3.6 intermolecular forces, electronegativity and bond properties
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
18 Terms
Describe hydrogen bonding
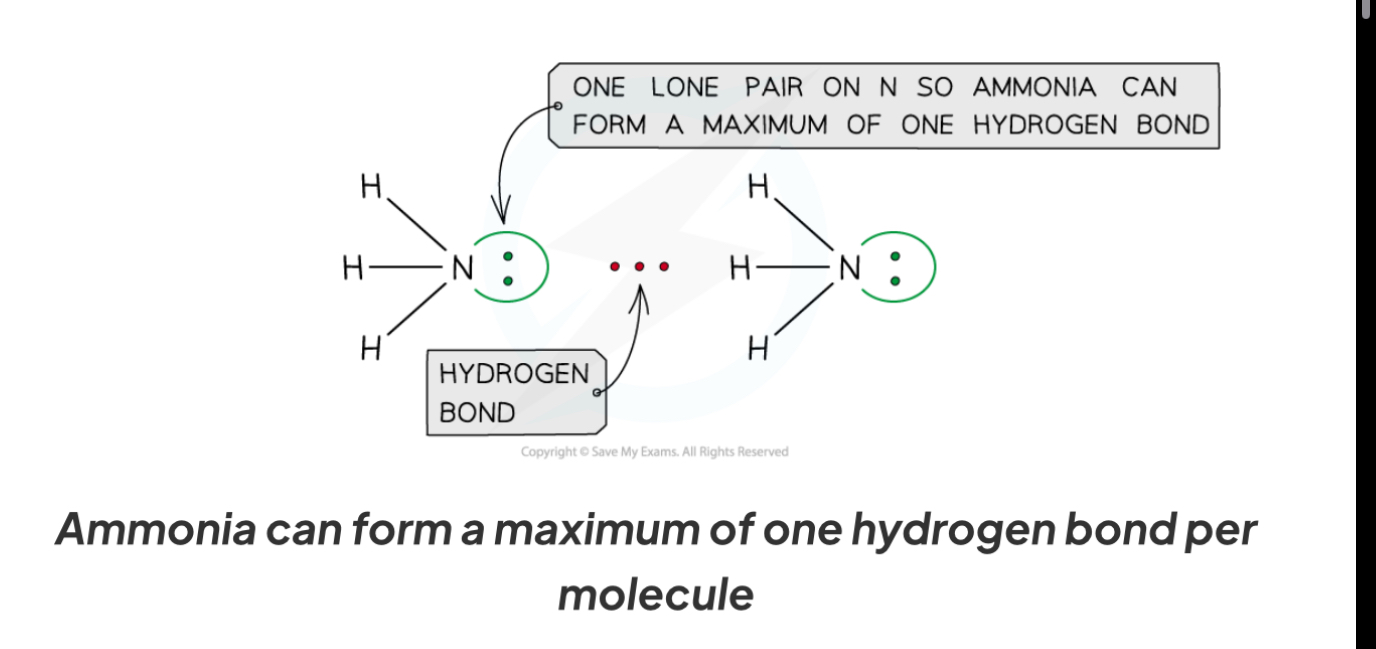
strongest form on intermolecular bonding
Type of permanent dipole- permanent dipole bonding
Molecule must contain highly electronegative atom with a lone pair
H atoms overlap to must be covalently bonded
Describe the hydrogen bonding in ammonia
Describe the hydrogen bonding in water
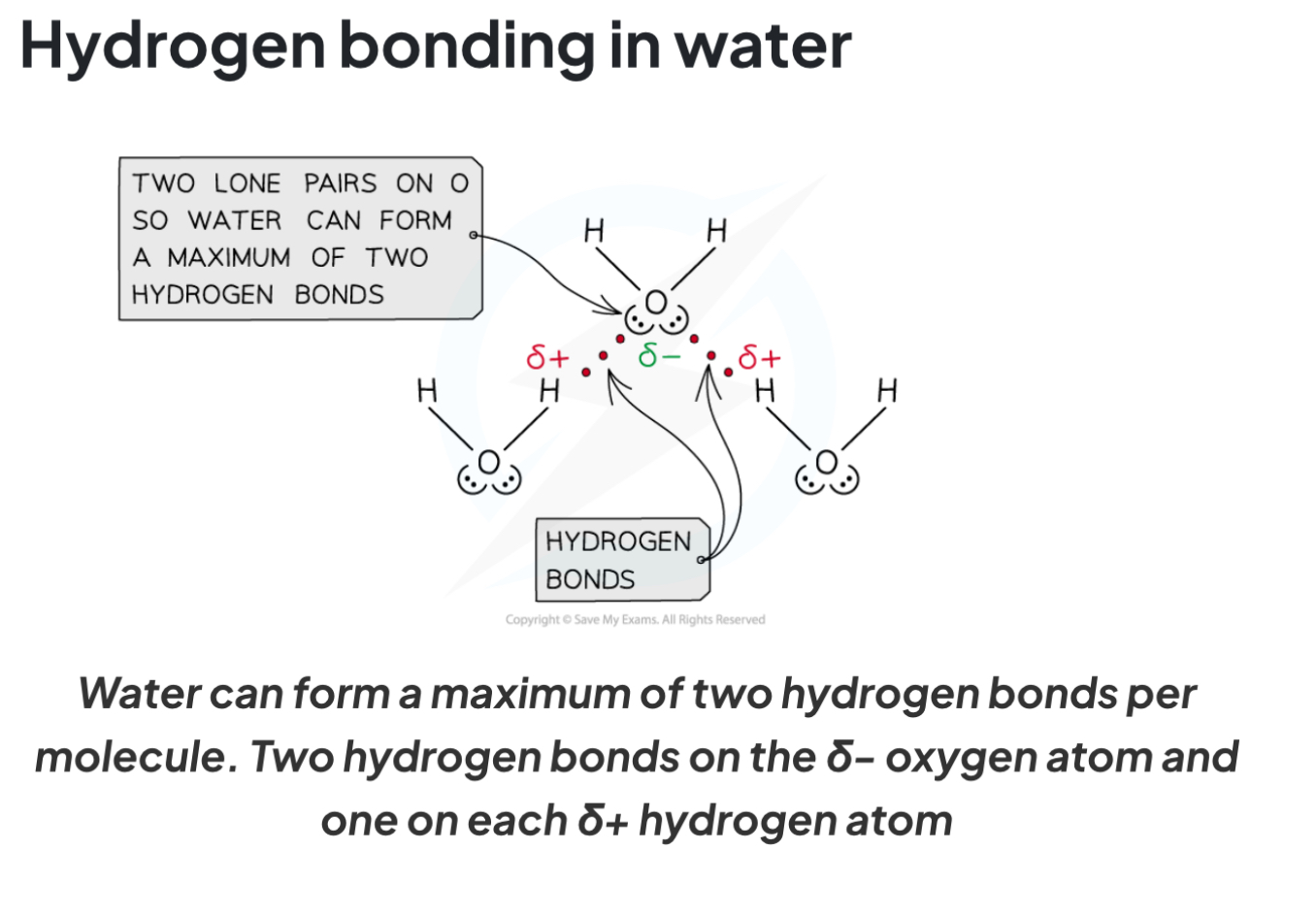
What properties does hydrogen bonding cause water to have?
