Airport
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
35 Terms
Describe an “airport”
A tract of land or water with facilities which has been established as a landing area for the regular use of aircraft
What are the 3 main purposes/objectives of an airport?
Commercial purpose
Military purpose
Training purpose
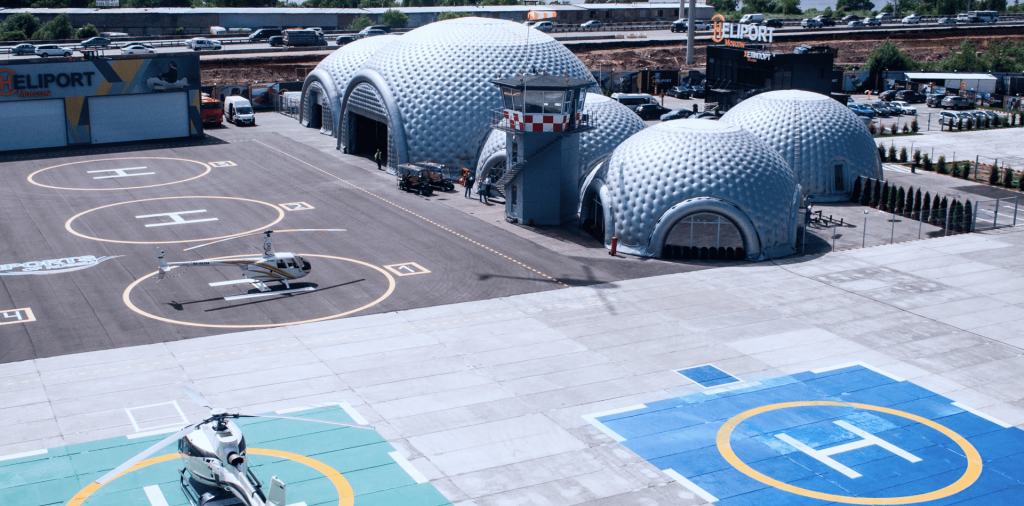
Helipad (definition, function)
A simple, designated area for helicopters (rotorcraft) and other vertical lift aircraft to land and takeoff.
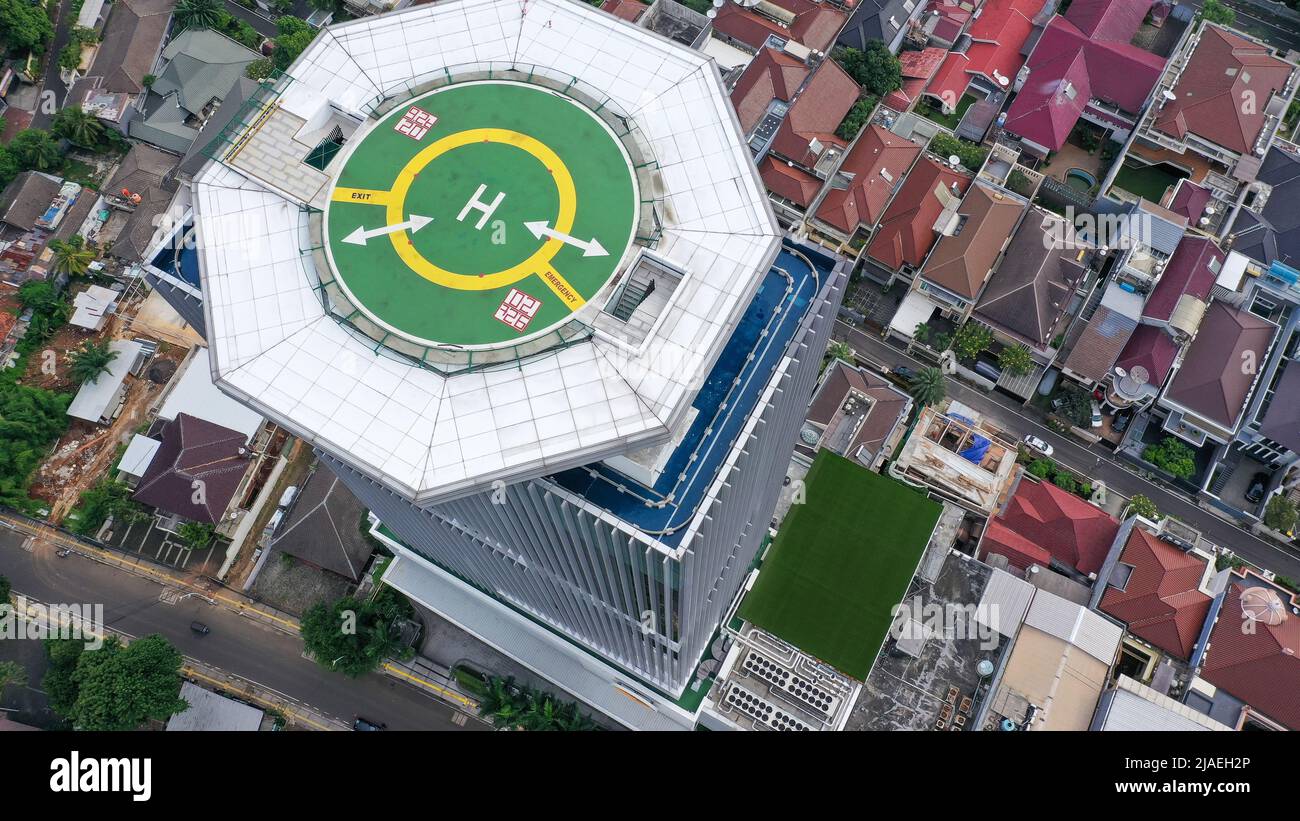

Heliports (definition, function)
“an airport for helicopter”
Has facilities like multiple helipads, fueling and hangars

What are the 2 factors of classifying airports?
