AP Psych Unit 1: Part 2 Sensation and Perception
1/76
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
77 Terms
parallel processing
The ability of the brain to simultaneously process incoming stimuli of differing quality. Parallel processing is associated with the visual system in that the brain divides what it sees into four components: color, motion, shape, and depth

sensation
what occurs when a stimulus activates a receptor
perception
the organization of sensory information into meaningful experiences

absolute threshold
the weakest amount of a stimulus that a person can detect half the time

Just noticeable difference threshold
the smallest change in a physical stimulus that can be detected between two stimulus

Weber's law
the principle that the layer or stronger a stimulus, the larger the change required for an observer to notice a difference

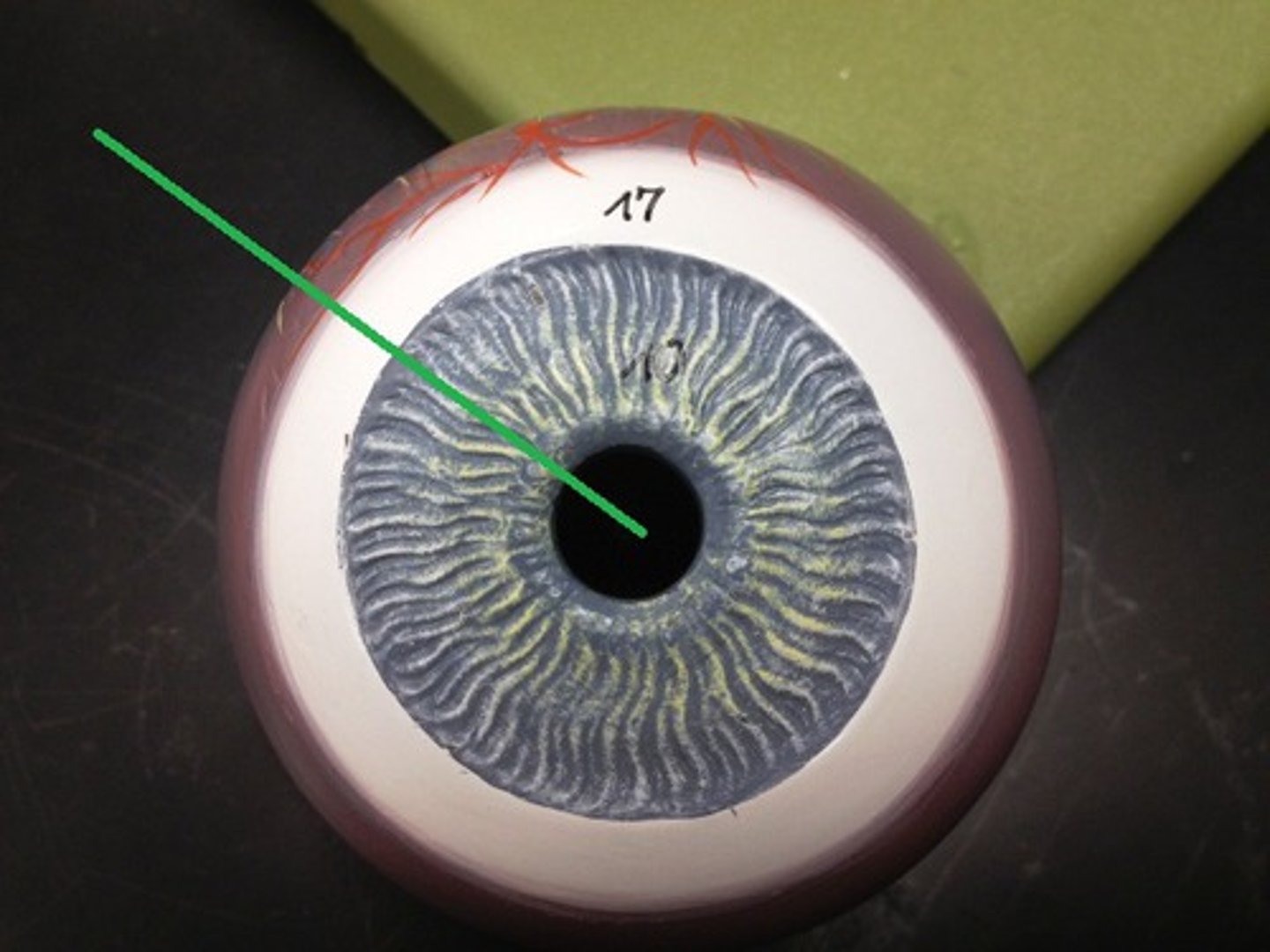
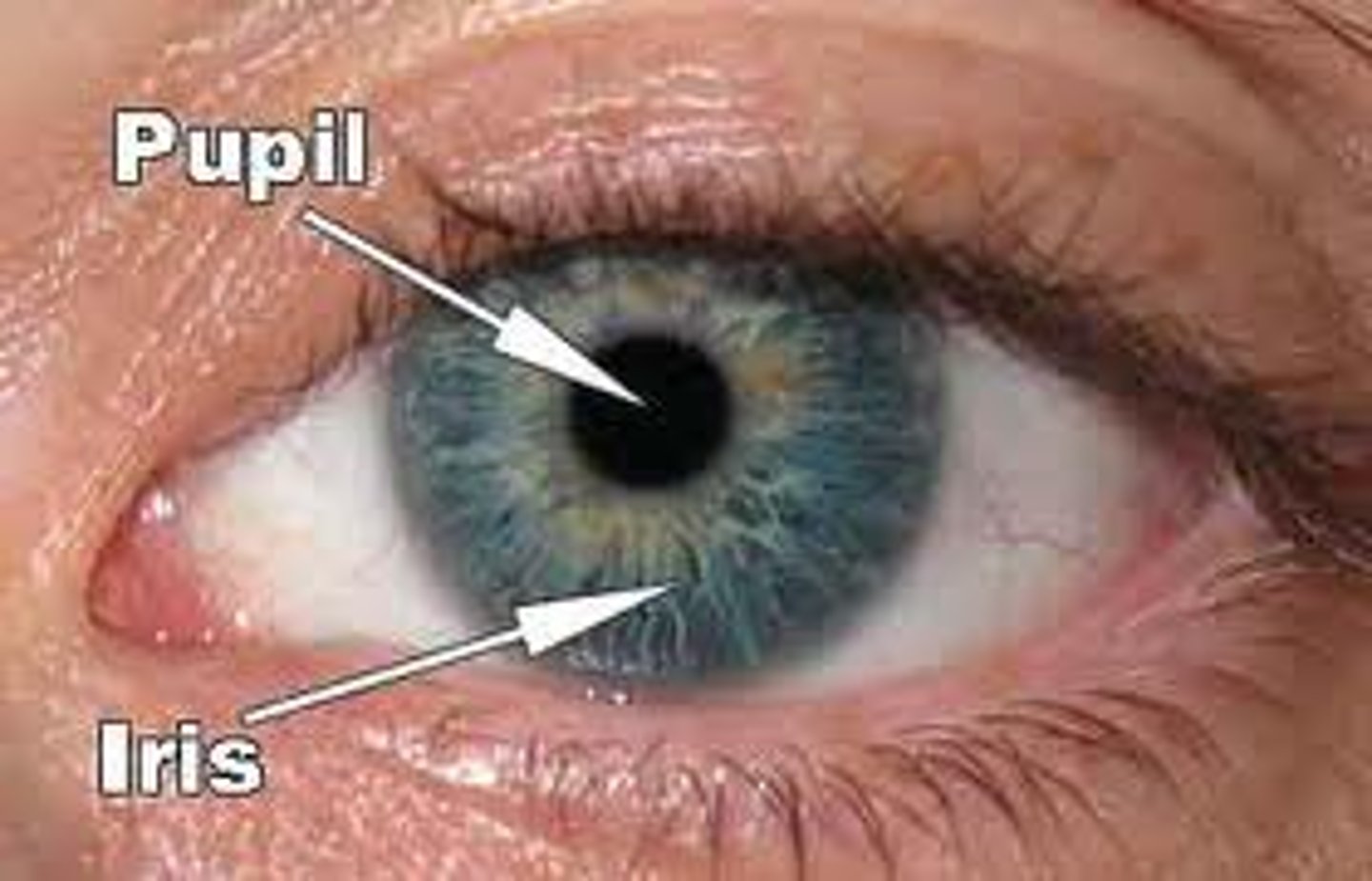
pupil
the opening in the iris that regulates the amount of light entering the eye
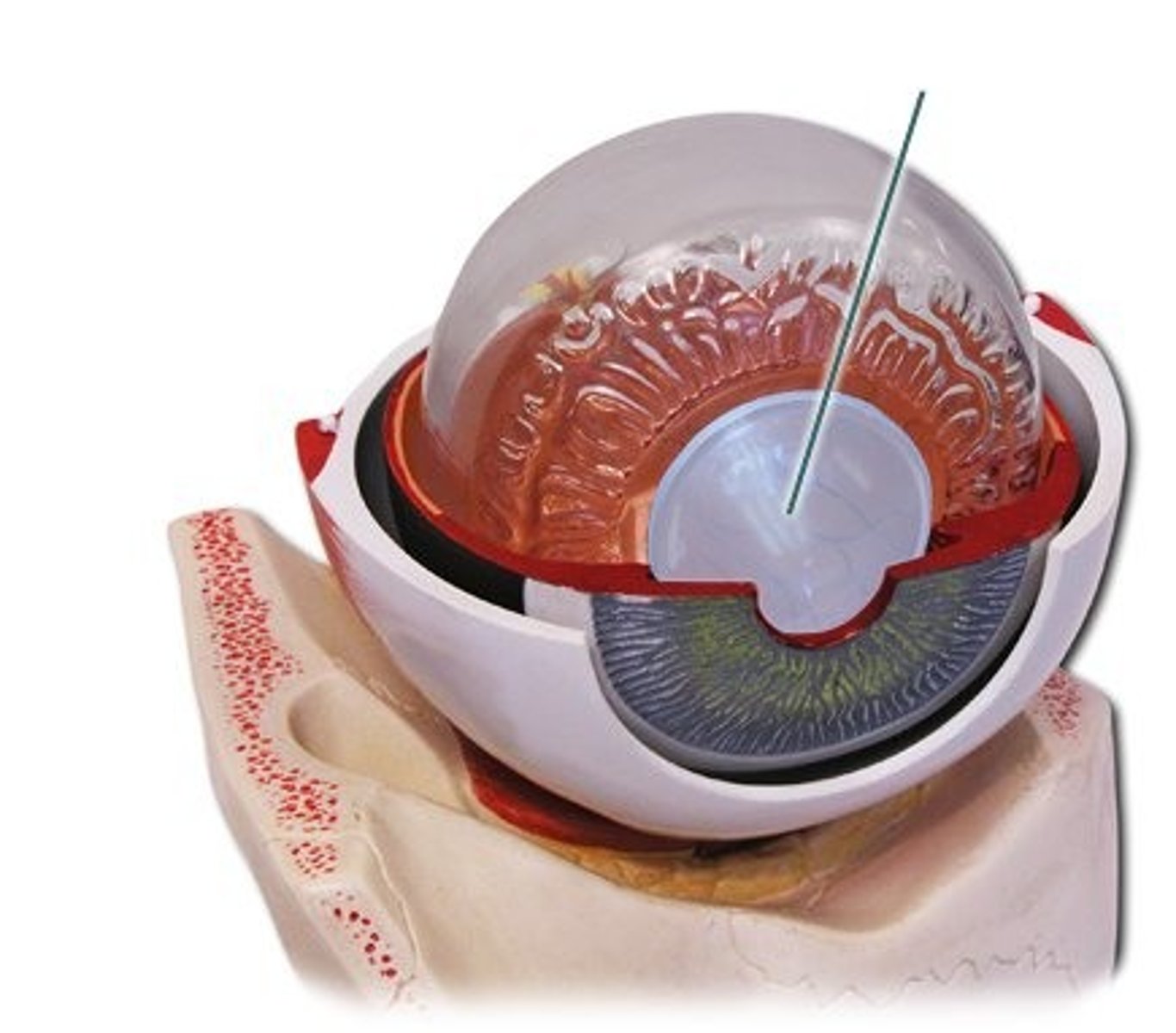
lens
a flexible, transparent structure in the eye that changes its shape to focus light on the retina
retina
the innermost coating of the back of the eye, containing the light sensitive receptor cells
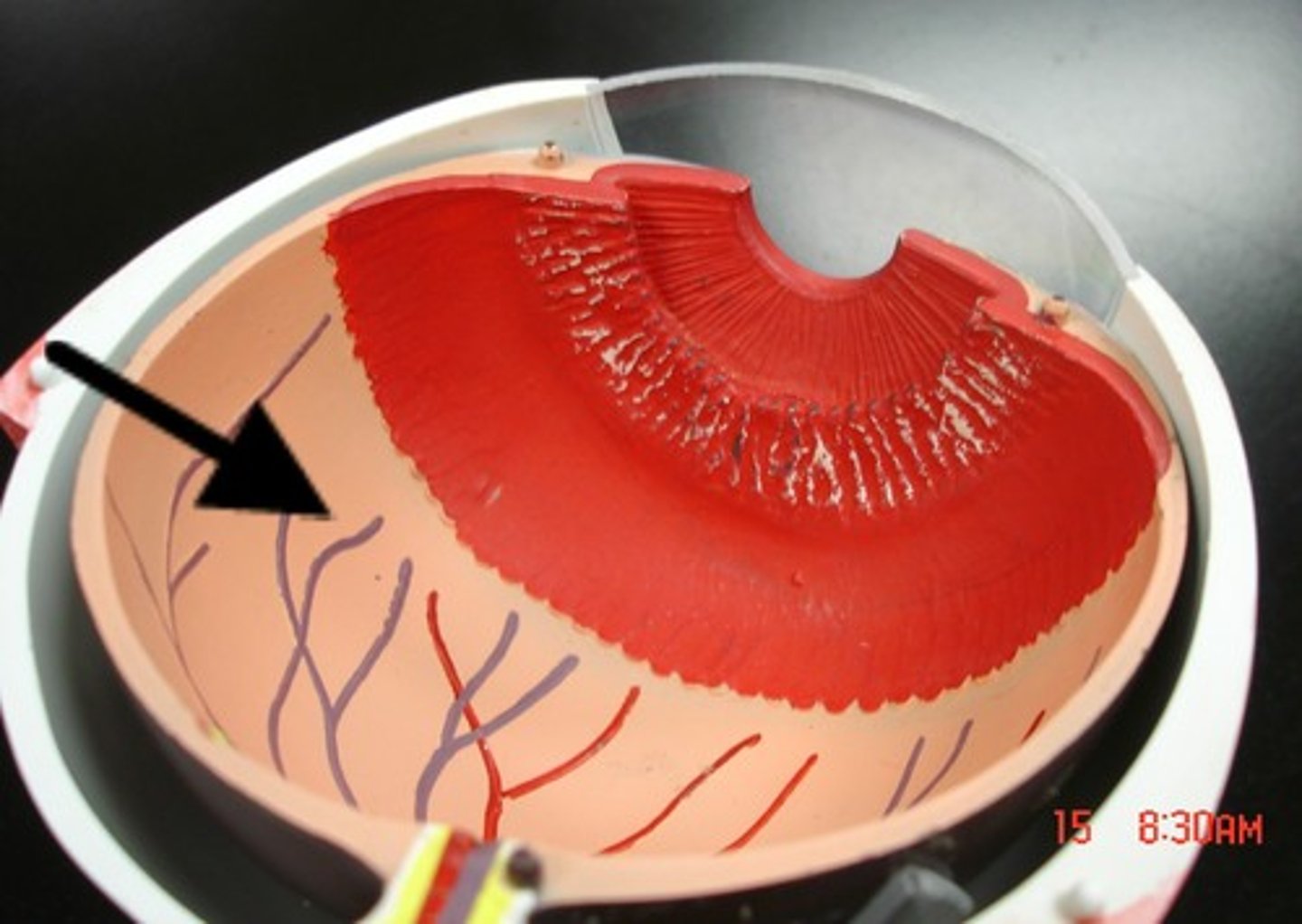
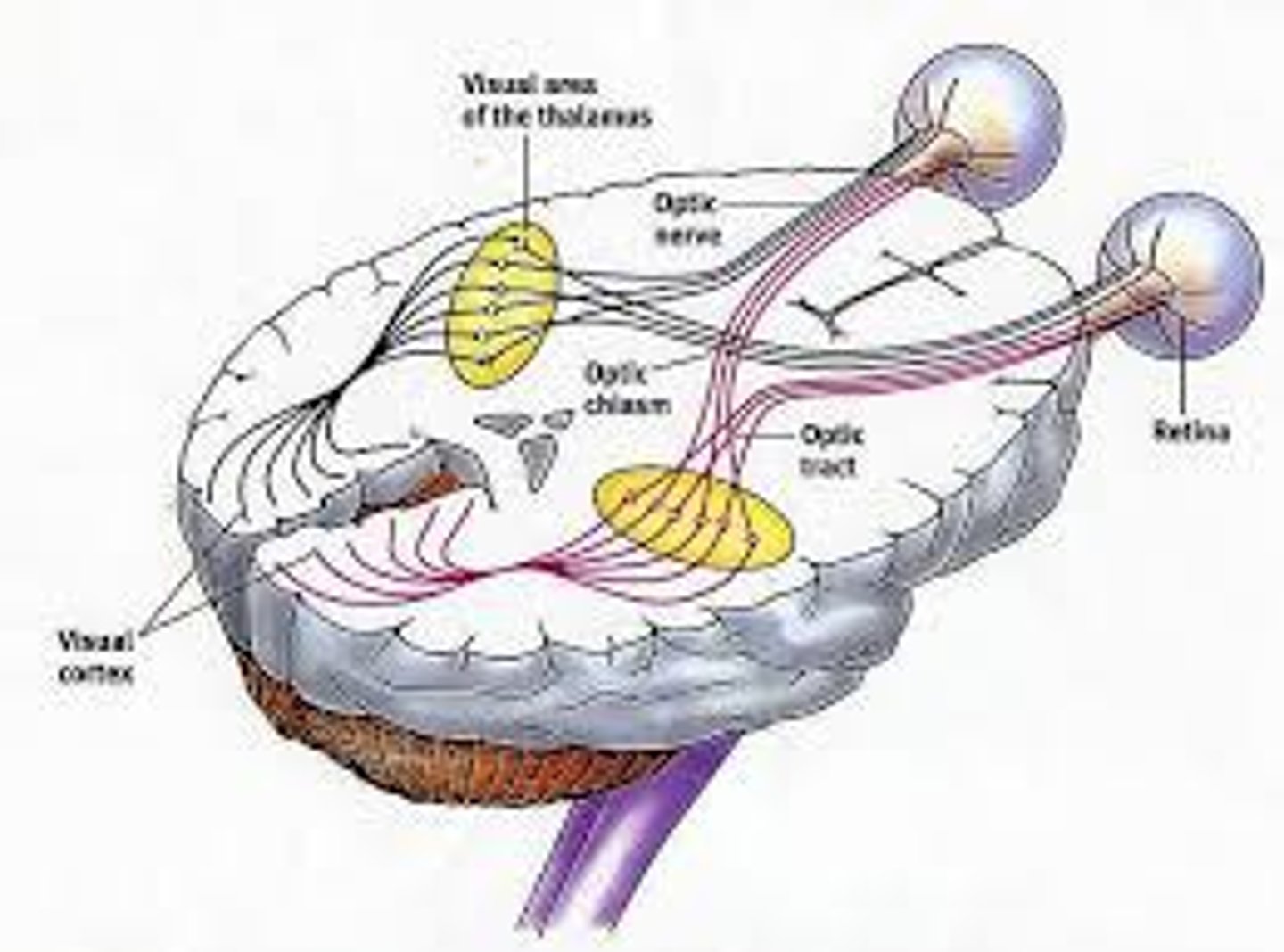
optic nerve
the nerve that carries impulses from the retina to the brain
auditory nerve
the nerve that carries impulses from the inner ear to the brain, resulting in the sensation of sound
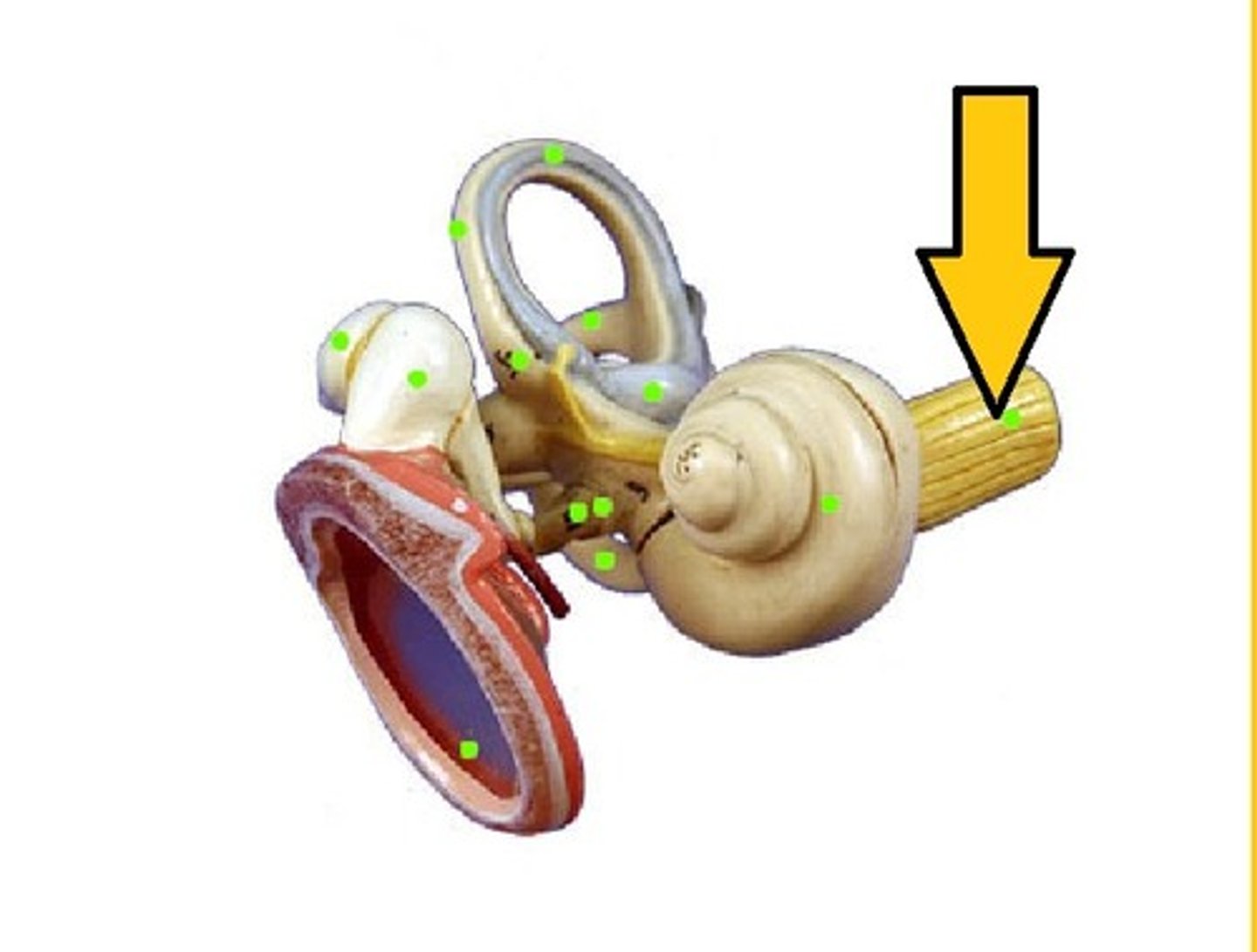
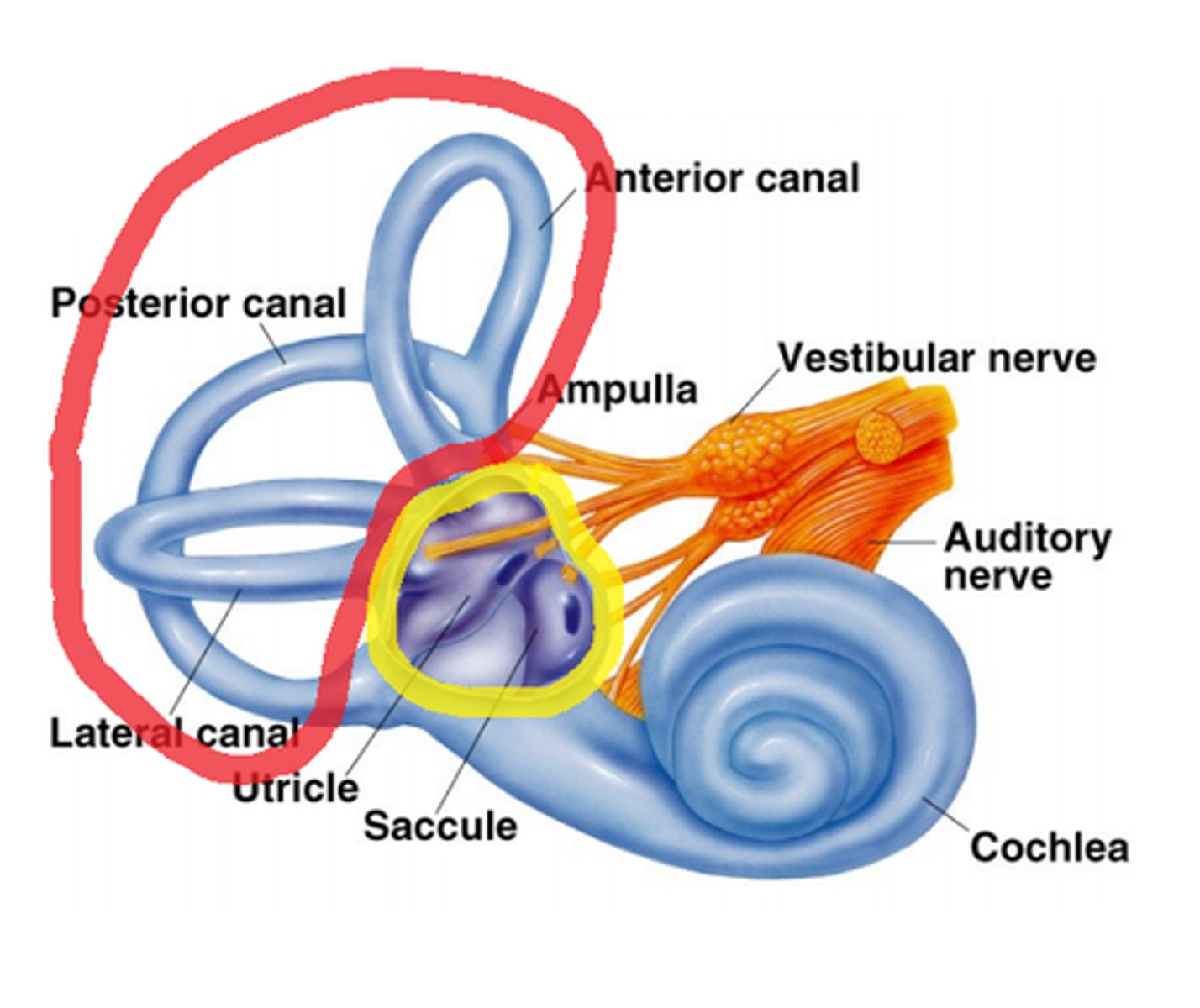
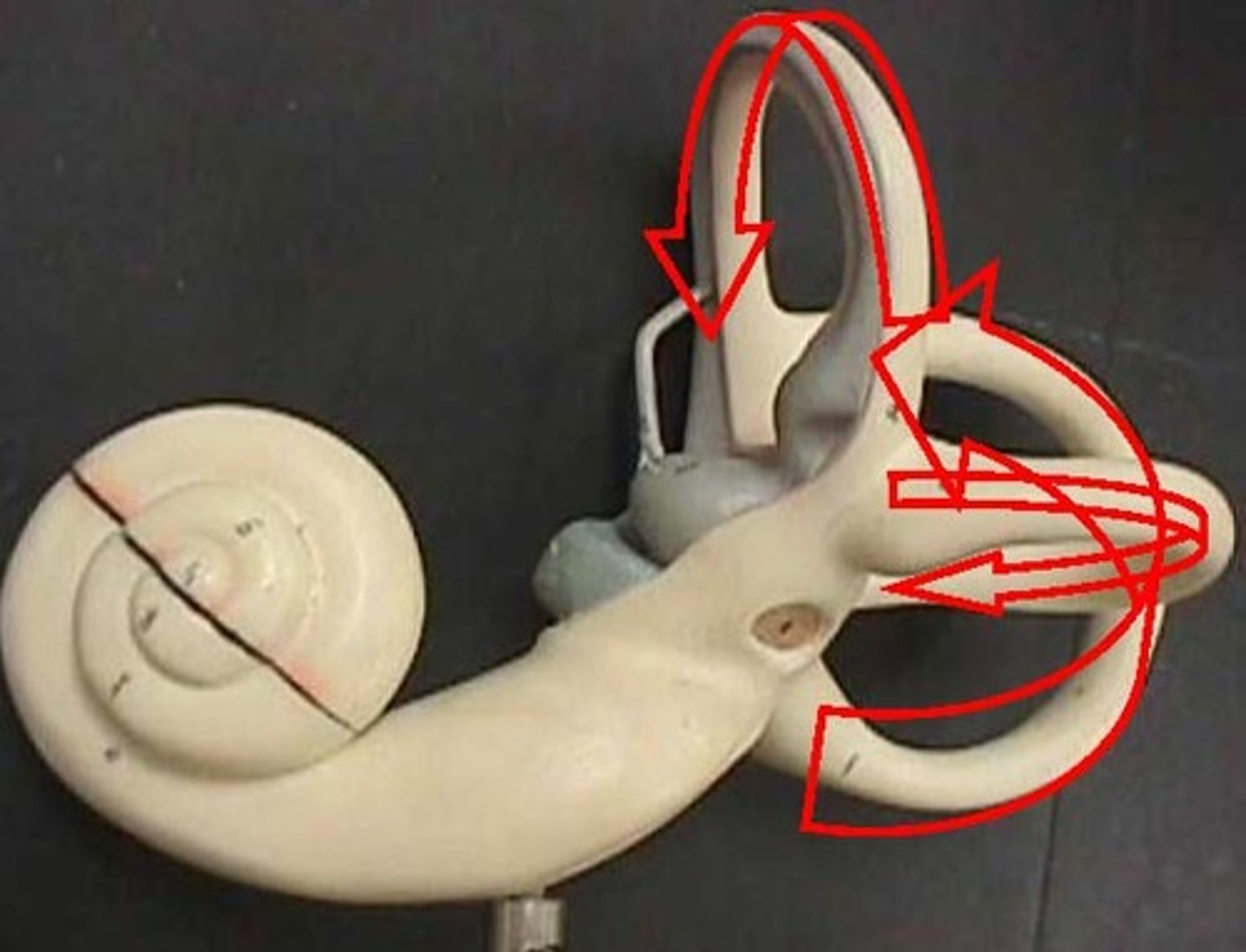
vestibular system
three semicircular canals that provide the sense of balance, located in the inner ear and connected to the brain by a nerve
olfactory nerve
the nerve that carries smell impulses from the nose to the brain
kinesthesis
the sense of movement and body postition
gestalt psychology
the study of experience that comes from organizing bits and pieces of information into meaningful wholes
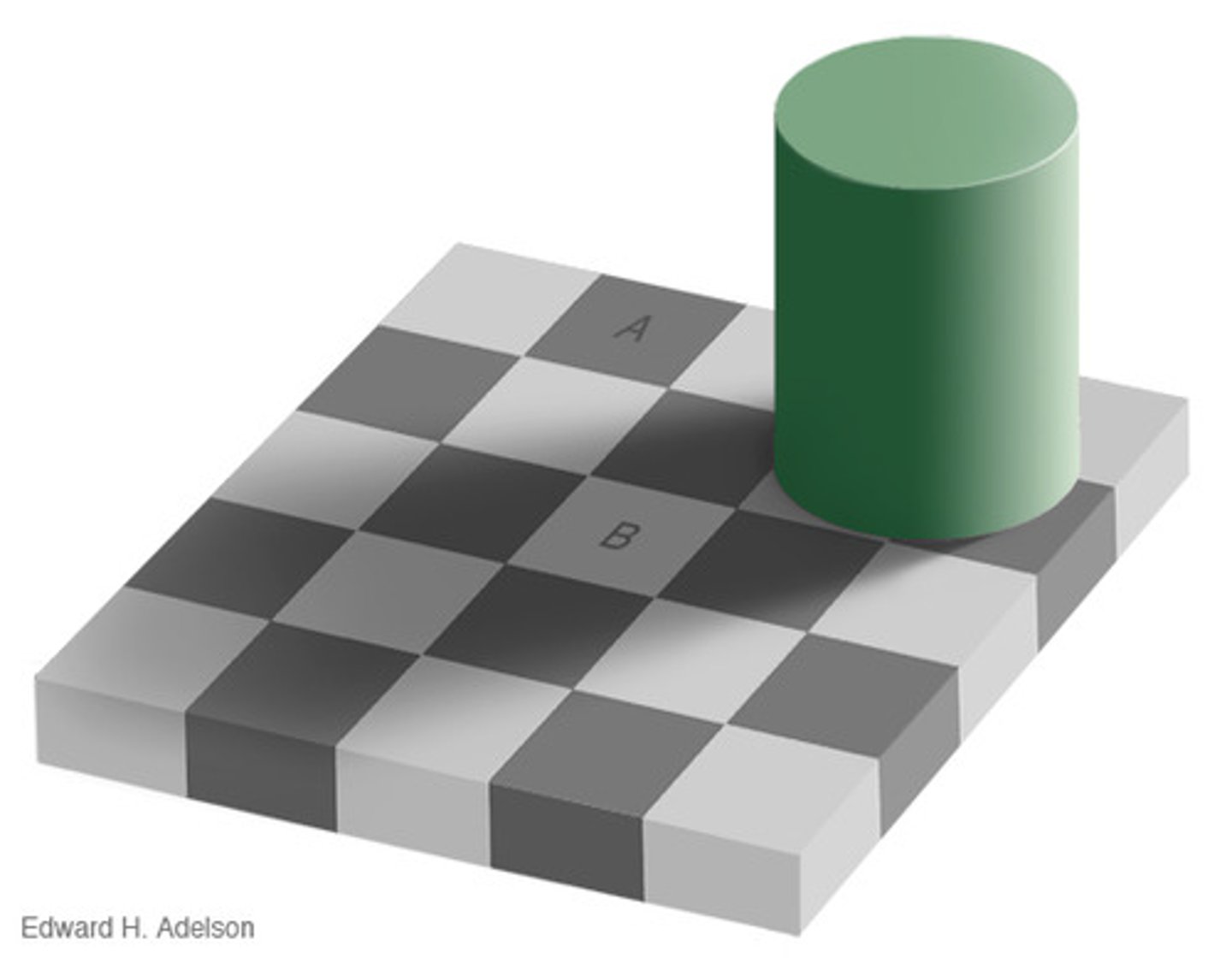
constancy
the tendency to perceive certain objects in the same way regardless of changing angle, distance or lighting
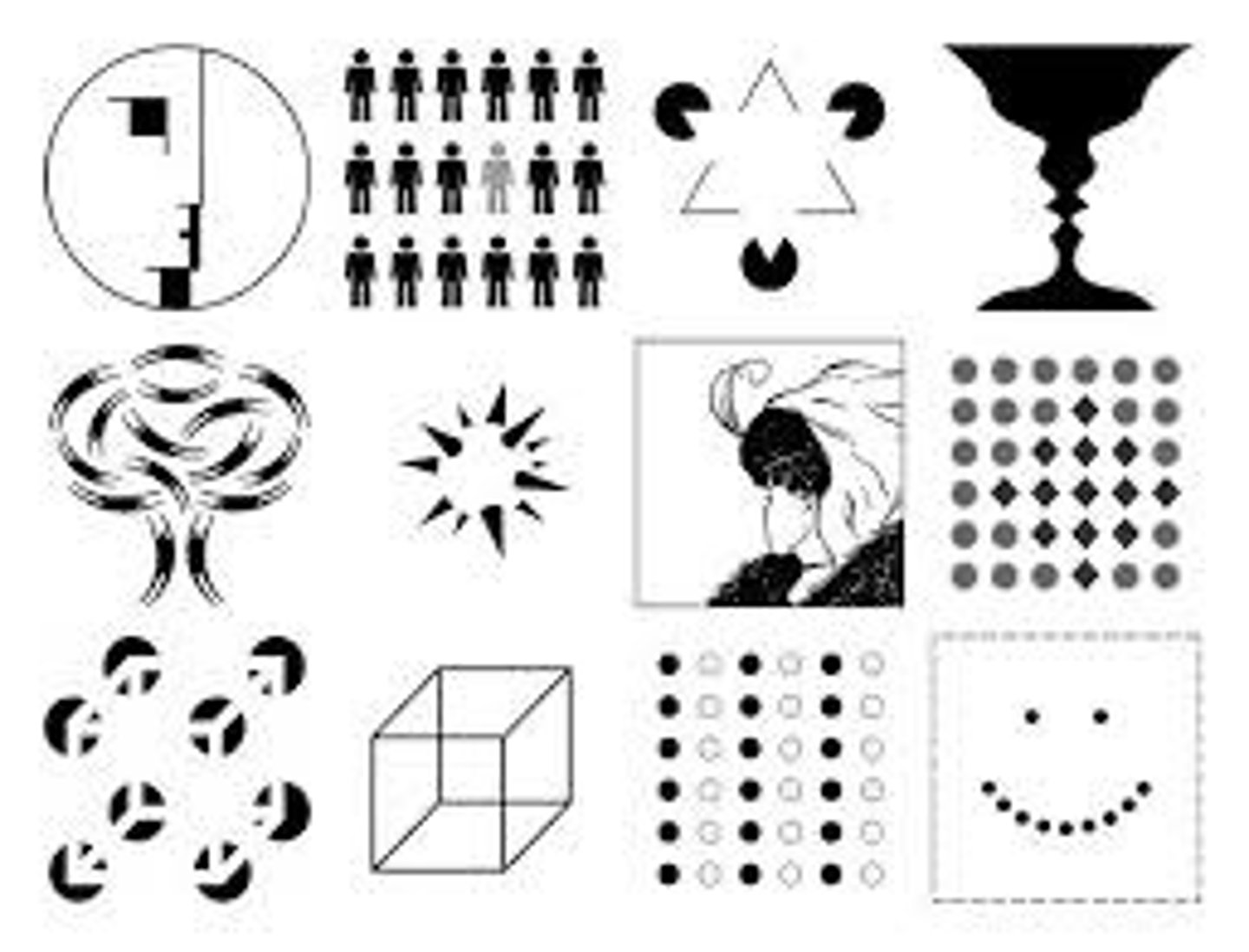
illusions
perceptions that misrepresent physical stimuli
extrasensory perception
(ESP) an ability to gain information by some means other than the ordinary senses

