Anatomy Revision
1/191
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
192 Terms
Anterior
Referring to the front of the body or structure, opposite of posterior.
Posterior
Referring to the back of the body or structure, opposite of anterior.
Inferior
Referring to a position below or lower than another part of the body, opposite of superior.
Superior
Referring to a position above or higher than another part of the body, opposite of inferior.
Midline
An imaginary line that divides the body into equal left and right halves, serving as a reference for anatomical position.
Lateral
Referring to a position farther from the midline of the body or towards the sides.
Medial
Referring to a position closer to the midline of the body or towards the center.
Distal
Referring to a position further away from the point of attachment or the trunk of the body.
Proximal
Referring to a position closer to the point of attachment or the trunk of the body.
Superficial
Closer to the surface of the body
Deep
Away from the surface of the body
Coronal plane
Plane seperating the body from front and back
Median plane
Plane splitting you right between the legs.
Sagittal plane
Plane splitting you vertically but can be uneven left and right sides.
Transverse plane
Horizontal plane splitting you across the hips.
How does air pass through to the lungs?
Nasal Cavity + Oral Cavity → Pharynx → Larynx → trachea → primary bronchi → lungs.
Which bones make up the roof of the nasal cavity?
Frontal bone (+ frontal sinus), sphenoid bone (+ sphenoid sinus) and ethmoid bone.
Is the nasal cavity anterior or posterior to the nasopharynx?
The nasal cavity is anterior to the nasopharynx.
What does the oral cavity do for speech?
Shapes the sounds eg. tonuge, jaw and lips.
What does the pharynx do for speech?
Alters resonance, oral vs nasal.
What’s the main driver of respiration?
Diaphragm
How does the diaphragm change when contracted?
It goes into a flat shape, when relaxed it turns into a bendy banana shape.
What nerve supplies the diaphragm?
Phrenic nerve.
What does the larynx do for speech?
Adds vibration.
Where is the oesophegus?
Continuous with the inferior border of the pharynx and is posterior to the trachea.
What does the larynx do?
Helps in speaking and breathing. Prevents food and drink entering the airway. Effortful closure. Swallowing.
What is the main function of the respiratory system?
Exchange gases between internal and external environments.
