Anatomy of the spine,pelvis, urogential, reproductive
1/241
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
242 Terms
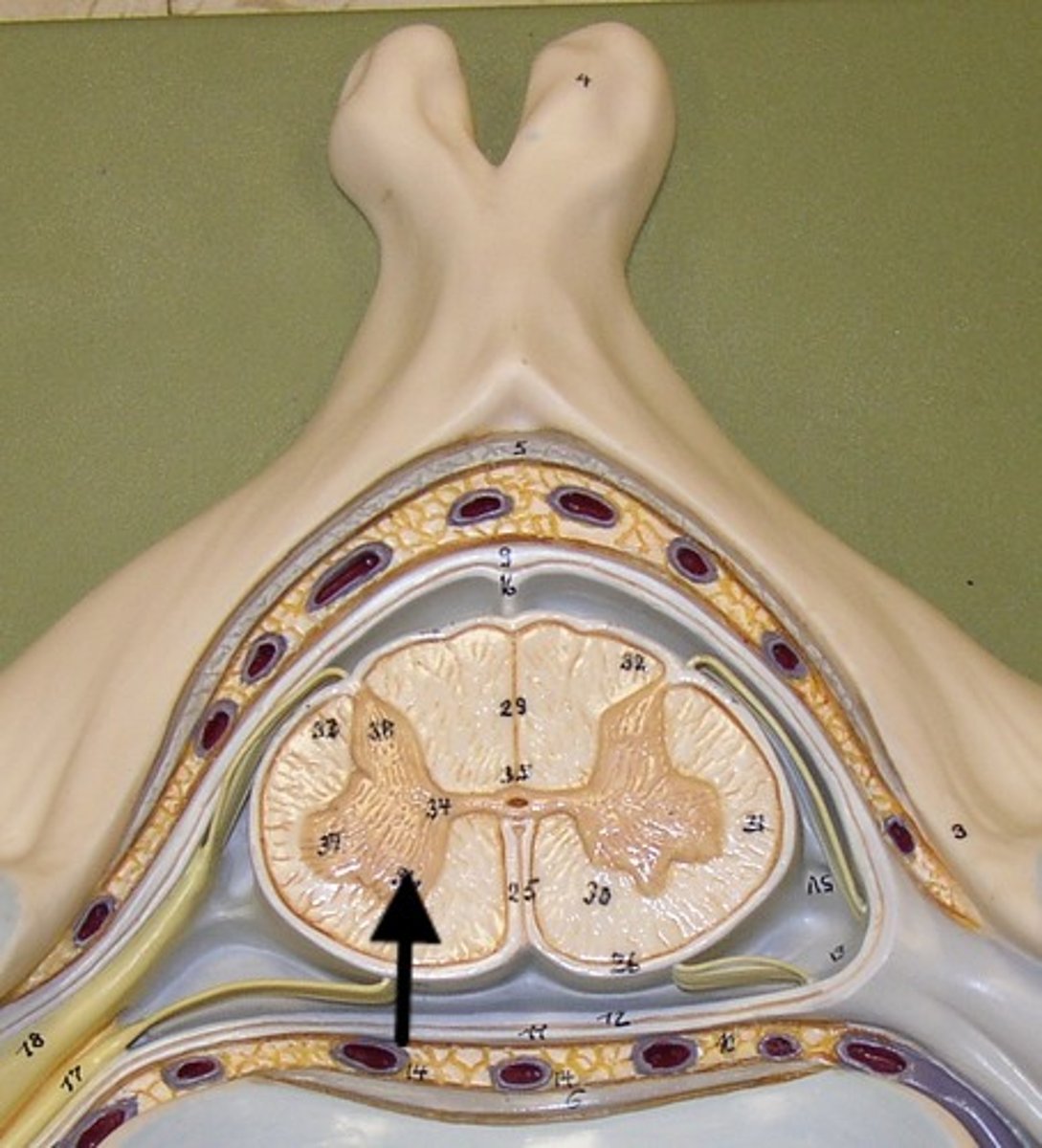
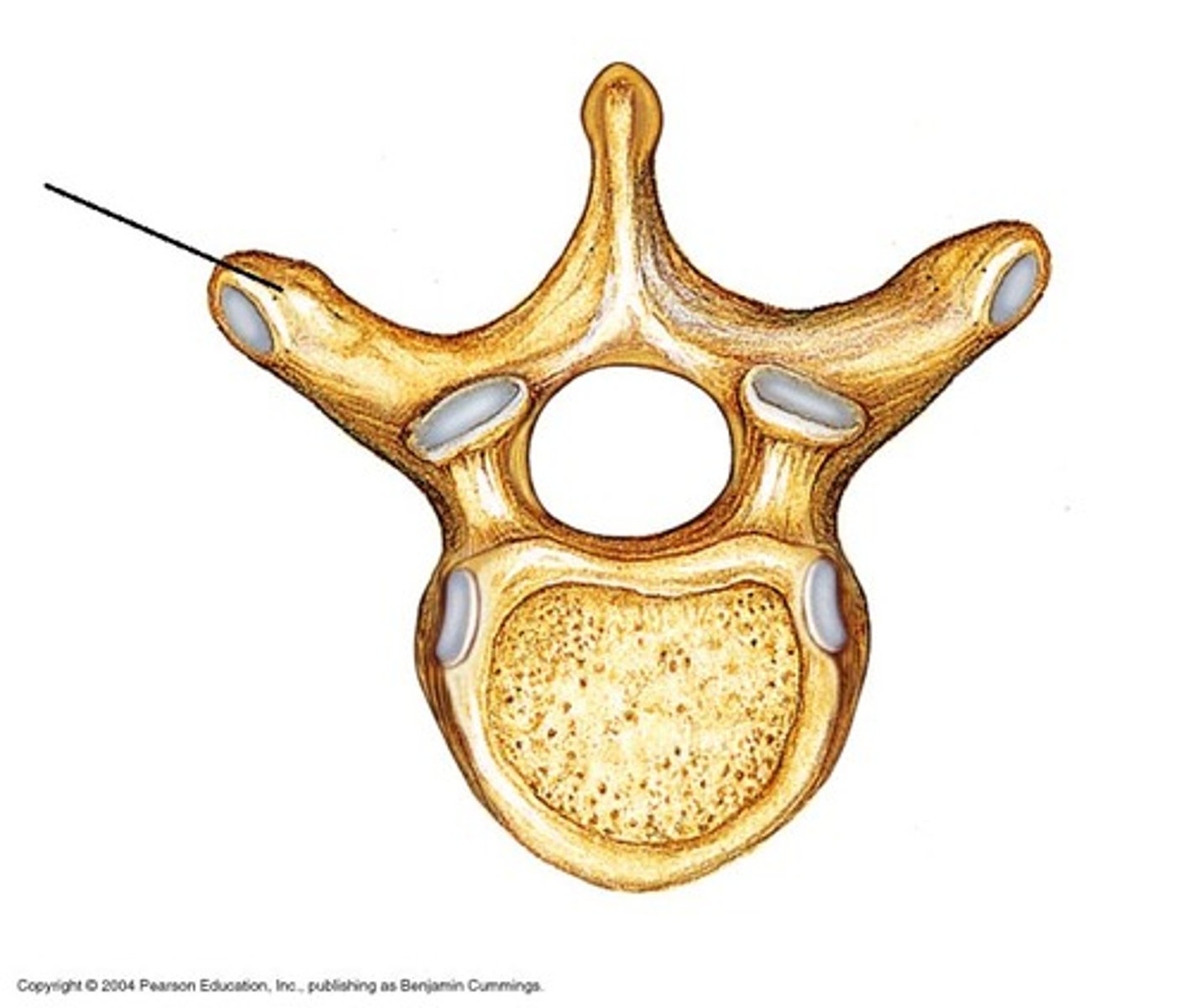
transverse process
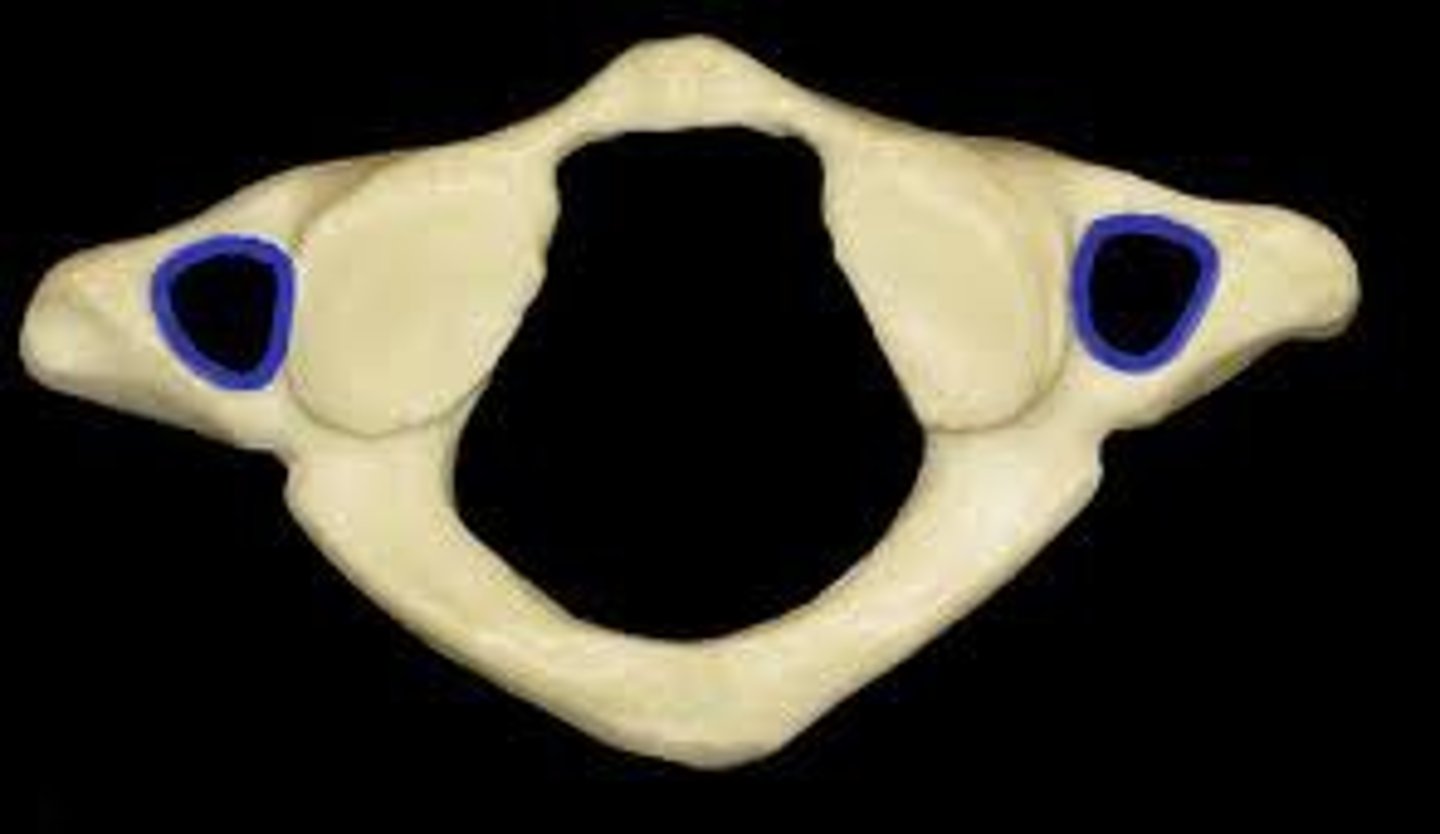
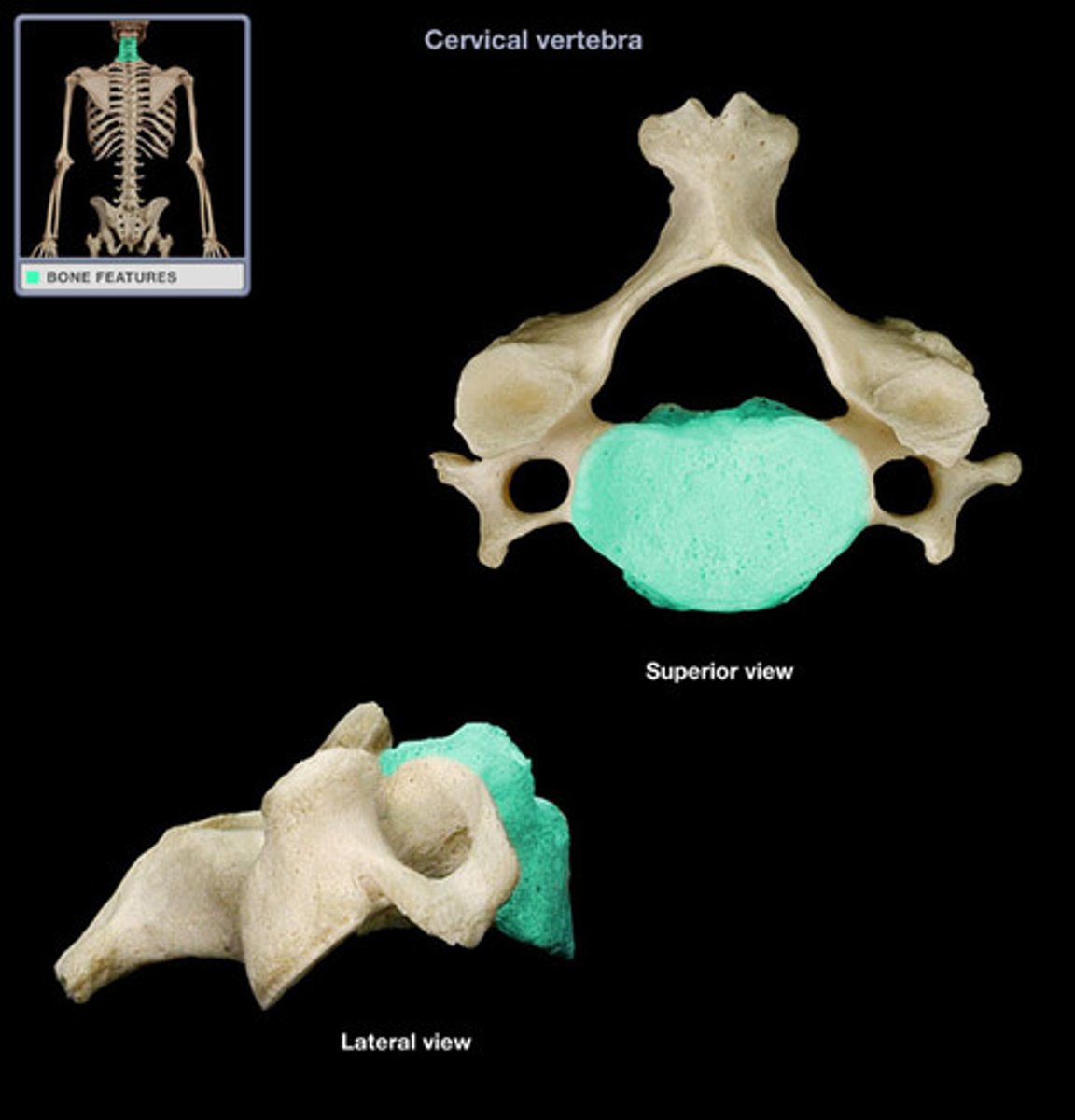
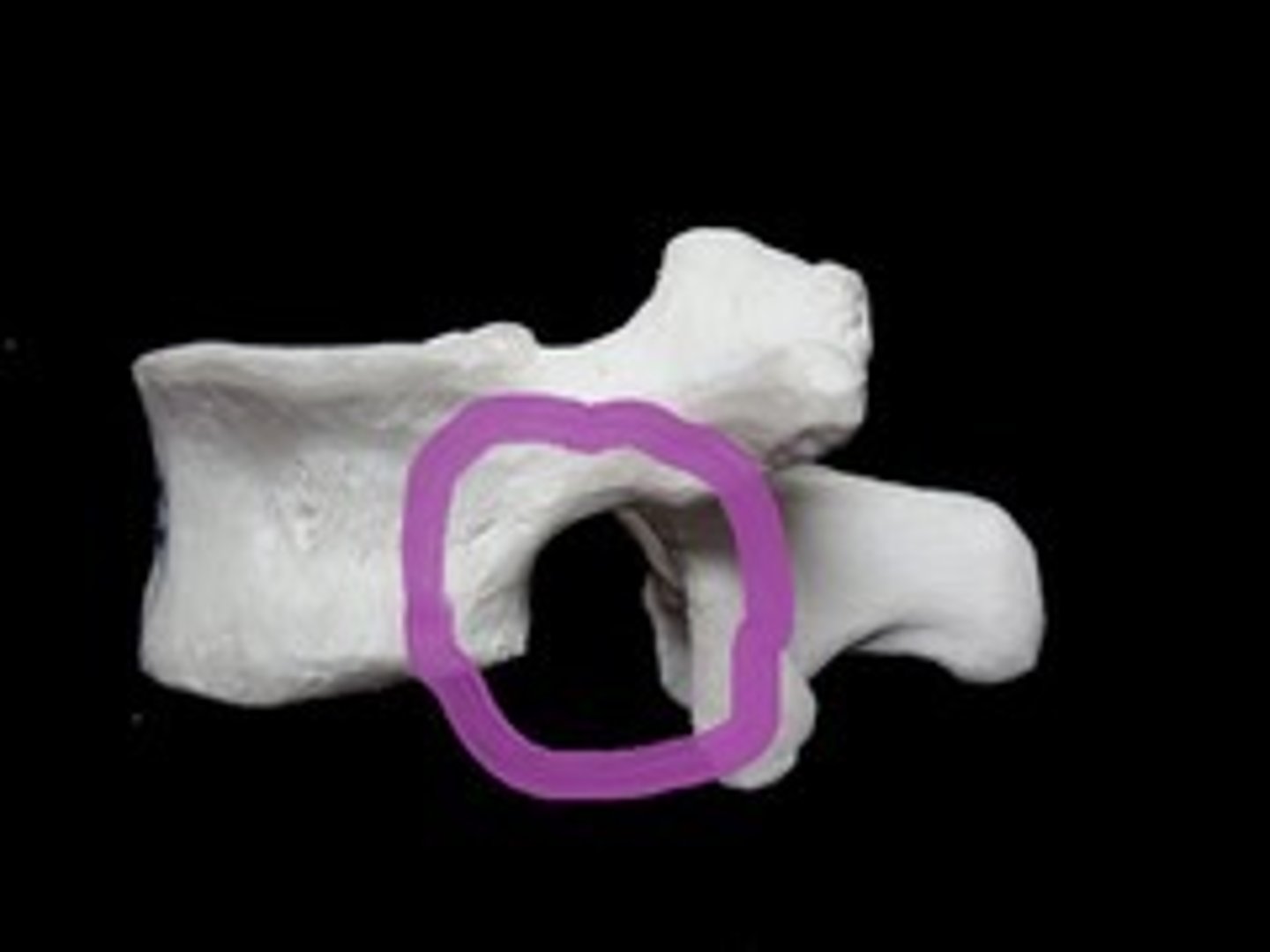
transverse formen (cervical)
superior articular facet of occipital condyle
vertebral formen
posterior arch
posterior tubercle
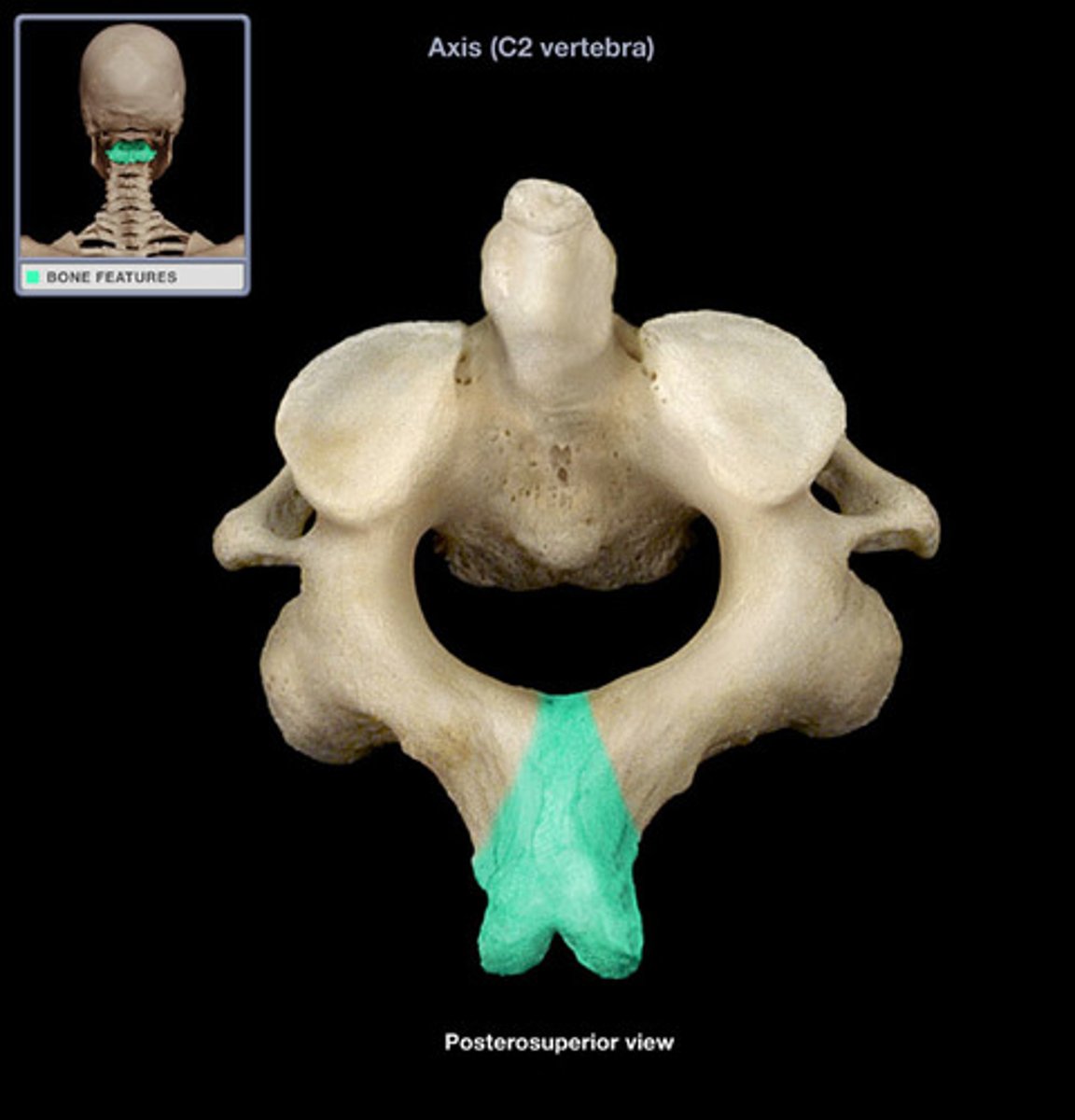
dens (odontid process)
pedicle
body of vertebra
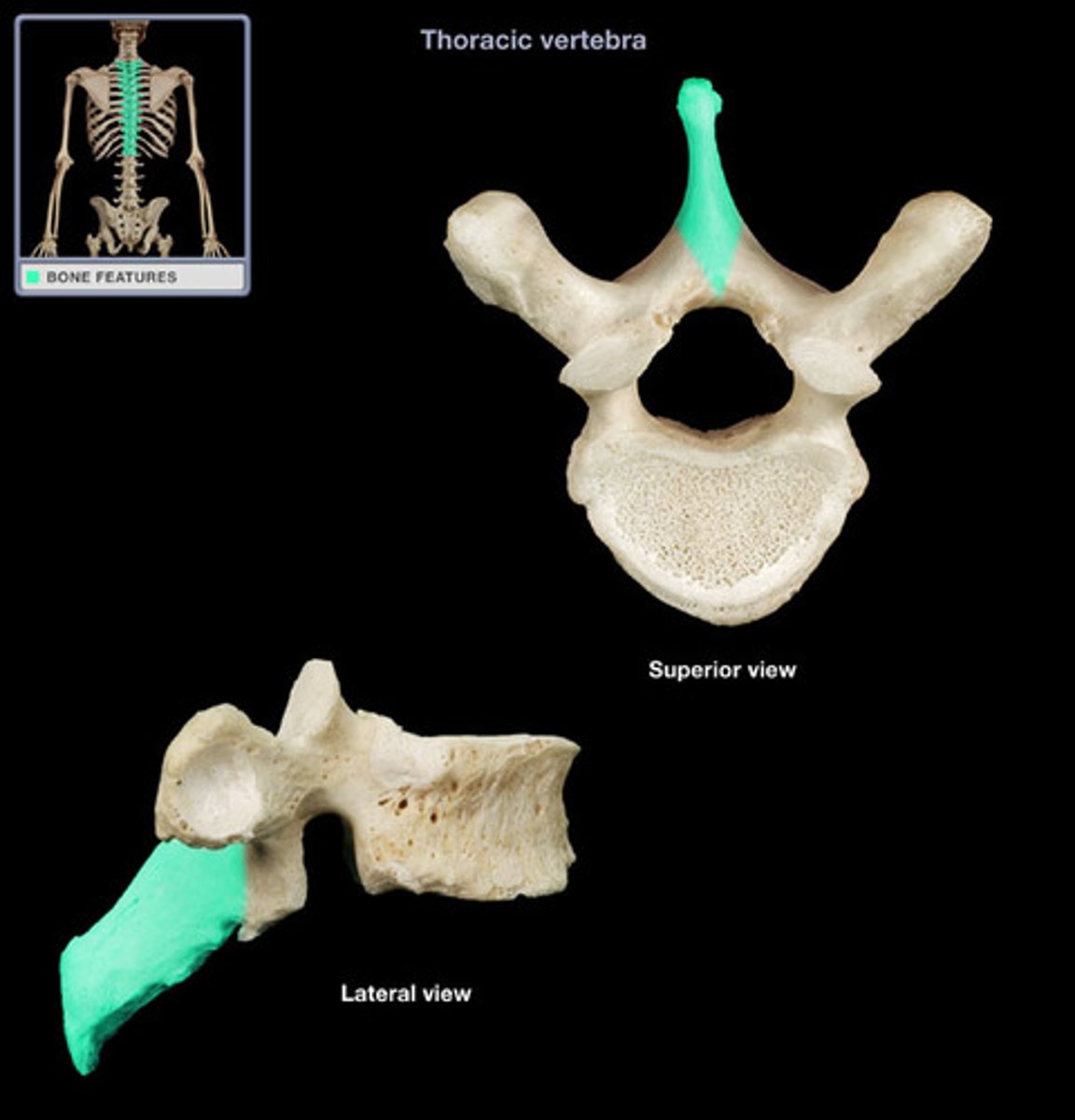
spinous process
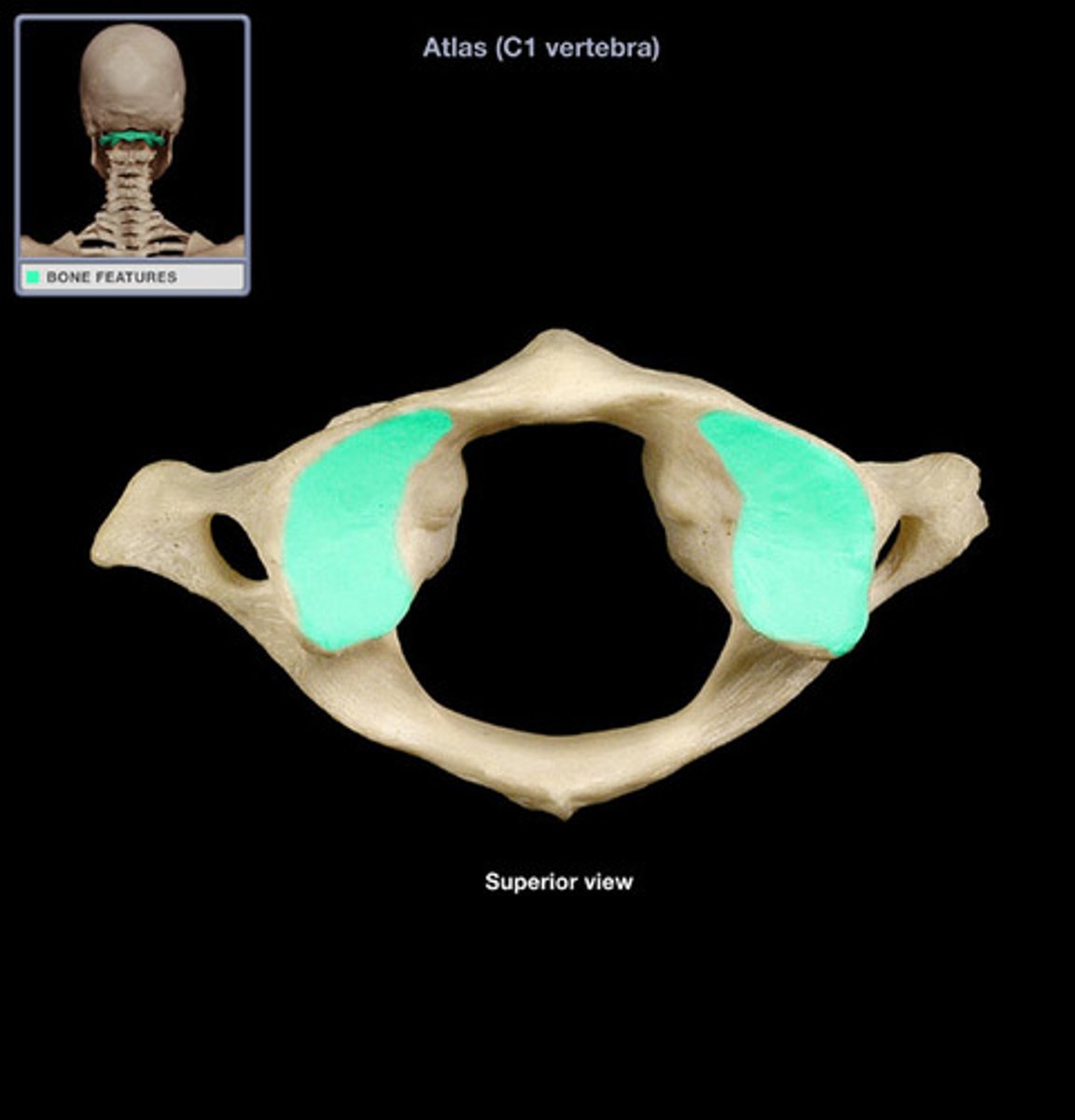
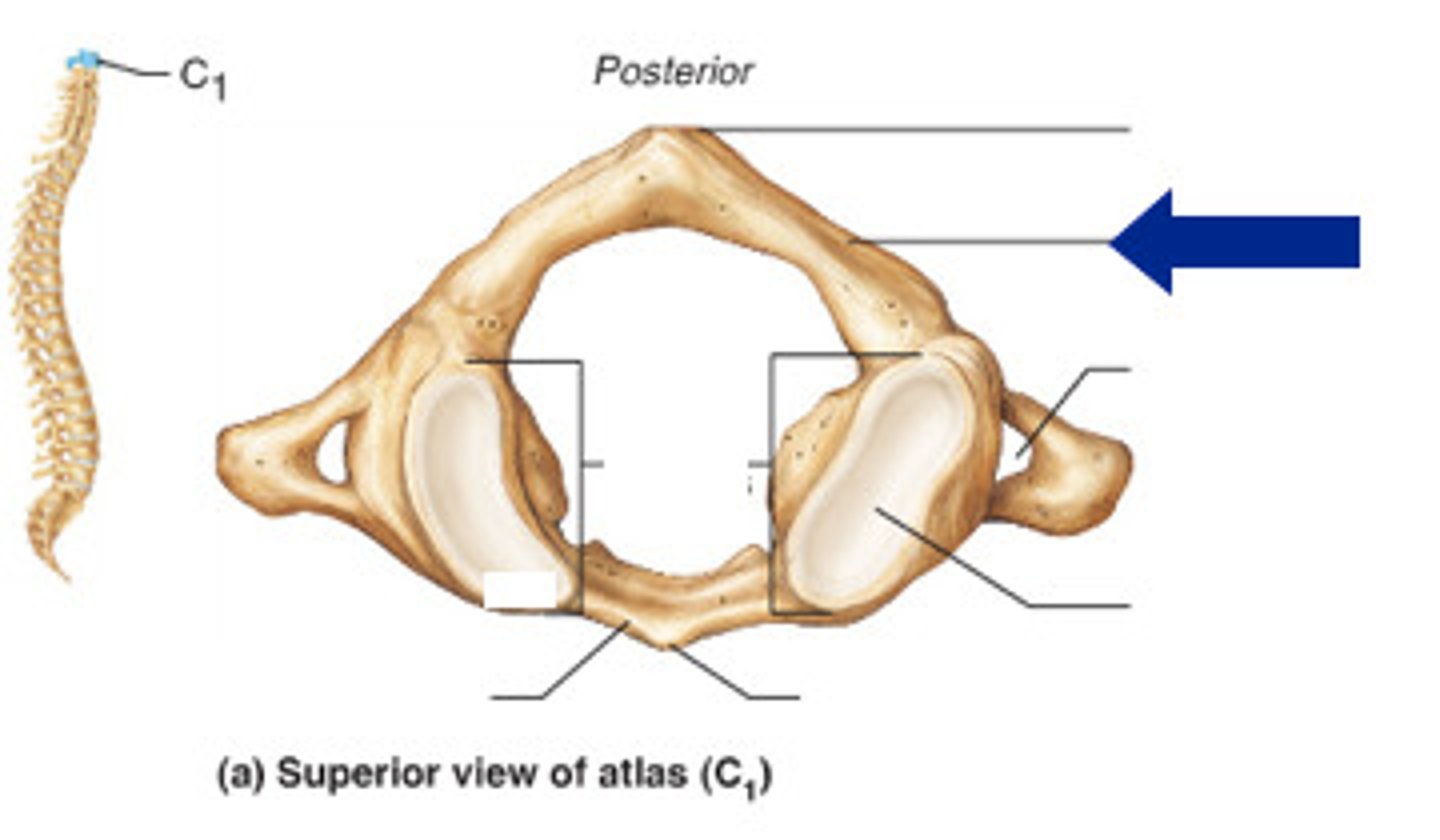
atlas C1
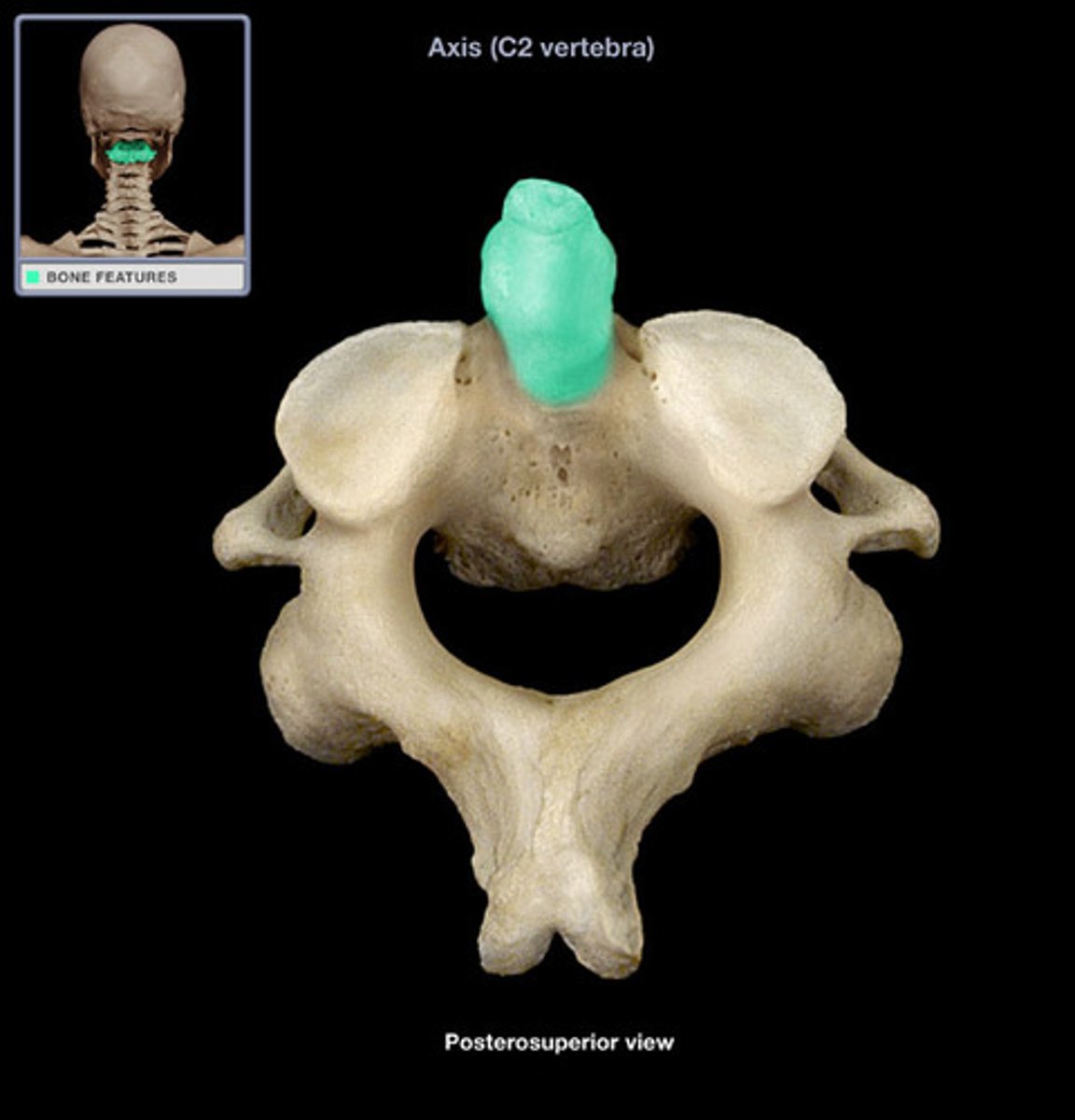
axis C2
the transverse formean (where vertebral artery passes thru)