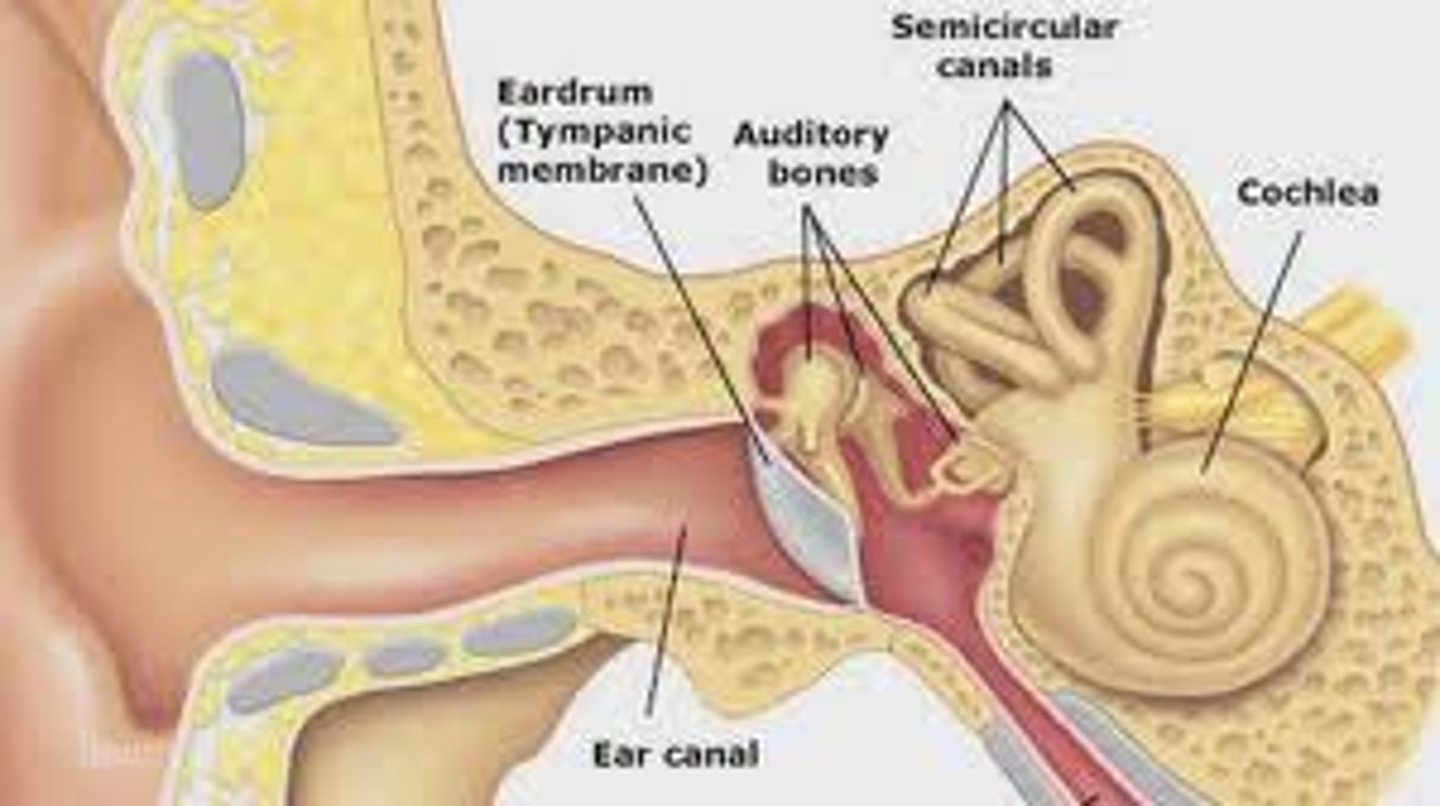
Hammer, anvil, stirrup (Malleus, Incus, Stapes)
the three tiny bones in the middle ear (linked to cochlea & eardrum)
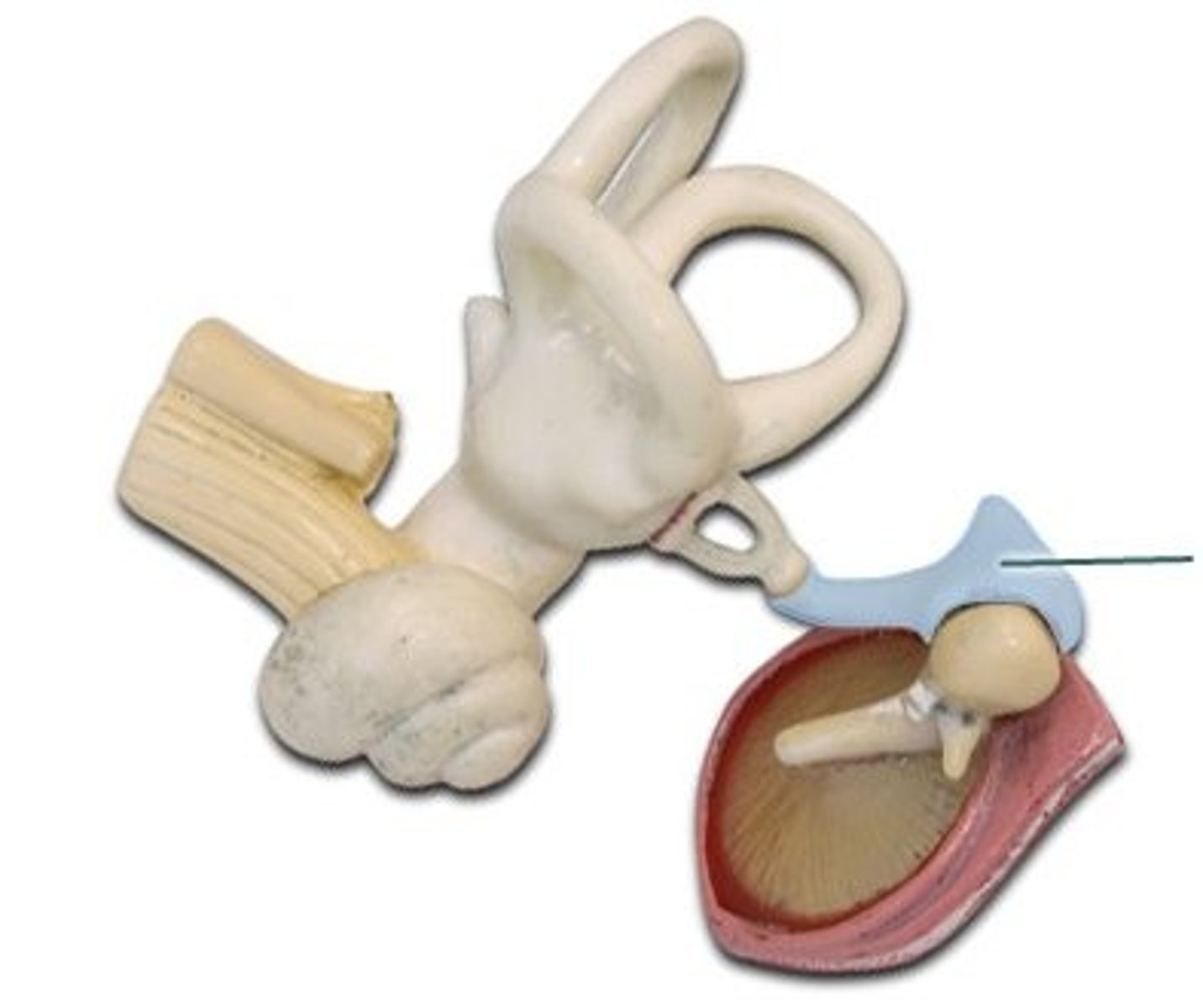
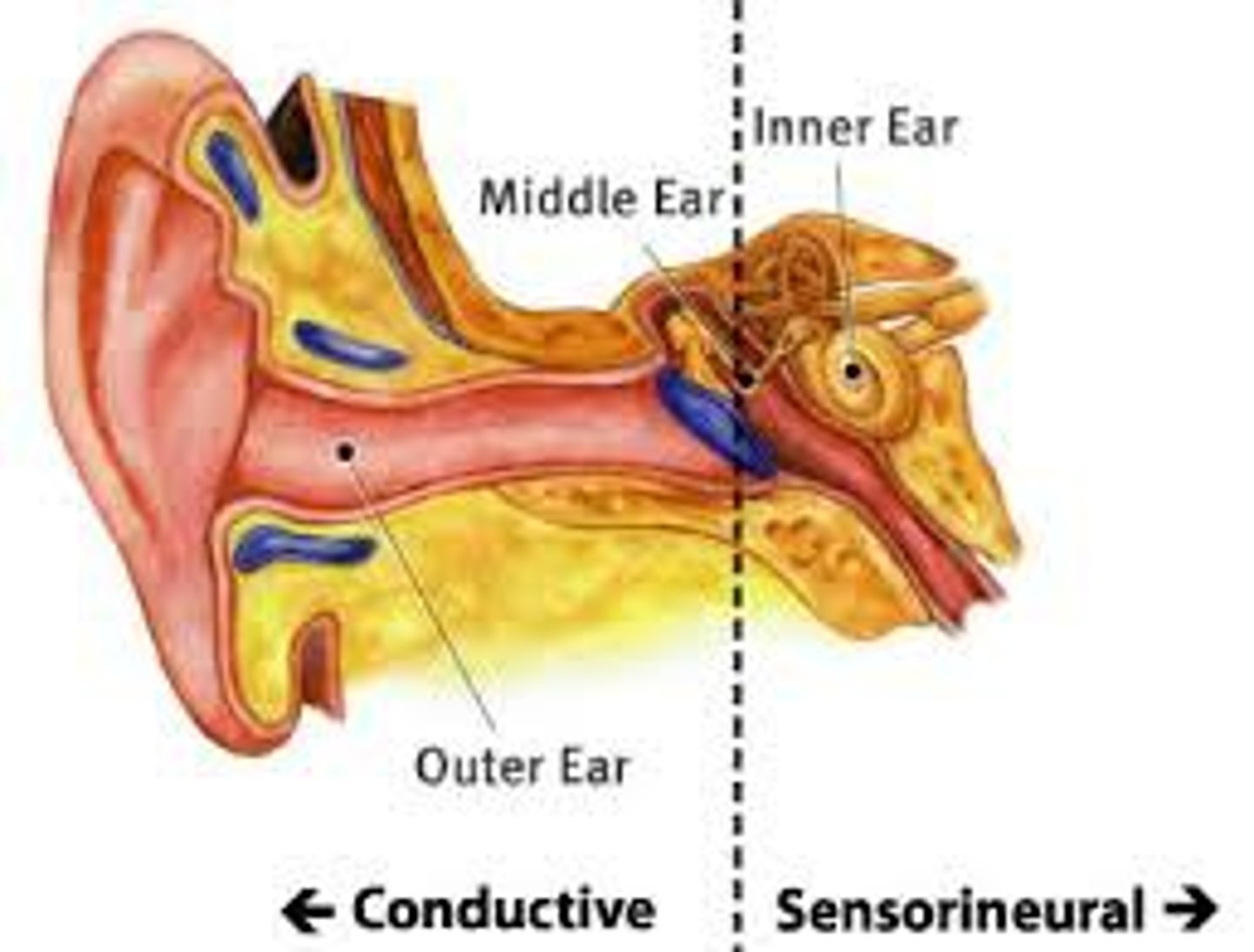
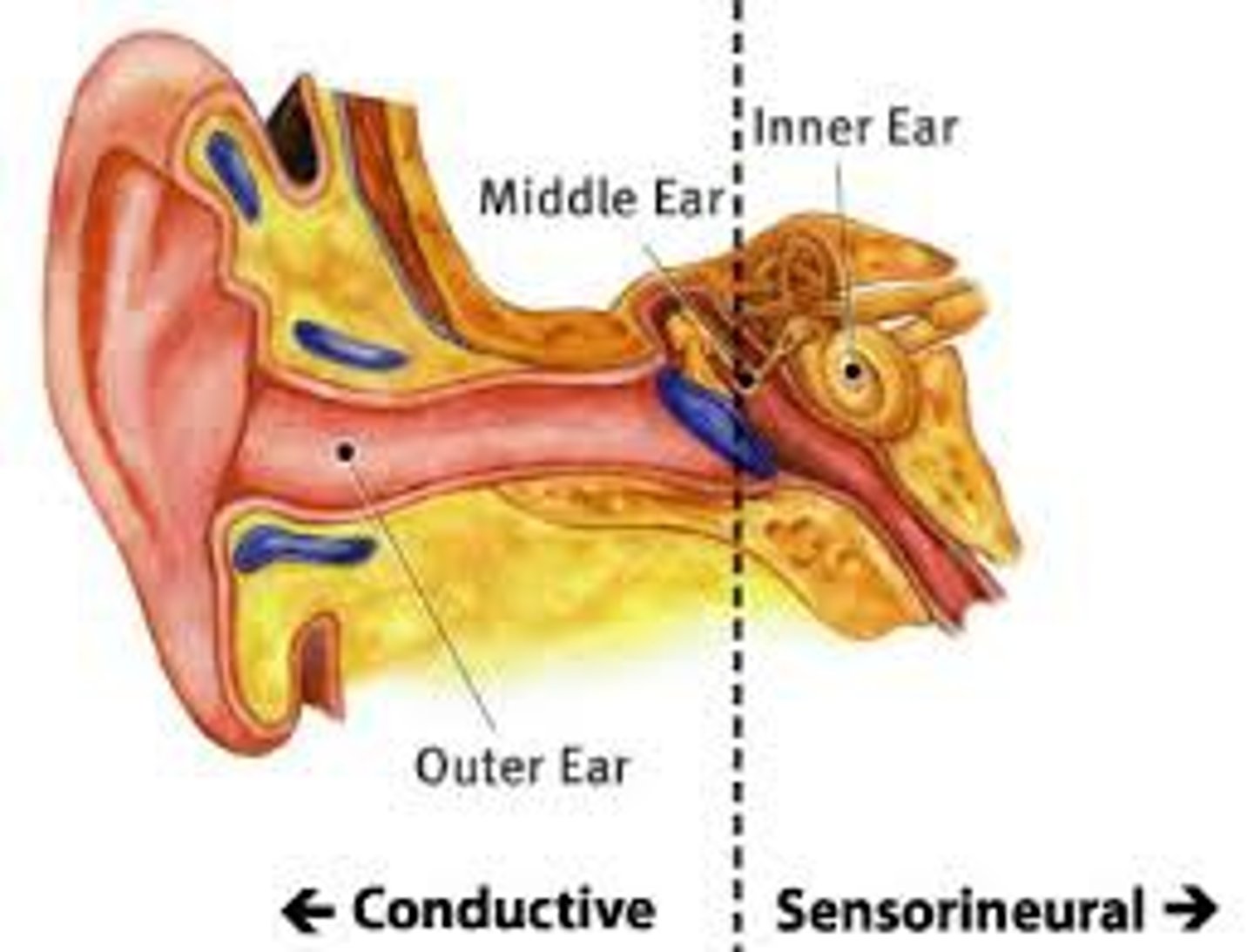
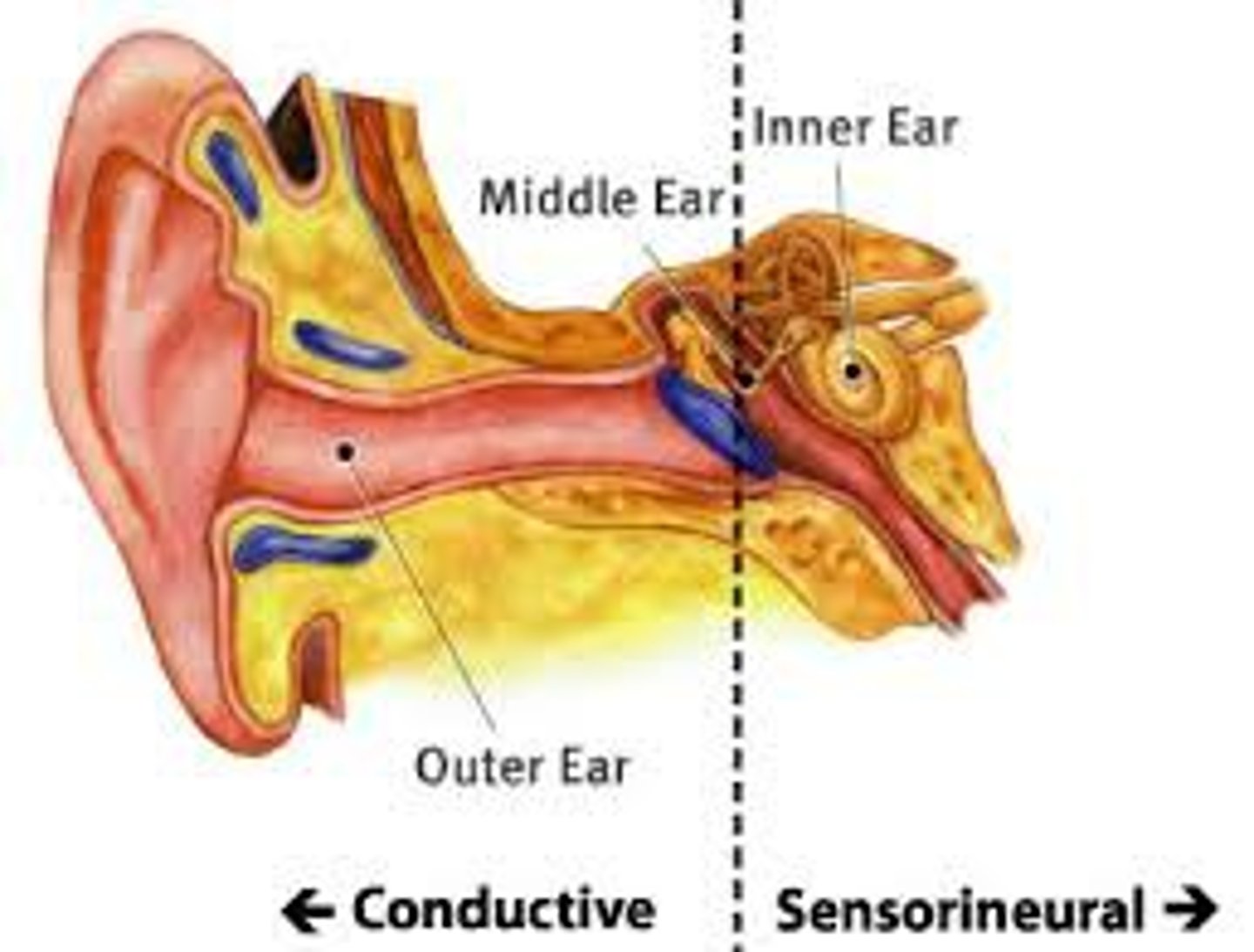
conduction deafness
occurs when anything hinders physical motion through the outer or middle ear or when the bones of the middle ear become rigid and cannot carry sounds inward
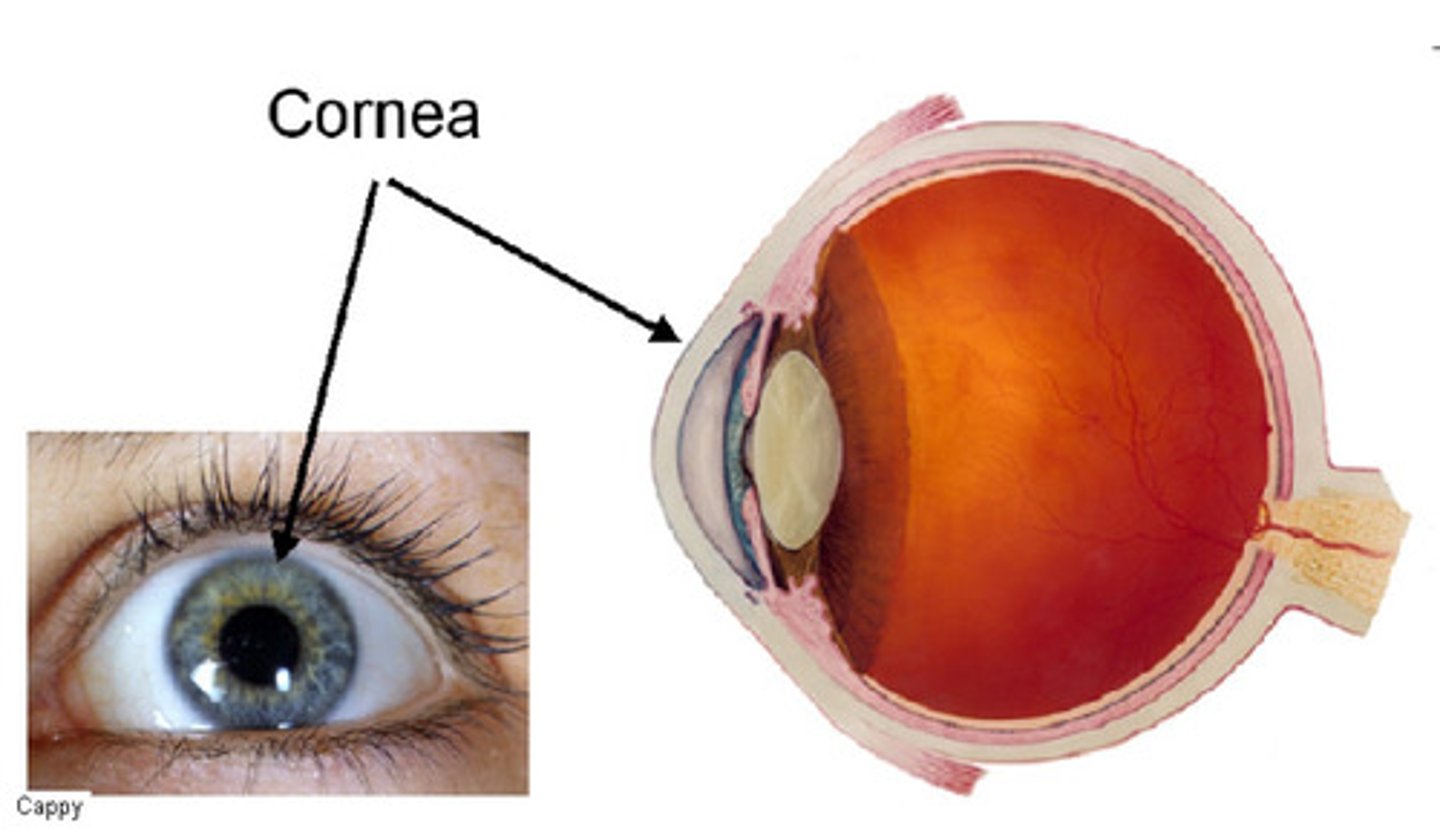
cornea
this cover that is in the front of the human eye
eardrum
where sound waves vibrate to start the hearing processes and is located at the end of the ear canal
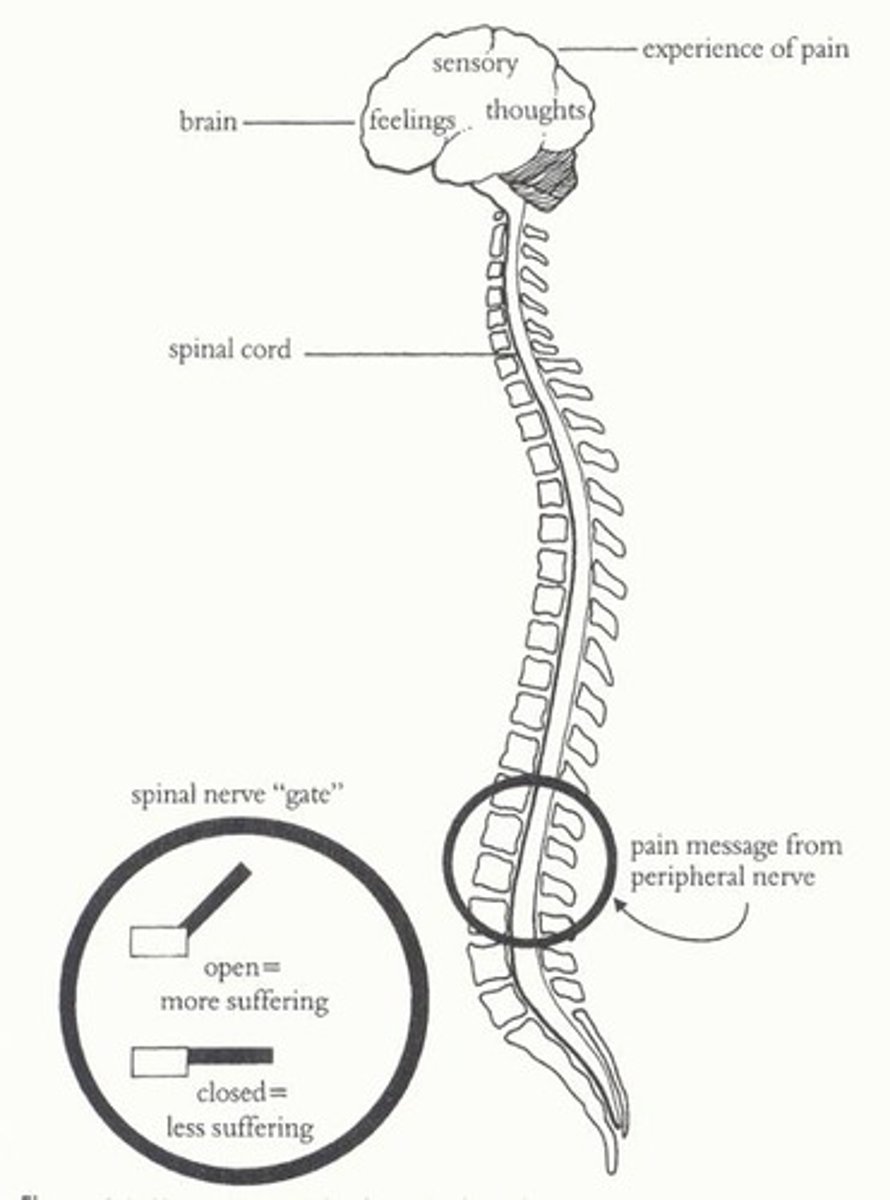
gate control theory
the theory that we can lessen some pains by shifting our attention away from the pain impulses or by sending other signals to compete withe the pain signals
semicircular canals
prominent features of the vestibular system enclosed in the inner ear
sensorineural deafness
occurs from damage to the cochlea, the hair cells or the auditory neurons.
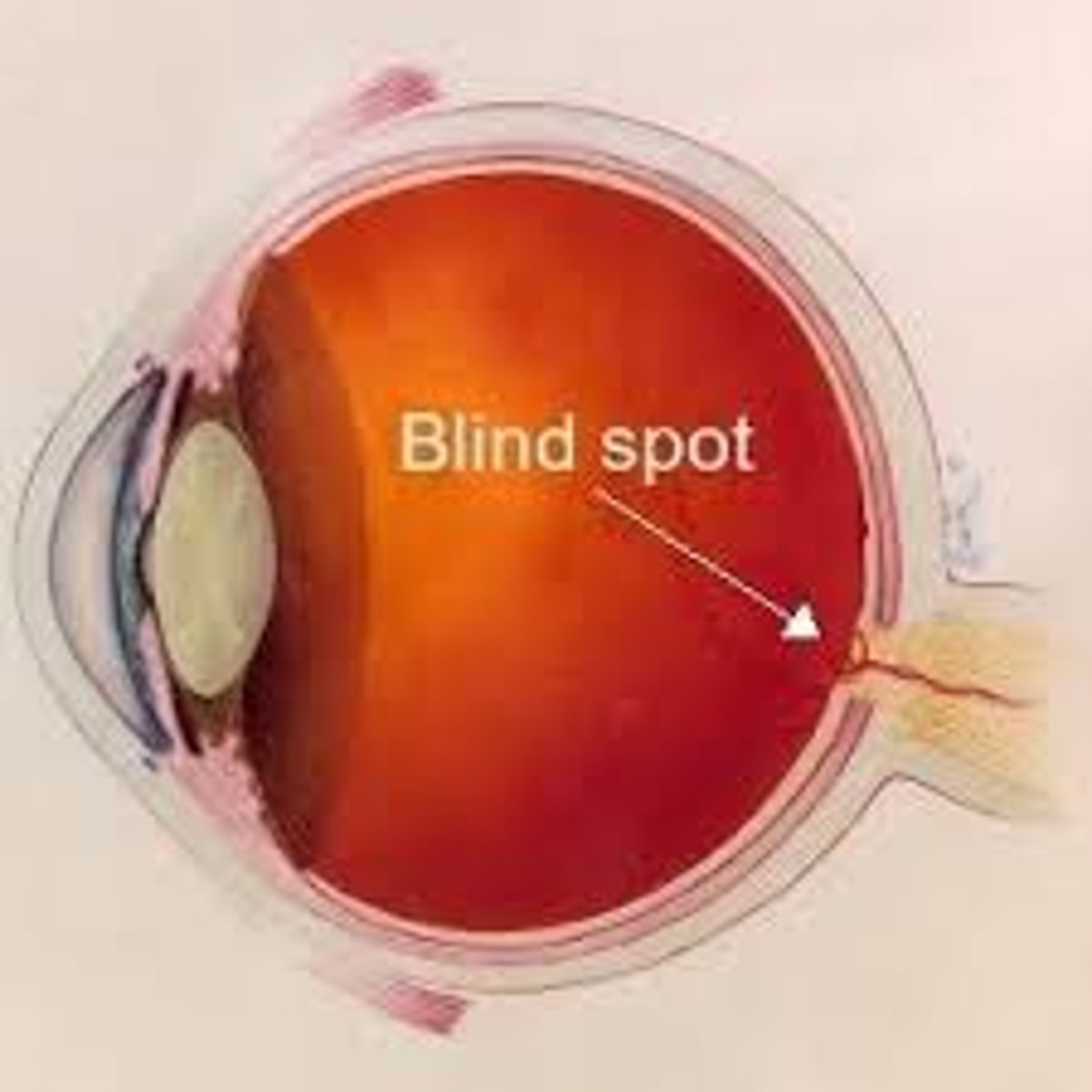
blind spot
the small are, insensitive to light, in the retina of the eye where the optic nerve enters
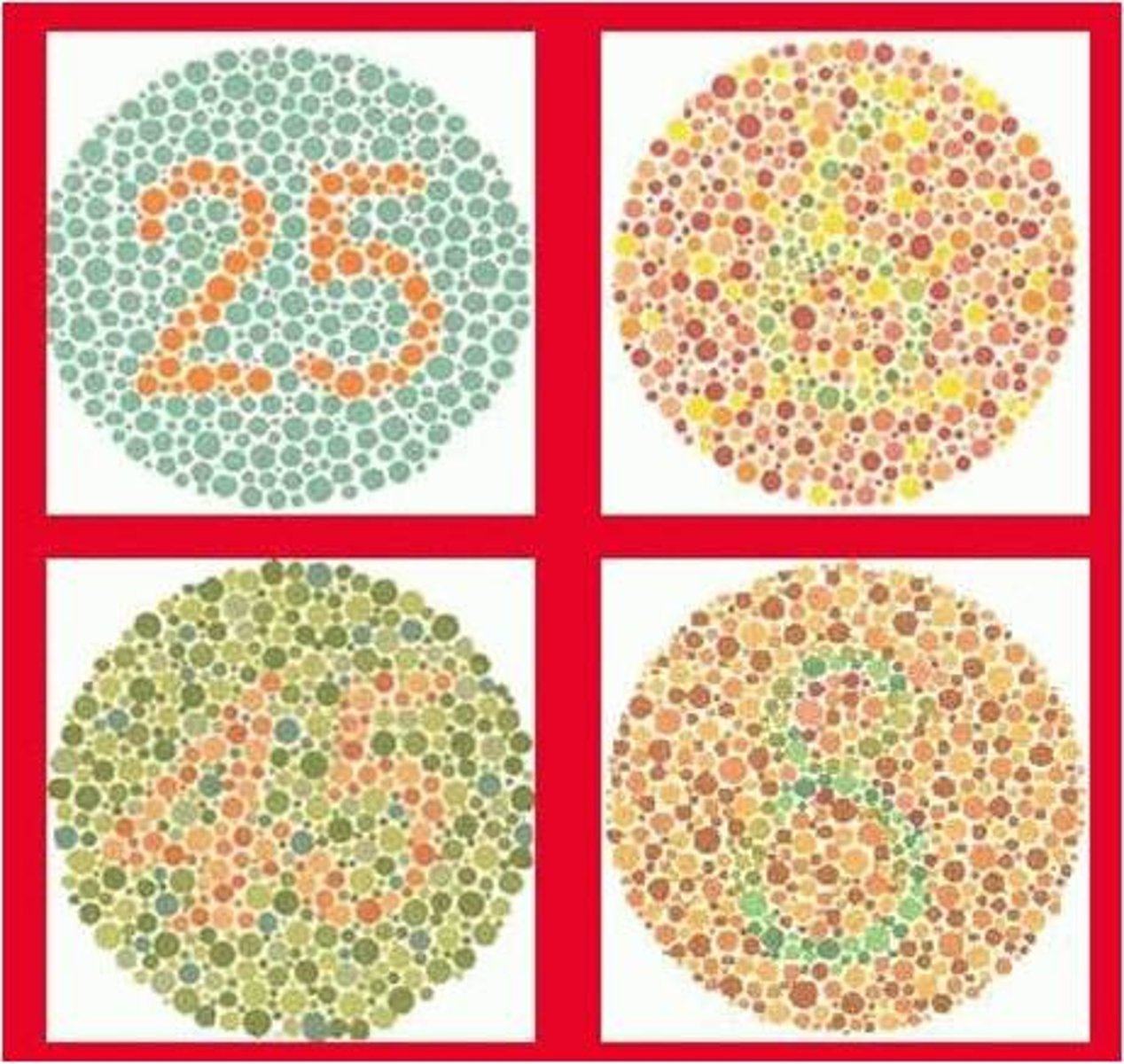
color deficiency
when a person can only see some colors (Dichromatism) or not all (monochromatism )
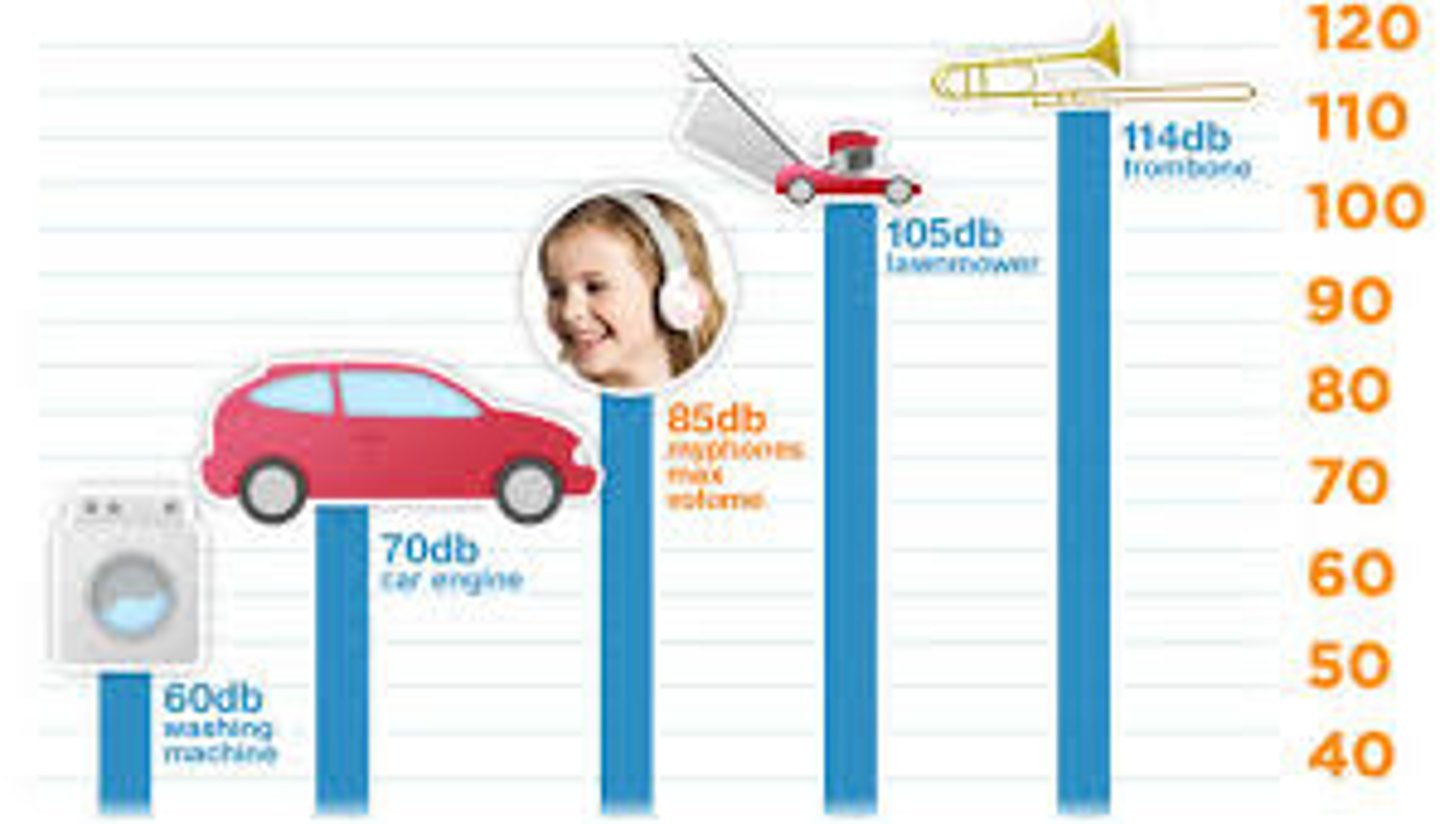
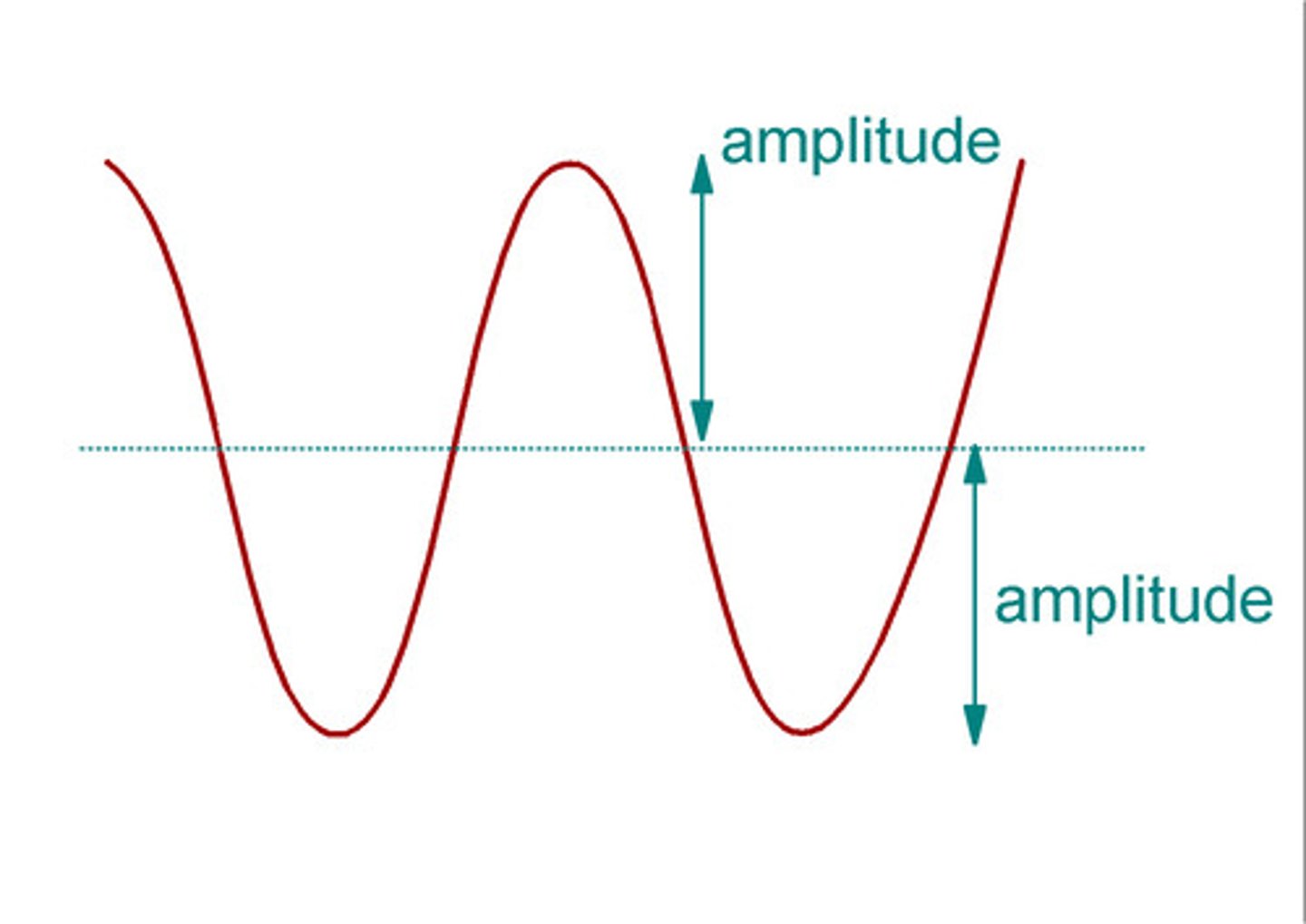
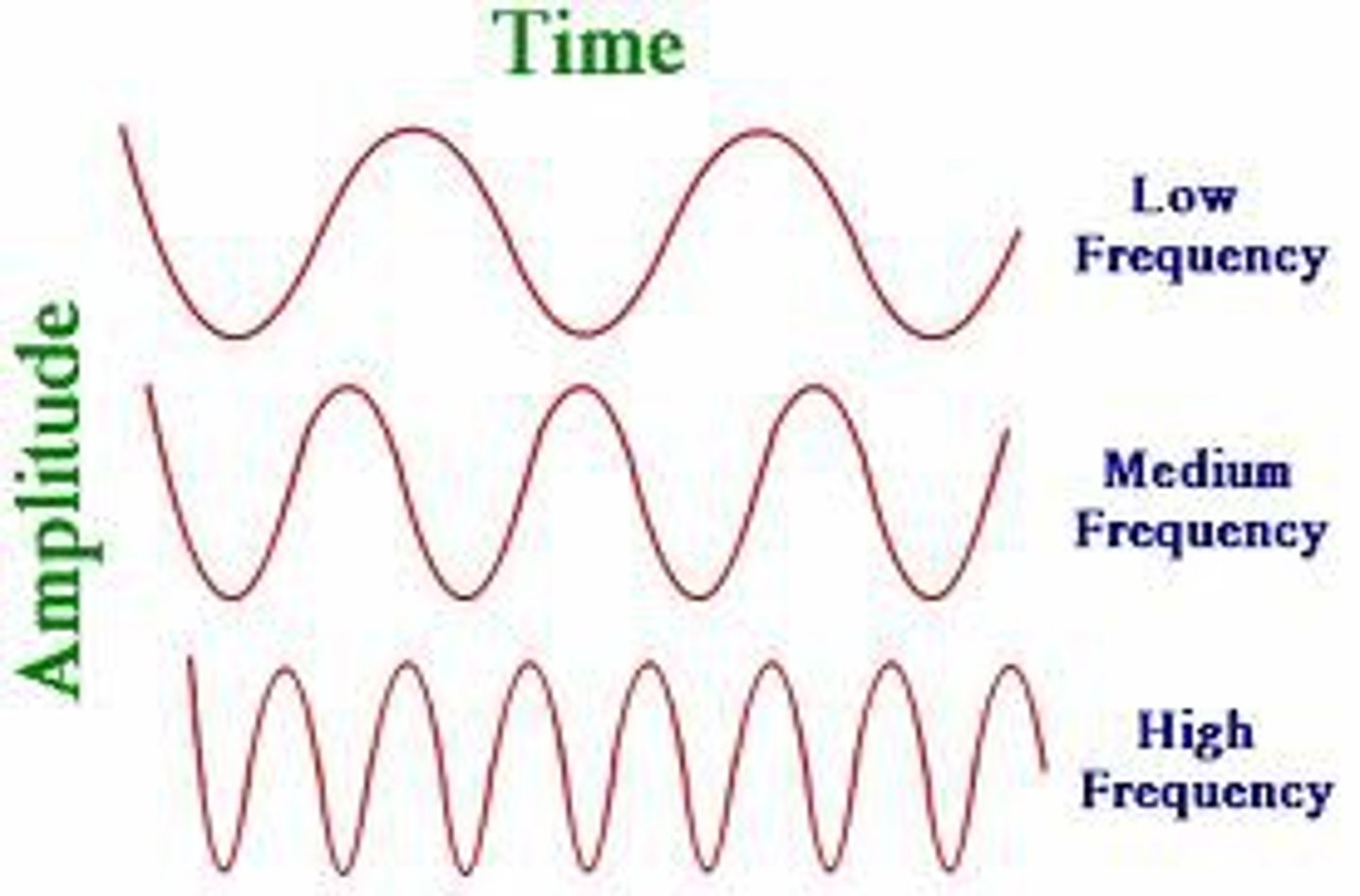
Amplitude
For a wave or vibration, the maximum displacement on either side of the equilibrium (midpoint) position. In Sound it is measured in decibels
Frequency theory
the pitch of a sound wave depends on frequency or the rate of the vibration of the medium through which the sound wave is transmitted
sensory adaptiation
the sense of adapting to an environment