Air conduction system.
Airways purify, warm and humidify.
Alveolar gas exchange.
Acidity regulation of the blood.
Where is the pharynx?
13cm long funnel extending from the internal nares (internal nostrils) to the larynx.
What is the function of the pharynx?
Passage for air and food.
Resonating chamber for speech.
Houses the tonsils.
Contains the orifices from the Eustachian tubes.
Where do the Eustachian tubes connect to?
From the orifices in the pharynx to the middle ear.
Where is the oropharynx?
Velum is above, hyoid bone is below.
Where is the laryngopharynx?
Bounded anteriorly by the epiglottis and inferiorly by the esophagus.
Where is the nasopharynx?
Space above the soft palate. Bounded posteriorly by the occipital bone and by the nasal conchae is front. Also contains the orifice of the Eustachian tube.
Where is the hard palate?
Roof of the mouth.
Where is the velum?
Velum is the soft palate, so just behind the hard palate.
What is epithelial tissue?
Outer layer of mucous membranes and the cells in our skin, lining of body cavities and all the tubes in our body. Protective layer. In vocal folds, it keeps the tissues from becoming dehydrated.
What is the trachea?
Tube that runs from inferior border of larynx into mainstem bronchi which serve left and right lungs.
What are the main bronchi?
Left and right mainstem bronchi branch off from the trachea to serve left and right lungs.
Where is the Esophagus?
Posterior to the trachea.
What is the Esophagus?
Long collapsed tube running behind the trachea. It’s collapsed except when occupied by a bolus of food.
What is the ethmoid bone?
Complex structure in the cranial, nasal and orbital spaces. If the cranium were an apple, the ethmoid would be the core.
What is the sphenoid bone?
At the base of the cranium, behind the eye and below the front part of the brain. Two lateral wings and two sinuses.
What is the mandible?
Jawbone. Lower jawbone in mammals.
What is a sinus?
A gap in the bone where air resides.
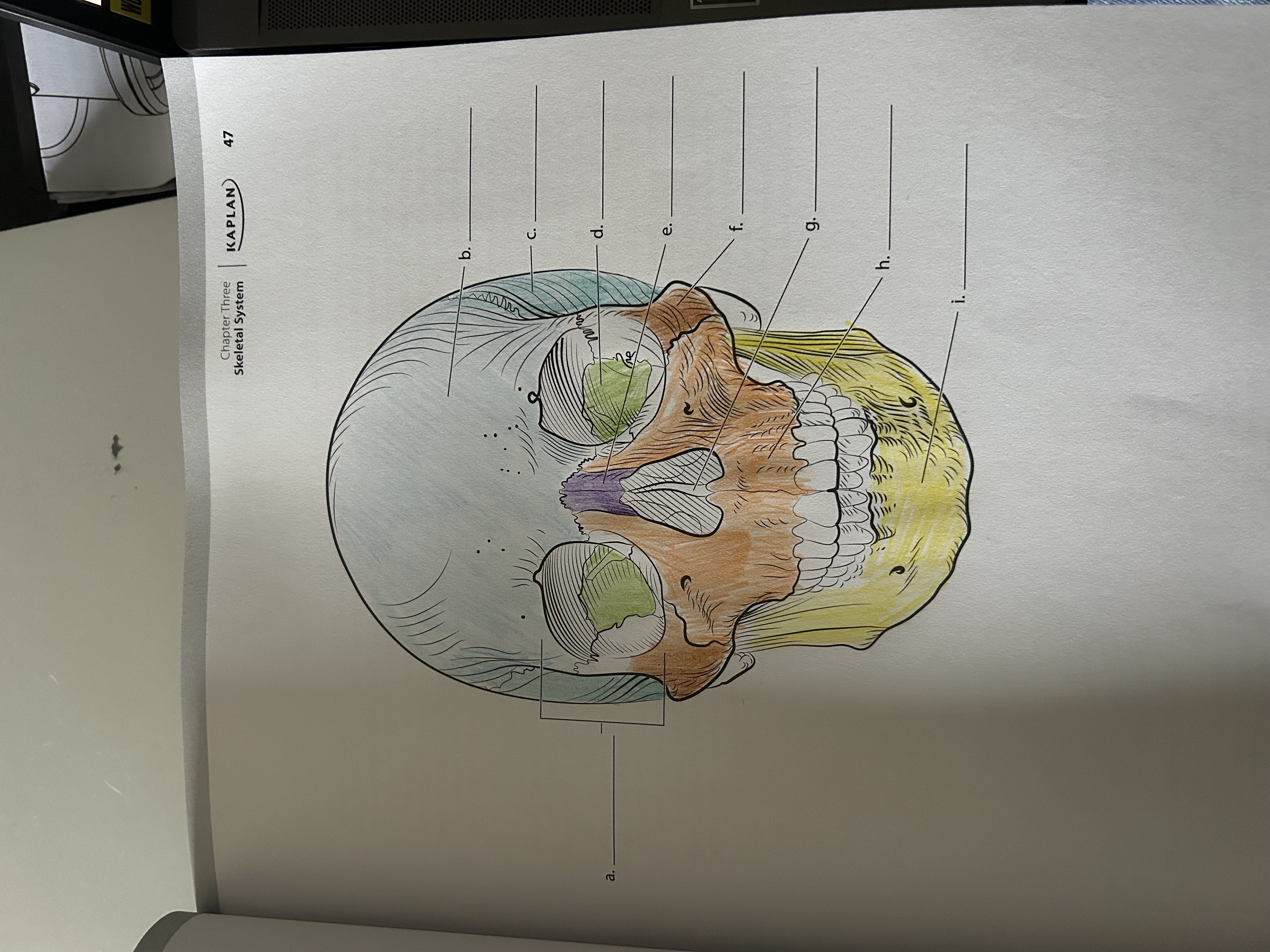
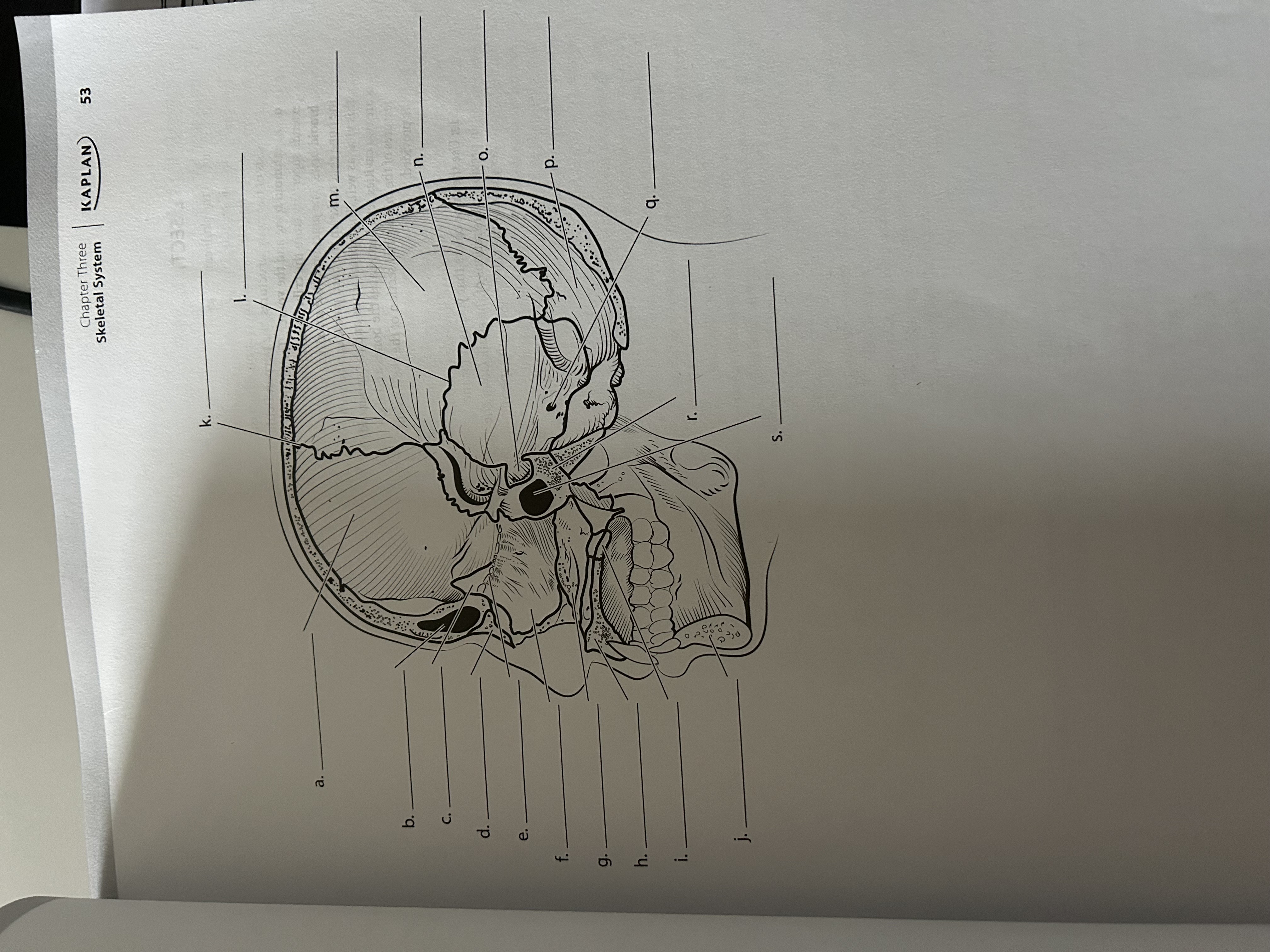
Where is the frontal bone?
b

Where is the parietal bone?
b

Where is the parietal bone?
h

Where’s the temporal bone?
d
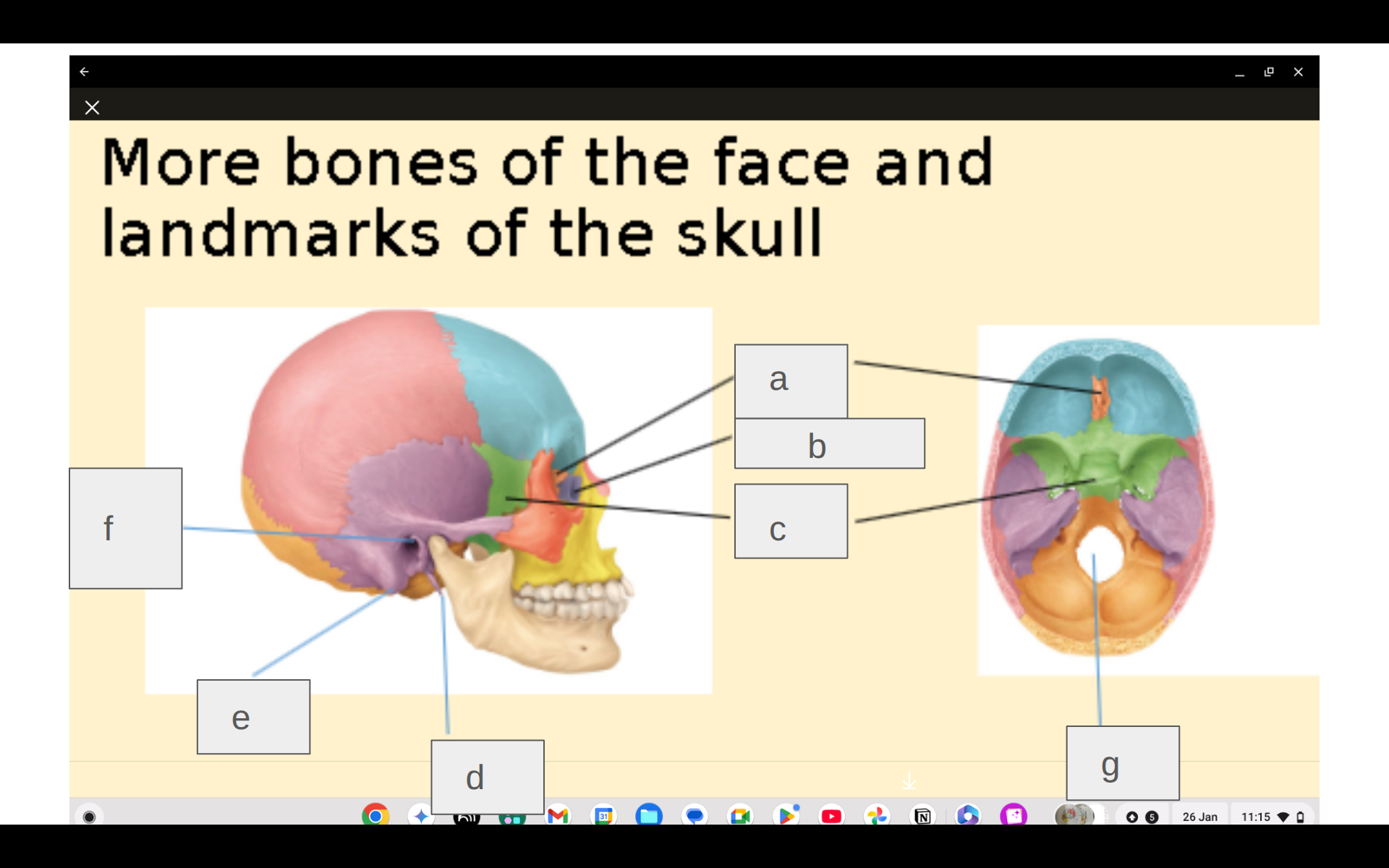
Where is the ethmoid bone?
a

Where is the maxilla?
m

Where is the mandible?
l

Where is the sphenoid bone?
q

Where is the mastoid process?
i
Where is the frontal sinus?
