CAMS UA 102: Child and Adolescent Mental Illness Review
1/251
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
252 Terms
What does the acronym ABCS in Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) stand for?
A = Activating Event, B = Beliefs, C = Consequences.
What is the first step in controlling negative thoughts according to CBT?
Becoming aware of automatic thoughts and tracking negative thoughts.
What should you do to deal with activating events in CBT?
Ignore them, avoid them, change them, change the way you respond to them, and cope with them.
What are cognitive distortions?
Irrational beliefs or thought patterns that negatively affect emotions and behavior.
Name two examples of cognitive distortions.
All or nothing thinking and catastrophizing.
What is the focus of Interpersonal Therapy (IPT)?
How interpersonal relationships affect emotions and mood.
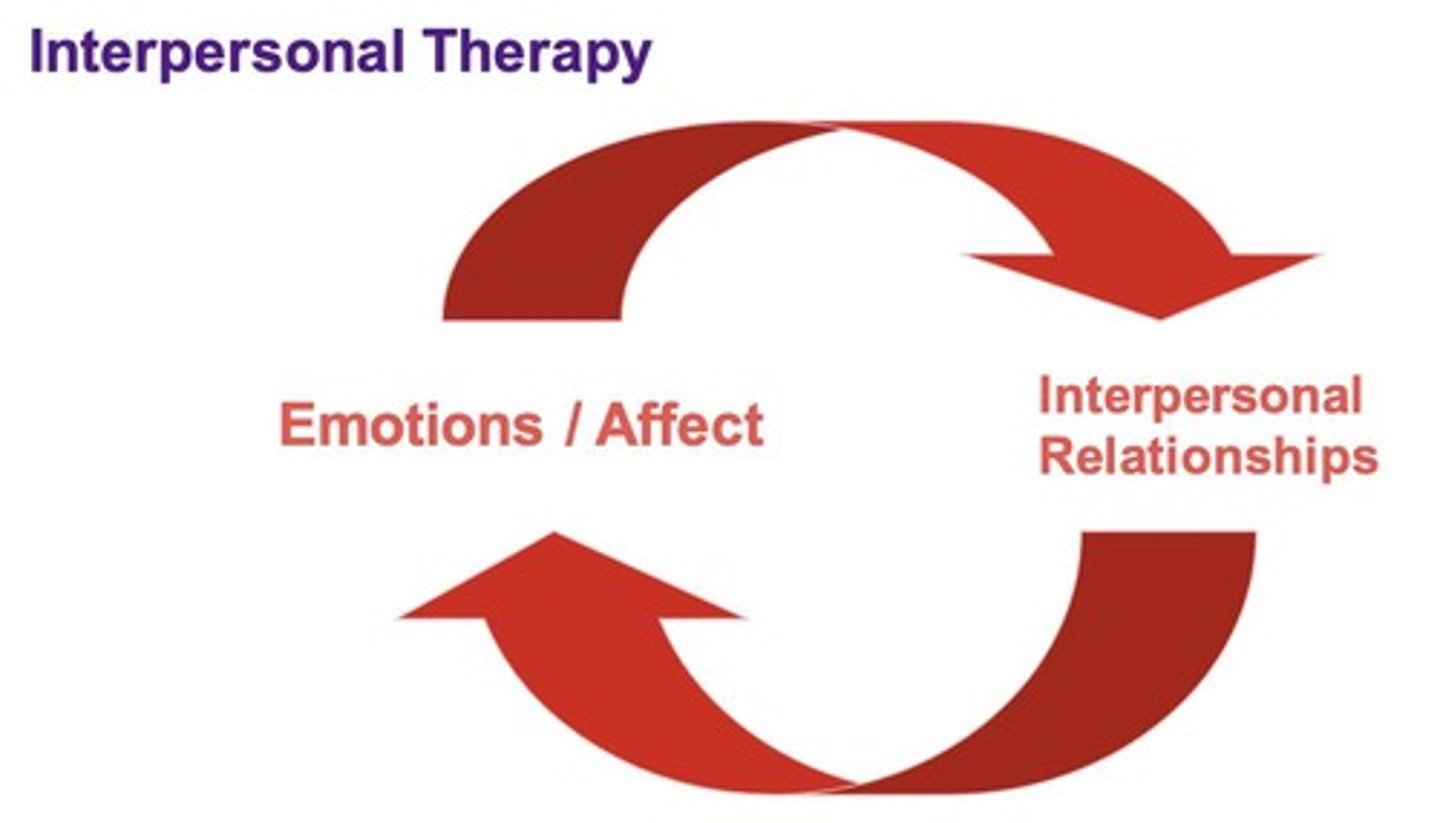
Describe the initial phase of IPT.