cochlea
makes up the inner ear. a bony tube that contains fluids and neurons
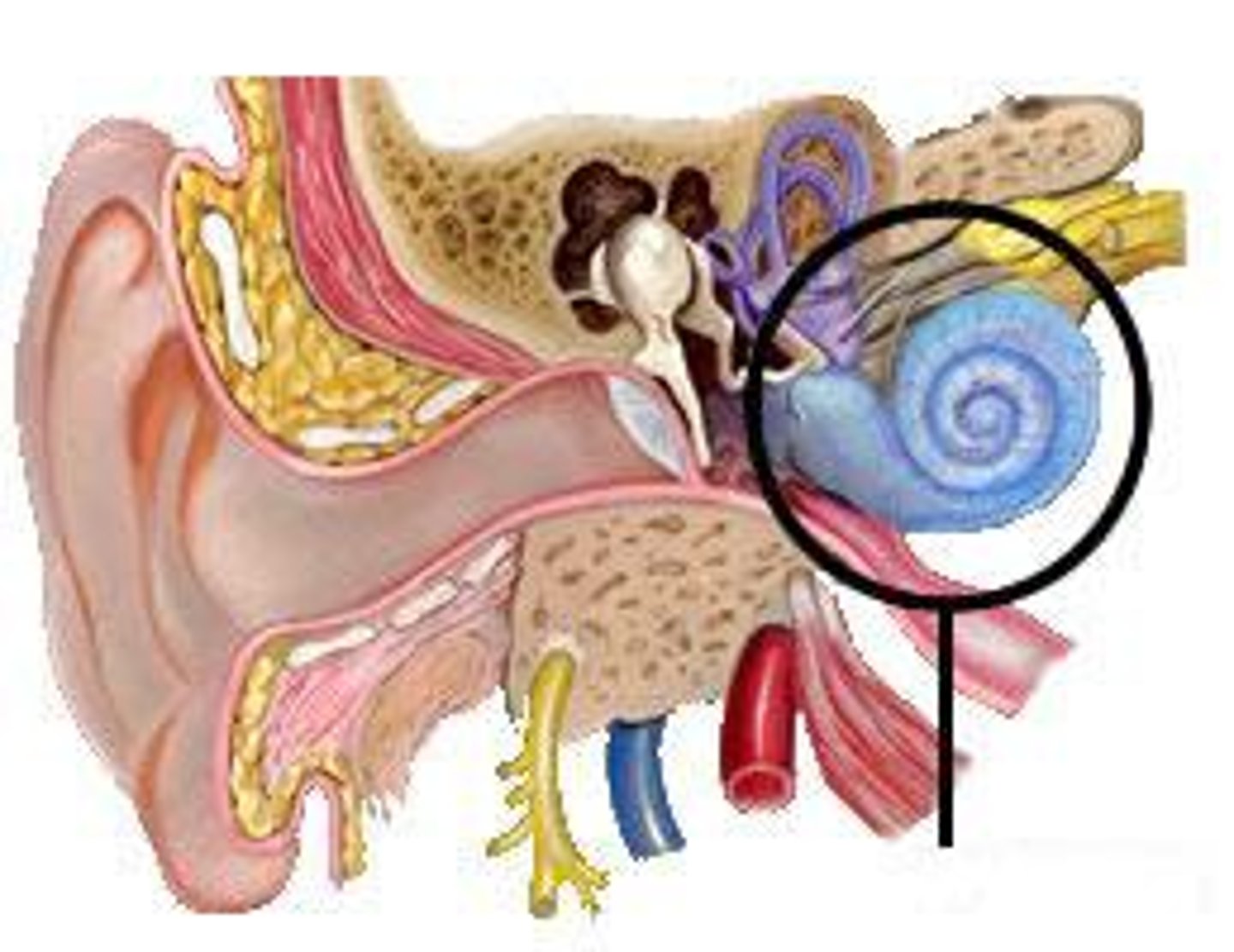
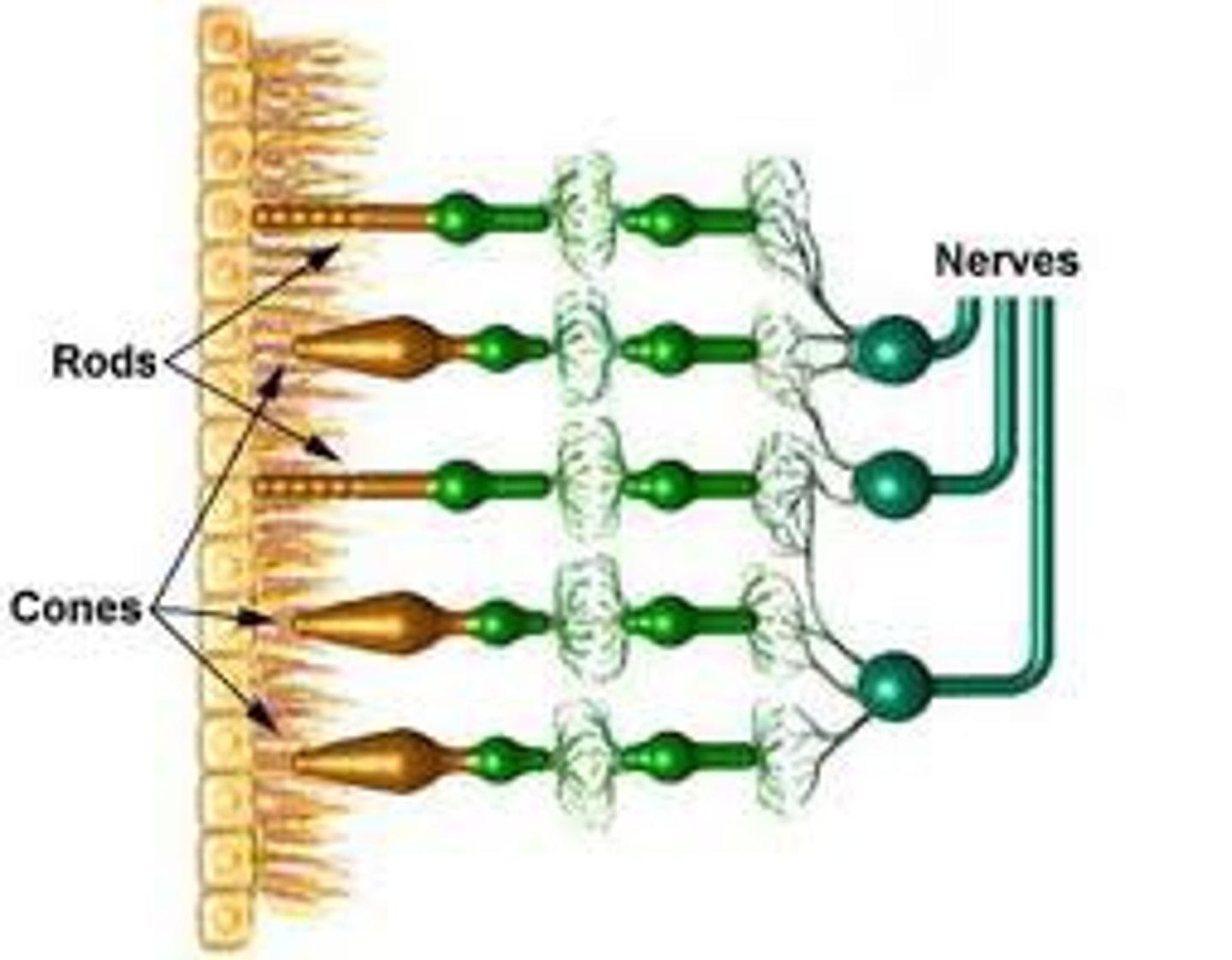
cones
a light sensitive receptor cell or photoreceptor
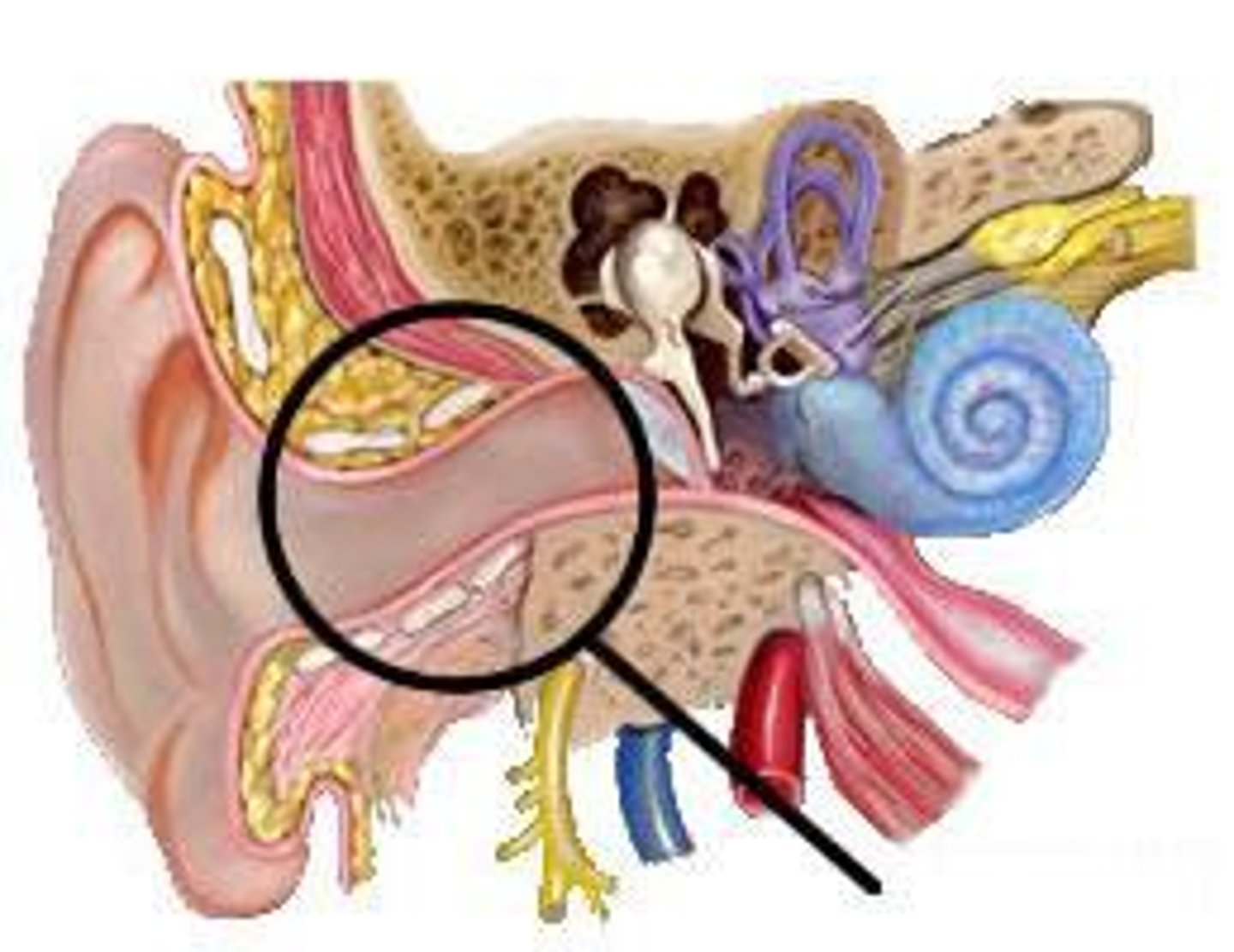
ear canal
tube that sound enters into to reach the eardrum
flavor
the combination of taste, smell and tactile sensations.

