Long-Term Memory: Encoding, Retrieval, and Consolidation
1/75
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
76 Terms
Long-Term Memory
Storage of information over extended periods.
Encoding
Transforming information into a memory format.
Retrieval
Accessing information from long-term memory.
Consolidation
Stabilizing a memory after initial acquisition.
Maintenance Rehearsal
Repetition that keeps information in short-term memory.
Elaborative Rehearsal
Using meanings to enhance memory transfer to LTM.
Levels of Processing Theory
Memory retention depends on the depth of processing.
Shallow Processing
Focus on physical features, leading to poor memory.
Deep Processing
Focus on meanings, leading to better memory retention.
Self-Reference Effect
Better recall of information related to oneself.
Visual Imagery
Using mental images to enhance memory encoding.
Generation Effect
Improved memory from generating information actively.
Survival Value
Relating information to survival enhances memory retention.
Organizing Information
Structuring information improves recall and memory.
Retrieval Practice
Practicing retrieval enhances long-term memory retention.
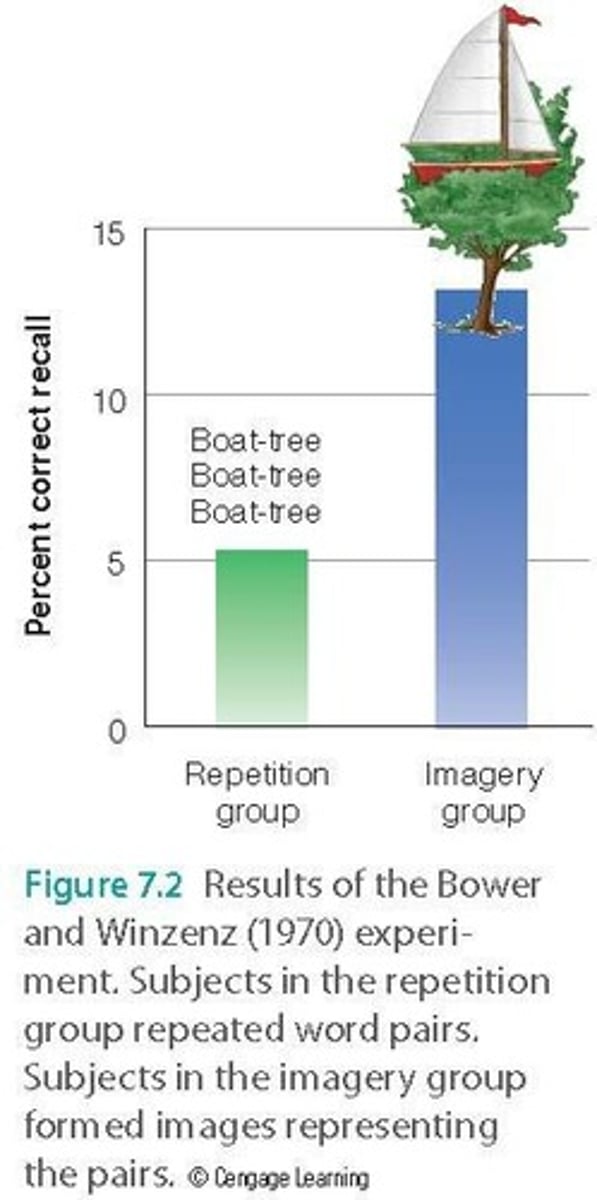
Bower & Winzenz Study
Compared visual imagery and repetition for memory.
Craik & Tulving Study
Investigated depth of processing on memory recall.
