Ch 6 - Ligand-Gated Ion Channels of Fast Chemical Synapses
1/115
Earn XP
Description and Tags
complete
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
where are ligand gated ion channels expressed?
in all cell types
are ligand-gated channels selective?
generally, no
ligand channels produce ___ (in relation to AP firing)
generator potentials necessary to open voltage-gated channels
ligand gated channels are most structurally similar to
K+ channels (they require multiple subunits to form a channel)
nicotinic family: how many subunits/transmembrane segments?
5 subunits, 4 transmembrane segments
Glutamate family: how many subunits/transmembrane segments?
4 subunits, 3 transmembrane segments
P2X family: how many subunits/transmembrane segments?
3 subunits, 2 transmembrane segments
which ligand gated channels are trimeric?
P2X
which ligand gated channels are tetrameric?
glutamate family
which ligand gated channels are pentameric?
nicotinic family
ATP channels are an example of
P2X
AMPA receptors and NMDA receptors are examples of
glutamate receptors
nicotinic receptors, serotonin receptors, and GABA A receptors are examples of what kind of channel?
nicotinic receptors
ligand gated ion channels respond to ___ to generate ___
respond to neurotransmitters to generate postsynaptic potentials
stimulation of motor neurons releases
acetylcholine
describe how a post-synaptic potential is produced at the neuromuscular junction.
stimulation of motor neuron causes release of NT (ACh)
ACh binds to ACh receptors on muscle
opening of ACH-gated ion channels generates depolarization due to cation influx
farther away from motor neuron → ___ depolarization
smaller
which of the following could not be a multimeric channel made up of different alpha subunit subtypes? nAChR, AMPA, GABA, vg-K+ channel, vg-Ca2+ channel
vg-Ca2+ channel because the rest are made of multiple subunits
how are nicotinic and muscarinic acetylcholine receptors differentiated?
nicotinic ACh receptors respond to nicotine, muscarinic ACh receptors are G-protein coupled
where are nACHRs found?
neuromuscular junction, autonomic ganglia, and throughout the nervous system
nACHRs are involved in…
movement, cognition, perception, attention, depression, pain, reward
what ions are nACHRs permeable to?
Na+, K+, and sometimes Ca2+
nAChRs are (excitatory/inhibitory)
excitatory
nACH receptor agonists
nicotine, varenicline, carbachol, galantamine
nACh receptor antagonists
curare/pancuronium, buproprion
ACh is degraded by
acetylcholinesterases
acetylcholinesterase inhibitors
Donepezil, pesticides, chemical warfare agents
inhibitors of acetylcholinesterases are used for treatment of
alzheimers
describe nAChR structure
5 subunits (2 are alpha, the other 3 vary). the channel has an extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular domain
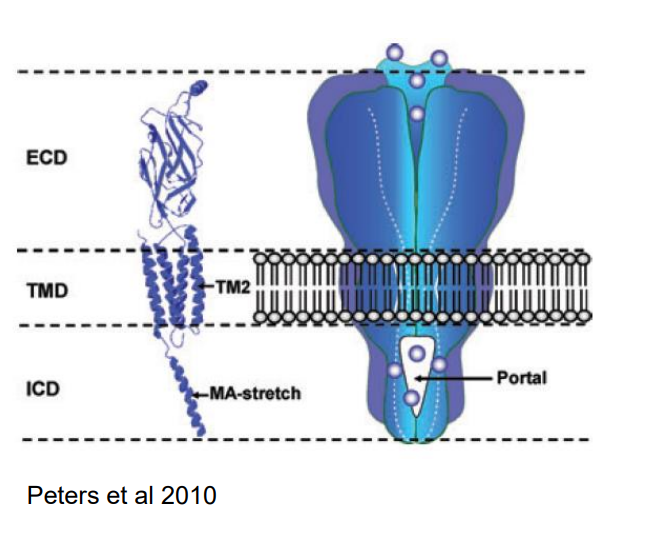
once ligand gated channels are open, they generate currents that are sensitive to
voltage
how does amplitude of the current change depending on the holding voltage?
more hyperpolarized → larger current
ligand gated ion channel reversal potential
around 0 (due to being non-selective)
how do you calculate the reversal potential for a channel that is permeable to sodium and potassium?
