lecture 8, the axial skeleton
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
lateral
to the side (left or right)
anterior (ventral)
to the front
ex. ventral bone
posterior (dorsal)
to the back
ex. dorsal bone
superior
to the top
ex. superior vena cava
inferior
to the bottom
ex. inferior vena cava
articulate
attach to
ex. muscle articulates with bone via the tendon
proximal
near to
closest to body
distal
far from
distance
medial
to the middle
ex. duplicated chromosome move to middle
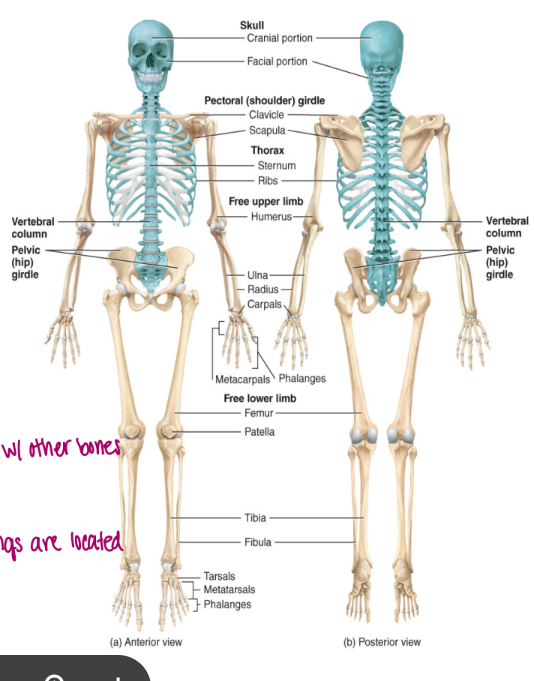
the skeleton
the skeletal system is divided into two components
axial
appendicular skeleton
axial skeleton
this is the skeletal system that can be found down the midline of the body
composed of 80 bones including
a. the skull
b. the hyoid bone
c. the vertebral column
d. thoracic cage: composed of the sternum and the ribs
cartilage is in between the bones
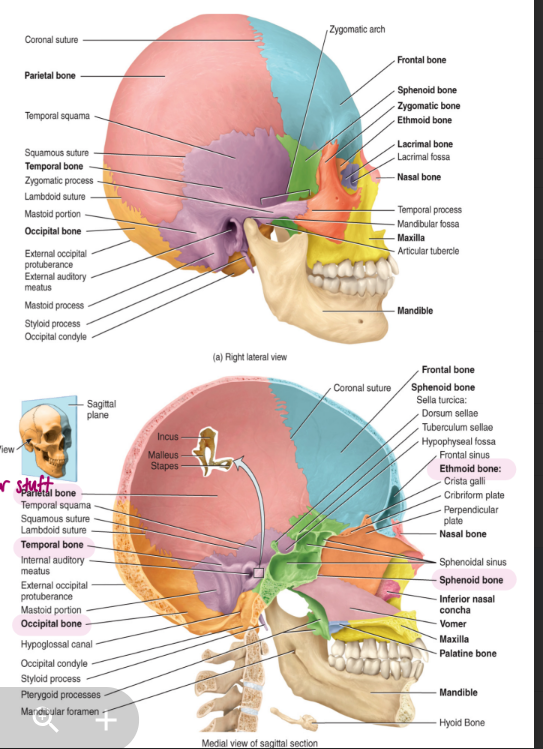
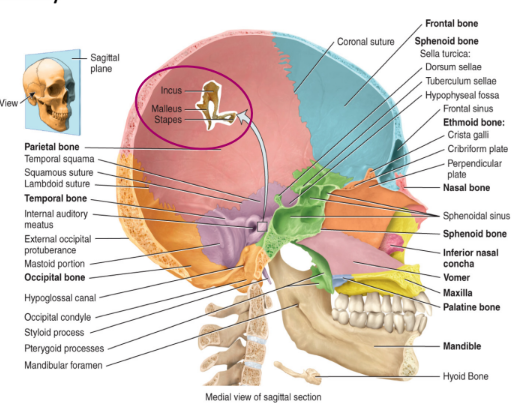
axial skeleton: the skull
i. cranium
encages the brain
8 bones that function to protect the brain
1 frontal bone
2 parietal bones
2 temporal bones
1 occipital bone (if damage could loose vision and worse)
1 sphenoid bone (connected in middle as it shows on both sides, unpaired)
1 ethmoid bone: superior and middle nasal conchae
in babies there is more flex in the cranium so they can actually be birthed
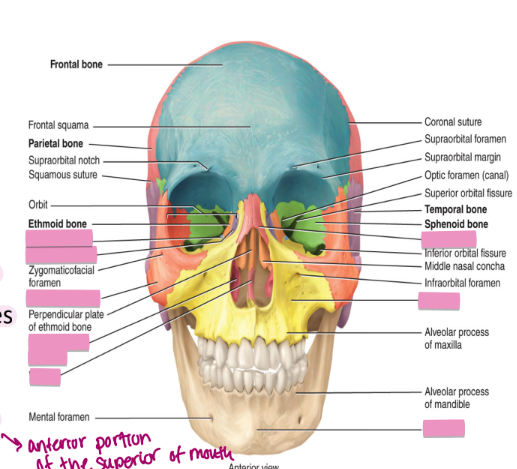
axial skeleton the skull: facial bones
14 bones in total
2 nasal bones
2 maxillae: form upper jaw
