Penny Ch 30- Chromosomal abnormalities
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
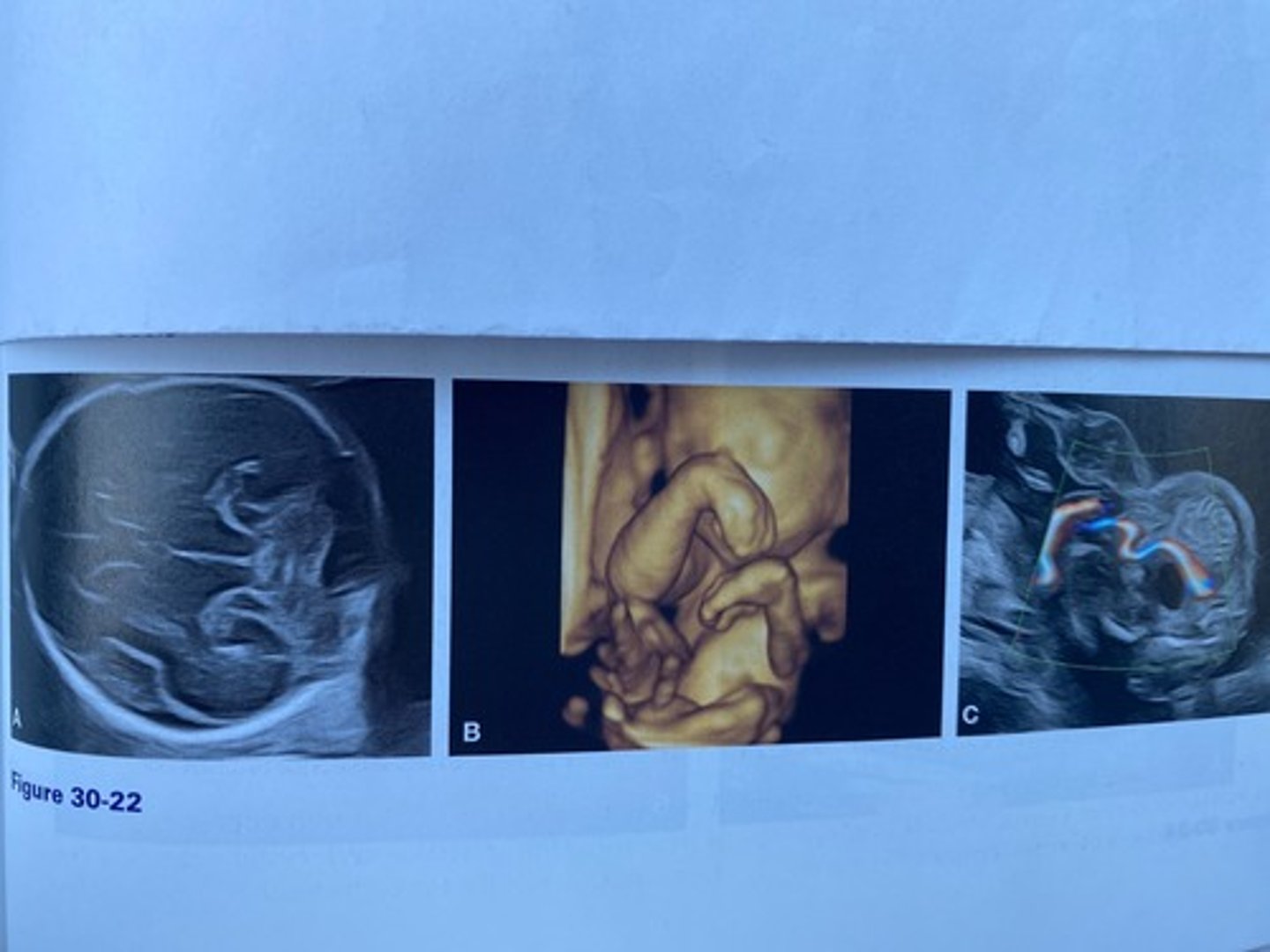
b. Trisomy 18
What is the most likely diagnosis based on the sonographic findings in Figure 30-22?
a. Trisomy 21
b. Trisomy 18
c. Trisomy 13
d. Turner syndrome
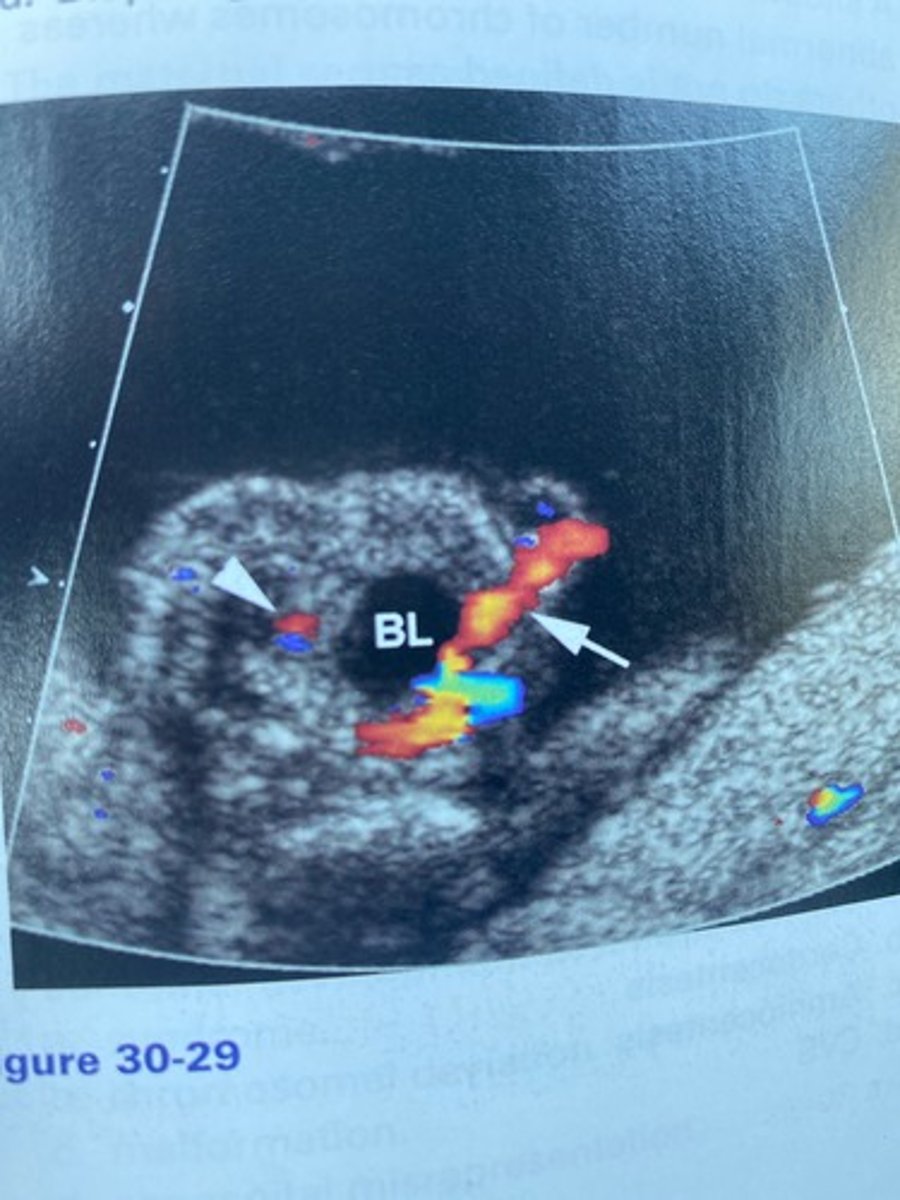
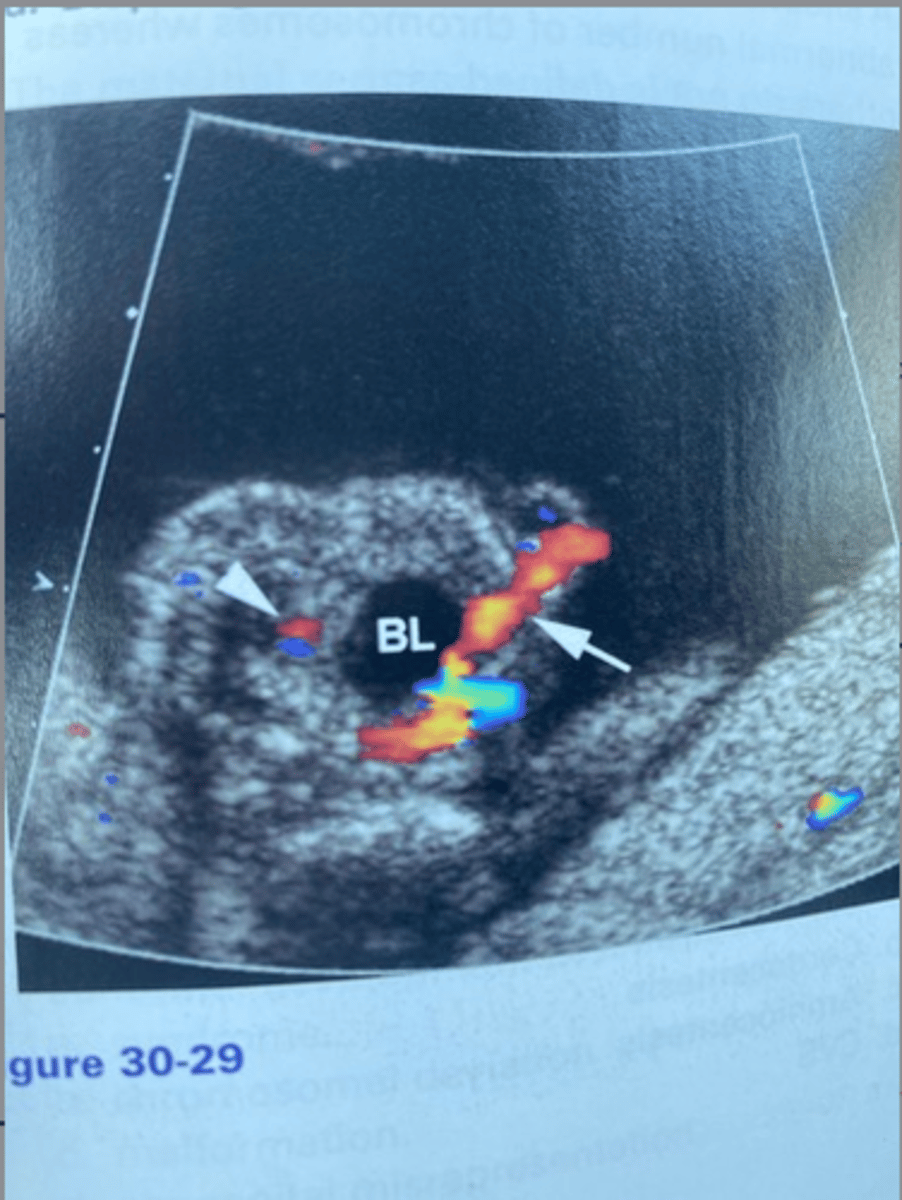