Vmrev = [nernst + nernst]/2
= (+67 + -98)/2
= -31/2
= -15.5
Erev changes at every ___. why?
it changes at every synapse. this is because the extra- and intra-cellular concentrations change
Activation curve is a ___ curve where response is ___.
concentration-response curve
current amplitude
ligand gated ion channels exist in multiple states that are influenced by whether ___ is bound
ligand/agonist
receptor is ___ when unbound
closed
agonist binding promotes the ___ state of channels
open
what is an A burst?
the period of time where a channel is mostly open, but closes briefly
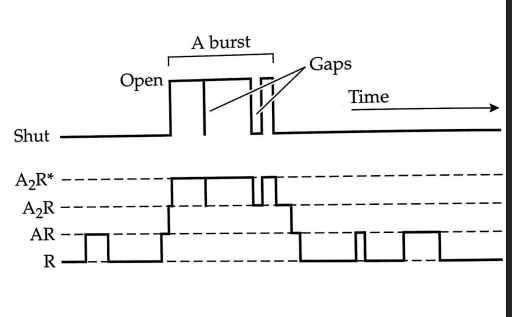
openings of LGICs cause ___ that add up to ___
small depolarizations, reach threshold
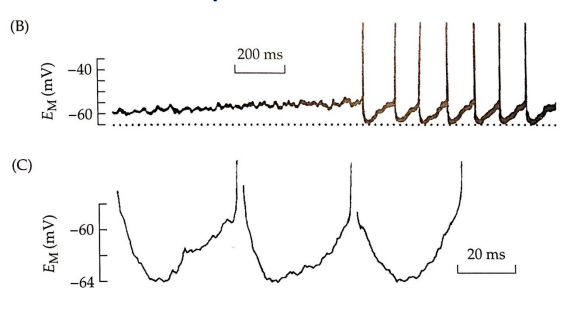
what is this graph showing?
small depolarizations adding up to threshold, where you start to see APs.
C is magnified view of B, showing how binding/unbinding of agonist causes channel openings/closings that result in the depolarization cycles
how are ligand-gated channels different than voltage-gated channels in terms of the process of gating?
ligand-gated requires a conformational change instead of a voltage sensor moving in response to voltage.
when an LGIC opens, the rotation of channel subunits breaks ___ that are blocking the pore.
hydrogen bonds
what determines the cation specificity of nACh receptors? what else does it do?
rings of high negative charge on the cytoplasm side. these also remove the hydration shell of the passing ions
which kinds of receptors make up the nicotinic/cys-loop superfamily? (4)
nACh receptors
GABA receptors
Glycine receptors
Serotonin/5-HT3 receptors
what is a cys-loop and what does it do?
cysteine-cysteine disulfide bond. it participates in ligand binding.
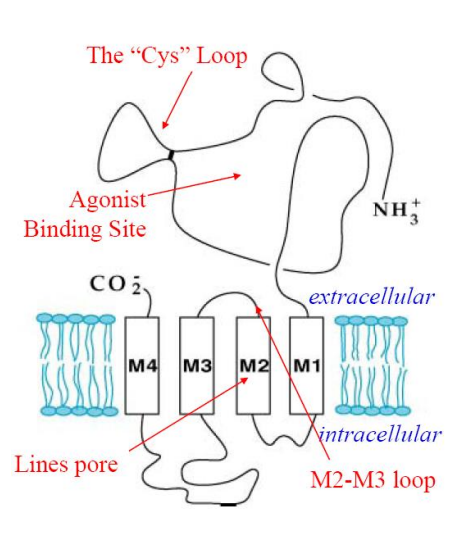
which transmembrane domain typically lines the pore in cys-loop receptors?
