light
1/13
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms

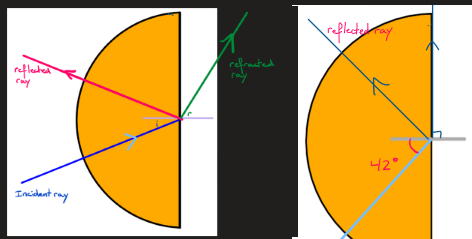
what is the normal line
an imaginary line, perpendicular to the object the light is travelling through and where it hits it
which way does light refract when the object it’s travelling trough is denser
towards the normal line
which way does light refract when light travels through a less dense object
away from the normal line
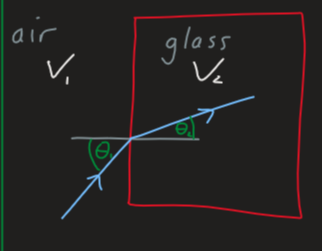
what is the calculation of Snell’s law
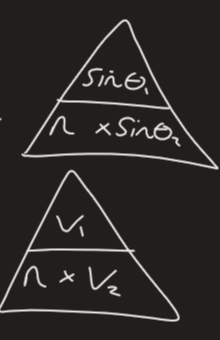
how do you use Snell’s law

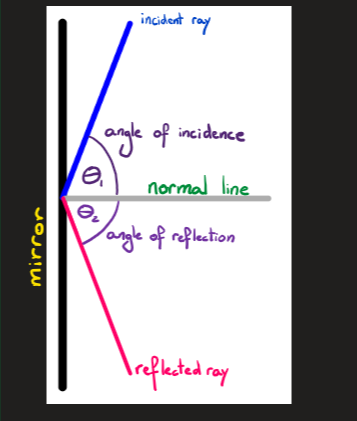
what are the propreties of reflection
angle 1 = angle 2
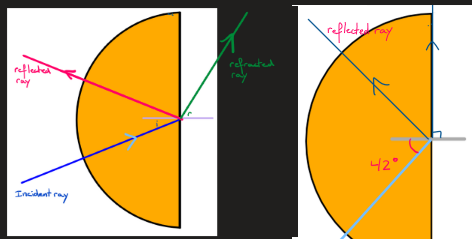
what is the critical angle
the angle at which the light only reflects and doesn’t refract
—> if the angle of incidence is bigger than the critical angle, it only reflects
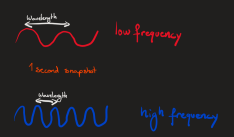
what is the order of the dispersion of light
-Red
-orange
-yellow
green
-blue
-indigo
-violet

why do colours disperse when refracting
because hot colours have a lower frequency than cold colours
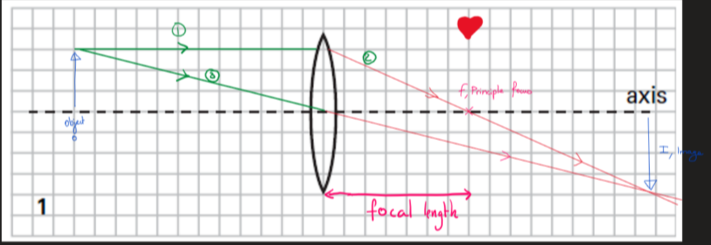
what are the propreties of a this ray diagram
the image is :
-inverted
-larger
real (projection onto a screen)

what are the propreties of this ray diagram
the image is:
-virtual
-upright
magnified
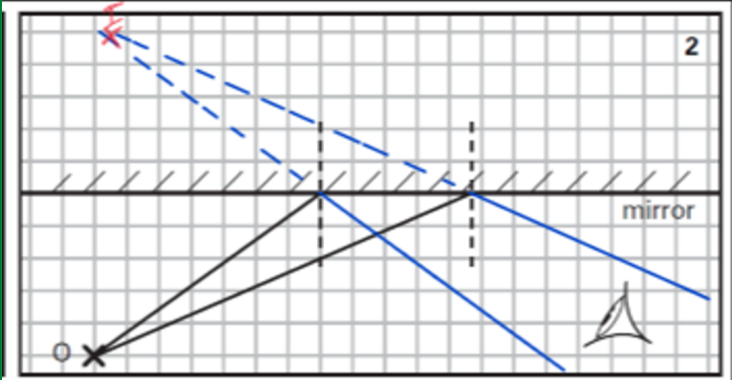
what does this diagram show
the optical images by mirrors
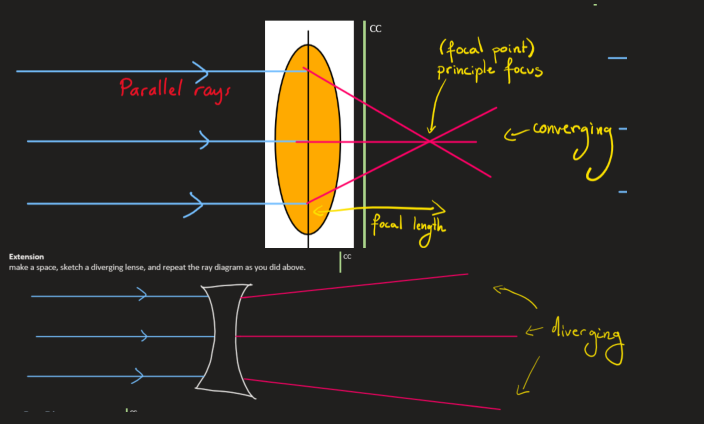
focal point and length
what is the density of air
3 × 108 m/s