chem final review
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
dalton
atomic theory that the atom is an indivisible sphere
rutherford
bombarded gold foil with alpha particles. atoms are mostly empty space and have a small, dense, positively charged nucleus
bohr
atomic theory that electrons stay in circular orbits/shells
wave-mechanical
atomic theory that electrons are in orbitals
spectroscope
an instrument to see the bright line spectrum of an element to identify it. when an electron goes from a high to low level, it emits energy in the form of light
transmutation
a change in the nucleus of an atom changes it to a new type of atom
diagnosis and treatment of thyroid issues
131I
cancer treatment
60Co
estimate age of organic remains
14C
estimate age of geological formations
238U
properties of ionic substance
high melting and boiling points, form crystals, dissolve in water, conduct electricity in solution and as liquid
properties of covalent substance
lower melting and boiling points, do not conduct electricity
metallic bonding
bonding where valence electrons are mobile in a free moving sea of electrons
chromatography
separation based on attraction of mixture components for transporting medium
filtration
allows smaller particles to pass through and trap larger particles
separatory funnel
separate immiscible liquids (not soluble with each other) on density differences
distillation
separate solids dissolved in liquids or separate liquid mixtures based on boiling point difference
kinetic molecular theory
particles are:
in random motion
no forces of attraction between them
have a negligible volume compared to distances between them
have collisions that result in the transfer of energy fro one particle to another, but there is no net loss of energy from the collision
alkali metals
group 1 elements
alkali earth metals/alkaline
group 2 elements
