Respiratory System
1/118
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Year 1 - Semester 2
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
respiration
the exchange of gas at the alveoli
ventilation
the movement of air through the airways
Which structures are included in the respiratory zone?
alveoli
Which structures are included in the ventilatory zone?
all tubes that transport air from the atmosphere to the alveoli
Which structures form the boundaries of the thorax?
thoracic inlet, diaphragm, ribcage, thoracic spine
What is the diaphragm?
a dome shaped musculotendinous sheet which allows air movement in the thorax to occur
Where does the costal portion of the diaphragm attach?
xiphoid process of the sternum and costochondral junctions of ribs 8-12
Where does the crural portion of the diaphragm attach?
ventral surfaces of L1-L4
pleura
a double layer of simple sqamous epithelium lying on connective tissue which lines the thoracic cavity
what are the 2 layers of the pleura?
visceral and parietal
pleural sac
the potential space between the parietal and visceral pleura which contains a small amount of fluid to enable the lung lobes to move freely over one another and other structures, it has a negative pressure
Where is the visceral pleura found?
attached to the lungs
Where is the parietal pleura found?
attached to the body wall
What are the 3 sections of the parietal pleura?
mediastinal, costal, diaphragmatic
Where is the mediastinal pleura found?
surrounding the mediastinum
Where is the diaphragmatic pleura found?
lining the diaphragm
Where is the costal pleura found?
lining the inner surface of the ribs
Plica vena cava
a fold of pleura in which the caudal vena cava runs to the heart
What is the importance of the negative pressure in the pleural sac?
It holds the lung against the body wall
Pathway of air into the body
external nares/ nostrils
turbinates/ conchae in nasal cavity
nasopharynx
vestibule through the glottic cleft
larynx
trachea
turbinates/conchae
4 scrolls of bone lined with vascular mucosa which contains mucous glands, left/right dorsal/ventral
function of turbinates/conchae
To warm, humidify and filter air
meati
the 4 interconnected pathways through the nasal cavity created by the tubrinates/conchae
How does the epiglottis protect the trachea?
It diverts food material away from the airway toward the oesophagus to prevent aspiration of food
What happens when something contacts the vestibular mucosa?
An immediate reflex cough is stimulated
How do the vocal folds protect the trachea?
They close which blocks the glottic cleft during swallowing
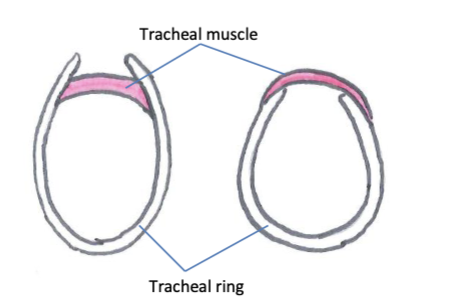
structure of the trachea
incomplete rings of cartilage joined by tracheal muscle form a fibrocartilaginous framework held by elastic connective tissue, the interior is lined with ciliated mucosa and exterior has a connective tissue layer
How do the trachea in cats and dogs differ from other species?
the tracheal muscle sits outside cartilage rings while it sits inside in other species
tracheal bronchus
an extra bronchus above the true left and right primary bronchi on the right hand side which supplies the cranial lobe of the right lung
which species is a tracheal bronchus found in?
ruminants and pigs
lobes of the right lung
cranial, middle, caudal, accessory
lobes of the left lung
cranial and caudal
how many primary bronchi are there?
2
Where do the primary bronchi split into secondary/lobar bronchi?
At the lobes of each lung
Which lung lobe does a horse lack?
right middle
How does the appearance of dog and horse lungs differ?
horse lacks a right middle lobe, dog has very obvious external fissures between lobes and horse has little external division
bronchopulmonary segment/ primary lobule
portion of lung tissue supplied by a tertiary bronchus, separated from others by connective tissue
What causes the marbled appearance of some lungs?
connective tissue dividing bronchopulmonary segments connects with the visceral pleura
what type of epithelium lines the airways of the ventilation system?
pseudostratified ciliated columnar containing goblet cells and submucosal glnads
mucociliary escalator
the movement of cilia which pushes mucous in the opposite direction to air, allowing mucous to move up the trachea and out of the mouth via coughing to expel particles it has trapped
What happens to bronchi as they continue to divide?
