MCB3020 Week 2: Cell Structure & Function
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
LUCA
Last universal common ancestor
Eukaryotic cell
DNA in nucleus, large & complex cells, has membrane-enclosed organelles; cytoplasmic membrane, ribosomes, nucleus, nucleolus, nuclear membrane, cytoplasm, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi, mitochondria, chloroplast
Prokaryotic cell
DNA in nucleoid, small & fast cells, no membrane-enclosed organelles; cytoplasm, nucleoid, ribosomes, plasmid, cytoplasmic membrane, cell wall
Plasmid
In some prokaryotic cells, this organelle is responsible for special properties such as antimicrobial resistance
Virus
Not considered alive or cells, carries genetic information but relies on a host to function
Coccus
Spherical shape of cell
Rod
Cylindrical shape of cell
Spirilla
Spiral shape of cell
Spirochete
Like spirillum but longer
Filamentous bacteria
Like rod but longer
Smallness
Cells benefit from this due to having a higher surface area to volume ratio, allowing greater nutrient exchange, better waste exchange, and greater metabolic rate (faster growth), most cells like this are found in the open ocean
Prochlorococcus marinus
Good representative of a small, photosynthetic, marine microbe
Phospholipid bilayer
General structure for bacteria and eukarya cytoplasmic membranes, amphipathic where the hydrophobic tails are inside and the hydrophilic heads are outside. Made of fatty acids
Isoprene
In archaea, the membrane phospholipids are made of this
Membrane functions
Permeability barrier, protein anchor, energy conservation
Membrane stability
Embedded proteins, hydrogen bonds and hydrophobic interactions, Mg2+ and Ca2+ forming ionic bonds
Integral membrane proteins
In Bacteria, these proteins are firmly embedded in the membrane
Peripheral membrane proteins
In Bacteria, these proteins have one portion anchored in the membrane, such as lipoproteins
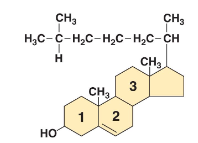
Sterols
In Eukaryotic membranes, this helps strengthen the membrane.
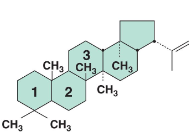
Hopanoids
In Bacterial membranes, this helps strengthen the membrane.
Ether
In Archaeal membranes, there are _ linkages in the phospholipids
Ester
In Bacterial and Eukaryotic membranes, there are _ linkages in the phospholipids
Lipid monolayer
Archaea has this type of membrane and doesn’t separate by heat easily
Simple transport
Driven by energy in the proton motive force; a proton travels with the transported substance
Group translocation
Chemical modification of the transported substance driven by phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP); chemical modification of the transported substance gains a phosphate thru phosphorylation
ABC system
Periplasmic binding proteins are involved, and energy comes from ATP; a periplasmic binding protein binds to the transported substance and ATP is turned back into ADP and phosphate on the inside. Displays high substrate specificity and affinity
Energy
The main different forms of are proton motive force, ATP, or phosphoenolpyruvate (PEP)
Uniporter
Simple transporter, one substance in
Antiporter
Simple transporter, one substance in, different substance out at the same time
Symporter
Simple transporter, two different substances in at the same time
Phosphotransferase system in E. coli
• Group translocation, energy comes from PEP
• Glucose, fructose, and mannose are moved
Enz 1 takes phosphate off PEP and transfers it to HPr
Enz IIa and Enz IIb transfer phosphate to the end of Enz IIc
Glucose comes in and gets bonded to the phosphate, creating a concentration gradient of sugar
Peptidoglycan
Rigid layer providing strength to the cell wall in bacteria. Porous meshwork
NAG, NAM, and peptide bonds
Gram-positive
Cell wall is thicker but only composed of a single molecule type; peptidoglycan with teichoic acid and lipoteichoic acids embedded, and a cytoplasmic membrane with embedded proteins
Teichoic acids
In gram-positive cell walls, these are embedded to help attract cations
Lipoteichoic acids
Teichoic acids covalently bound to membrane lipids
Gram-negative
Cell wall has at least two layers; outer membrane with LPS, peptidoglycan, and a cytoplasmic membrane with embedded proteins
Mycoplasmas
Prokaryote that lacks cell walls, has cholesterol in membrane like Eukaryotes and is very waxy
LPS/Lipopolysaccharide
In gram-negative cell walls, main component in outer half of outer membrane and contains lipid A, core polysaccharide, and O-polysaccharide going from bottom to top
Endotoxin
The toxic component of LPS, attributed to lipid A
Porins
Channels for movement of hydrophilic low molecular-weight substances found on the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria
Periplasm
Space located between cytoplasmic and outer membranes of gram-negative bacteria
Archaea
These cell walls have no peptidoglycan nor outer membrane, some have pseudomurein, but most have S-layers
Pseudomurein
In some archaea cell walls, similar to peptidoglycan
S-Layers
Found in most archaea, most common cell wall type among archaea and consists of a protein or glycoprotein
Capsule
In Bacteria, polysaccharide layers that aid in evading the immune system and help with attachment; has a tighter matrix that is often bonded to cell wall
Slime layer
In Bacteria, polysaccharide layers that aid in evading the immune system and help with attachment; loose, less connected to cell
Fimbriae
Filamentous protein structures, enables organisms to stick to surfaces or form pellicles (hair-like)
Pili
Filamentous protein structures, longer than fimbriae and facilitates genetic exchange between cells through conjugation
Flagella
Structure that aids in swimming/movement, moves by rotation where speed of rotation increases or decreases depending on the strength of the PMF (proton motive force)
Polar
Single flagellum at one pole
Lophotrichous
Tuft of flagella at one pole
Amphitrichous
Flagella at both poles
Peritrichous
Flagella all over
Amphilophotrichous
Tuft of flagella at both ends
Endospores
Cells resistant to heat, harsh chemicals and radiation, ideal for intense conditions and are only present in some gram-positive bacteria. Most studied in Clostridium and Bacillus species. Resistant to dyes and has a dehydrated core allowing high heat tolerance
Dipicolinic acid
In endospores, this is a characteristic component that aids with dye resistance
Taxis
Directed movement in response to chemical or physical gradients
Chemotaxis
Cell motion as a response to chemicals; best seen in E. coli and responds to chemical concentration sensed by chemoreceptors; run and tumble
Phototaxis
Cell motion as a response to light
Aerotaxis
Cell motion as a response to oxygen
Osmotaxis
Cell motion as a response to ionic strength
Hydrotaxis
Cell motion as a response to water