M2
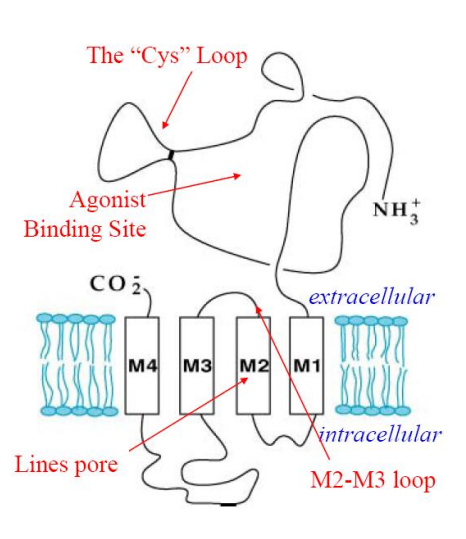
where is the agonist binding site on a cys-loop receptor?
near the cys loop (extracellular)
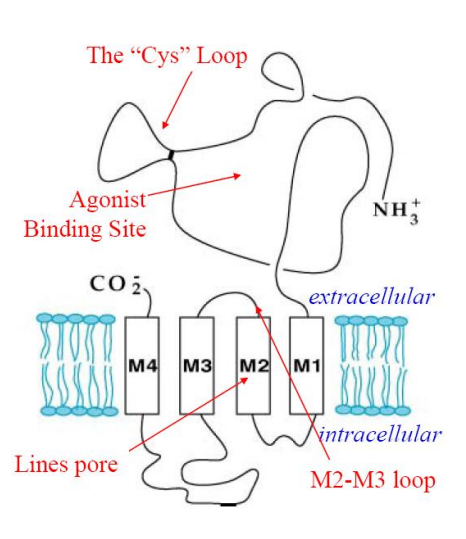
how are GABAA, GABAB, and GABAC different?
GABAA and GABAC are ligand-gated
GABAB is G-protein coupled
ion channels on GABA receptors are selective to what ions?
Cl- and HCO3-
GABA receptors have a ___ effect on neurons. why?
inhibitory/hyperpolarizing effect. this is due to the Cl- entering the cell
___ subunits form homomers (GABAC receptors) in the retina
ρ
GABA receptors are ___ (structure). what subunits?
pentamers.
alpha and beta + a combination of γ/δ/π/ε to make a pentamer
GABAA agonists
GABA, muscimol
GABAA antagonists
competitive: bicuculline and flumazenil
noncompetitive: picrotoxin
what do positive allosteric modulators do?
increase agonist affinity and/or efficacy
what are the five types of positive allosteric modulators for GABAA receptors?
Benzodiazepines
non-benzodiazepines that bind at the benzo site
Barbiturates
Anesthetics
Ethanol
what neurosteroids affect GABAA receptors?
negative: pregnenolone
positive: allopregnanolone
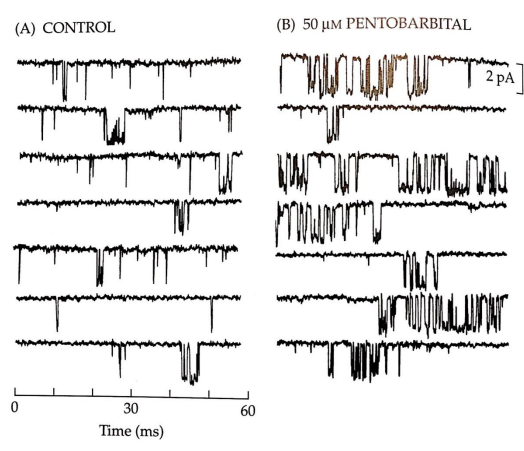
what do these graphs show?
A shows the opening and closing of GABA channels in response to agonist binding. B shows the influence of pentobarbital, a positive allosteric modulator.
→ even though barbiturates don’t directly open the channel, they modulate the channel in a positive way, increasing the activation
Opening of GABA-gated Cl- channels can cause
excitation
(increasing cellular Cl- makes the nernst more positive for Cl-. under these conditions, opening Cl channels will depolarize neuron.
what transmitter/associated receptor has a prominent impact on the developing brain?
