Cell Communication and Signal Transduction Pathways
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Cell Communication
Essential for unicellular and multicellular organisms.
Chemical signaling
The process by which cells communicate through chemical signals.
Fight or flight response
An example of cell communication that prepares the body to respond to threats.
Hunger satiation
An example of cell communication that signals the body to stop eating.
Embryonic development
An example of cell communication that guides the growth and differentiation of cells in an embryo.
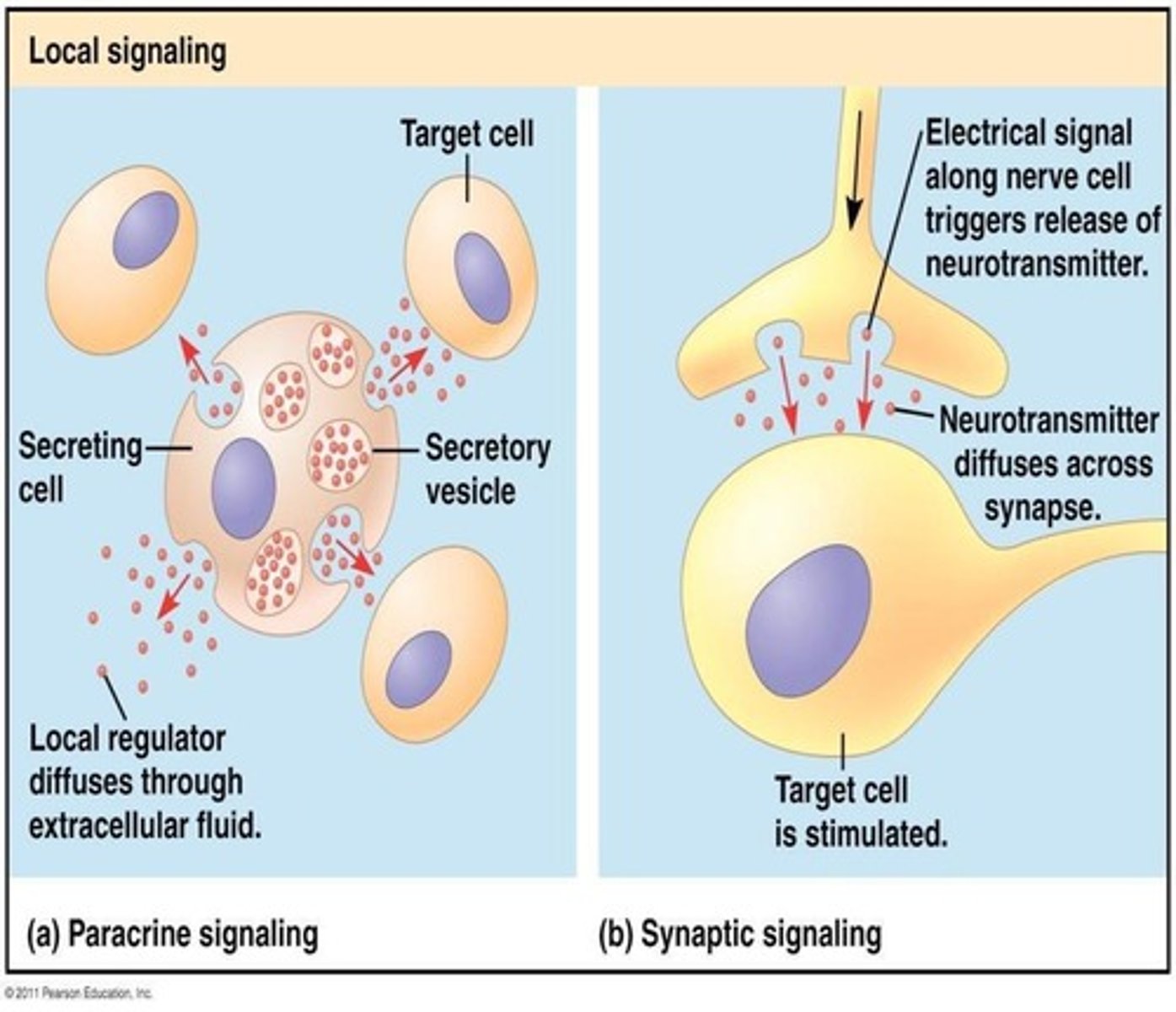
Neuron synapses
An example of cell communication where neurotransmitters are released to transmit signals between nerve cells.