what structure is the distingushing feature of the cervical vertebra
vertebral foramen
what structure is where the spinal cord passes thru
gets smaller, so does the vertebral foramen
does the spinal cord get smaller or larger as it goes from C1 downwards
bifid spinous process
C2-C6
what sections contain the bifid spinous process
lamina
C7
which cervical vertabra has no bifid process (not seperated into two little horns)
C7
what level is the vertebra prominens located
anulus fibrosus
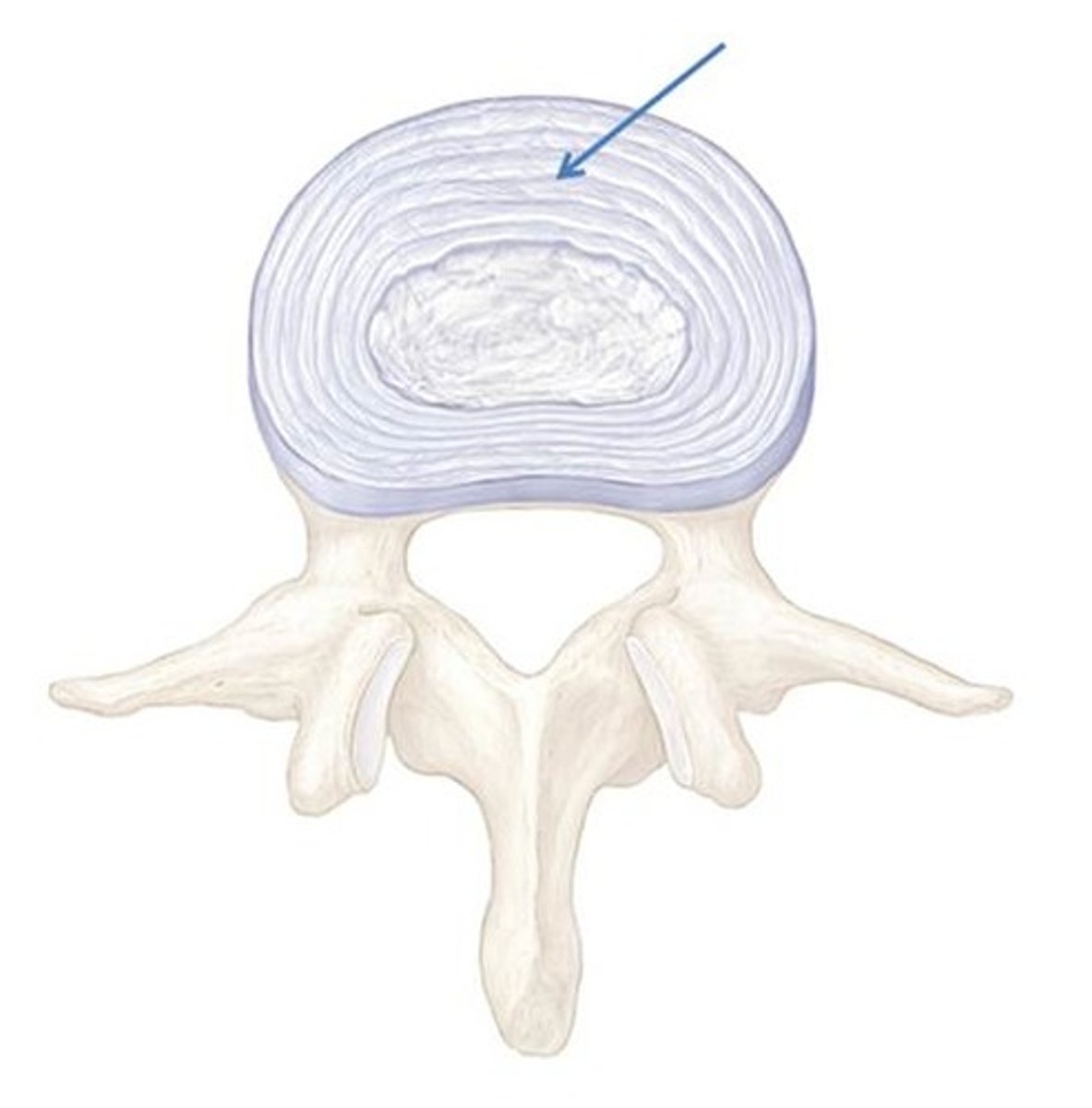
nucleus pulposus
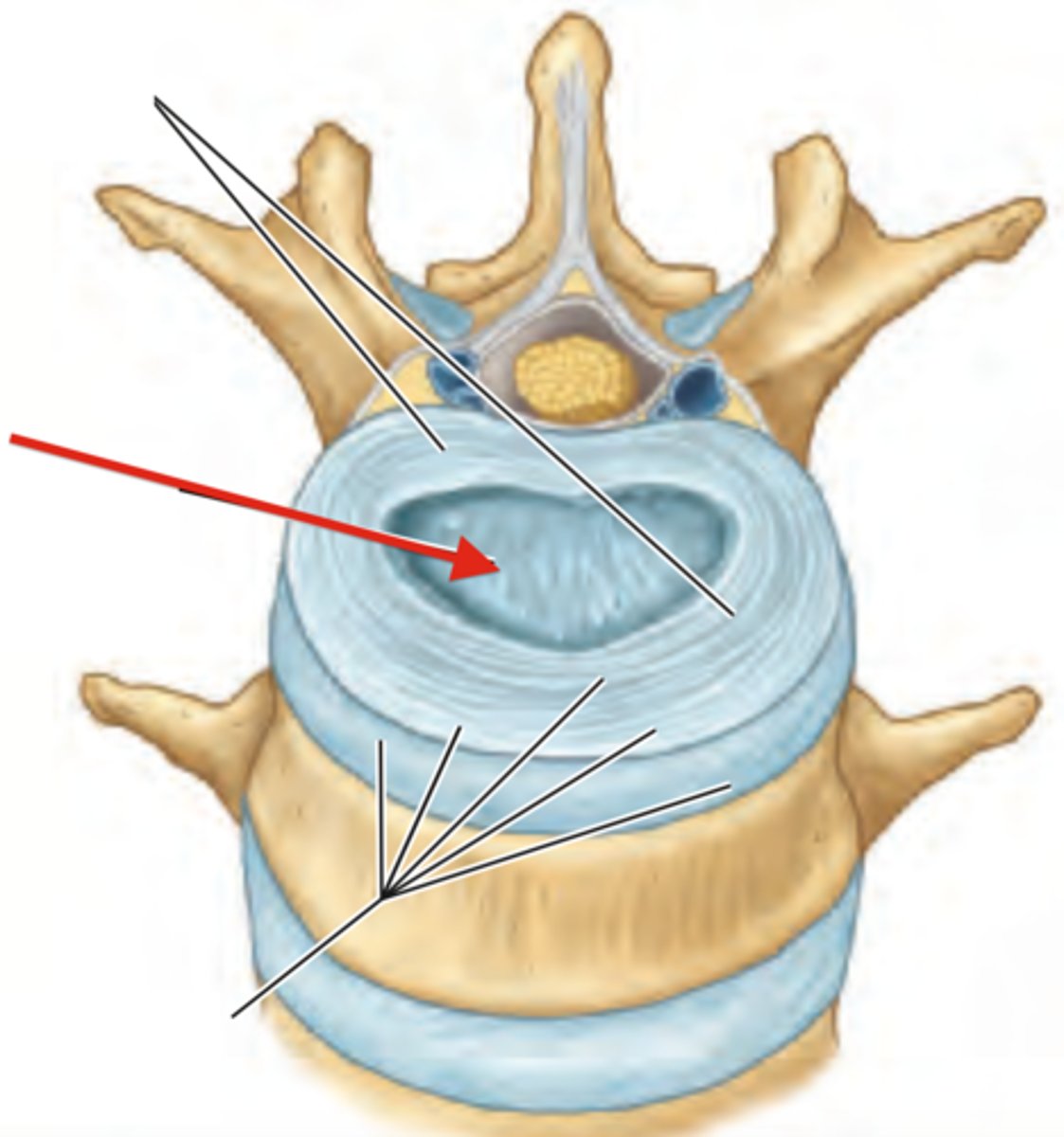
Shock absorbtion
what is the purpose of the intervertrebral disks
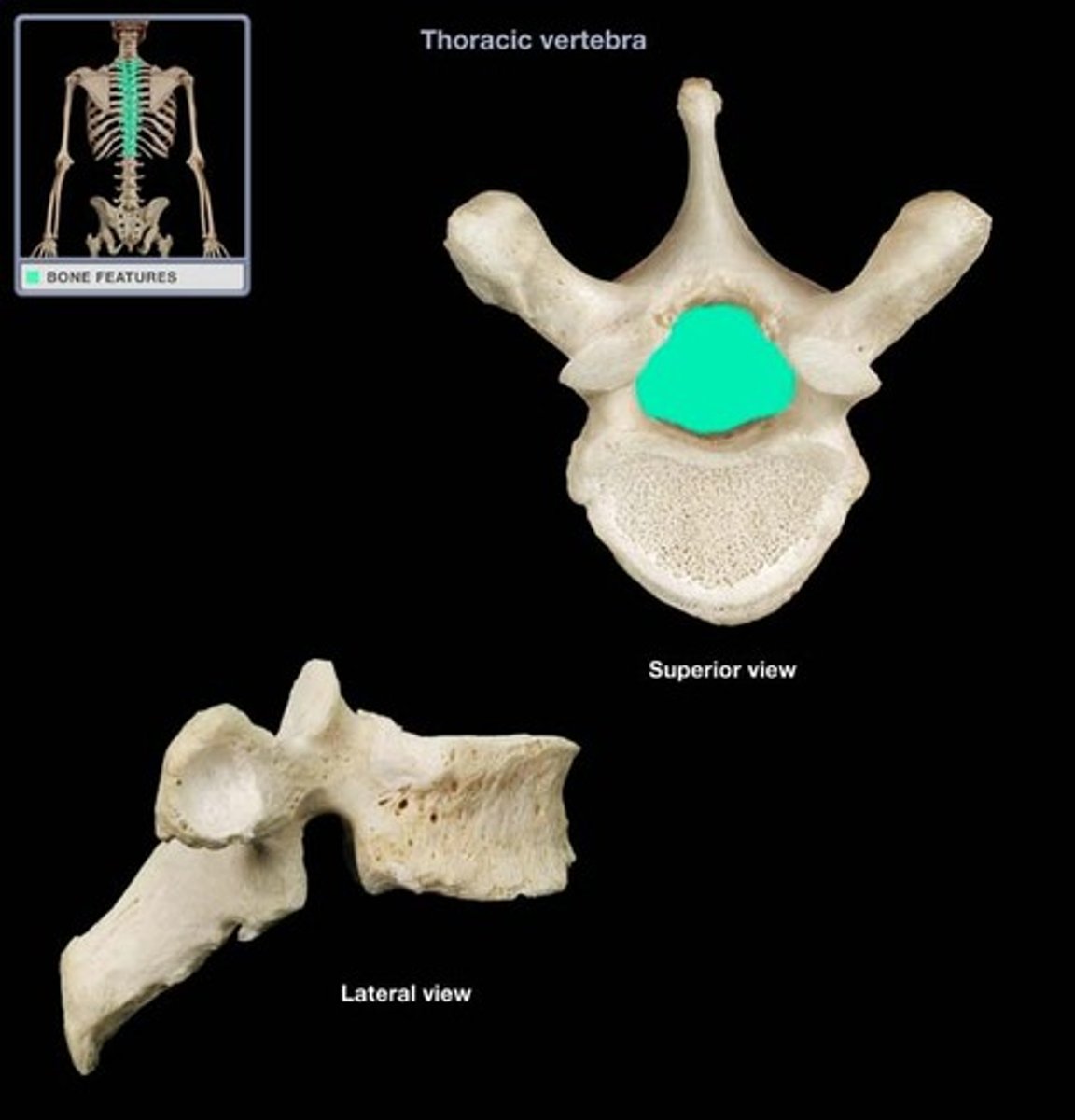
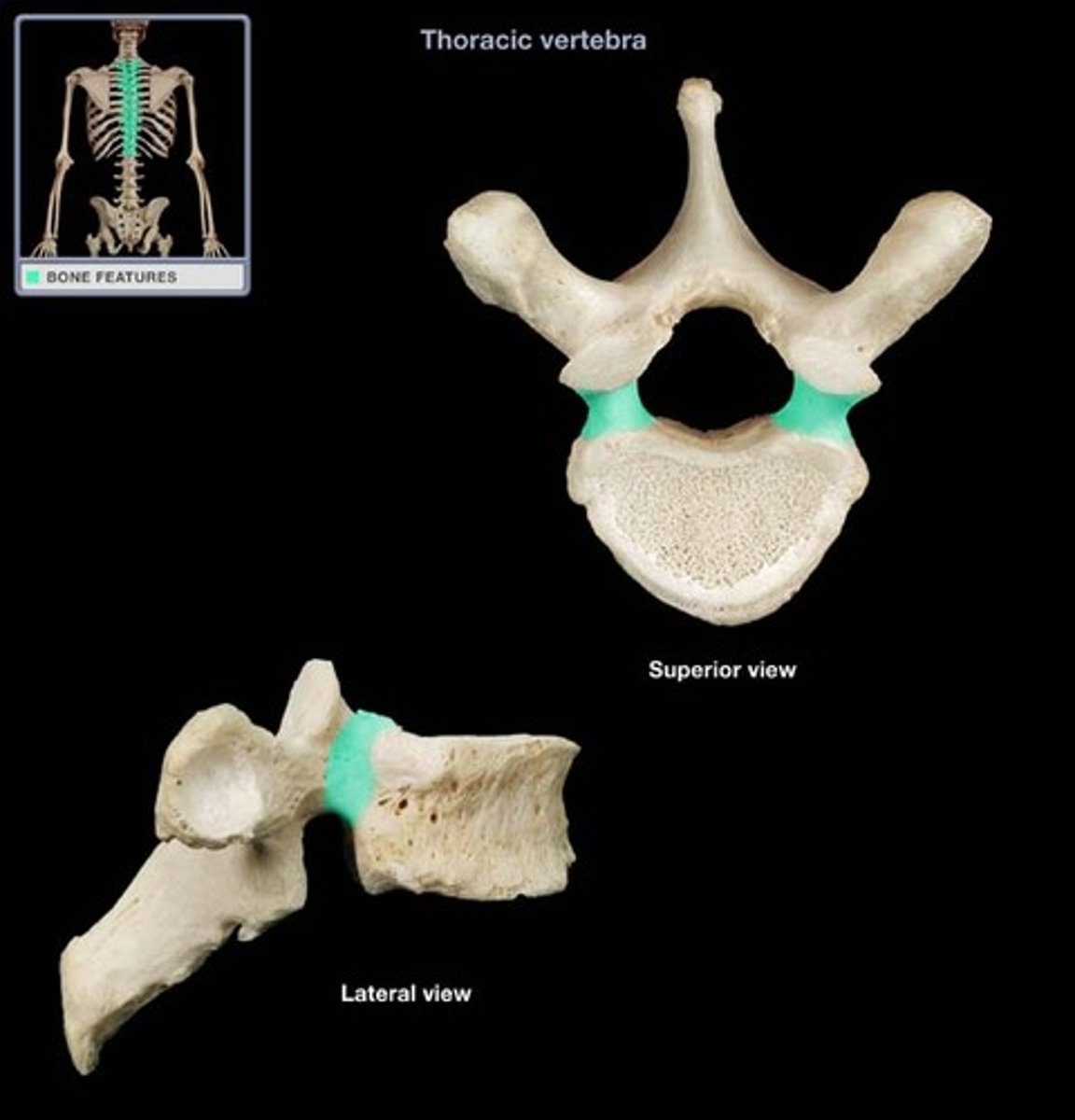
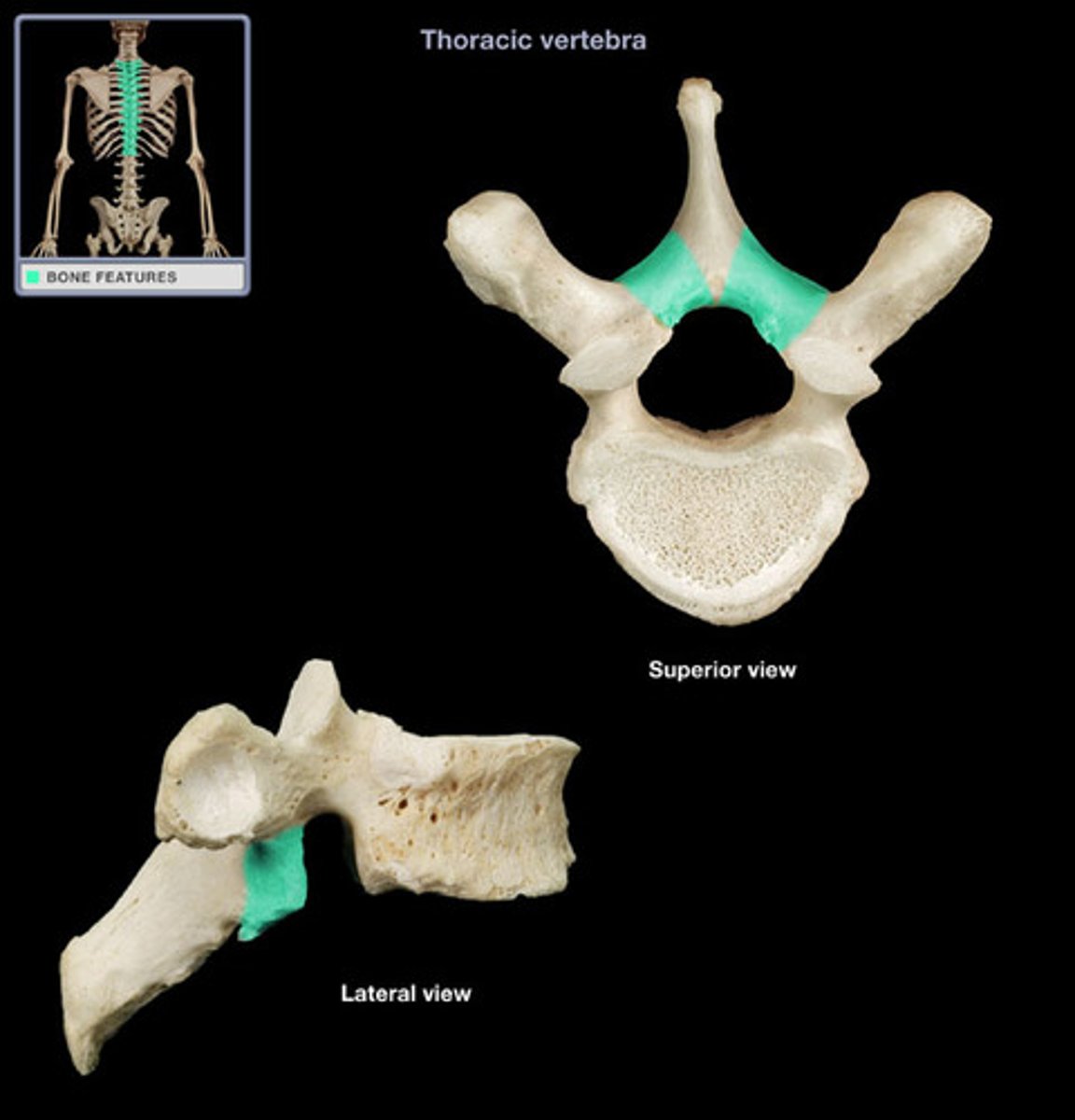
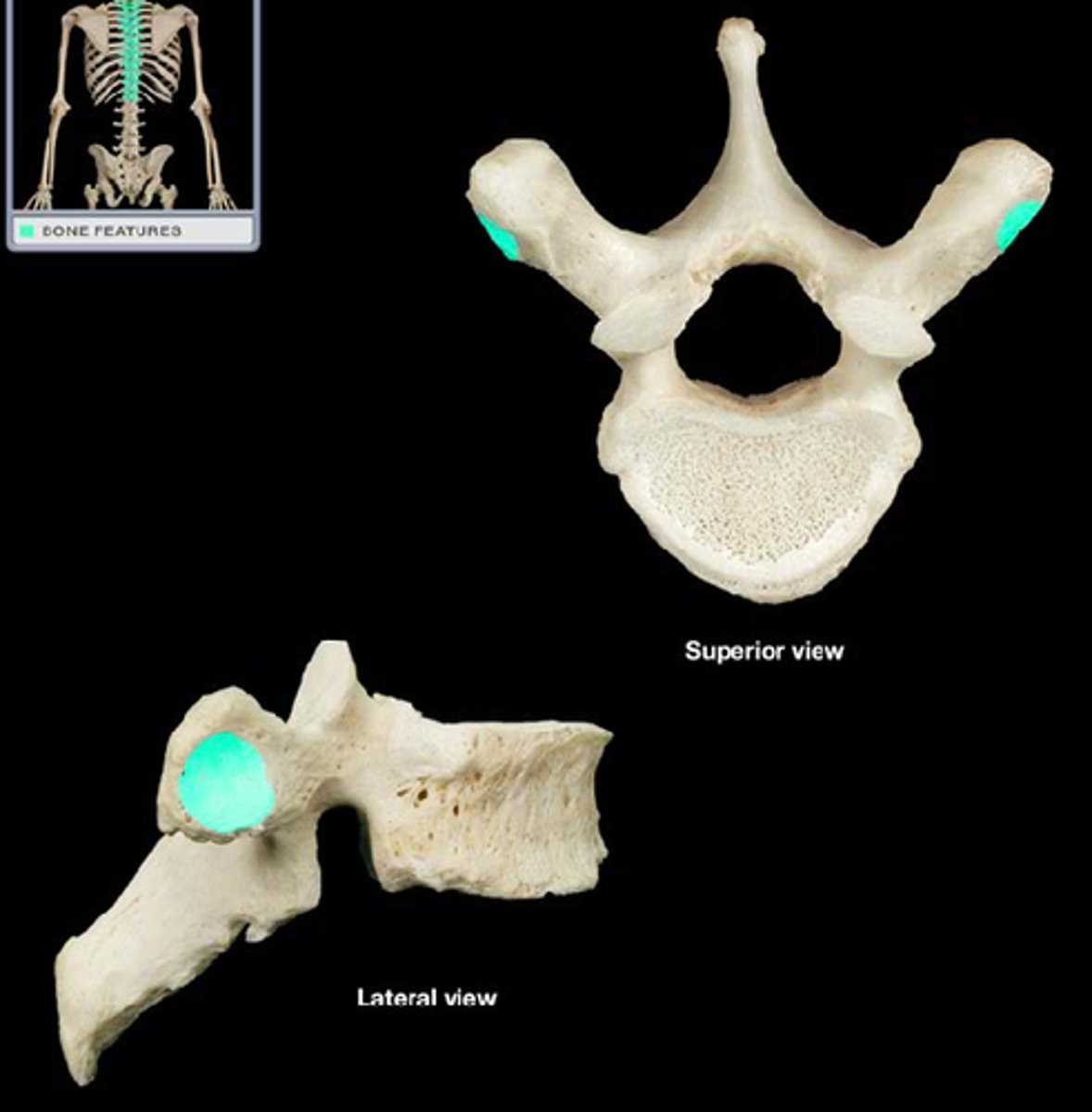