b
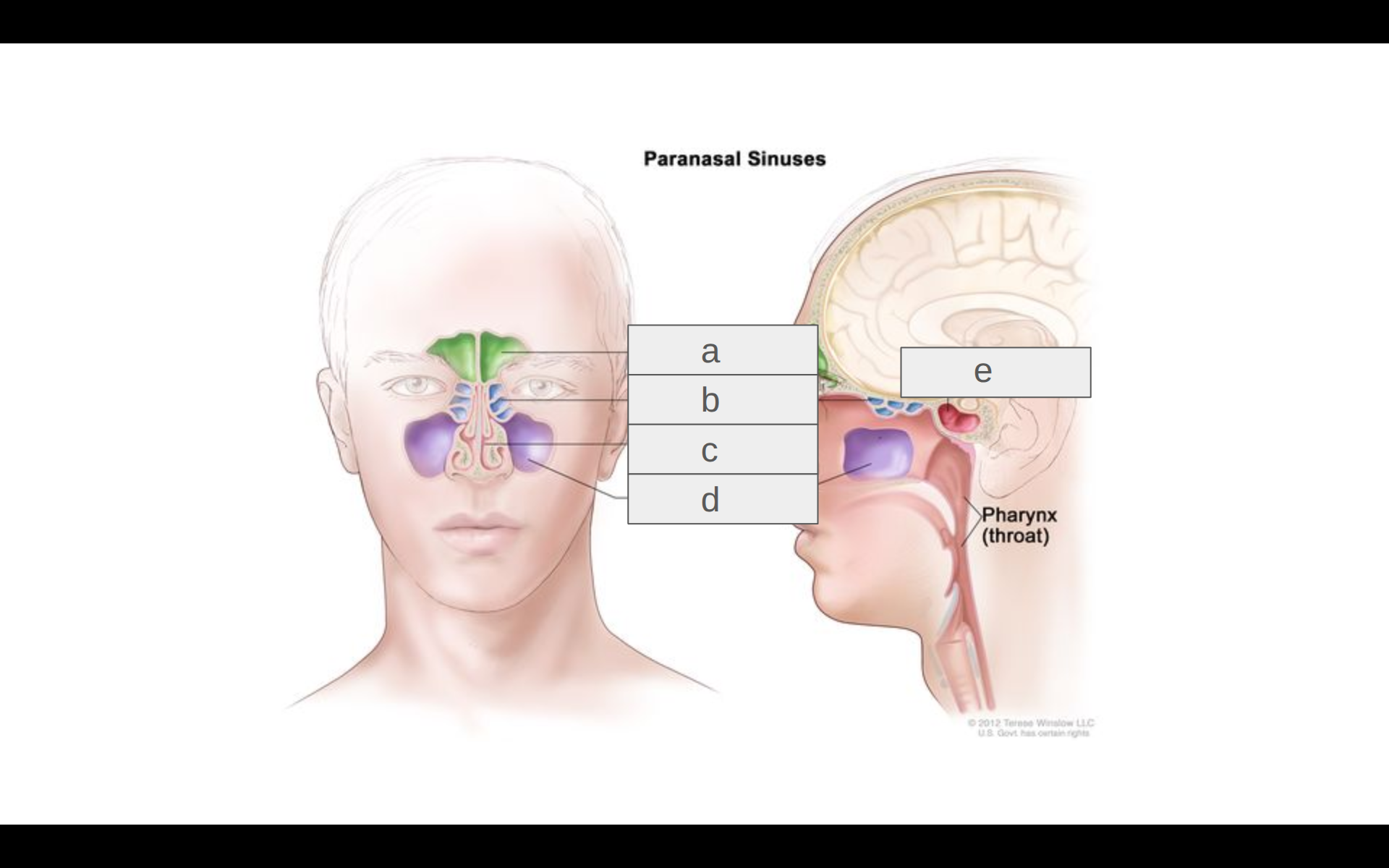
Where is the maxilliary sinus?
d
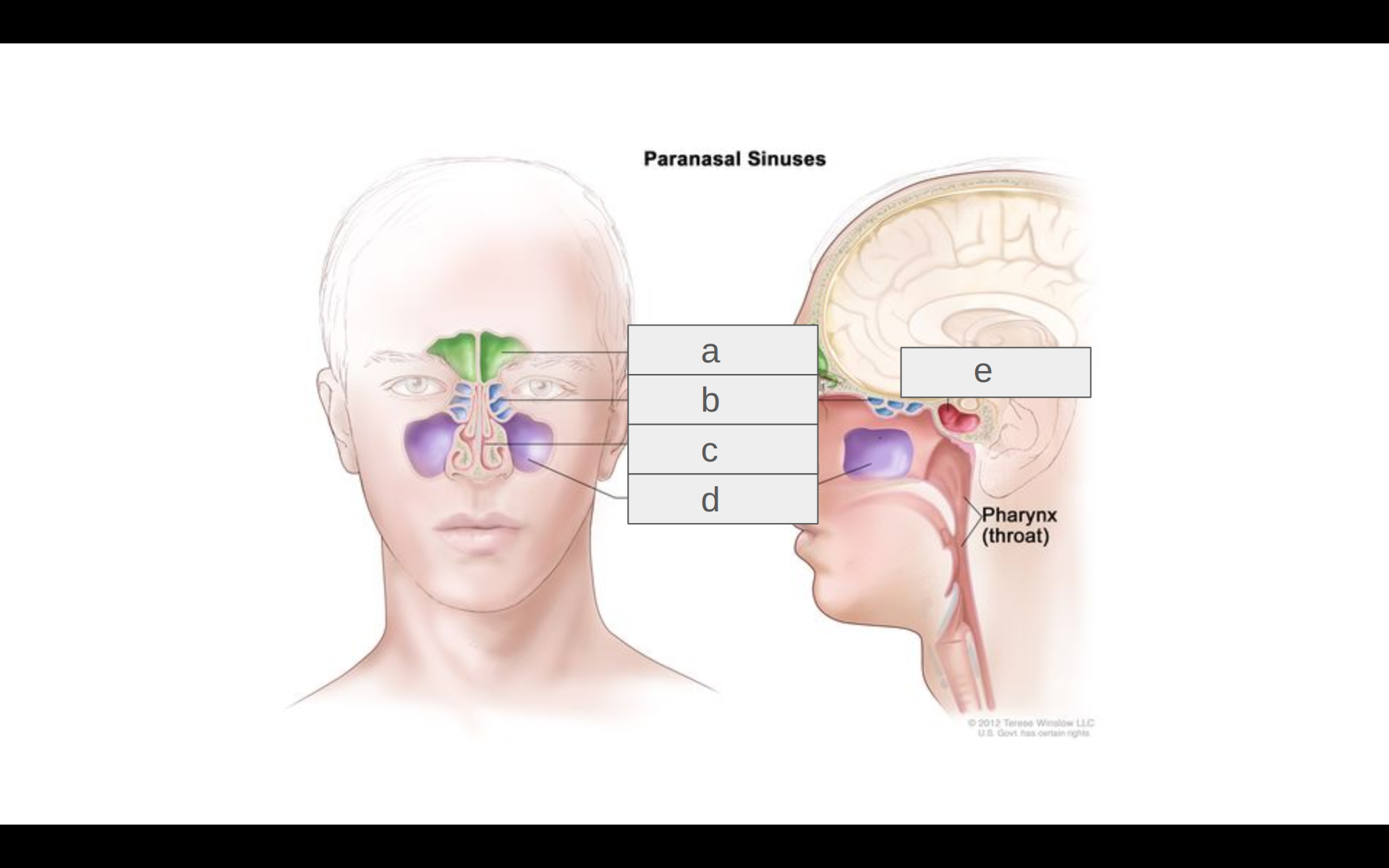
Where is the ethmoid sinus?