iris
part of the eye, regulates the amount of light entering the eye
rods
sensitive to low levels of light
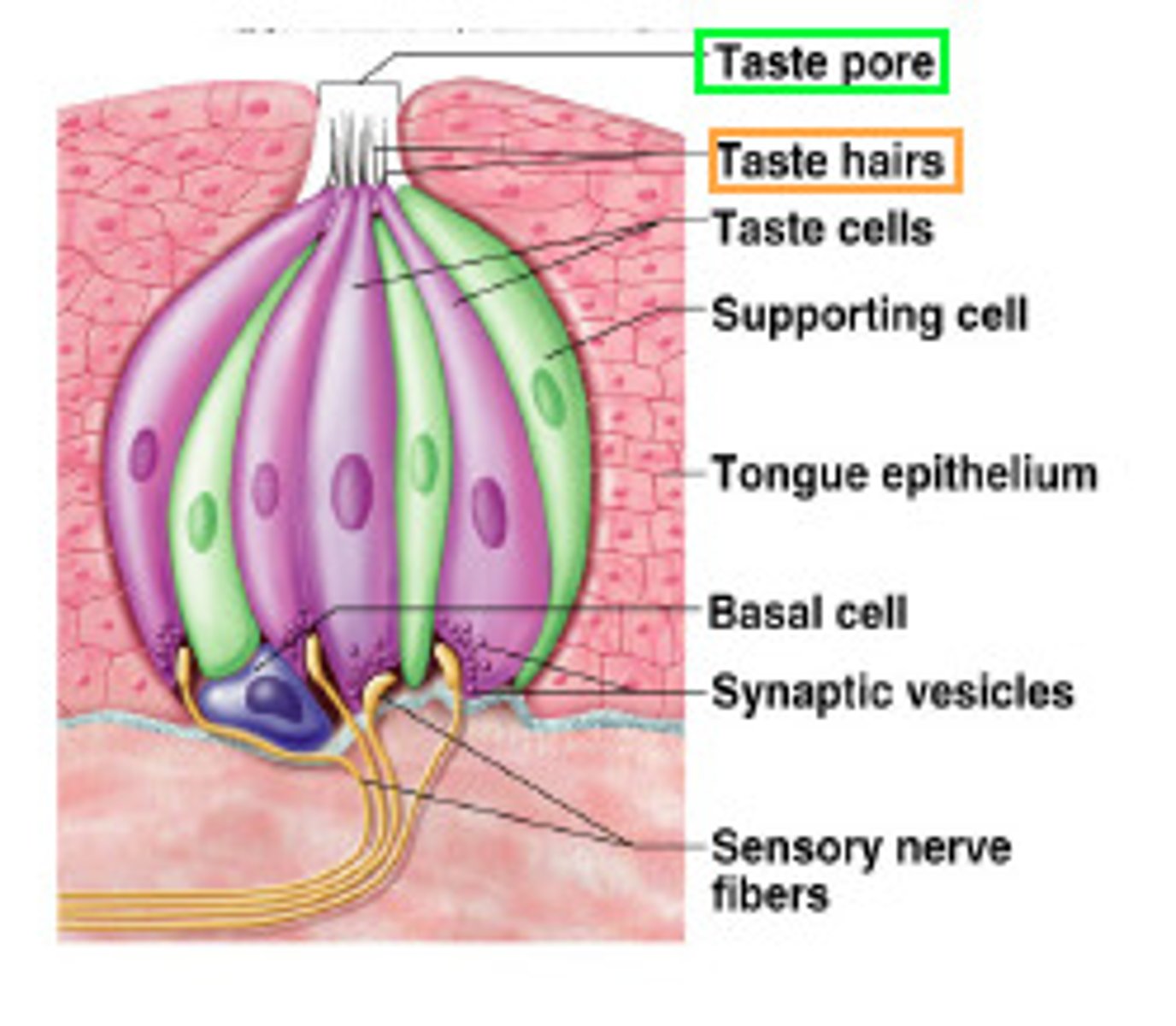
taste buds (receptors)
on the tongue, sense organs for taste (gustation)
Place Theory
the place on the cilia or sound receptors that is stimulated allows the brain to determine frequency (pitch) and amplitude (loudness)
Ganglion cells
In the retina, the specialized neurons that connect to the bipolar cells; the bundled axons of the ganglion cells form the optic nerve.