Conduct an interpersonal inventory, confirm diagnosis of depression, and choose a problem area.
What techniques are used in the middle phase of IPT?
Communication skills, dealing with conflict, recognizing emotions, problem solving, and role play.
What is the termination phase in IPT?
Review strategies from the middle phase, encourage mastery of new skills, and discuss feelings about ending therapy.
How does IPT differ from CBT?
IPT is simpler and not suitable for complex issues like OCD, anxiety, or psychosis.
What is the emphasis of Acceptance and Commitment Therapy (ACT)?
Acceptance and willingness to experience thoughts and feelings without attempting to change them.
How does ACT relate to mindfulness?
It is similar to mindfulness-based CBT and focuses on acceptance rather than disputing negative thoughts.
What is Beck's Negative Cognitive Triad?
A concept in CBT that describes the negative views individuals have about themselves, their world, and their future.
What is the goal of behavioral activation in CBT?
To increase engagement in positive activities to improve mood.
What is the purpose of tracking positive thoughts in CBT?
To become comfortable with having positive thoughts and counter negative thinking.
What is the significance of labeling irrational beliefs in CBT?
It helps individuals recognize and challenge cognitive distortions.
What is the role of counter thoughts in CBT?
To provide alternative perspectives that challenge irrational beliefs.
What is the aim of IPT in dealing with grief?
To help patients navigate their feelings and improve their interpersonal relationships during the grieving process.
What is meant by 'unstubborning the stubborn people' in ACT?
Encouraging individuals to let go of rigid beliefs and embrace acceptance for personal growth.
What is a common outcome of IPT for patients?
Patients often find IPT simpler and more manageable than CBT.
What are booster sessions in IPT?
Follow-up sessions scheduled after termination to reinforce skills learned.