b
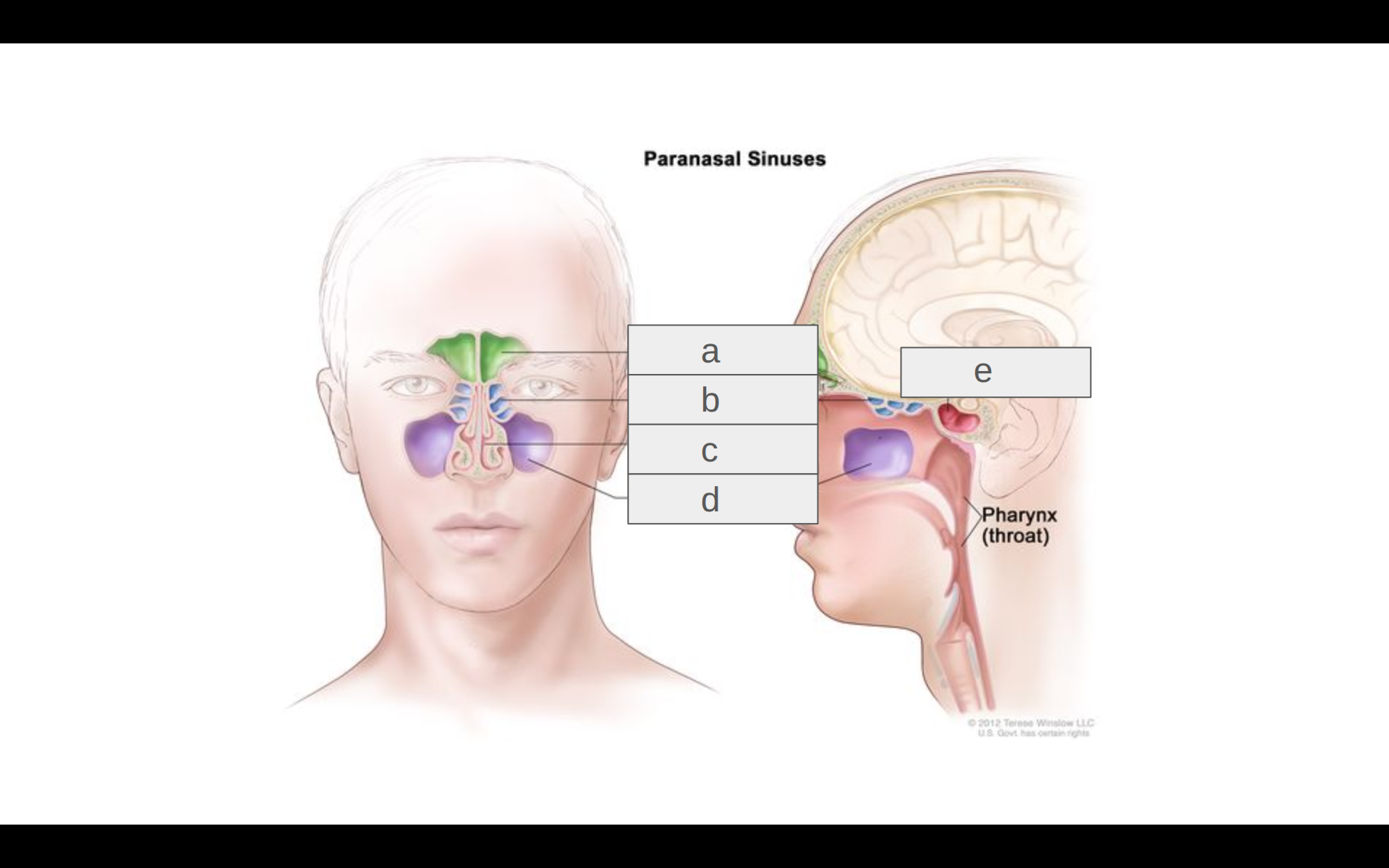
Where is the sphenoid sinus?
e
What is the nerve supply to facial muscles?
Facial nerve - VII
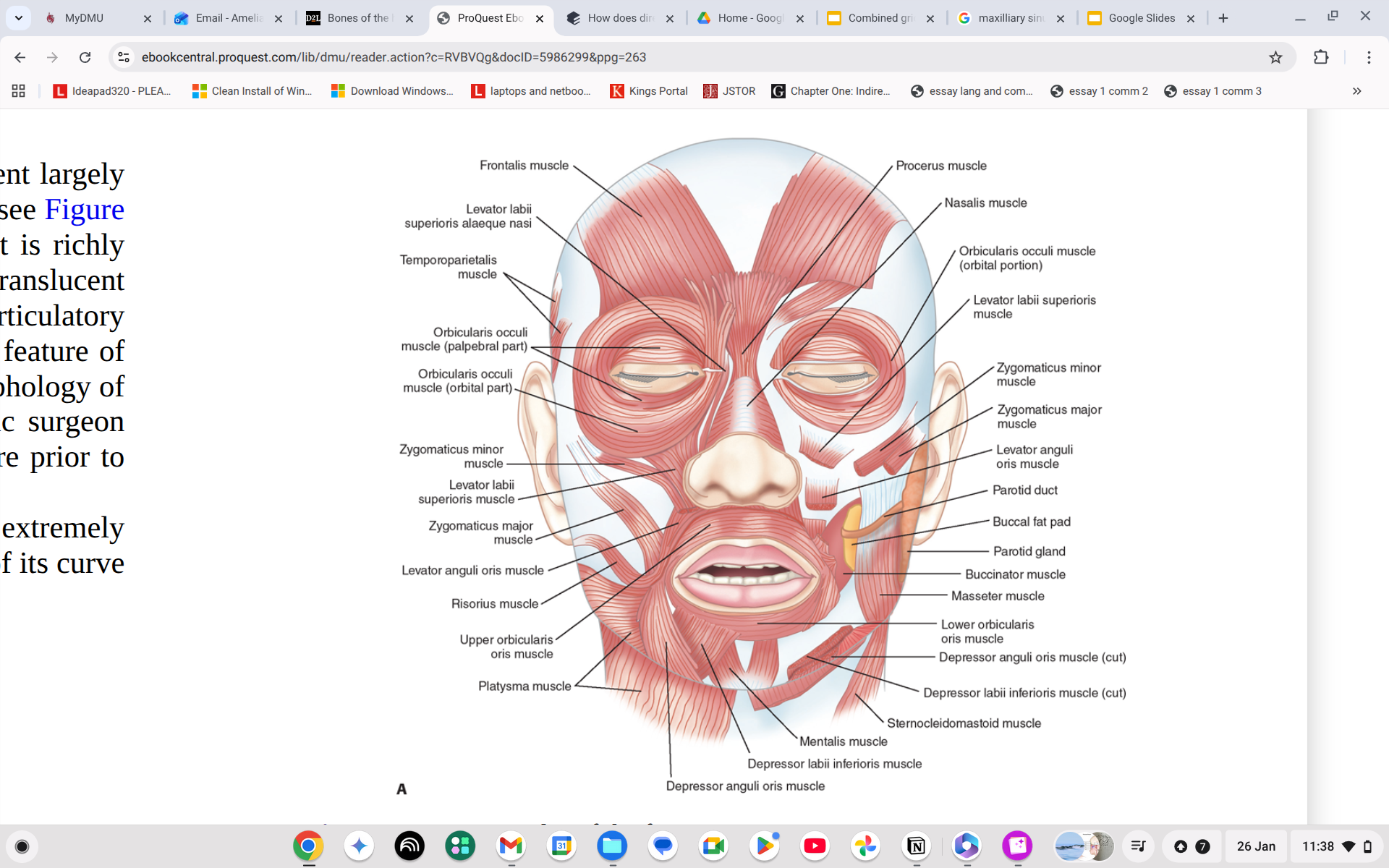
Where is the levator labii superioris?
Just to the sides of the nose
What does the Levator labii superioris do?
Elevates the upper lip
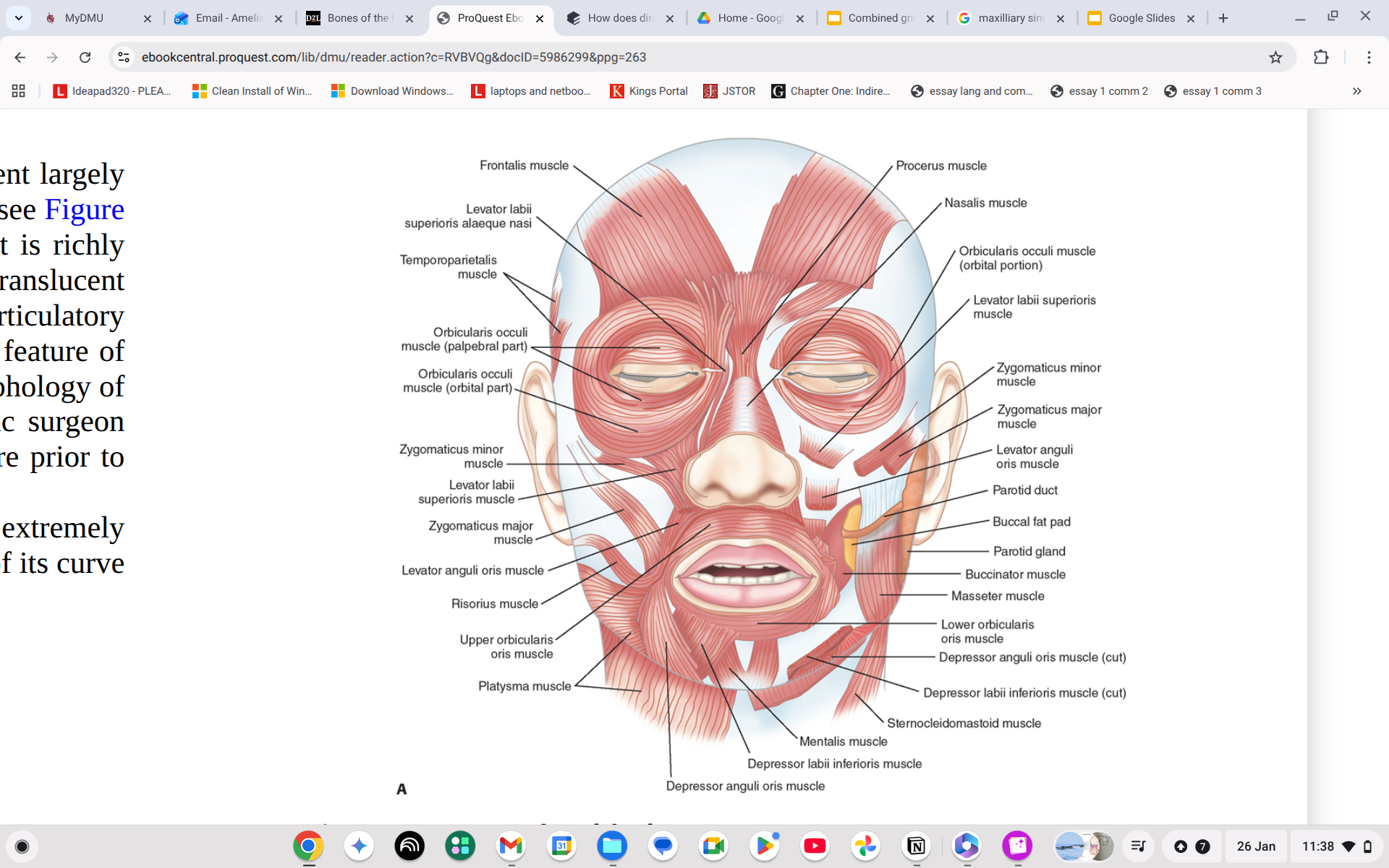
Where is the Depressor anguli oris?