GABA
in developing neurons, the intracellular Cl- concentration is controlled by ___, resulting in ___ intracellular levels of Cl-
the Na+/K+/Cl- co-transporter, resulting in high intracellular levels of Cl-
in adult neurons, the intracellular Cl- concentration is controlled by ___, resulting in ___ intracellular levels of Cl-
K+/Cl- (which pumps Cl- out of cell), results in low intracellular Cl- levels
if GABA is selective to Cl- ions and is considered an inhibitory neurotransmitter, why does it have an excitatory effect in the developing brain?
ECl- changes. In development, ECl- is more positive than AP threshold and the intracellular concentration of Cl- is high. Cl- moves out of GABA receptors, depolarizing response.
In adult cells, ECl- is much more negative and intracell Cl- concentration is low. Cl- moves into the cell, hyperpolarizing response.
___ GABA receptors mediate phasic inhibition while ___ GABA receptors mediate tonic inhibition
synaptic, extrasynaptic
what are GABA transporter proteins called?
GAT-1
which GABA alpha subtype(s) cause sedative, anterograde amnesia, and anticonvulsant effects?
α1
which GABA alpha subtype(s) cause anxiolytic and muscle relaxant effects
α2 and α3
which GABA alpha subtype(s) cause cognitive effects?
α5
the goal for an anxiety drug is to bind to which α subtype(s)?
α2 or α3, but not α1 (α5 is also not desirable)
the goal for a sedative is to bind to which α subtype(s)?
α1 (α5 not desirable)
glycine receptors are selective to which ion channels?
Cl-/HCO3-
glycine receptors have a(n) ___ effect on neurons
inhibitory, hyperpolarizing
glycine agonists (5)
glycine
β- or L-alanine
taurine
L-serine
proline
Glycine positive allosteric modulators (3)
anesthetics, neurosteroids, ethanol
Glycine negative allosteric modulator
strychnine
what are subconductance states?
states other than open or closed
define EPSP and IPSP
EPSP - excitatory postsynaptic potential
IPSP - inhibitory postsynaptic potential
EPSPs result from stimulation of ___, releasing what transmitter?
stimulation of sensory fiber releasing glutamate
IPSPs result from stimulation of ___, releasing what transmitter?
inhibitory interneuron, releasing glycine
GABA and Glycine are ___ transmitters found in…
both inhibitory
GABA - throughout CNS
Glycine - brainstem and spinal cord
5-HT3 serotonin receptors are selective to which ions?
non-selective for Na+, K+, Ca2+
5HT3 receptors have a ___ effect on neurons
excitatory, depolarizing effect
serotonin receptor agonists
serotonin, quipazine
serotonin receptor antagonists
ondansetron, granisetron, tropisetron (antiemetics)
what receptors are in the “vomiting center” within the pons?
5-HT3, NK1, dopamine
glutamate receptors differentiated by
response to NMDA, AMPA, and Kainate
each subunit of a glutamate receptor has ___ transmembrane segments and a ___ loop. how many subunits make up a channel?
3 TM segments, P-loop. 4 subunits make up a channel
GluR1-4
AMPA channels
GluR5-7
Kainate channels
NMDA receptors are permeable to which ions?
Na+, K+, and Ca2+
NMDA receptors are coactivated by
glycine and serine
NMDA antagonists
phencyclidine (PCP), ketamine, dextromethorphan, memantine, riluzole
NMDA is blocked by what ion? how is it unblocked?
blocked by Mg2+, requires depolarization to unblock
Glycine is an NMDA co-agonist at ___ channels. D-serine is an NMDA co-agonist at ___ channels
extrasynaptic, synaptic
activation of NMDA receptors requires depolarization of
AMPA or other receptors
describe the activation of NMDA receptors
depolarization removes Mg2+ from pore → ions can flow through channel
AMPA receptors are permeable to
Na+ and K+
AMPA/Kainate receptors have a ___ effect on neurons
excitatory, depolarizing effect
AMPA agonists
AMPA > glutamate > kainate