1). Tower (towered/non-towered)
2). User (civil/military/private)
What are the 2 types of airports?
Towered airport
Non-towered airport
What are the 3 subtypes of airports?
Commercial/Cilvil airports = open to the general public
Military/Federal Government airports =operated by the military, not open for public use
Private airports = for private or restricted use only
Towered airport (definition, examples)
Has an operating control tower
Must have radio communications between pilots and air traffic controllers.
E.g. most of the commercial airports.

Non-towered airport (definition, examples)
Doesn’t have an operating control tower
2-way radio communications are not required
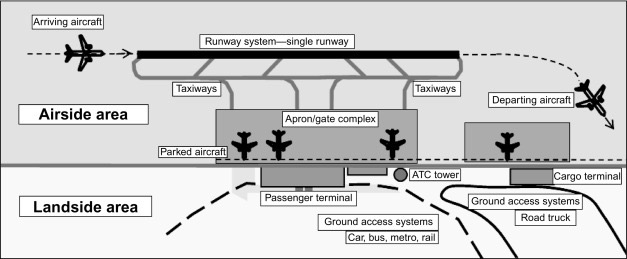
What are the 2 main areas in an airport? (HINT : “…side”)
Landside
Airside
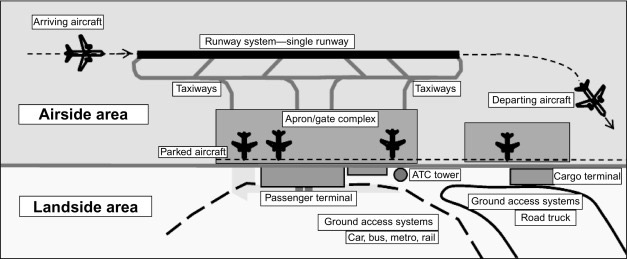
Landside area (definition, facilities)
“An area for passengers”
Area accessible to the general public, including passengers who have not yet passed through security or customs.
Connects the airport to the city or transportation network
Facilities : parking lots, public transport, railway stations
Airside area (definition, facility)
“An area for airplane”
The restricted area beyond security and customs, accessible only to authorized passengers and staff.
Tightly controlled.
Facilities : Boarding gates, duty-free shops, lounges, runways, taxiways, hangars.
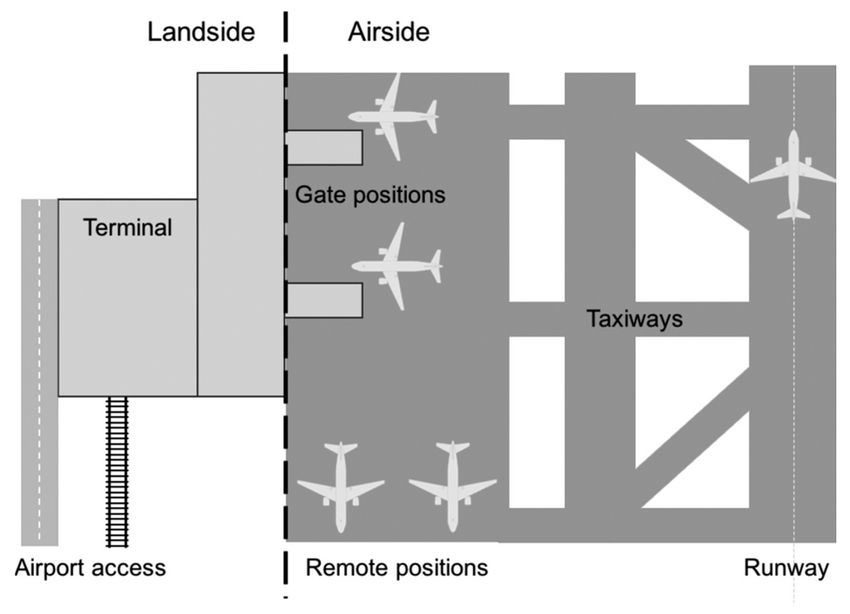
What are the 2 areas that airside is divided into?