Straight line across your jaw
What does the Depressor anguli oris do?
Depresses the corner of the mouth.
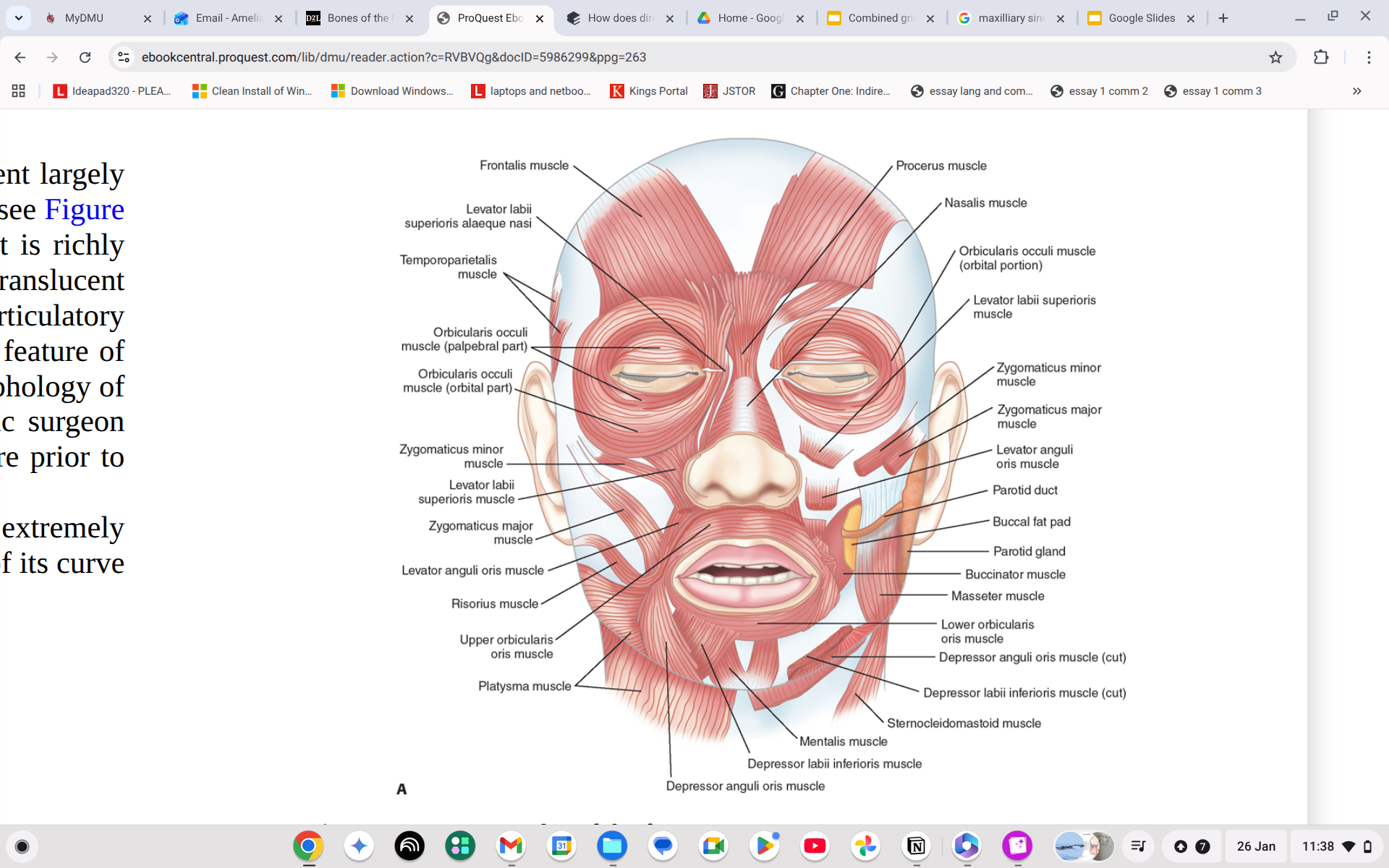
Where is the Depressor labii inferioris?
Just above the anguli oris, on top of jaw bone parallel to it.
What does the Depressor labii inferioris do?
Pulls the lips down and out.
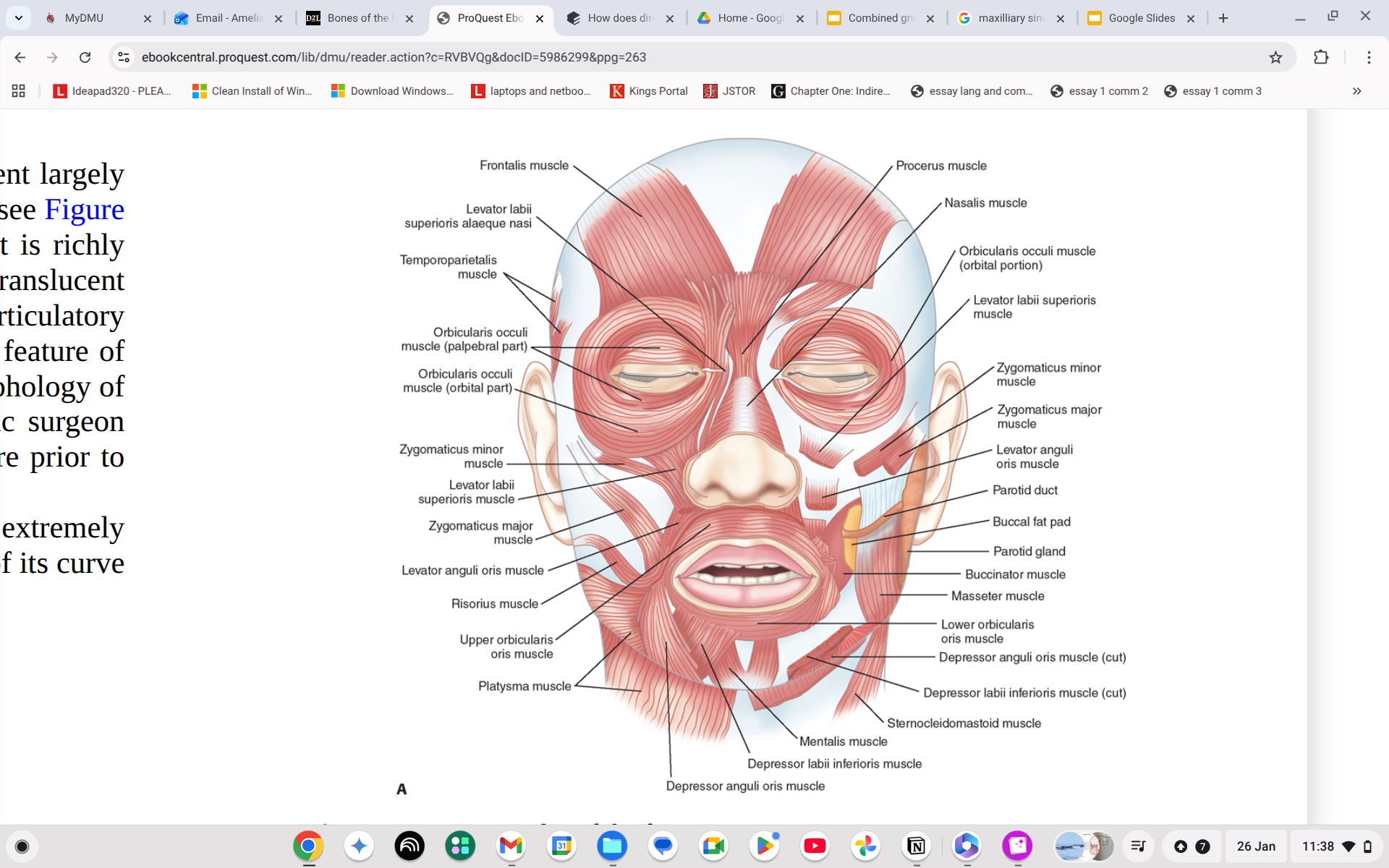
Where is the Levator anguli oris?