Ligand
A chemical signal that binds to a receptor.
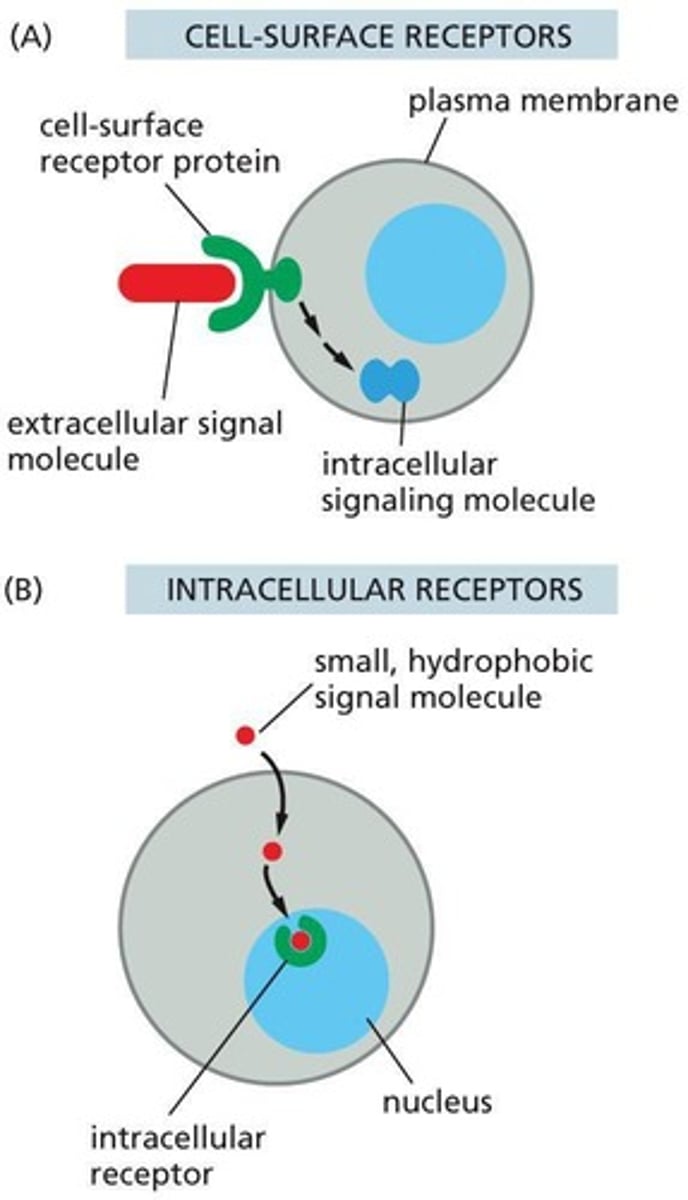
Intracellular receptor
A receptor located inside the cell that binds to small or nonpolar ligands.
Membrane receptor
A receptor located on the cell membrane that binds to large or polar ligands.
Kinase
An enzyme that adds a phosphate group to a substrate, often involved in signaling pathways.
Phosphatase
An enzyme that removes a phosphate group from a substrate, often involved in signaling pathways.
Second messenger
A molecule that transmits signals from a receptor to target molecules inside the cell.