What is the cognitive triangle in CBT?
A model that illustrates the relationship between thoughts, feelings, and behaviors.
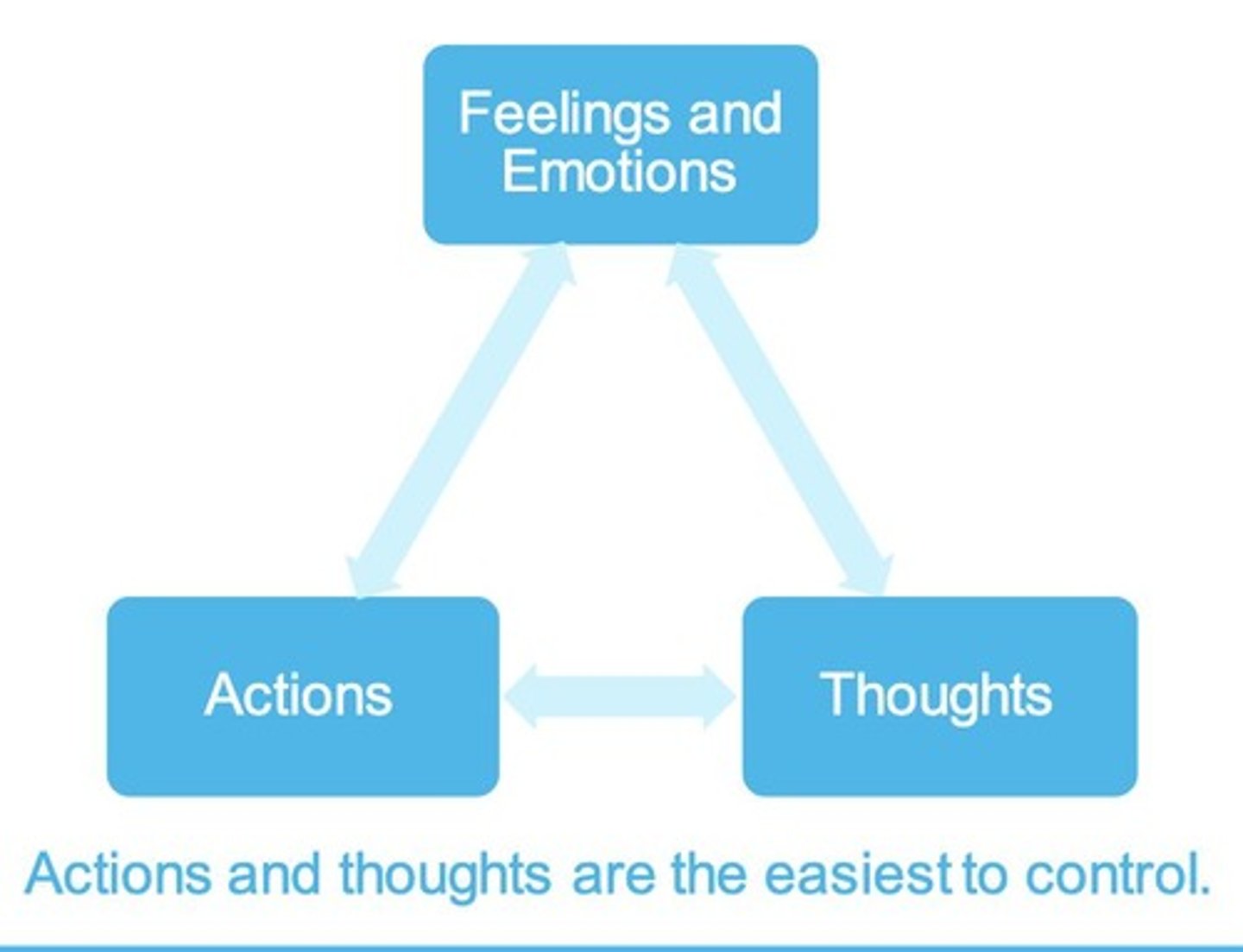
What is the significance of understanding automatic thoughts in CBT?
It allows individuals to identify and modify negative thought patterns that affect their mood.
What is psychological inflexibility?
It refers to the inability to adapt to situations, often leading to problems such as panic disorder, OCD, depression, and eating disorders.
What is cognitive fusion?
Cognitive fusion occurs when individuals conflate the meaning of their thoughts with literal events, failing to notice the process of thinking.
What is cognitive diffusion?
Cognitive diffusion is the practice of recognizing thoughts as just thoughts, without attempting to change their content.
What does 'self as context' refer to in psychological terms?
It helps individuals detach from their thoughts, memories, and histories, prompting the question, 'If I'm not my thoughts, then who am I?'
Why is being present important in therapy?
Being present undermines cognitive fusion, avoidance, and reason-giving, allowing individuals to connect with the current moment.
What are the consequences of focusing too much on the past and future?
It can lead to a lack of self-awareness and an inability to understand what is happening in the present.
What is inaction in the context of psychological issues?
Inaction refers to the inability to behave in accordance with one's values due to a focus on feeling good or managing anxiety.
What is acceptance in the context of the six core therapeutic processes?
Acceptance is an alternative to avoidance, involving active awareness and embracing internal experiences without attempting to change them.
What is the purpose of the Coping Cat program?
Coping Cat is designed to treat anxiety in children ages 8-12 by teaching them to recognize anxious arousal and manage anxiety.
What techniques are taught in the Coping Cat program?
