Action potential
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
What creates the resting membrane potential difference of a typical cell?
Equal charges inside and out
Sodium leak channels causing the cell to be more negative
Potassium leak channels causing the cell to be more negative
Chloride leak channels causing the cell to be more positive
Potassium leak channels causing the cell to be more negative
In a resting cell, potassium leak channels allow potassium to _________ to follow its ____________. ]
Influx / concentration gradient
Efflux / concentration gradient
Influx / concentration and electrical gradient
Efflux / concentration and electrical gradient
Efflux / concentration gradient
A graded potential may trigger an action potential if:
It reaches a dendrite
It depolarizes the cell above a threshold level
It hyperpolarizes the cell below a threshold level
It changes the membrane potential at all
It depolarizes the cell above a threshold level
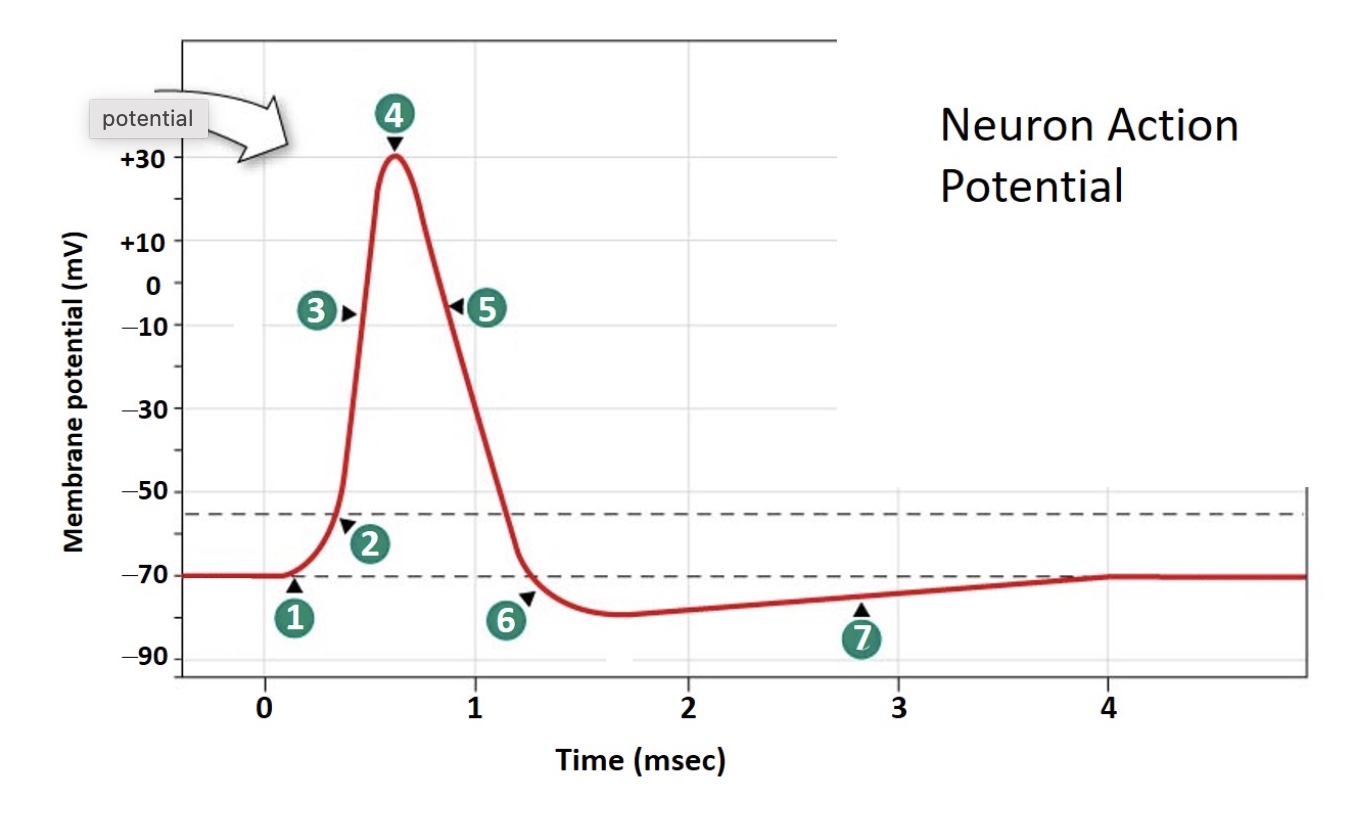
Which number indicates the point at which the stimulus reaches the depolarization threshold?