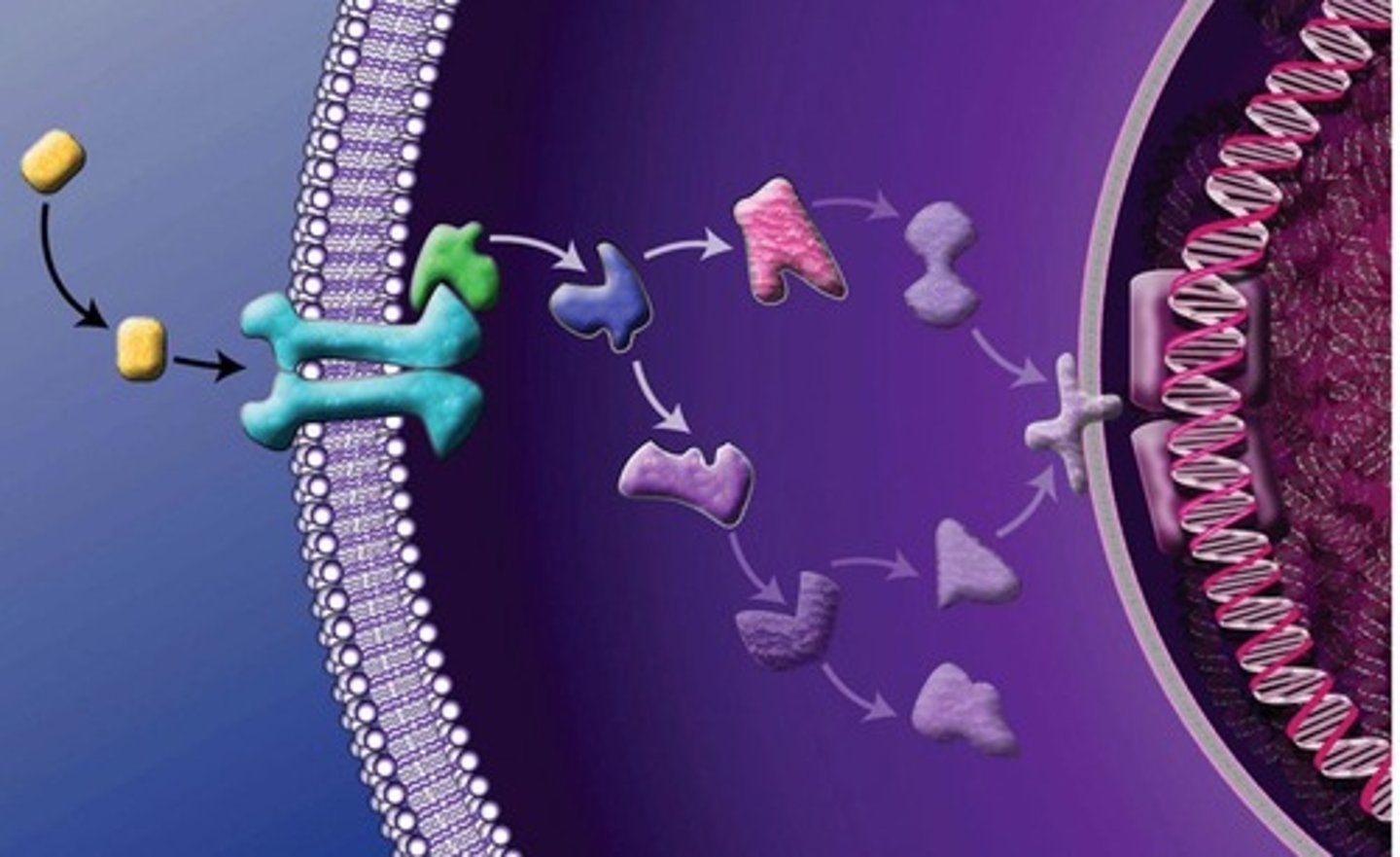
Signal Transduction Pathway
A sequence of molecular events and chemical reactions that lead to a cell's response to a signal.
Chemical signal
A ligand that initiates a response in a cell.
Receptor
A protein that receives signals from ligands.
Juxtacrine signaling
A type of signaling where cells communicate through direct contact.
Hormonal signaling
A type of signaling where hormones travel to distant cells, usually via the circulatory system.
Paracrine signaling
A type of signaling that affects nearby cells.
