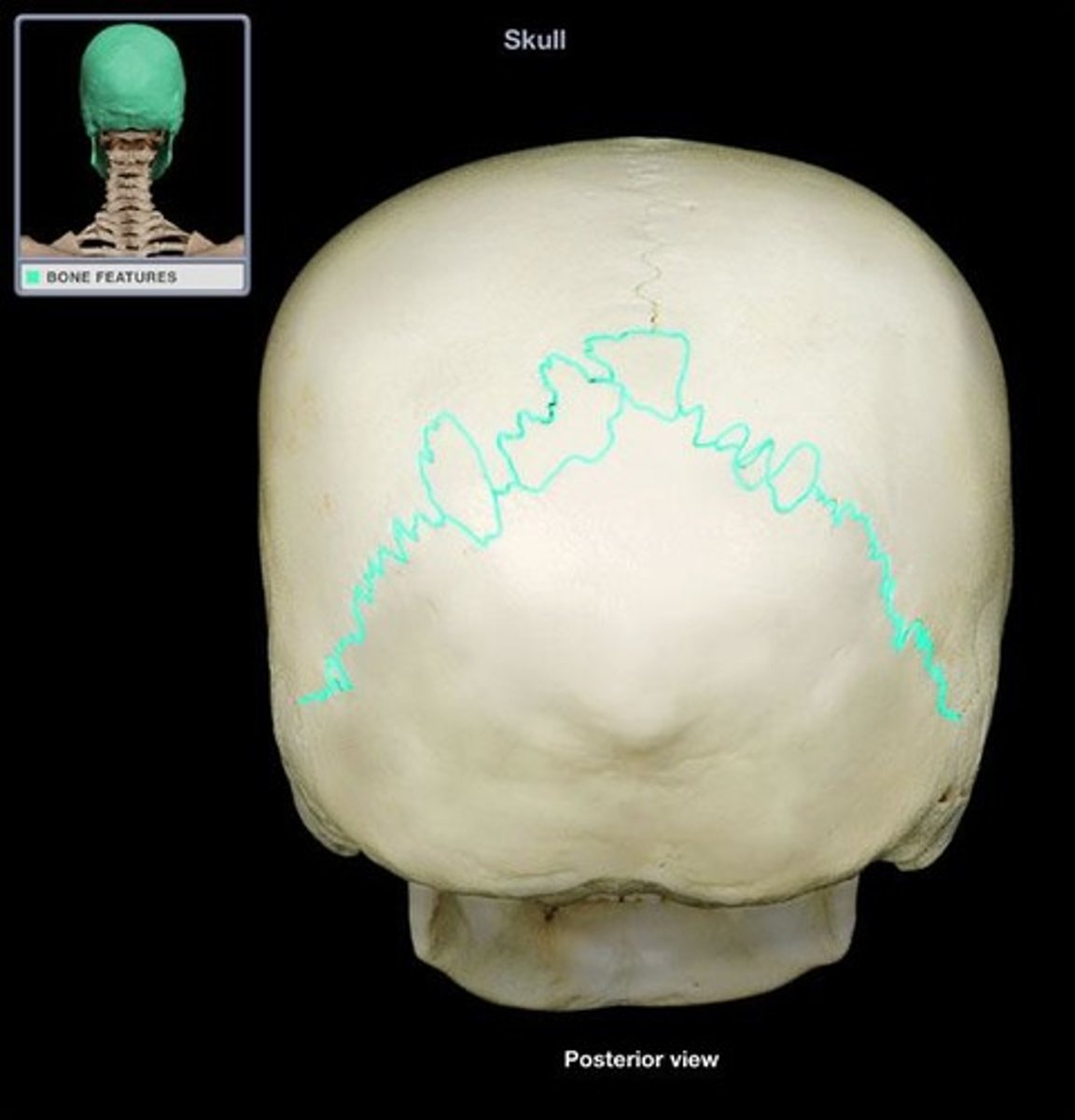
lamboid suture
the suture between the occipital and parietal bones
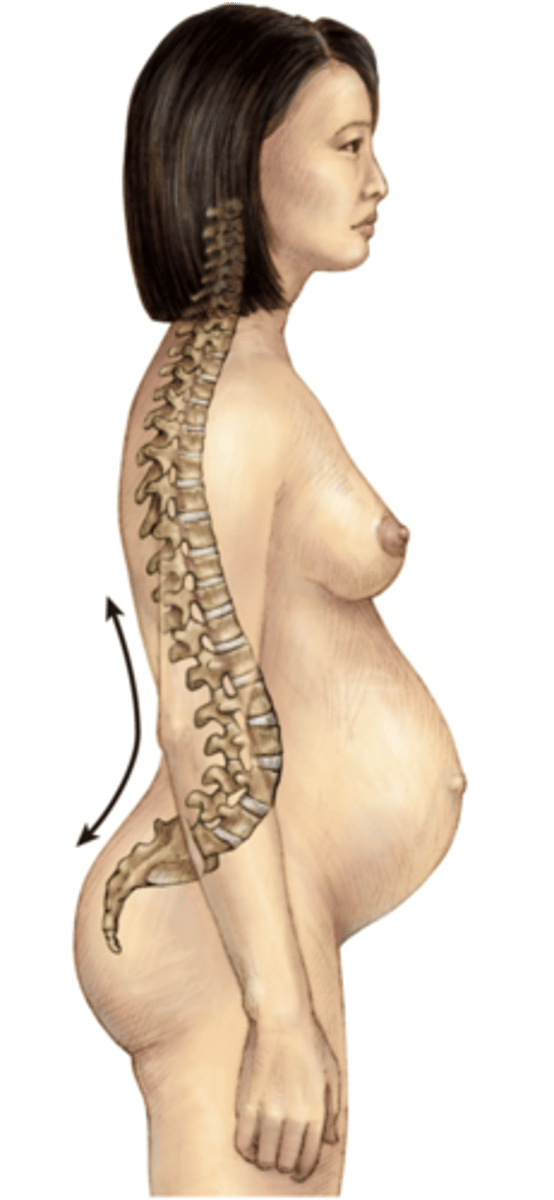
Lordosis
The excessive curvature of the lumbar spine
Lumbar curve
often referred to as the lower back, L1-L5
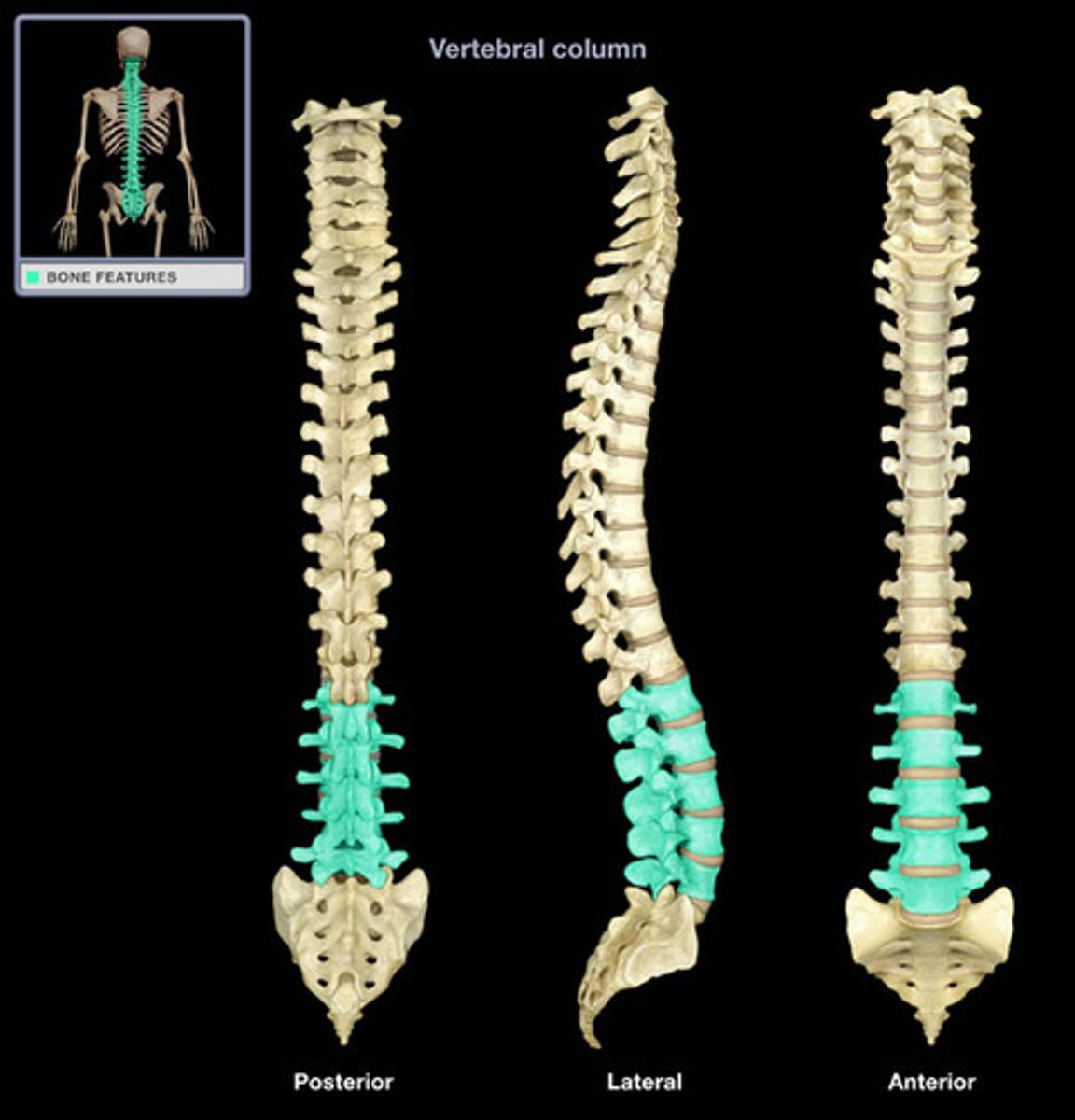
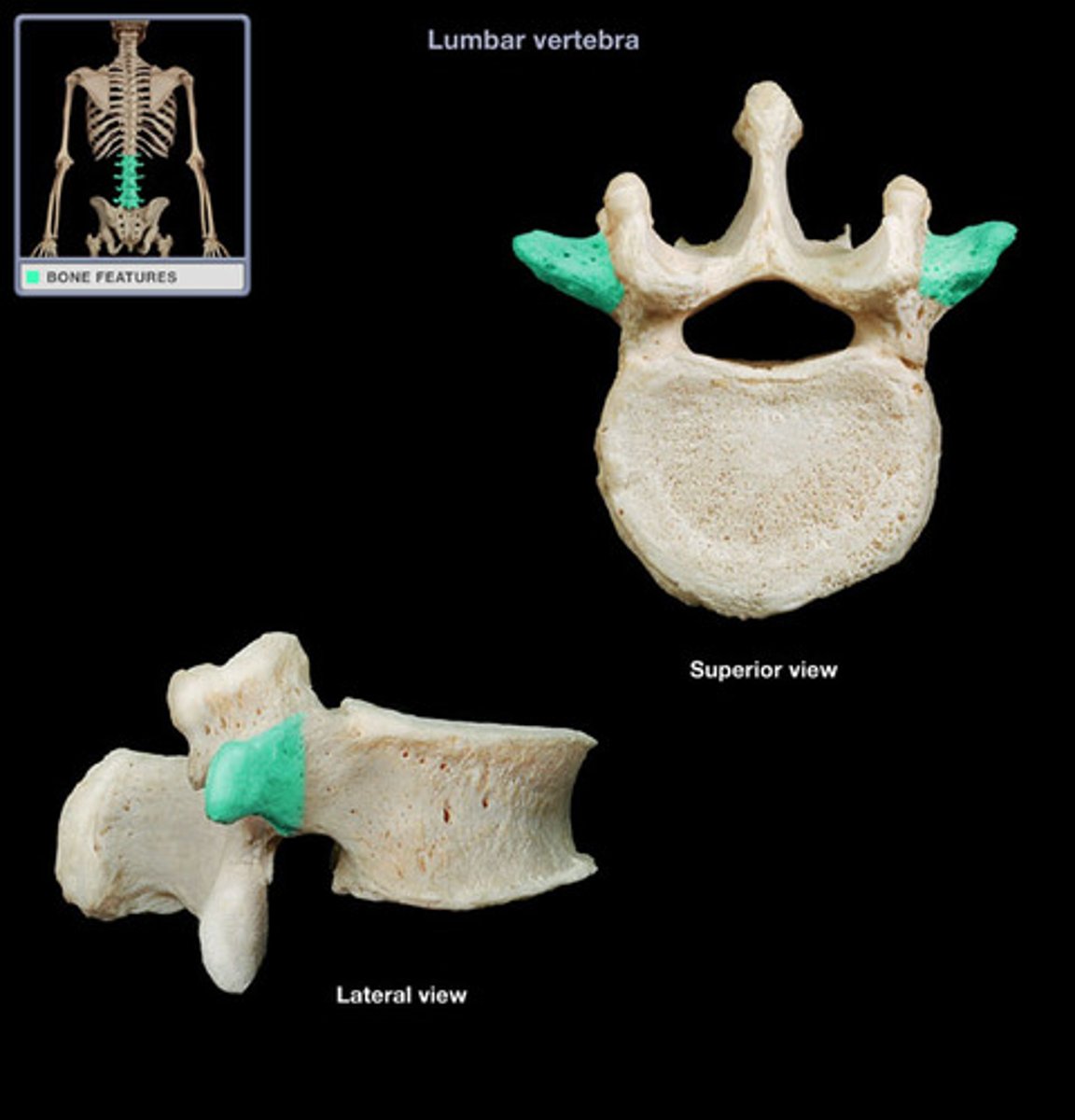
Lumbar vertebrae
Have a shorter spinous process and larger centrum or body
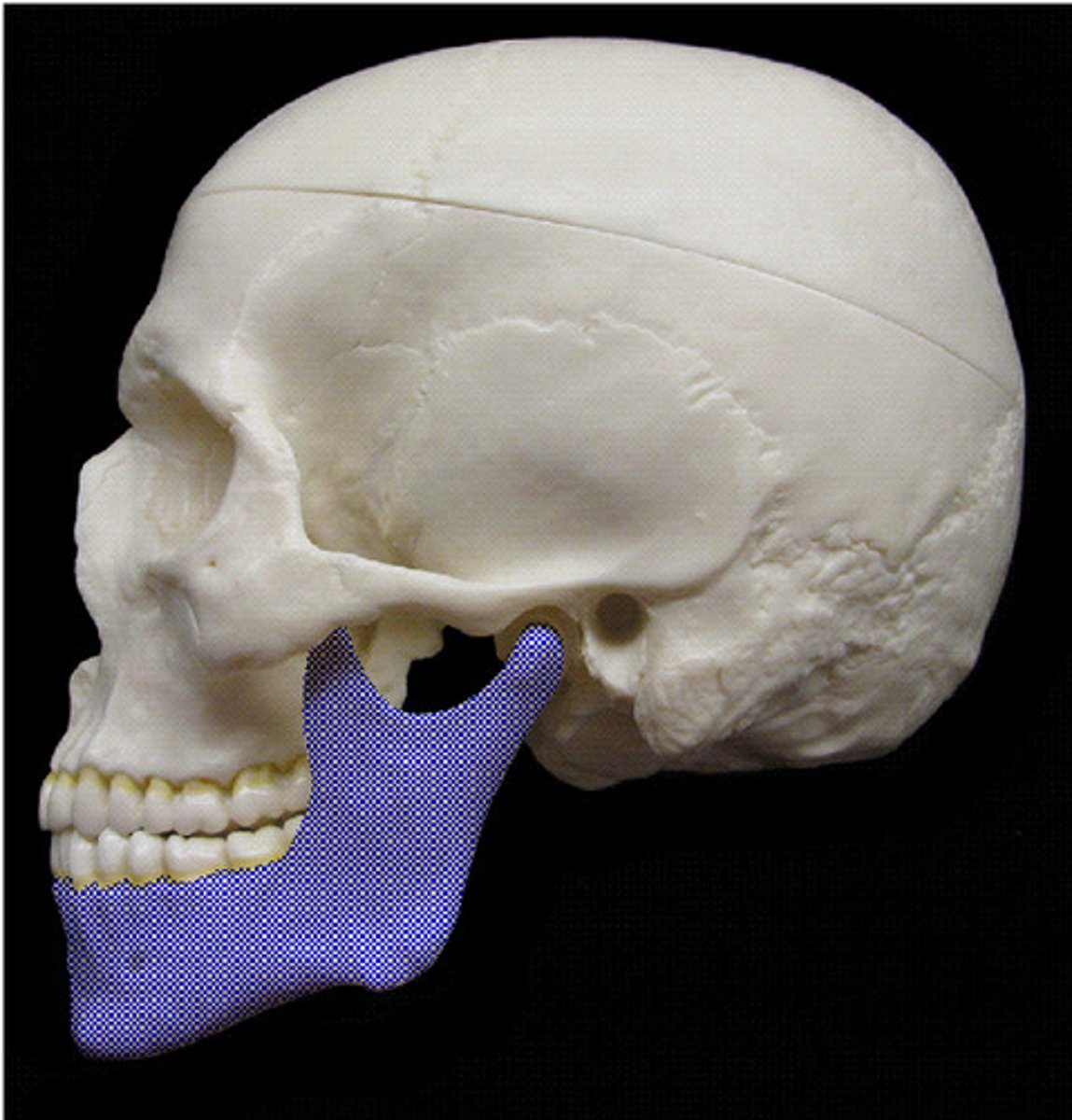
Mandible
lower jaw
Manubrium
the upper portion of the sternum, connects to clavicle
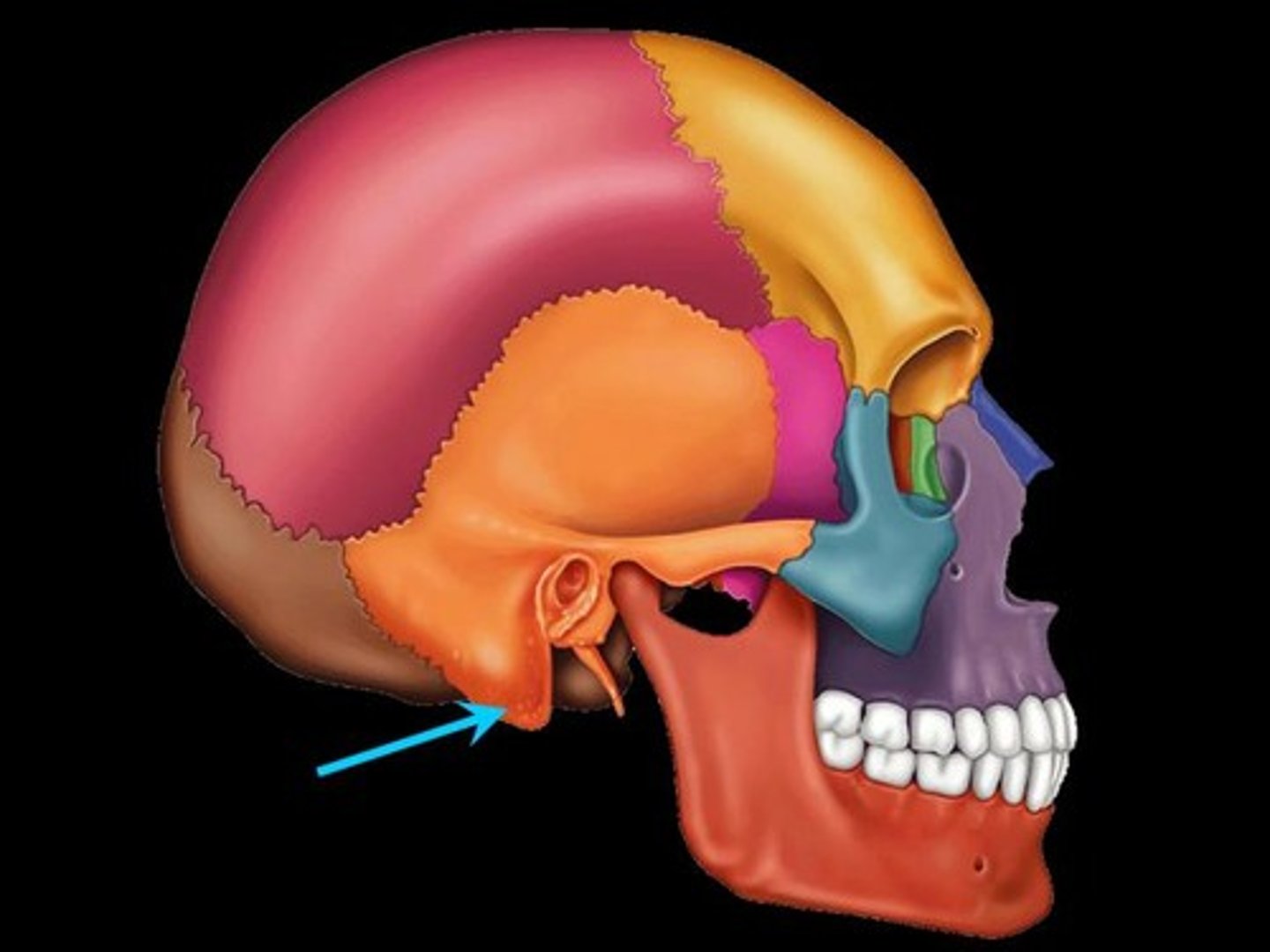
mastoid process