2
Which of the following options is most responsible for depolarizing the neuron during the action potential?
Sodium influx
Sodium efflux
Potassium influx
Potassium efflux
Sodium influx
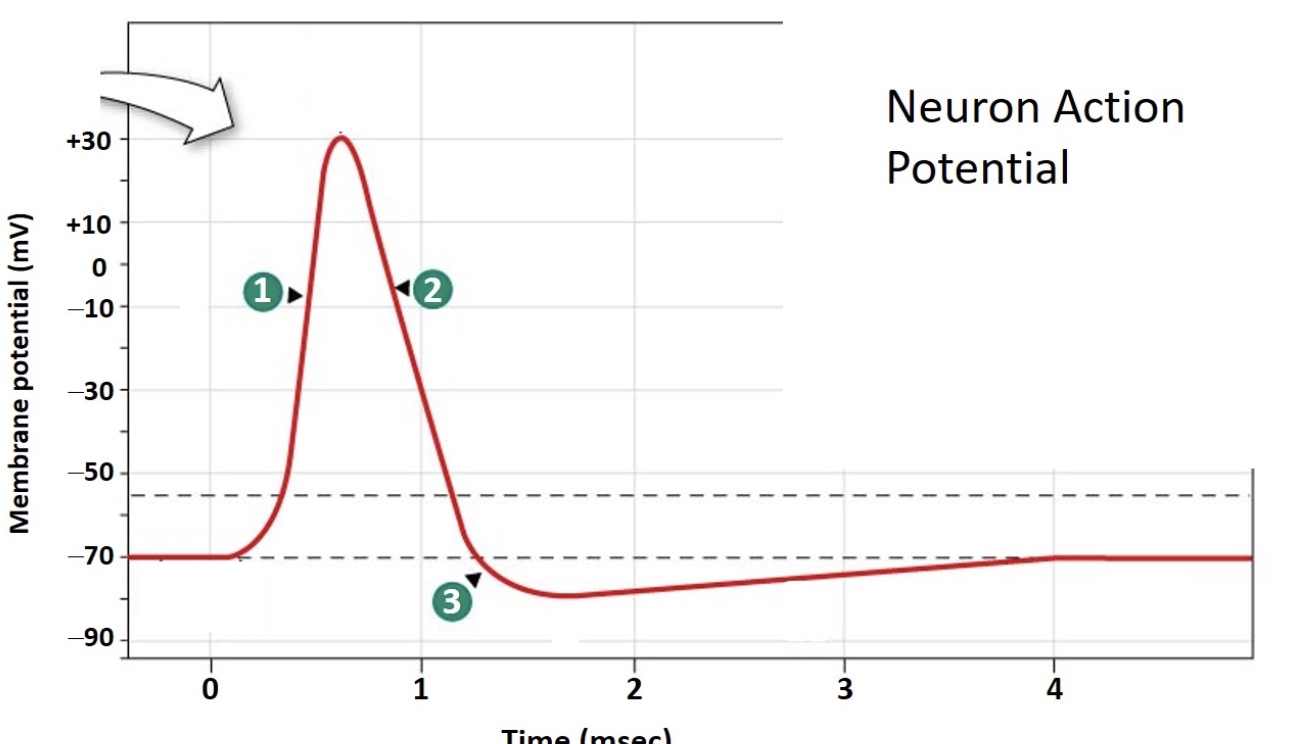
Which number indicates the depolarization phase?