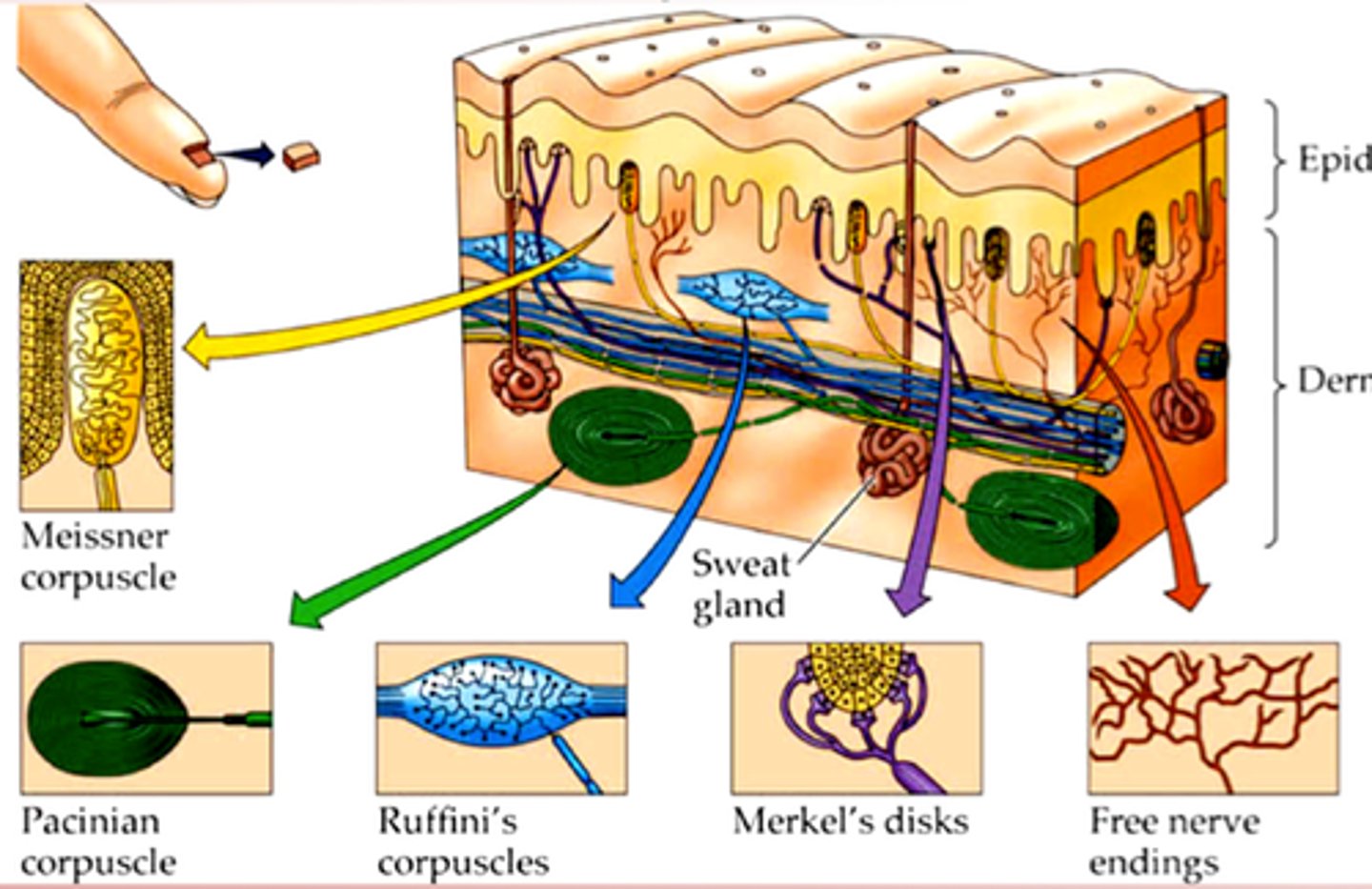
touch receptors
sensory neurons on hands, lips or feet
farsightedness
medically known as hyperopia or hypermetropia, is a condition that is the result of the eye's physical inability to focus an image correctly on the retina at the back of the eye. Farsightedness is the result of the eyeball being too short, and/or the lens of the eye not being flexible enough, for proper focus to occur.
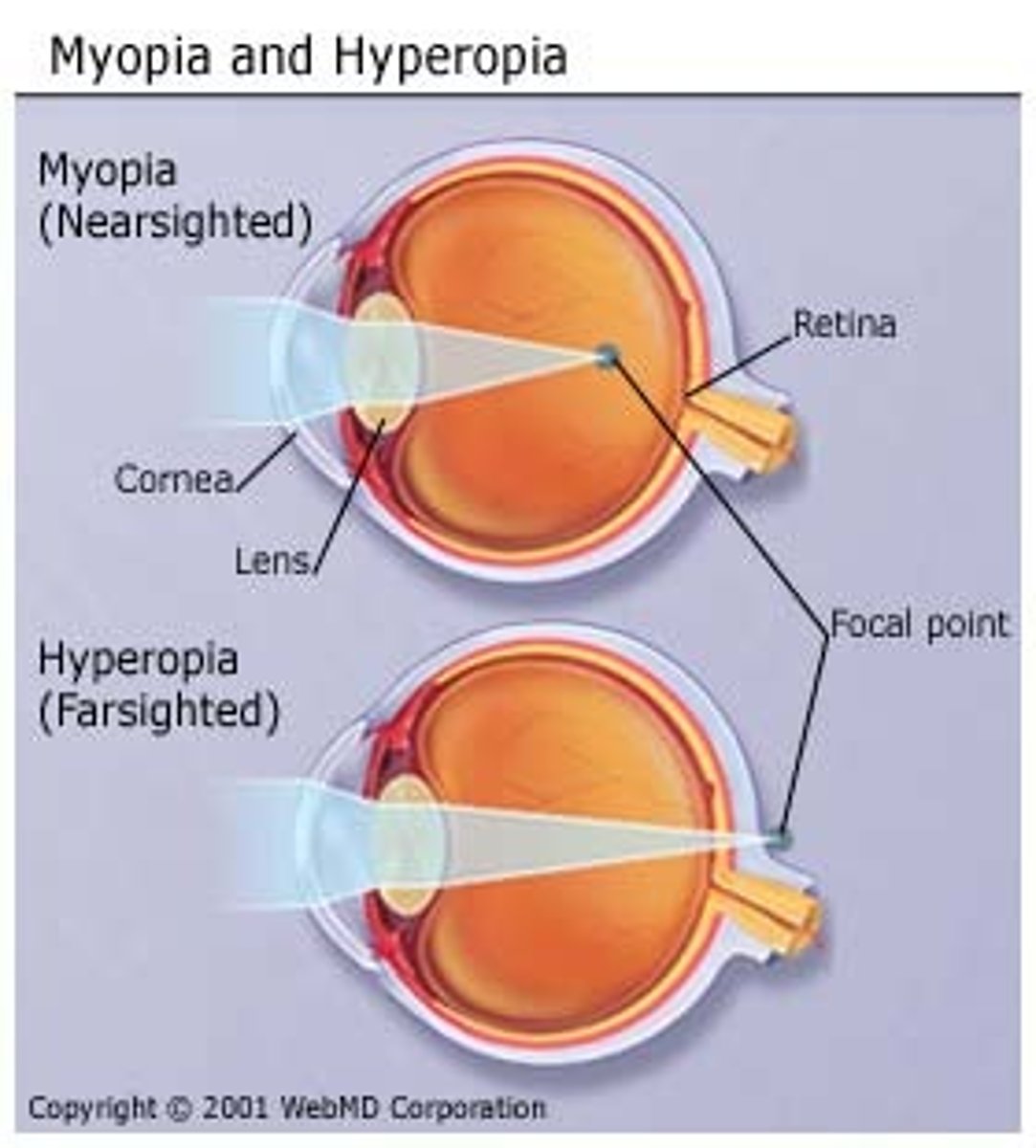
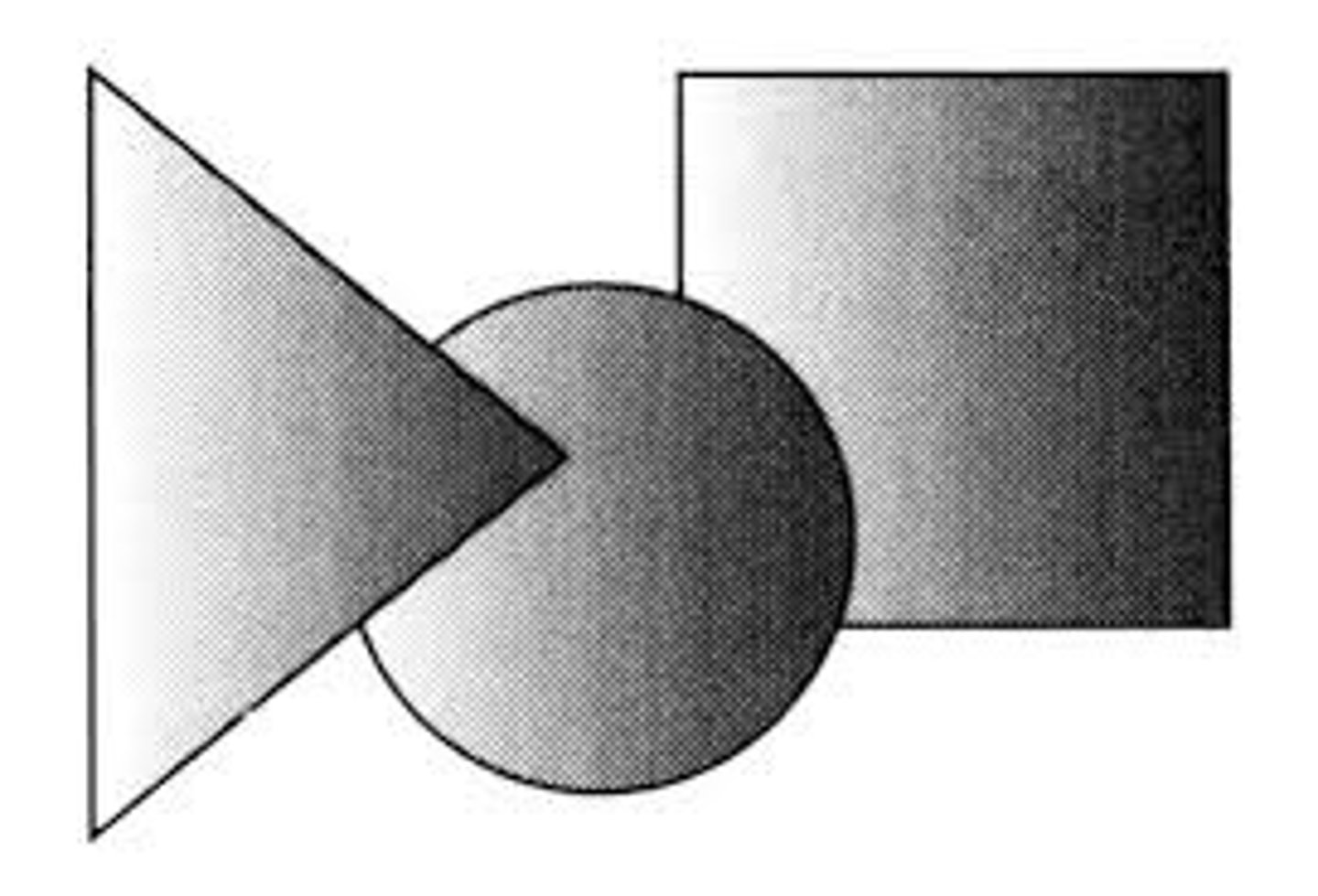
figure-ground perception
our visual system organizes images into figures that we see and a ground or background