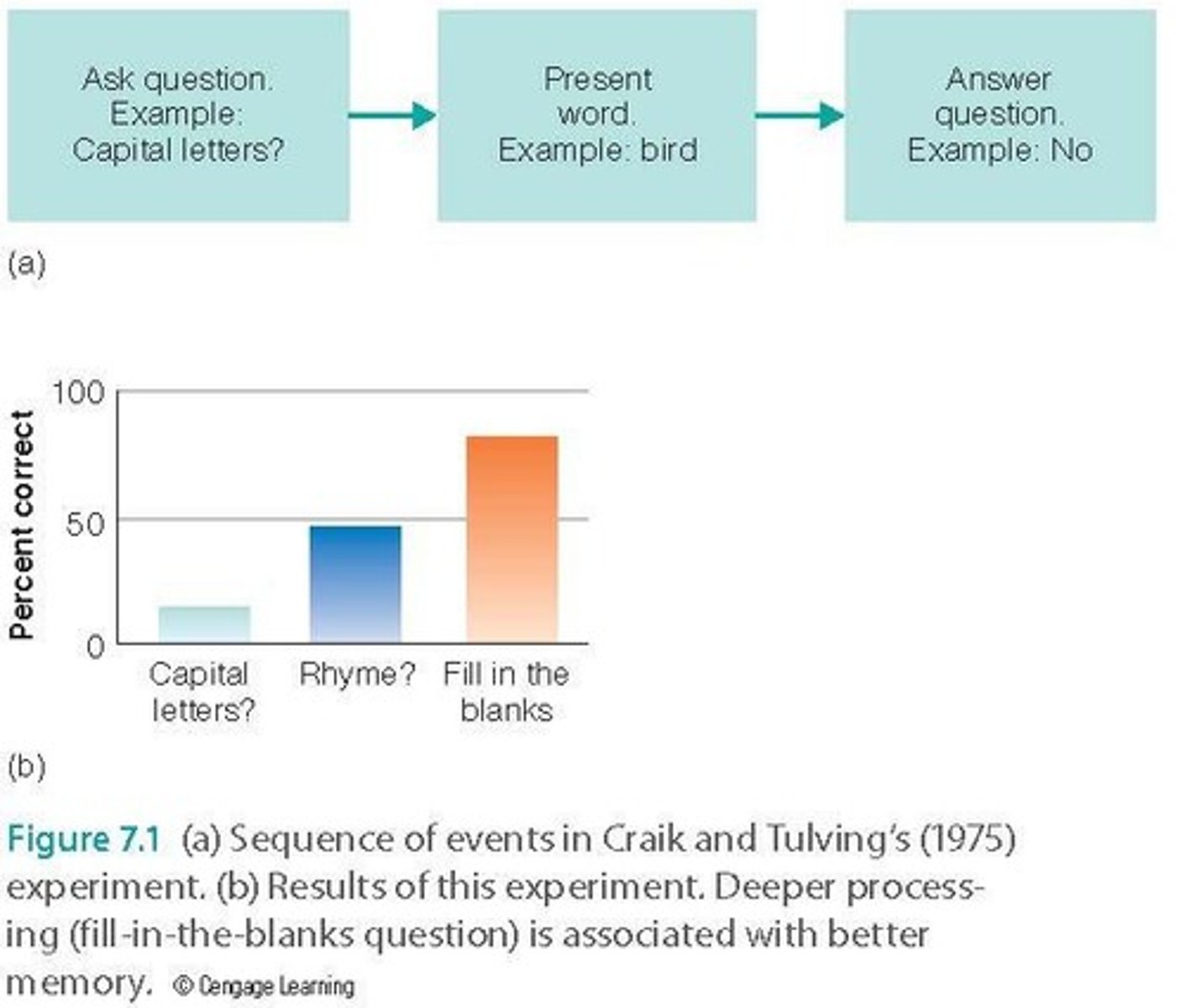
Physical Features
Characteristics of stimuli that affect shallow processing.
Meaningful Connections
Linking new information to existing knowledge aids memory.
Memory Techniques
Strategies developed from memory research for effective studying.
Survival Value
Words related to survival enhance recall ability.
Bransford & Johnson (1972)
Study on comprehension's effect on memory encoding.
Experimental Group 1
Saw a picture before reading the passage.
Experimental Group 2
Saw a picture after reading the passage.
Control Group
Did not see any picture during the study.
Mental Framework
Aids memory encoding and retrieval processes.
Testing Effect
Testing improves memory retention over re-reading.
Roediger and Karpicke (2006)
Study comparing testing vs. re-reading for memory.
