INTEGRATED SCIENCES MYP 5: UNIT 1 - 3 HEREDITY , ENERGY, PHYSICS
1/60
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
61 Terms
Gamete
Sex cells that have half the usual number of chromosomes (haploid), allowing them to combine with another gamete to form a complete set (zygote).
Prophase I
First stage of meiosis where chromosomes condense, pair up, and crossing over occurs, exchanging DNA between homologous chromosomes.
Metaphase I
The stage where paired homologous chromosomes (tetrads) align in the middle of the cell, preparing for separation.
Anaphase I
The stage where homologous chromosomes (each with two chromatids) are pulled to opposite ends of the cell.
Telophase I
The stage where two new nuclei form around separated chromosomes, followed by cell division to form two cells.
Chromatid
One of two identical halves of a duplicated chromosome, connected by a centromere.
Crossing Over
The process in Prophase I where homologous chromosomes exchange sections of DNA, increasing genetic diversity.
Homologous Chromosomes
Chromosome pairs (one from each parent) that are similar in size, shape, and gene content. They pair up during meiosis I.
Haploid
A cell containing half the usual set of chromosomes (e.g., gametes: sperm and egg).
Diploid
A cell containing two copies of each chromosome (e.g., somatic cells).
Meiosis
The process of cell division where one cell divides into four genetically unique daughter cells, each with half the number of chromosomes (haploid). Meiosis is essential for sexual reproduction.
Gene Mutations
Changes in DNA sequences that can lead to different amino acids being translated, altering the structure and function of proteins.
Single Point Mutations
Changes caused by a deletion, addition, or substitution of a single base in DNA.
Germline Mutations
Mutations that occur in gametes (sperm or egg) and are hereditary, meaning they are passed to offspring during sexual reproduction.
Chromosome Mutations
Errors in the separation of chromosomes during meiosis I, leading to changes in the number or structure of chromosomes.
Asexual Reproduction
A single parent gives rise to clones, which are genetically identical to the parent.
Sexual Reproduction
Requires two parents and combines genetic material to produce genetically diverse offspring.
Genotype
The genetic makeup of an organism (e.g., homozygous dominant, heterozygous).
Phenotype
Observable physical traits resulting from a genotype (e.g., eye color, freckles).
Allele
Different forms of a gene that exist at a specific locus on a chromosome.
Chromosome
A structure made of protein and a single molecule of DNA that carries genetic information from cell to cell.
Diffusion (In Bio)
The movement of particles from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached.
Exothermic Reaction
Releases energy to the surroundings; temperature increases (e.g., combustion).
Endothermic Reaction
Absorbs energy from the surroundings; temperature decreases (e.g., photosynthesis).
Energy
The capacity to do work or transfer heat, existing in forms such as kinetic, potential, thermal, chemical, and electrical.
Heat
The transfer of thermal energy between systems or objects with different temperatures, flowing from hotter to cooler.
Bond Enthalpy
Energy change = Total energy of bonds broken (reactants) - Total energy of bonds formed (products).
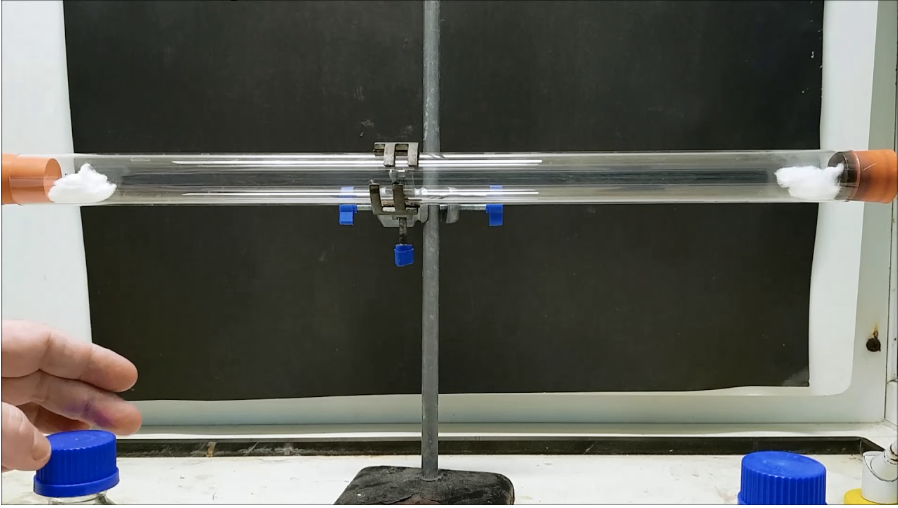
Diffusion in chem:
Example with HCL and NH3
Molecular motion
guide through concentration gradients
influence through particle mass
Enzyme
Biological catalyst that increases the rate of a reaction
Lipases
This group of enzymes help digest fats in the gut.