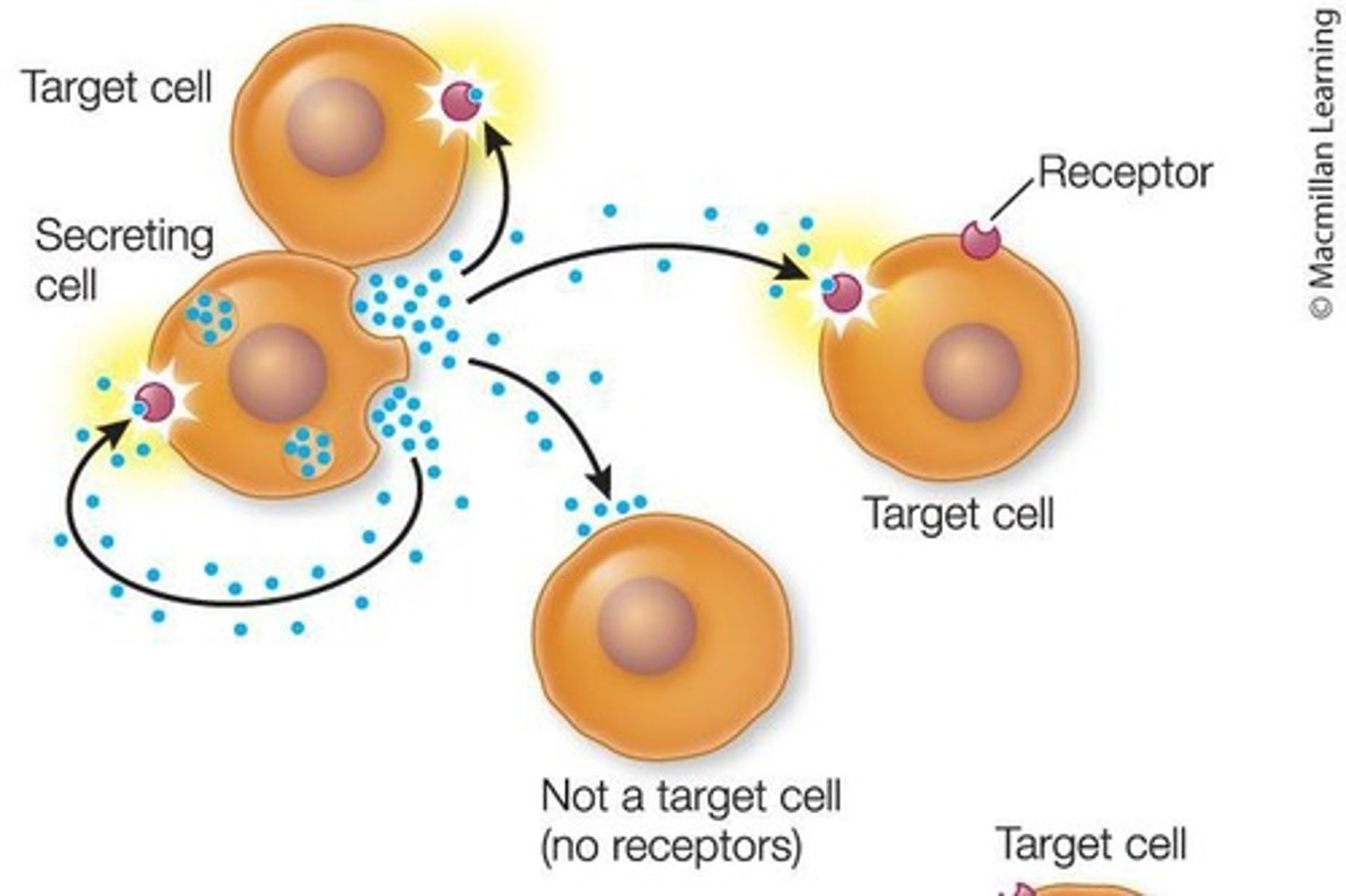
Autocrine signaling
A type of signaling that affects the cells that made them.
Aldosterone
A steroid compound synthesized in the adrenal glands that binds to receptors in kidney cells.