transverse costal facet
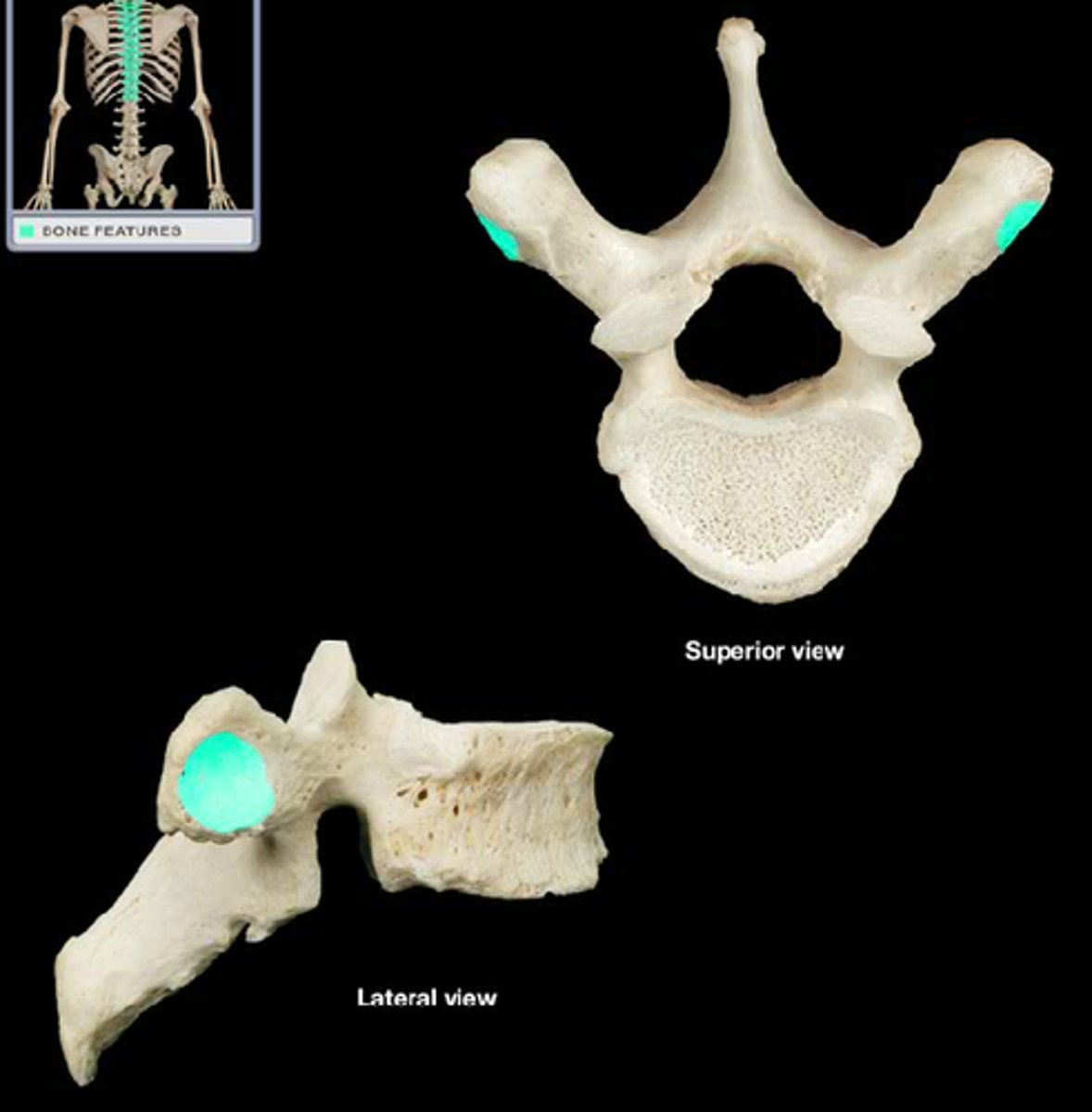
rib articulation (attachment) ONLY FOUND IN T1-T12
what is the purpose of the transverse costal facets
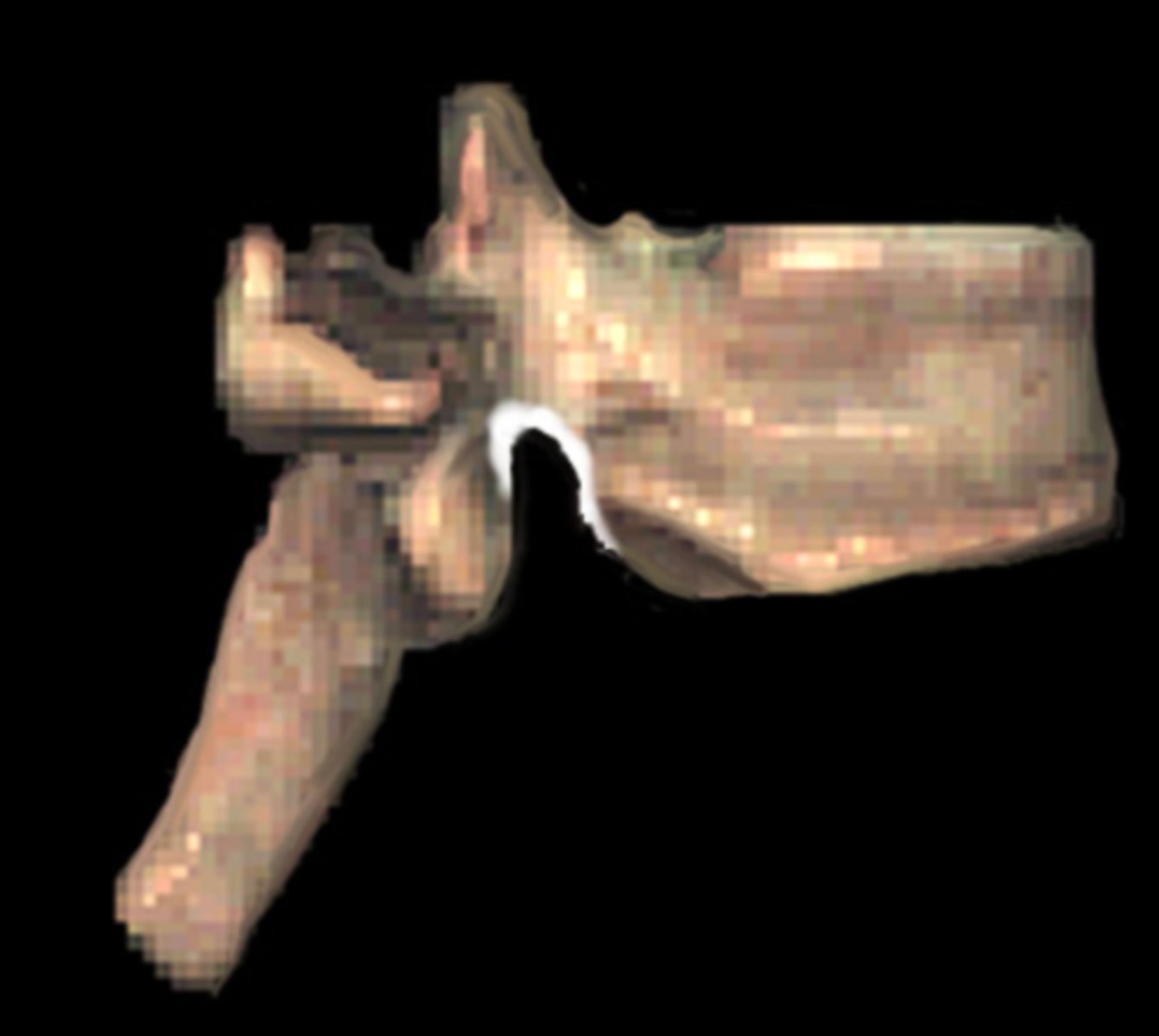
Inferior vertabral notch (intra vertabral foreman)
12 (T1-T12)
how many transverse costal facets for rib articulation (attachment) are there
inferior articular process
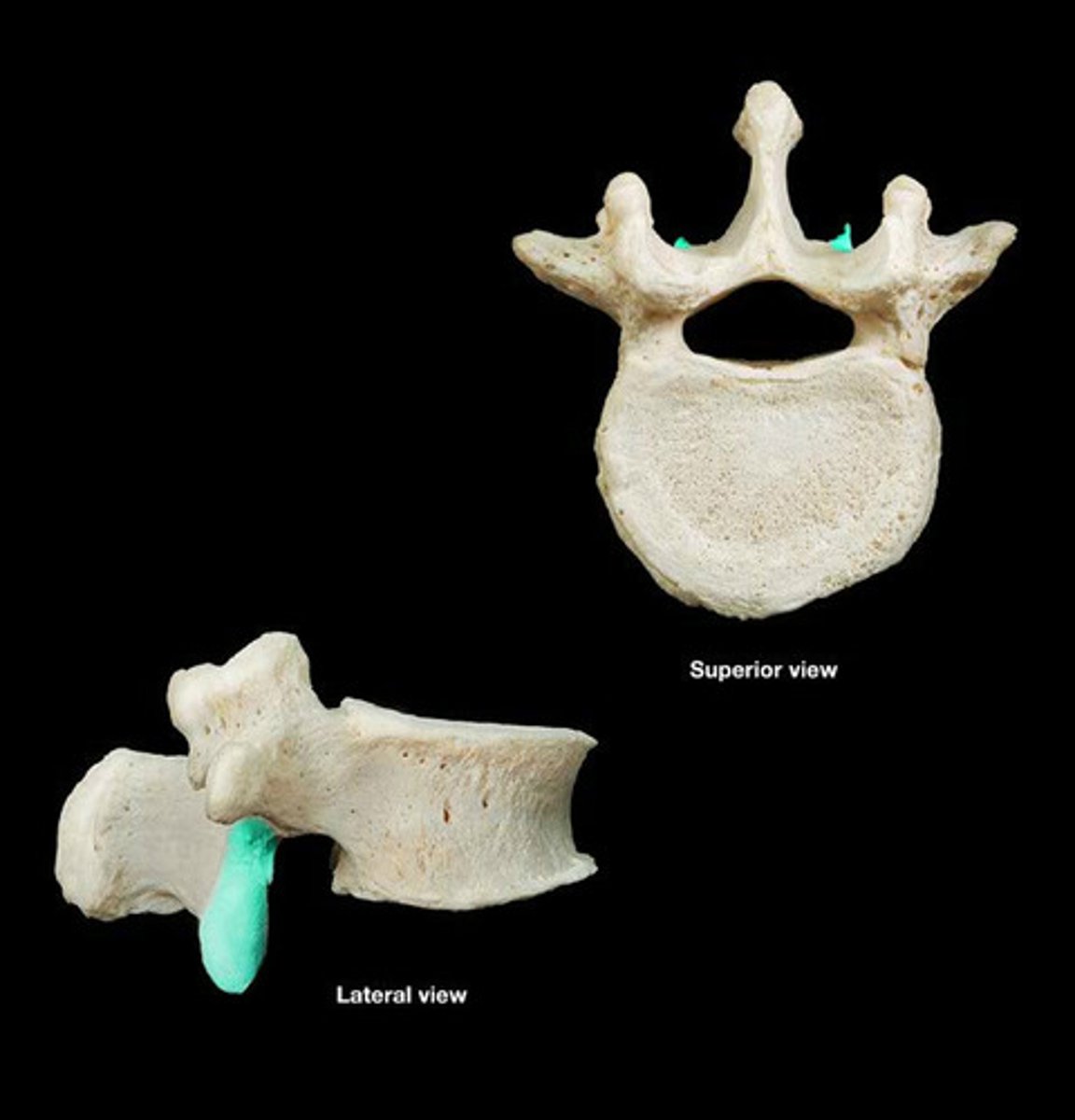
to form a joint, joint segment
what does articulation mean
increases
does the vertabral body increase or decrease in size when going down the spine
7 (C1-C7)
how many transverse foramen are there
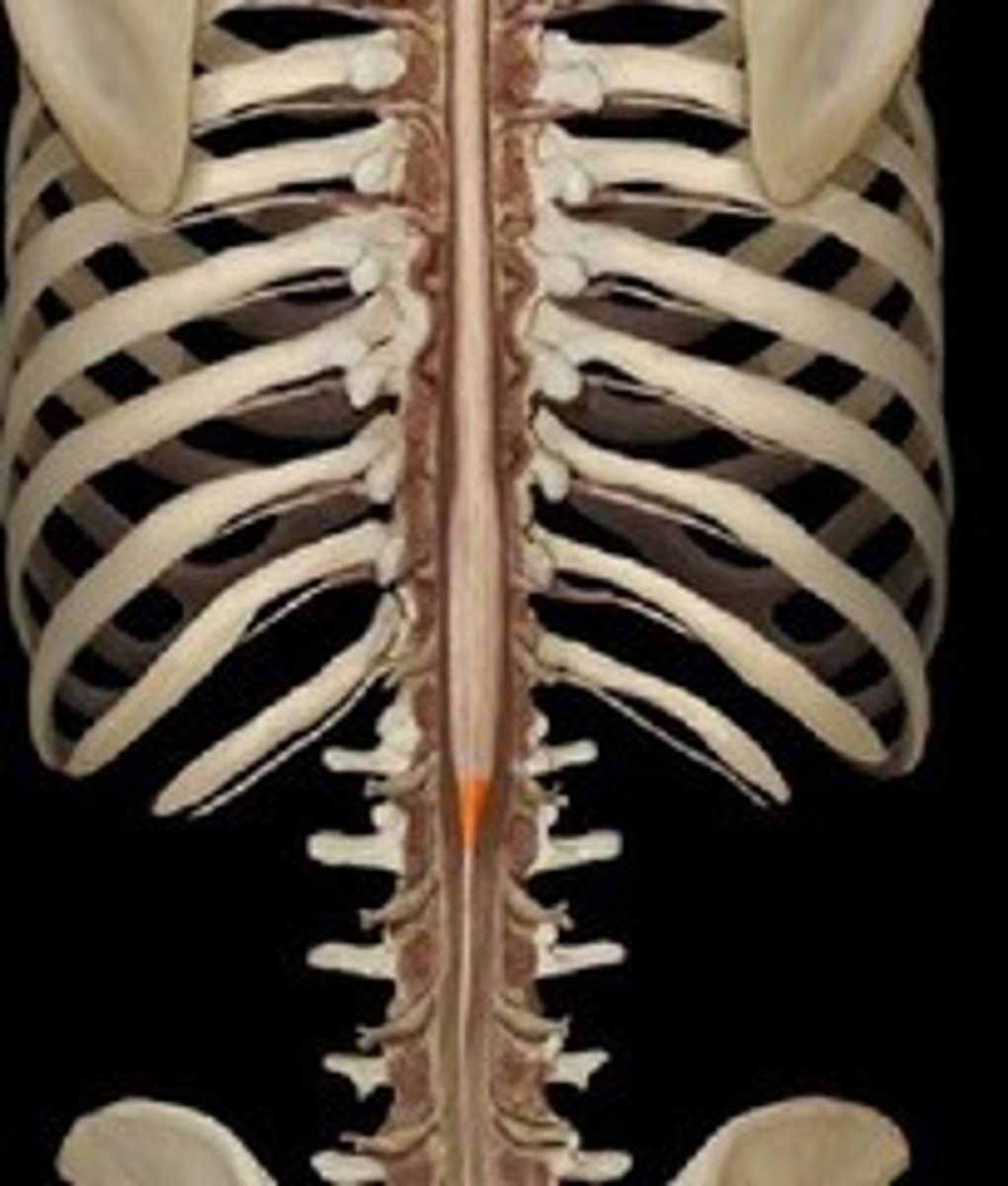
conus medullaris
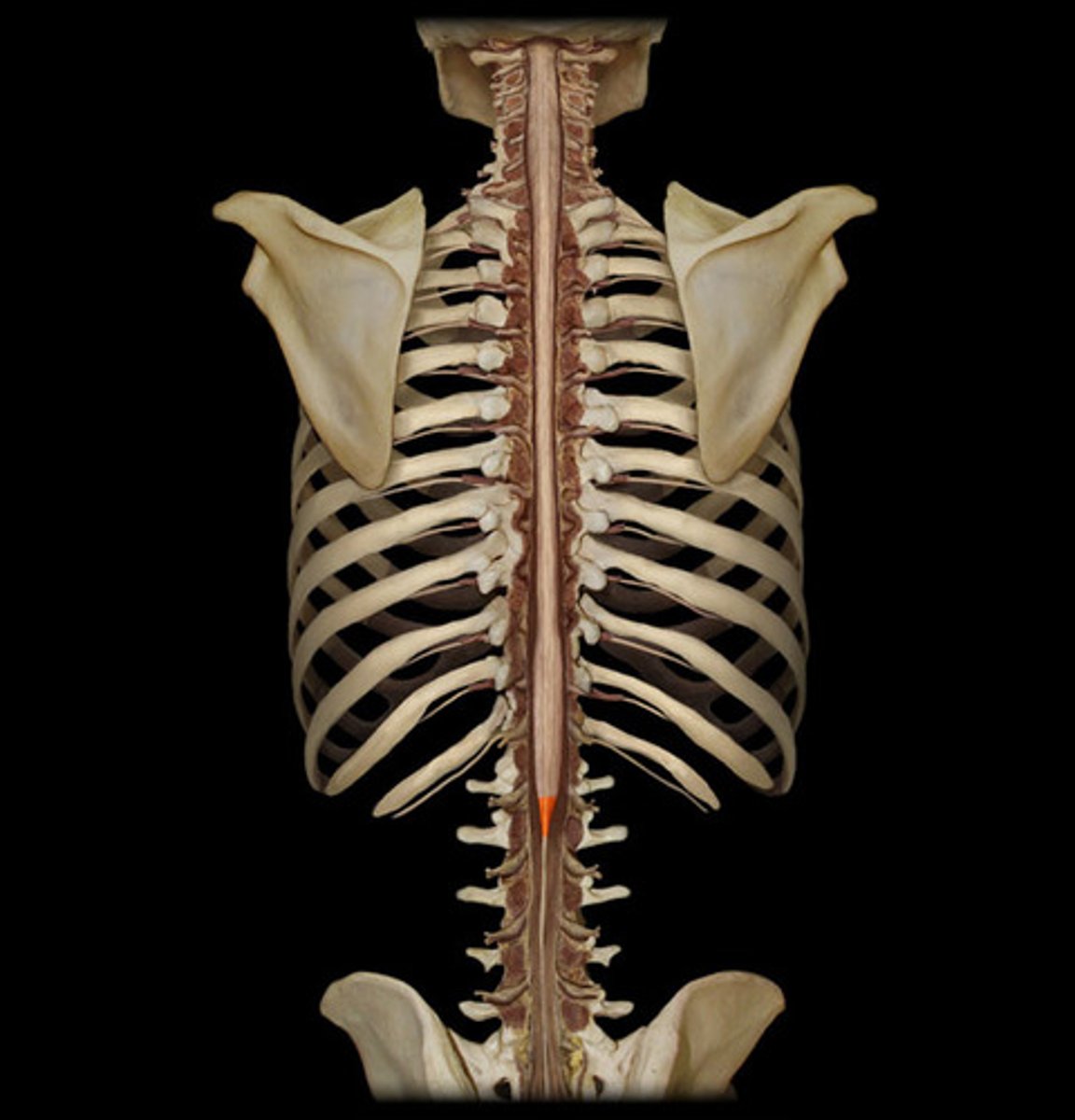
L1/L2
what level is the conus medullaris located
S1-S5
how many sacral vertebra are fused together
1-3
