Cell Cycle Control Systems
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
What controls the cell cycle?
Progression through cell cycle controlled primarily by oscillating activity of cyclin-dependent protein kinases (Cdks)
Cdk
S/T kinases that phosphorylate substrate proteins to activate a specific phase of cell cycle; Protein levels remain constant but activity changes >> dependent on cyclins
Cyclin
co-factor for Cdk enzymes; Protein levels “cycle” up and down with the cell cycle
Yeast - Cdk is called
Cdk1
Major Cell Cycle CDKs
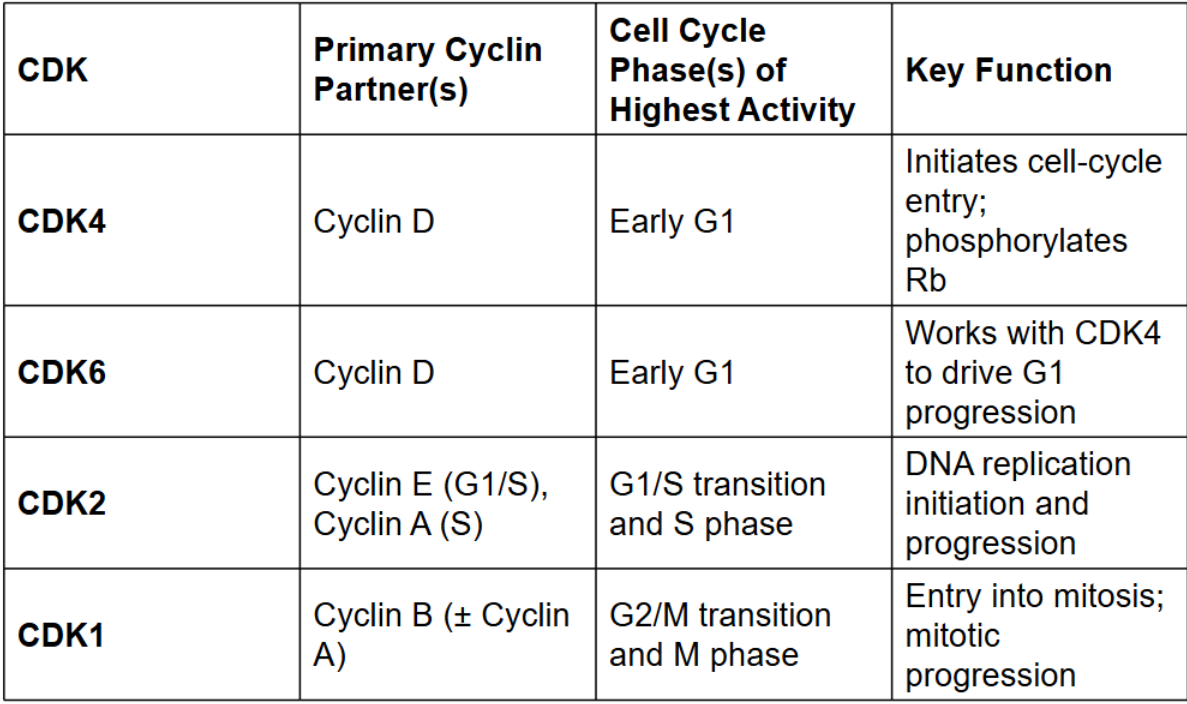
Without cyclins, CDKs are
inactive
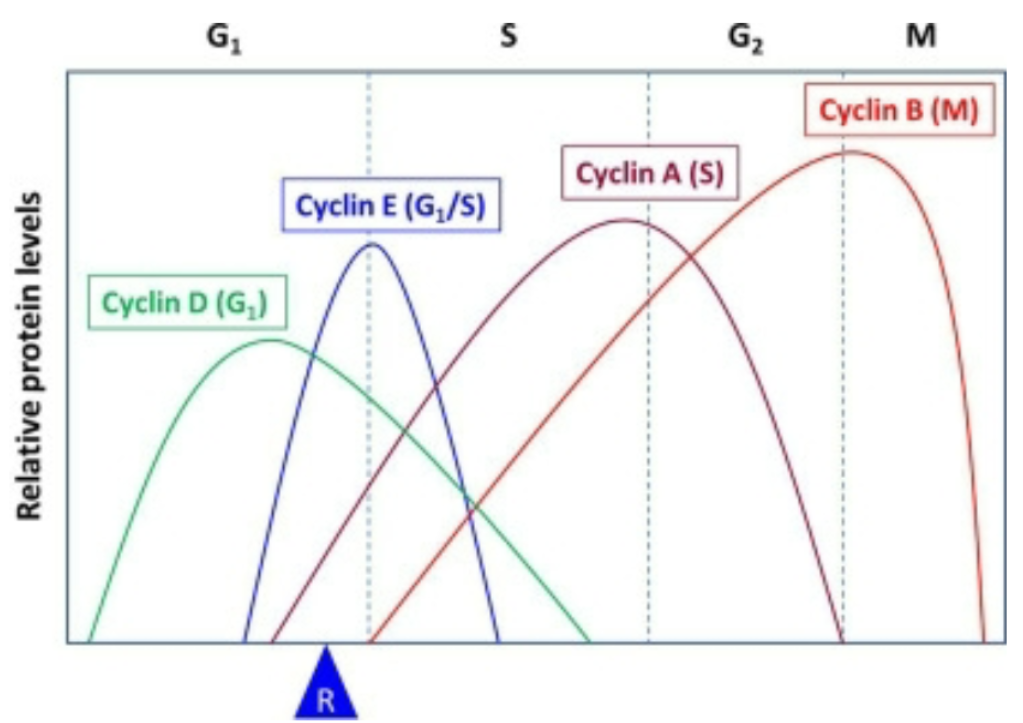
Cyclic Expression Patterns
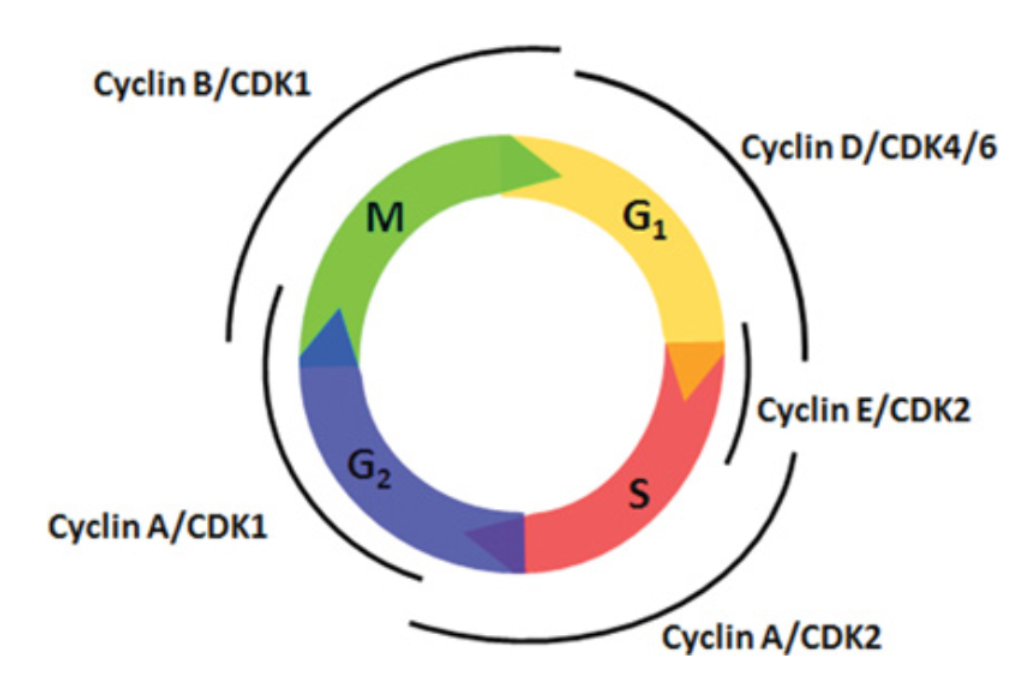
Cyclin - CDK Partners
Wee1 Kinase and Cdc25 Phosphatase
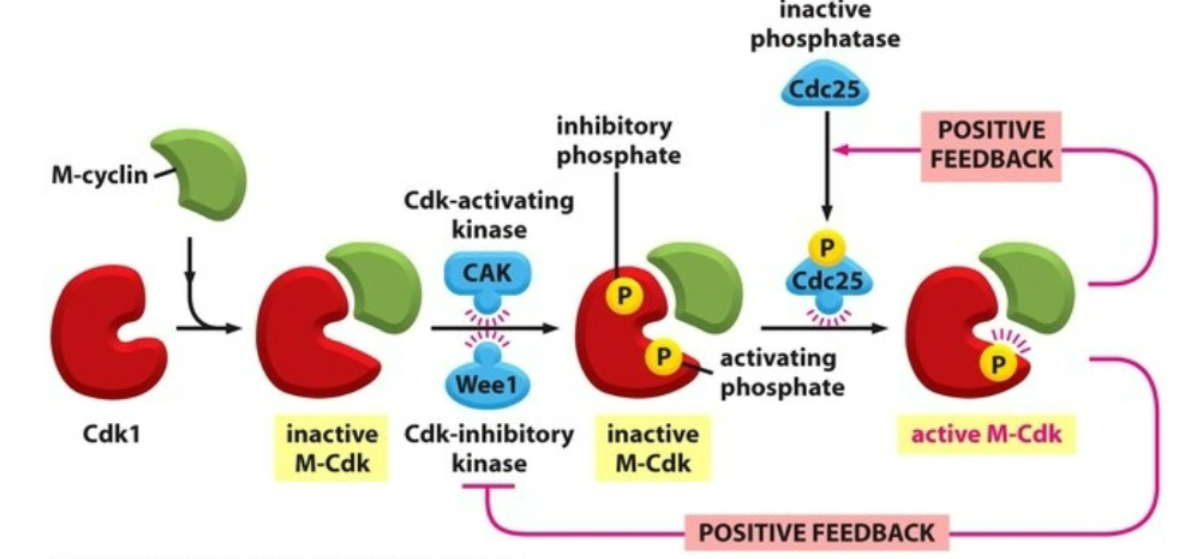
Wee1
adds an inhibitory phosphate to Cdk
Cdc25
removes the inhibitory phosphate from Cdk