Example of paracrine signaling
Acetylcholine acting at a synapse.
Shortest Distance
The minimum length between two points.
Longest Distance
The maximum length between two points.
Extracellular signal
A signal that is outside the cell and influences the cell's behavior.
Cell's response to a signal
Can be fast or slow depending on the nature of the signal.
Adenosine
A ligand that initiates a signal transduction pathway in nerve cells, reducing brain activity and wakefulness.
Caffeine
An antagonist that binds to adenosine receptors, allowing continued nerve cell activity.
Agonists
Compounds that have the same effect as the ligand.
Antagonists
Inhibitors that bind to the receptor, preventing the ligand from binding without activating signal transduction.
Signal Transduction
A sequence of molecular events and chemical reactions that lead to a cell's response to a signal.
Second Messengers
Molecules that relay signals onward, amplify the signal, and integrate signals from multiple pathways.
cAMP
A secondary messenger produced from ATP by adenylyl cyclase that binds to ion channels and protein kinases.
Crosstalk
The interconnection of signal transduction pathways, allowing pathways to branch or converge.
Gated ion channels
Membrane receptors that open or close in response to specific signals.
Signal transduction pathway
A series of changes in molecules resulting in a cellular response.
Relay the signal
The function of second messengers to help spread the signal through the cell.
Amplify the signal
The ability of second messengers to strengthen the signal and produce a large intracellular response.
Integrate signals
The process by which second messengers combine signals from multiple pathways.
Distribute the signal
The function of second messengers to send the signal to multiple effector proteins.
Protein kinase cascade
A series of protein modifications that amplify the signal and lead to a cellular response.
Chemical or mechanical stimulus
The cell's detection of external signals that can trigger a response.
Ligand
A molecule that binds to a receptor to initiate a signal transduction pathway.
Enzyme activation
A direct response in signal transduction that can occur quickly.
Alter DNA transcription
A more complex response in signal transduction that involves multiple steps.
Crosstalk
Interaction of signal transduction pathways
Gated ion channels
Allow ions to enter or leave a cell; signal binding results in change in shape of the channel protein, and the channel opens.
Example of Gated ion channel
The acetylcholine receptor on muscle cells is a ligand-gated ion channel.