how many coccyx vertebra are fused together
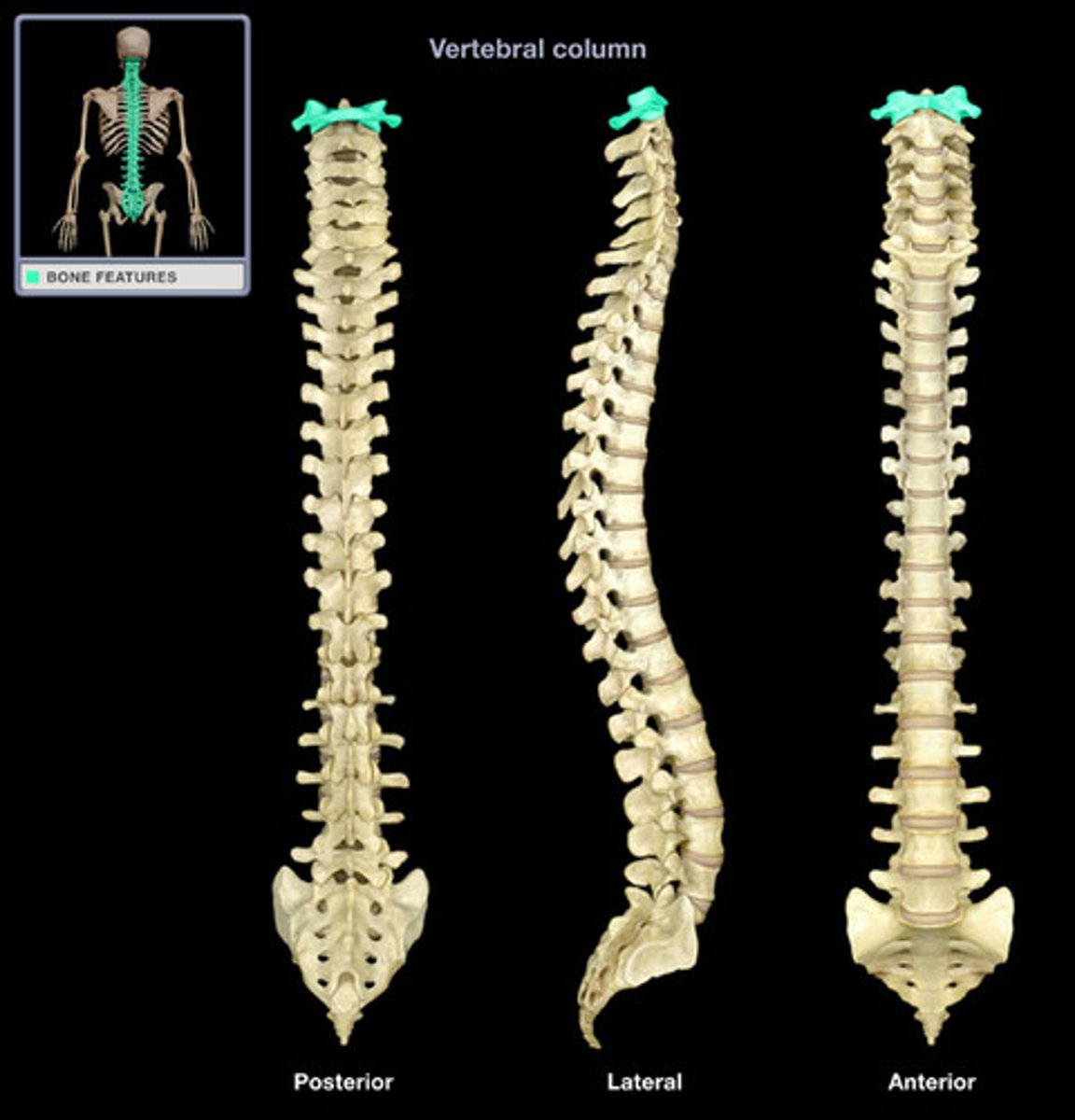
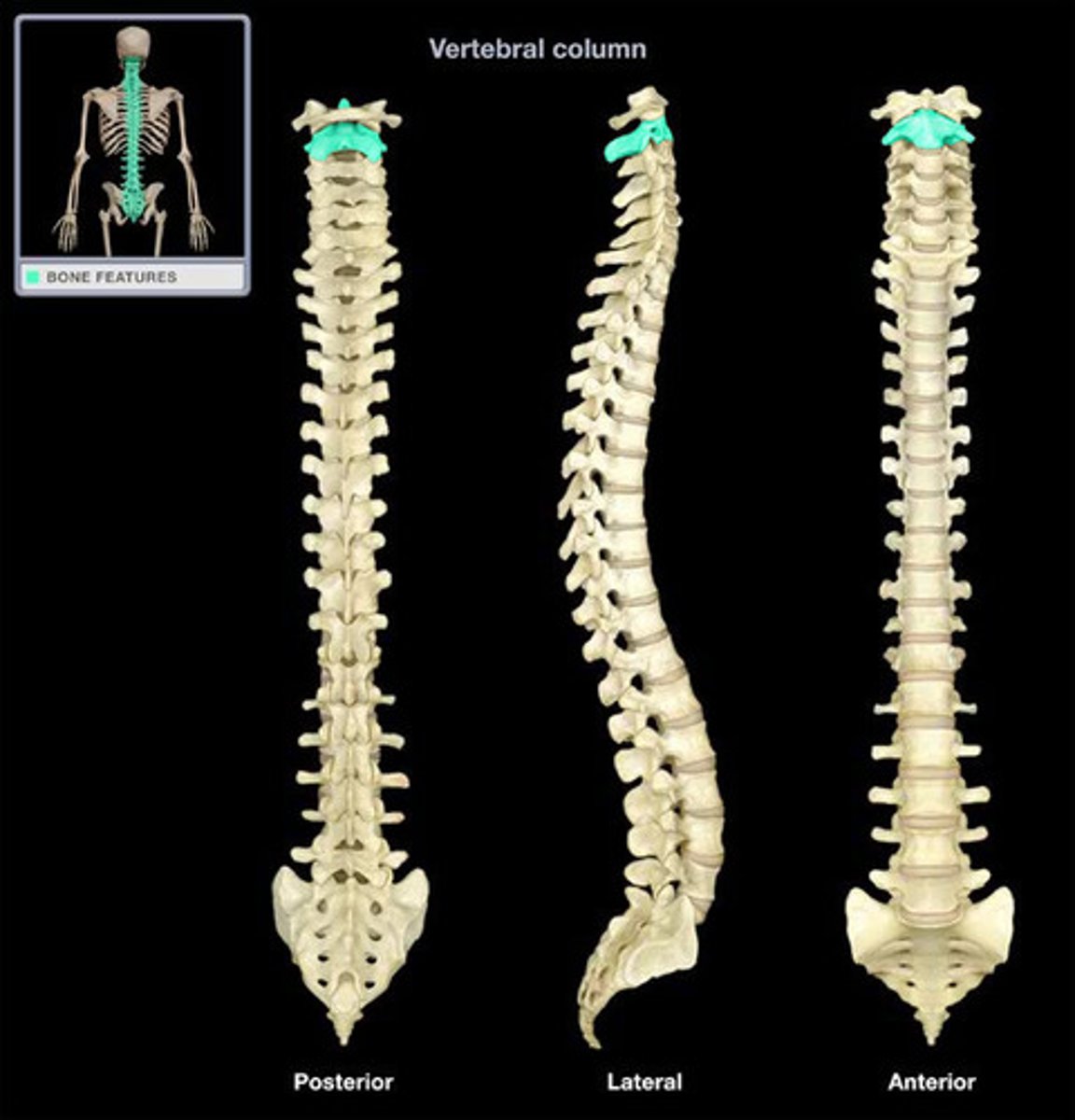
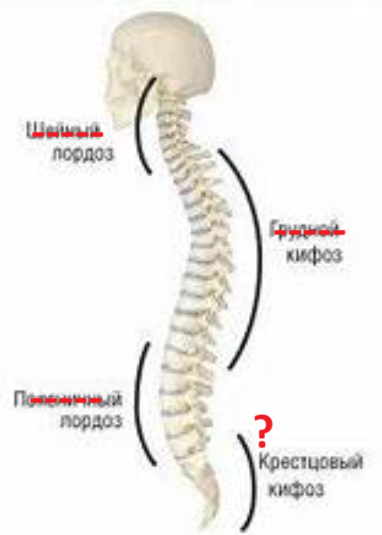
cervial lordosis (convex forwards)
thoracic kyphosis (convex backwards)
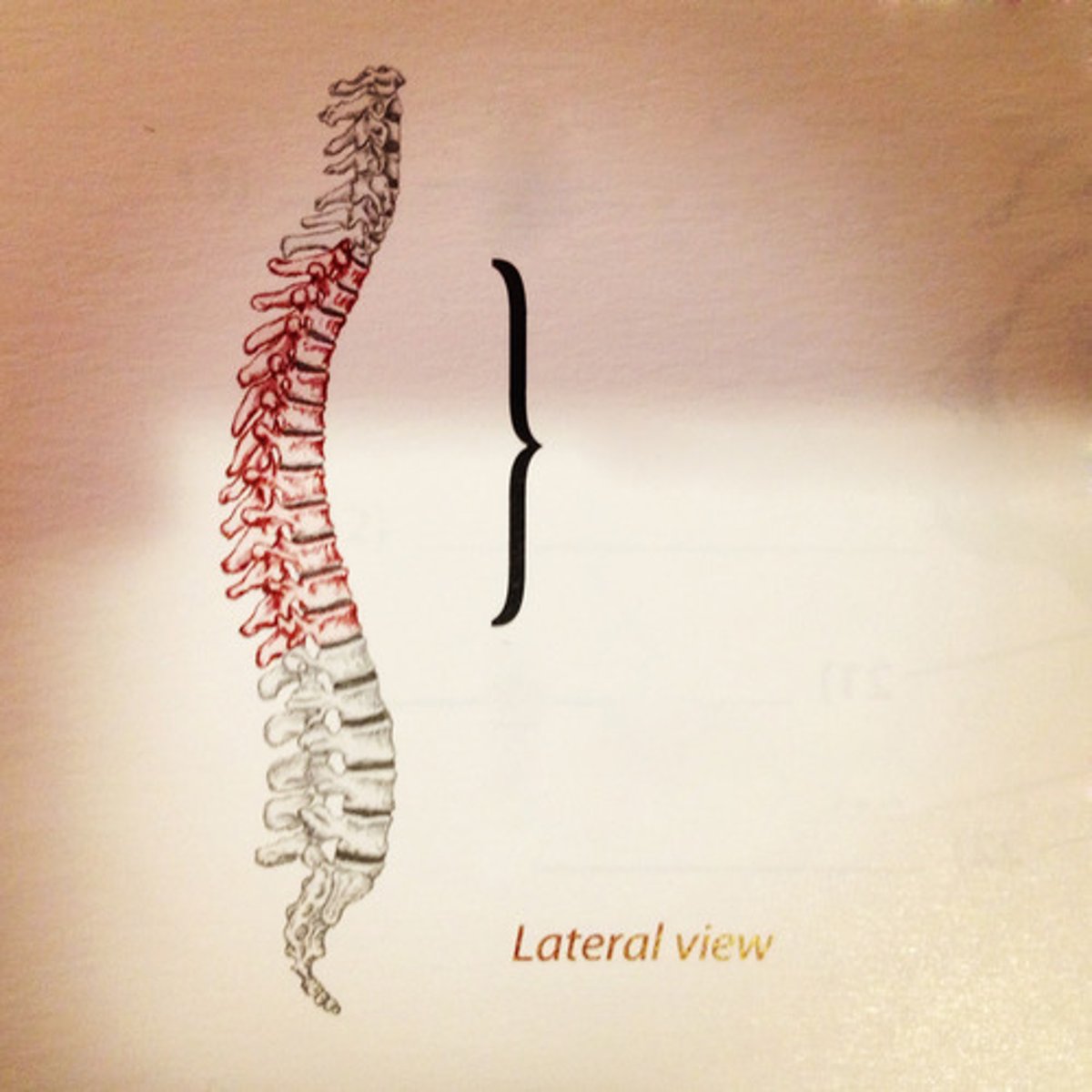
lumbar lordosis (convex forwards)
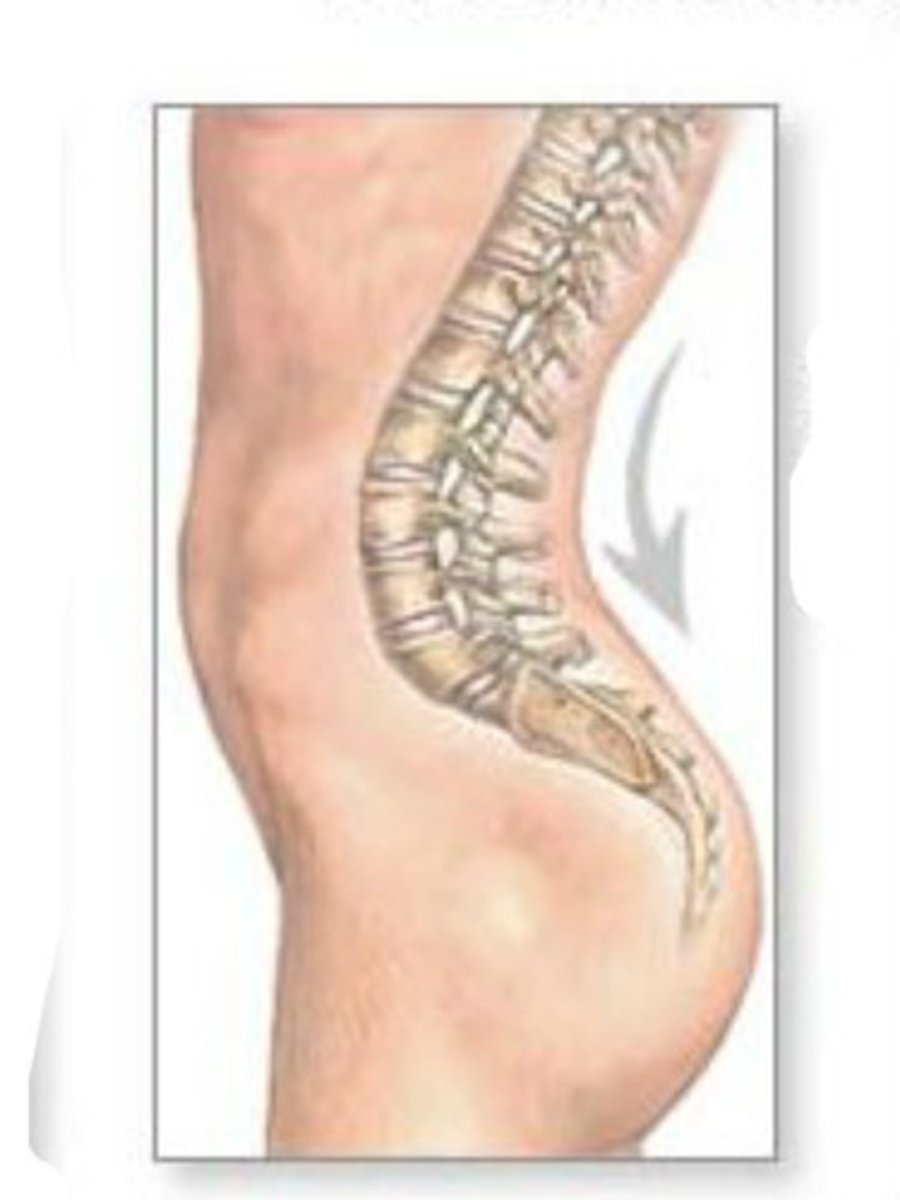
sacral kyphosis (convex backwards)
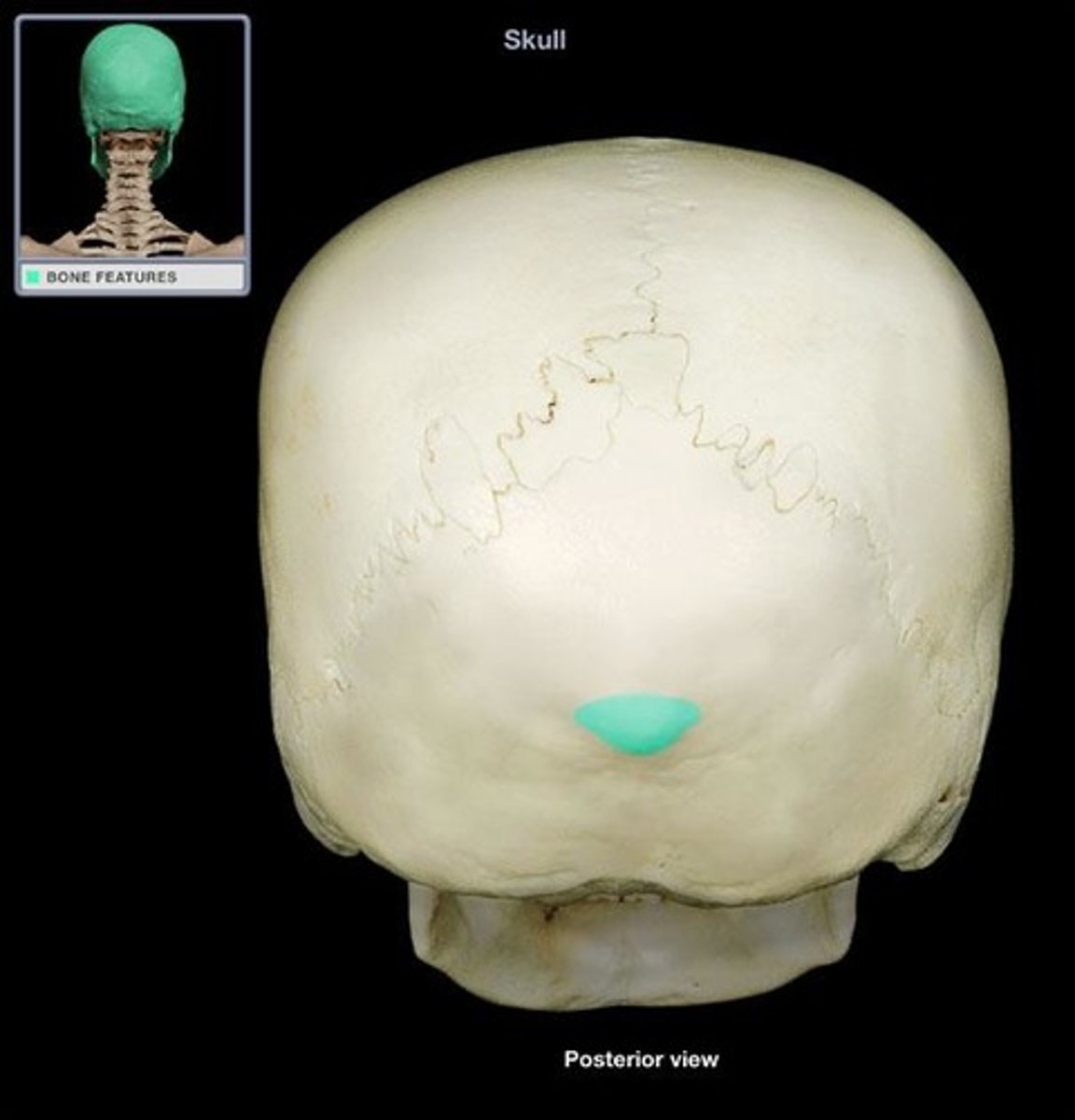
external occipital protuberance
L4
at what level is the ilac crest
T2
at what level is the sternal notch
L5
what is the site of muscle attachment for the back
C1
what vertebra is considered the atlas
C2
what vertebra is considered the axis
subaracnoid space (part of meningies)
where does the cerebral fluid flow
distinguishes between abdomin and pelvic region
what does the sacral promonatory line tell u