round projection on the temporal bone behind the ear, attachment site of neck muscles
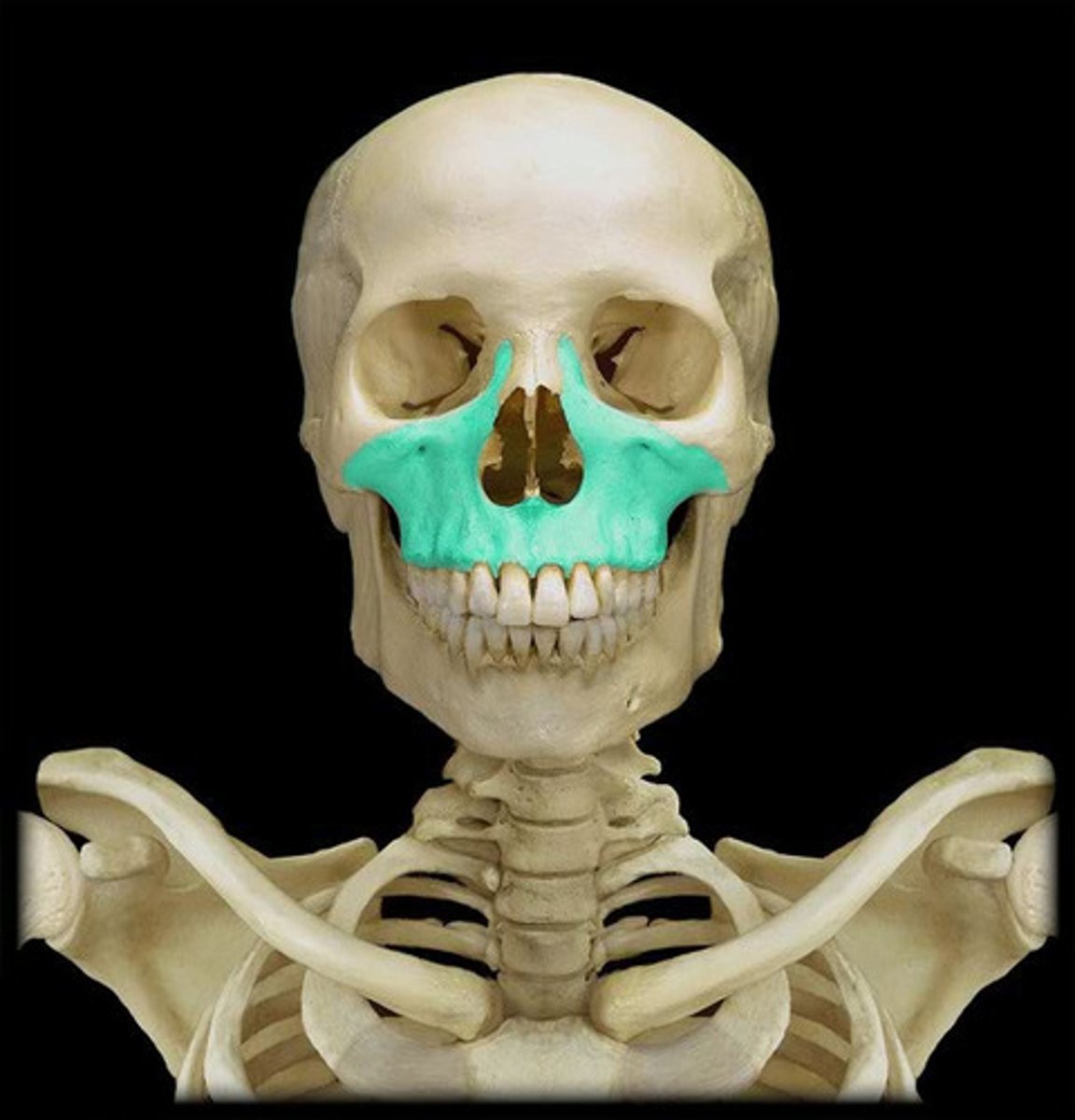
Maxillary bones
The upper jawbones that assist in the formation of the orbit, the nasal cavity, and the palate and hold the upper teeth.
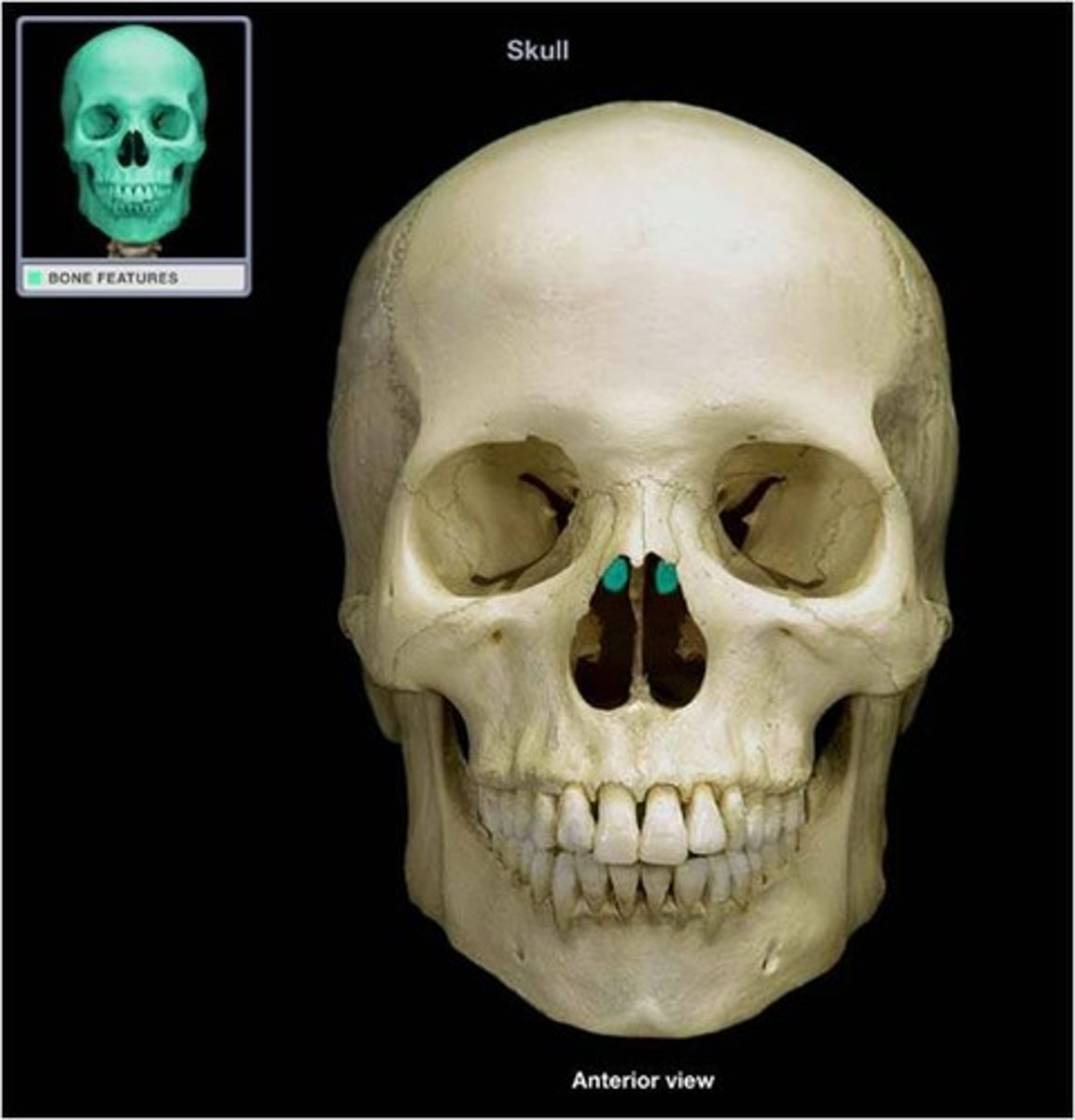
middle nasal conchae
projections that can be seen as the upper portion of the nasal cavity from anterior view
Nasal bone
forms the bridge of the nose
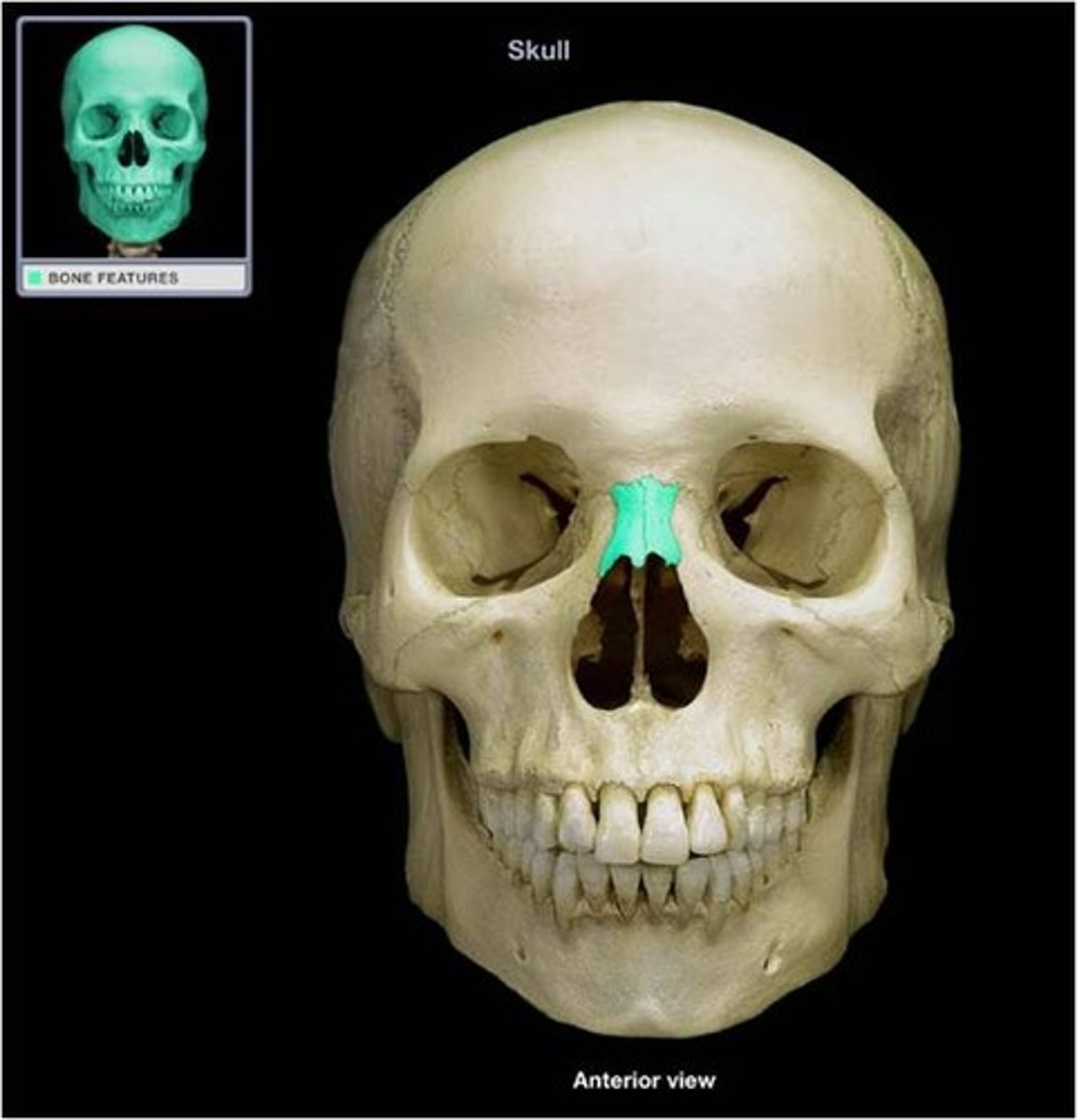
Nasal septum
partition separating the right and left nasal cavities; formed by ethmoid and lower vomer bone
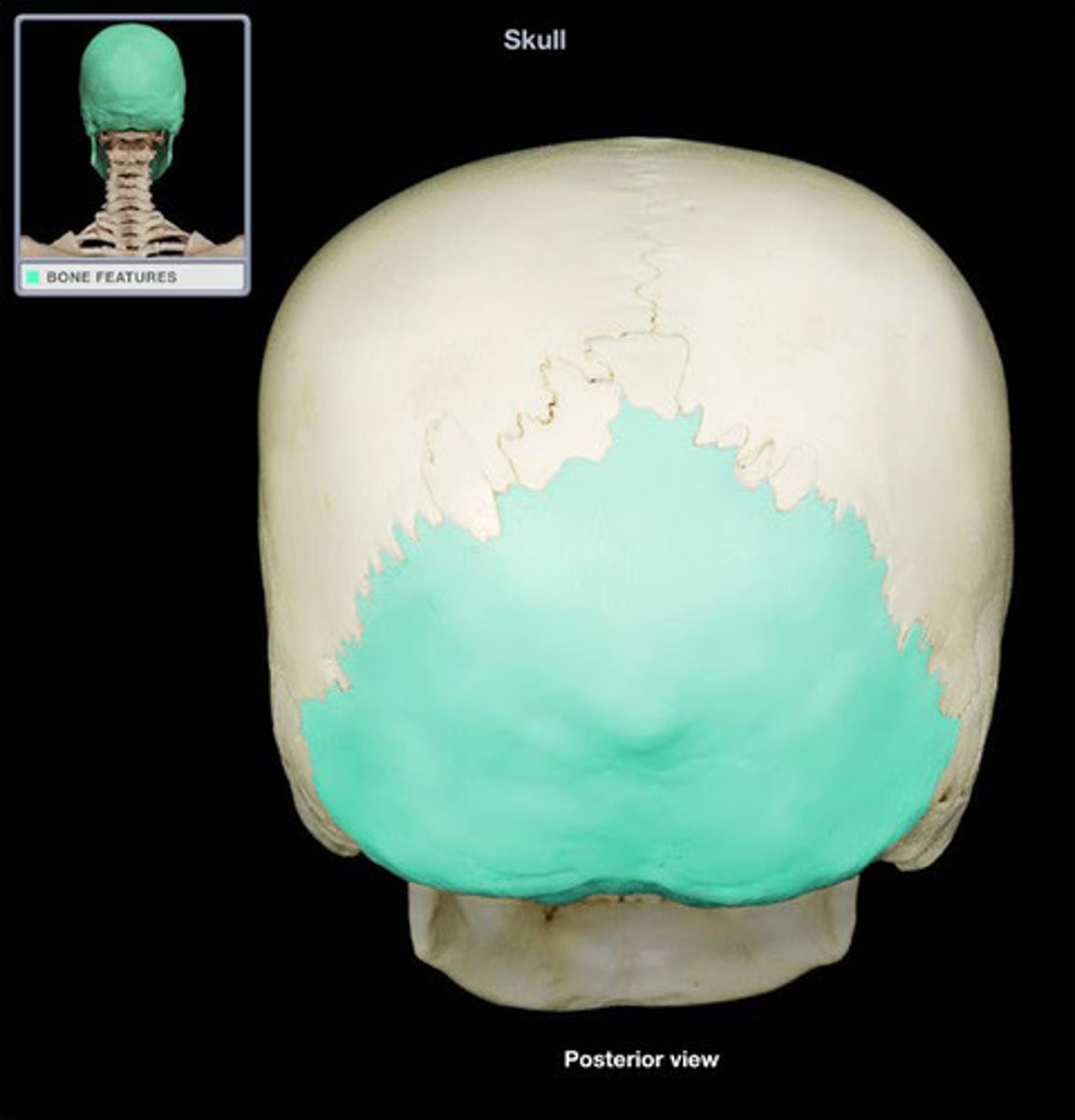
Occipital bone
