Contemporary Economics - Inflation
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
For exam on the 22nd Jan
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
Inflation definition
An increase in the general price level
Inflation formula
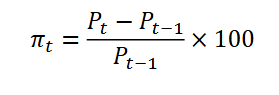
Inflation evaluation
If inflation > 0 prices will continue to rise
Main measures of inflation in the UK
Consumer Price Index (CPI)
Retail Price Index (RPI)
Consumer Price Index (CPIH)~ including owner occupied housing costs
Problems with measures of inflation
Not an indicator of price level
Substitution bias - When price of smt increases ppl sub away but inflation measure doesnt change whats in the basket so quickly
Inequality - Low income families may be especially affected
The affects of inflation are not clear from a singular number
Why can it not be argued that inflation has a limited effect?
Distorted economic signals - If prices rise this may hide the changes in relative prices that should provide signals to producers and consumers
How can economic individuals use inflation to influence their economic decisions?
Savers to borrowers - they use it to distinguish between nominal and real IR
SAVERS: if nominal IR rt = 5% but prices rise over the year by 𝜋t = 5% then by the end of the year no interest is gained
Inflation erodes the real value of savings
BORROWERS: if you borrow at nominal rate rt = 10% but prices rise over the year at rate 𝜋t = 20% then by the end of the year the real value of the money you owe wouldve fallen
Inflation lowers debt in real terms
Main types of inflation
Cost push inflation
Demand pull inflation
What is cost push inflation?
inflation caused by higher production costs
What does cost push inflation do?
Forces businesses to raise prices to cover those higher costs
Causes of cost push inflation?
Disrupted supply chains
Shocks to input costs
Weakening of the exchange rate
Example of cost push inflation
Ukraine war - Caused an increase in energy costs
European wholesale increased by 237%
What is demand pull inflation?
inflation caused by high demand
What de=oes demand pull inflation do?
Increase pries because goods and services are in short supply
Causes of demand pull inflation
High levels of money supply
Interest rates
Example of demand pull inflation
QE during financial crisis
Used to increase money supply in the economy by buying bonds to lower IR and encourage lending and spending
Solutions to inflation
BoE set an inflation target of 2%
set to be achieved via monetary policy (manipulating IR)