Maneuvering area
Movement area
Maneuvering Area (description, include what?)
“Where aircraft fly and taxi”
The part of an airport used by aircraft for taxiing, taking off, and landing, excluding the aprons (parking and loading areas).
Include : Runway & Taxiway
Movement area (description, include what?)
“Maneuvering area + parking aprons”
Entire area where aircraft move, including aprons
Include : Runways, Taxiways, Aprons
Why is knowing prevailing wind direction is important for establishing an airport?
Knowing the prevailing wind direction helps align runways so aircraft can take off and land safely, efficiently, and with minimal risk from crosswinds.
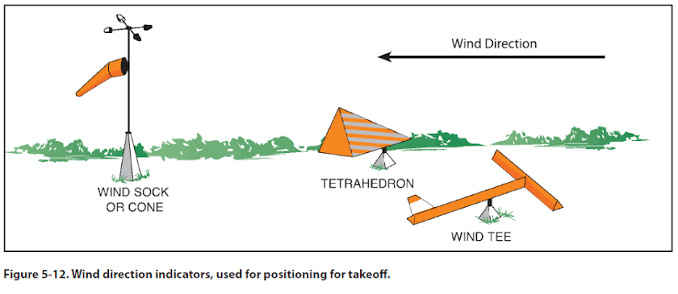
Wind Direction Indicators (definition, function)
A device used at airports and airfields to show the direction and strength of the wind.
Helps pilots determine the best runway direction for takeoff and landing.
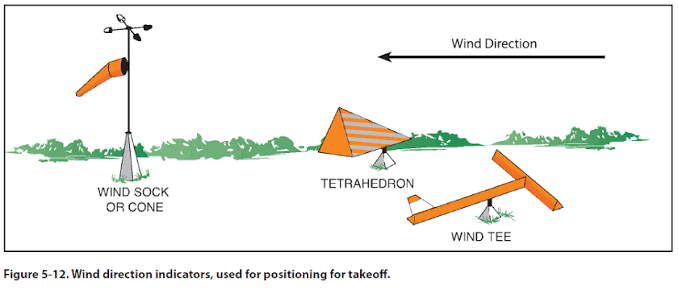
What are the 3 most common wind direction indicators?
Wind sock/wind cone
Wind tee
Tetrahedron
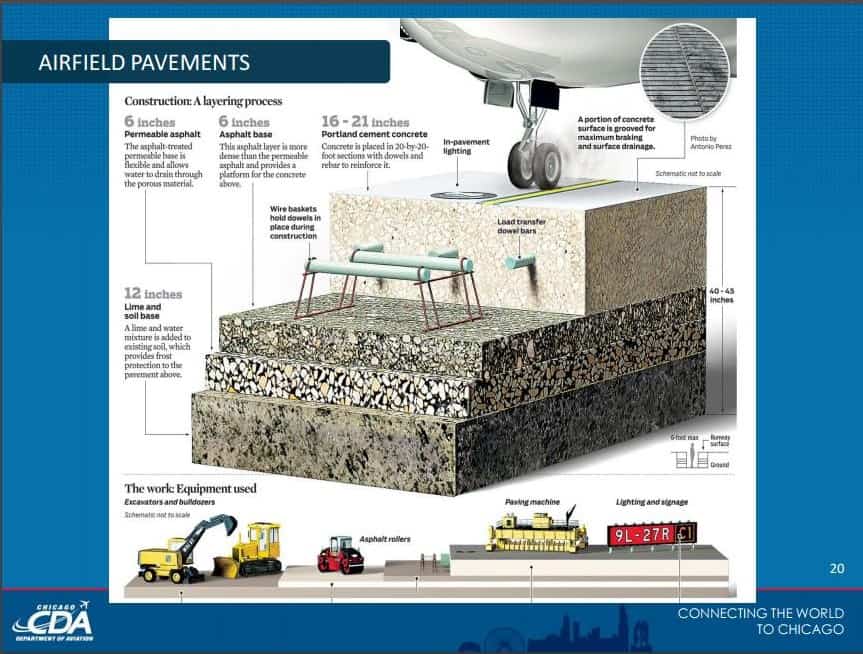
Why do most commercial airports’ runways have to be thick?