Children learn relaxation techniques, recognize anxious feelings, implement diaphragmatic breathing, and practice coping self-talk.
What does the FEAR plan stand for?
Feeling frightened, Expecting bad things to happen, Attitudes and actions that will help, Results and rewards.
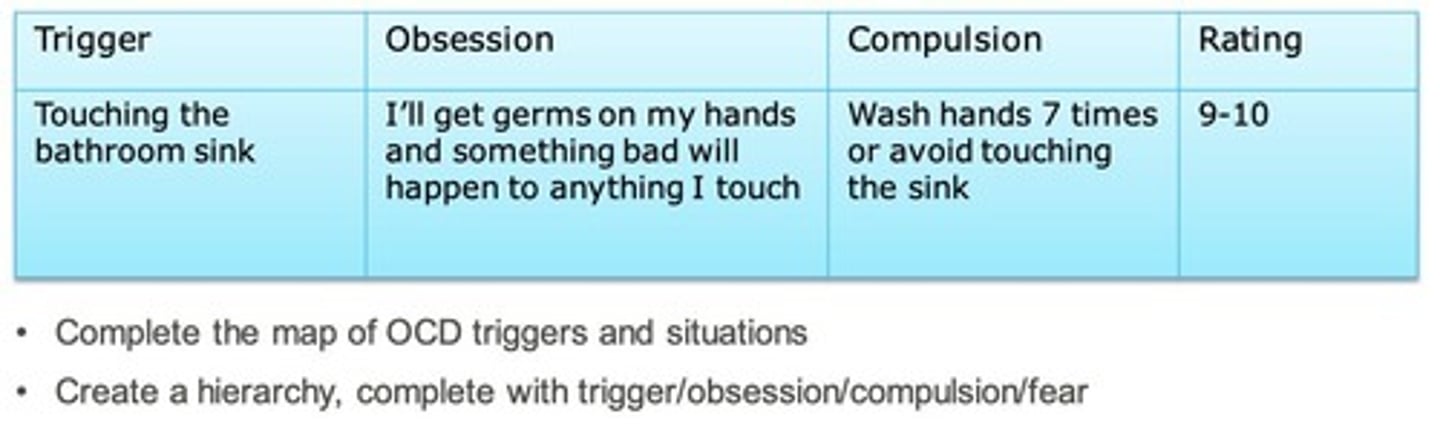
What is the purpose of a fear hierarchy?
A fear hierarchy is used to gauge the level of anxiety around certain situations and to tackle anxiety through exposure.
How is OCD framed to help patients?
OCD is framed as a malfunctioning brain, similar to a computer chip sending incorrect messages, helping patients externalize the disorder.
What is the mapping technique in OCD treatment?
Mapping involves identifying what aspects of anxiety are controlled by OCD, what is owned by the patient, and areas of overlap.
What is the goal of externalizing OCD in therapy?
The goal is to help patients view OCD as a problem separate from themselves, allowing them to manage it more effectively.
What is the importance of self-evaluation in the FEAR plan?
Self-evaluation helps individuals assess their progress and rewards them for overcoming fear and anxiety.
What is the role of modeling or role-playing in exposure therapy?
Modeling or role-playing prepares patients for facing their fears by practicing responses ahead of time.
What is the significance of assessing anxiety throughout therapy sessions?
Continuous assessment helps track progress and adjust treatment strategies based on the patient's current anxiety levels.
How can children distinguish between levels of anxiety in OCD treatment?
Children are taught to differentiate levels of anxiety rather than adopting an 'all or nothing' mindset.
What are some cognitive strategies taught to children in the Coping Cat program?
Children learn to recognize anxious self-talk, practice problem-solving, and implement coping strategies.
What is the ultimate goal of CBT for anxiety and OCD?
The goal is to equip individuals with strategies to manage their anxiety and reduce the impact of OCD on their lives.
What is the core of OCD?
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD) is characterized by persistent, unwanted thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) performed to alleviate the anxiety caused by these obsessions.
What does CRAFTS stand for in the context of Trauma-Focused CBT?