Bone at the base of the skull
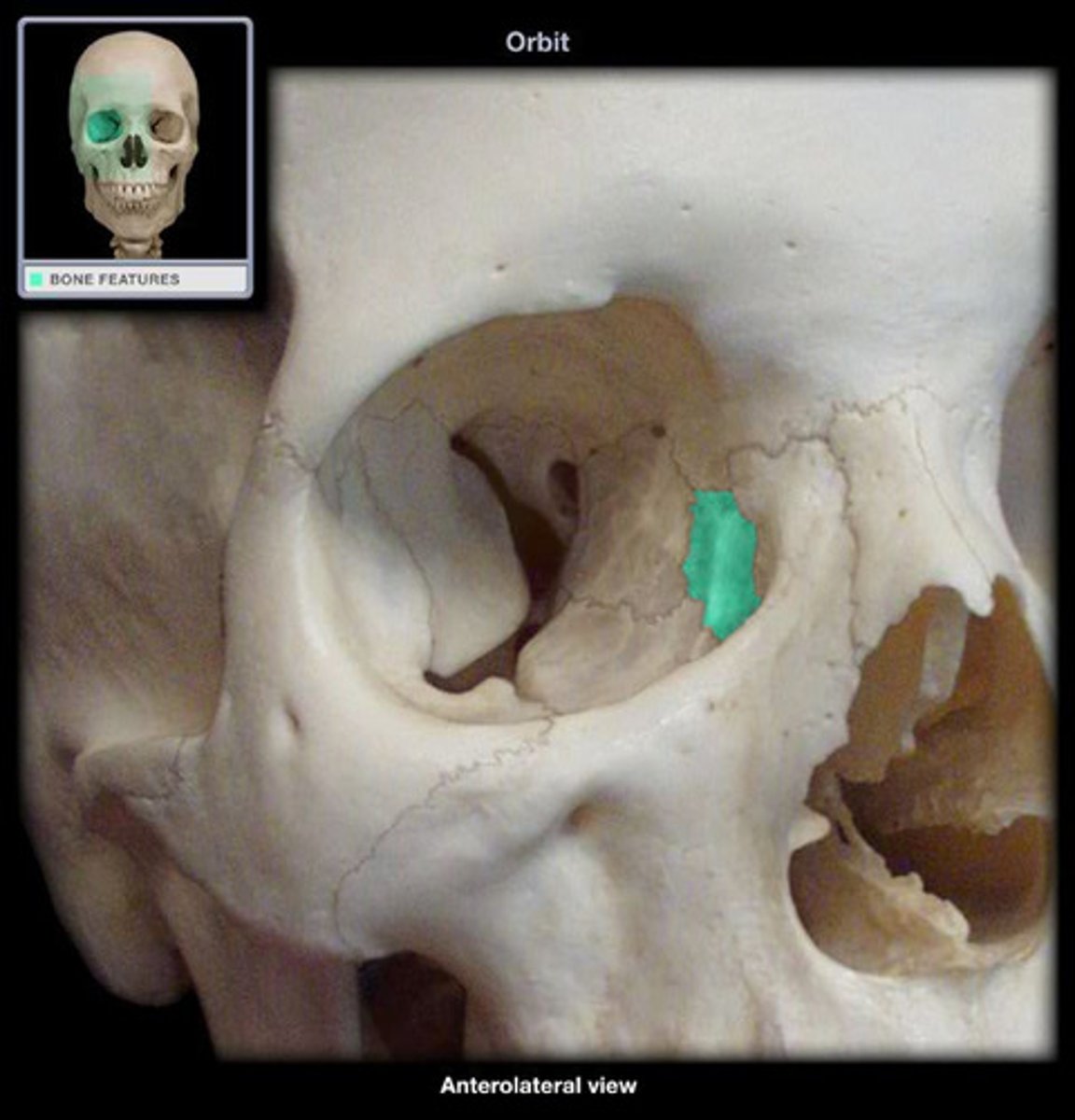
Orbit
bony cavity that holds eyeball
Parietal bones
form most of the roof and upper sides of the cranium
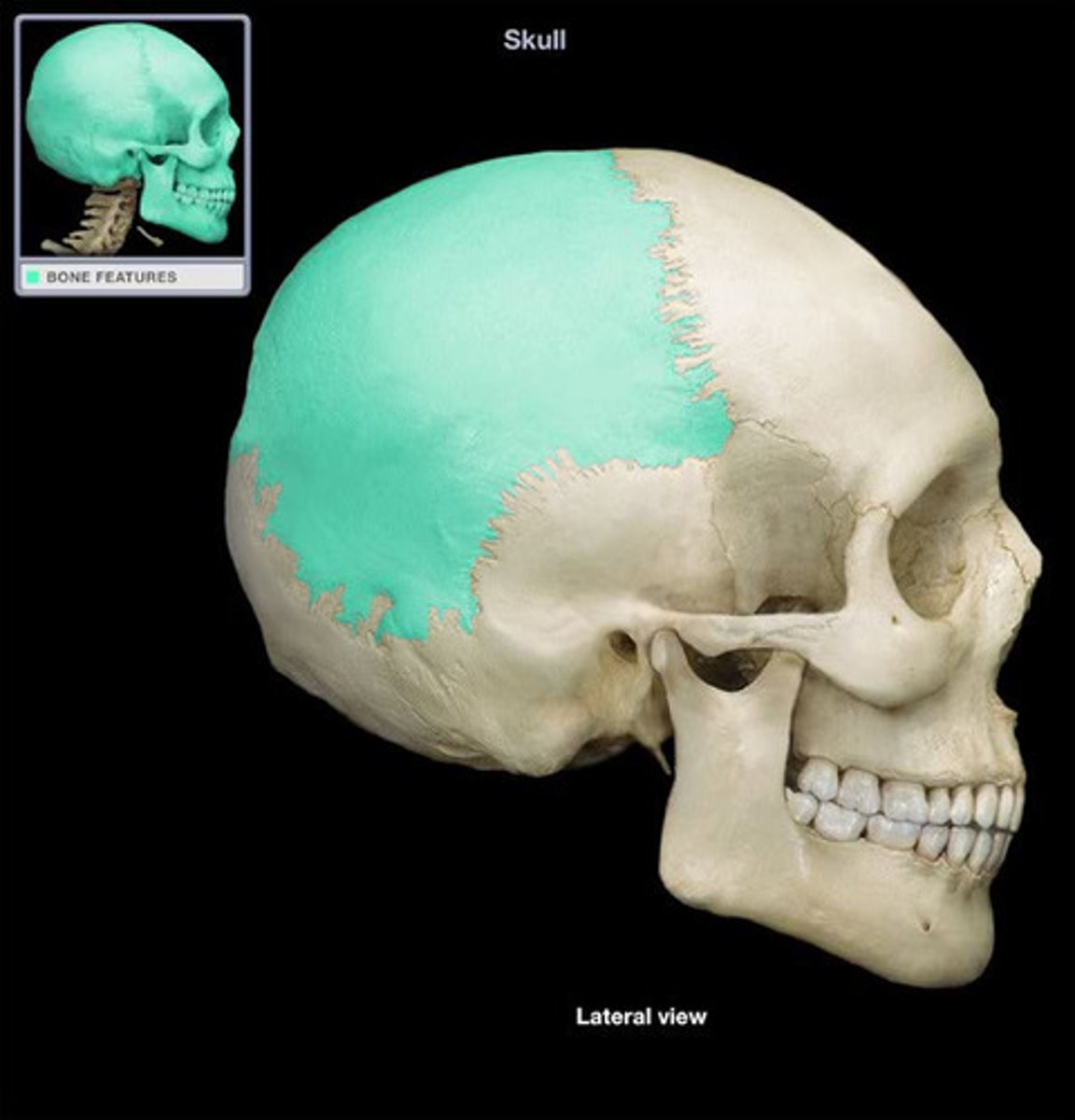
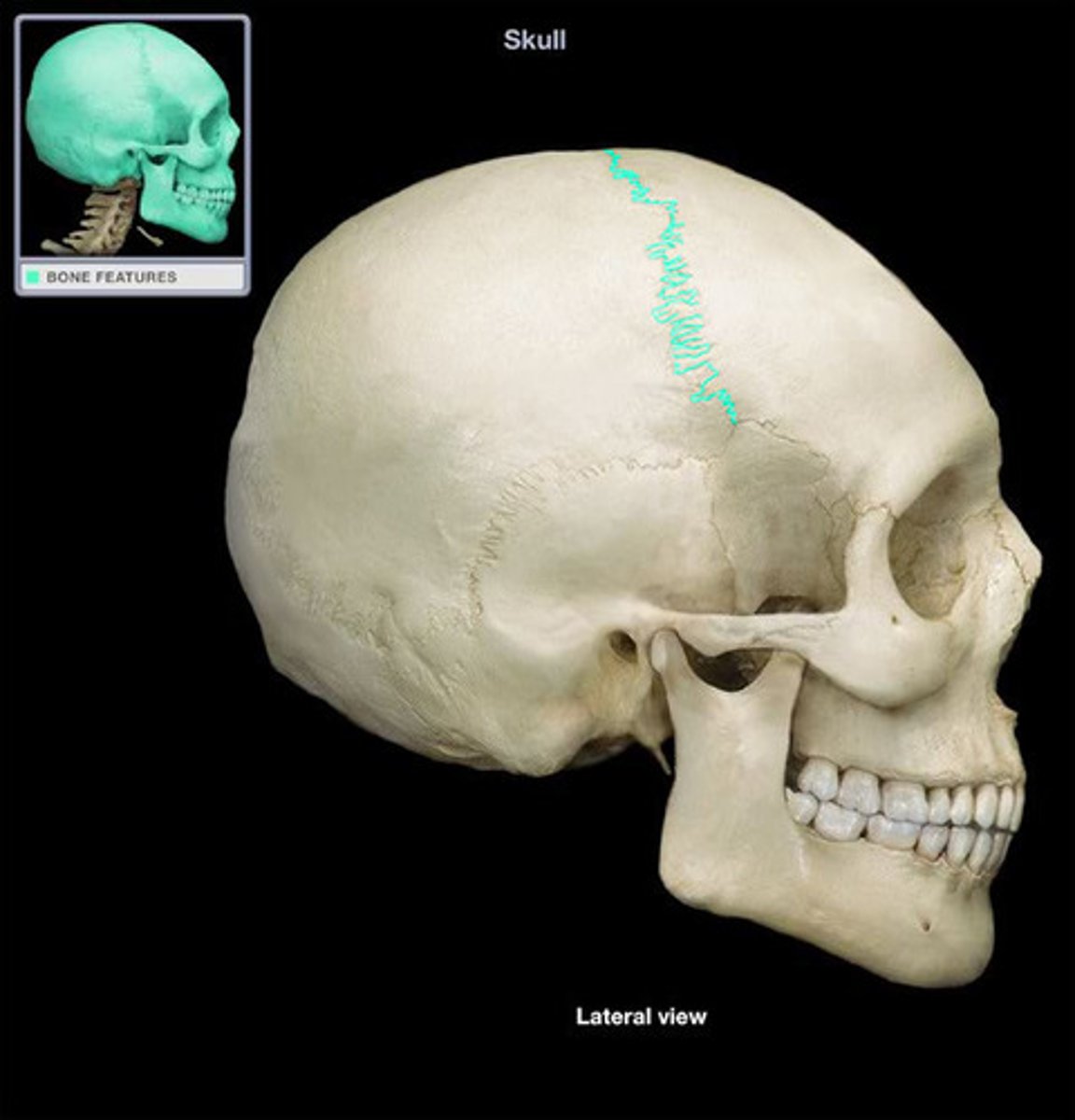
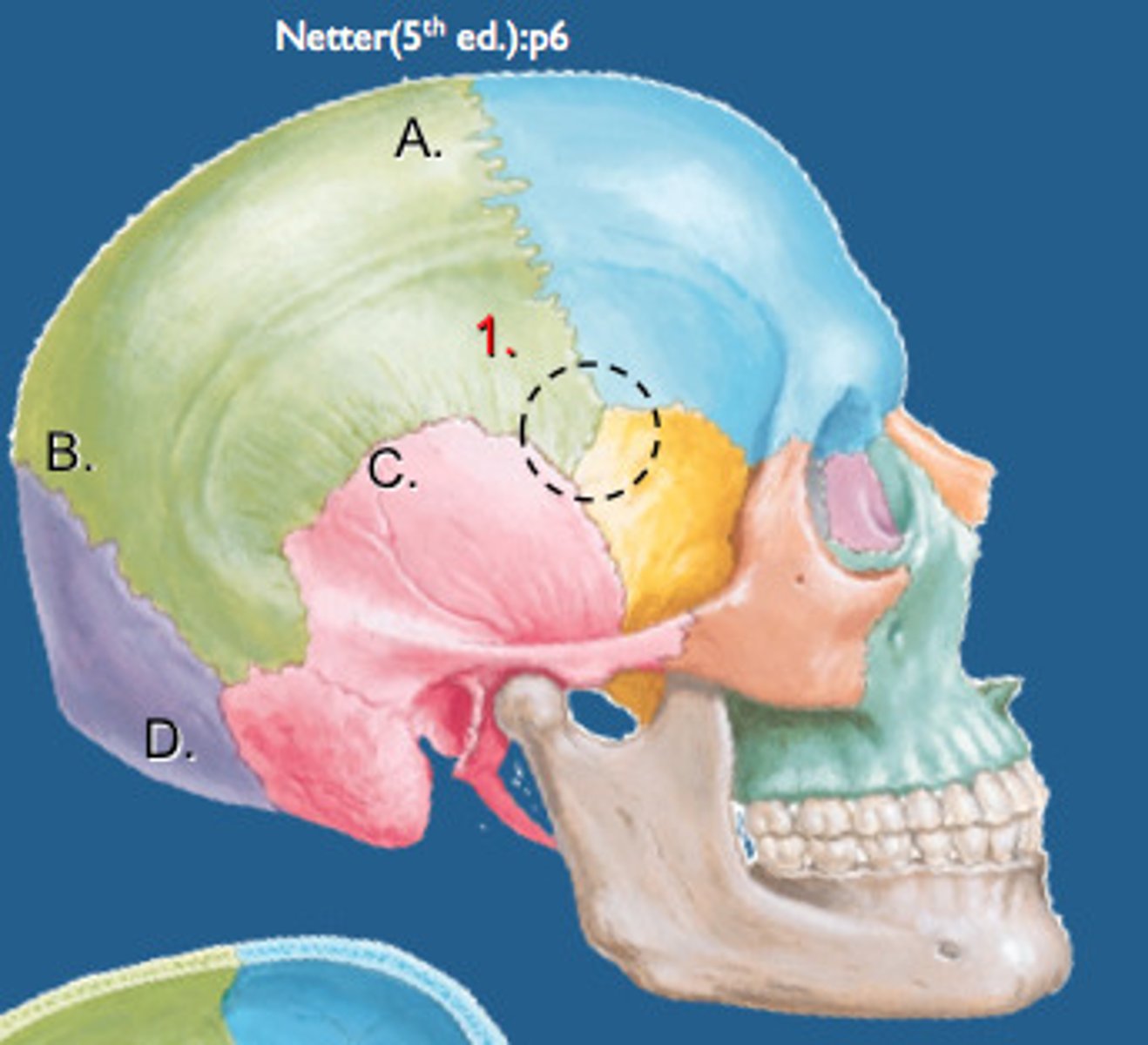
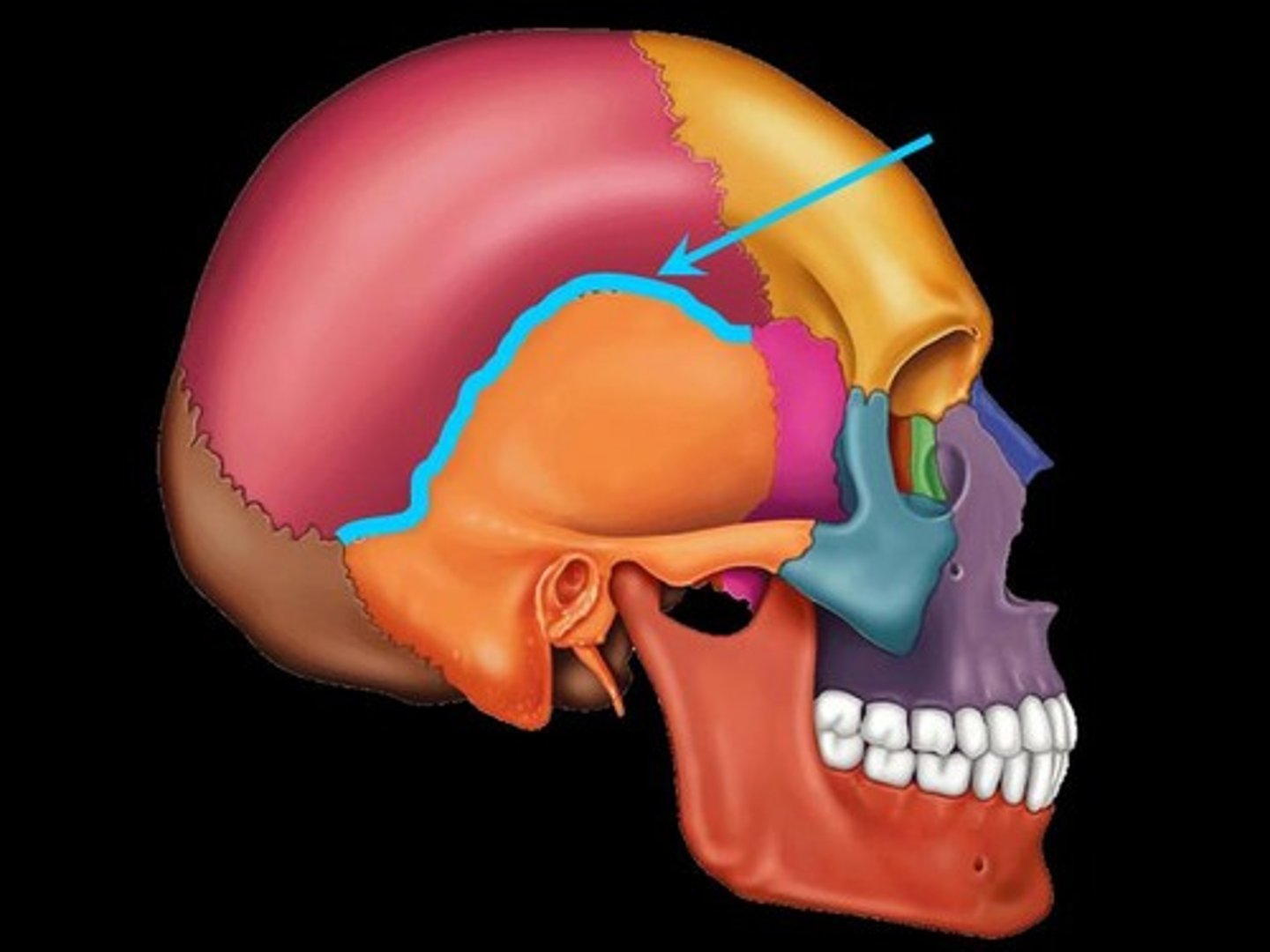
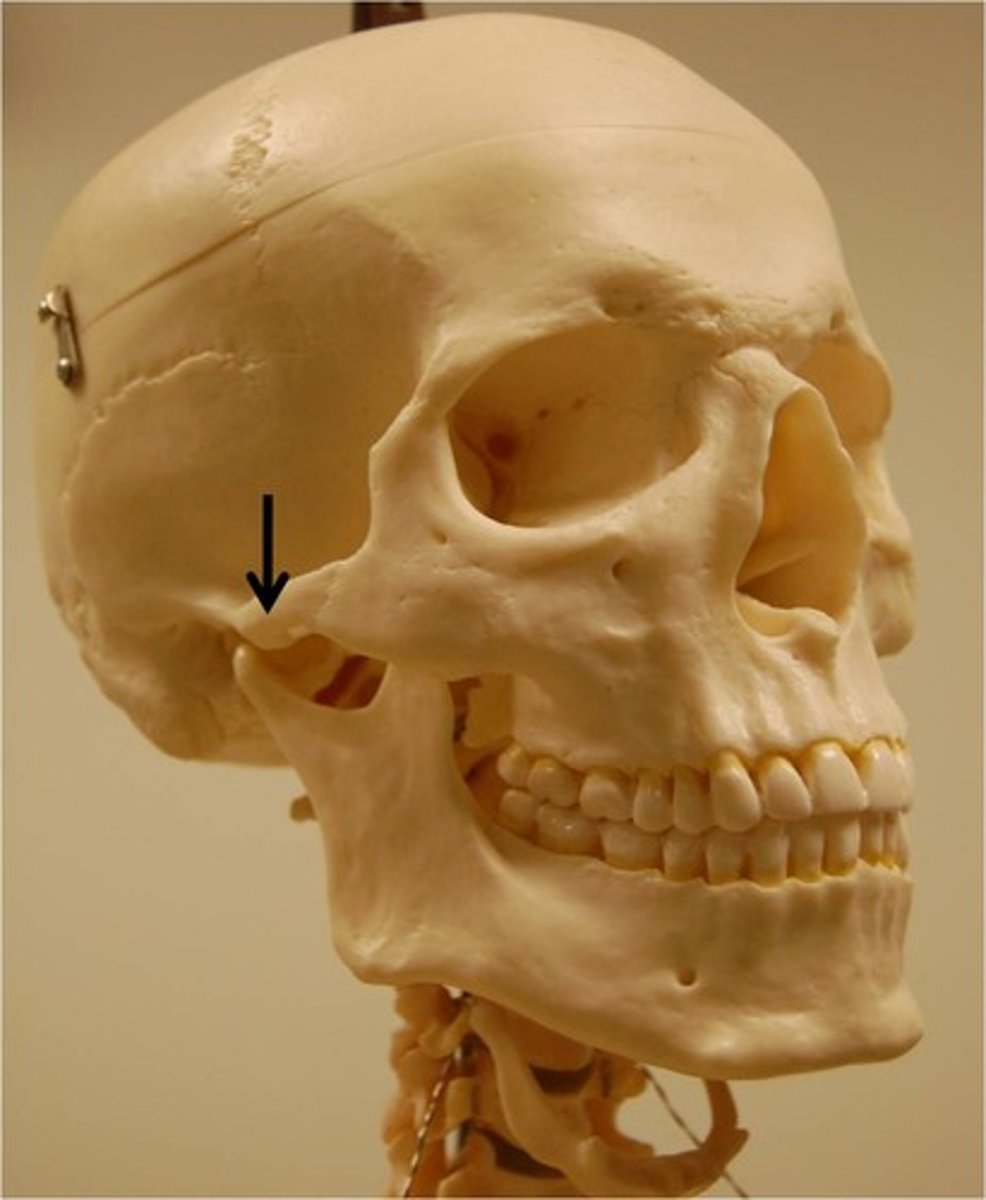
Pterion
the suture between all bones but occipital, weakest part of the skull
Sacral curve
the last curve, houses the sacrum and coccyx
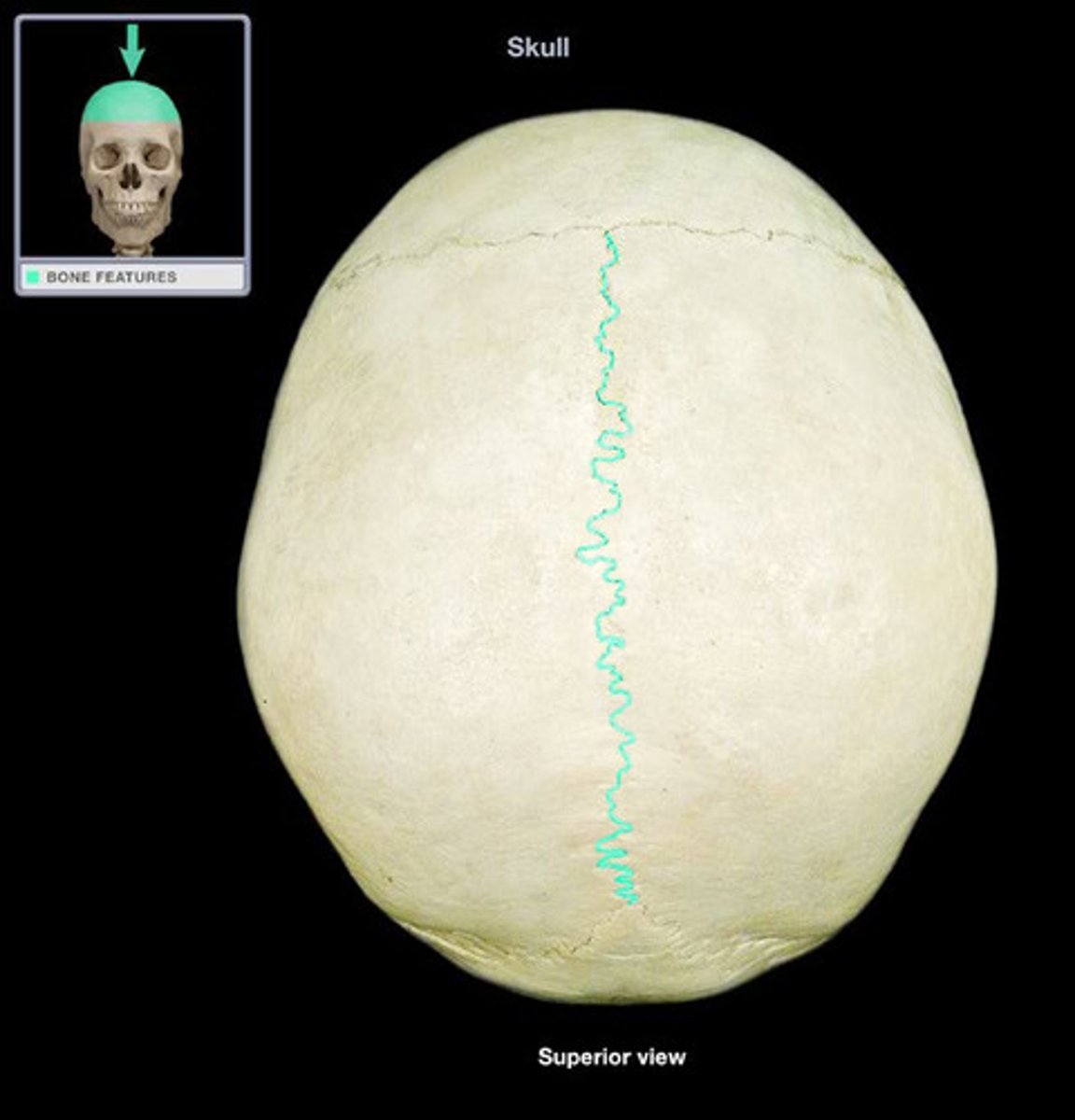
Sagittal suture
the suture between parietal bones