2 zygomatic bones: form the eye socket and the cheekbone
2 lacrimal bones: form the sides of the nose and the remaining portion of the eye socket
2 palatine bones: in the pallet (anterior portion of the superior of mouth)
2 inferior nasal conchae
1 vomer: found behind the pallet
1. mandible: forms the lower jaw
the axial skeleton the skull: auditory ossicles
found in the middle ear
the smallest bones found in the body consists of
2 malleus
2 incus
2 stapes
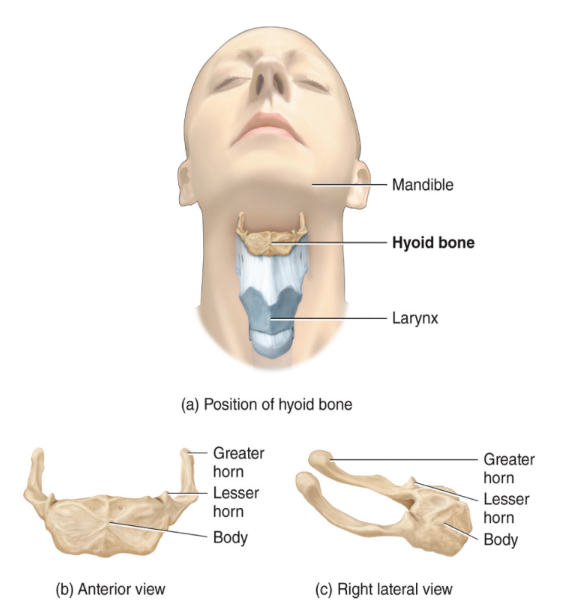
axial skeleton: the hyoid bone
this bone forms no articulations with bone
functions to attach muscles of the tongue, neck, and pharynx
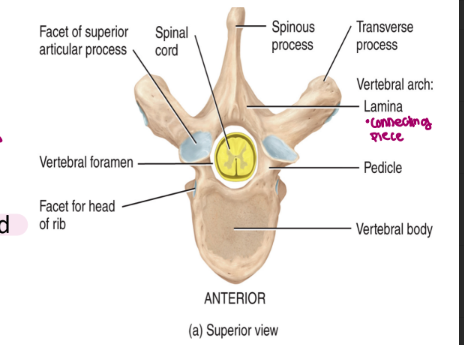
axial skeleton: the vertebral column
also called the spinal column (protection for the nervous tissue within)
each vertebra of the spinal column consists of
body: thick and located on the anterior end
lamina
pedicle
vertebral arch
vertebral foramen: line up for each individual vertebra forming a canal through which the spinal cord passes
spinous process (only 1, landmark)
serve as attachment sites for muscles and ligaments
two transverse processes
serve as attachment sites for muscles and ligaments
superior and inferior articular processes: contain smooth surfaces formed from hyaline cartilage → called facets
serve as attachment sites for vertebra above and vertebra below
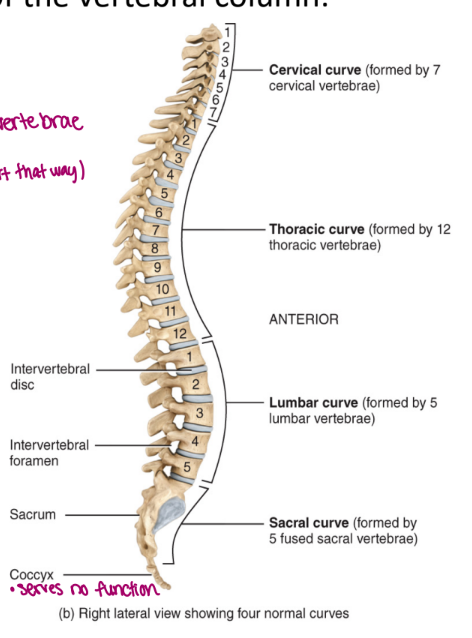
the axial skeleton: the vertebral column five regions
cervical → neck
thoracic → lungs
lumbar → biggest of the vertebrate
sacral → 3-5 bones (didn’t start that way, fuse)