halogens
group 17 metals
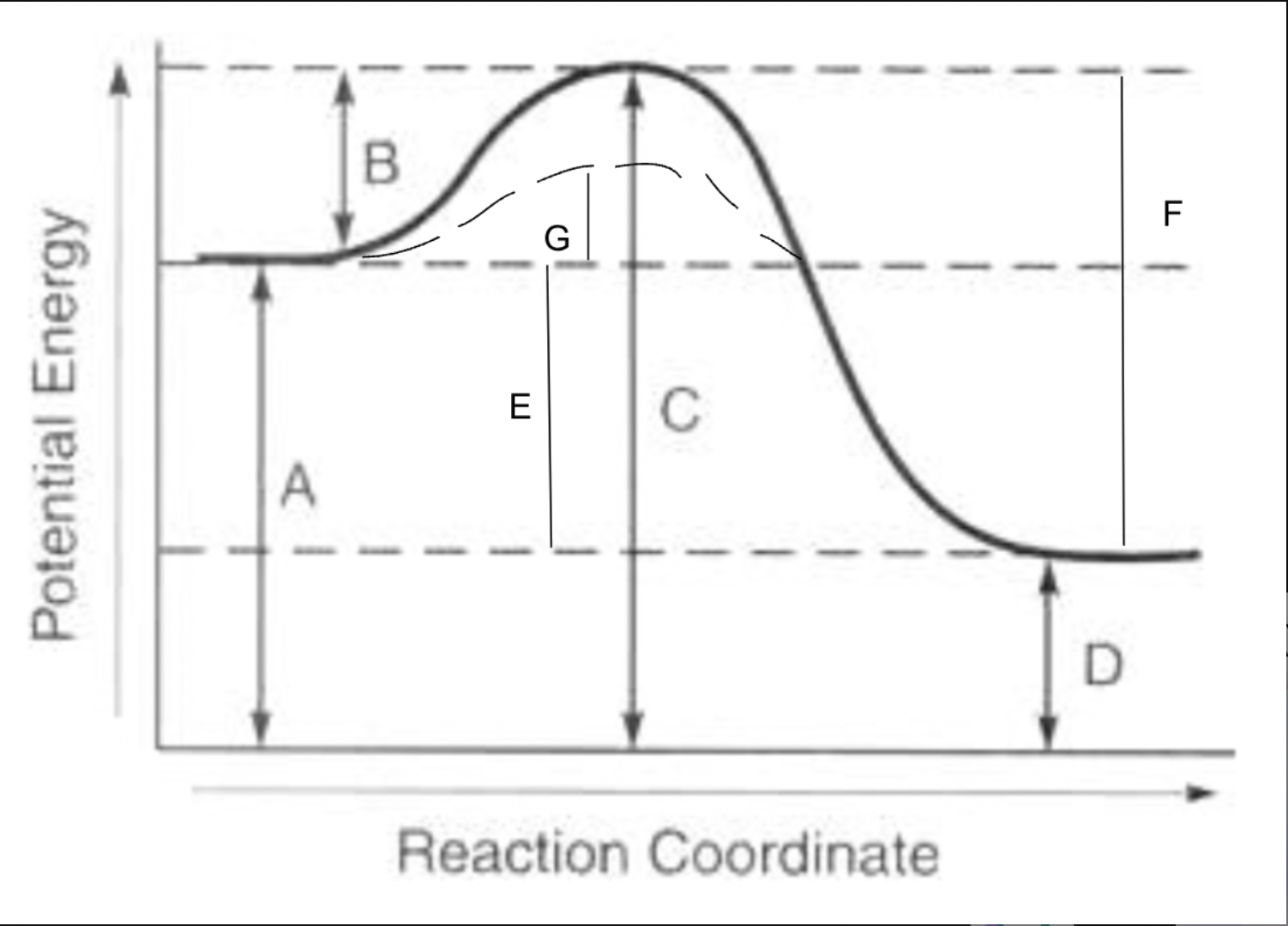
potential energy of reactants
A
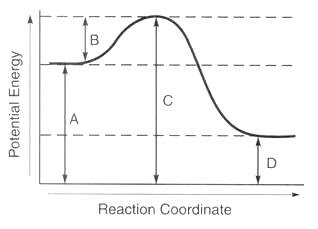
potential energy of products
D
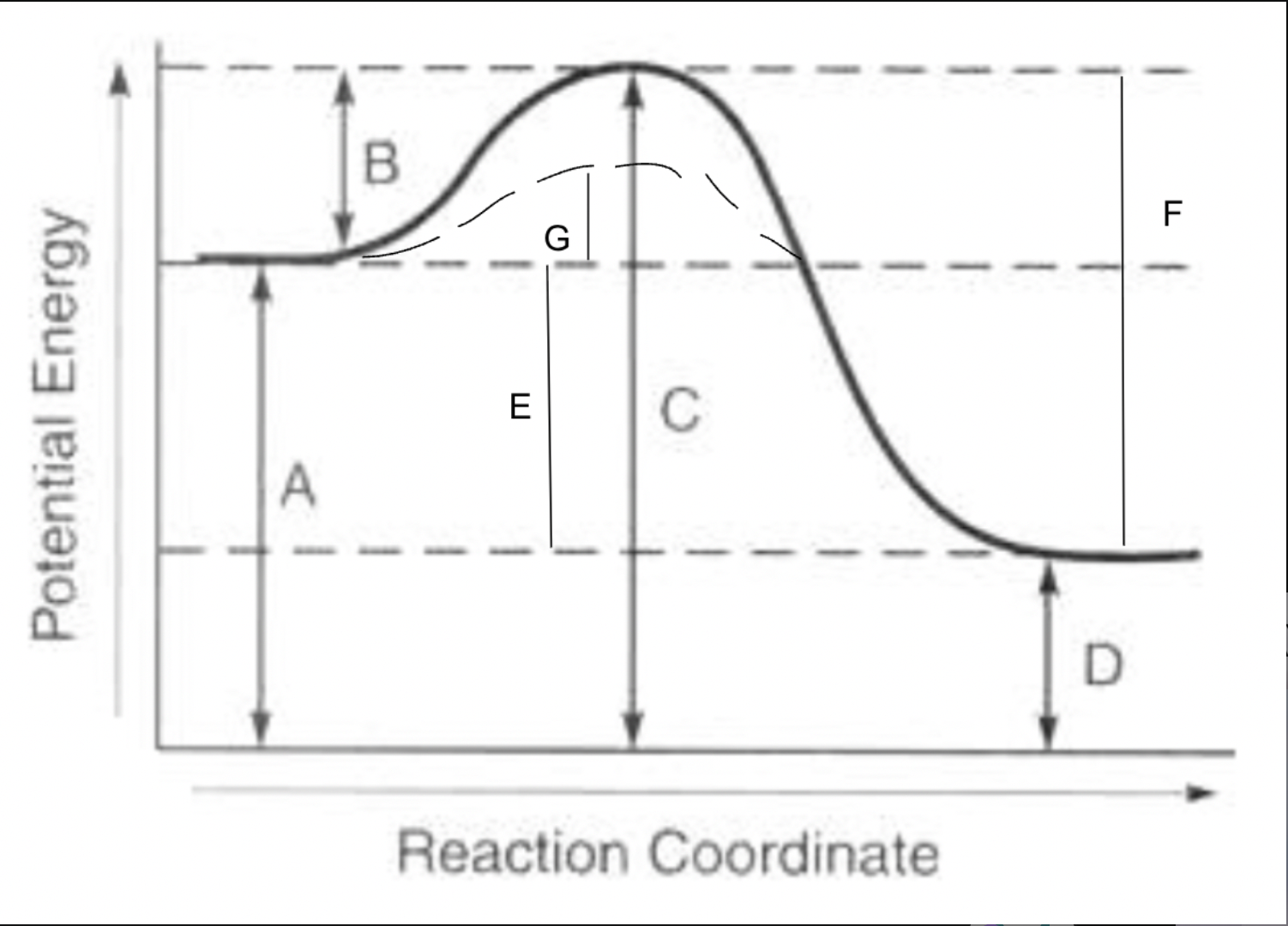
potential energy of activated complex
C
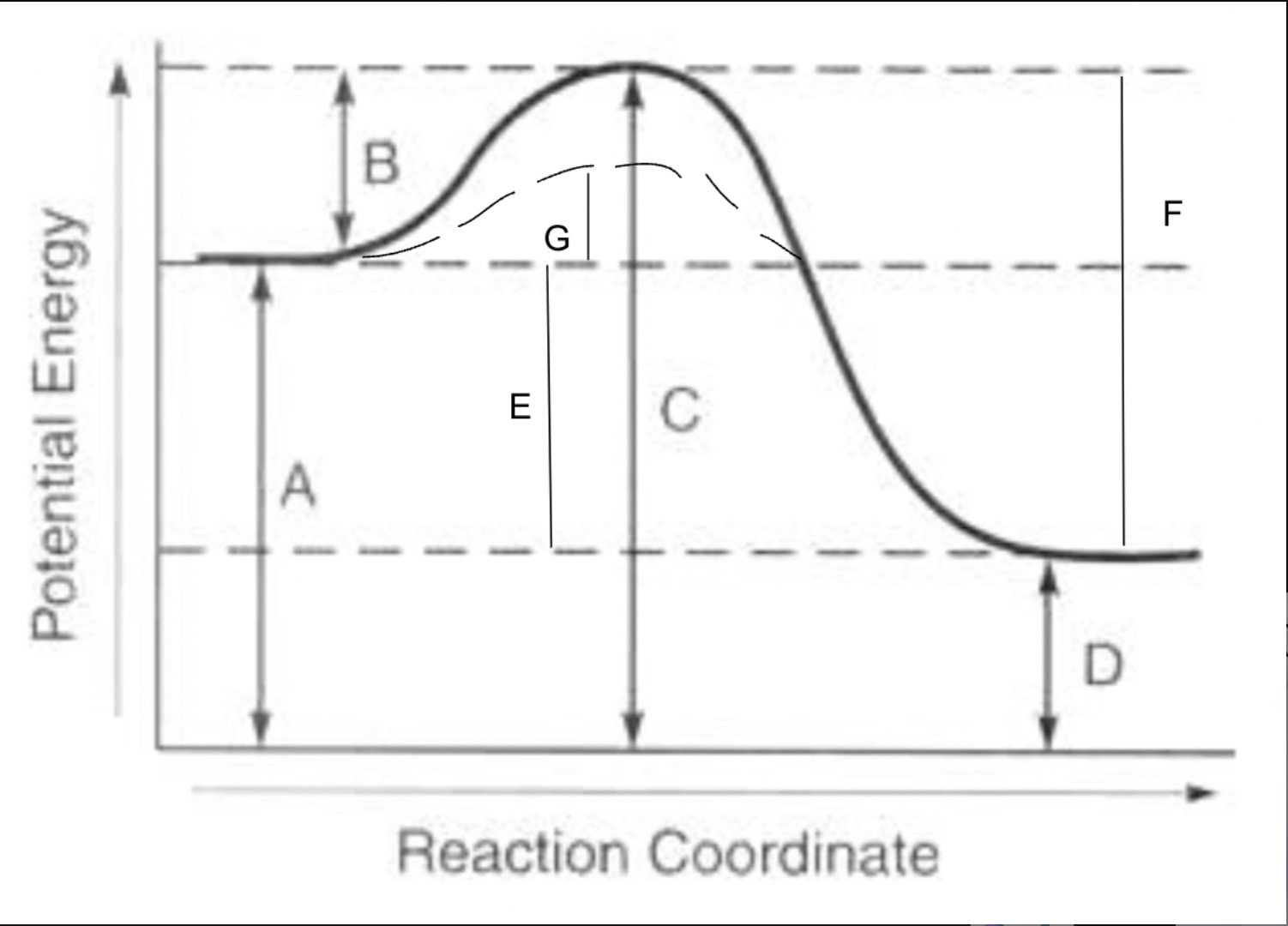
activation energy of forward reaction
B
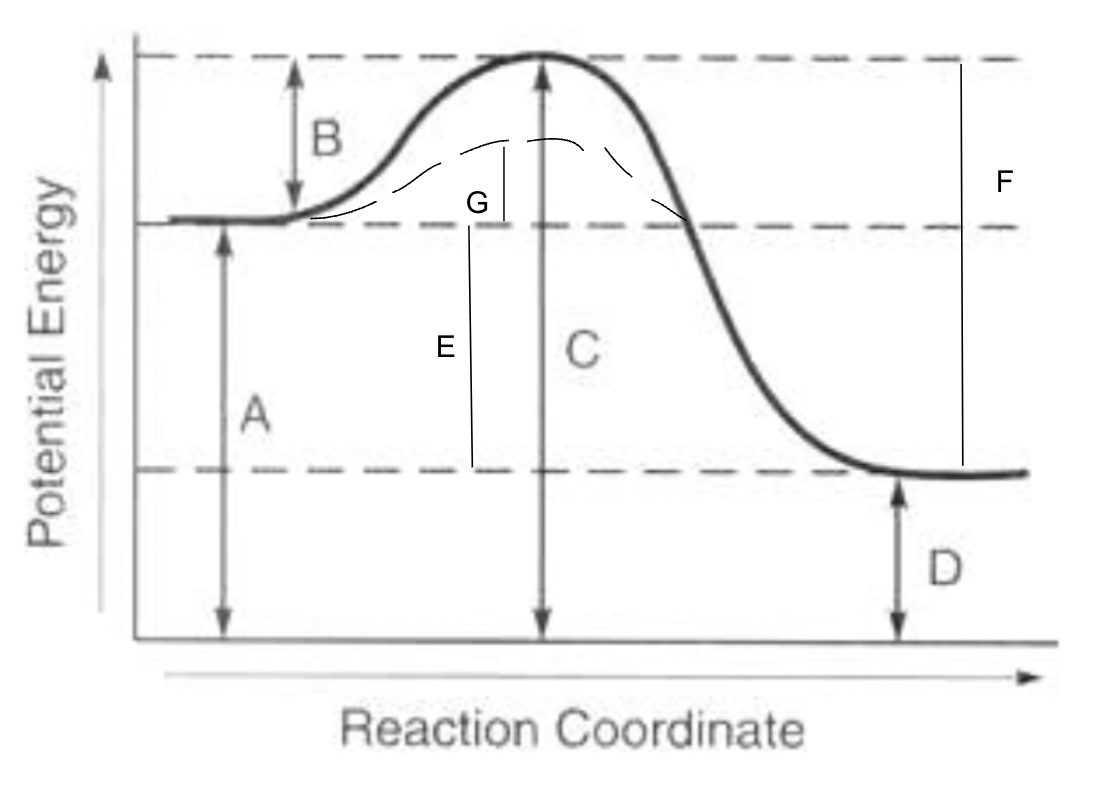
activation energy of reverse reaction
F
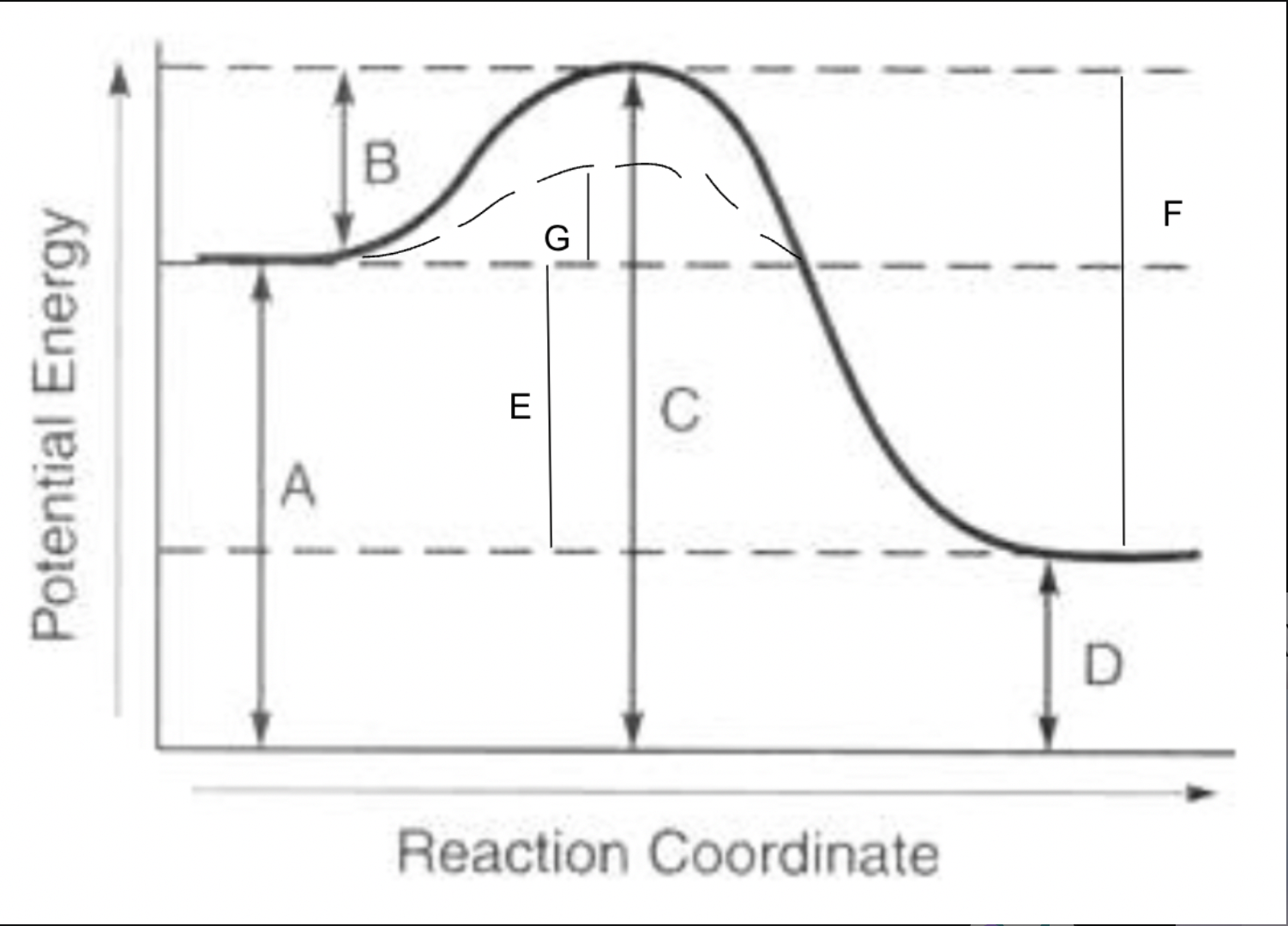
heat of reaction