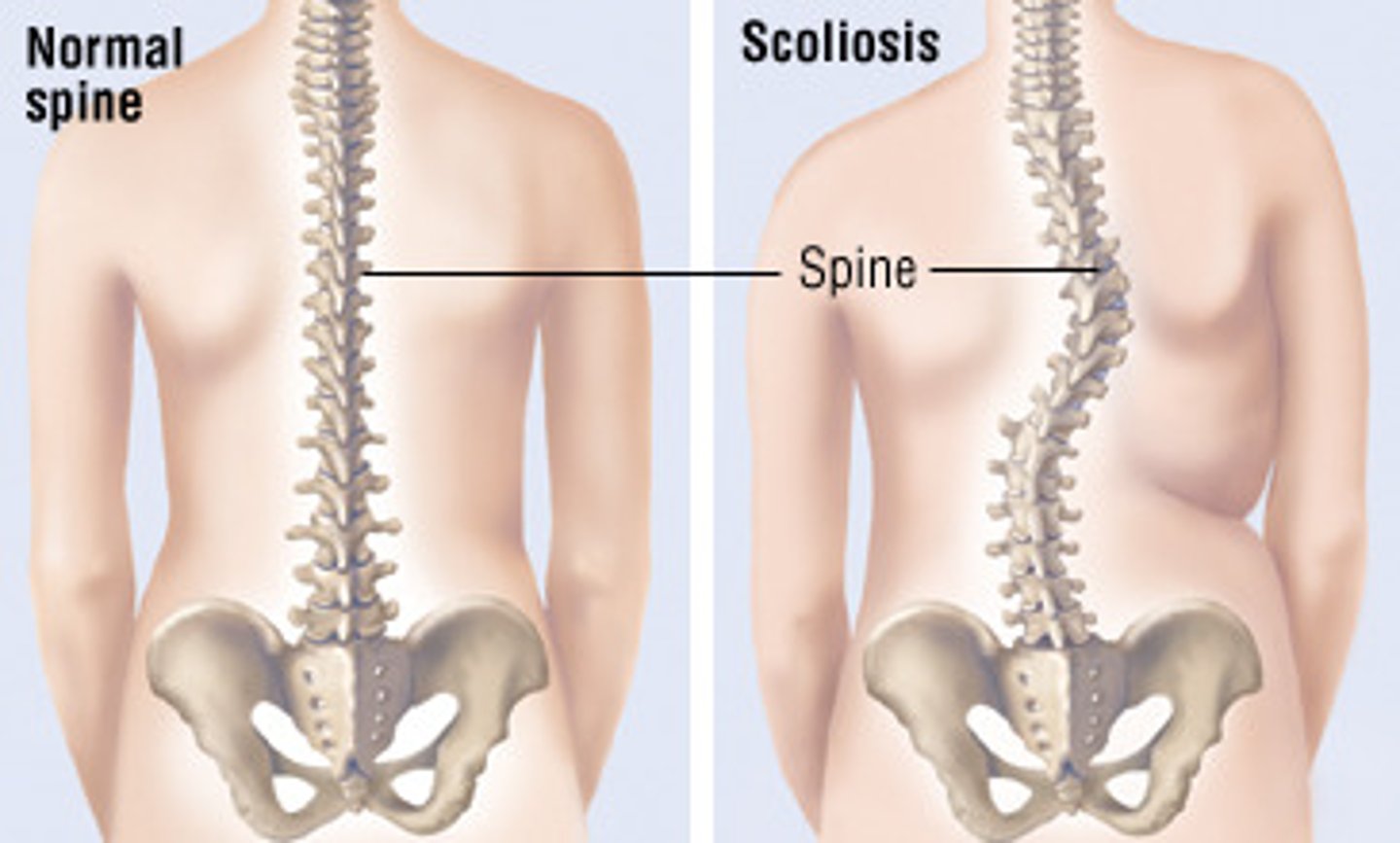
Scoliosis
abnormal lateral curvature of the spine
Sella turcica
cavity in the skull that contains the pituitary gland
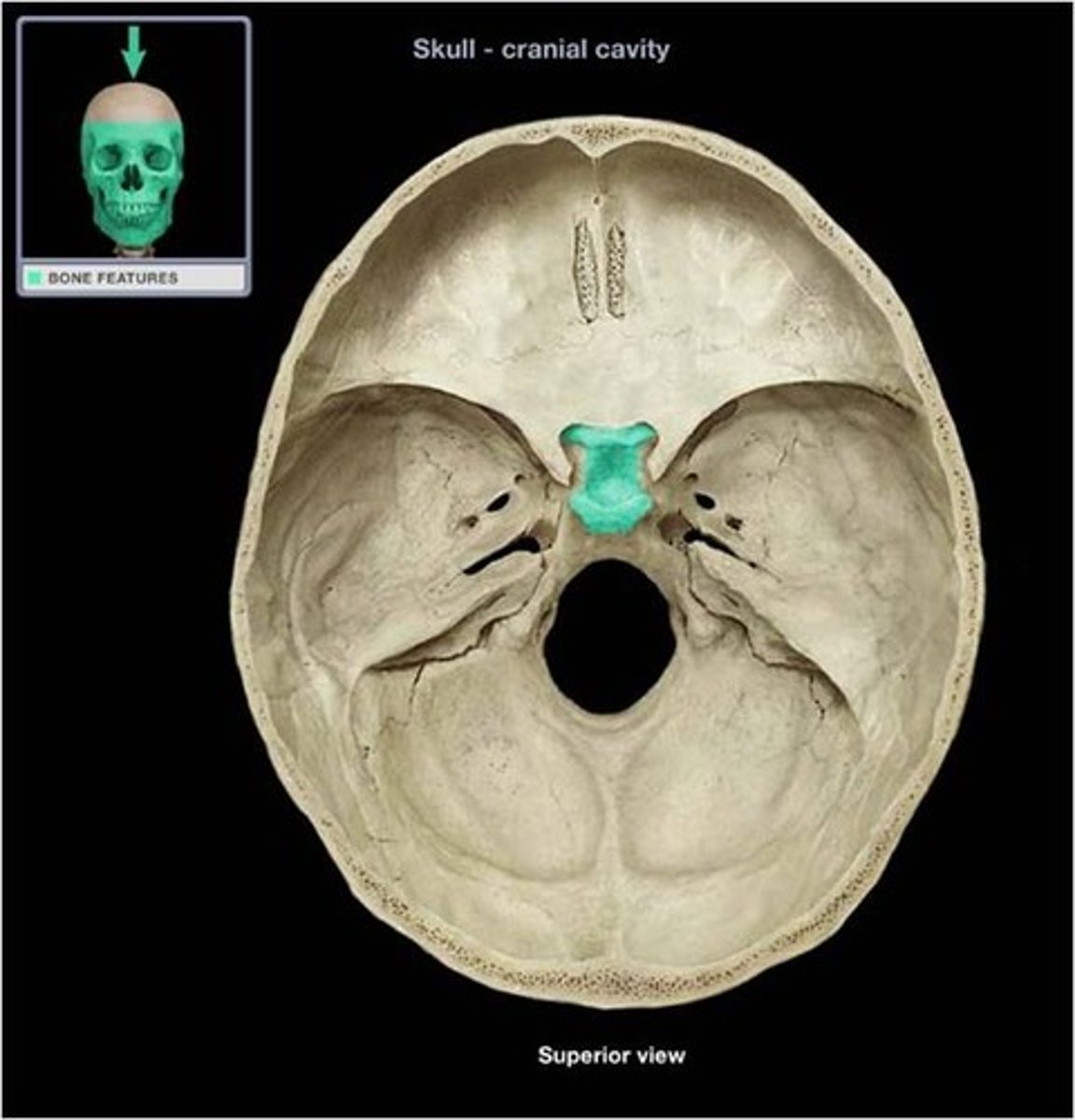
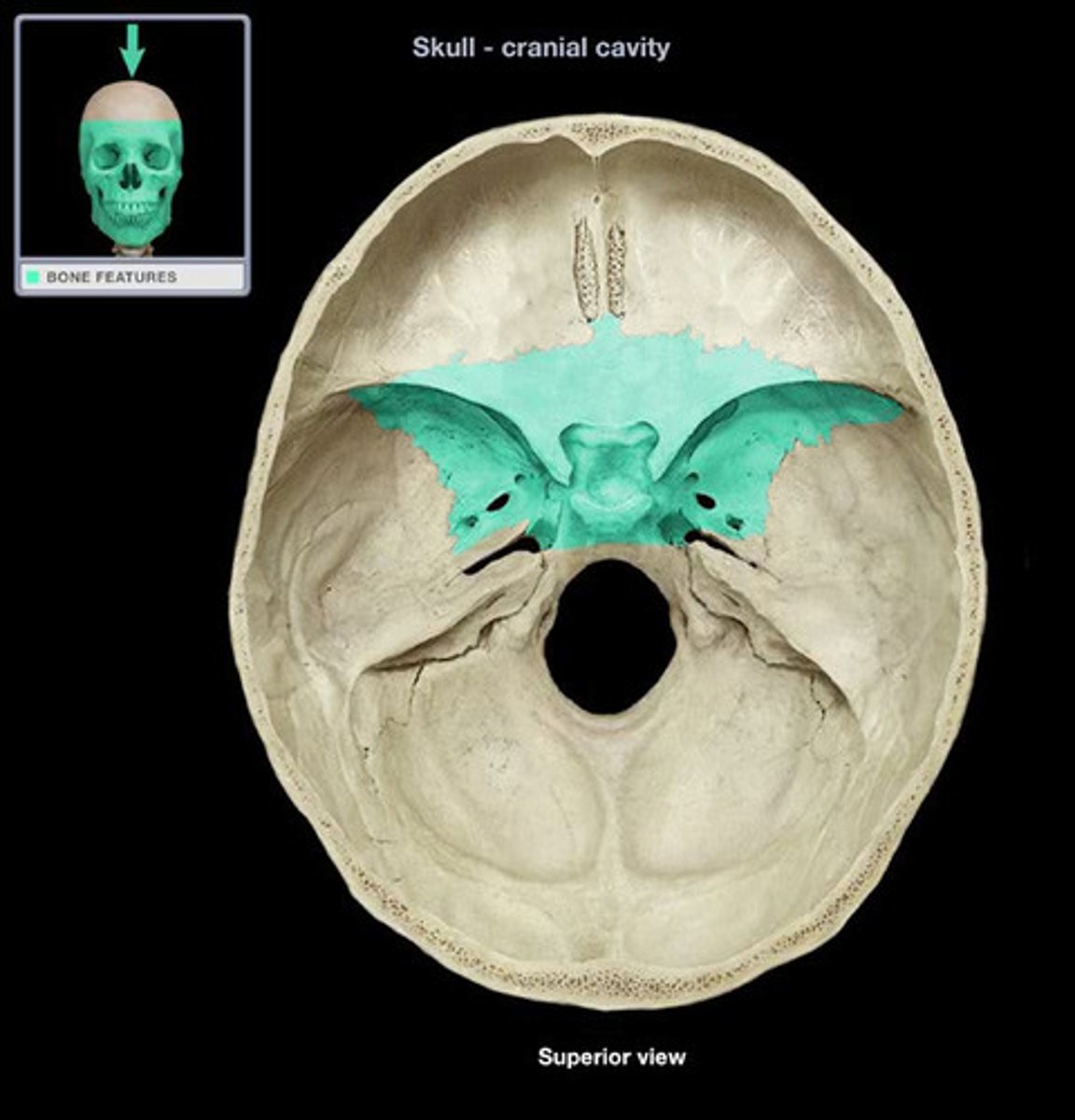
Sphenoid bone
Bone that joins all of the bones of the cranium together, can only be seen a little bit from the lateral view of the head, but much more from the superior view of the cranial cavity as it makes up most of the middle fossa
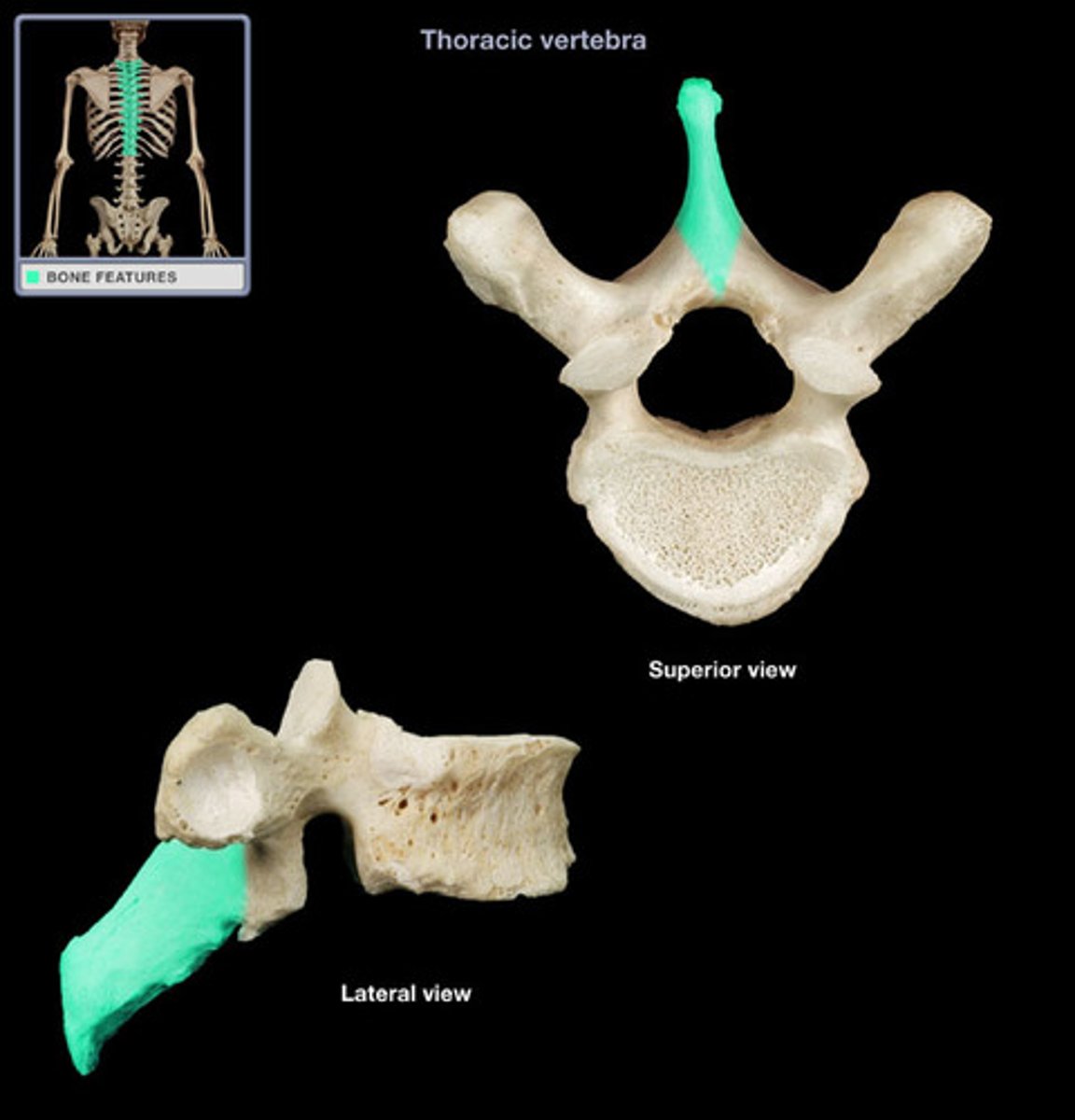
Spinous process
downward facing projection that acts as ligament and muscle attachment site
Squamous suture