1
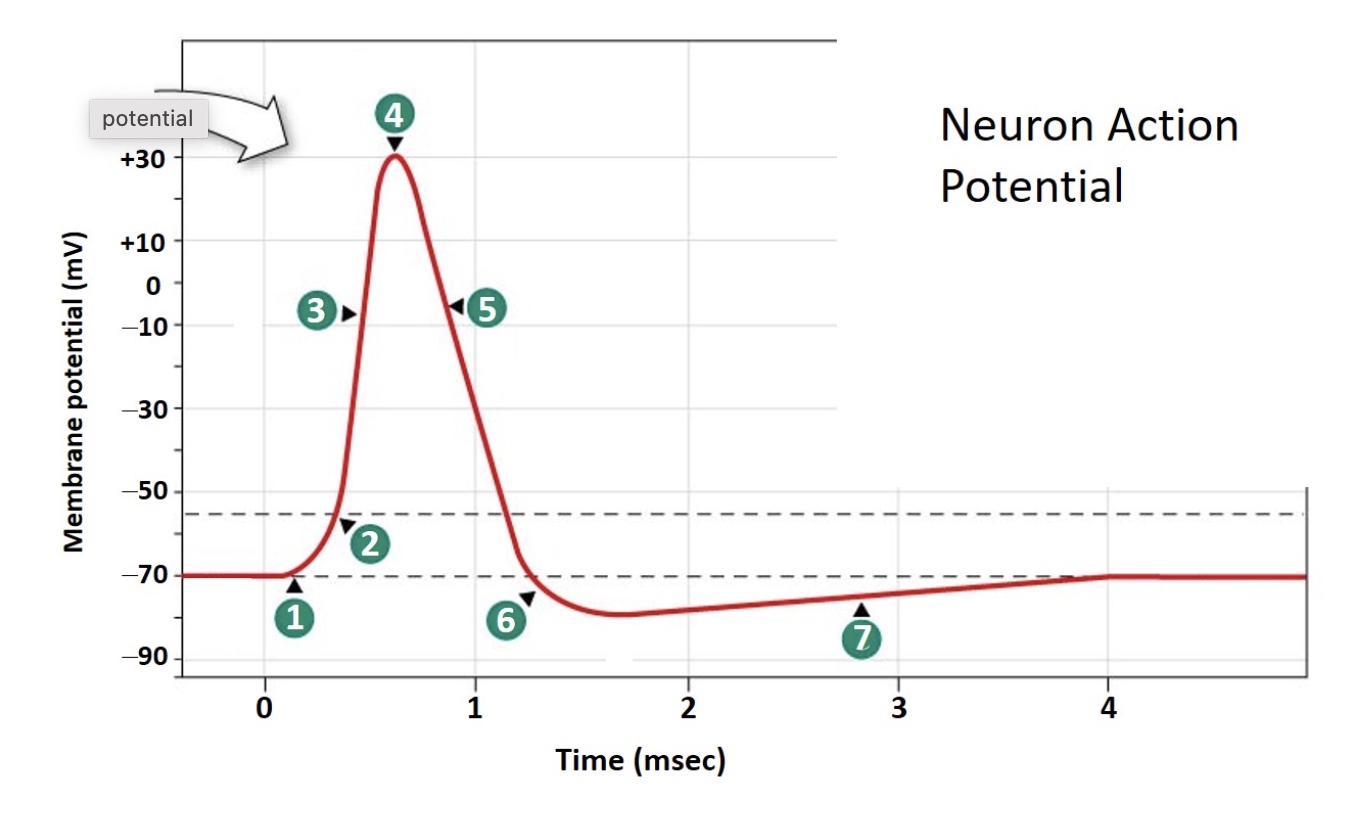
Which number indicates the point at which voltage-gated sodium channels are triggered to OPEN?