c. Single umbilical artery
What does the arrow in Figure 30-29 indicate?
a. Umbilical vein varices
b. Nuchal cord
c. Single umbilical artery
d. Single umbilical vein
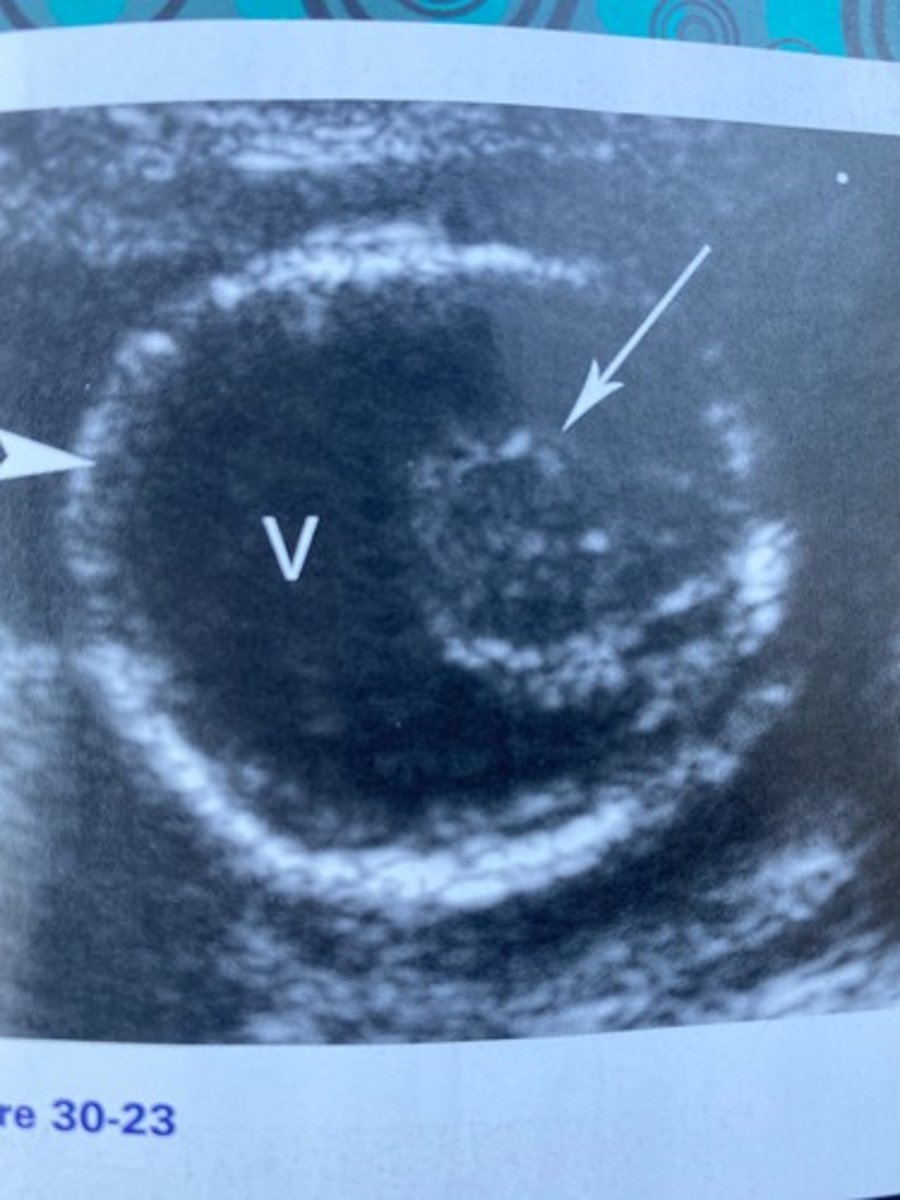
a. Patau syndrome
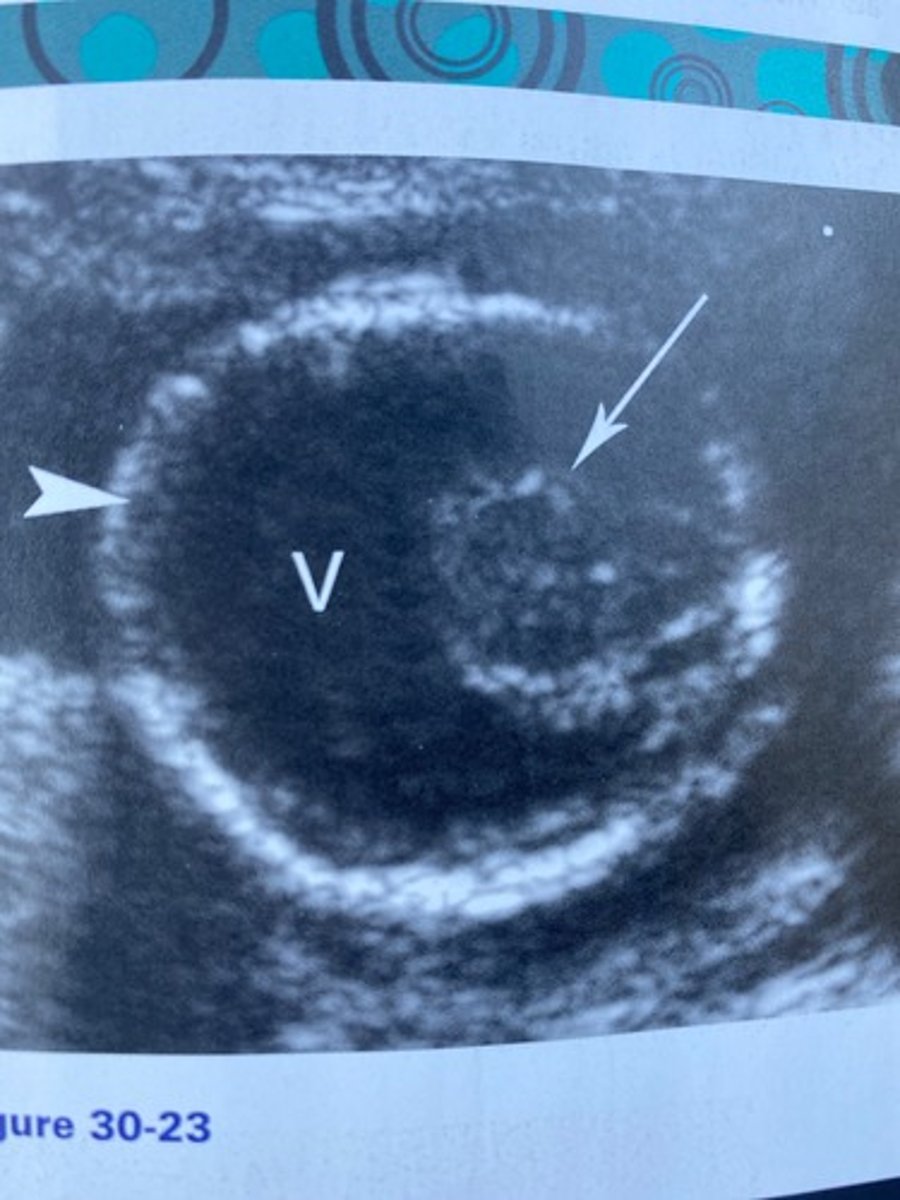
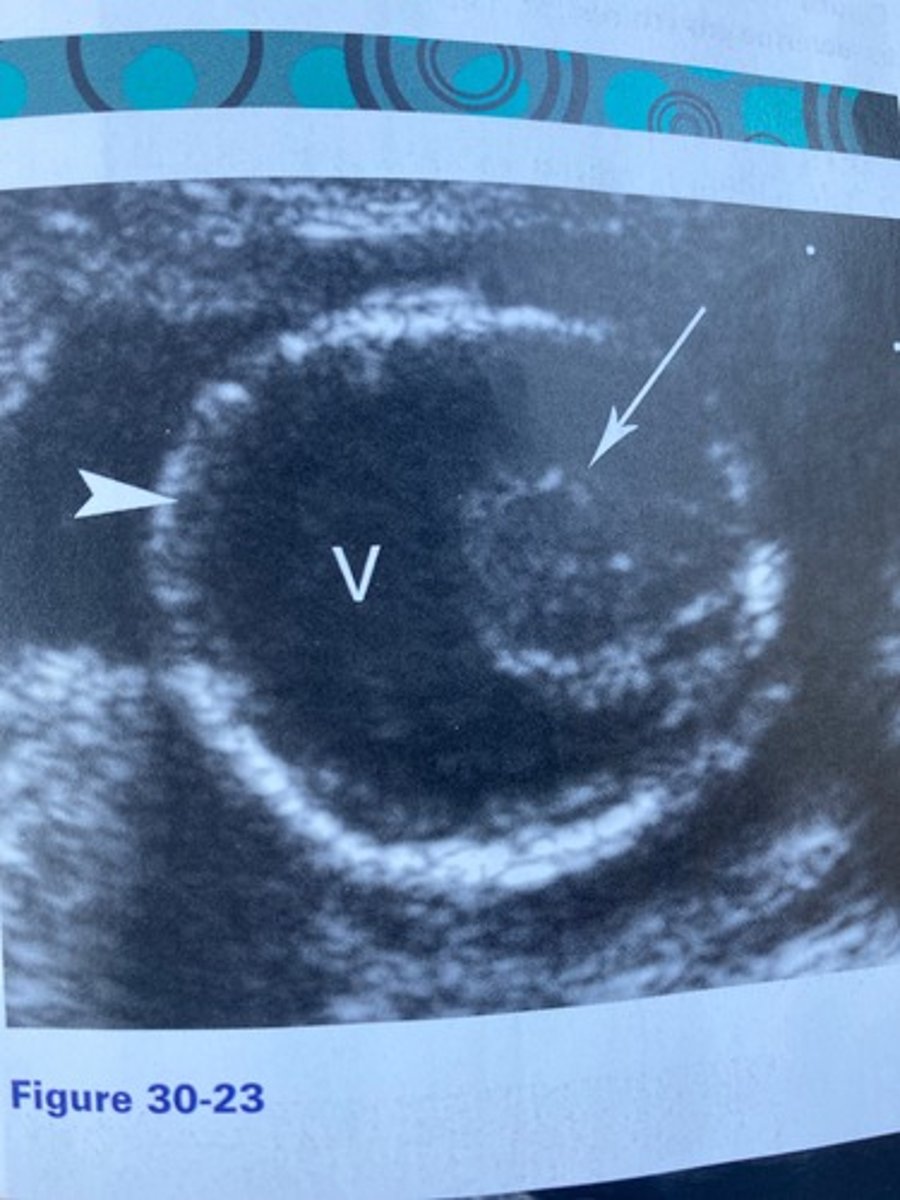
What is the syndrome associated with the findings in Figure 30-23?
a. Patau syndrome
b. Edwards syndrome
c. Down syndrome
d. Turner syndrome
a. Trisomy 18
Which of the following is the finding in Figure
30-29 most likely associated with?
a. Trisomy 18
b. Klinefelter syndrome
c. Trisomy 8
d. Turner syndrome
b. Fused thalami
What does the arrow in Figure 30-23 indicate?
a. Cerebellum
b. Fused thalami
c. Brainstem
d. Proboscis
c. umbilical region.