suture between parietal and temporal bones
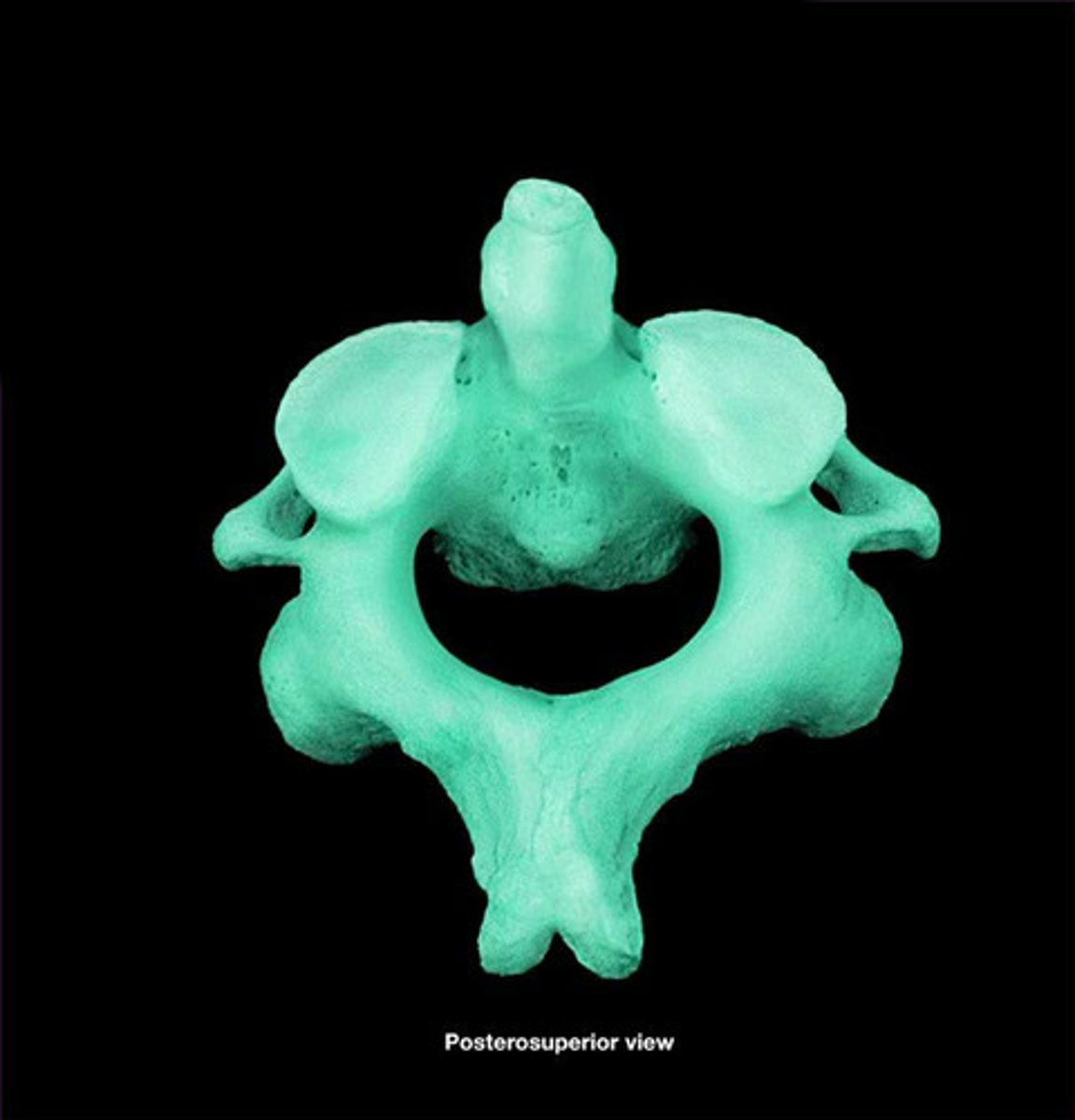
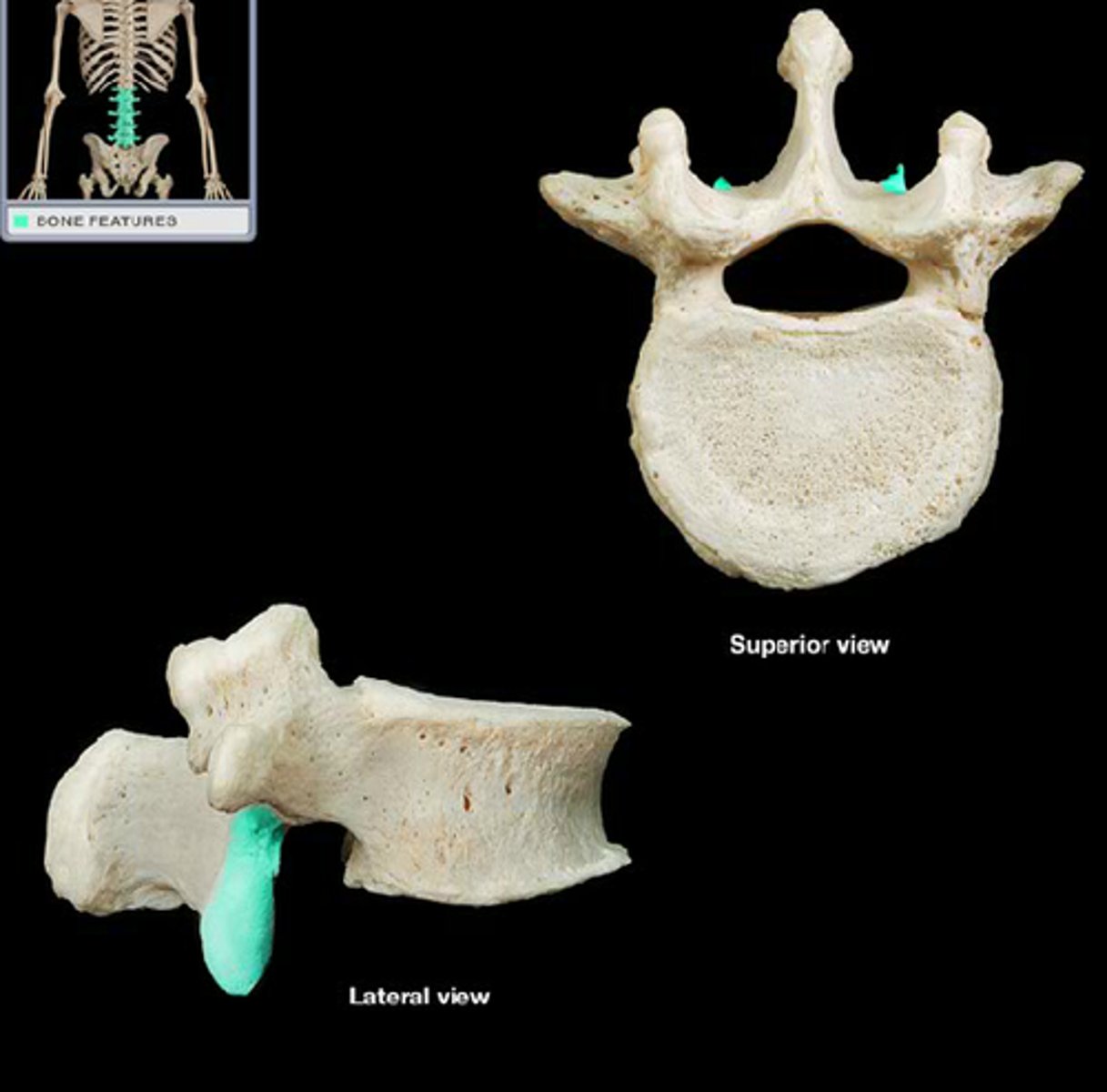
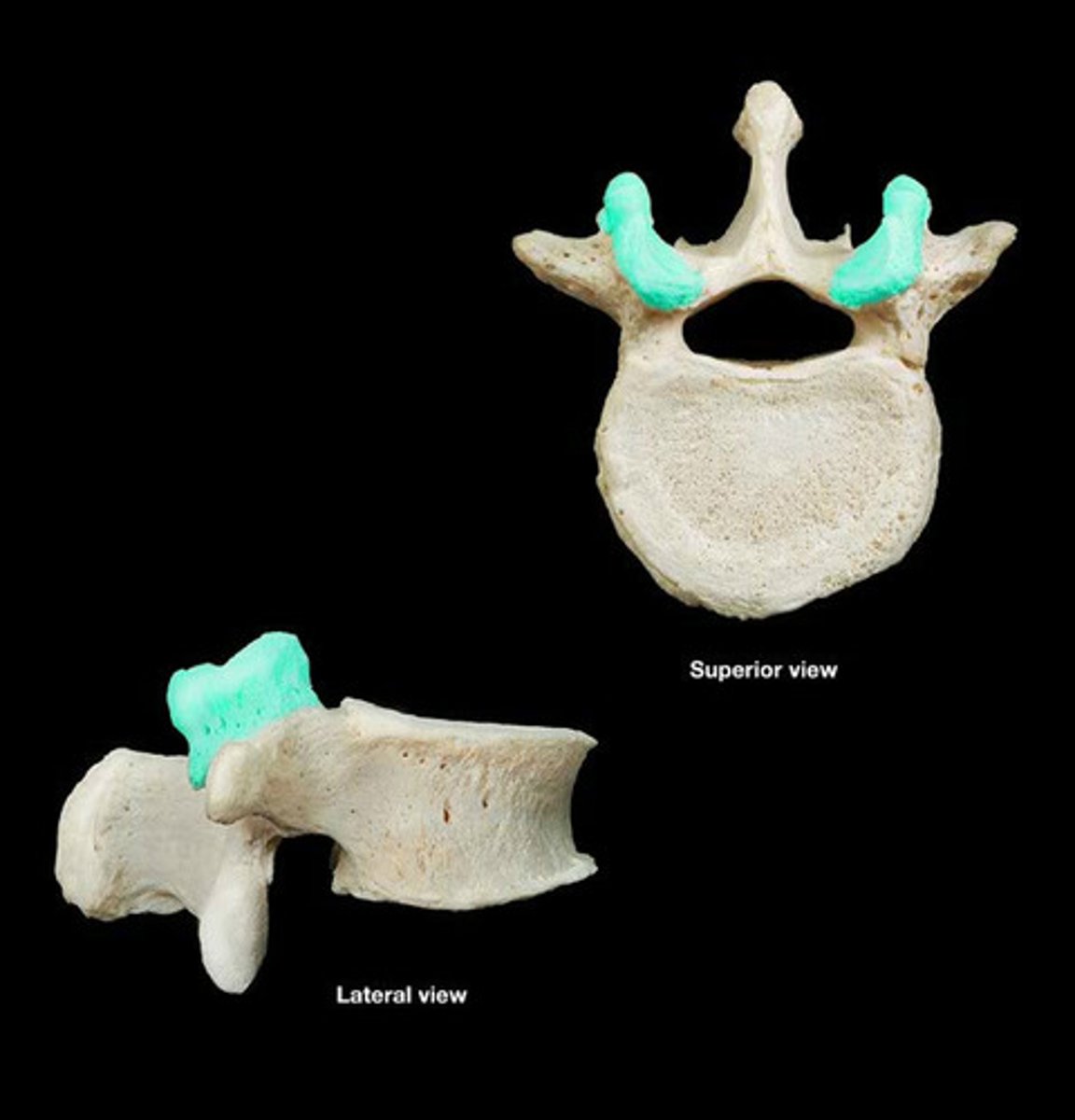
Superior articular process of vertebrae
upward facing projection that articulates with the head of ribs (for thoracic vertebrae only) and connects to the above vertebrae
Superior nasal conchae
above the middle nasal conchae, cannot be seen by the anterior view of the face (too deep in nasal cavity)
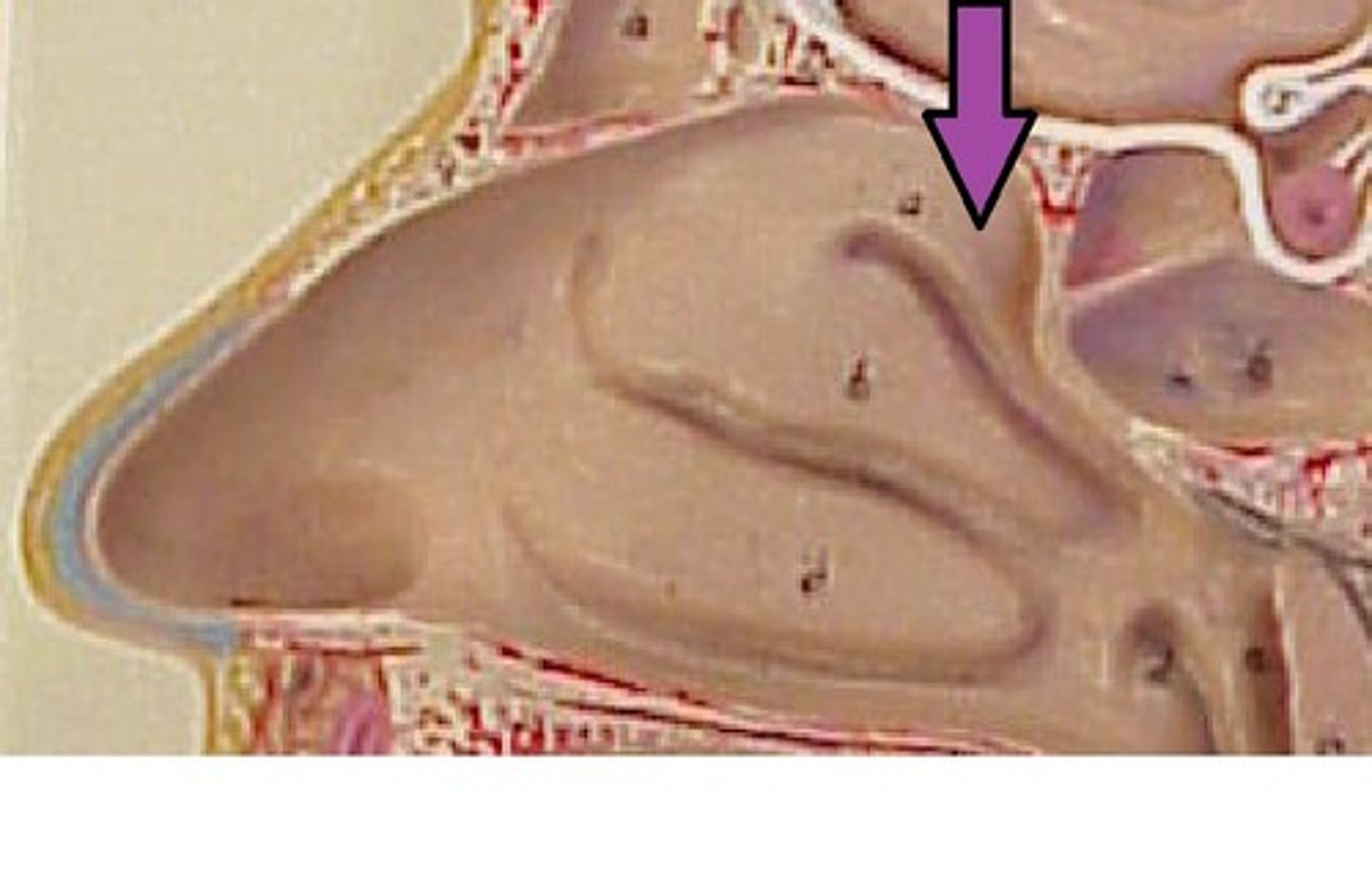
Temporal bone
seen on the most lateral sides of the head, forms parts of the side of the skull and floor of the cranial activity.