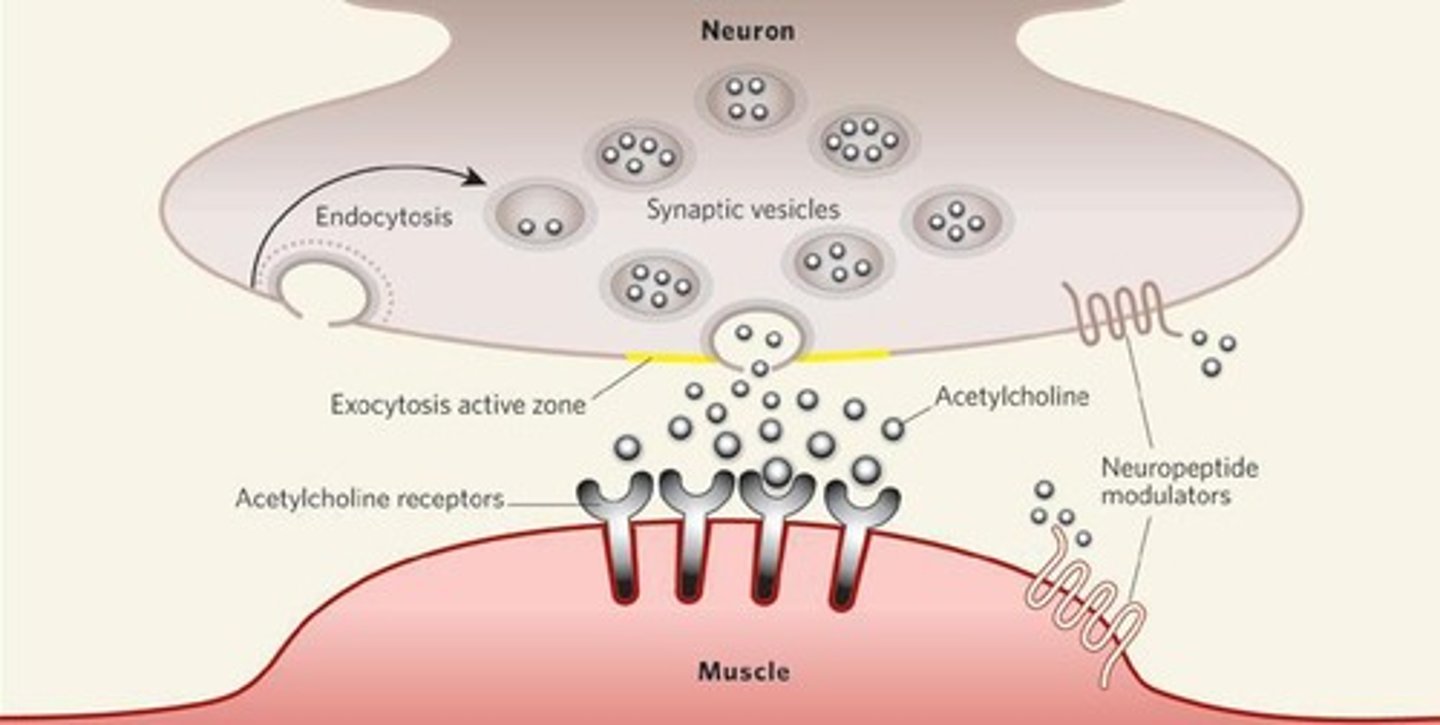
Protein kinase receptors
Catalyze phosphorylation of themselves and/or other proteins, which changes their shape.
Example of Protein kinase receptor
The insulin receptor phosphorylates itself and other insulin response substrates, which initiates insertion of glucose transporters into the cell membrane.
Protein kinase cascade
One protein kinase activates the next, amplifying the signal at each step.
Ras
A GTPase bound to plasma membrane that sends a growth signal to the nucleus.
Ras in cancer
~30% of human cancers have hyperactive forms of Ras with GTP permanently bound.
Signal Transduction regulation
The balance between enzymes that activate and inactive pathways determines the cellular response.
Signal transduction pathway control
Kinases add phosphate groups (ON) and phosphatases remove phosphate groups (OFF).
G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs)
Cell surface receptors that associate with heterotrimeric G proteins; signal binding activates a G protein, which then activates an effector protein.
Inactive G Protein
GTP bound α subunit separates and activates effector protein.
Active G Protein
One subunit moves through the cell membrane to an effector protein.
G proteins and adenylyl cyclase
G proteins interact with adenylyl cyclase to produce cAMP, a small intracellular signaling molecule (second messenger).
Epinephrine
Also known as adrenaline.
Sense of Smell
Odorant molecules bind to receptors in the nose, activating adenylyl cyclase to catalyze formation of cAMP.
Signal amplification
Multiple steps in an intracellular signaling pathway allow for the signal to be amplified, enabling small amounts of a ligand to have dramatic effects.
Activation of adenylyl cyclase
It becomes phosphorylated, dephosphorylated, binds ATP, changes conformation, or is hydrolyzed.
Cholera toxin
Enters the human intestinal epithelium and modifies alpha subunit Gs, locking it in the active state and causing excessive outflow of Cl- and water.
Pertussis toxin
Colonizes the lungs and modifies the α subunit of G protein locking it in the inactive (GDP-bound) state leading to coughing.
Stimulation of GPCRs
Activates G-Protein Subunits by inducing the α subunit to exchange its GDP for GTP.
Bacterial Toxins and G Proteins
Some bacterial toxins cause disease by altering the activity of G proteins.
Cyclic AMP Signaling Pathway
Can promote glycogen breakdown.
Classes of receptors
Receptors can be divided into intracellular and membrane receptors.
Positive Feedback Examples
Blood Clotting and Child Birth.
Negative Feedback Examples
Temperature Regulation.