They have to be able to support the enormous weight of airplanes when they touchdown without cracking/ breaking
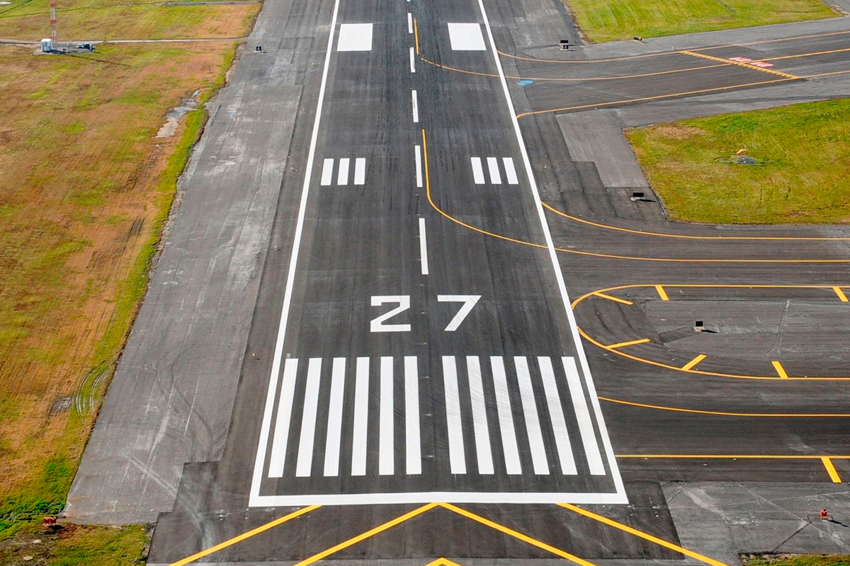

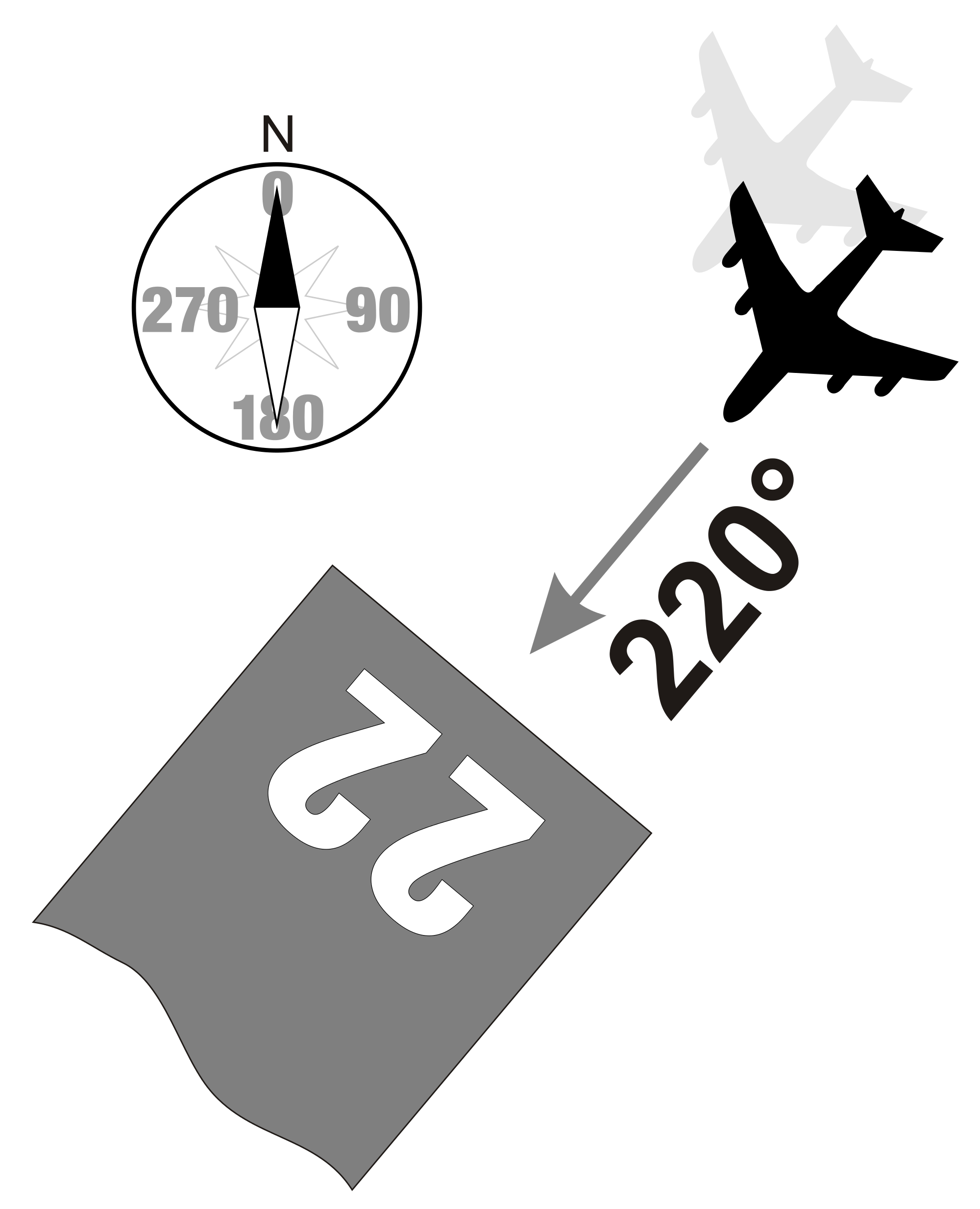
Runway number (definition, usage, examples)
A two-digit number painted on each end of an airport runway that shows the runway’s direction (orientation) relative to magnetic north.