The term omphalo refers to the:
a. neck.
b. cord.
c. umbilical region.
d. neck.
d. Microcephaly
What cranial abnormality is often associated with
Figure 30-23?
a. Macrocephaly
b. Anencephaly
c. Strawberry skull
d. Microcephaly
a. Syndrome
What is defined as a group of clinically observable findings that exist together and allow for classification?
a. Syndrome
b. Chromosomal deviation
c. Malformation
d. Congenital association
b. Monosomy X
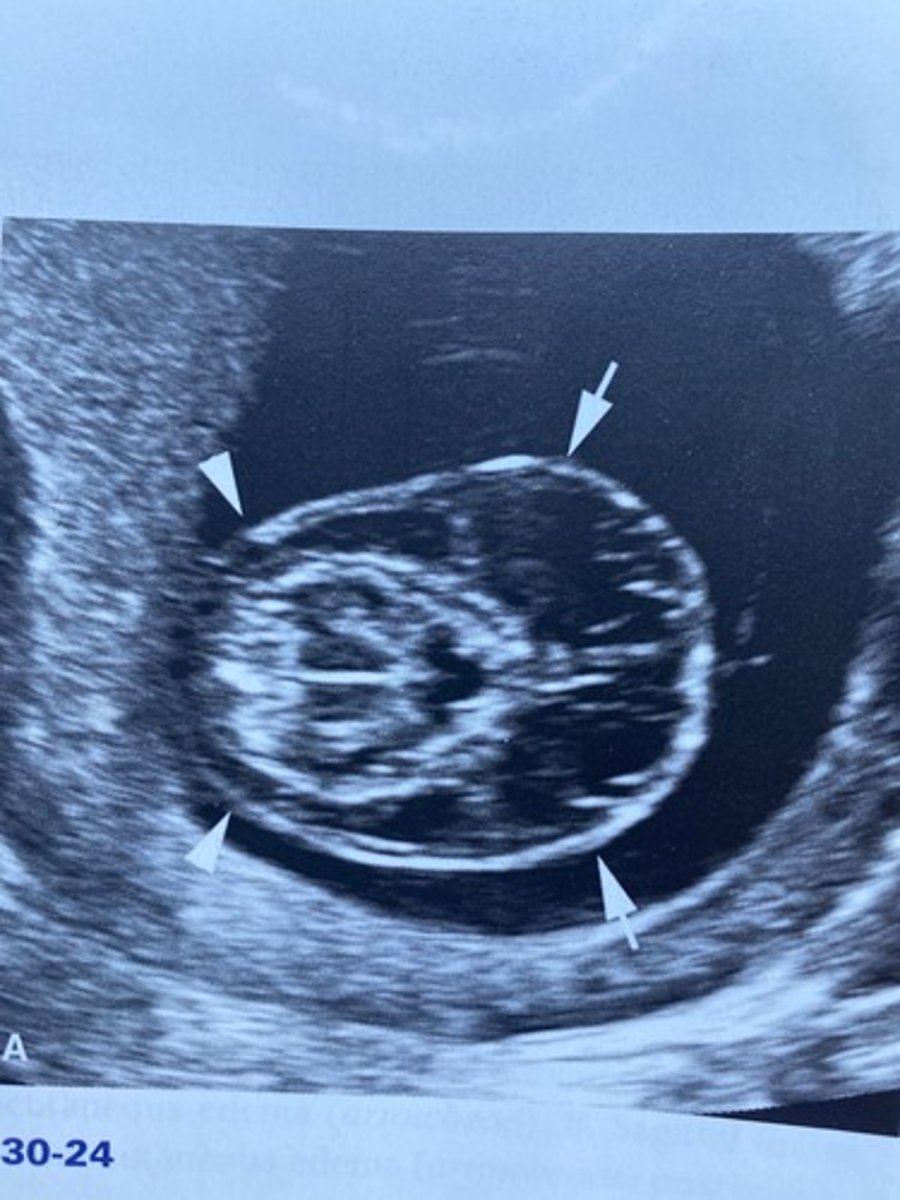
Which of the following would most likely be associated with Figure 30-24?
a. Trisomy 13
b. Monosomy X
c. Klinefelter syndrome
d. Meckel-Gruber syndrome
b. trisomy.
A cell having three copies of an individual chromosome is referred to as an):
a. syndrome.
b. trisomy.
c. triploidy.
d. tetralogy.
c. Triploidy
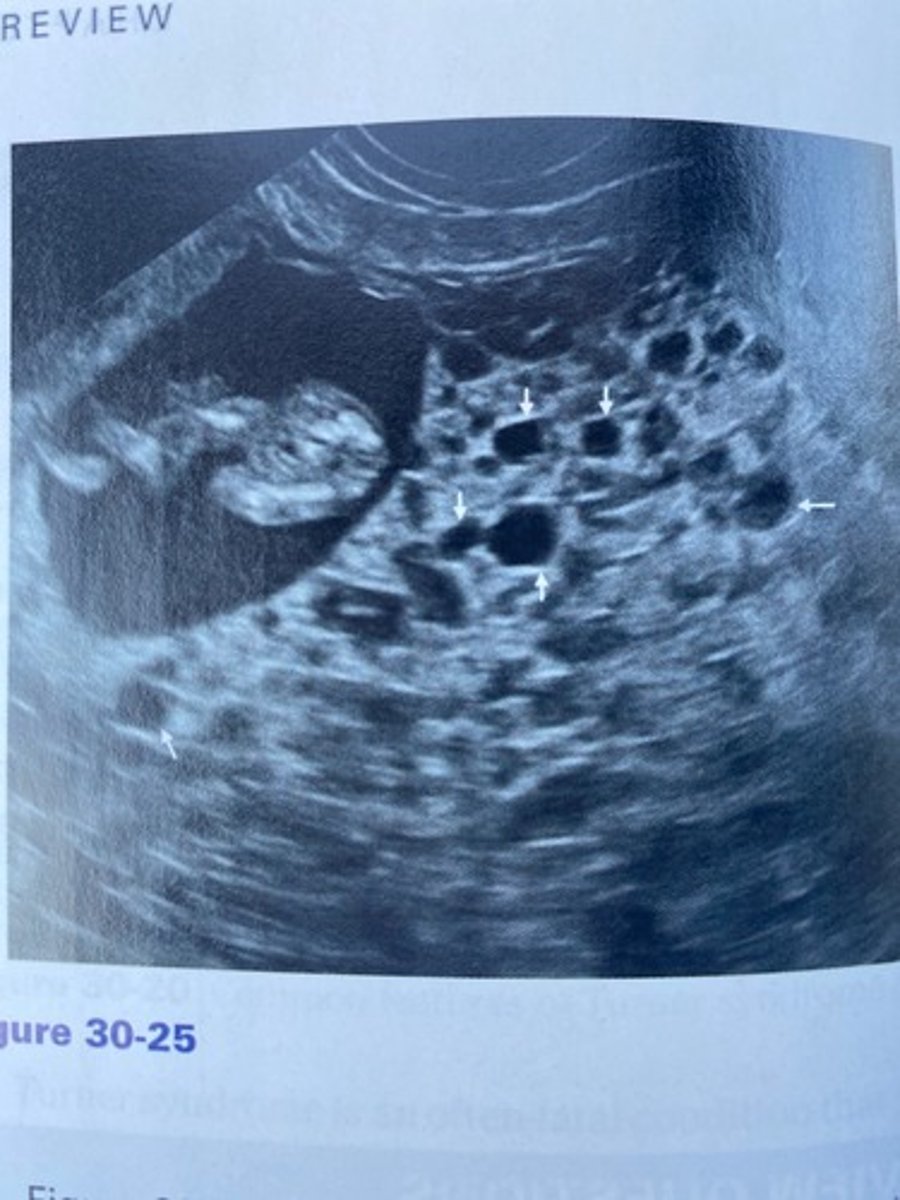