Active cyclin-Cdk
exhibits positive feedback loops on both
CKI KIP
inhibits Cyclin; acts as a break in the cell cycle
CIP/KIP examples and what they do
p21, p27; bind multiple cyclin-Cdk complexes that prevent activation or inhibit kinase activity
INK protein examples and what they do
p15, p16; specific for Cdk4/6 and cyclin D; bind Cdk and inhibit the binding of cyclin D
p27
growth factor withdrawal and contact inhibition
CDK Inhibitors Table
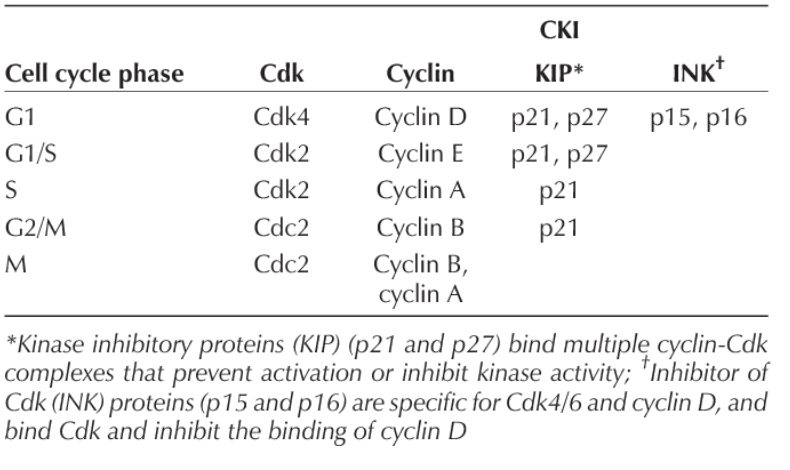
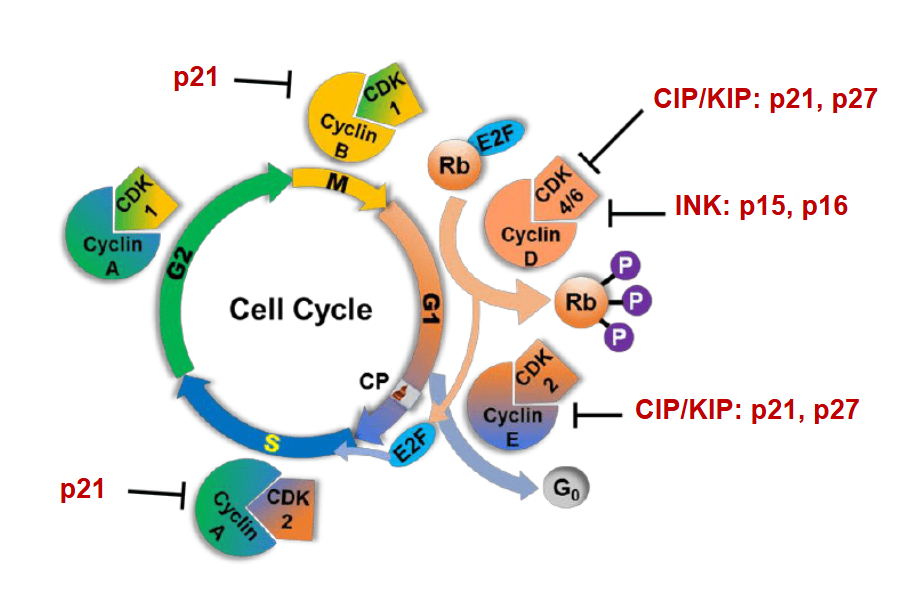
CDK Inhibitors Cycle
UPS System table - definitions
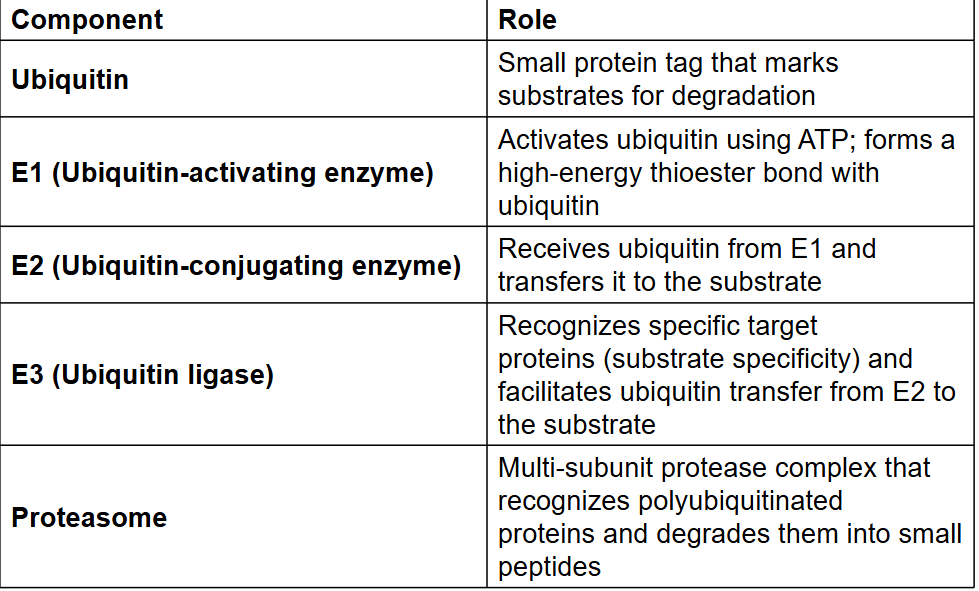
two large, complexes are primary ubiquitin ligases for cell cycle control
SCF complex – G1/S transition
APC complex – metaphase-to-anaphase transition
Anaphase Promoting Complex
securin keeps chromosomes together and separase pulls the chromosomes apart
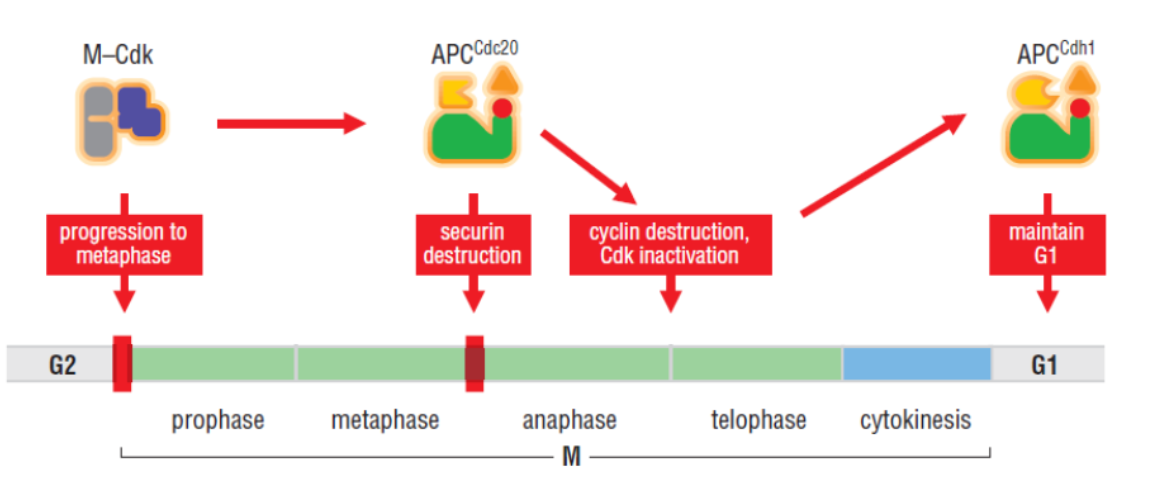