Helps pilots line up for takeoff and landing.
E.g. 09 = 90 degrees (east), 33 = 330 degree (northwest)
Runway configuration (description, usage)
The layout or arrangement of runways at an airport — how many there are, how they are positioned, and how they are used relative to each other and to the wind direction.
Ensure safe, efficient takeoff and landing operations, depending on prevailing winds, terrain, and traffic volume.
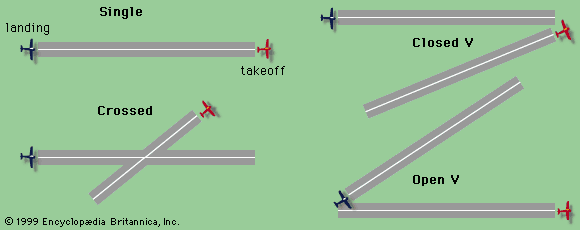
Give 2-3 examples of runway configuration
Single runway
Parallel runway
Intersecting runway
Open-V (diverging) runway
Closed-V (converging) runway
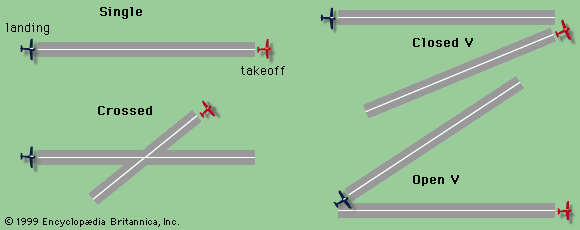
Why do we need runway & taxiway lighting system at an airport?
To help pilots see, navigate, and operate safely during night or low-visibility conditions — ensuring smooth and safe airport operations.
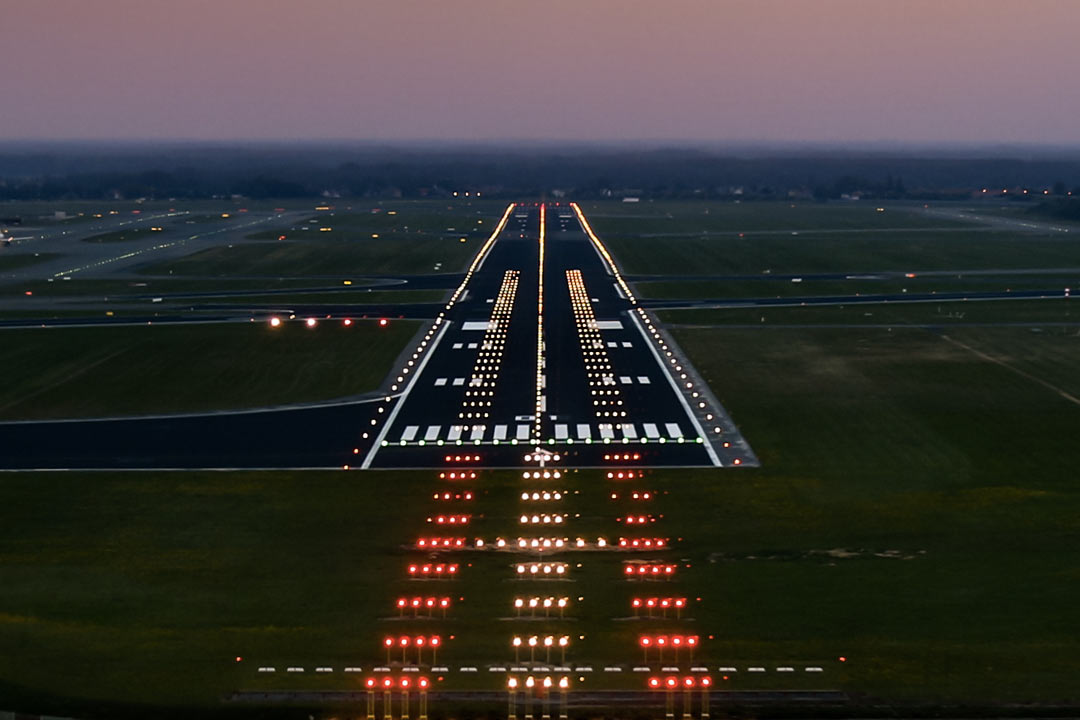

True or False : all airports have the exact same runways & taxiway lighting colours
True!