high melting and boiling points
High surface tension
A lower density in ice compared to water
Explain why ice is less dense than water
the water molecules are packed in 3D H-bonded network in a rigid lattice
Each oxygen atom is surrounded by hydrogen atoms
This way of packing the molecules in a solid and the relatively long bond lengths of the hydrogen bonds means that the water molecules are slightly further apart than in the liquid form
When is a covalent bond polar? What does it cause?
When 2 atoms in a covalent bond have different electronegativities:
the electron distribution is asymmetric
Partial charges form
Define dipole moment
Measure of how polar a bond is
Arrow points to delta negative of dipole
Some molecular have polar bonds but why are they not polar overall?
The molecule is arranged in such a way that individual dipole moments cancel each other out
Define Vander Waal’s forces
Intermolecular forces between molecular entities other than those due to bond formation
State the types of vander Waals’ forces
ID-ID forces (London Forces)
PD-PD forces
Including hydrogen bonding
In general ionic, covalent and metallic bonding are … than intermolecular forces
Stronger
Explain ID-ID forces
instantaneous dipole-induced dipole forces
Electron charge cloud in non polar molecules is constantly moving
This can cause a temporary dipole to arise
This can induce a dipole on neighbouring molecules
ID-ID forces increase with:
Increasing number of electrons (and atomic number) in the molecule
Increasing the places where the molecules come close together
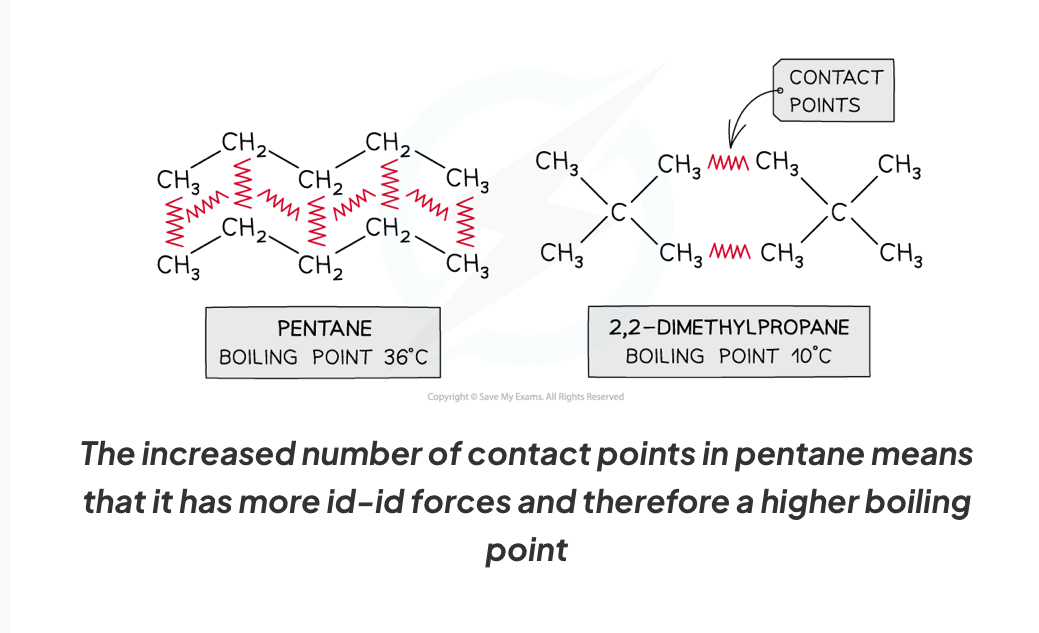
How do contact points affect id-id forces and thus boiling point
Increased number of contact points means more id id forces therefore higher boiling point
Explain pd-pd forces (Permanent dipole- permanent dipole
Polar molecules have permanent dipoles
The molecule will always have a negatively and positively charged end
Compare the boiling points of butane and propanone
Butane and propanone have the same number of electrons
Butane is a non polar molecule so will have id-id forces
Propanone is a polar molecule so will have pd-pd forces
Therefore, more energy is needed to break the intermolecular forces between propanone.
Therefore propanone has higher bp
Hydrogen bonds are … than pd pd forces
Stronger