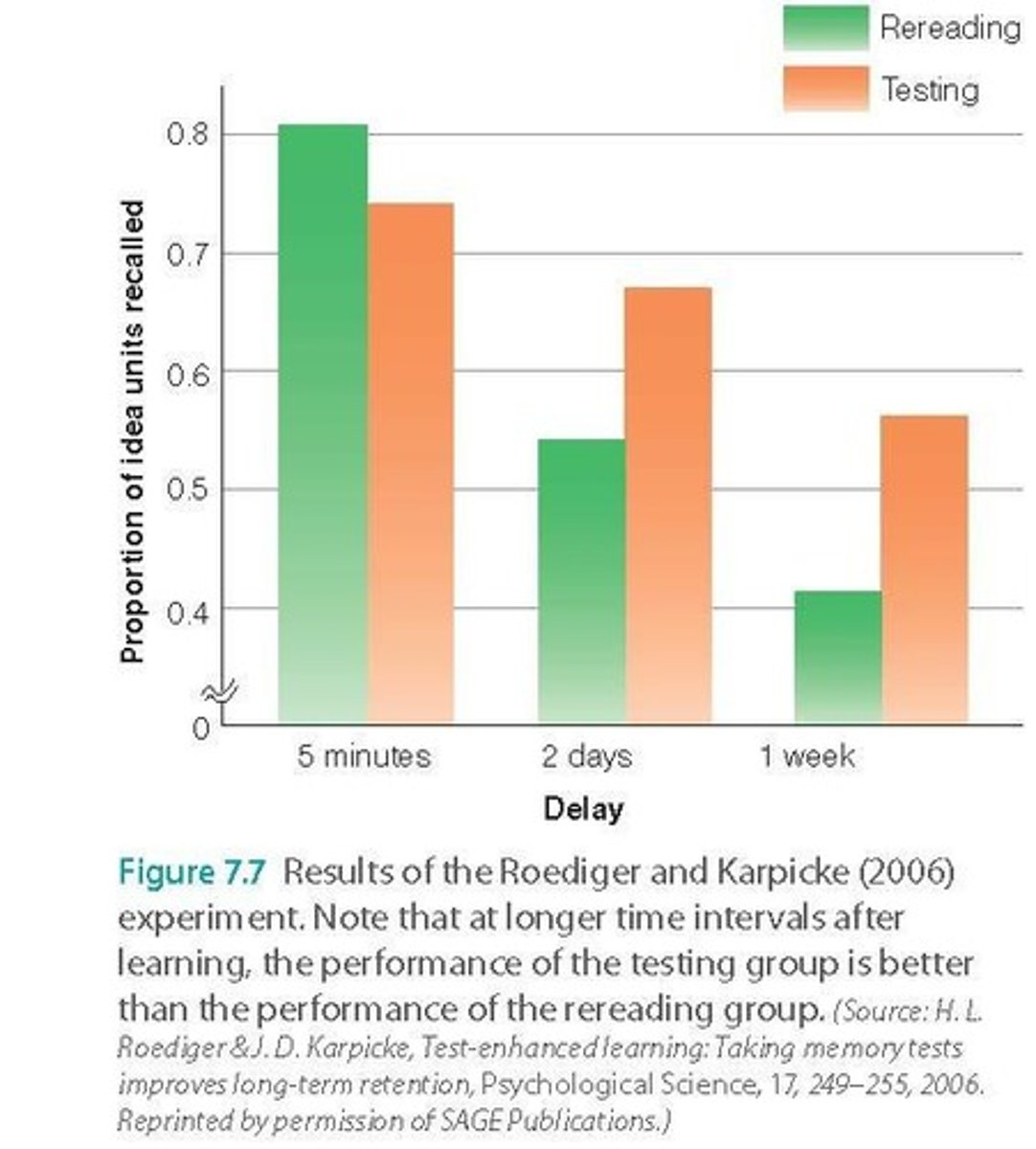
Recall Test
Participants tested on material after reading.
Cued Recall
Using prompts to aid memory retrieval.
