Cardiorespiratory
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Transportation system
Transfers oxygen, fuel, nutrients, waste products,
immune cells, and hormones from one part of the
body to another
Cardiovascular System
Heart
Blood vessels
Arteries, veins, capillaries
Blood
Lymphatic System
Upper Respiratory Tract
Nose, Mouth, Pharynx (throat), Larynx (voice box),
Trachea
Lower Respiratory tract
Bronchi, Bronchioles, Alveoli, Lungs, Diaphragm
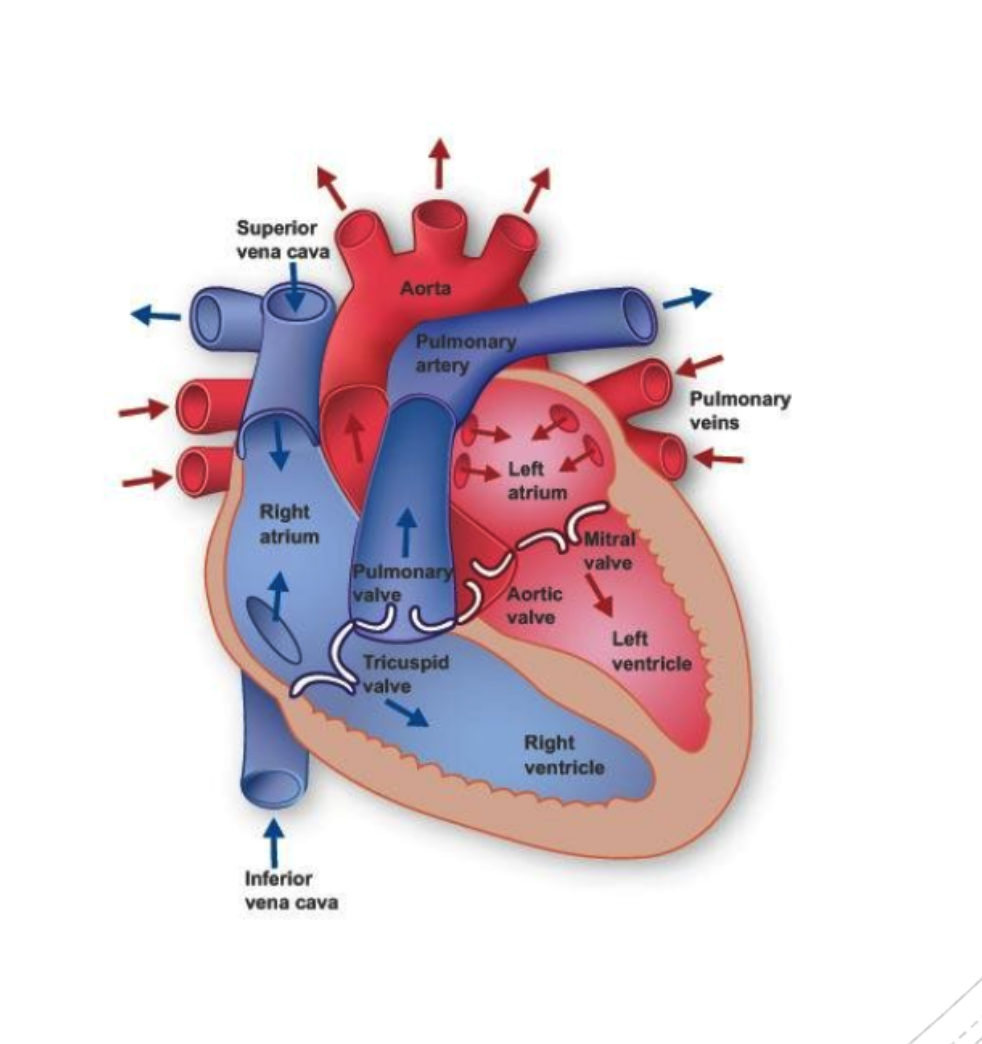
HEART
Amount of blood in the average human adult
5-6 Liters
Liquid portion of the blood in its anticoagulated (or
unclotted) state;
Plasma
What % of the blood volume is plasma
55-65%
Serum
Liquid portion of the blood that remains after the blood has
coagulated
Platelets (thrombocytes)
Small cells in blood that help with clotting
Red blood cells (RBCs) (erythrocytes)
Produced in the bone marrow and live ~120 days
Hemoglobin
Iron-containing protein in RBCs that transports oxygen
Responsible for the reddish color of the blood.
Deoxygenated bloodflow
1 superior and
2 inferior vena cava
3 right atrium
4 tricuspid valve
5 right ventricle
6 pulmonary valve
pulmonary arteries
Oxygenated blood flow
8 pulmonary veins
9 left atrium
10 mitral valve
11 left ventricle
12 aortic valve
13 aorta
What is the lymphatic system?
Speen, thymus, lymph nodes, white blood cells (WBCs)
What does the lymphatic system do?
Keeps fluid levels in check and defends the body against infections
Neutrophils
Most common WBCs
Defend the body against infectious diseases.
Lymphocytes
2nd most common WBCs
Provide a boost to immune defense of the body
Respond to viruses, when necessary
Monocytes
largest cells in normal blood
Phagocytic cells that provide support in cell-mediated immunity
Eosinophils
Allergic or inflammatory responses
Basophils
Least numerous WBCs
Contain histamine
Provide aid in allergic states