CRAFTS stands for Cognitive problems, Relationship problems, Affective problems, Family problems, Traumatic behavior problems, and Somatic problems.
What are the principle values of Trauma-Focused CBT (TF-CBT)?
The principle values include being components-based, respectful of cultural values, adaptable and flexible, family-focused, emphasizing the therapeutic relationship, and promoting self-efficacy.
What does the acronym PRACTICE represent in TF-CBT?
PRACTICE includes Psychoeducation, Relaxation, Affective Modulation, Cognitive Processing, Trauma Narrative, In Vivo Desensitization, and Conjoint parent-child sessions.
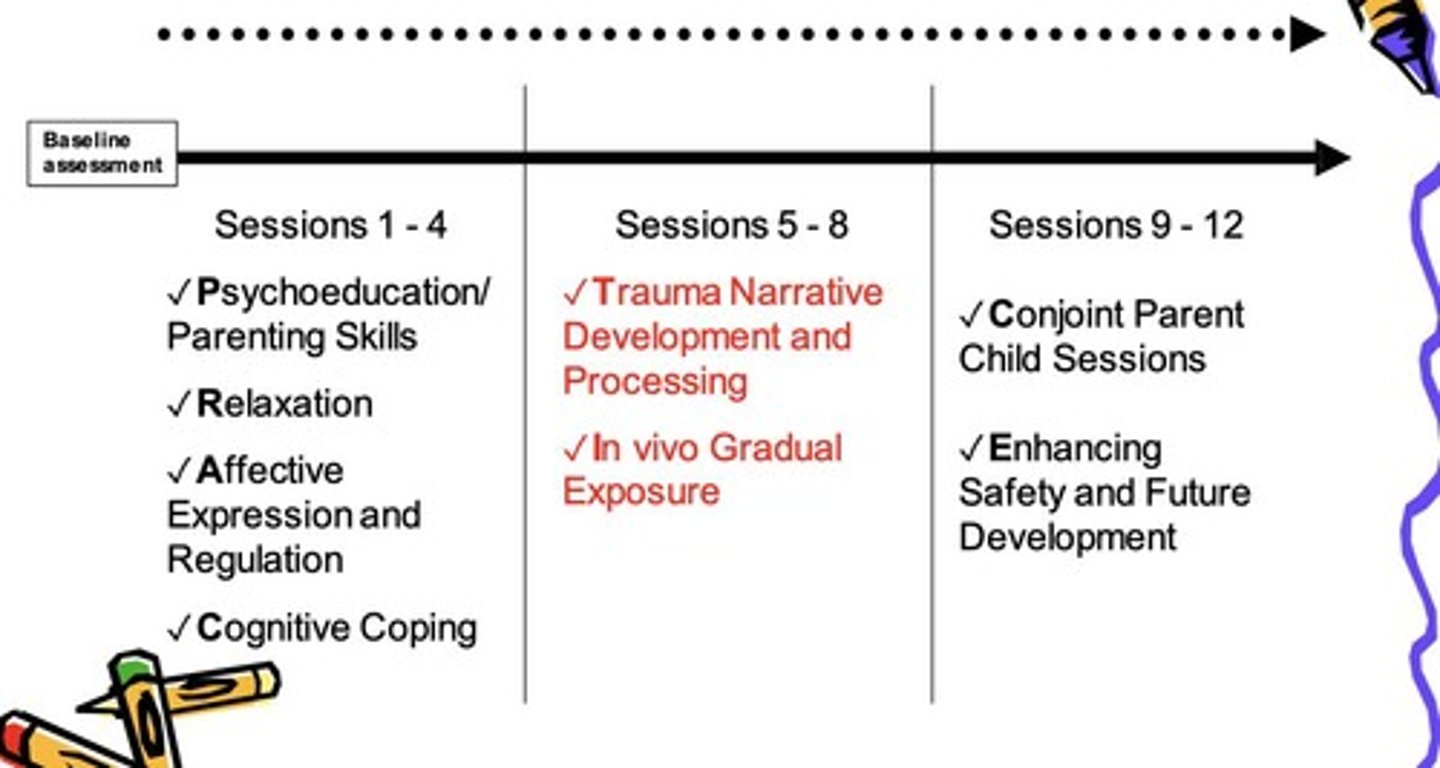
What is the purpose of psychoeducation in TF-CBT?