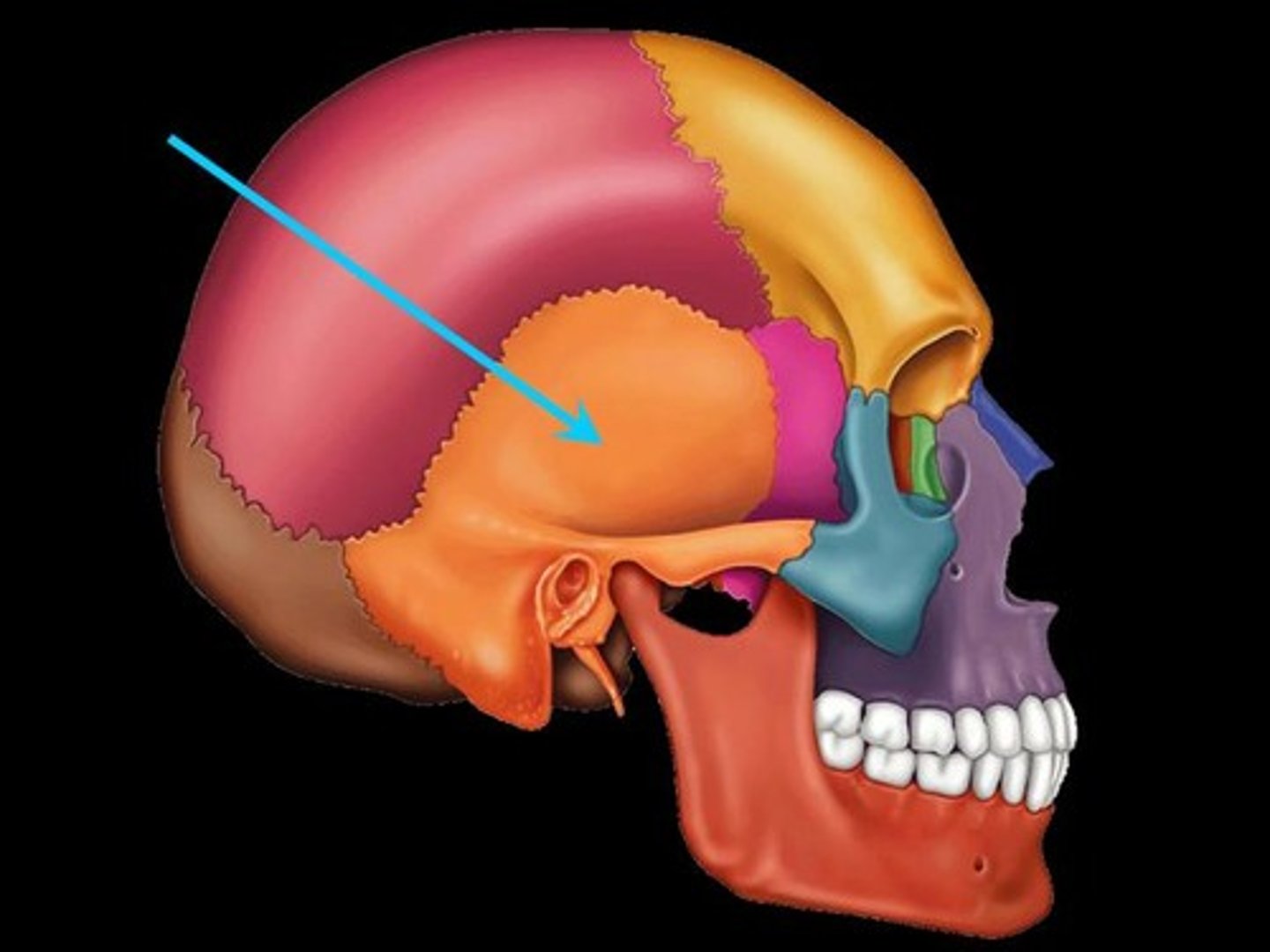
Temporal fossa
Mandible articulation point on the temporal bone; works with infratemporal fossa to allow chewing movement
Thoracic curve
2nd curve, T1-T12, connects to ribs
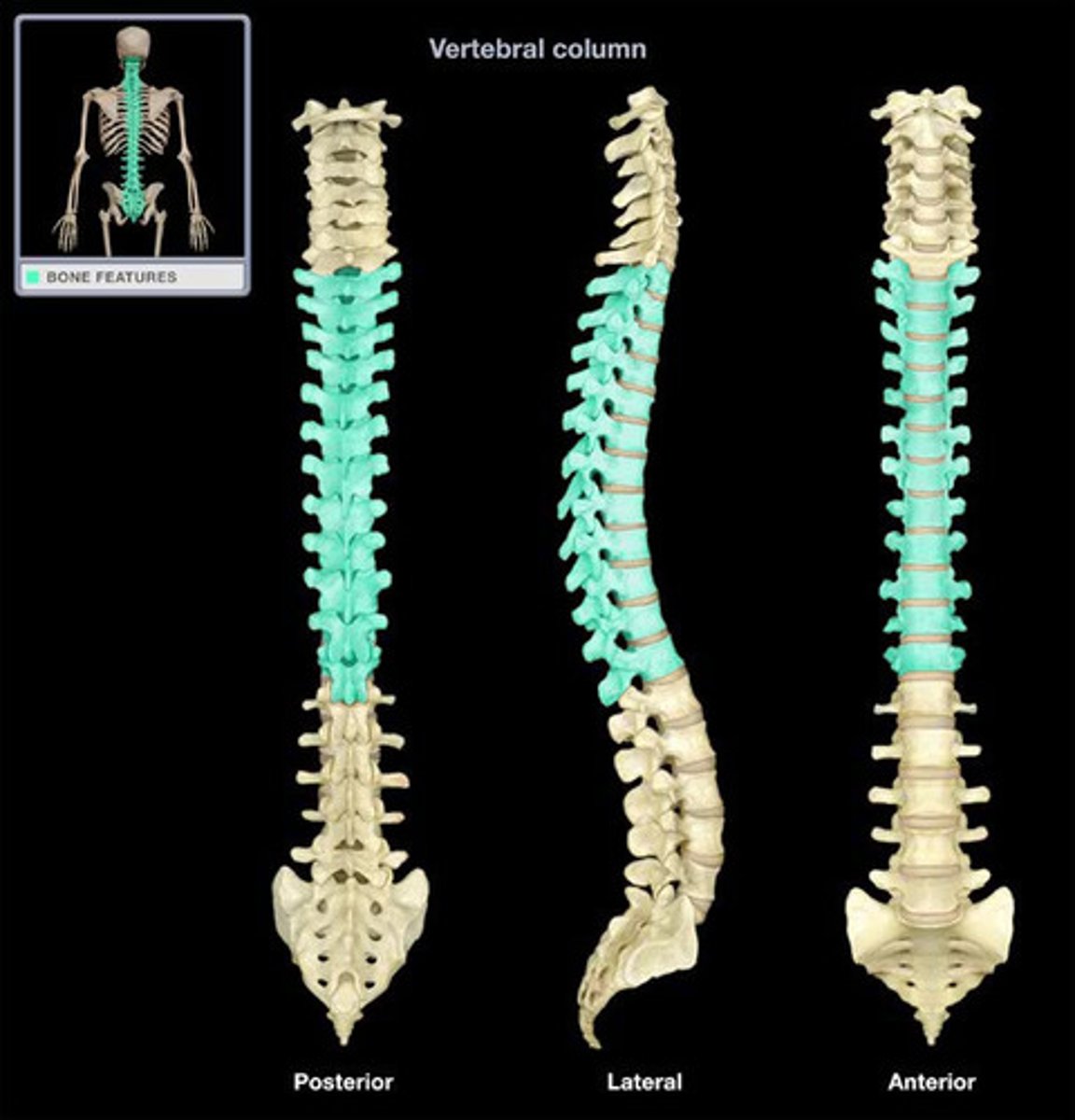
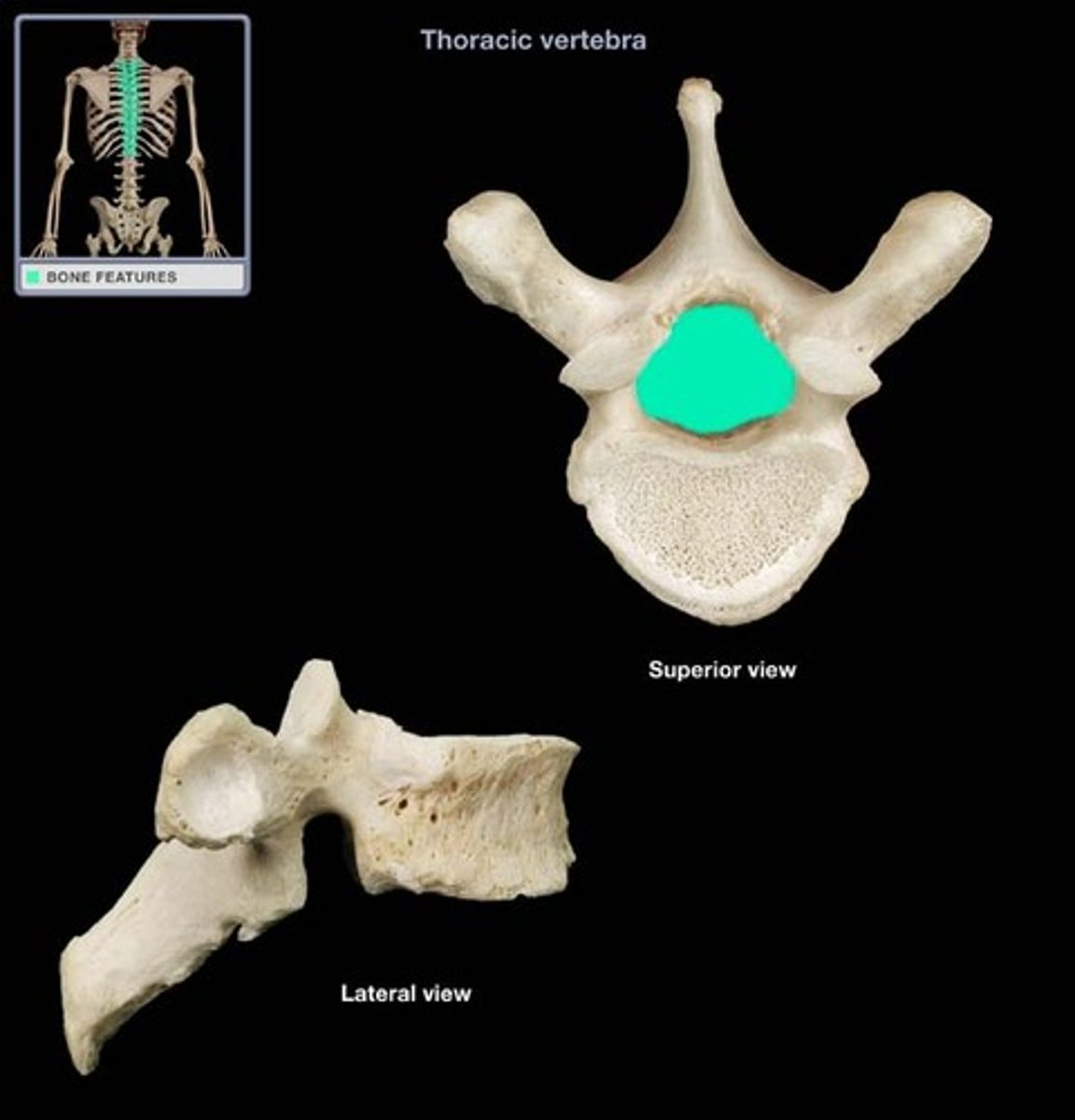
Thoracic vertebrae
Have an elongated, downward-facing transverse process with a longer spinous process
Transverse foramen of vertebrae
only found in cervical vertebrae, house veins, arteries, and nerves
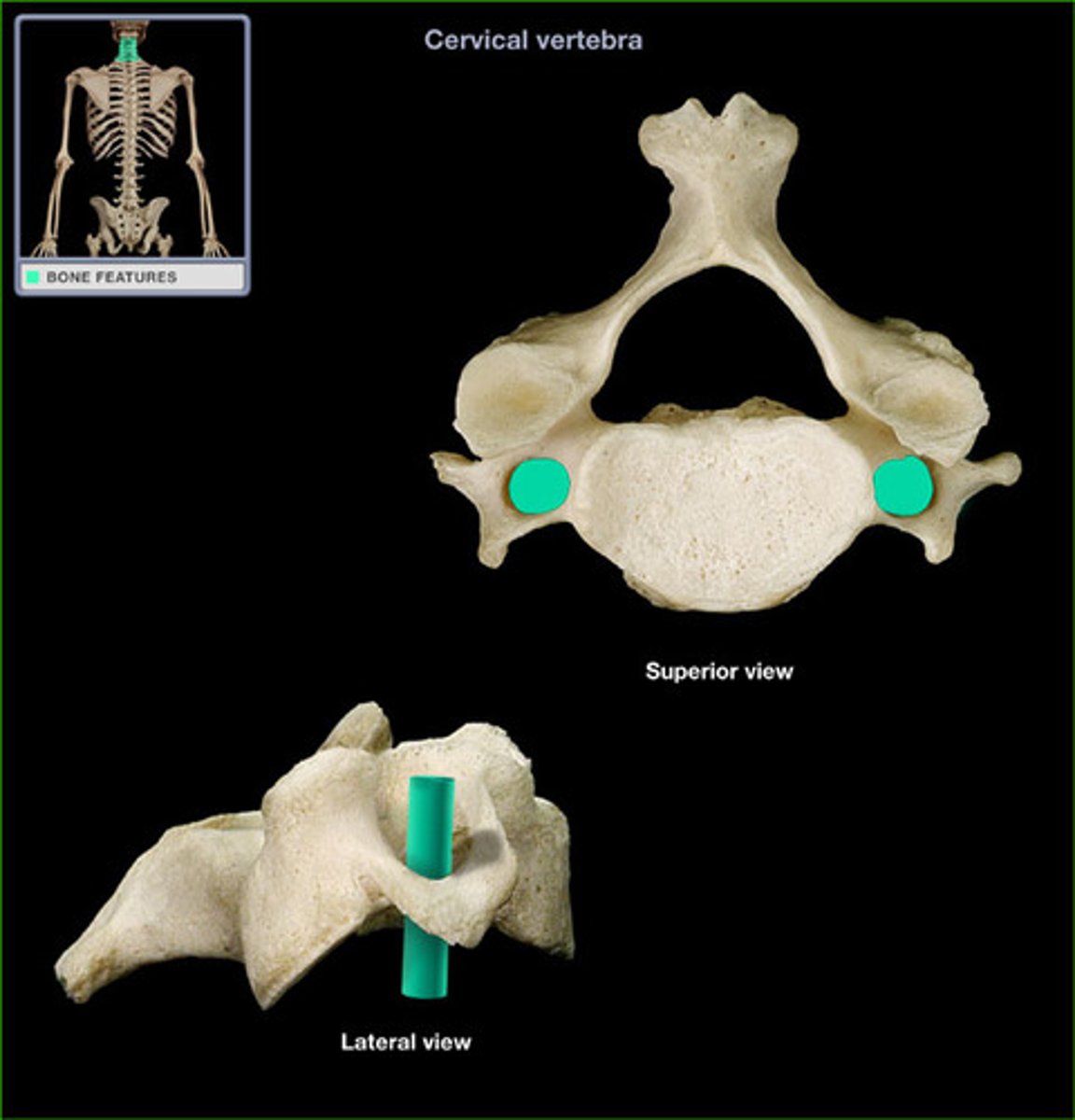
Transverse process of vertebrae
projection that point laterally, attachment site for spinal muscles and articulates with ribs for thoracic vertebrae
True ribs
first 7 pairs of ribs; attach directly to sternum via costal cartilage