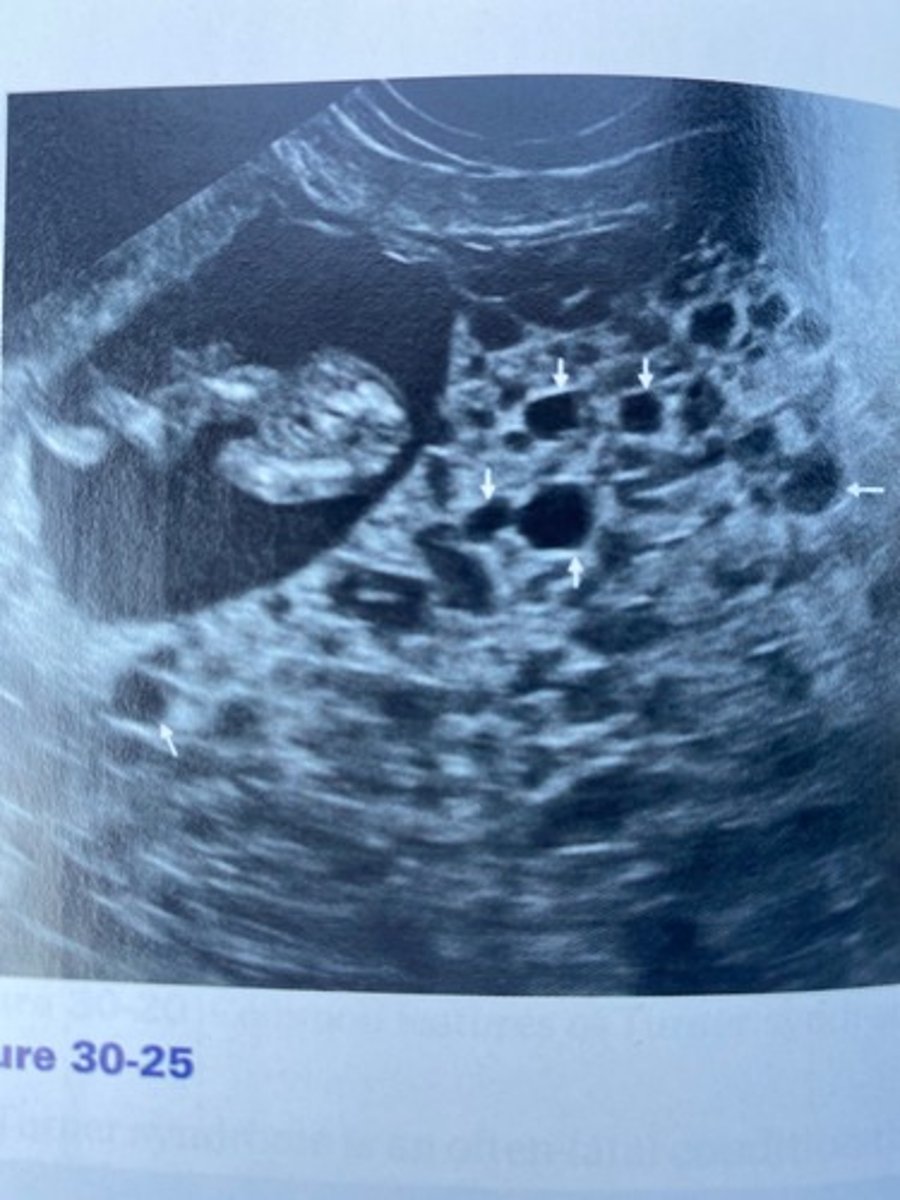
A fetus was discovered in Figure 30-25. What chromosomal abnormality would the fetus likely suffer from?
a. Trisomy 21
b. Trisomy 18
c. Triploidy
d. Turner syndrome
b. monosomy.
A situation in which some cells have an abnormal number of chromosomes whereas others do not is defined as:
a. triploid.
b. monosomy.
c. mosaic.
d. haploid.
a. Partial molar pregnancy
The patient in Figure 30-25 had a markedly elevated hCG level. What is the likely diagnosis given the sonographic findings?
a. Partial molar pregnancy
b. 45,X
c. Patau syndrome
d. Edwards syndrome
d. aneuploid
A cell that has an abnormal number of whole chromosomes is referred to as:
a. triploid.
b. mosaic.
c. haploid.
d. aneuploid.
c. Trisomy 18
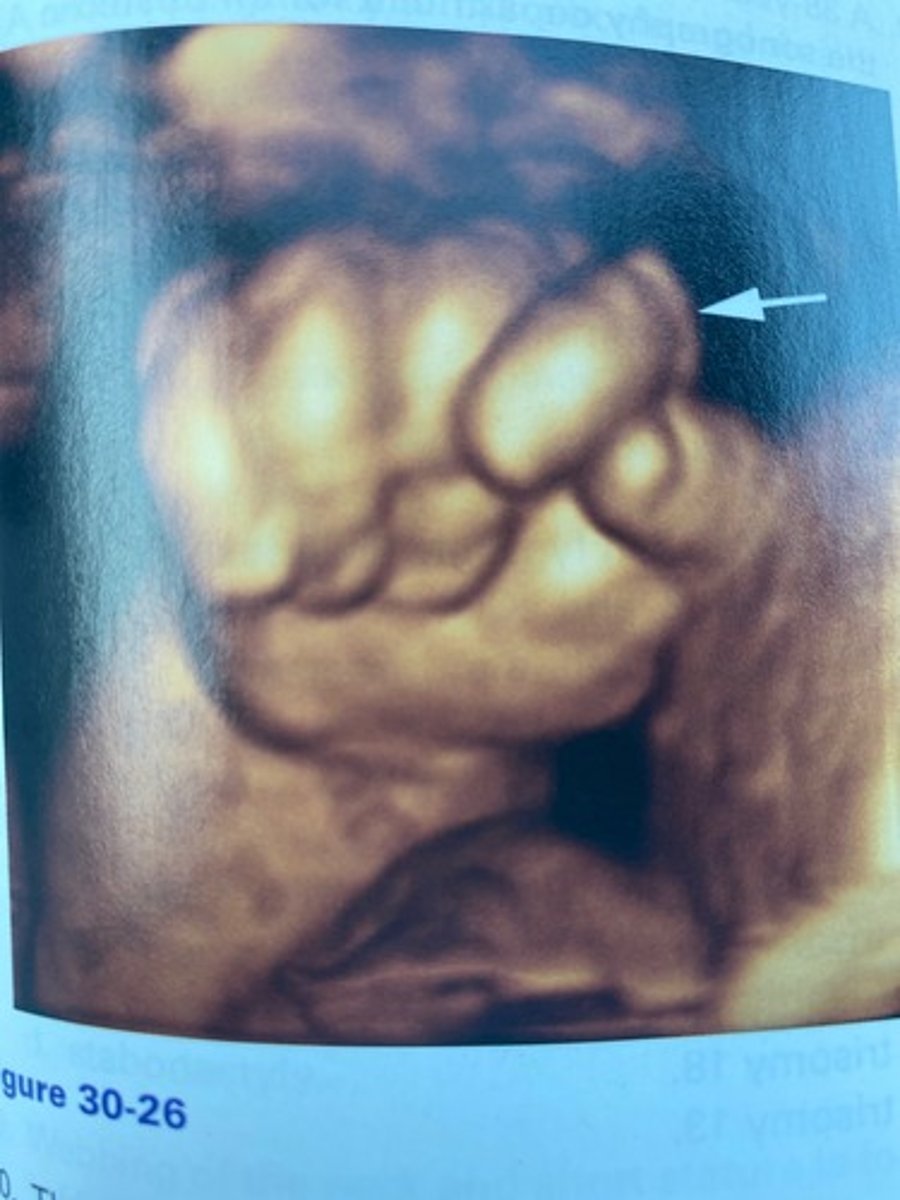
Figure 30-26 would most likely be associated with which chromosomal abnormality?