Psychoeducation ensures that the child understands trauma and develops basic emotion identification and coping skills for managing anxiety or discomfort.
What is the significance of creating a trauma narrative in TF-CBT?
Creating a trauma narrative is essential for processing trauma; however, it should not be done without prior psychoeducation due to potential risks like discomfort and self-harm.
What are some barriers to starting a trauma narrative in TF-CBT?
Barriers include discomfort among all parties involved, legal issues, risk for self-harm, and instability in the living environment or treatment.
What are the major classes of antidepressants?
The major classes include Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs), Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAO-Is), and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs).
What is the mechanism of action for Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs)?
TCAs block the reuptake of norepinephrine and serotonin by neuronal presynaptic receptors.
What are common side effects of TCAs?
Common side effects include dry mouth, blurred vision, urinary retention, constipation, hyperthermia, anxiety, restlessness, and potential cardiac arrhythmias.
What is the risk associated with Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAO-Is)?
MAO-Is can lead to hypertensive crises if tyramine-rich foods are consumed, as they irreversibly inactivate monoamine oxidase.
What is the primary action of Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)?
SSRIs selectively block the reuptake of serotonin in the synaptic cleft, increasing serotonin levels.
What are some advantages of SSRIs compared to TCAs?
SSRIs generally have a decreased side effect profile and do not block acetylcholine, histamine, or norepinephrine receptors like TCAs.
What is a potential risk when using SSRIs?
SSRIs can unmask bipolar disorder and may lead to the emergence of hypomania or mania.
What is discontinuation syndrome in the context of antidepressants?
Discontinuation syndrome refers to withdrawal symptoms that can occur when an antidepressant is abruptly stopped, particularly with medications that have a short half-life.
What is the significance of the half-life of an antidepressant?
The half-life affects how long the drug stays in the body and can influence the risk of discontinuation syndrome; longer half-lives may reduce this risk.
How long does it typically take for SSRIs to take effect?
SSRIs usually take 4-6 weeks to show therapeutic effects after starting treatment.
What are some side effects of SSRIs?
Side effects can include nausea, insomnia, headaches, brain zaps, and sexual dysfunction.
What is the 'cheese effect' associated with MAO-Is?
The 'cheese effect' refers to hypertensive crises caused by the consumption of tyramine-rich foods when taking MAO-Is.
What role does family play in Trauma-Focused CBT?
TF-CBT is family-focused, involving conjoint parent-child sessions to enhance support and understanding.
What is the goal of in vivo desensitization in TF-CBT?
The goal of in vivo desensitization is to gradually expose the child to trauma reminders in a safe environment to reduce anxiety.
What is the importance of the therapeutic relationship in TF-CBT?
The therapeutic relationship is central to TF-CBT, fostering trust and safety, which are crucial for effective treatment.
What is Paroxetine known for in terms of its half-life?
Paroxetine has a short half-life of 1 day.
What side effect is associated with Paroxetine that is believed to be dose dependent?
Feeling numb, which is reversible and can sometimes cause resurgence of depression or apathy syndrome.
What are SNRIs and when did they come to market?
SNRIs, or Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors, came to market in the 1990s.
What neurotransmitters do SNRIs selectively block the reuptake of?
SNRIs selectively block the reuptake of serotonin and norepinephrine in the synaptic cleft.
List some conditions for which SNRIs are used.
Depression, Anxiety, PTSD, OCD, and Chronic pain.
What is a notable side effect of long-term use of SNRIs?
Long-term use of SNRIs has been associated with weight gain.
What additional side effect is associated with SNRIs?
Elevated blood pressure.
What is the mechanism of action of Bupropion (Wellbutrin)?
