action potential
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
nerve
“tracts” found in the peripheral nervous system
(PNS)
tract
“nerves” that are found in the central nervous system
ganglion
“nucleus” (which is in the cns) found in the PNS
myelin sheath in CNS
one cell, many axons connect thru oligodendrocyte
myelin sheath in PNS
Each Schwann cell wraps its whole body around one segment of one axon
synapse
where neuron meets its target cell,
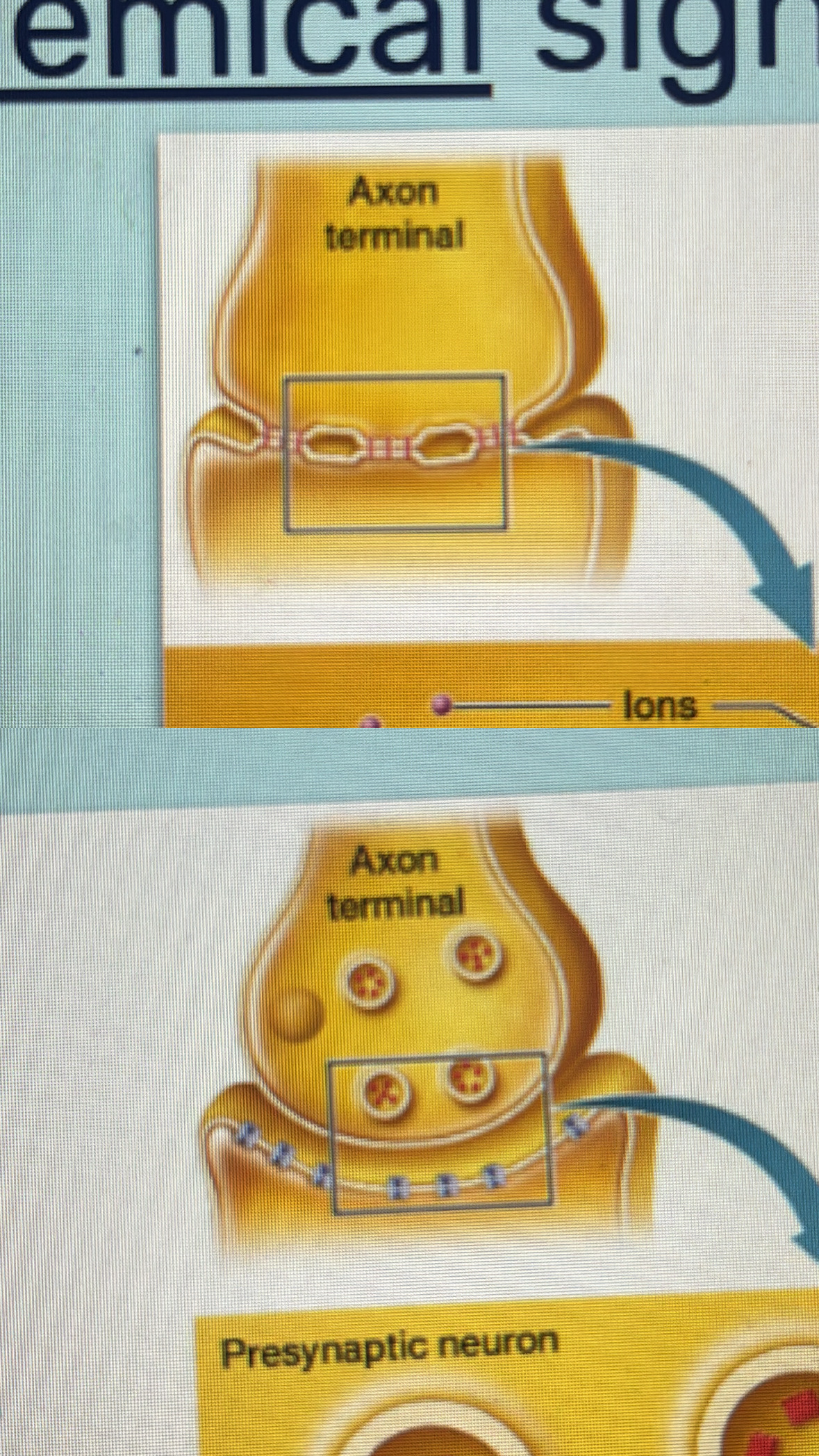
neurotransmitter
chemical messenger released by the presynaptic neuron to send signals to another cell across a synapse to the postsynaptic neuron
types of neurotransmitters
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Biogenic Amines
Amino Acids
Neuropeptides
potential generation
the cell is negative inside, positive outside
a stimulus connects to the channels
channel opens and Na+ fills in= positive inside
at -30 mV the Na+ channel closes and K+ channel opens
K+ flows out and inside is negative again
After one part of the membrane depolarizes, it triggers the next segment. which continues along the full axon
voltage gated ion channel
Open in response to changes in membrane potential.
Key for action potentials.
Na+
goes inside the postsynaptic neuron and makes it positive inside
K+
exits the postsynaptic neuron and makes it negative again
Ca2+
allows for stimuli to exit in the axon cell
ligand gated ion channels
Open when a specific molecule (ligand) binds.
Key for synaptic transmission
when ACh binds and lets Na+ in
mechanically gated ion channels
respond to pressure in sensory neurons
leak channel
passive channels that are always open
K⁺ leak channels → more K⁺ leaves → inside stays negative at rest.
saltatory conduction
action potential travels fast, jumping, only happens in myelinated axons.
continuous conduction
action potential travels slow, step-by-step, only happens in unmyelinated axons