a. Trisomy 21
b. Turner syndrome
c. Trisomy 18
d. Klinefelter syndrome
a. Cell-free DNA
Which of the following is a maternal serum test that is used to determine the gender, as well as detecting some chromosomal abnormalities?
a. Cell-free DNA
b. Cordocentesis
c. Amniocentesis
d. CVS
b. Sandal gap
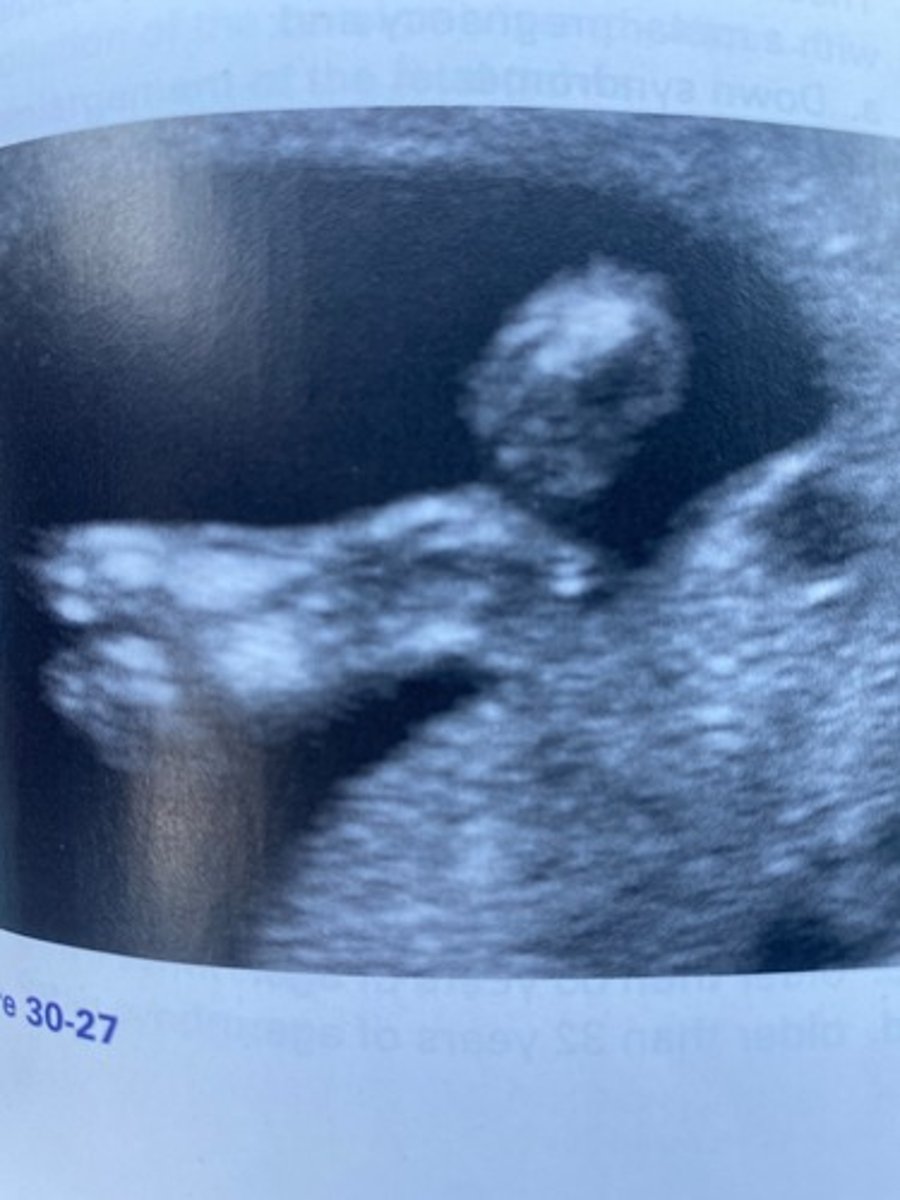
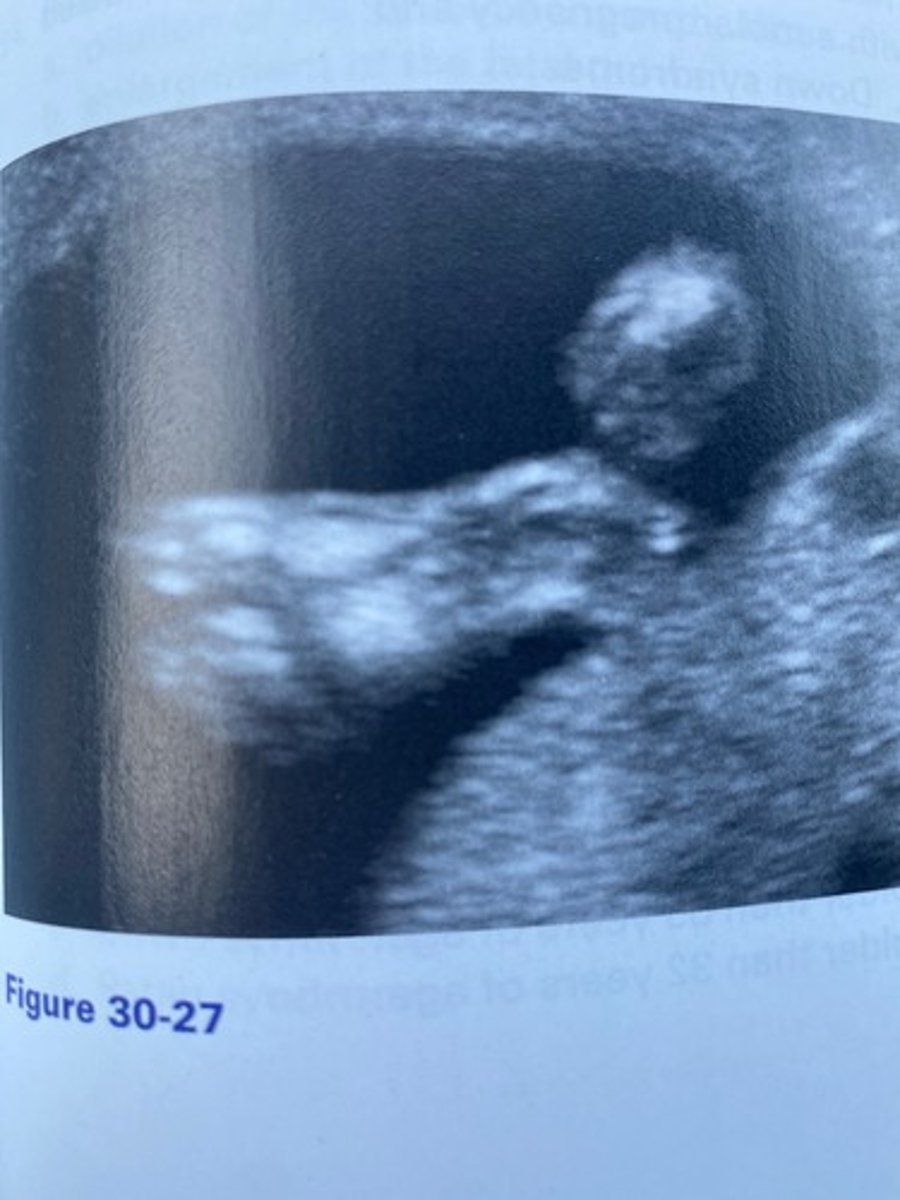
What abnormality of the fetal foot can be noted in Figure 30-27?
a. Clubfoot
b. Sandal gap
c. Amelia
d. Rocker-bottom foot
a. 46 chromosomes.