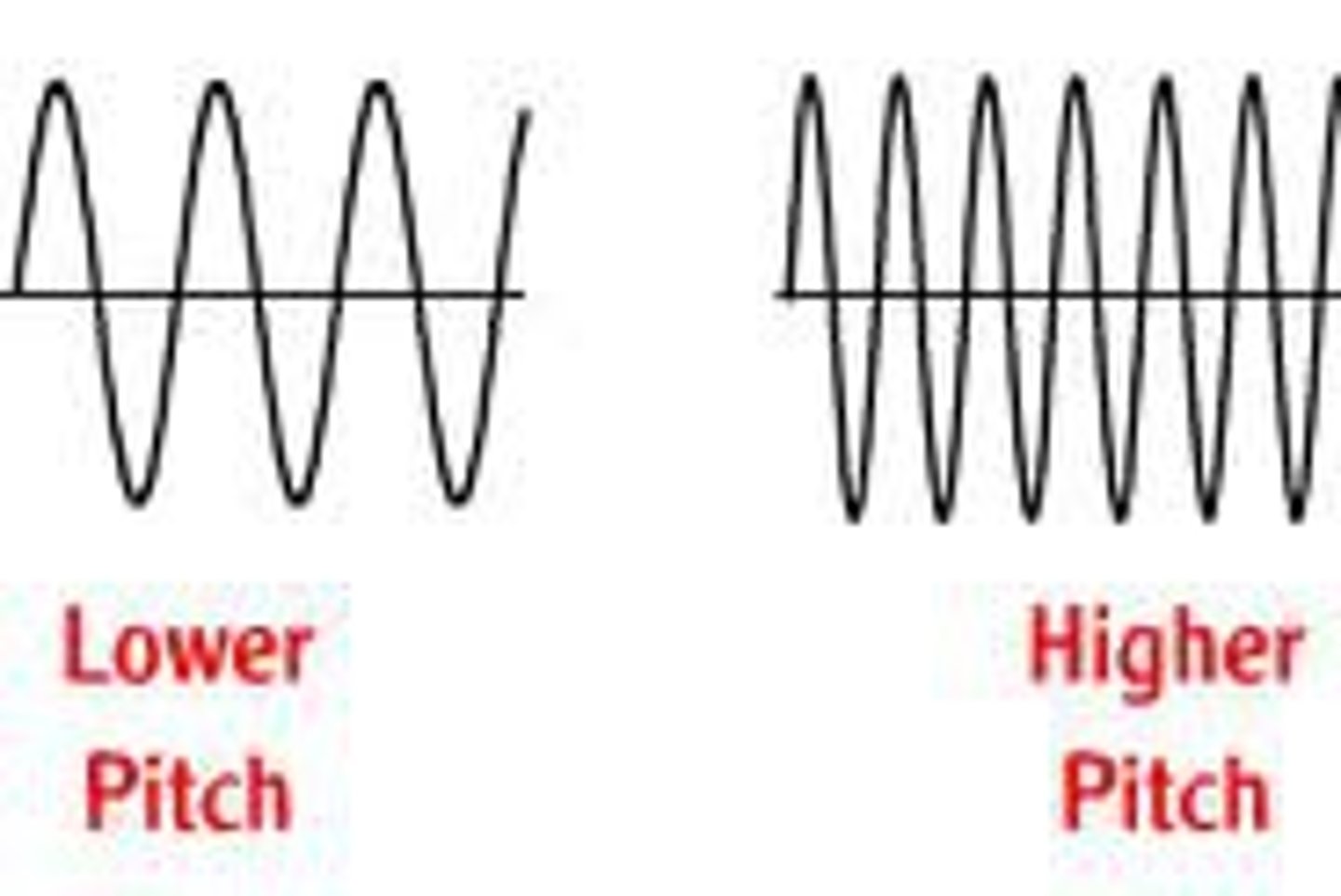
frequency
wavelength of each wave (pitch or hue)
interposition
depth cue involves one object partially covering up another object
nearsightedness
known as Myopia, an elongated eye causes light rays from each eye to meet before they hit the retina causing a distortion
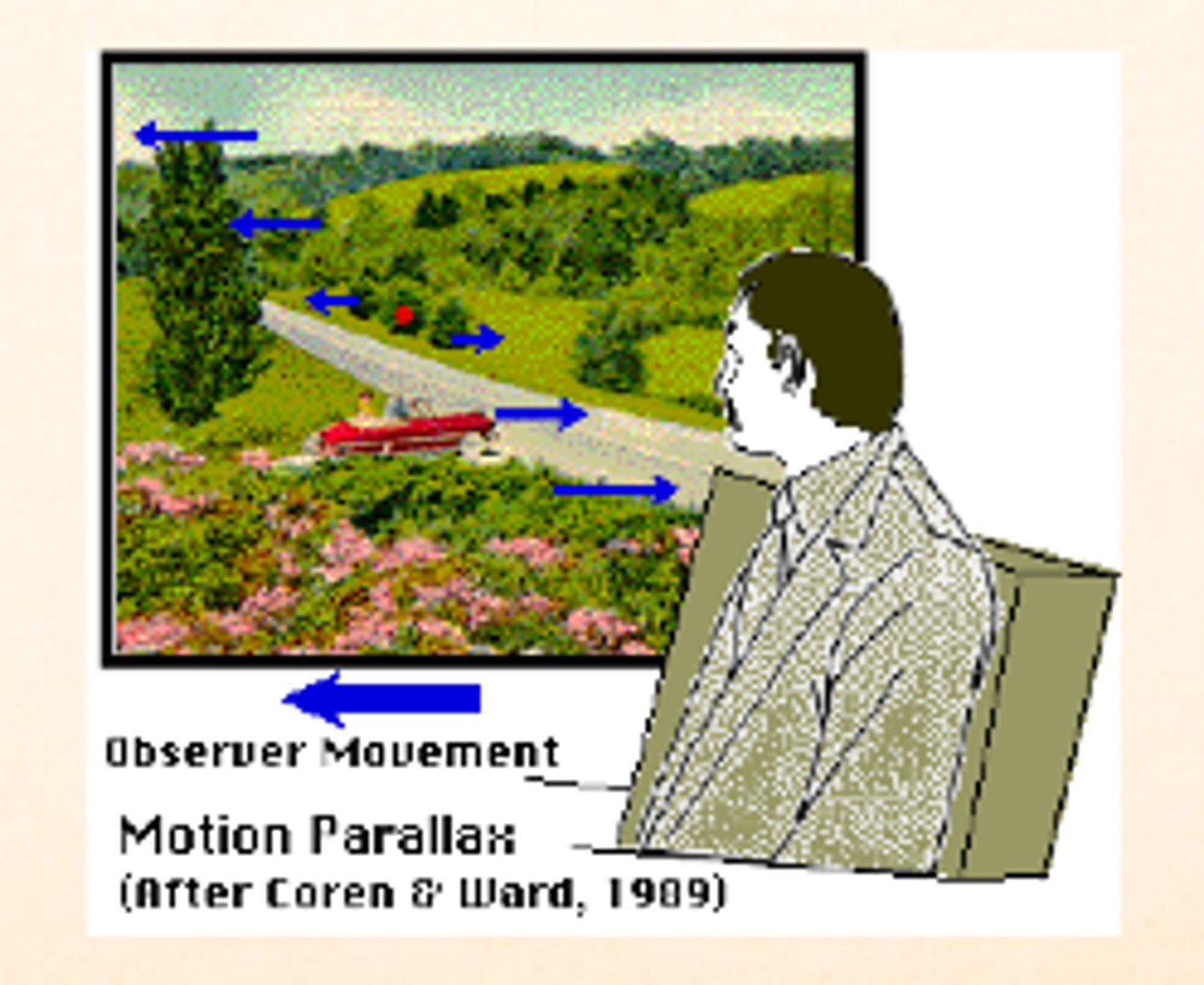
apparent motion
When you are riding in a car, (for example), and look at distant mountains, the objects in a nearby field seem to be moving in the opposite direction to your movement, Yet, when you look at distant mountains, the objects in a nearby or land beyond the animal seem to be moving in the same direction that you are
afterimage
after staring at an image for a while, when you close your eyes or look away you see the negative image.

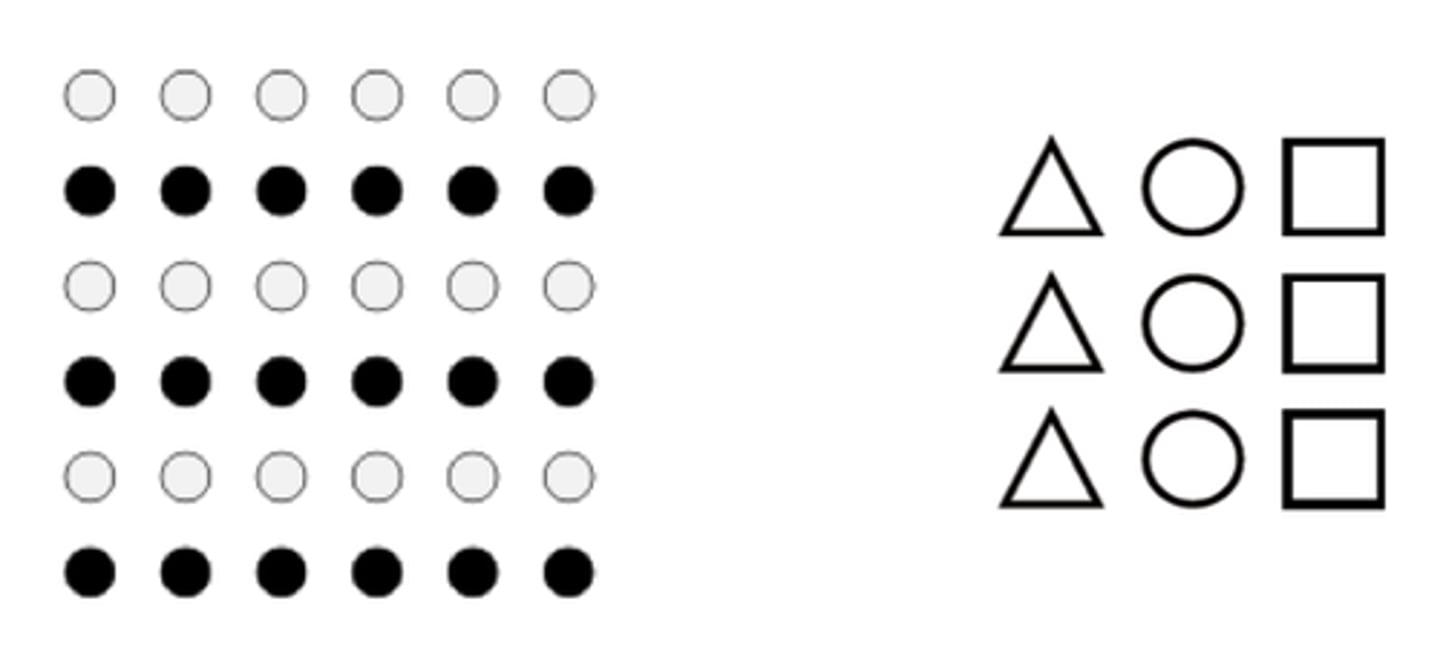
proximity
when we see a number of similar objects, we tend to perceive them as groups or sets of those that are close to each other
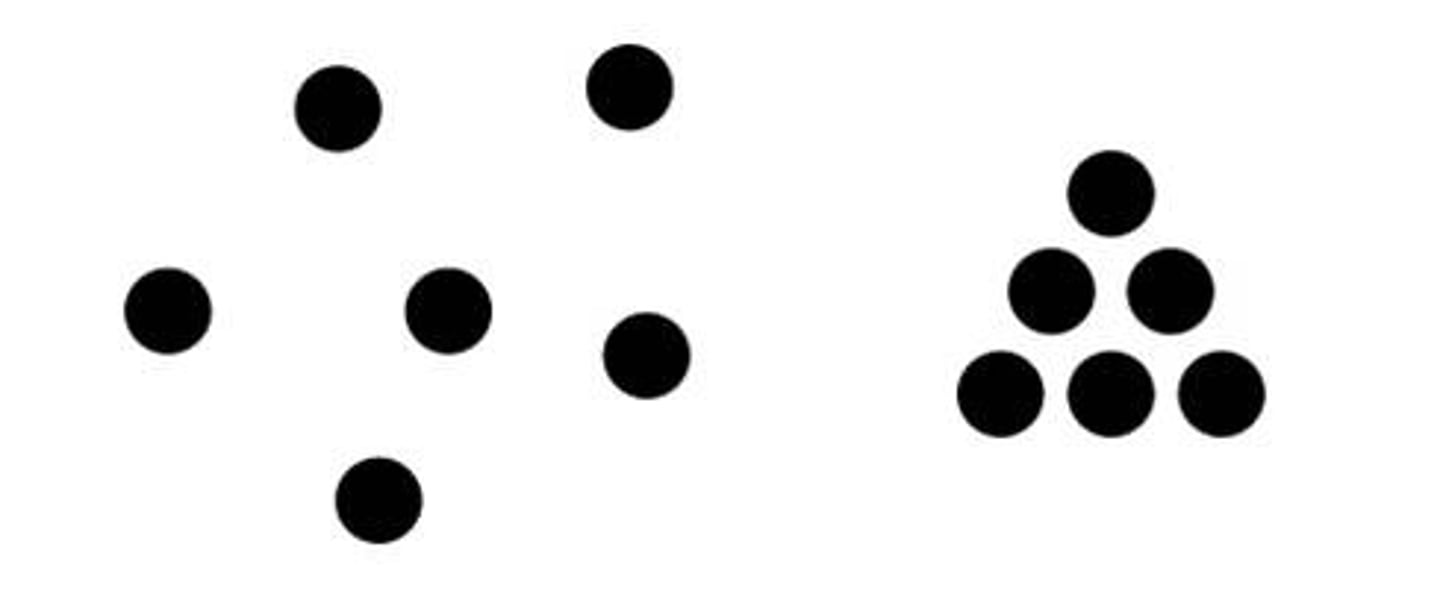
similarity
when similar and dissimilar objects are mingled, we see the similar objects as groups
closure
when we see a familiar pattern or shape with some missing parts, we fill in the gaps

relative clarity
The farther removed an object is, the less detail we can identify. It is one of your monocular depth cues.

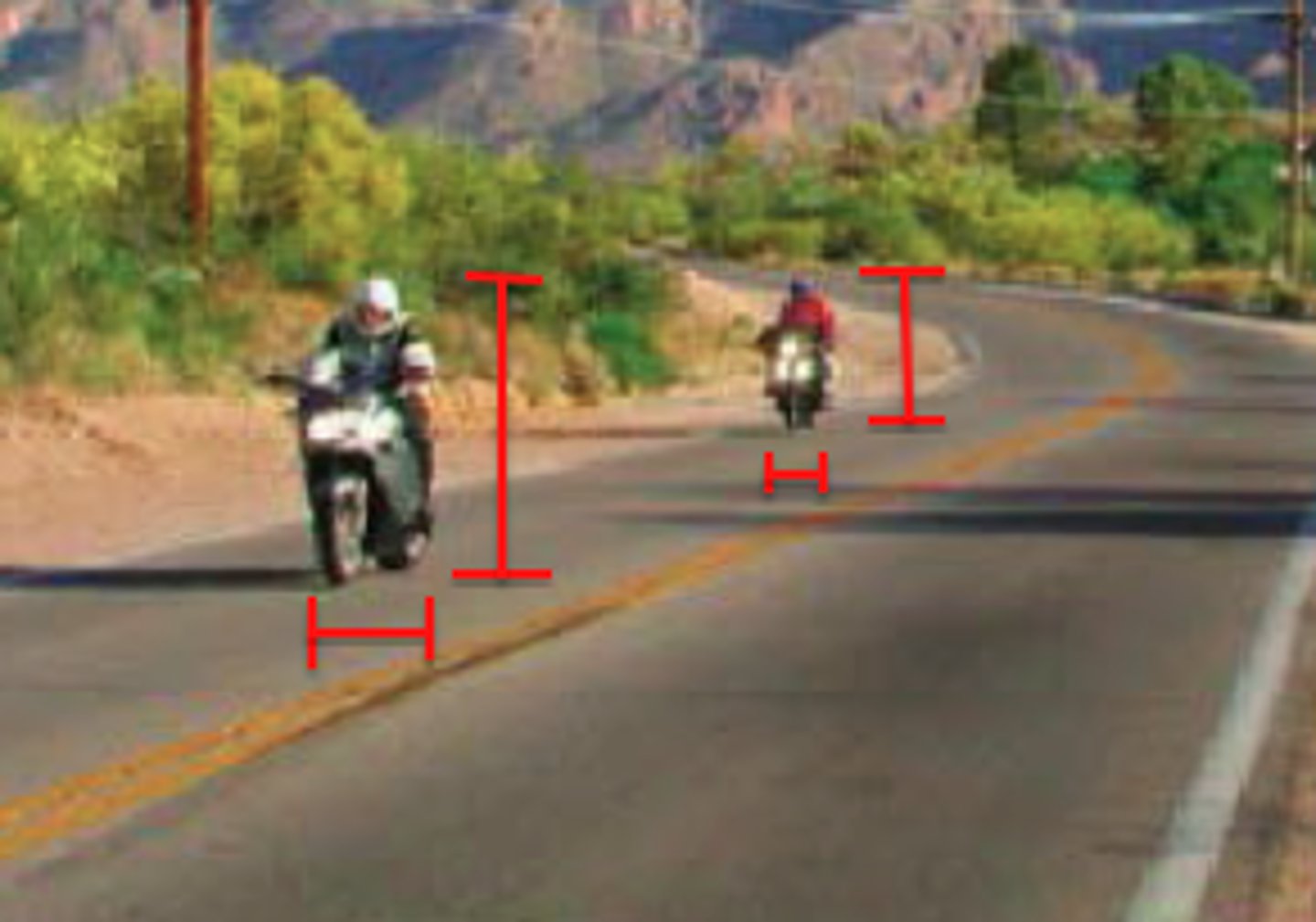
monocular cues
depth cues, such as interposition and linear perspective, available to either eye alone

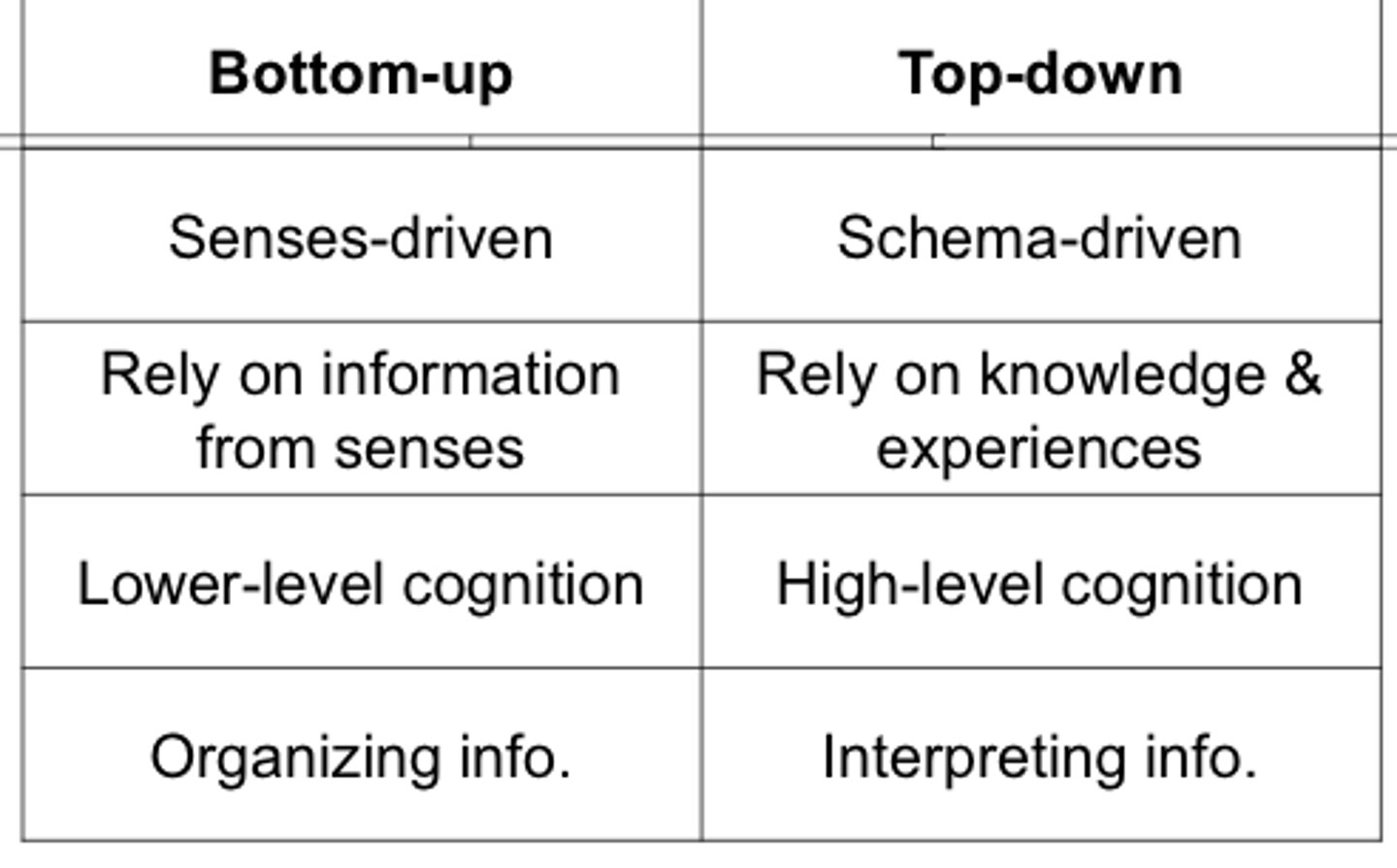
top-down processing
information processing guided by higher-level mental processes, as when we construct perceptions drawing on our experience and expectations