they gradually lose cartilage rings and gain smooth muscle
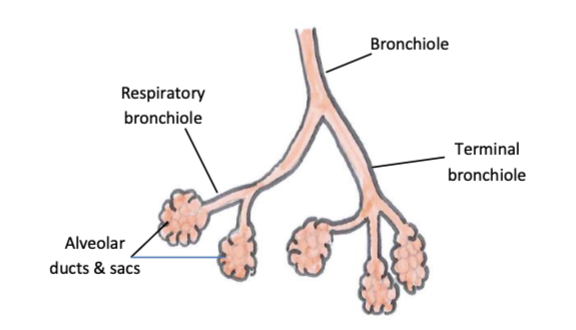
terminal bronchioles
the last division of bronchioles before the respiratory zone
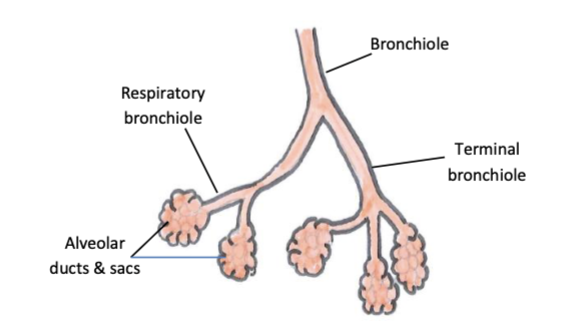
features of terminal bronchioles
no cilia, goblet cells or submucosal glands
features of respiratory bronchioles
alveolar outpouchings in walls enable gas exchange to occur, bronchioles feed into alveolar ducts and sacs
what type of epithelium are type 1 alveolocytes?
simple squamous
what type of epithelium are type 2 alveolocytes?
cuboidal
function of type 1 alveolocytes/pneumocytes
to allow alveoli to participate in gas exchange
function of type 2 alveolocytes/pneumocytes
to produce surfactant and alveolar macrophages
where are club/clara cells found?
in terminal bronchioles
function of club/clara cells
to detoxify pollutants, secrete proteins and produce some surfactant (replace cilia and goblet cells)
bronchovascular bundle
a bundle of connective tissue containing a bronchus, artery and vein which is found in bronchopulmonary segments
Which vessels supply the tissues of the lung with oxygen?
bronchial arteries
Which vessels drain the tissues of the lung?
bronchial veins which empty into the azygous vein
which nerve provides parasympathetic innervation to the lungs?
vagus nerve
which plexus provides innervation to the lungs?
pulmonary plexus
how can blood supply to the lungs be modified?
via sympathetic and parasympathetic nerve vessels
Which structures are the sympathetic nerve supply able to innervate in the lungs?
blood vessels only
How are airway smooth muscles controlled?
adrenaline and noradrenaline acting on B2 adrenoreceptors
eupnoea
normal breathing
resting respiratory rate
number of breaths taken in a minute at rest
tachnypnoea
increased respiratory rate
hyperpnoea
increased respiratory depth
dyspnoea
increased respiratory effort
apnoea
absence of breathing
bradypnoea
decreased respiratory rate
Which direction do external intercostal muscles run?
caudoventrally
What prevents the lungs from collapsing during expiration?
negative pressure within the pleural space
What happens during inspiration at rest?
the diaphragm contracts and flattens caudally and external intercostal muscles contract and lift the ribs out and cranially which increases the volume of the thoracic cavity, lungs expand due to negative pressure in the pleural space
What happens during expiration at rest?
elastic properties of the lungs and muscles cause recoil of the thorax which increases pressure inside the alveoli above atmospheric pressure which forces air out
What happens during active expiration?
abdominal muscles contract and push abdominal contents cranially which forces the relaxed diaphragm to dome up into the thorax and costal portions of the internal intercostal muscles pull the ribs caudally and inwards which reduced the volume of the thorax and increases pressure inside the alveoli
What usually follows active expiration?
passive inspiration
Which species has active and passive phases to both inspiration and expiration?
horse
which species has an active phase of expiration at rest?
dogs
compliance of lungs
the degree to which a decrease in transpulmonary pressure leads to an increase in volume of the lungs (ability of lungs to expand to take up air when pressure decreases)
which factors determine the compliance of the lungs?
elasticity of the lungs and thoracic cage and surface tension in the alveoli
how is surface tension created in the alveoli?
fluid which lines the alveoli to facilitate diffusion and dissolution of gases forms hydrogen bonds between water molecules
why is surface tension a problem in the lungs?
it reduces surface area of the alveoli and resists expansion of the lung by creating an inward force that promotes alveolar collapse and causes fluid to be drawn into air spaces
function of surfactant in alveoli
to reduce the formation of hydrogen bonds between water molecules to reduce surface tension in alveoli
how does the size of alveoli affect their internal pressure?
smaller alveoli have a higher internal pressure which would cause them to collapse if they didn’t have a higher concentration of surfactant to balance it out
why do premature neonates often struggle to breathe?