Normal diploid cells have:
a. 46 chromosomes.
b. 23 chromosomes.
c. 21 chromosomes.
d. 69 chromosomes.
b. Trisomy 21
The abnormality in Figure 30-27 is likely associated with which of the following?
a. Trisomy 13
b. Trisomy 21
c. Trisomy 18
d. Turner syndrome
d. Down syndrome.
A 38-year-old pregnant woman presents to the sonography department for an obstetric sonogram with abnormal maternal serum screening. Her AFP and estriol are low, whereas her hCG is elevated. These laboratory findings are most consistent with:
a. Edwards syndrome.
b. Patau syndrome.
c. triploidy.
d. Down syndrome.
d. Skin edema
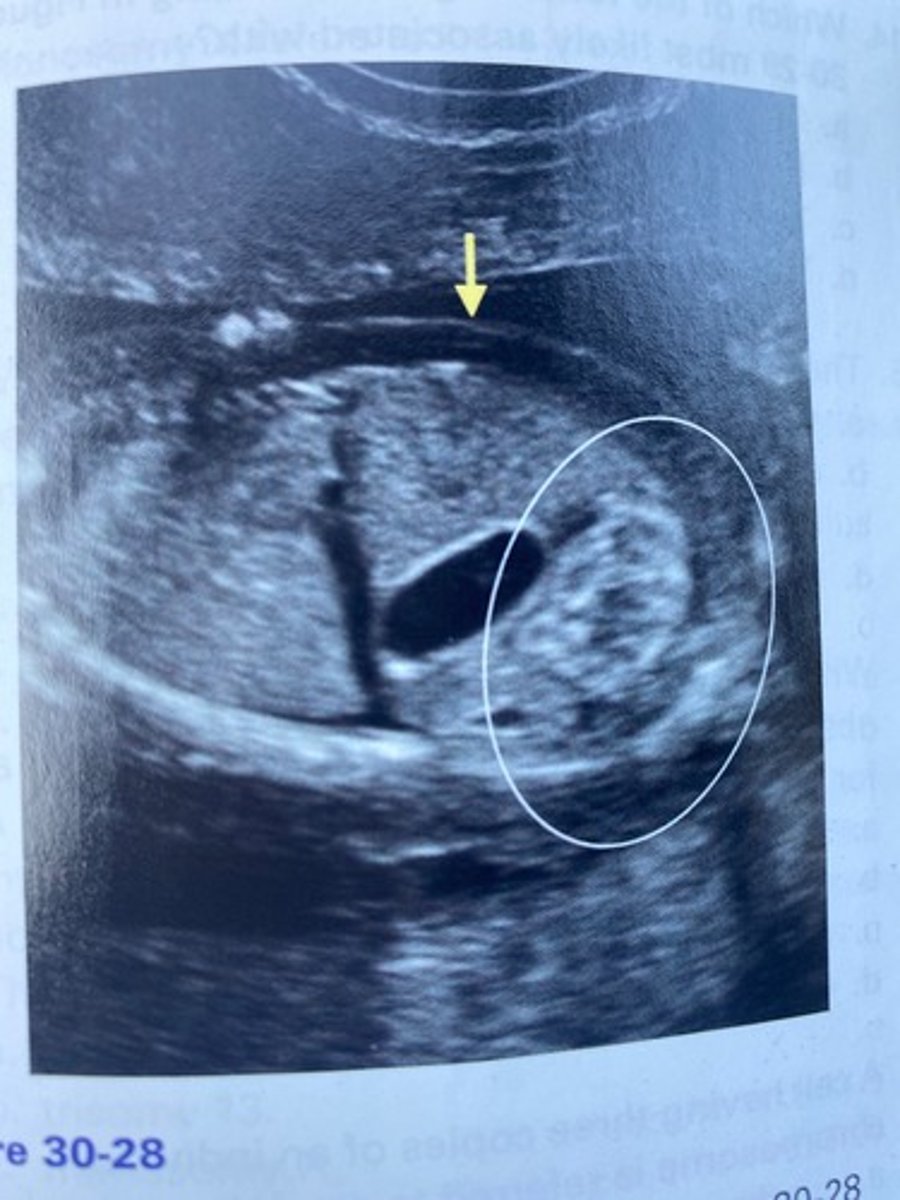
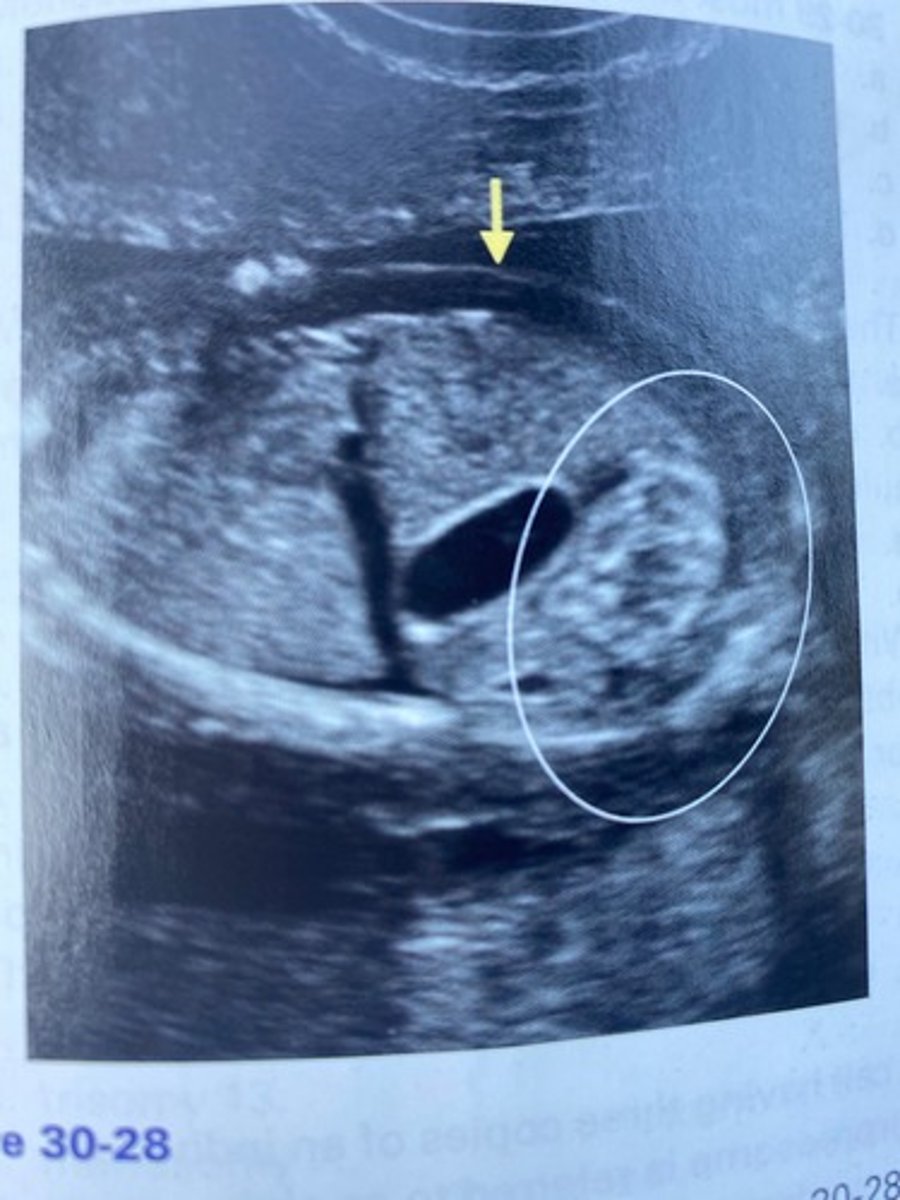
What does the arrow in Figure 30-28 indicate?
a. Nuchal thickening
b. Cystic hygroma
c. Turner syndrome
d. Skin edema
a. AFP, estriol, and hCG.