2
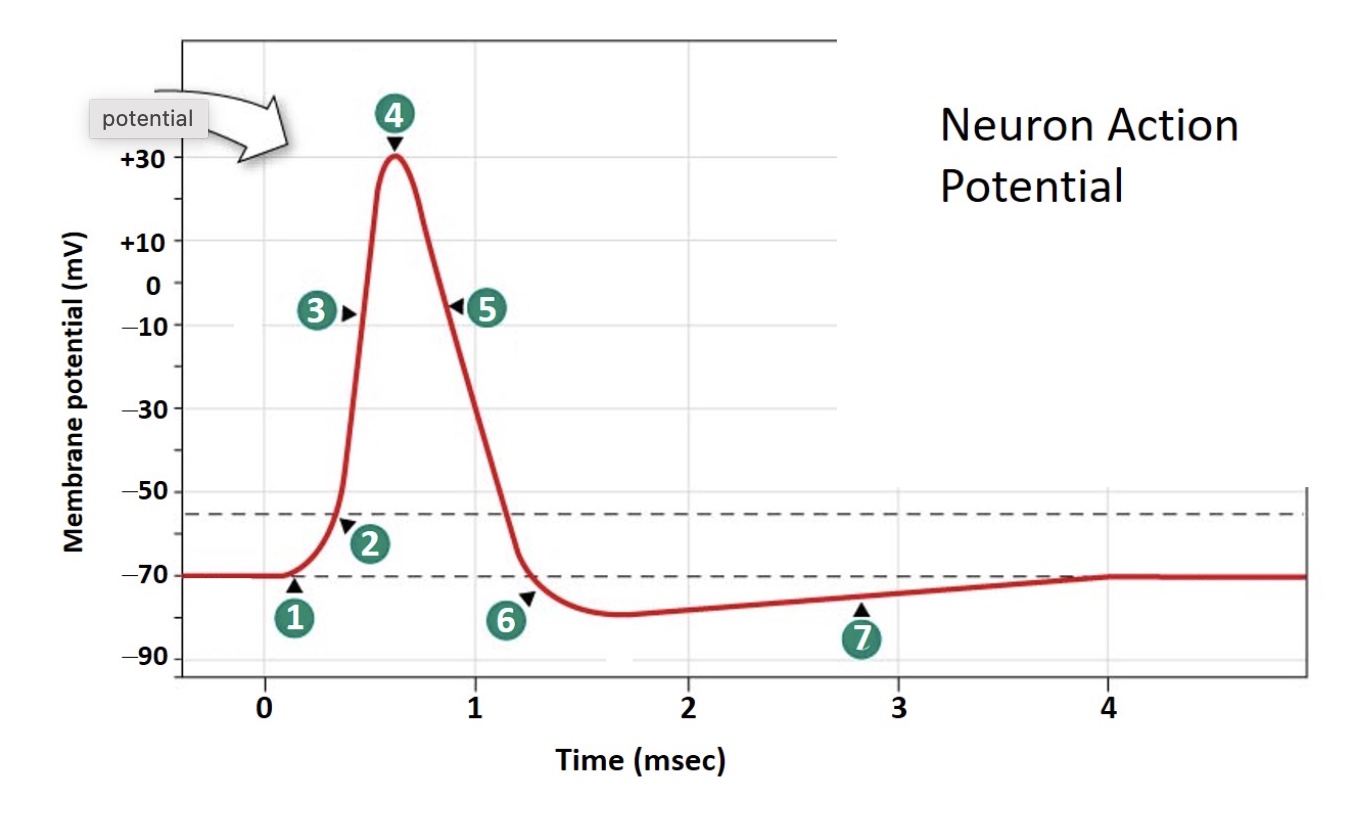
Which number indicates the point at which voltage-gated sodium channels CLOSE (inactivate)?