They are not yet producing enough surfactant so lungs cannot fully expand
How is the release of surfactant stimulated in adults?
by sighing
Why is resistance in the lower airways lower during inspiration?
they are distended during inspiration as bronchial connective tissue is attached to the visceral pleura so is pulled open when the lungs expand
Why is resistance in the upper airways higher during inspiration?
the negative pressure generated to pull air into the lungs tends to collapse the compliant, non-rigid airway walls and turbulence is greater as the speed of flow of air is the highest
which nervous system innervates the smooth muscle in airway walls?
autonomic
How does the sympathetic nervous system affect airways?
beta-2 adrenoreceptors are stimulated which causes the airways to dilate
How does the parasympathetic nervous system affect the airways?
causes constriction
tidal volume
the volume of air moved during a respiratory cycle
What is the average tidal volume in a normal resting dog?
10ml/kg
formula for minute ventilation
tidal volume x respiratory rate
residual volume
the volume of air that remains in the lungs after a full expiration
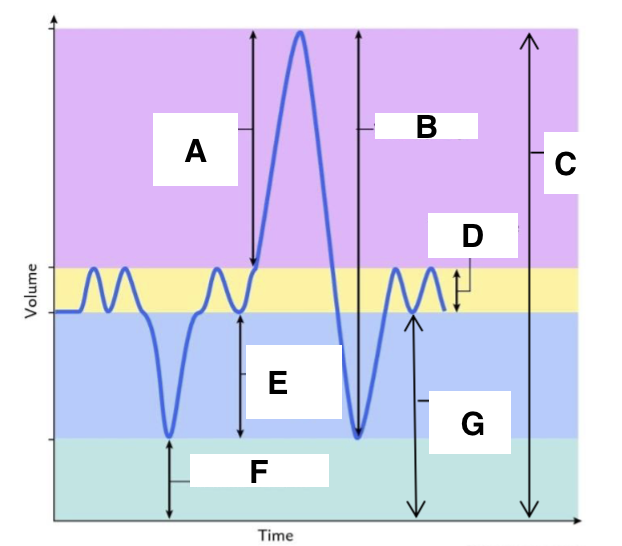
A
inspiratory reserve volume
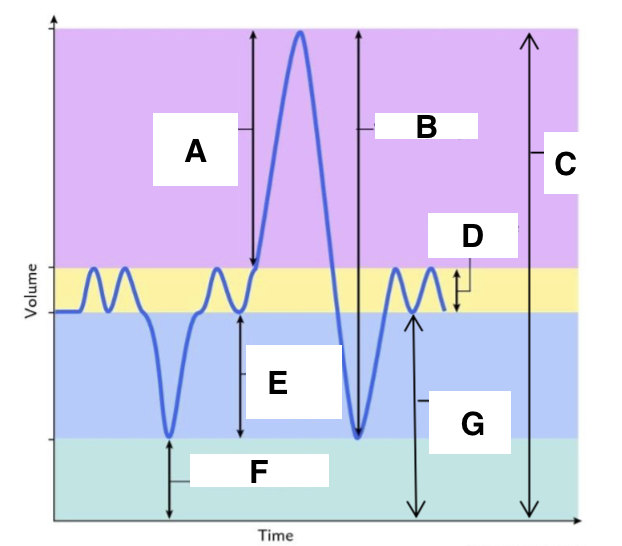
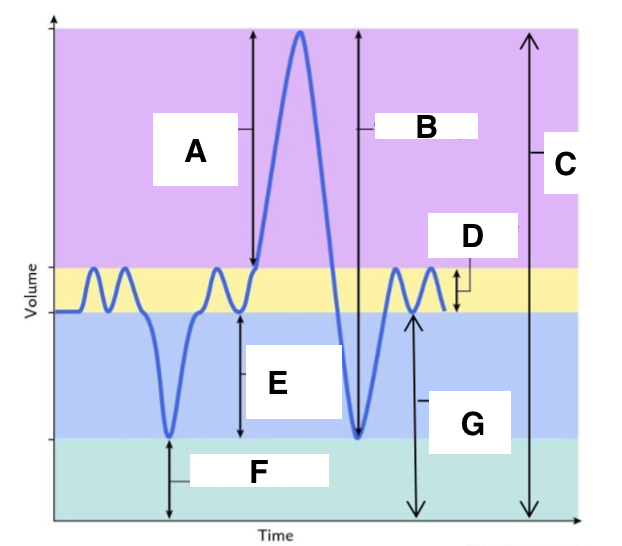
B
vital capacity
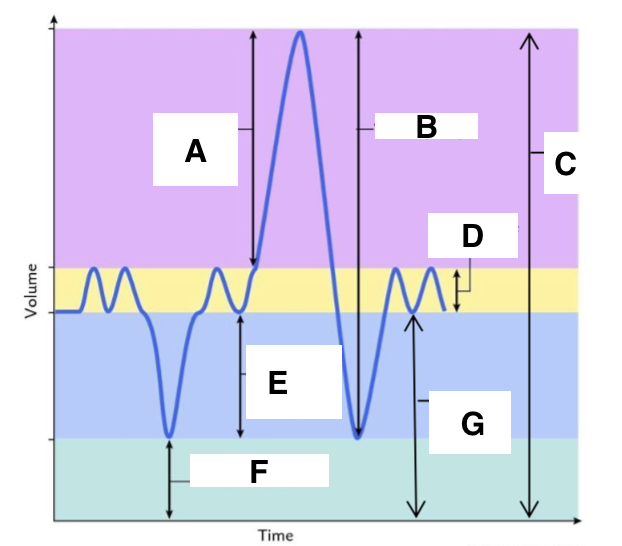
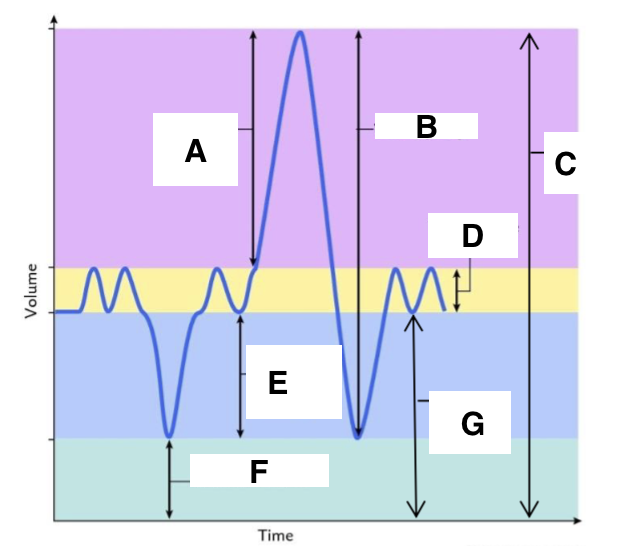
C
total lung capacity
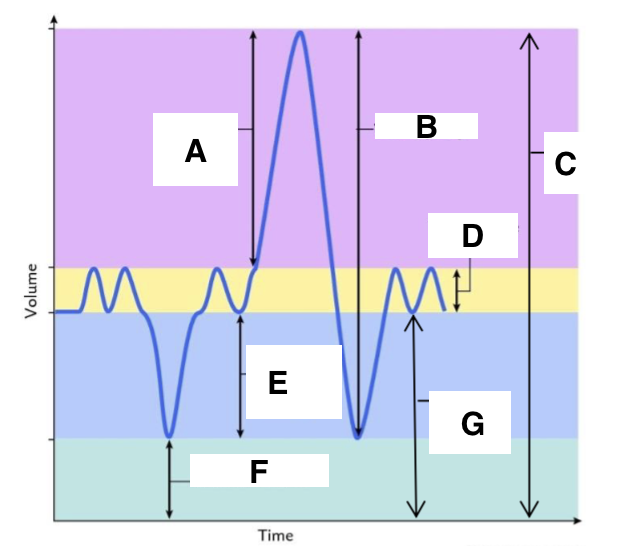
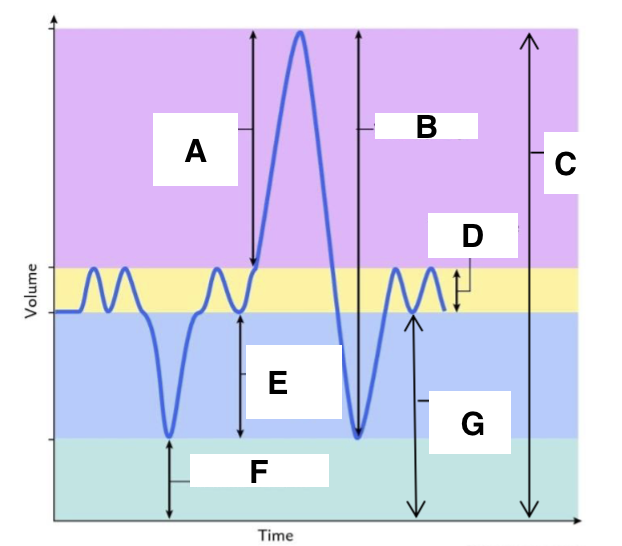
D
tidal volume (at rest)
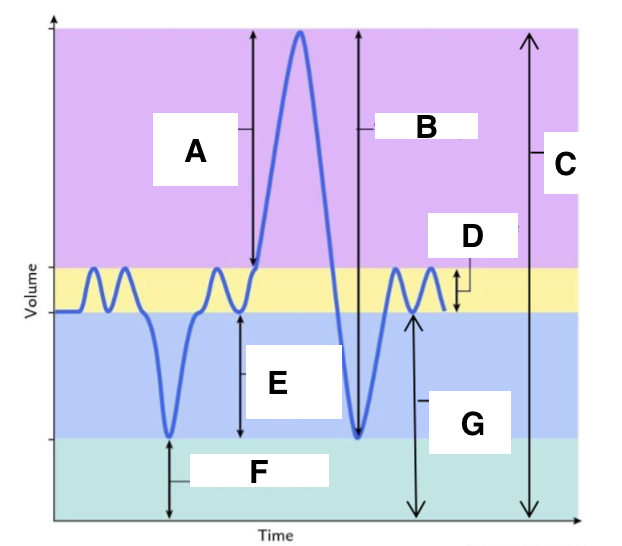
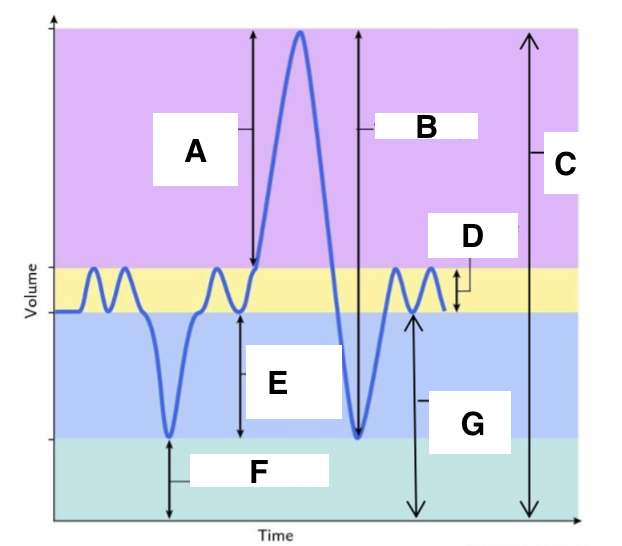
E