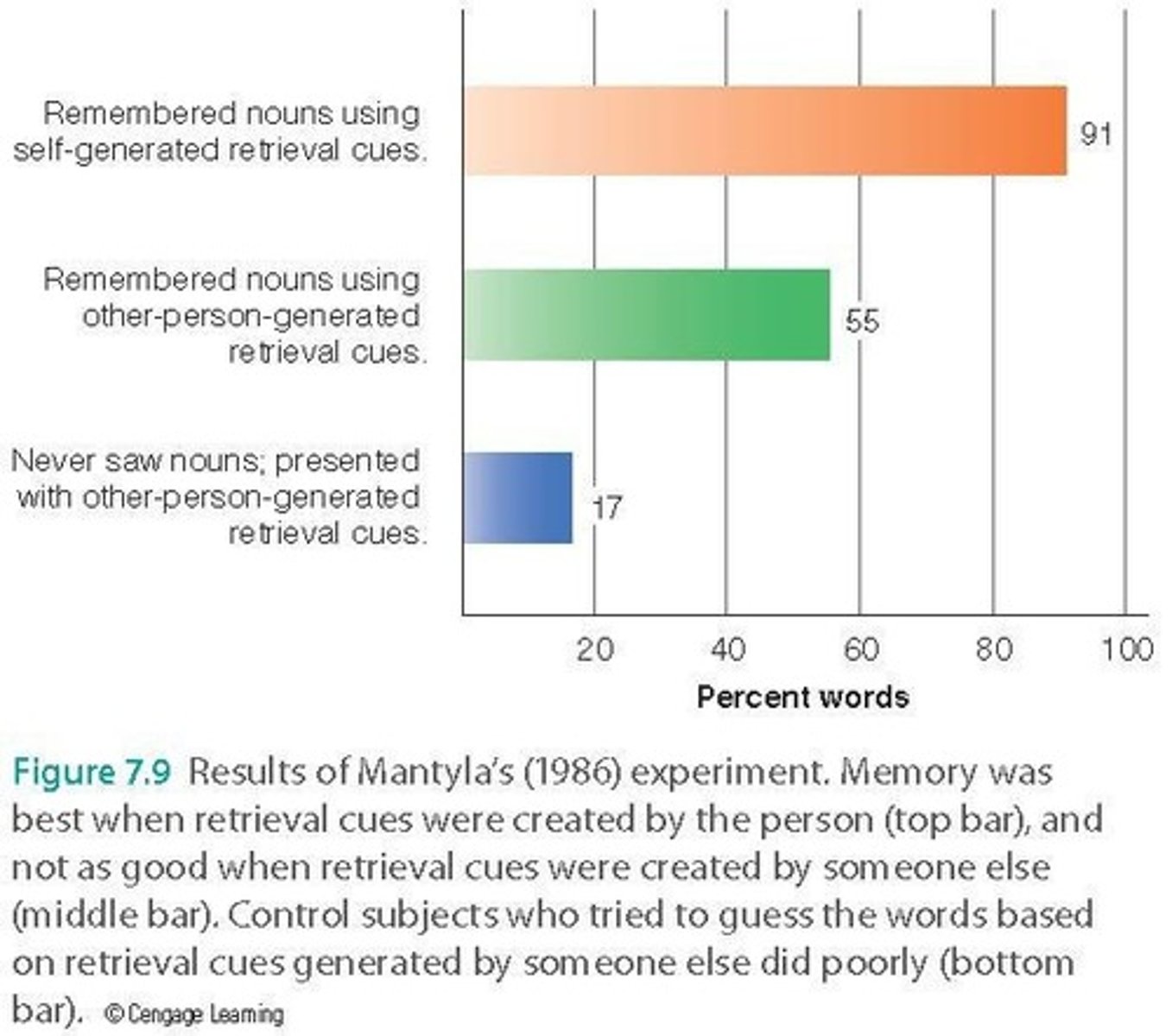
Mantyla (1986)
Study on effectiveness of self-generated retrieval cues.
Free-Recall
Recalling information without any prompts or cues.
Encoding Specificity
Better recall when context matches learning environment.
Godden & Baddeley (1975)
Study demonstrating context-dependent learning effects.
Diving Experiment
Participants recalled better in the same underwater context.
Context-Dependent Learning
Recall improved when context during encoding matches retrieval.
Memory Retrieval
Transferring information from long-term to working memory.
Recall Performance
Measured effectiveness of memory retrieval strategies.
Information Transfer
Moving data from long-term memory to conscious awareness.
Memory Failures
Often due to inability to retrieve information.
Retrieval Cues
Prompts that enhance the recall of information.
State-Dependent Learning
Memory retrieval is enhanced by matching internal states.
Mood Congruence
Better recall occurs when mood aligns during encoding and retrieval.
Crime Victim Assistance
Police use mood re-experiencing to aid memory recall.
Distributed Practice
Learning over multiple sessions improves recall effectiveness.
Massed Practice
Cramming information in one session hinders memory retention.
Attention Maintenance
Sustained attention is challenging in lengthy study sessions.
Feedback from Breaks
Studying after breaks helps assess existing knowledge.
Transfer-Appropriate Processing
Memory performance improves with matching encoding and retrieval processes.
Morris et al. (1977) Study
Tested encoding strategies using rhyming versus semantic methods.

Rhyming Strategy
Learning words through sound similarity for better recall.
Semantic Strategy
Learning words based on meaning for improved memory.