4
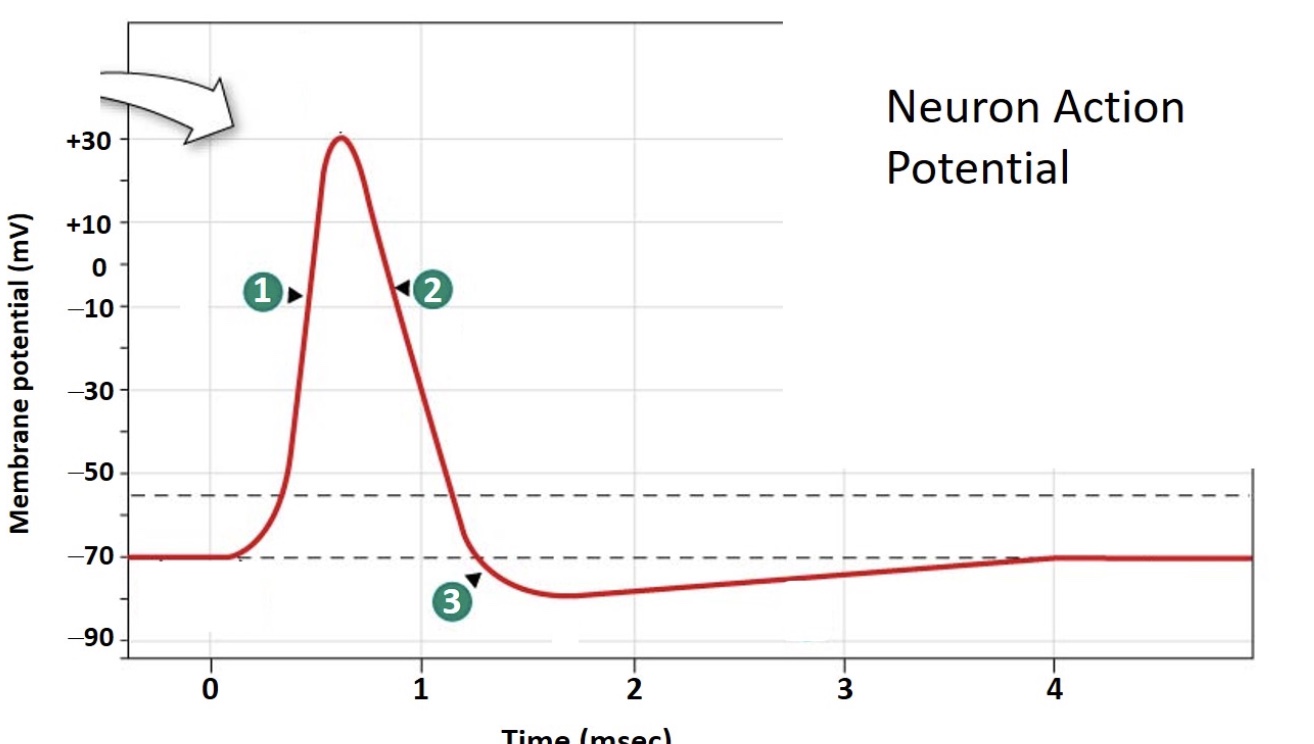
Which of the following options is most responsible for repolarizing the neuron from +30 to -70 mV (indicated by phase 2 below)?
Sodium Influx
Sodium Efflux
Potassium influx
Potassium efflux
Potassium efflux
In the resting state, BOTH gates of the voltage-gated sodium channel are closed.
True or False
False
What event triggers the voltage-gated sodium channel activation gate to OPEN? Neuron is depolarized maximally to +30 mV
A depolarizing stimulus that reaches a threshold voltage
Sodium concentrations reach a maximum
Potassium efflux hyperpolarizes the cell
A depolarizing stimulus that reaches a threshold voltage
What event triggers the voltage-gated sodium channel inactivation gate to CLOSE?
Potassium channels open
Positive charges accumulating outside the cell
Positive charges accumulating inside the cell
Neuron hyperpolarizes
Positive charges accumulating inside the cell
Changing membrane potential requires so many ions to move that concentrations gradients may be altered.
True
False
False
Why can't another action potential fire during the absolute refractory period?
All of the sodium has left the cell
The sodium channels are still open
The sodium channels have not reset, their deactivation gates are still closed
The sodium channels have not reset, their activation gates are still closed
The sodium channels have not reset, their deactivation gates are still closed
During the absolute refractory period, the sodium channel activation gate is ___________ and the inactivation gate is _____________.
Closed / closed
Closed / open
Open / open
Open / closed
open/closed
When the sodium channel has reset to resting state, the activation gate is ___________ and the inactivation gate is _____________.
Closed / closed
Closed / open
Open / open
Open / closed
closed/open
In the relative refractory period:
Neuron is depolarized, making it easier to fire another action potential.
All of the sodium channels have reset and are ready to fire
Potassium channels have closed
Another action potential may be fired, but it will require a stronger stimulus
Another action potential may be fired, but it will require a stronger stimulus