Airport lighting is standardized to avoid confusion
Embarkation & Disembarkation (definition)
Embarkation = boarding/getting in the aircraft
Disembarkation = getting off the aircraft
True or False : General public can access the apron/ramp
False!
The apron is not usually open to the general public and a license may be required to gain access.
True or False : You will find customs and immigration sections in a “domestic airport”
False!
It is a terminal for people traveling within the country.
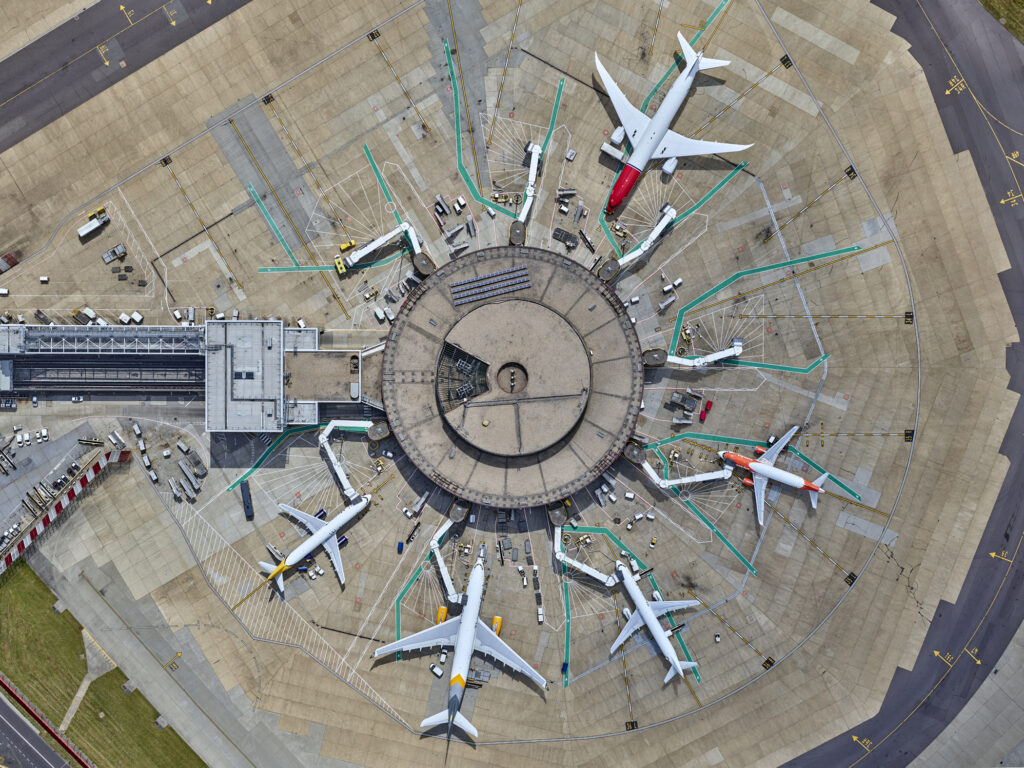
Satellite terminal (definition, usage)
A round/star-shaped building detached from other airport buildings.
Aircrafts are parked around its circumference

True or False : Cargo terminal is massive
True!
Cargo takes a lot of space, and usually must be stored for a relatively long period of time.