Recall Testing
Memory retrieval assessed through specific task types.
Encoding Context
The environment during learning influences memory retrieval.
Consolidation
Transforming new memories into a permanent state.
Synaptic consolidation
Rapid changes at synapses during memory formation.
Systems consolidation
Gradual reorganization of brain circuits over time.
Muller and Pilzecker
Researchers who studied memory through nonsense syllables.

Nonsense syllables
Meaningless syllables used to study memory retention.
Learning delay
Time interval between learning sessions affecting retention.
Hebb's theory
Learning represented by physiological changes at synapses.
Neural record
Physiological changes that encode experiences in the brain.
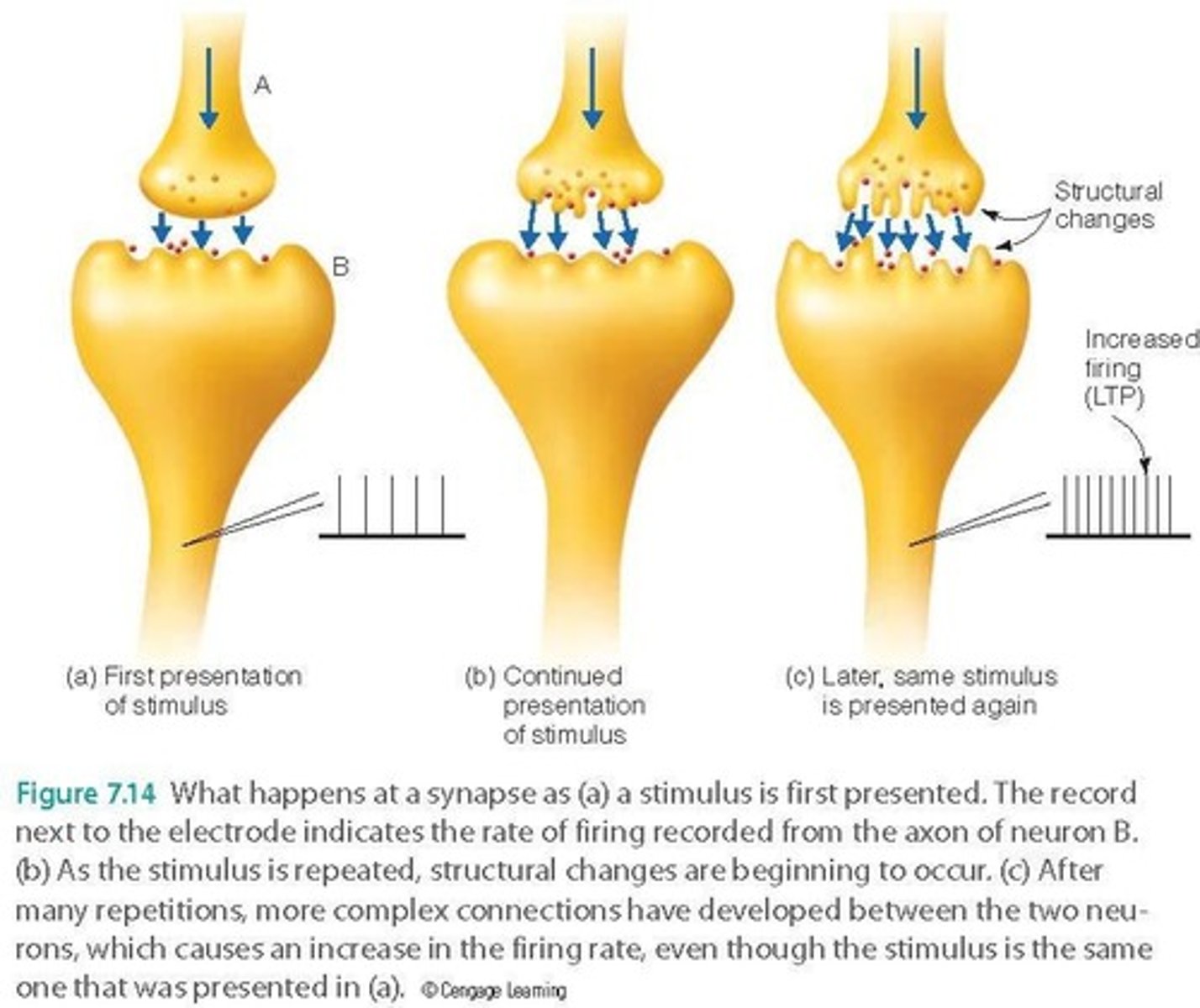
Long-Term potentiation (LTP)
Enhanced neuron firing after repeated stimulation.
