ap bio unit 2
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
Cell membrane
A protective barrier that surrounds the cell and regulates what enters and exits. Ex: Keeps toxins out while letting nutrients in.
Chromosomes
Thread-like structures made of DNA and proteins that carry genetic information. Ex: Humans have 46 chromosomes.
Ribosomes
Small structures that make proteins by linking amino acids. Ex: Found floating in cytosol or on rough ER.
Cytosol
The fluid inside the cell where organelles are suspended. Ex: Like water in a swimming pool for organelles.
Compartmentalization
Organizing the cell into sections with membranes to increase efficiency. Ex: Lysosomes digest waste without harming other organelles.
LUCA
Last Universal Common Ancestor of all living organisms. Ex: Shared by bacteria, plants, and humans.
Genome
The complete set of DNA in an organism. Ex: Human genome has ~3 billion base pairs.
Nucleus
Organelle that contains DNA and controls cell activities. Ex: “Brain” of the cell.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
A network of membranes that helps make and transport proteins/lipids.
Smooth ER
ER without ribosomes, makes lipids and detoxifies. Ex: Liver cells have lots of smooth ER.
Rough ER
ER with ribosomes, helps make and fold proteins. Ex: Insulin production in pancreas.
Golgi apparatus
Packages, modifies, and ships proteins. Ex: Like a post office.
Vacuoles
Storage sacs in cells. Ex: Plant vacuoles store water for turgor pressure.
Lysosomes
Organelles with enzymes that break down waste. Ex: Digest worn-out organelles.
Autophagy
Process where lysosomes recycle cell parts.
Apoptosis
Programmed cell death. Ex: Cells between fingers die during development.
Endomembrane system
Network of organelles (ER, Golgi, vesicles, etc.) that transport materials.
Vesicles
Small membrane sacs that move molecules. Ex: Neurotransmitter vesicles in neurons.
Membrane-bound organelles
Organelles surrounded by membranes. Ex: Nucleus, mitochondria.
Mitochondria
Organelle that makes ATP through cellular respiration. Ex: “Powerhouse of the cell.”
Cristae
Folded inner membrane of mitochondria that increases surface area for ATP production.
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate, the cell’s main energy currency.
Chloroplasts
Plant organelles that carry out photosynthesis.
Photosynthesis
Process where plants make glucose using sunlight, CO₂, and water.
SA:V ratio
Surface area to volume ratio, affects cell efficiency. Ex: Smaller cells exchange materials faster.
Specialized structures for different functions
Unique organelles for certain tasks. Ex: Cilia for movement.
Phospholipid
Molecule with hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail, makes up membranes.
Amphipathic
Molecule with both hydrophilic and hydrophobic parts. Ex: Phospholipid.
Peripheral proteins
Proteins on membrane surface. Ex: Enzymes or anchors.
Integral proteins
Proteins embedded in membrane. Ex: Transport channels.
Functions of integral proteins
Transport, signaling, recognition, joining, attachment.
Transport
Moving substances across membranes. Ex: Channel proteins.
Cell-to-cell recognition
Cells identifying each other. Ex: Immune system recognizing bacteria.
Enzymes
Proteins that speed up chemical reactions.
Signal transduction
Process where signals are passed into the cell through receptors.
Intercellular joining
Cells connecting through junctions.
Attachment for extracellular matrix or cytoskeleton
Proteins link the membrane to outside or inside structures.
Fluid mosaic model
Model of membranes as flexible with proteins floating in phospholipids.
Cholesterol
Molecule in membranes that regulates fluidity.
Glycoproteins
Proteins with carbohydrate chains, used for recognition.
Glycolipids
Lipids with carbohydrate chains, used for recognition.
Channel proteins
Proteins that form pores for molecules to pass.
Carrier proteins
Proteins that change shape to transport molecules.
Cell wall
Rigid outer layer in plants, bacteria, fungi.
Plasmodesmata
Channels in plant cell walls for communication.
Concentration gradient
Difference in concentration across space.
Equilibrium
When concentrations are balanced.
Passive transport
Movement across membranes without energy.
Active transport
Movement across membranes with energy (ATP).
Simple diffusion
Molecules move freely from high to low concentration.
Facilitated diffusion
Molecules move via channel/carrier proteins.
Endocytosis
Process of taking in large molecules by forming vesicles.
Phagocytosis
“Cell eating” – engulfing solids.
Pinocytosis
“Cell drinking” – engulfing liquids.
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Endocytosis triggered by specific molecules binding to receptors.