Side of your moustache area, like biker tash
What does the Levator anguli oris do?
Draws the corner of the mouth up and medially.
What does the buccinator do?
Move food onto the grinding surfaces of the molars.
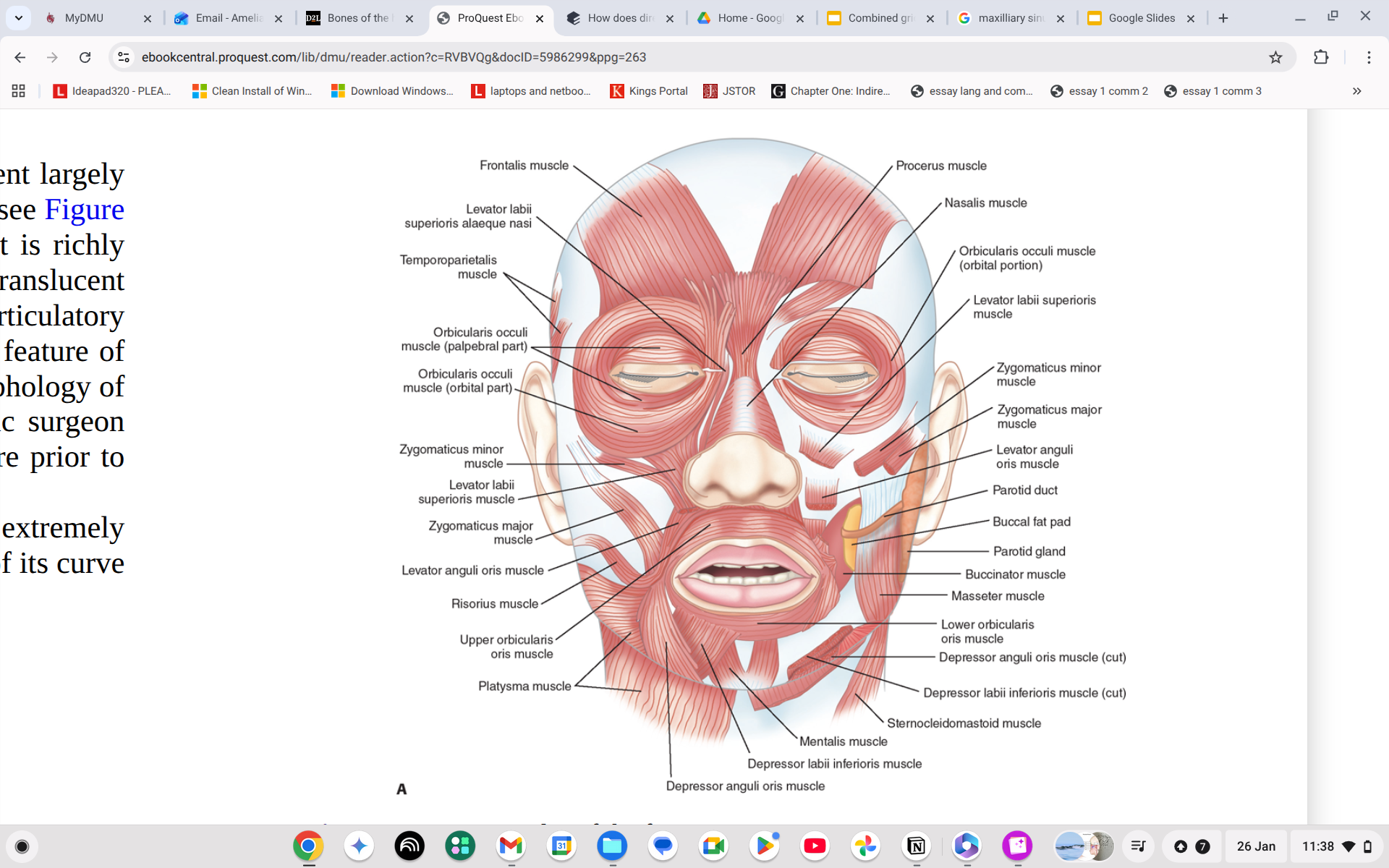
Where is the buccinator?
Just below and to the left of your dimples.
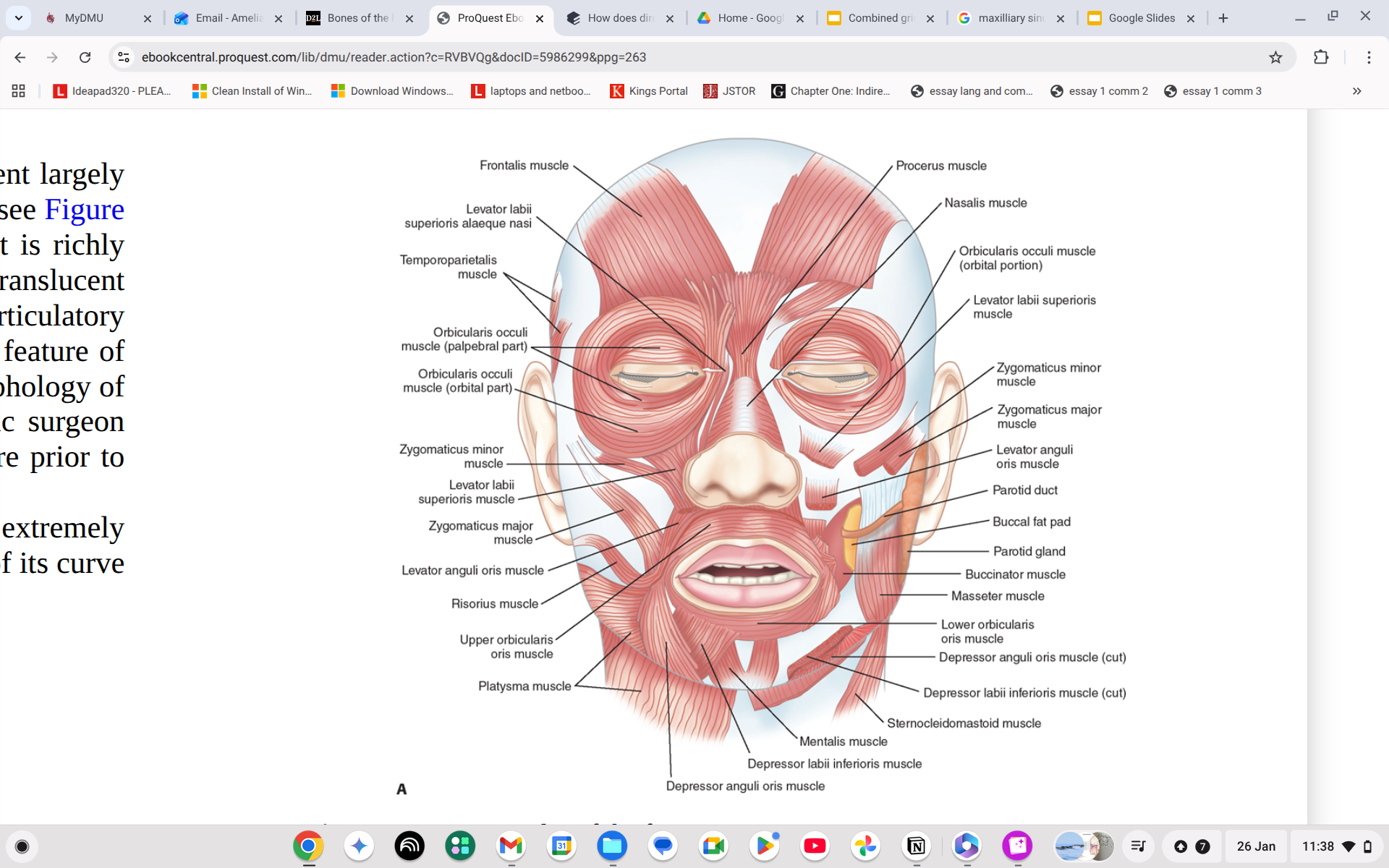
Where is the Orbicularis oris?