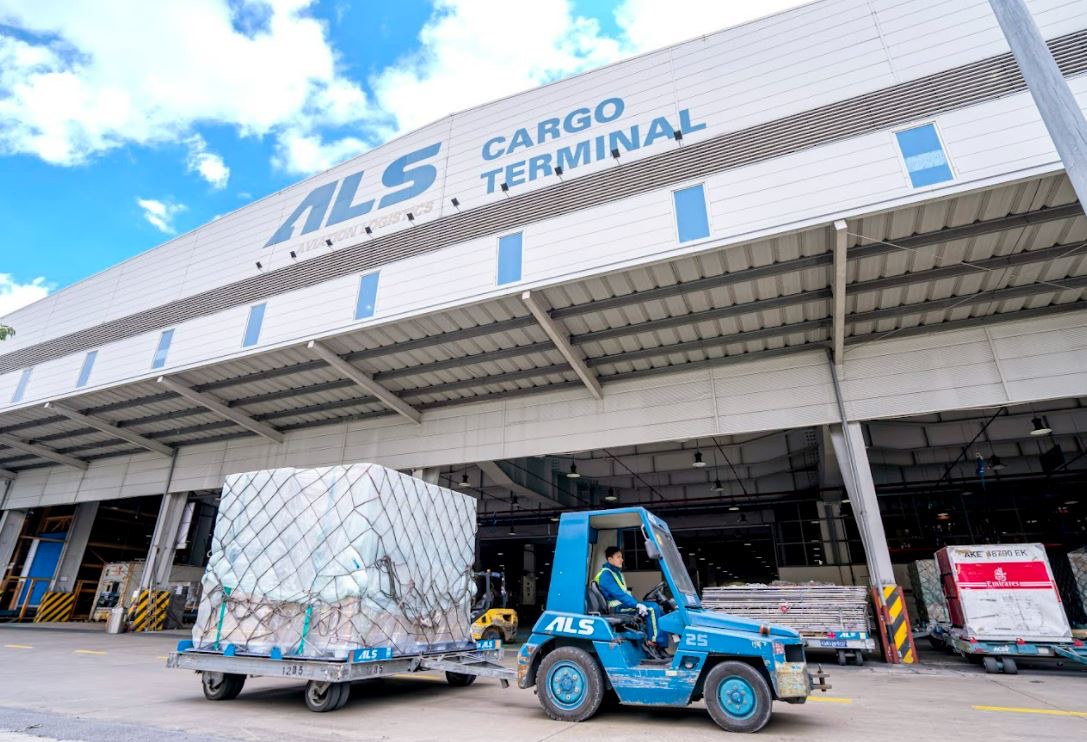

True or False : You will see BOTH customs and immigration officers in the international cargo terminal
False!
You will ONLY see “customs officers” because cargo = goods (not people)
True or False : The control tower is the tallest building in an airport
True!
The air traffic controllers must be able to see everything that is moving on the airport maneuvering area.
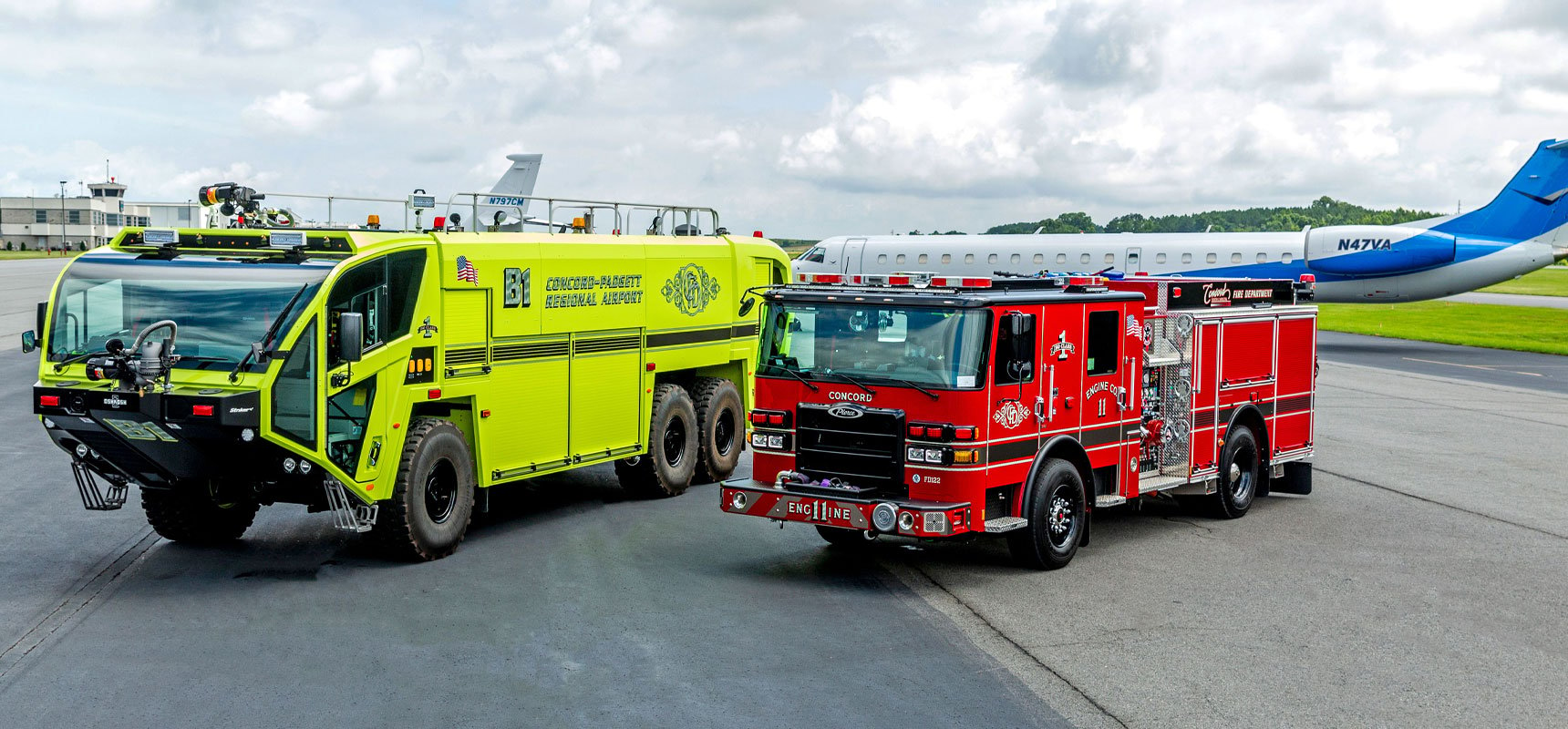

What is the responsibility of the fire and crash truck department in an airport?