APC and Cyclin B/CDK1
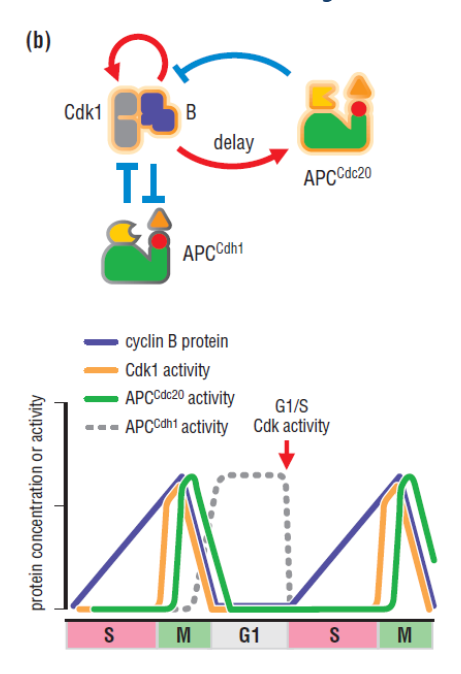
Cyclin B/CDK1 activates
APC (cdc20)
APC (cdc20) then degrades
cyclin B
APC (cdh1) persists into G1 phase and maintains
low levels of M cyclins until SCF takes over
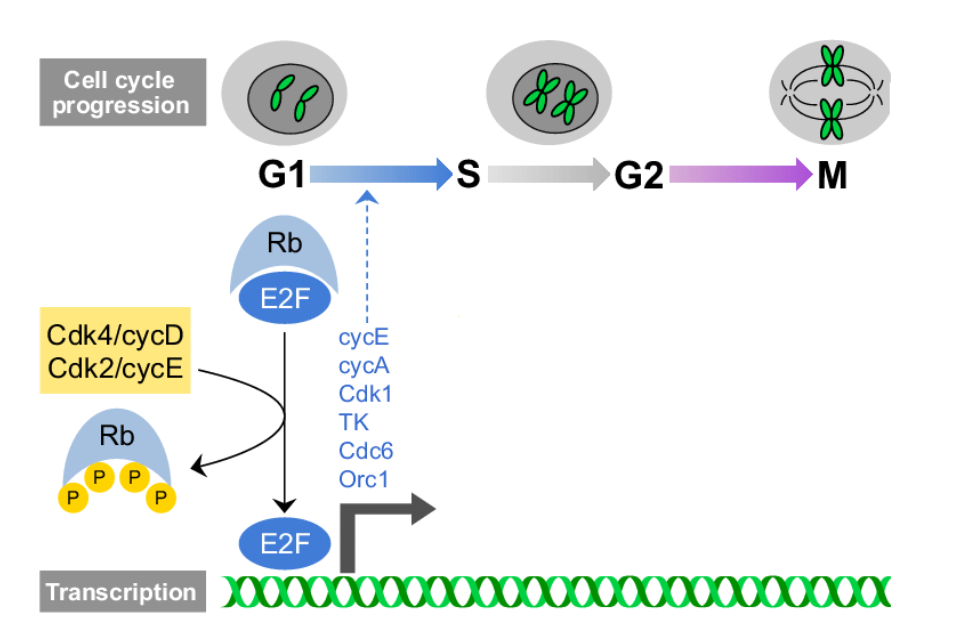
Cyclin D and E2F/Rb System
drives the progression into S phase from G1
Rb when bound to E2F keeps E2F inactive
When Rb is P by Cdk4/cycD and Cdk2/cycE then E2F transcribes DNA