Vertebral arch
structure that encloses the nerve cord
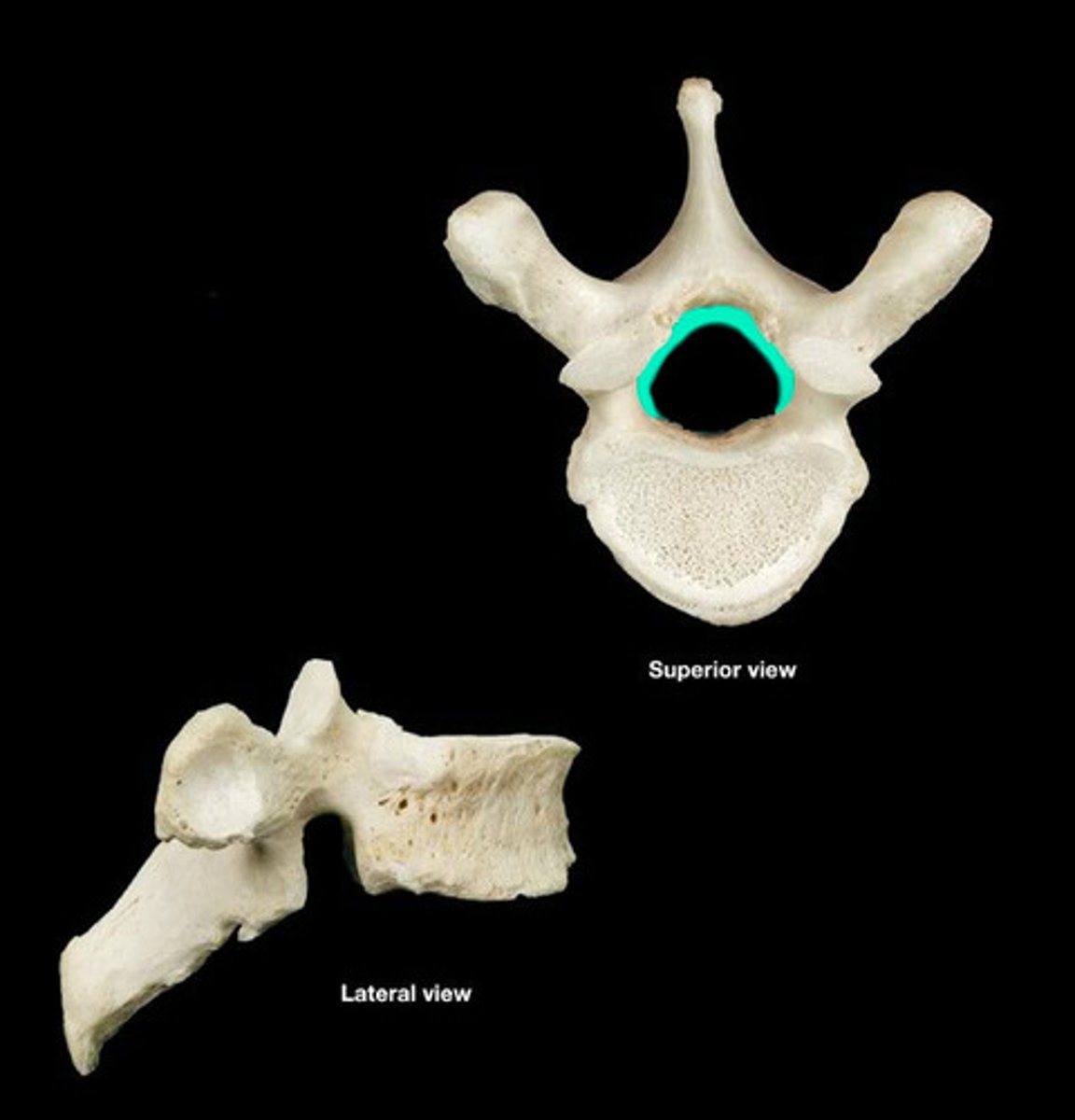
Vertebral foramen
canal through which spinal cord passes
Vomer bone
Flat, thin bone that forms part of the nasal septum
xiphoid process
lower portion of the sternum
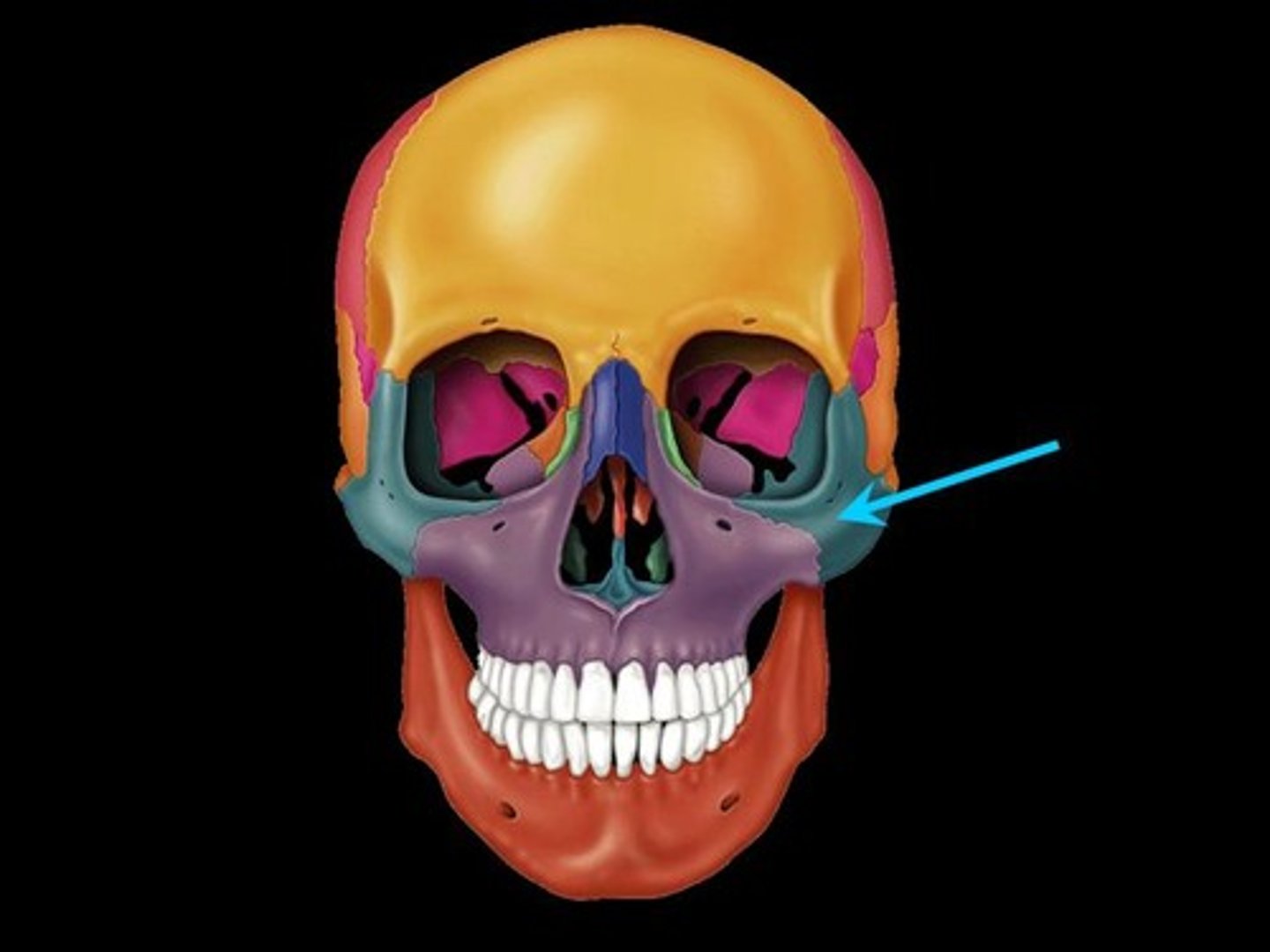
Zygomatic bone
bone below frontal bone, lateral to maxilla
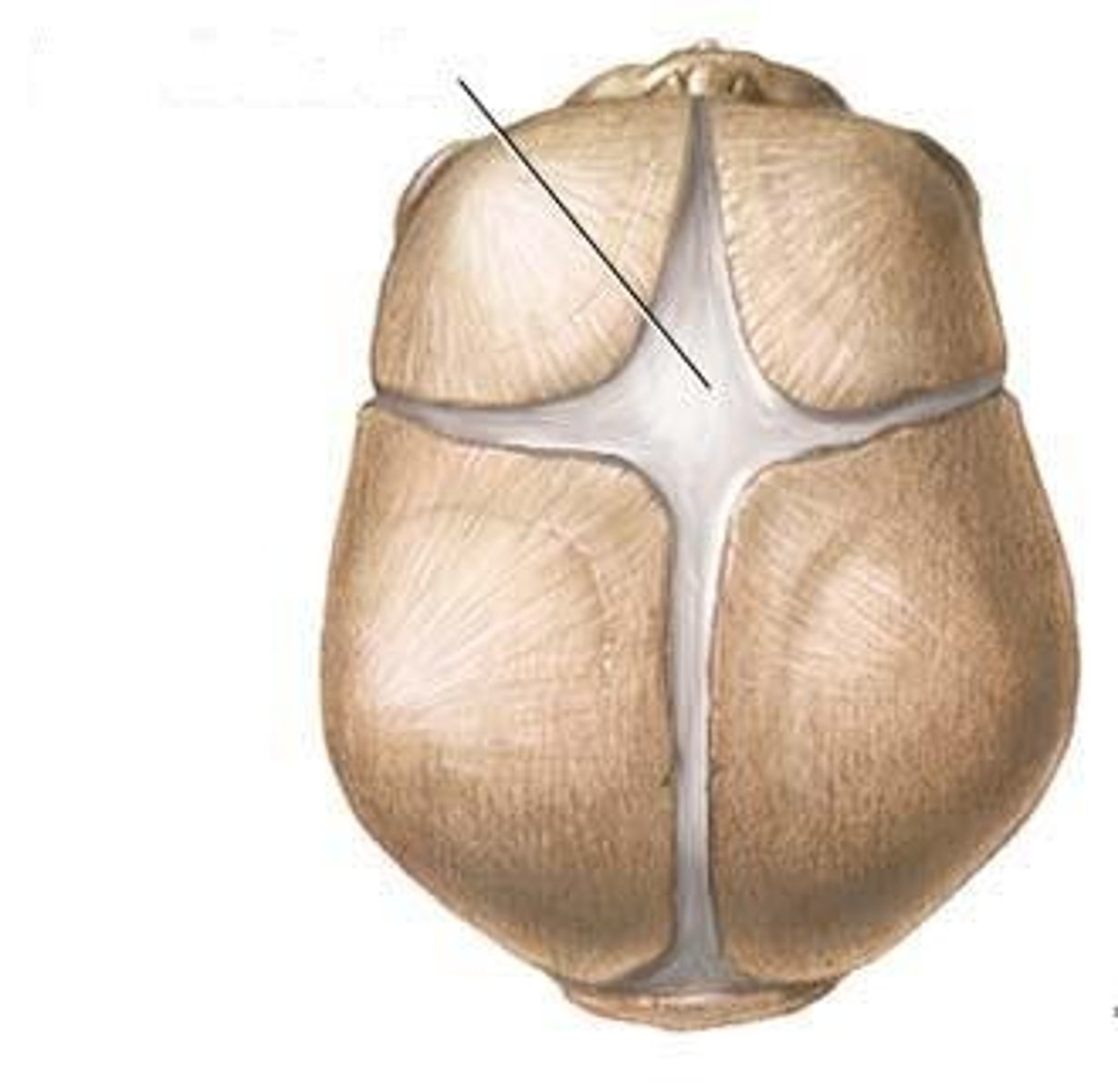
Fontanelles
large fibrous areas between the cranial bones found in infant skulls, slowly shrink as cranial bones grow closer together
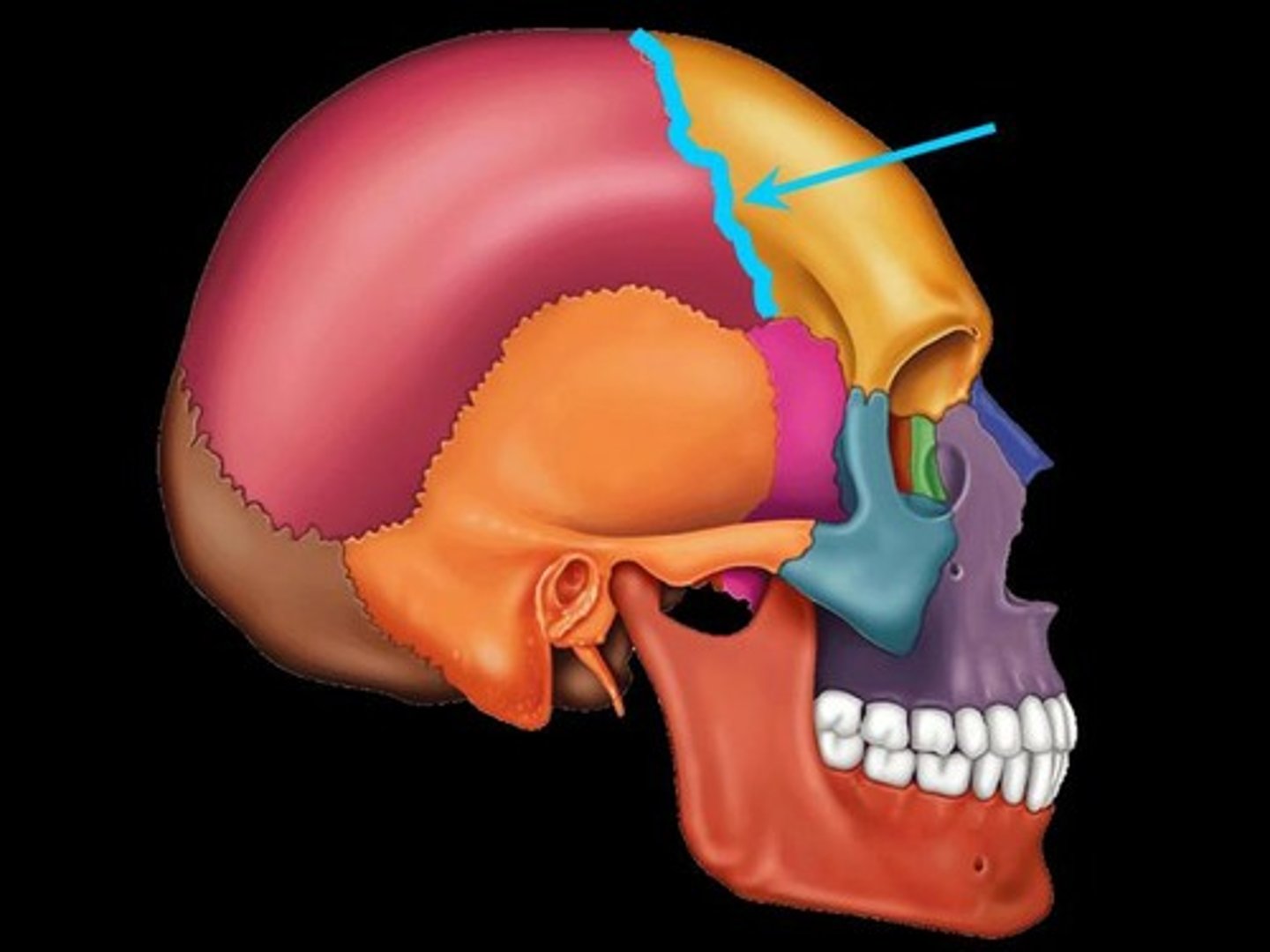
Suture
dense fibrous connective tissue that connects cranial bones together
How many vertebrae are there that fuse together after puberty for both the sacrum and coccyx?