coccyx → tail bone
the vertebral column: cervical region
there are 7 vertebrae found within the cervical region: C1-C7
these are the smallest and the lightest weight vertebrae (delicate)
C1 is the atlas
has no body (very delicate)
has no spinous process (allows for head to move “yes”)
the absence of these joints allow you to move your head up and down in a yes motion
articulates superiorly with occipital condyle
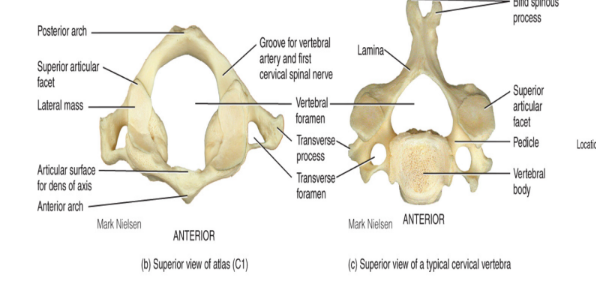
the vertebral column: cervical region C2, C3-C7
C2 is the axis
contains all of the typical vertebral components (body/spinous process)
not as specialized as the atlas
contains knoblike process called the dens (odontoid process) that projects superiorly from the body of the vertebrae
acts as a pivot atlas rotation allowing you to move your head in a ‘no’ motion
fits into C1 like a puzzle piece
C3-C7
distinguishing feature found on all of these vertebrae is the transverse foramina (hole on side)
opening found in transverse process where the vertebral arteries pass in order to service the brain
very large
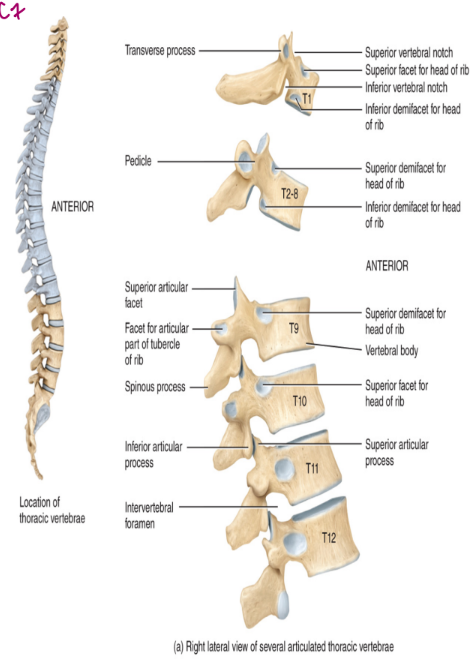
the vertebral column: thoracic region
the thoracic region contains 12 vertebrae labelled T1-T12
these articulate posteriorly with the ribs
the thoracic vertebrae increases in size from first to last
the distinguishing feature it the articular facet (made from cartilage)
used for rib articulation
protects against erosion
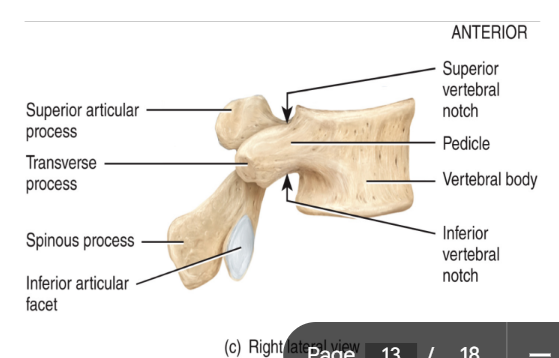
the vertebral column: lumbar region
this region has 5 vertebrae: L1-L5