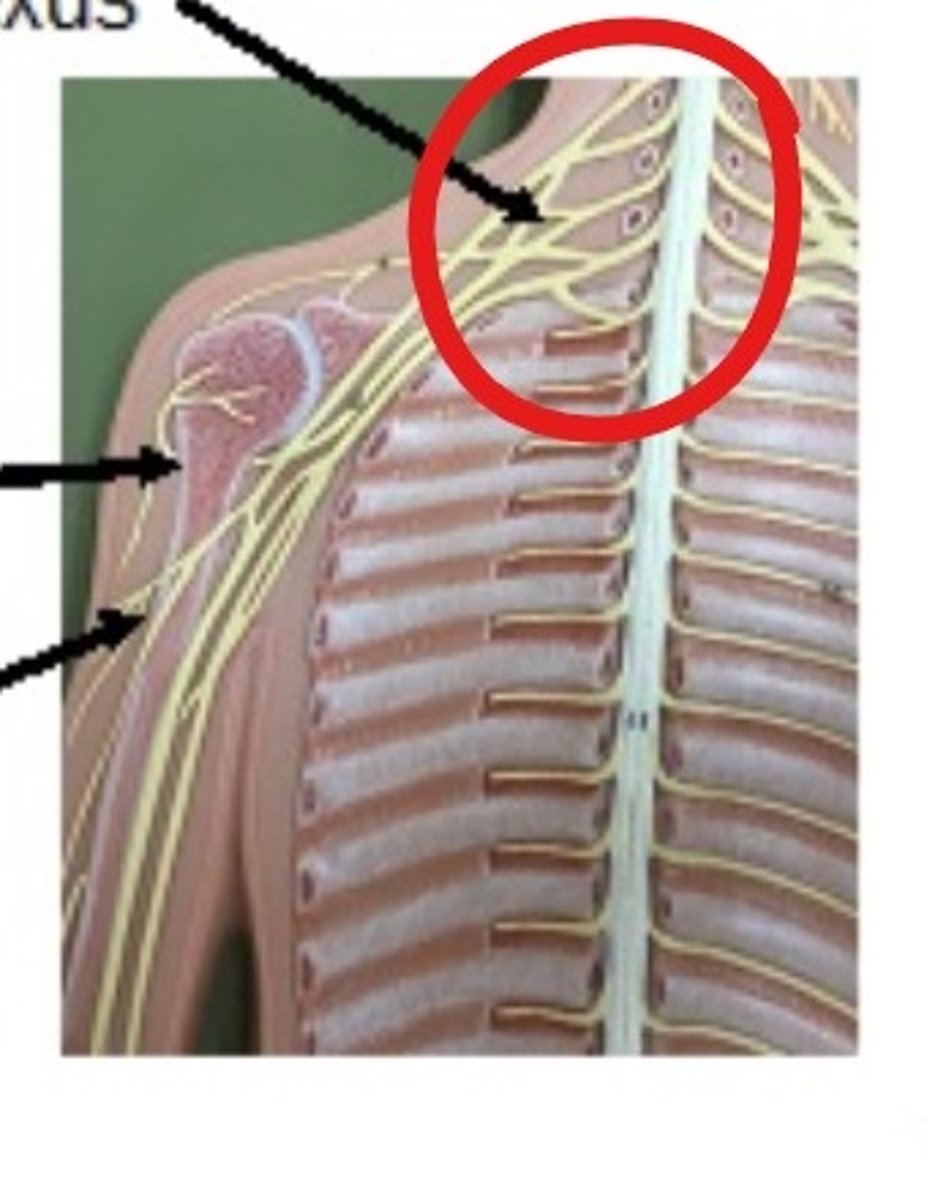
brachial plexis
L4-L5
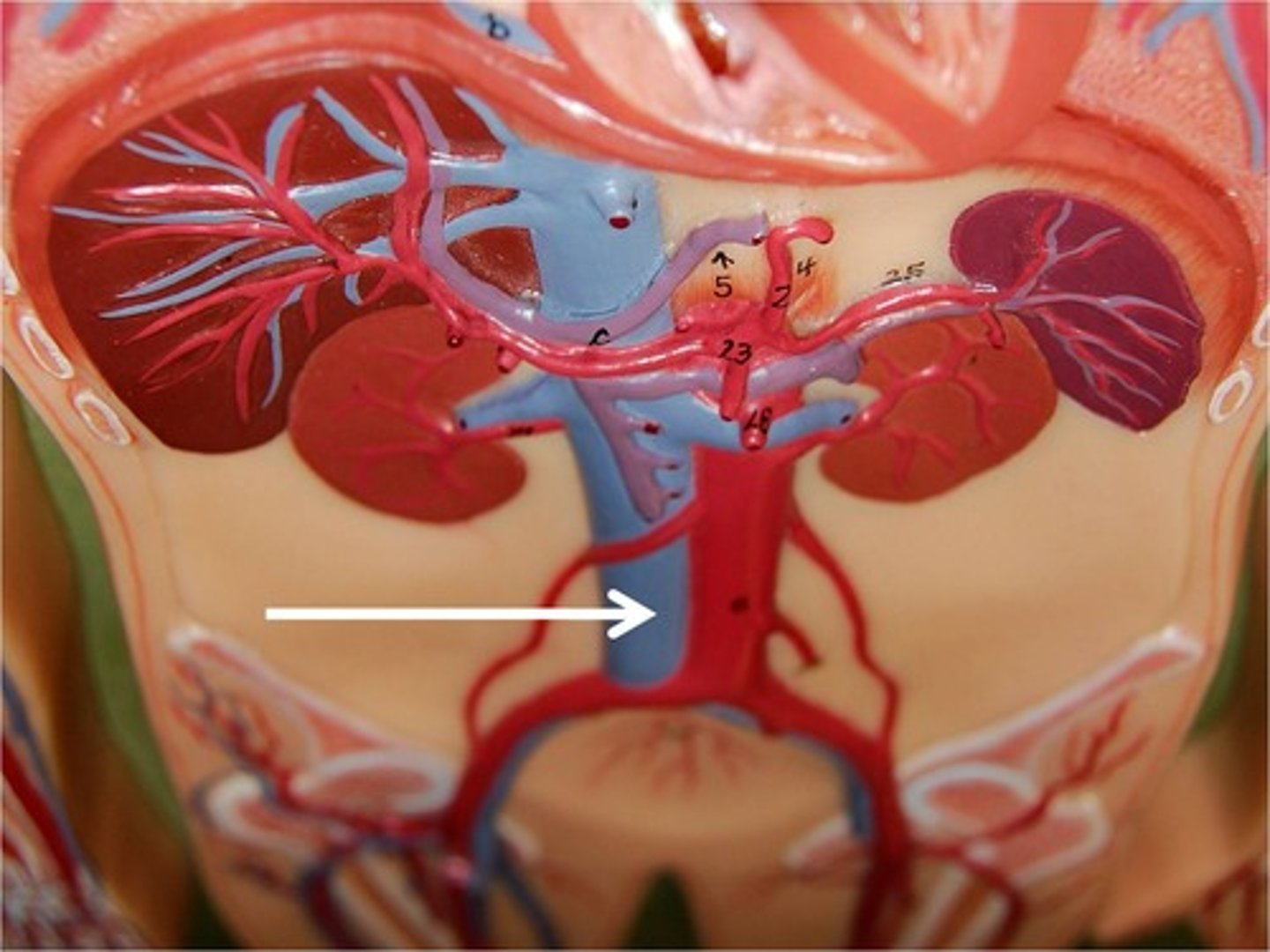
what level of vertebra is the inferior vena cava located
right atria
Where does the inferior vena cava dump its blood
inferior vena cava
transverse costal facets (articulations) where ribs attach to
what differenciates the T spine vertebra
big blocky vertebra to sustain body weight
what differenciates the L spine vertebra
hold head up
what is the purpose of C1
allows u to turn head
what is purpose of c2
c1
what vertebra is visually a flat bone
C7
which cervical vertebra is nonbifid
L1,L2
what level does spinal cord end
condus medullaris
what is the name of where the spinal cord ends
inferior vertebral notch
superior vertebral notch
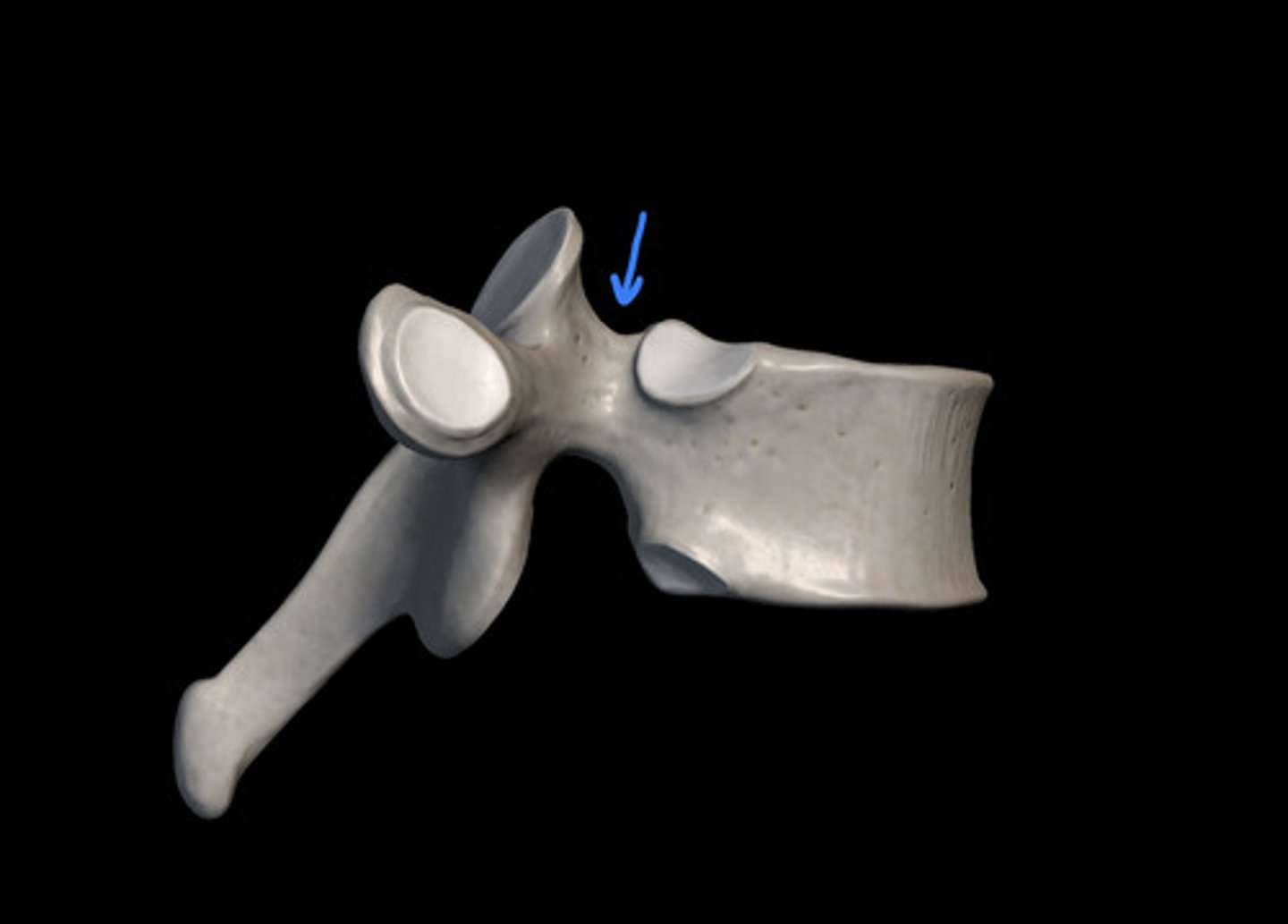
intervertebral foramen