expiratory reserve volume
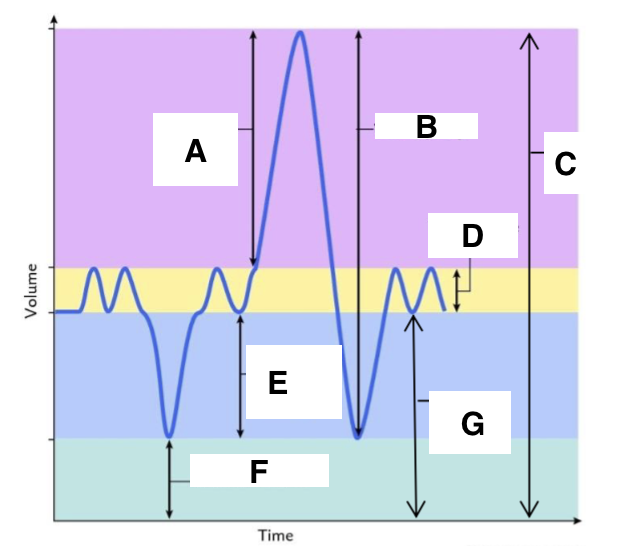
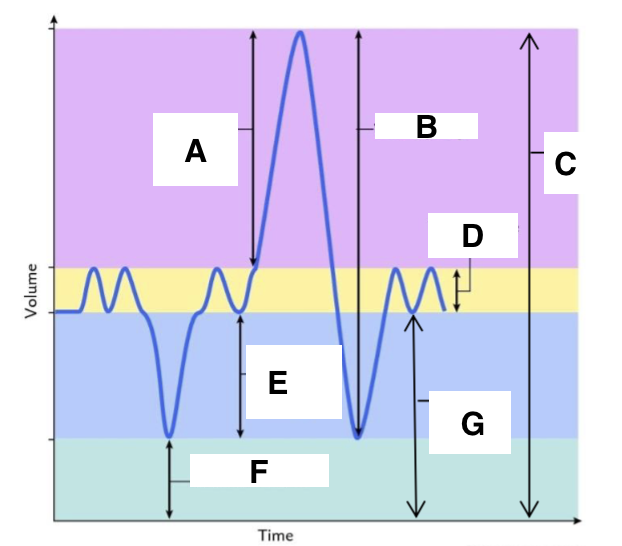
F
residual volume
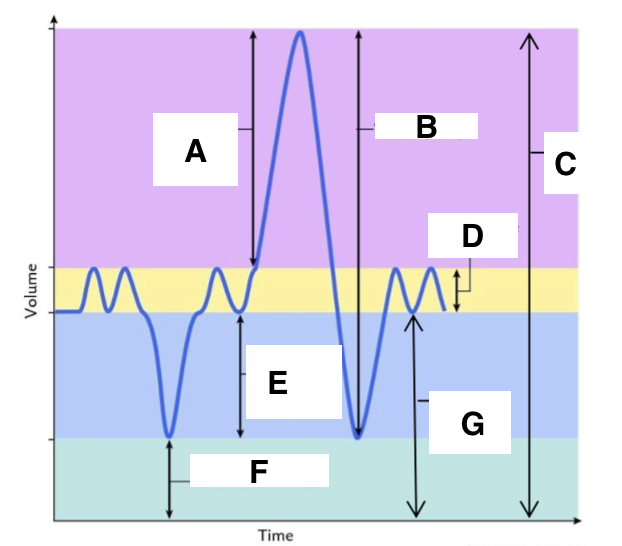
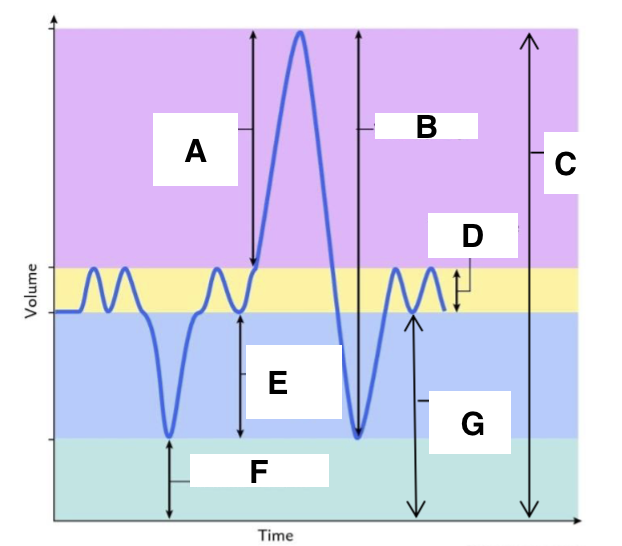
G
functional residual capacity
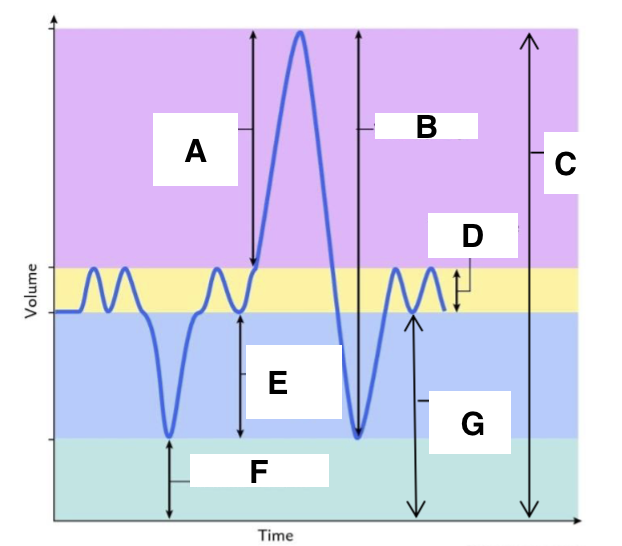
functional residual capacity
the total amount of air left in the lungs after a nromal expiration at rest
fraction of a gas
the proportion of a gase mixture that consists of the gas of interest
partial pressure of a gas
the pressure exerted by a specific gas within a gas mixture