Bupropion works on norepinephrine and dopamine.
What neurotransmitters does Mirtazapine (Remeron) affect?
Mirtazapine affects serotonin and norepinephrine.
What should you understand about the classification of antidepressants for exams?
You do not need to know specific names of antidepressants; the exam will specify the class (SSRI, TCA, MAO-I, SNRI) if needed.
What are the key presentations of hypertensive crisis?
Significantly elevated blood pressure and it is considered a medical emergency.
What can cause a hypertensive crisis?
Mixing MAO-Is with other medications/substances such as stimulants, cocaine, and Sudafed.
What are the symptoms of Serotonin Syndrome?
Delirium, hallucination, confusion, coma, hyperthermia, high blood pressure, high heart rate, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abnormal muscle twitches or jerks, and tremors.
What causes Serotonin Syndrome?
It can be caused by Tryptophan not being broken down or by combining with other medications that affect serotonin neurotransmission.
What does the monoamine hypothesis suggest about depression?
It suggests that depression is caused by a deficiency of monoamine neurotransmitters in the brain such as norepinephrine, serotonin, and dopamine.
What are some limitations of the monoamine hypothesis?
SSRIs are safer and have fewer side effects than older antidepressants, cannot fully explain the delayed response to antidepressants, and many patients do not respond to these medications.
What are some transient side effects of SSRIs?
Nausea/diarrhea, stimulation & insomnia, sedation, and headaches.
What are some persistent side effects of SSRIs?
Tremors, vivid dreams, weight gain, and sexual dysfunction.
What additional risks are associated with SSRIs?
Disinhibition in children, risk of unmasking bipolar disorder, emergence of hypomania or mania, discontinuation syndrome, and apathy syndrome.
What was the Black Box Warning issued by the FDA in 2003 regarding antidepressants?
It warned about increased suicidality in children and teens taking antidepressants.
What did the meta-analysis conducted by the FDA include?
It included 25 short-term placebo-controlled trials with 9 different antidepressants for children and adolescents.
What were the findings of the meta-analysis regarding suicidal ideation?
4% of patients on antidepressants had suicidal ideation compared to 2% on placebo.
What is the placebo effect?
The placebo effect is when people experience symptoms of a desired effect despite not receiving the actual intervention.
What is the placebo effect in the context of medication?
The placebo effect refers to the phenomenon where a patient experiences improved symptoms after taking an inactive medication due to expectations, conditioning, and the patient-provider relationship.
How much more effective are antidepressants compared to placebos according to studies?
Antidepressants are shown to be 33% more effective than placebos.
What improvement did placebo groups show compared to no treatment groups?
Placebo groups showed a 200% improvement over no treatment groups.
What is estimated about the drug effect in relation to the placebo effect?
It is estimated that up to half of the drug effect may be attributable to the placebo effect.
What key studies should be reviewed regarding treatment arms and outcomes for patients?
The TADS, TORDIA, CAMS, and POTS studies should be reviewed for patient inclusion, treatment arms, primary outcomes, and major findings.
What was the objective of the TADS Study?
To evaluate the efficacy of monotherapy treatments (CBT alone, fluoxetine alone) compared to combined treatment (CBT & antidepressant) for adolescents with MDD.
Who were the participants in the TADS Study?
439 outpatients, ages 12-17, who met criteria for MDD, with some having comorbidities like anxiety or OCD.
What were the exclusion criteria for the TADS Study?
Participants with bipolar disorder, conduct disorder, SUDS, pervasive developmental disorder, intellectual disabilities (IQ < 80), high risk for suicide, or prior poor response to treatment.
What were the treatment arms in the TADS Study?
CBT, fluoxetine, combined treatment (CBT & meds), and placebo.
What was the duration of the CBT treatment in the TADS Study?
12 weeks, consisting of 15 one-hour sessions.
What was the dosing schedule for fluoxetine in the TADS Study?
12 weeks with 6 thirty-minute medication appointments, dosed at 10-40 mg.