Circle around your lips.
What does the Orbicularis oris do?
Pull lips closer together to create a seal.
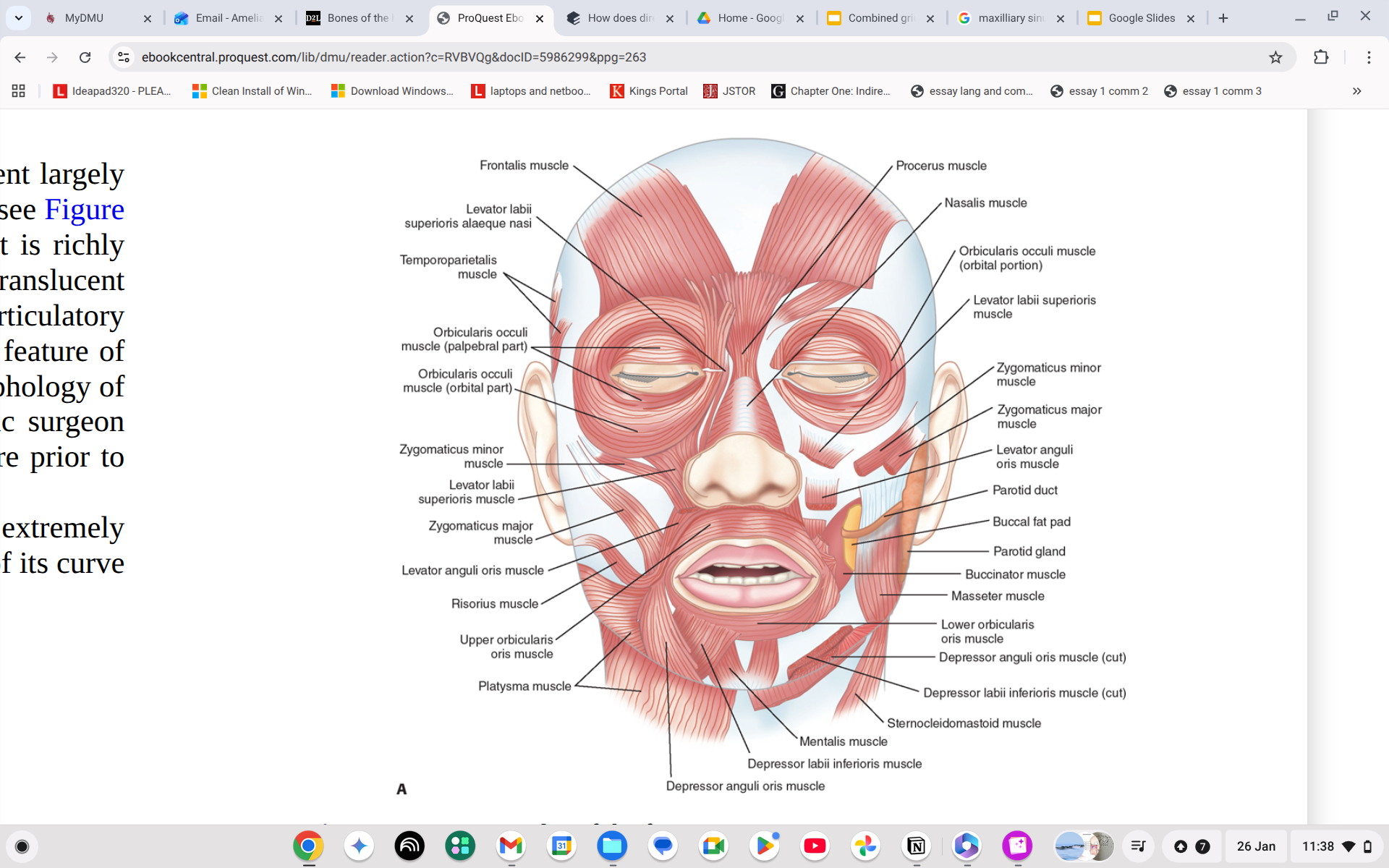
Where is the risorius?
Side of the moustache going from corner of mouth to ear.
What does the risourius do?
Retract lips at the corner to smile or grin.
Where is the zygomaticus?
Major is from corner of mouth to top of ear, minor is from side of nose meeting the major one just below.
What does the Zygomaticus do?
Elevates and retracts the angle of the mouth, smiling.
Where is the mentalis?
V shape on your chin
What does the mentalis muscle do?
Wrinkles the chin and pulls lower lip out- pouting.
What are the functions of the nasal cavity?
Primary entrance for respiration, it warms, humidifies and filters air before it reaches the lungs.
Where is the velum?
It’s the soft palate, just behind the hard palace.
What does the velum do?
Used to differentiate between nasal sounds eg. m from n.
Where is your septum, and what does it do?
Dividing plate between nasal cavities. Divide, support and direct air.
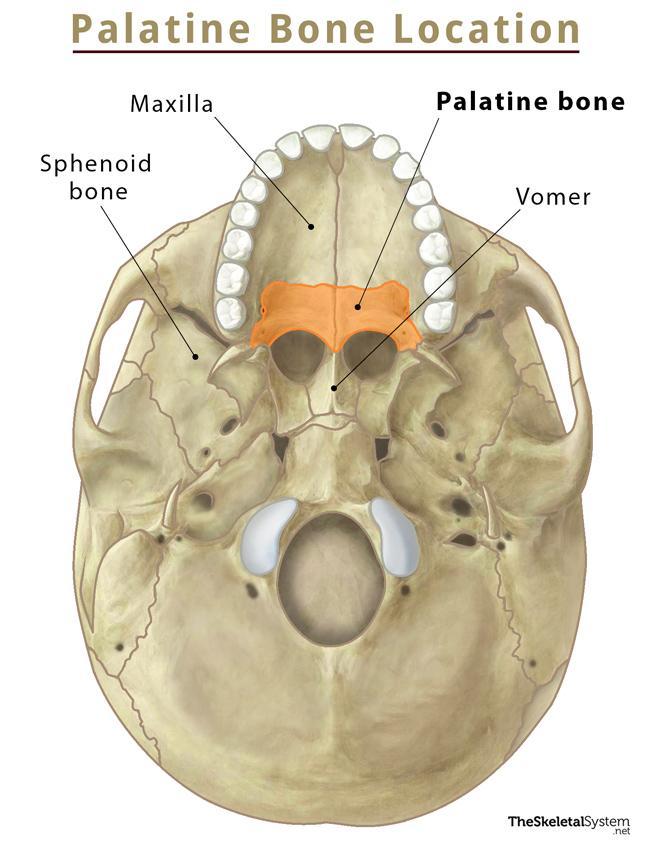
Where is the palatine bone?
Back of the nasal cavity, posterior part of the hard palate.
What are nasal chonchae (turbinates)?
Thin, curled ridges of bone.
Slow down the incoming air turbulence.
What does cilla do?
draw up mucus from the goblet cells in the epithelium to trap dirt, dust and foreign bodies.
Trap moisture from the outgoing air which is then evaporated by incoming air.
Pushes mucus into the pharynx where it can be swallowed away.
Where is the palatine process of maxilla?
Forms most of the hard palate on your maxilla.
Where is the lingual frenulum?
Under your tongue, small flexible fold of mucous membrane.
What is it called when there is an issue with your lingual frenulum?
Tongue-tie, ankyloglossia.
What is the palatine raphe?
The raised ridge running along the midline of the hard palate.
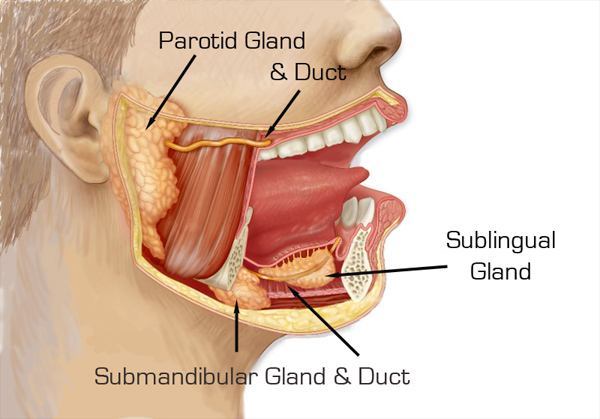
Where is the sublingual duct?
Under the tongue. Little pocket of beans under the tongue.
What does the sublingual duct do?
Adds mucus for lubrication, aiding food passage and oral health.