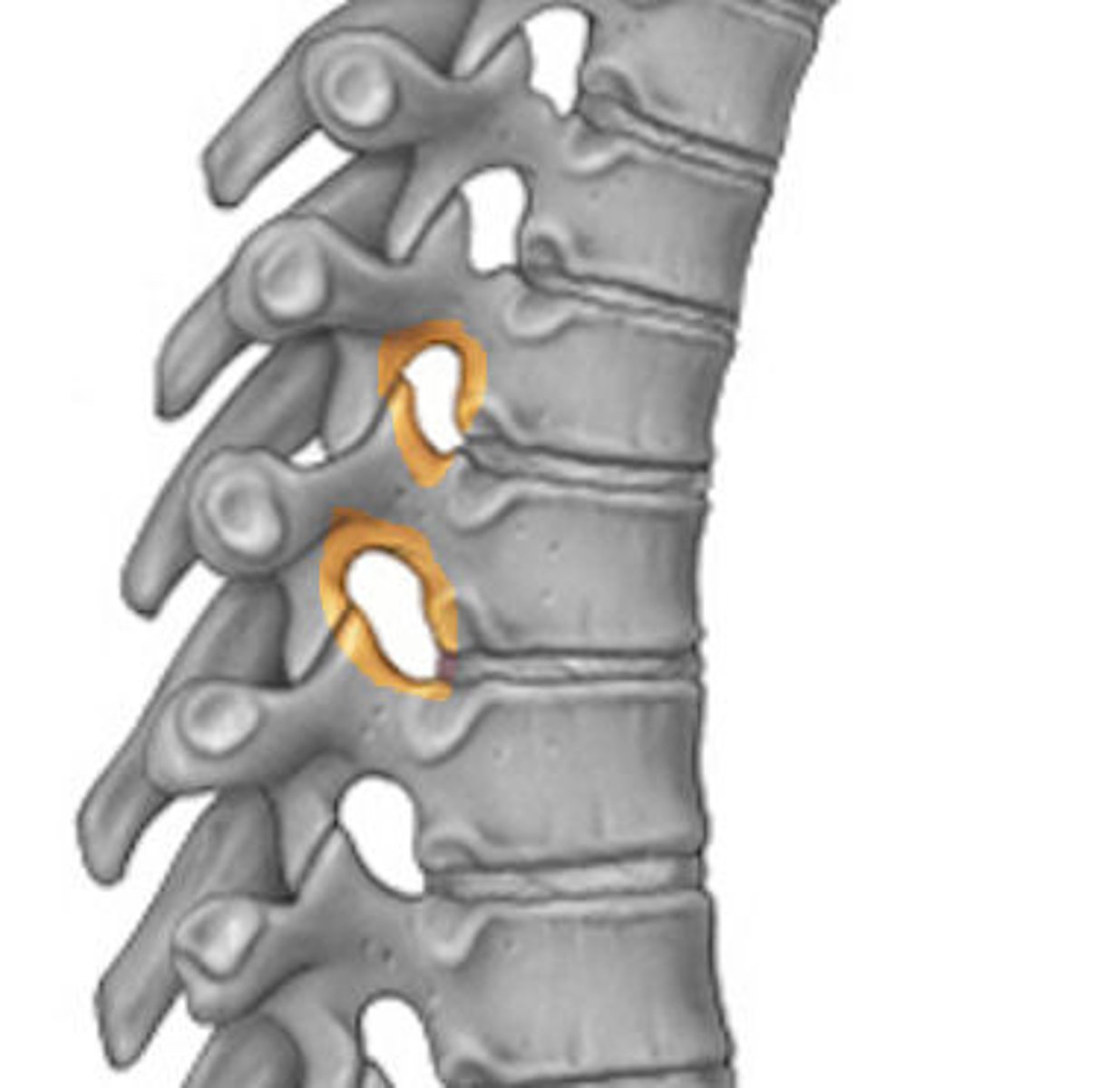
passage for spinal nerves
what is the purpose of the intervertebral foreman
31 pairs
how many spinal nerves are there
12 pairs
how many cranial nervers are there
cauda equina
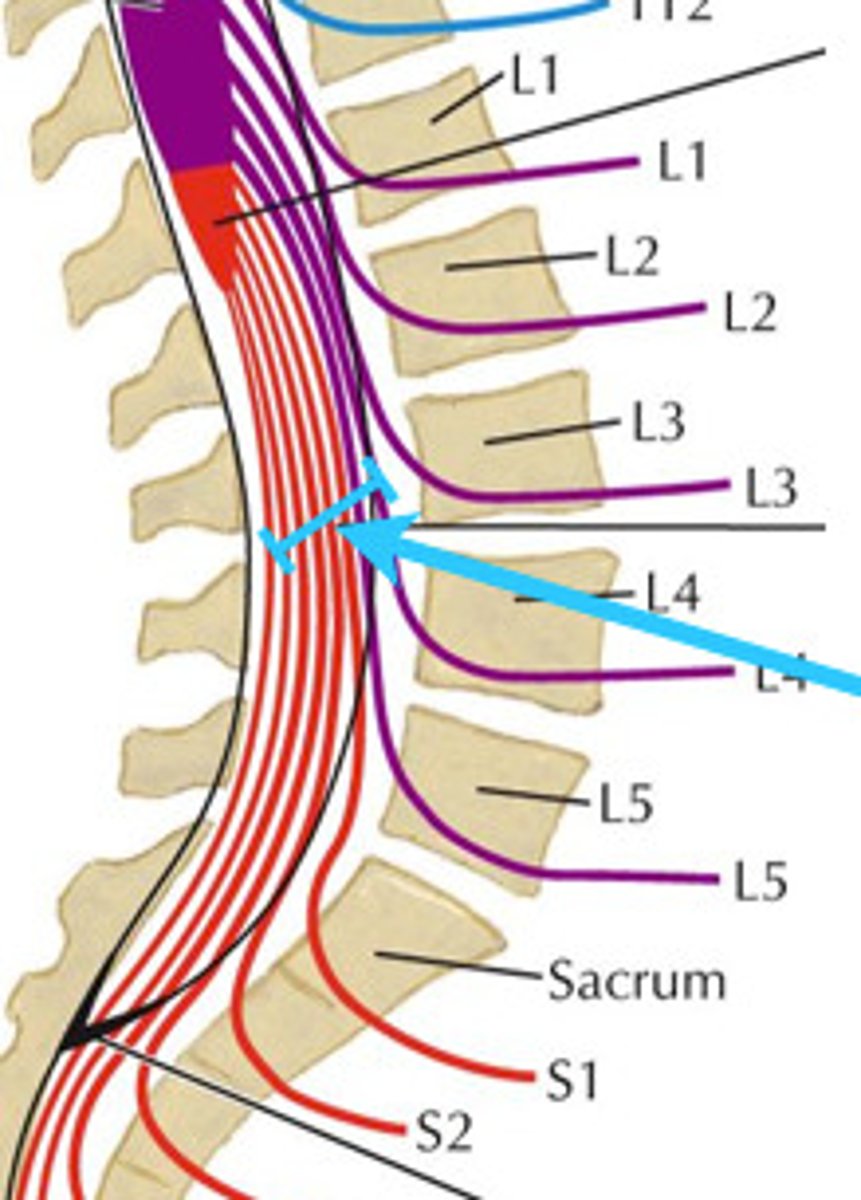
condus medullaris
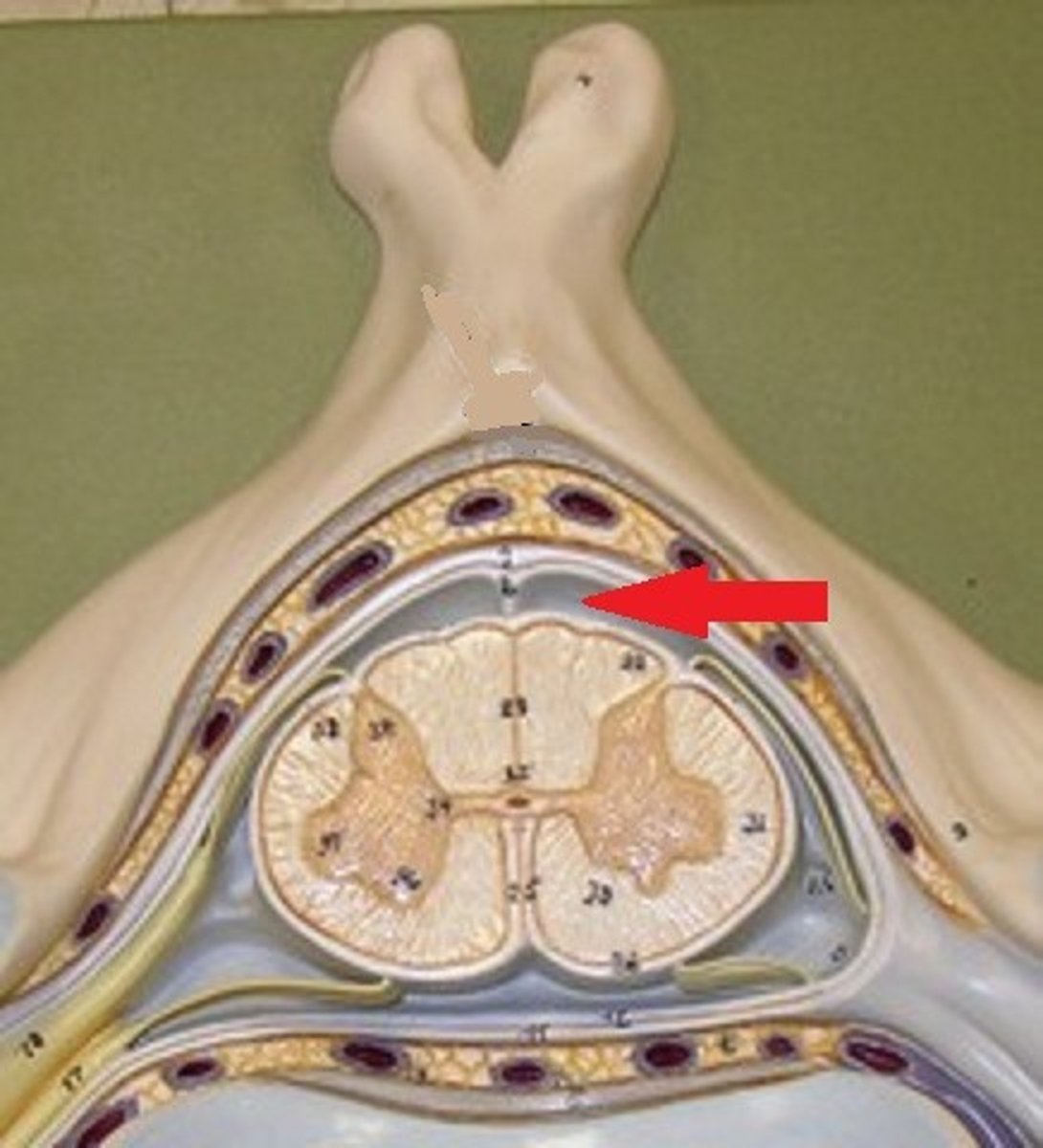
subarachnoid space anatomy
L1-L2
what vertebra is the condus medullarius located
subachnoid space
where does the spinal fluid flow
ventricles of the brain
Where is the cerebral spinal fluid made (non specific)
lateral, 3rd and 4th ventricle
what are the ventricles of the brain
chordoid plexius
where in the ventricles of the brain is the cerebral spinal fluid made
S2, dural/thecal sac
the cerebral spinal fluid travels all the way down to the
subarchnoid space
where does brain cancer metatisize to