There are 5 sacral vertebrae that fuse after puberty, and 4 coccyxal vertebrae that fuse after puberty
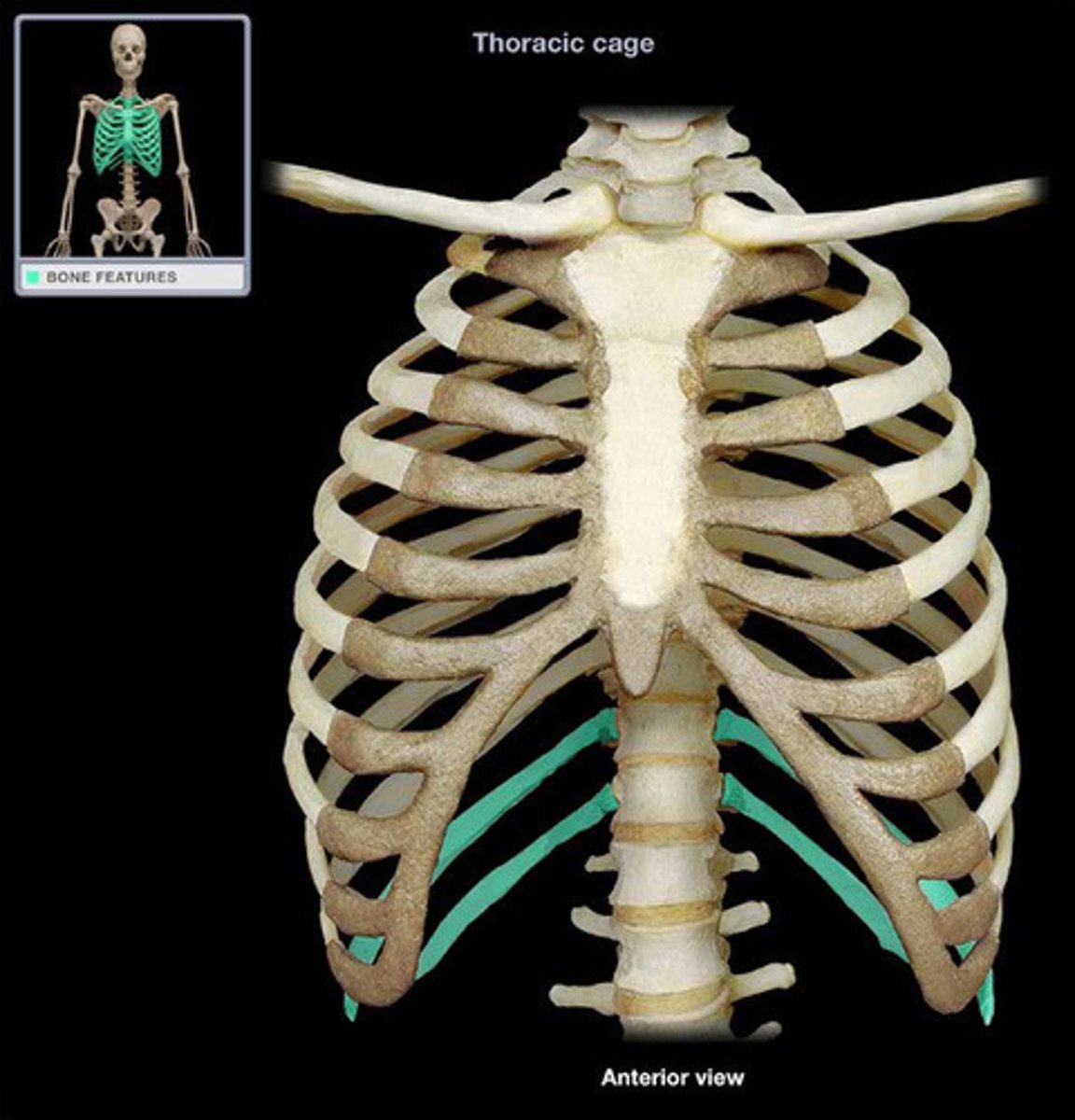
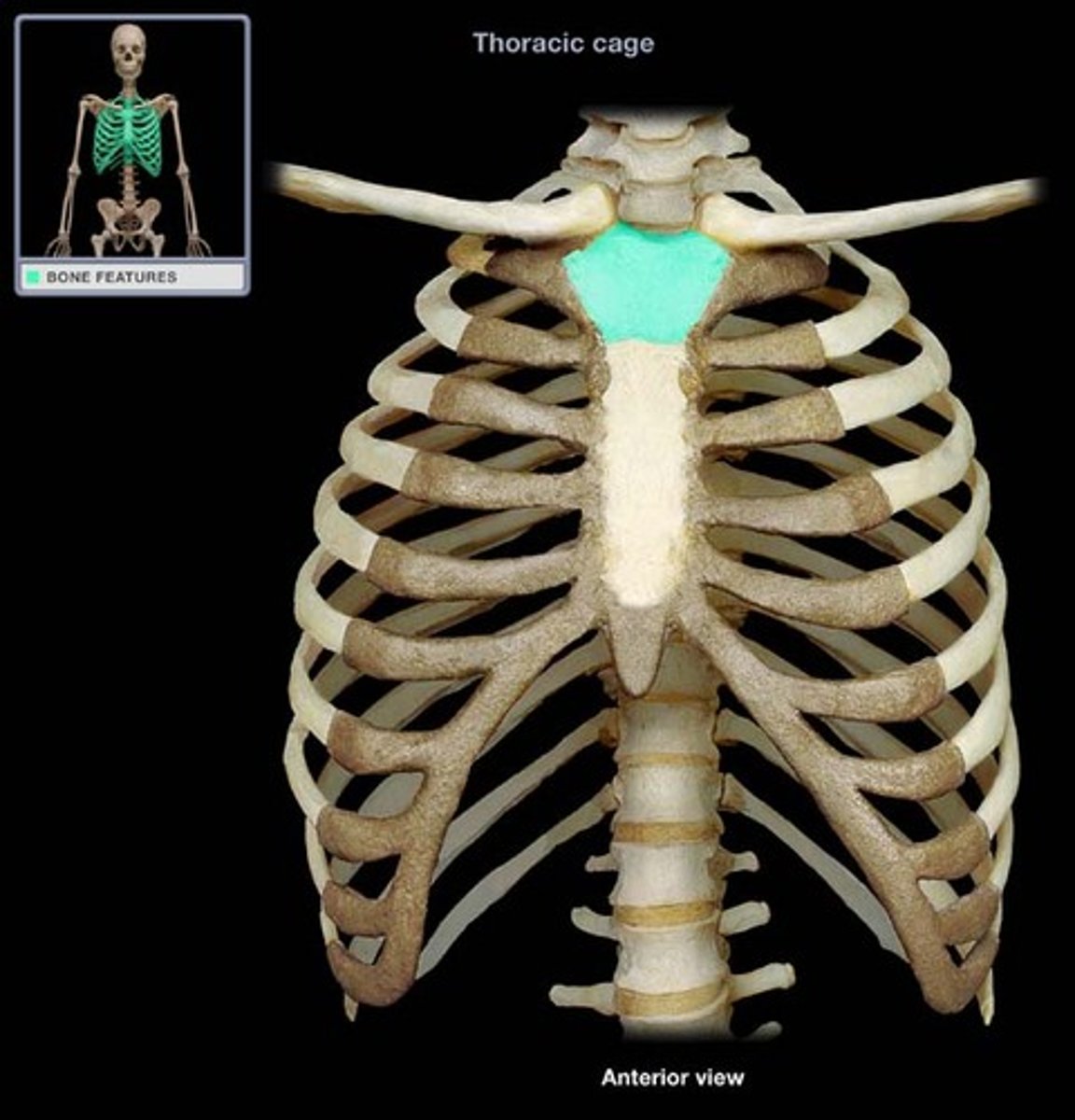
The thoracic cage consists of
thoracic vertebrae, sternum, ribs
Temporal process of the zygomatic bone
short extension from the zygomatic bone that forms the anterior portion of the zygomatic arch
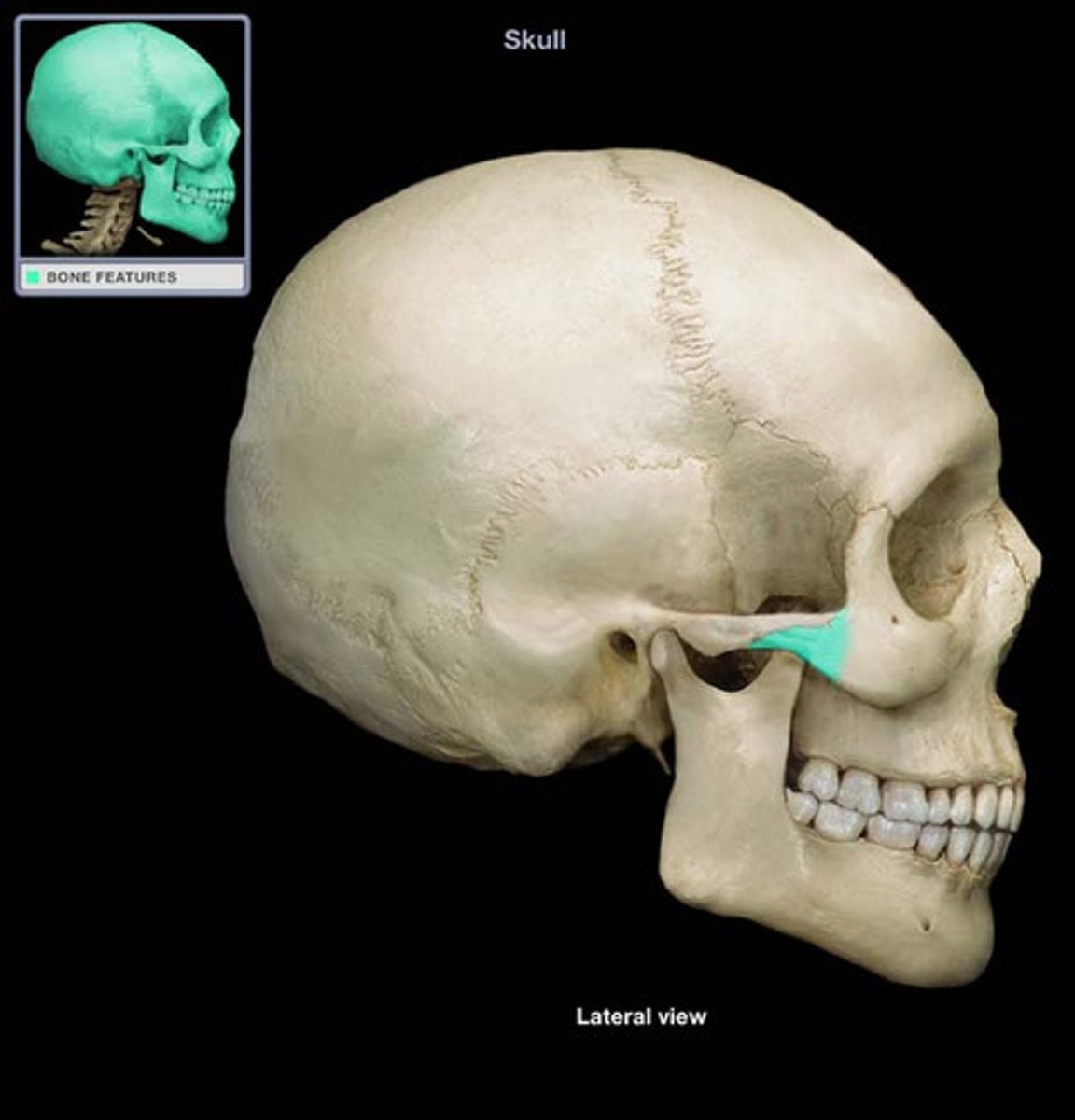
Zygomatic arch
temporal and zygomatic process
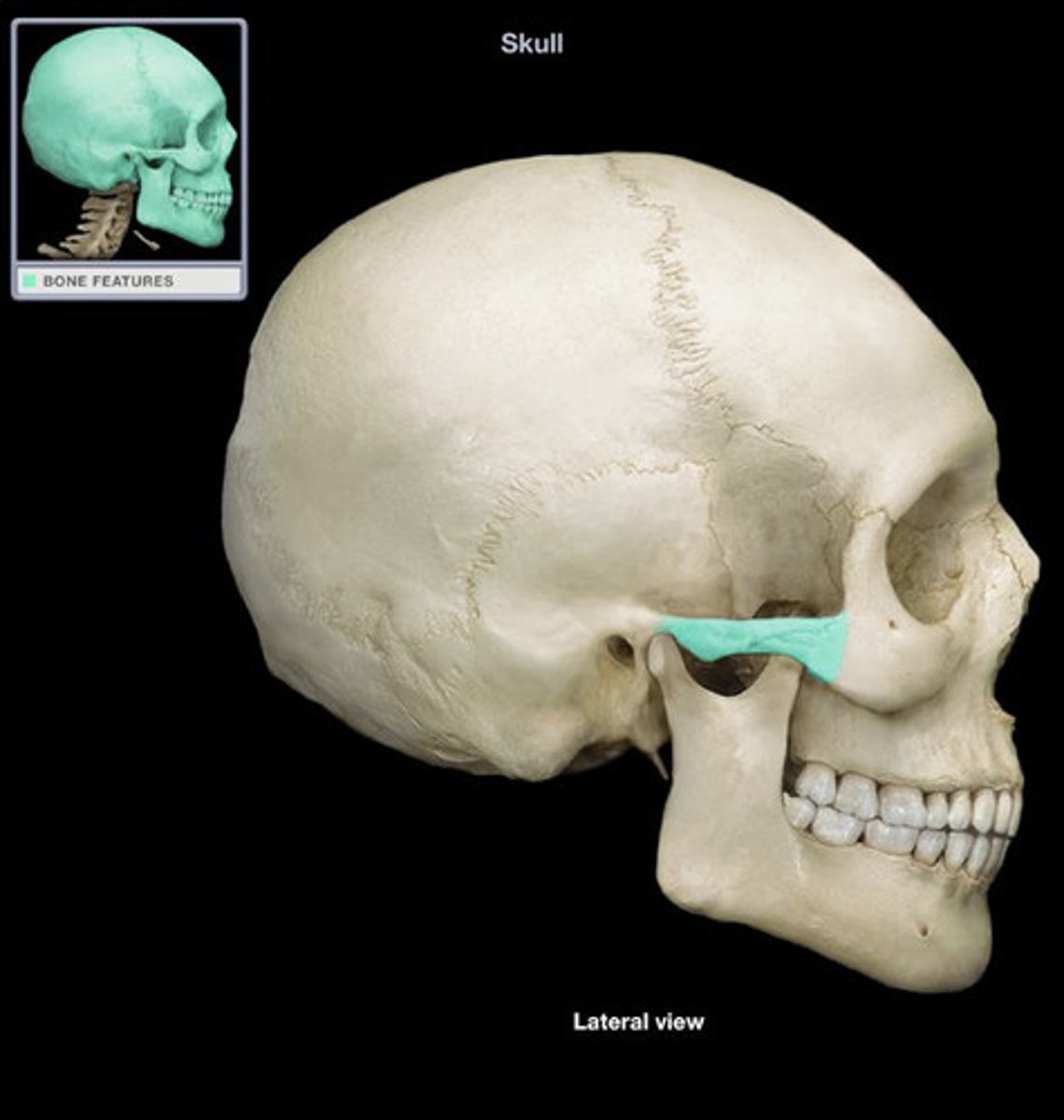
Zygomatic process of the temporal bone
extension from the temporal bone that forms the posterior portion of the zygomatic arch
Function of the axial skeleton
protects major organs such as the brain, spinal cord, heart, and lungs
Function of the appendicular skeleton
facilitates movement and supports limbs
What causes a cleft palate?
Improper fusion of the palatine process of the maxilla (and sometimes the palatine bone)
Which of these statements about the nasal septum is true?
The septum is composed of bone (ethmoid and vomer) and septal cartilage
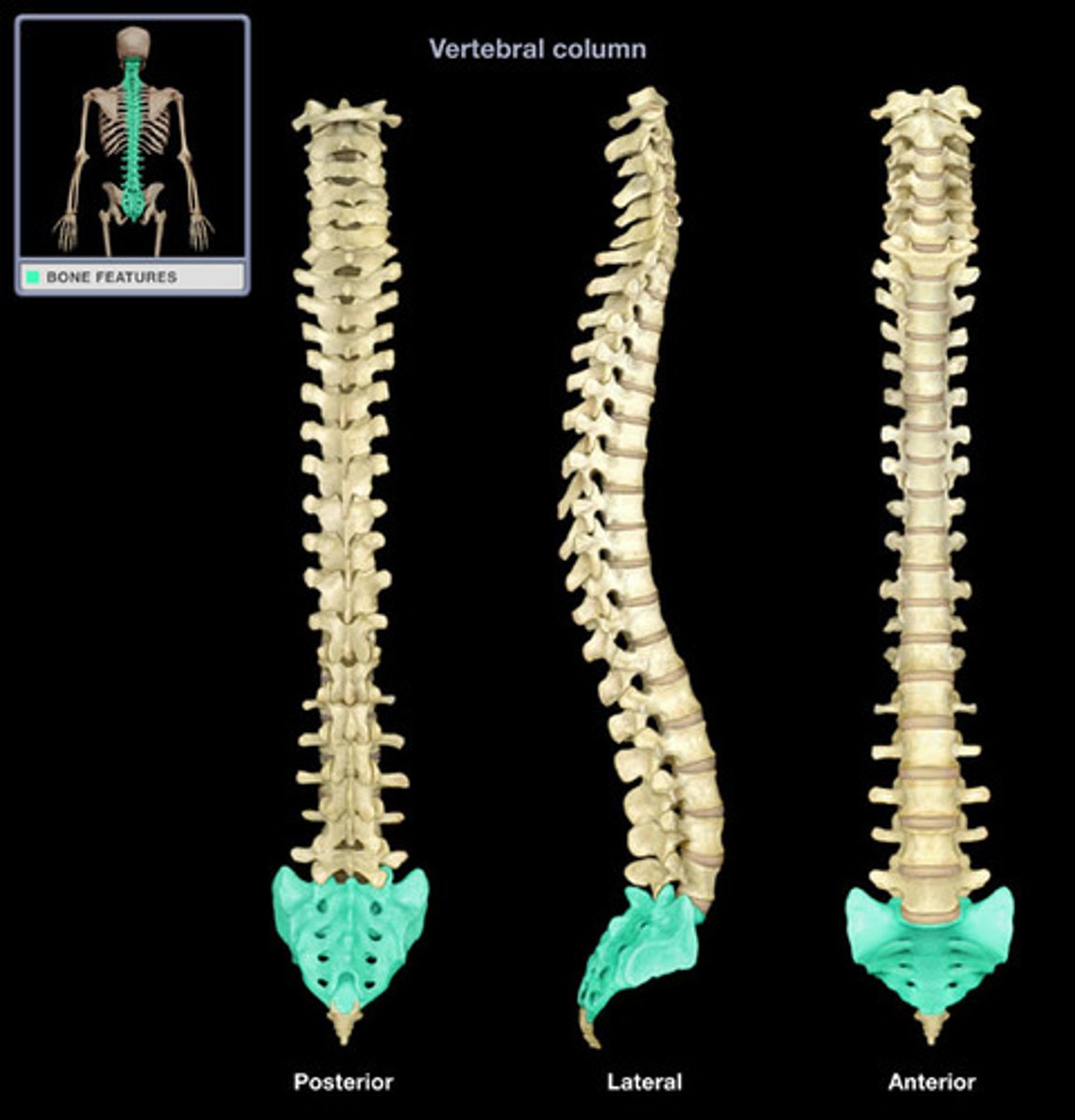
The three sections of the vertebral column, in order from superior to inferior, are:
Cervical, thoracic, lumbar
Intervertebral discs are made of
fibrocartilage
During CPR, hand placement is extremely important. If hands are placed too far towards the inferior end of the sternum ________________ might break off and cause damage.
The xiphoid process
Epicondyle
protuberance above a condyle (region on end of long bone)
Fissure
narrow, slit-like opening
Fossa
depression or dip
Foramen
hole
Groove
Furrow on a bone that protects long blood vessels or nerve segments
Meatus
short canal that opens to another part of the body
Process
large, bony projection
Tubercle
small, rounded projection or protuberance
Tuberosity
large, raised, roughened region for muscle/connective tissue attachment