E
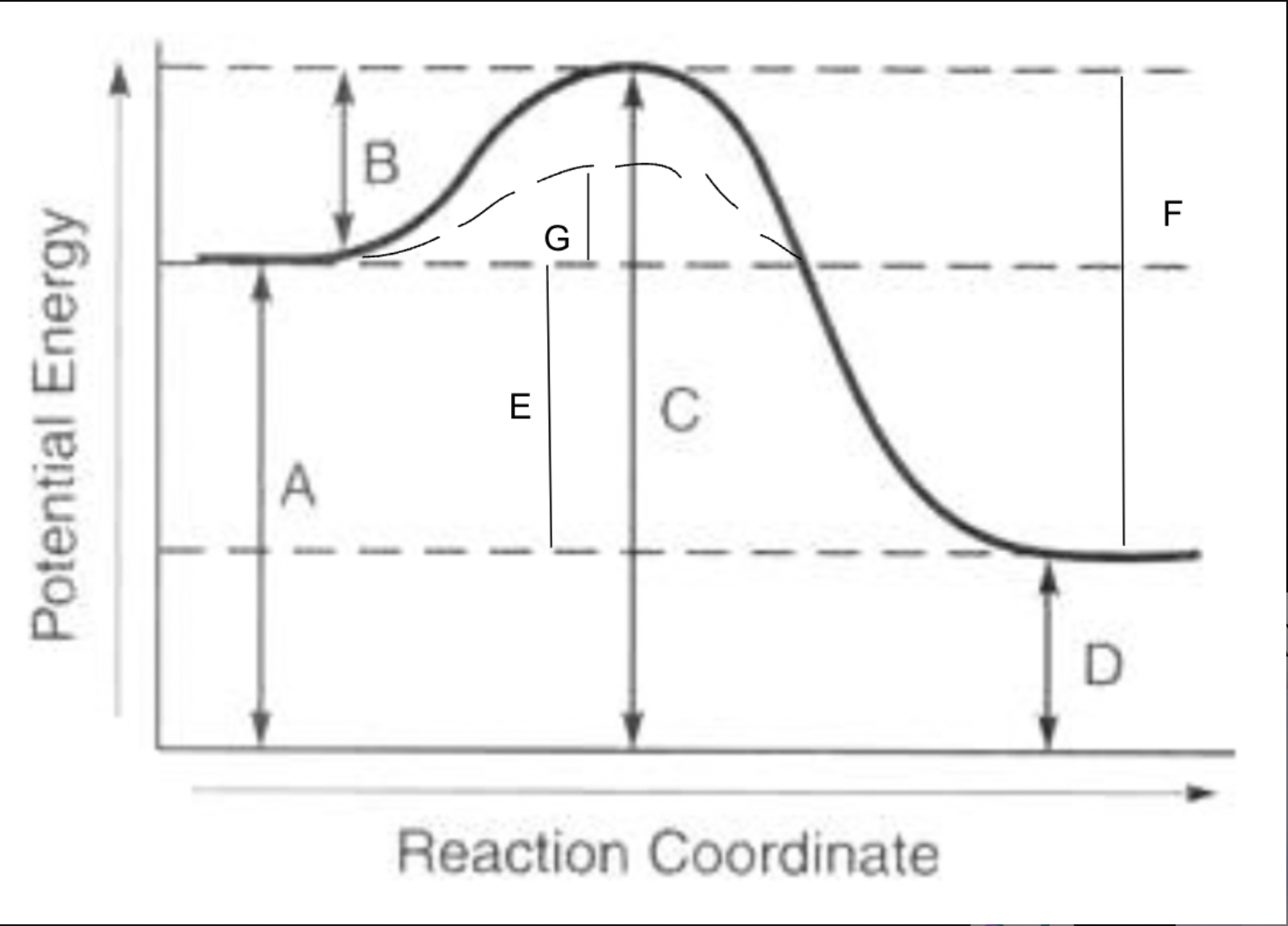
activation energy with catalyst for forward reaction
G
endothermic
exothermic
addition
add atoms to unsaturated hydrocarbon
substitution
products are rearranged reactants
polymerization
monomers joined together
esterification
reactants: organic acid and alcohol. products: ester and water
fermentation
products: CO2 and alcohol
saponification
reactants: bases and ethers. products: soap
combustion
fire. products: water and CO2