Where is the sublingual vein?
On the underside of the tongue.
What does the sublingual vein do?
Drains blood from the tongue.
What is the nerve supply to the parotid gland?
Number 9 - only 9 beans.
What is the nerve supply to the submandibular gland?
Number 7
What is the nerve supply to the sublingual gland?
Number 7.
Where is the submandibular gland?
Under your jaw.
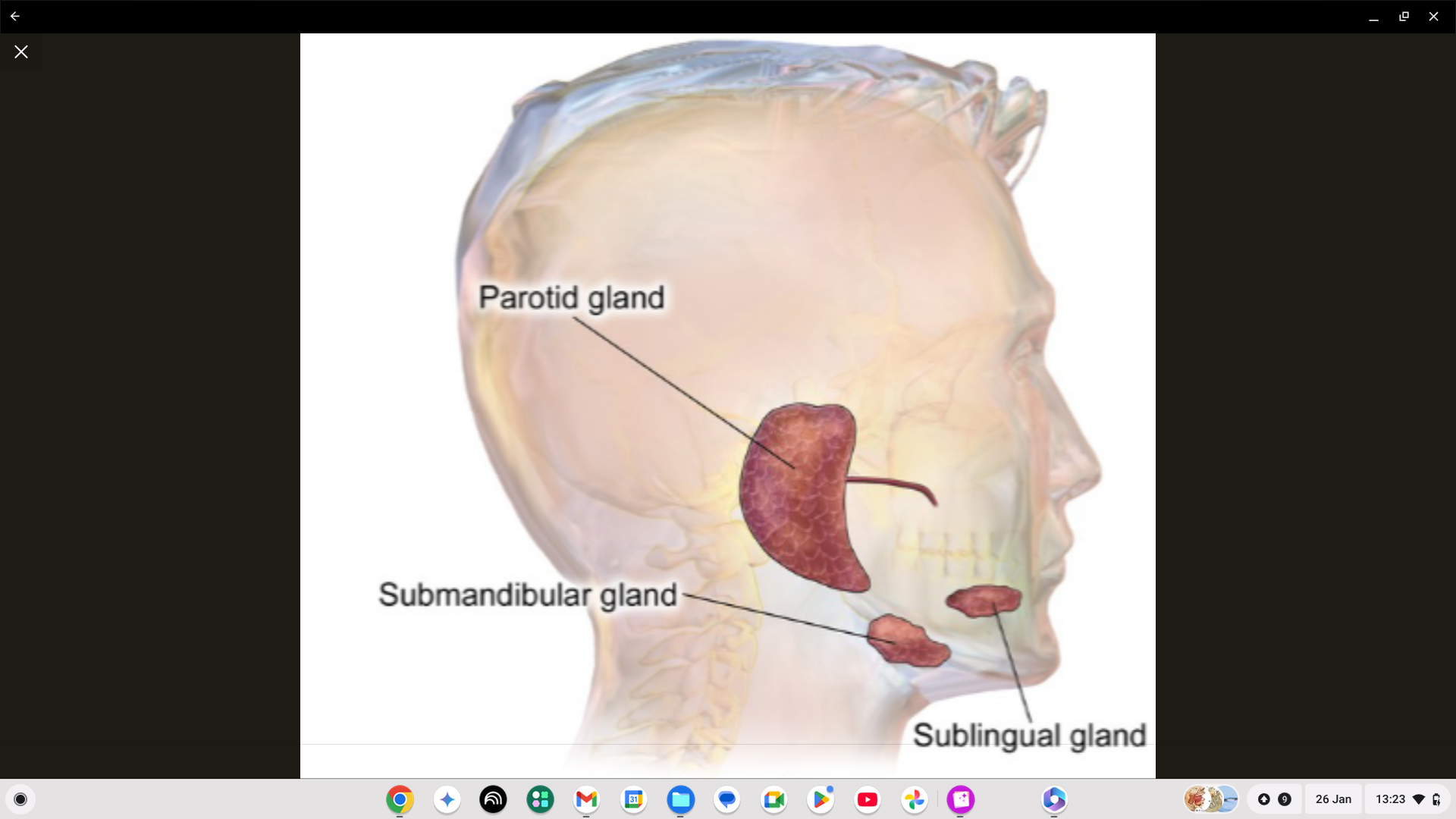
Where is the sublingual gland?
Under your tongue.
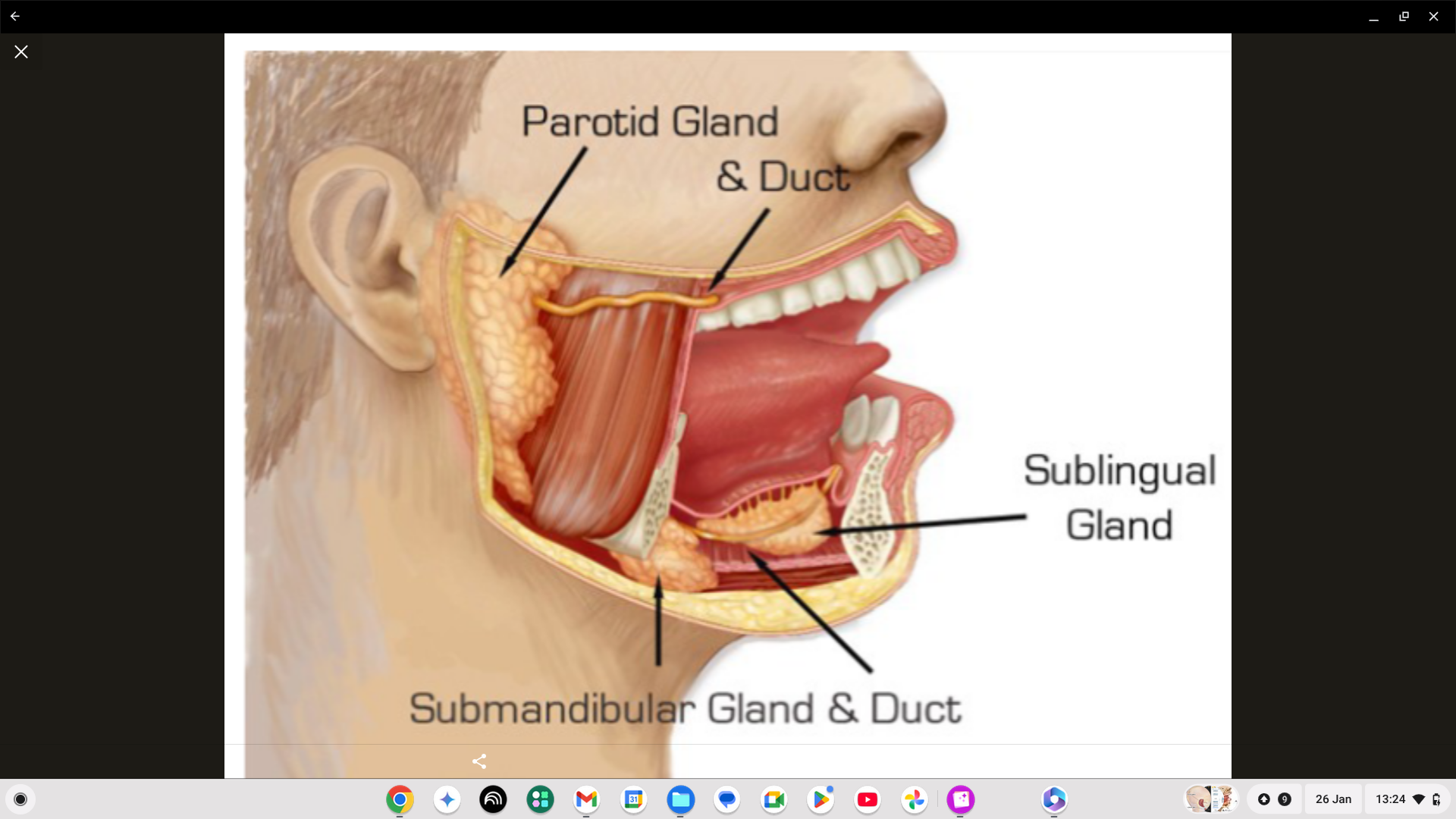
What does the submandibular gland do?
Produces saliva.
What does the sublingual gland do?
Produces mucus rich saliva to moisten food for swallowing and lubricate the mouth.
What are the key features of intrinsic muscles of the tongue?
Not attached to any bone
Change shape of tongue for speech and swallowing
Vertical and transverse fibres.
What type of fibres cause tongue tip elevation and deviation?
Superior longitudinal fibres.