Standard model of consolidation
Hippocampus essential during initial memory consolidation.
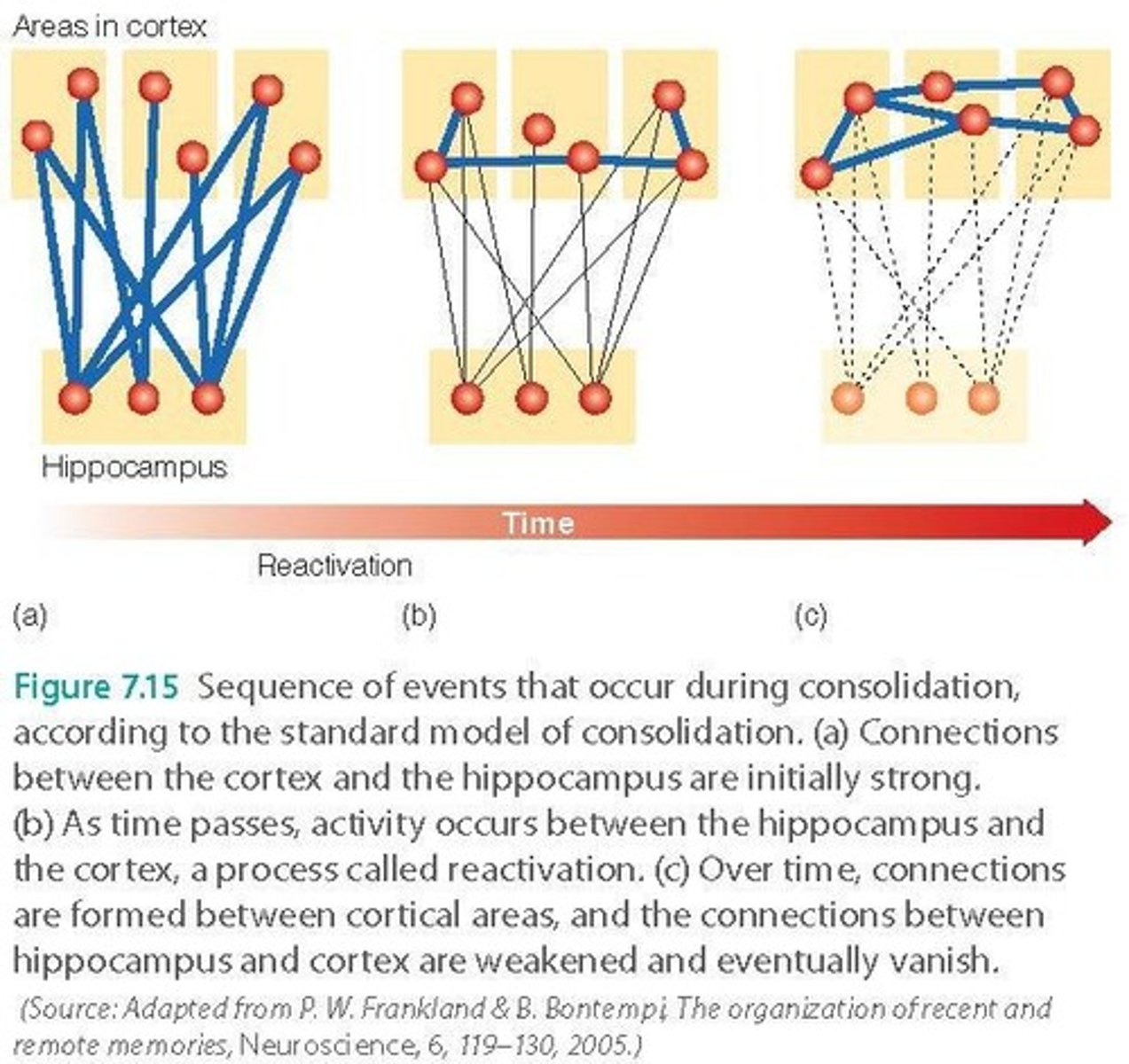
Reactivation
Hippocampus replays neural activity for memory retrieval.
Multiple trace hypothesis
Hippocampus involved in retrieval of all memory types.
Retrograde amnesia
Loss of memory for events before trauma.