false, no lymph system in brain
t/f: brain cancer metastisizes thru the lymph system
promonatory
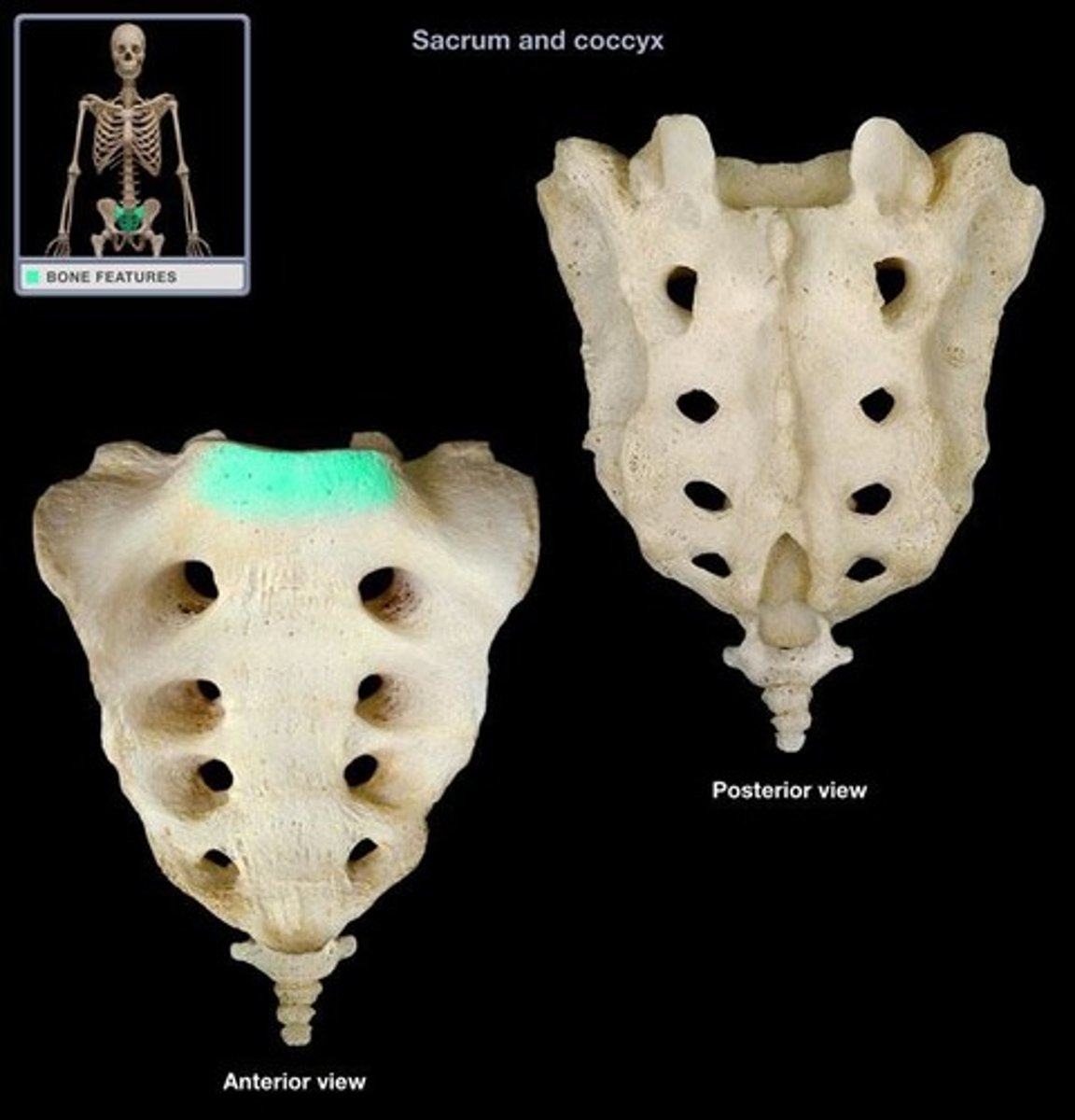
S1
what level is the promonatory located
sacral canal
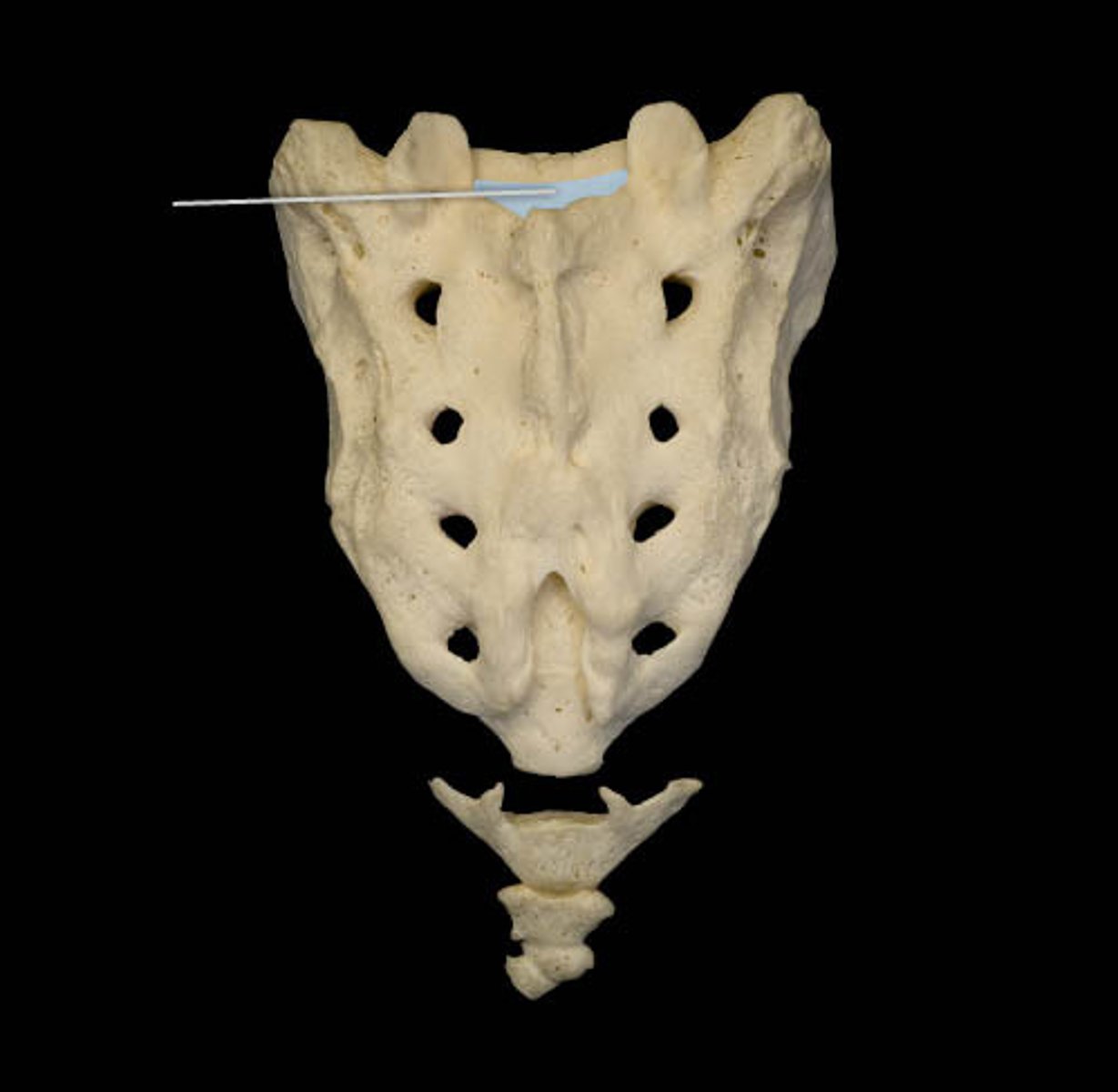
nerves coming from cauda equina, extension of vertebral formamen
what runs thru the sacral canal
true
t/f: rectum follows curve of the sacrum
true
t/f: there are lymph nodes that follow the curve of the sacrum
S1 down
what are the vertebral ranges for the pelvic region
s1 up til diaphram
what are the vertebral ranges for the abdominal region
diaphram to shoulder
what the ranges for the thoracic region
sigmoid colon and rectum
what part of the large bowl is in the pelvis
C7
what vertebra has the vertebral prominance
adontoid process (dens)
what structure allows for head rotation in C2
adontoid process (dens)
6000 cGy (whole)
td5/5 for brachial plexus
dural/thecal sac
what area is considered the end/termination of the spinal canal
S2
what level of vertebra is the dural/thecal sac located
S2 the dural/thecal sac
until what point does the subarchnoid space(where spinal fluid exists) flow down to
coccyx
can cause paralysis
what can happen if spinal cord is over eradiated (more then td55 of 4500cGy)
can cause neuropathy (numb and tingling down the hands)
what can happen if brachial plexius is over eradiated (more then td55 of 6000cGy)
covers that cover spinal cord and brain
what are the menengies
dura mater, archnoid mater, pia mater
what are the layers of the menengies from outer to inner
between the archnoid mater (under it) and the pia mater
where is the subarchnoid space in the menengies
gray mater spinal