bottom-up processing
the analysis of the smaller features to build up to a complete perception
perceptual set
a mental predisposition to perceive one thing and not another
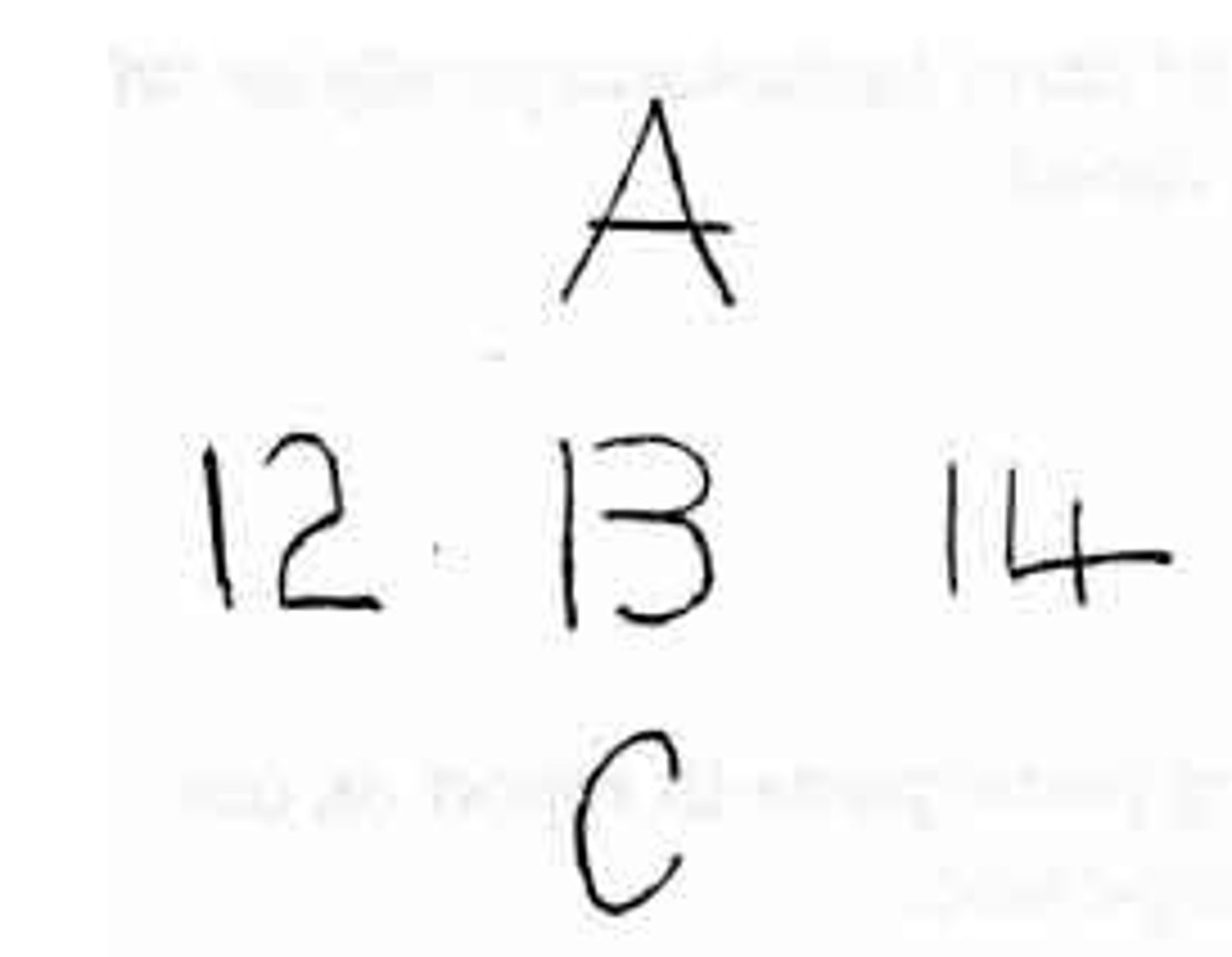
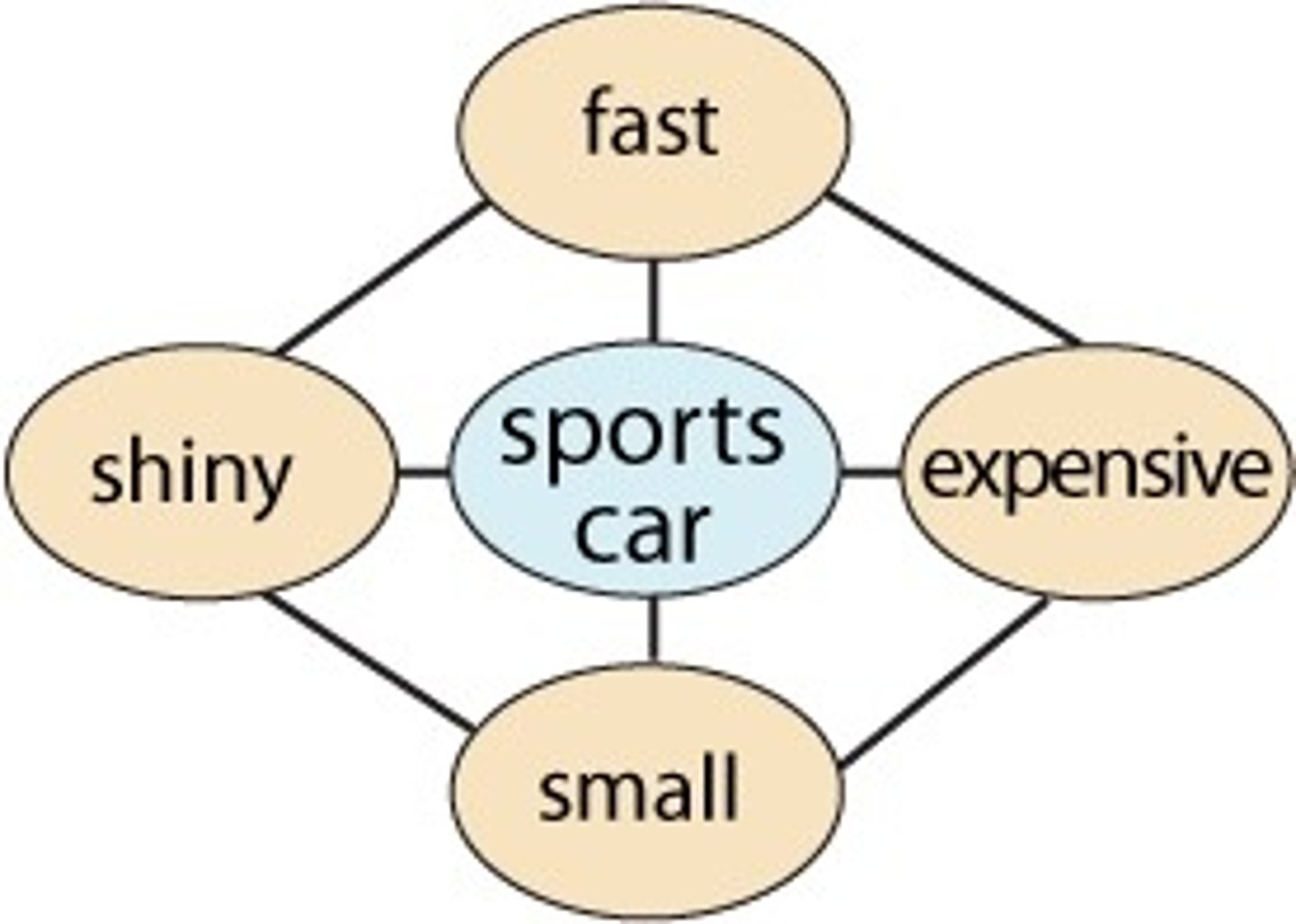
Schema
a concept or framework that organizes and interprets information
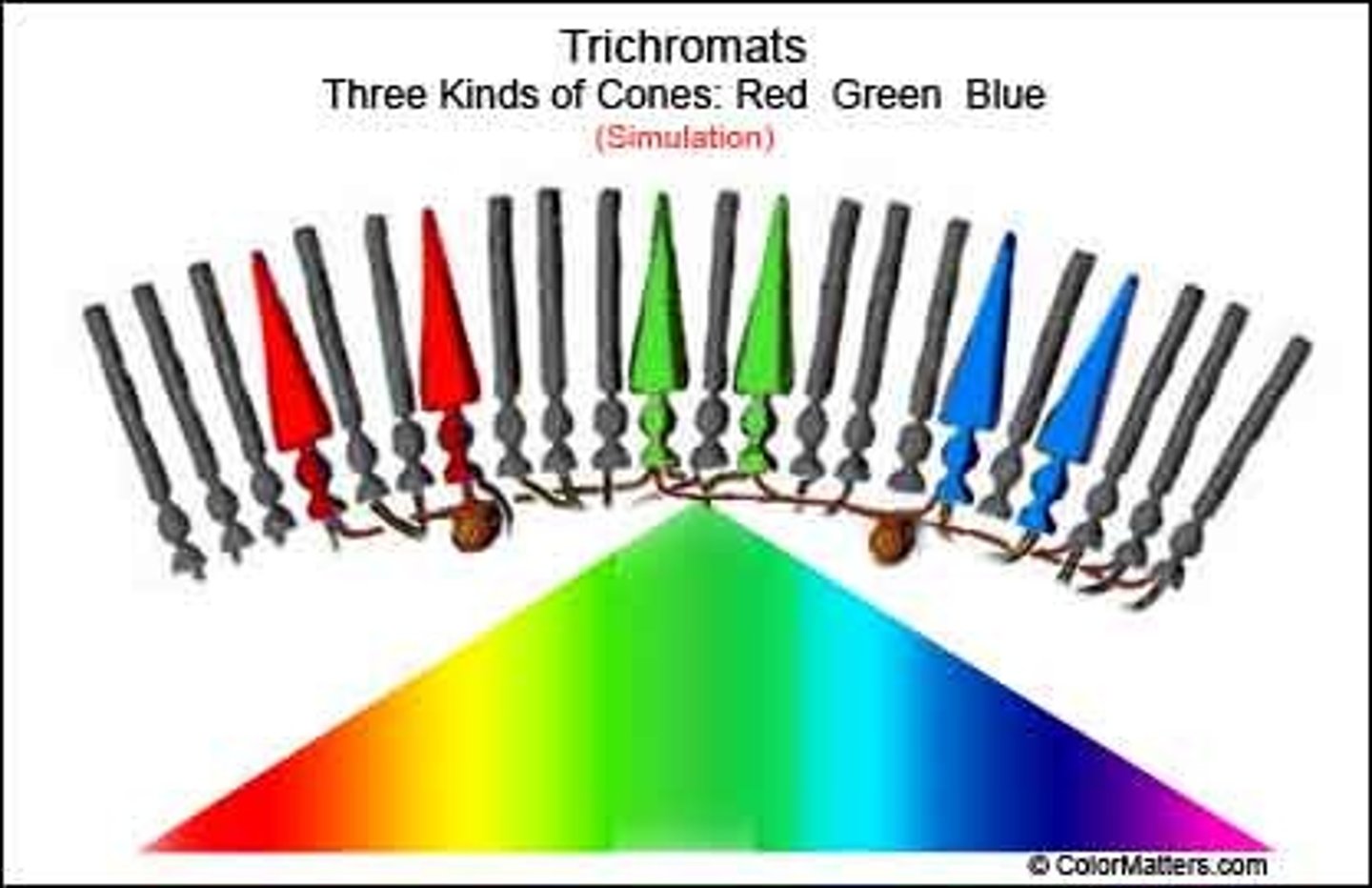
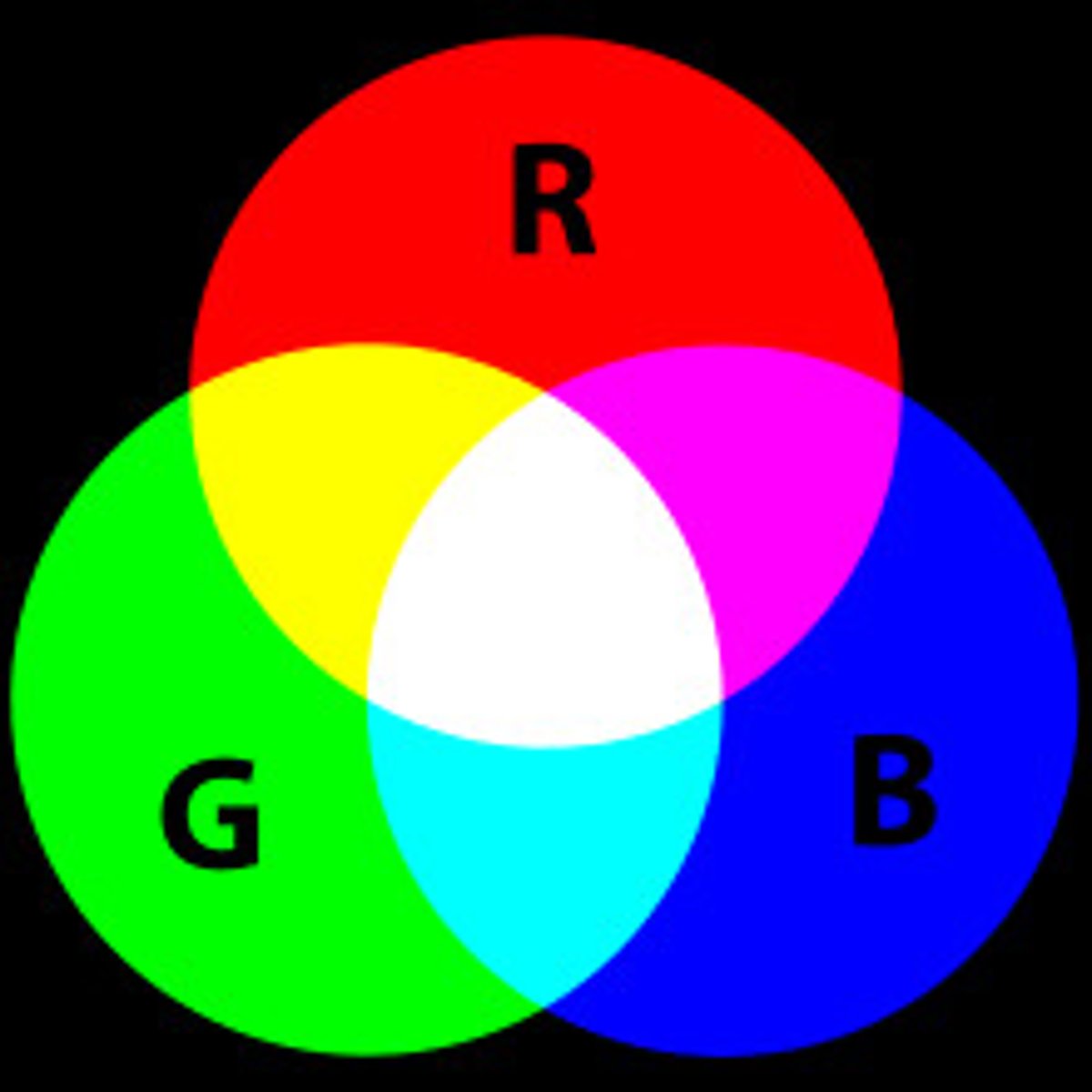
Trichromatic Color Theory
also known as the component theory; proposed by Thomas Young and Hermann van Helmholtz suggests that there are three types of receptors in the retina: cones that respond to red, blue or green
Synesthesia
describing one kind of sensation in terms of another ("a loud color", "a sweet sound")

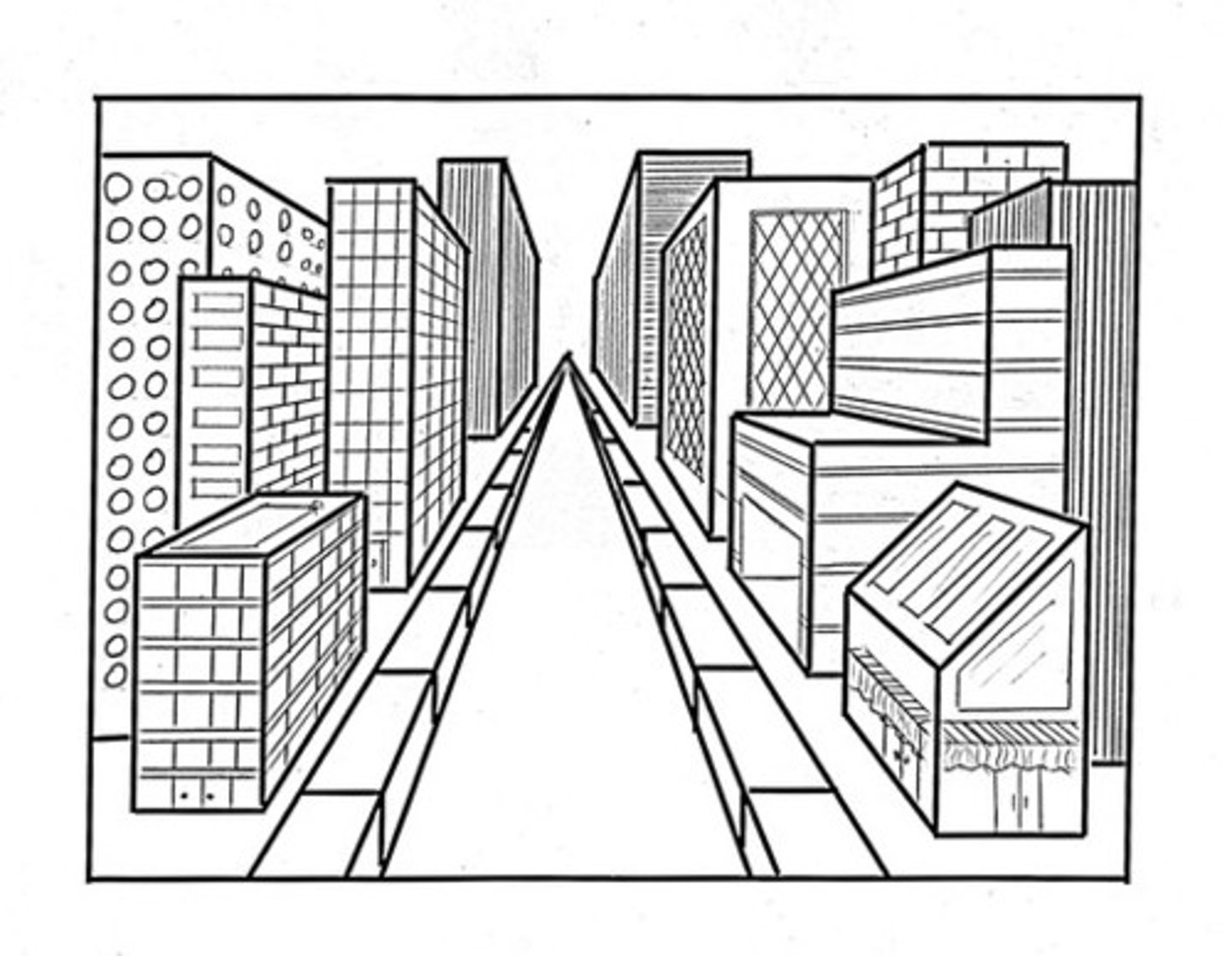
linear perspective
A monocular cue for perceiving depth; the more parallel lines converge, the greater their perceived distance.
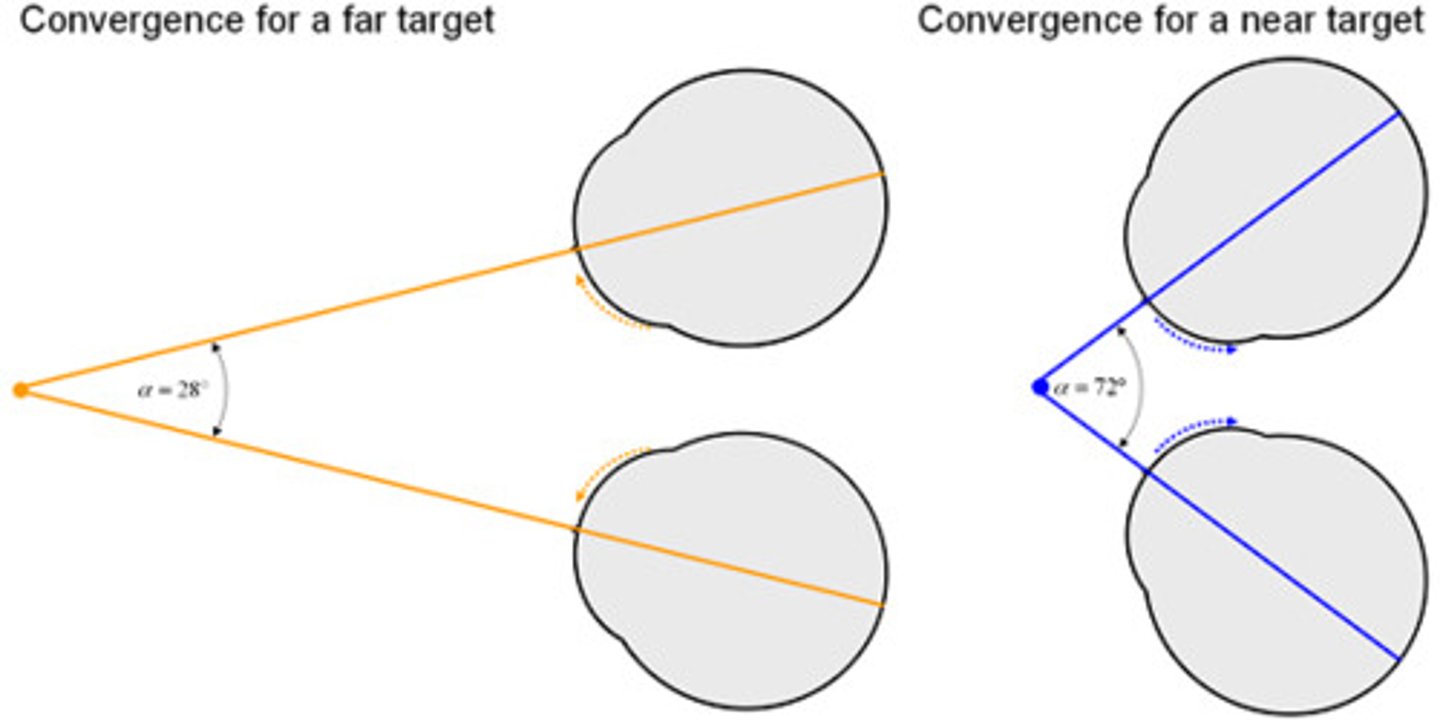
convergence
A binocular cue for perceiving depth; the extent to which the eyes converge inward when looking at an object
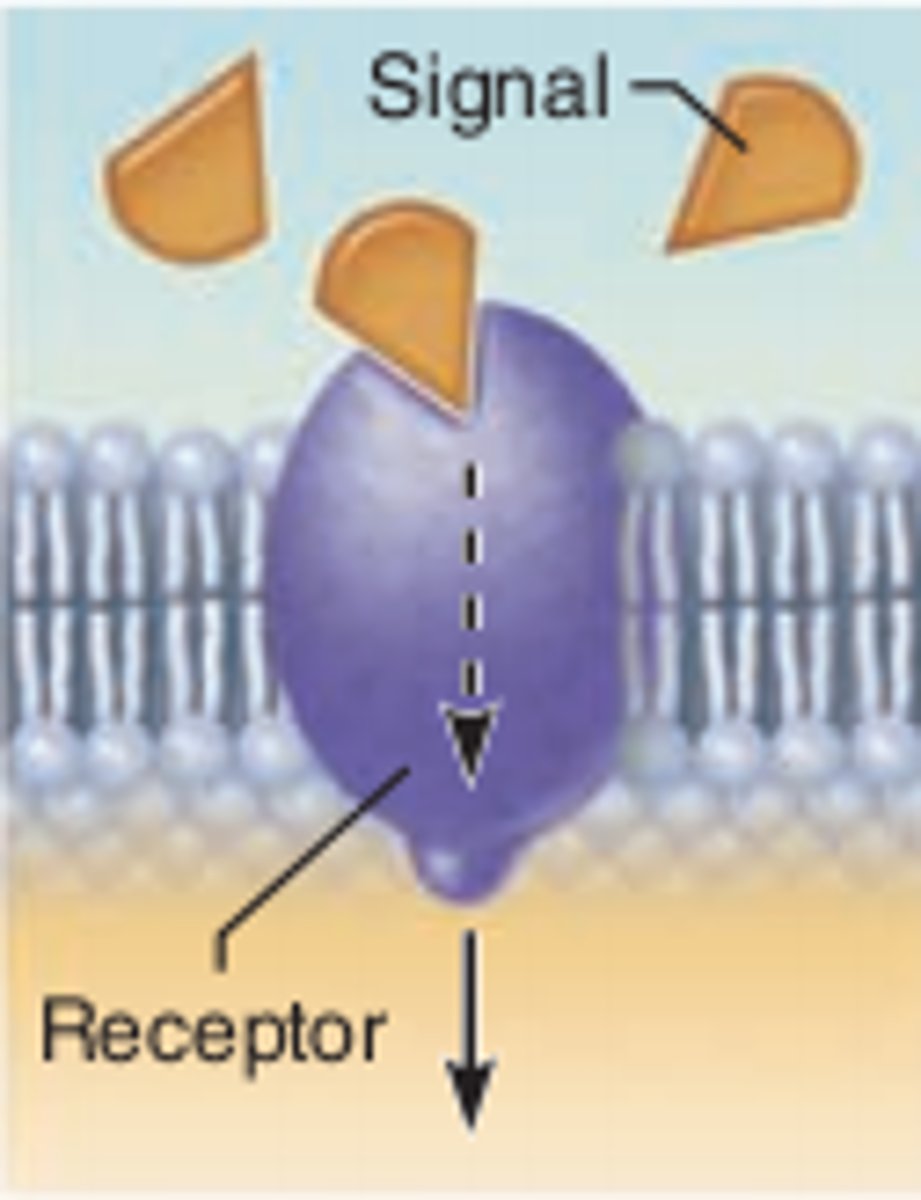
Transduction
conversion of one form of energy into another. In sensation, the transforming of stimulus energies, such as sights, sounds, and smells, into neural impulses our brains can interpret.
change blindness
failing to notice changes in the environment

inattentional blindness
a failure to perceive objects that are not the focus of attention

selective attention
the ability to focus on only one stimulus from among all sensory input