Amylase
In the saliva, helps change starches into sugars.
Maltase
Occurs in the saliva, and breaks the sugar maltose into glucose.
Trypsin
Beak proteins down into amino acids in the small intestine.
Lactase
breaks lactose, the sugar in milk, into glucose and galactose.
Acetylcholinesterase
These enzymes break down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine in nerves and muscles.
Helicase
Helicase enzymes unravel DNA.
DNA polymerase
These enzymes synthesize DNA from deoxyribonucleotides.
Wavelength
Distance between a point on one wave and the same point on the next wave, measured in meters.
Frequency
A number of waves produced by a source each second, common units of measurement: Hertz (Hz)
Speed of a wave
The distance a wave can travel in a certain amount of time. The unit it is measured in is m/s
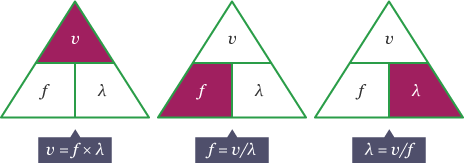
Formula
v is the wave speed in metres per second, m/s
f is the frequency in hertz, Hz
λ (lamda) is the wavelength in metres, m
Crest
Labelled as the highest surface part of a wave
Trough
Labelled as the lowest surface part of a wave
Amplitude
A measurement of amount of energy transferred by the wave from its resting position and the highest position.
Refraction
the bending of a wave, like light, as it passes from one medium to another.
Factors affecting refraction
the density of the mediums
the angle of incidence.
Electromagnetic Spectrum
Continous spectrum of electromagnetic radiation
Types of wave
Radio waves, micro waves, infrared light, visible light, ultra violent light, x-rays, and gamma rays
Radio wave qualities
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Wavelength | > 1 meter |
Frequency | < 300 MHz |
Speed | 3 × 10⁸ m/s (in vacuum) |
Energy | Very Low |
Common Uses | Radio and TV broadcasting, communication systems, satellites |
Dangers | Generally safe; prolonged exposure to strong fields may affect health |
Microwaves qualities
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Wavelength | 1 meter – 1 millimeter |
Frequency | 300 MHz – 300 GHz |
Speed | 3 × 10⁸ m/s (in vacuum) |
Energy | Low |
Common Uses | Microwave ovens, mobile phones, radar systems |
Dangers | Can cause tissue heating and internal burns if exposed at high intensity |
Infrared light qualities
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Wavelength | 1 millimeter – 700 nanometers |
Frequency | 300 GHz – 430 THz |
Speed | 3 × 10⁸ m/s (in vacuum) |
Energy | Moderate |
Common Uses | Night vision, remote controls, heating lamps |
Dangers | Prolonged exposure can cause skin burns and eye damage |
Visible light qualities
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Wavelength | 700 nm (red) – 400 nm (violet) |
Frequency | 430 THz – 750 THz |
Speed | 3 × 10⁸ m/s (in vacuum) |
Energy | Moderate |
Common Uses | Enables human vision, lighting, photography |
Dangers | Very bright or laser light can damage eyes |
ultra violent light qualities
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Wavelength | 400 nm – 10 nm |
Frequency | 750 THz – 30 PHz |
Speed | 3 × 10⁸ m/s (in vacuum) |
Energy | High |
Common Uses | Sterilization, tanning beds, detecting counterfeit items |
Dangers | Causes sunburn, skin aging, and increases skin cancer risk |
X-ray qualities
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Wavelength | 10 nm – 0.01 nm |
Frequency | 30 PHz – 30 EHz |
Speed | 3 × 10⁸ m/s (in vacuum) |
Energy | Very High |
Common Uses | Medical imaging (e.g., broken bones), security scanners |
Dangers | Can damage living tissue, increases cancer risk with overexposure |
Gamma ray qualities:
Property | Description |
|---|---|
Wavelength | < 0.01 nm |
Frequency | > 30 EHz |
Speed | 3 × 10⁸ m/s (in vacuum) |
Energy | Extremely High |
Common Uses | Cancer radiotherapy, sterilizing medical tools, nuclear research |
Dangers | Extremely hazardous; causes severe cellular and DNA damage |
Snell’s Law
describes the relationship between the angles at which light enters and exits different materials
Snell’s Law formula
Snell's Law Formula: n₁sin(θ₁) = n₂sin(θ₂)
Snell Law Formula explanation
n₁ = refractive index of the first medium
n₂ = refractive index of the second medium
θ₁ = angle of incidence
θ₂ = angle of refraction
What is titration?
a technique where a solution of known concentration is used to determine the concentration of an unknown solution.
How to carry out titration
A titration is performed by slowly adding a titrant of known concentration to a reaction vessel containing a solution of unknown concentration, using a burette. The end point is detected using a suitable indicator that changes color when the reaction is complete.