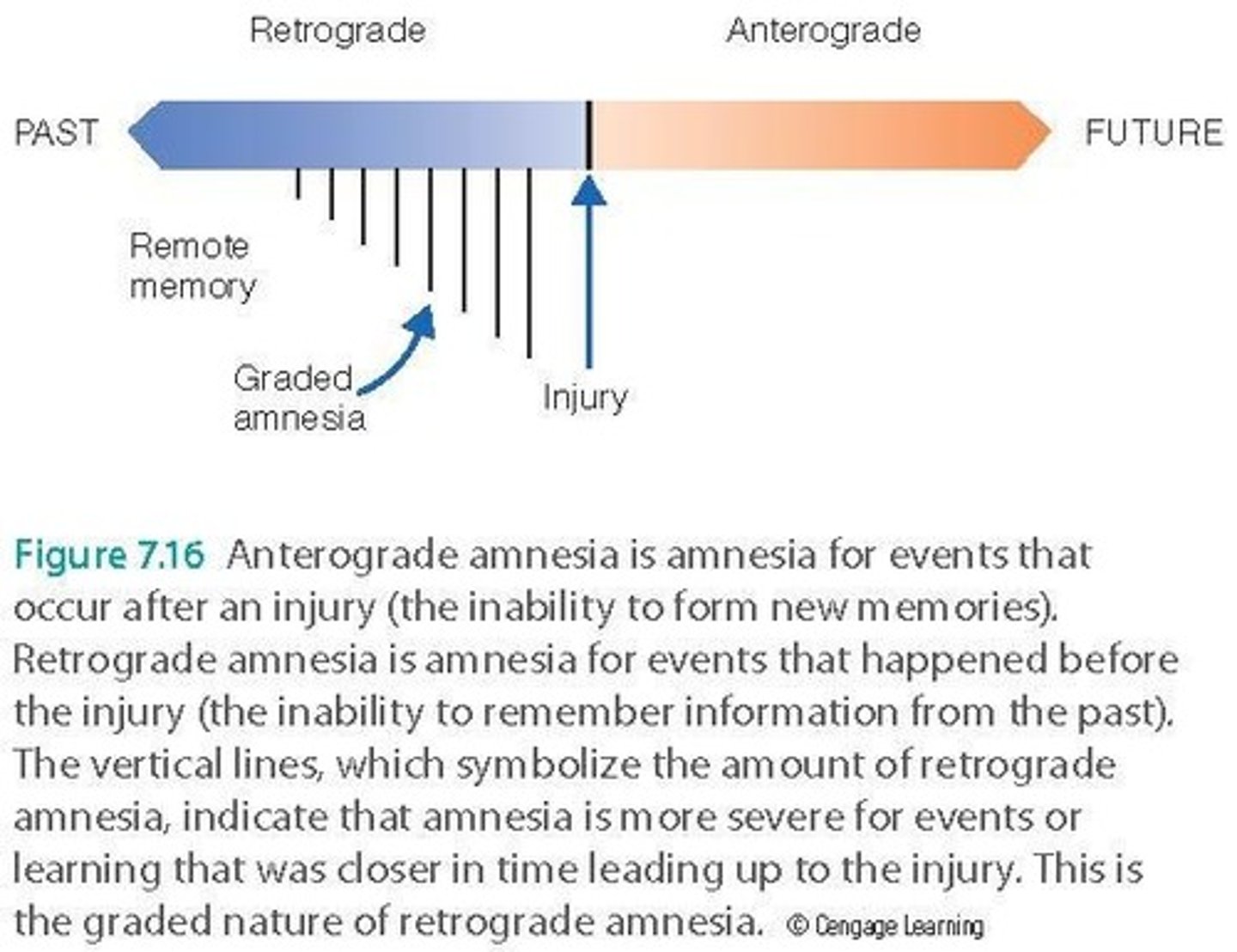
Graded amnesia
Recent memories are more fragile than older ones.
Elaboration
Connecting new information to existing knowledge.
Generation effect
Improved memory through self-generated learning methods.
Spacing effect
Better retention from multiple short study sessions.
Sleep and consolidation
Sleep enhances memory retention after studying.
Illusion of learning
Familiarity does not equate to true understanding.
Comprehension vs familiarity
Understanding requires deeper processing than mere recognition.
Practical suggestions
Strategies to enhance learning and memory retention.
Neurology of consolidation
Brain processes involved in stabilizing new memories.