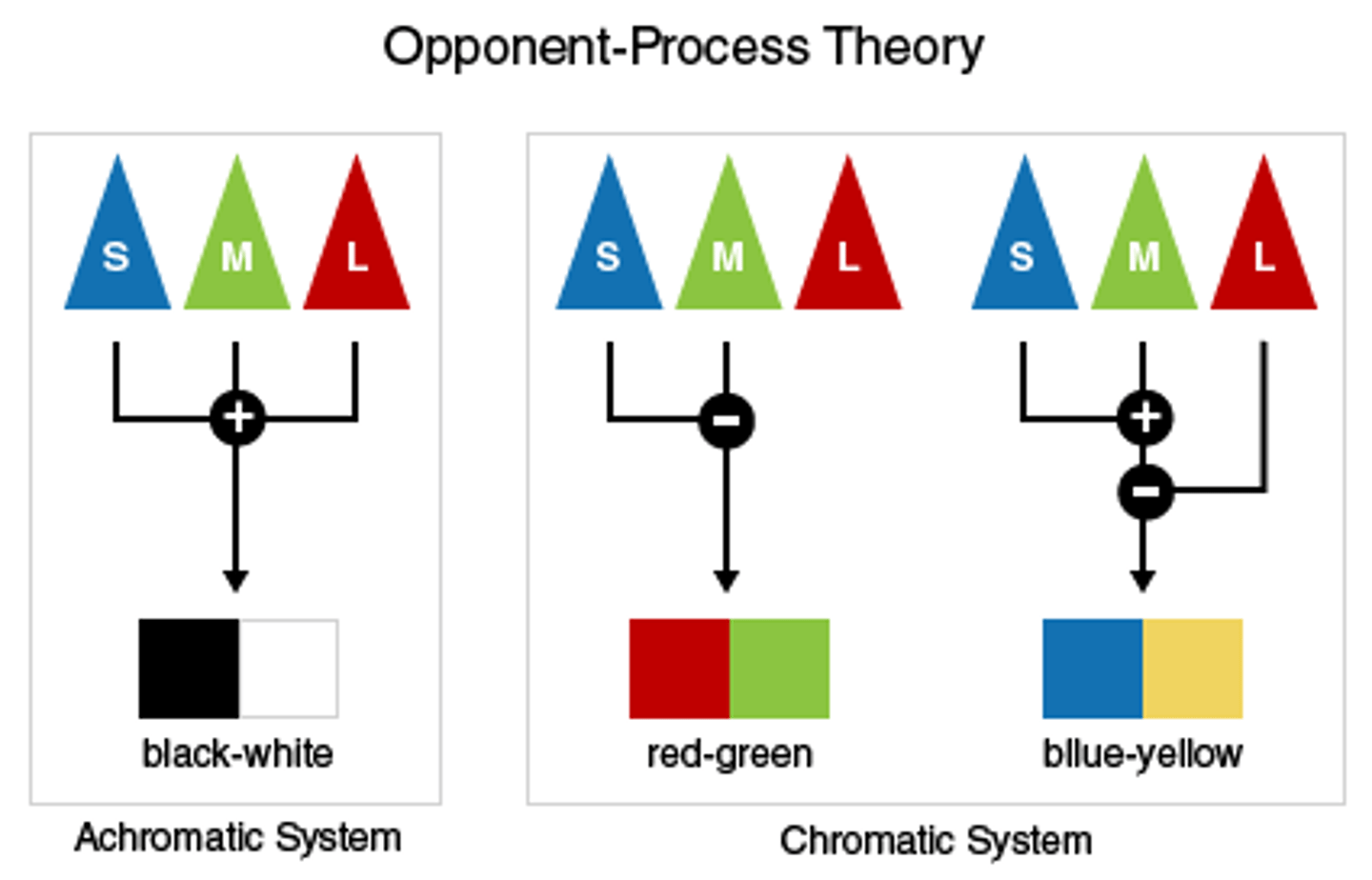
opponent-process theory
the theory that opposing retinal processes (red-green, yellow-blue, white-black) enable color vision. For example, some cells are stimulated by green and inhibited by red; others are stimulated by red and inhibited by green
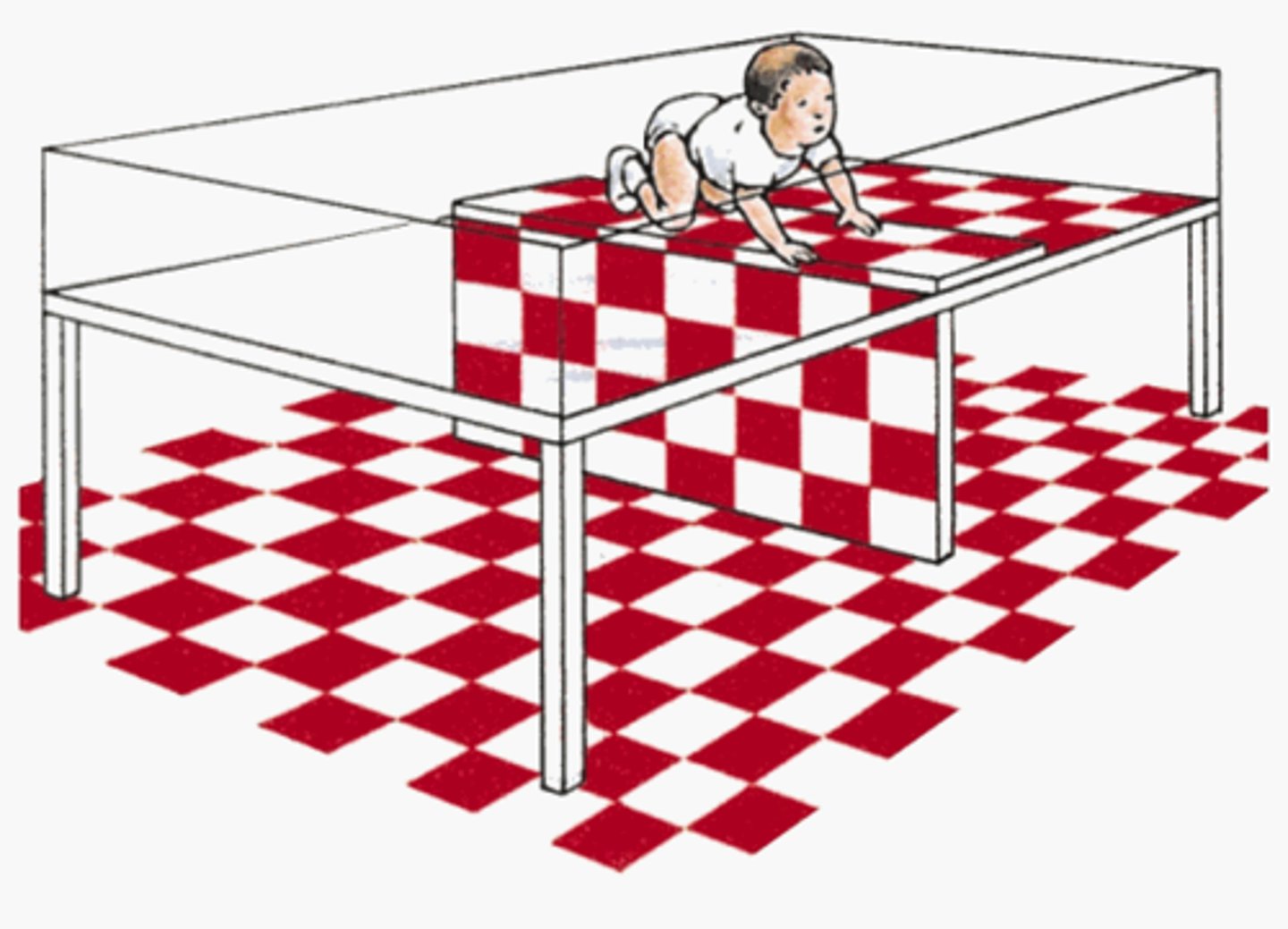
visual cliff apparatus
developed by Eleanor Gibson and Richard Walk to study whether depth perception is innate
Binocular depth cues
clues about distance based on the differing views of the two eyes
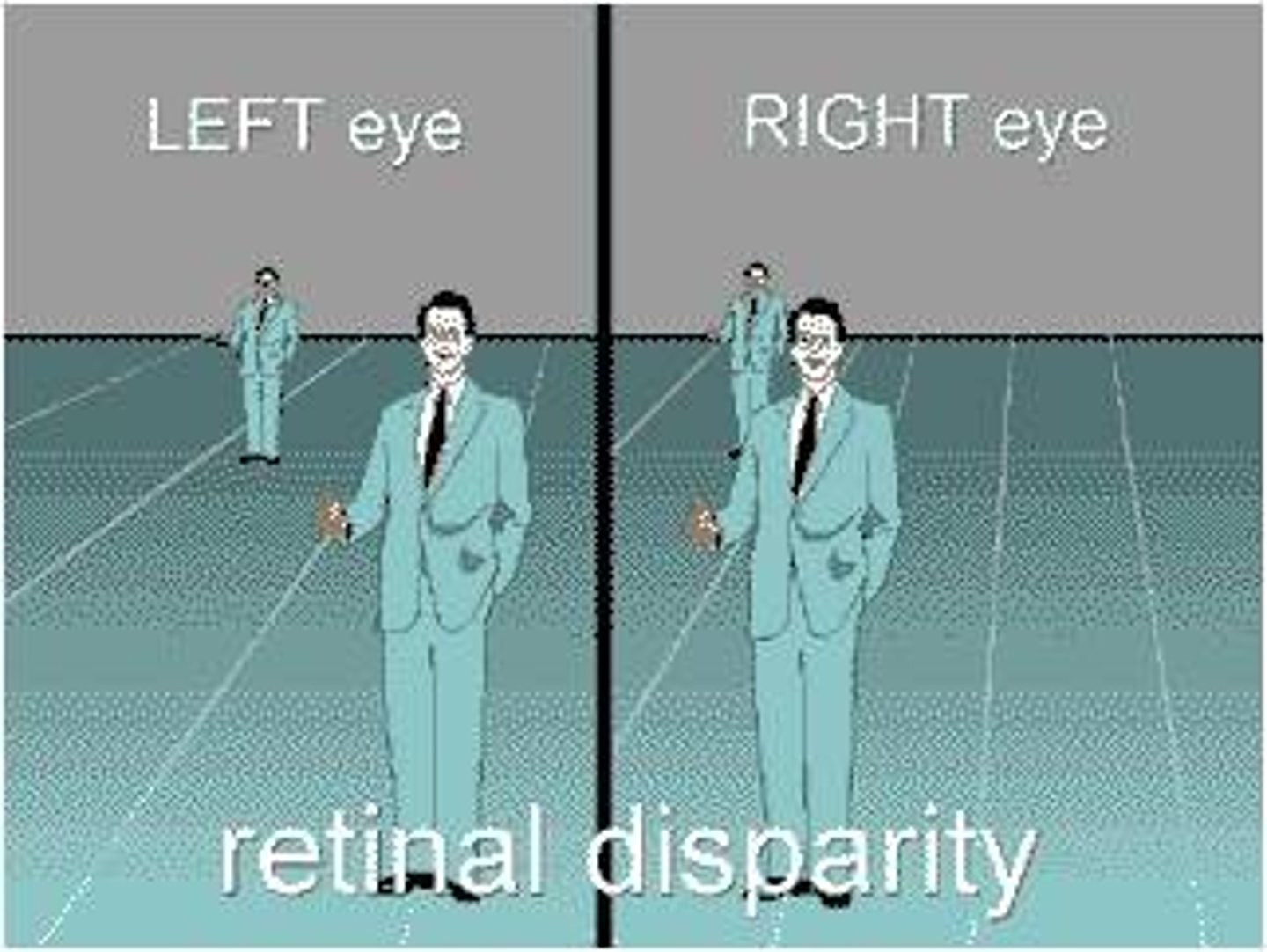
Retinal Disparity
a binocular cue for perceiving depth by comparing images from the retinas in the two eyes, the brain computes distance—the greater the disparity (difference) between the two images, the closer the object.
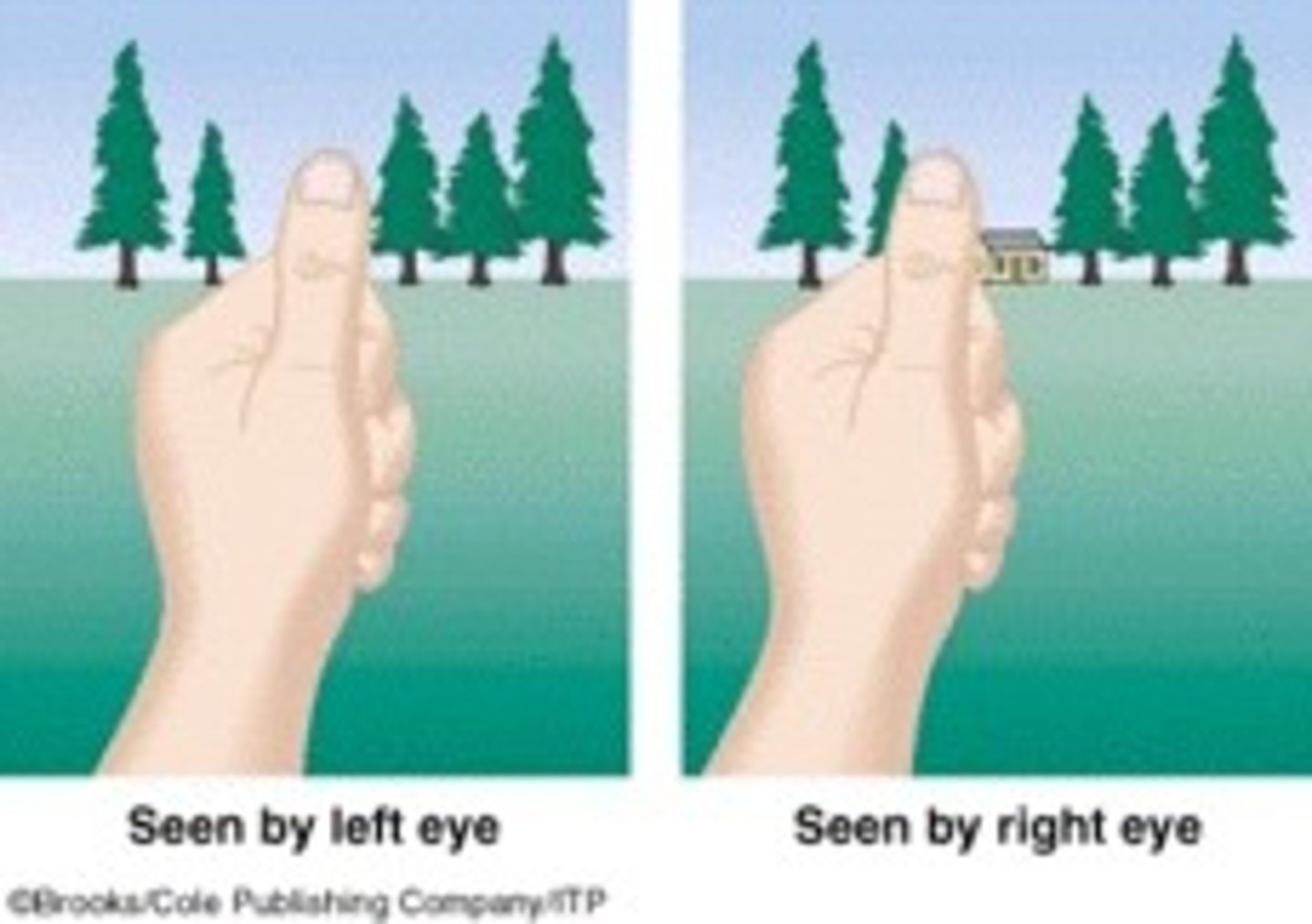
Relative size
a monocular cue for perceiving depth; the smaller retinal image is farther away

Texture/Gradient
the tendency for textured surfaces to appear to become smaller and finer as distance from the viewer increases
Cocktail party effect
Ability to concentrate on one voice amongst a crowd

Sensory Interaction
the principle that one sense may influence another, as when the smell of food influences its taste

Accommodation
the process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina

Fova
central point in the retina, around which the eye's cones cluster
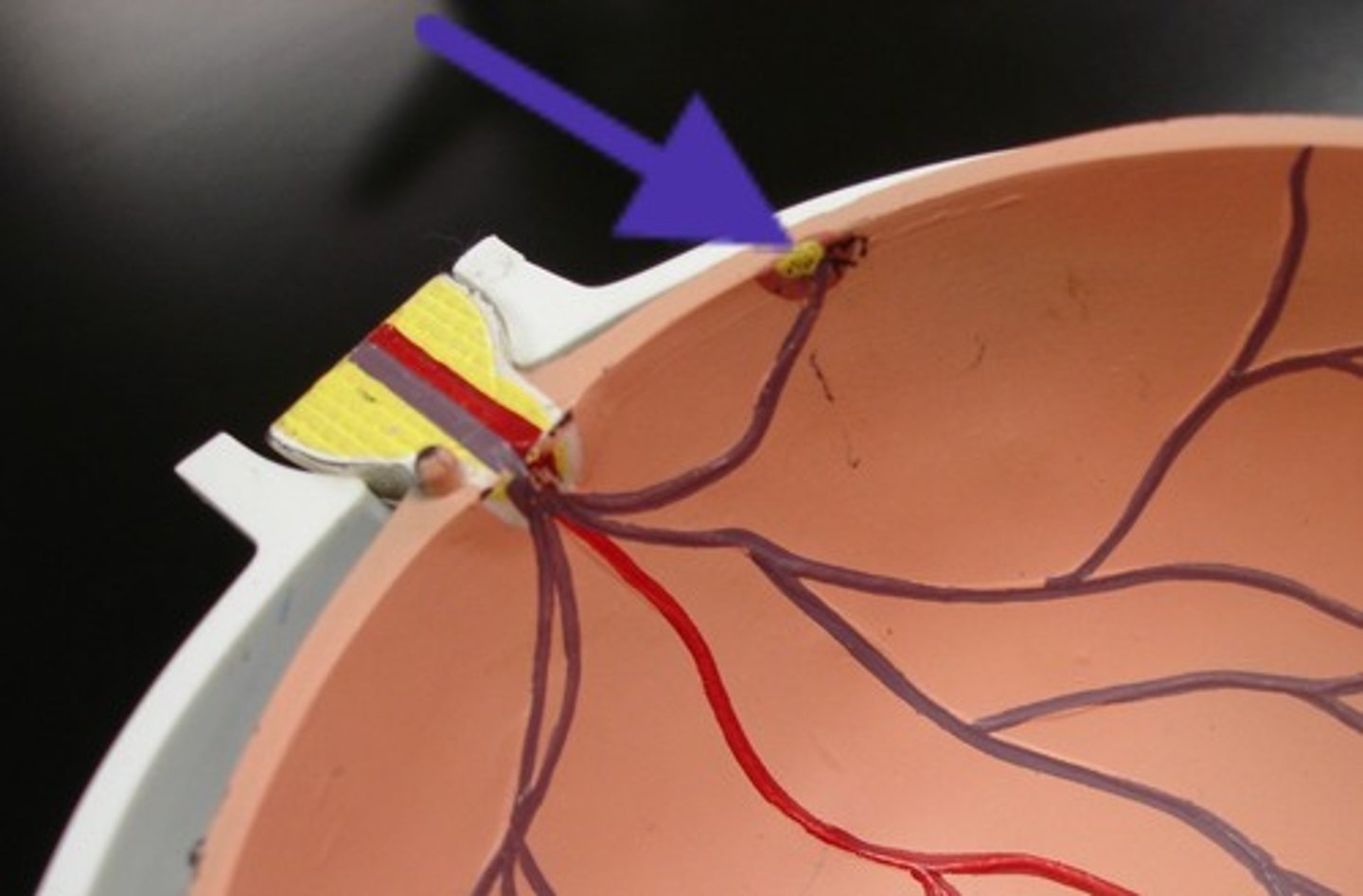
Blindsight
a condition in which a person can respond to a visual stimulus without consciously experiencing it

Phantom limb sensation
patients who have had a limb amputated may still experience sensations such as itching, pressure, tingling, or pain as if the limb were still there

Sensorineural deafness
deafness that results from damage to the auditory nerve