The triple screen typically includes:
a. AFP, estriol, and hCG.
b. AFP, amniotic fluid index, and hCG.
c. AFP, estriol, and PAPP-A.
d. PAPP-A, inhibin A, and hCG.
b. Echogenic bowel
What does the circled region in Figure 30-28 indicate?
a. Bowel obstruction
b. Echogenic bowel
c. Duodenal atresia
d. Diaphragmatic hernia
d. trisomy 13.
Another name for Patau syndrome is:
a. trisomy 21.
b. trisomy 16.
c. trisomy 18.
d. trisomy 13.
b. brachycephaly.
Rounded head shape is referred to as:
a. dolichocephaly.
b. brachycephaly.
c. cebocephaly.
d. craniosynostosis.
c. triploidy.
Theca lutein cysts would most likely be linked with a molar pregnancy and:
a. Down syndrome.
b. intrauterine growth restriction.
c. triploidy.
d. monosomy X.
c. Down syndrome
With which of the following syndromes is brachycephaly associated most often?
a. Edwards syndrome
b. Patau syndrome
c. Down syndrome
d. Turner syndrome
c. older than 35 years of age.
Advanced maternal age is considered to be:
a. older than 25 years of age.
b. older than 30 years of age.
c. older than 35 years of age.
d. older than 32 years of age.
d. 45,X
Which of the following is a sex chromosome anomaly?
a. Edwards syndrome
b. Trisomy 13
c. Down syndrome
d. 45,X
d. triploidy.
A molar pregnancy, omphalocele, and small, low-set ears are found most often with:
a. trisomy 21.
b. trisomy 18.
c. trisomy 13.
d. triploidy.
c. CVS
With what procedure is placental tissue obtained?
a. Amniocentesis
b. Cordocentesis
c. CVS
d. Trophoblastic resection technique
b. clinodactyly.
The bending of the fifth digit toward the fourth digit is called:
a. syndactyly.
b. clinodactyly.
c. polydactyly.
d. stabodactyly.
d. Turner syndrome.
Webbing of the neck and short stature is found in infertile female patients with a history of
a. trisomy 21.
b. triploidy.
c. trisomy 13.
d. Turner syndrome.
a. dilation of the renal pelvis and calices.
Pelvocaliectasis refers to:
a. dilation of the renal pelvis and calices.
b. enlargement of the fetal pelvis.
c. ectopic location of the kidney within the pelvis.
d. dilation of the ureter within the pelvis.
c. CVS.
The earliest invasive fetal karyotyping technique that can be performed is:
a. amniocentesis.
b. cordocentesis.
c. CVS.
d. PUBS.
a. Edwards syndrome.
A strawberry-shaped skull is associated with:
a. Edwards syndrome.
b. Turner syndrome.
c. Down syndrome.
d. Patau syndrome.
c. trisomy 13.
Cleft lip, hypotelorism, and microphthalmia are all sonographic features of:
a. trisomy 21.
b. trisomy 18.
c. trisomy 13.
d. Turner syndrome.
d. Turner syndrome.
Monosomy X refers to:
a. Edwards syndrome.
b. Patau syndrome.
c. Down syndrome.
d. Turner syndrome.
c. Chorionic villi
What are the fingerlike projections of gestational tissue that attach to the decidualized endometrium?
a. Decidua capsularis
b. Decidua vera
c. Chorionic villi
d. Placental substance
a. trisomy 21.
A 22-week fetus with clinodactyly, an echogenic intracardiac focus, and hyperechoic bowel is noted during a screening obstetrical sonogram.
These findings are most consistent with:
a. trisomy 21.
b. trisomy 13.
c. monosomy X.
d. trisomy 18.
a. microphthalmia.
The term for small eyes is:
a. microphthalmia.
b. micrognathia.
c. microcephaly.
d. microglossia.
d. decreased hCG, AFP, and estriol.
The maternal serum screening of a mother with a fetus with trisomy 18 will reveal:
a. decreased hCG, elevated AFP, and normal estriol.
b. increased hCG, AFP, and estriol.
c. increased AFP, increased hCG, and decreased estriol.
d. decreased hCG, AFP, and estriol.
d. Patau syndrome.
Fusion of the orbits and holoprosencephaly is associated with:
a. Edwards syndrome.
b. Turner syndrome.
c. Down syndrome.
d. Patau syndrome.
c. malformation.
A structural abnormality that results from an abnormal development describes:
a. syndrome.
b. chromosomal deviation.
c. malformation.
d. congenital misrepresentation.
a. trisomy 21.
Absent nasal bones and an increased nuchal fold measurement are most consistent with the sonographic markers for:
a. trisomy 21.
b. trisomy 13.
c. triploidy.
d. trisomy 18.
d. sandal gap.
A large space between the first and second toes is termed:
a. polydactyly.
b. clubfoot.
c. ulnaration.
d. sandal gap.
c. trisomy 18.
Bilateral choroid plexus cysts, micrognathia, and rocker-bottom feet are sonographic findings of a 27-week fetus with an omphalocele. These findings are most consistent with:
a. trisomy 21.
b. trisomy 13.
c. trisomy 18.
d. triploidy.
d. Turner syndrome.
Nonimmune hydrops and ovarian dysgenesis are
found in fetuses affected by:
a. trisomy 21.
b. trisomy 18.
c. trisomy 13.
d. Turner syndrome.
a. Trisomy 21
What is macroglossia most often associated with?
a. Trisomy 21
b. Trisomy 18
c. Triploidy
d. Turner syndrome
c. triploidy.
A fetus with a karyotype revealing it has 69 chromosomes and sonographic findings of webbed fingers and intrauterine growth restriction most likely has:
a. trisomy 21.
b. trisomy 18.
c. triploidy.
d. Turner syndrome.
c. Down syndrome
What is another name for the most common chromosomal abnormality?
a. Edwards syndrome
b. Triploidy
c. Down syndrome
d. Turner syndrome
c. Down syndrome.
Widened pelvic angles and duodenal atresia are most consistent with the sonographic markers for:
a. triploidy.
b. Patau syndrome.
c. Down syndrome.
d. Edwards syndrome.
d. Trisomy 13
Sonographically, you identify a fetus with fusion of the thalami and a monoventricle. Which chromosomal abnormality would be most likely?
a. Trisomy 8
b. Trisomy 21
c. Trisomy 18
d. Trisomy 13
a. AFP
Which protein is not produced by the developing placenta?
a. AFP
b. hG
c. Estriol
d. PAPP-A
a. High AFP
Which of the following laboratory findings would not be consistent with trisomy 21?
a. High AFP
b. Low estriol
c. High hCG
d. Low PAPP-A
d. trisomy 13.
Cyclopia would most likely be associated with:
a. trisomy 8.
b. trisomy 21.
c. trisomy 18.
d. trisomy 13.
b. syndactyly.
Webbed fingers or toes are termed:
a. clinodactyly.
b. syndactyly.
c. polydactyly.
d. Werner syndrome.
c. Klinefelter syndrome
Which of the following is a sex chromosome anomaly associated with hypogonadism and subnormal intelligence in males?
a. Down syndrome
b. Edwards syndrome
c. Klinefelter syndrome
d. Turner syndrome
a. Hypoplastic mandible
Which of the following is not consistent with the diagnosis of nonimmune hydrops?
a. Hypoplastic mandible
b. Pleural effusion
c. Ascites
d. Subcutaneous edema
a. Down syndrome.
Echogenic small bowel is most often associated with:
a. Down syndrome.
b. Edwards syndrome.
c. Patau syndrome.
d. Turner syndrome.