Protection against fire, and assistance in the event of a crash at the airport

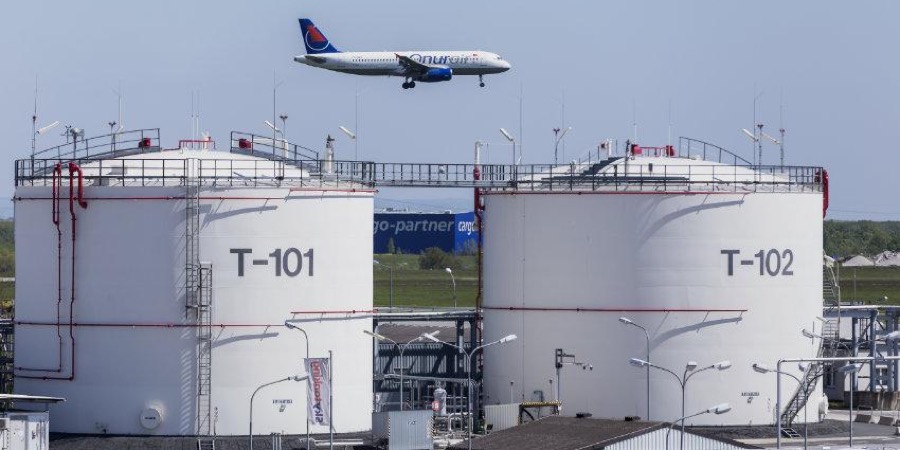
Fuel Depot (description, usage)
“tank farm”
The area where the large amount of fuel used by the aircraft is stored.

Airport Beacon (description, usage)
“airport/aerodrome beacon”
A light/beacon installed an at airport
Helps a pilot identify an airport at night/during low-visibility conditions
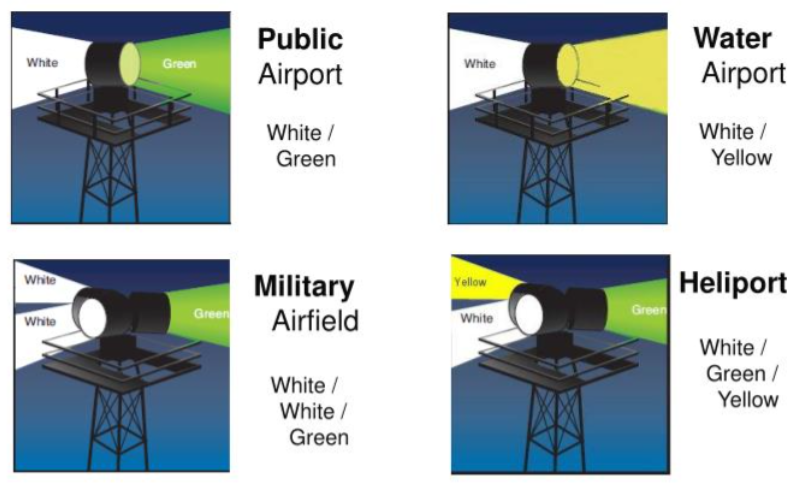
True or False : A taxiway connects runway to the ramp/apron area
True!