Exocytosis
Vesicles fuse with membrane to release molecules.
Polarized cell membrane
Unequal distribution of charges across membrane. Ex: Neurons at rest.
Na⁺/K⁺ pump (Sodium-potassium pump)
Active transport protein pumping Na⁺ out, K⁺ in.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a membrane.
Aquaporins
Channel proteins for water.
Osmolarity
Concentration of solutes in solution.
Tonicity
Effect of a solution on cell water balance.
Hypertonic
Solution with more solutes
Isotonic
Solution with equal solutes
Hypotonic
Solution with fewer solutes
Turgor pressure
Pressure of water pushing against plant cell walls.
Turgidity
State of being swollen with water.
Osmoregulation
Control of water balance in cells/organisms.
Homeostasis
Maintaining stable internal conditions.
Water potential
Potential energy of water
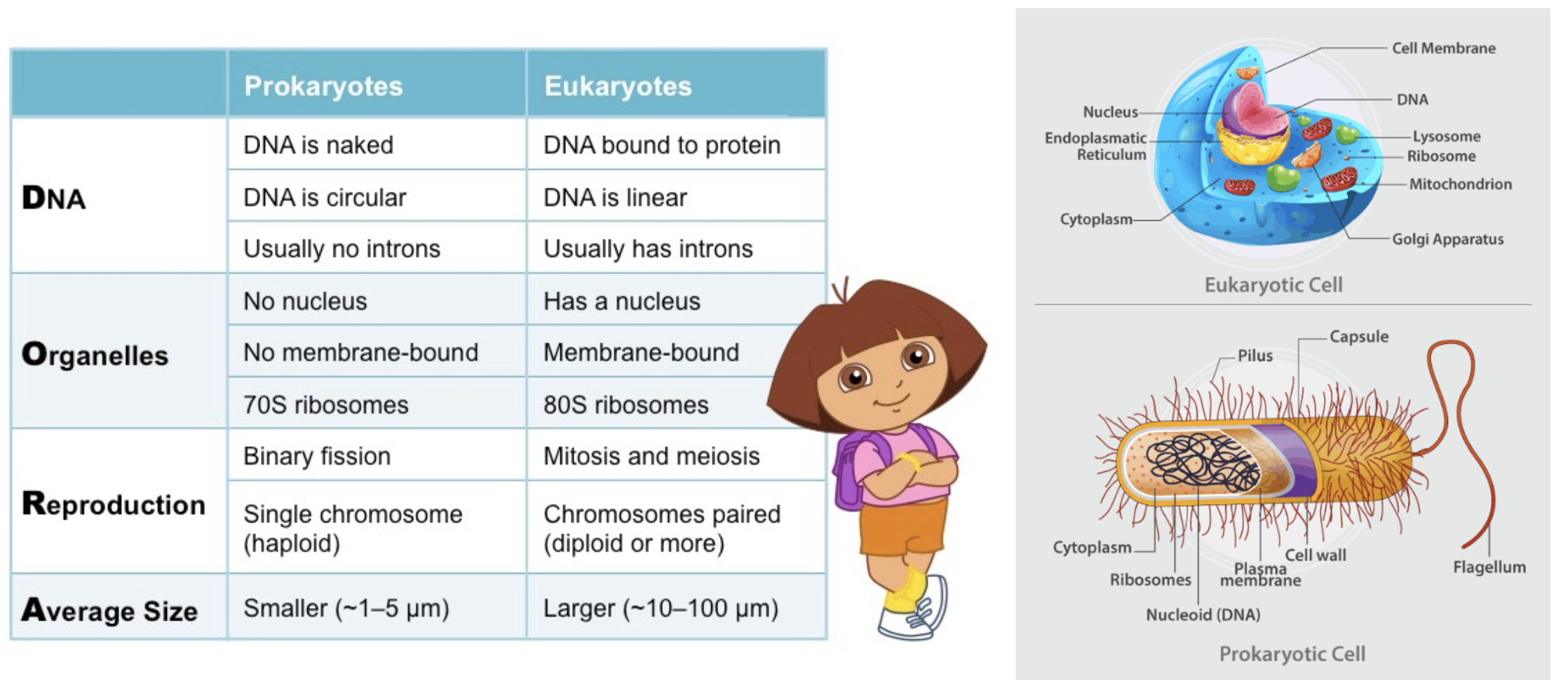
DORA
Differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Endosymbiotic theory
Theory that mitochondria/chloroplasts came from engulfed bacteria.
Endosymbiosis
When one organism lives inside another in mutual benefit.