these vertebrae function to support the body’s weight
commonly referred to as the “small of the back”
contain a large, very thick body
processes are heavy and rectangular
takes a lot to break
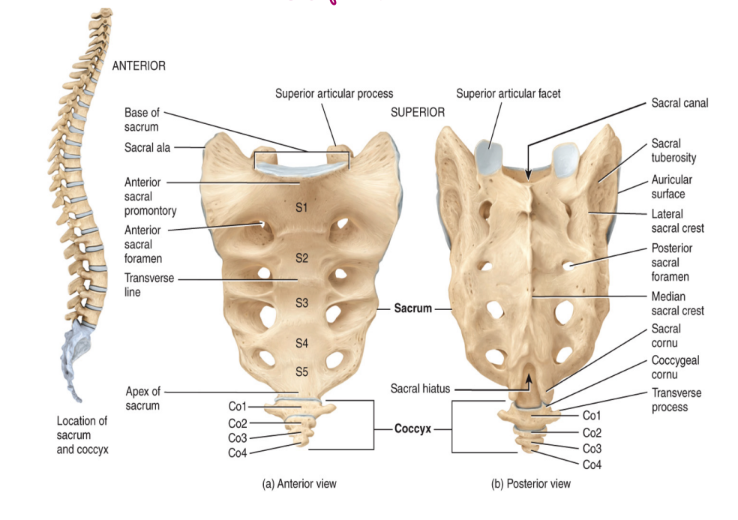
the vertebral column: the sacrum
the sacrum consists of five fused vertebrae
articulate with the ilium, a part of the appendicular skeleton, specifically the pelvis
also articulates with the 5th lumbar vertebra superiorly (sits on top of sacrum)
contain intervertebral foramina
exit sites of spinal nerves
sensory information that needs to come back
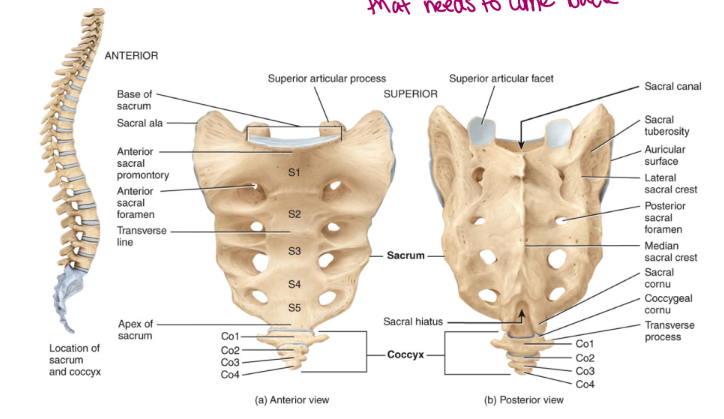
the vertebral column: the coccyx
the coccyx consists of 3-4, but usually 4 fused vertebrae
known as tailbone
generally useless
soft tissue there that easily bruises
spinal curvature
normal curvature of the vertebral column
the cervical and the lumbar sections are curved concave posteriorly
the thoracic and the sacral sections are curved convex posteriorly
abnormal curvature of the vertebral column
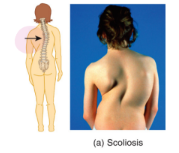
scoliosis
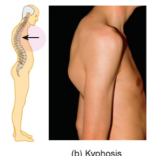
kyphosis
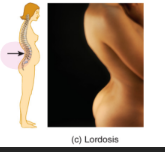
lordosis
scoliosis
the spinal column cure laterally
as though you continually carried a heavy bag on the same shoulder
kyphosis
hunchback
caused by an exaggerated thoracic curve which can be caused by osteoporosis
lordosis
swayback
caused by an exaggerated lumbar curve which can be caused be pregnancy or pot bellies
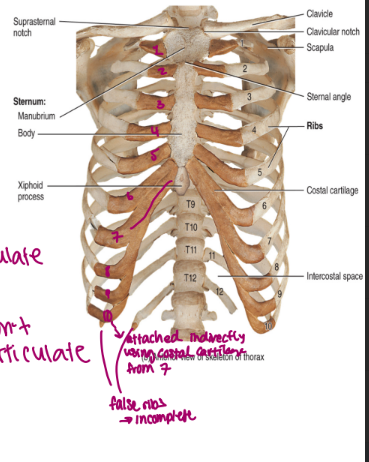
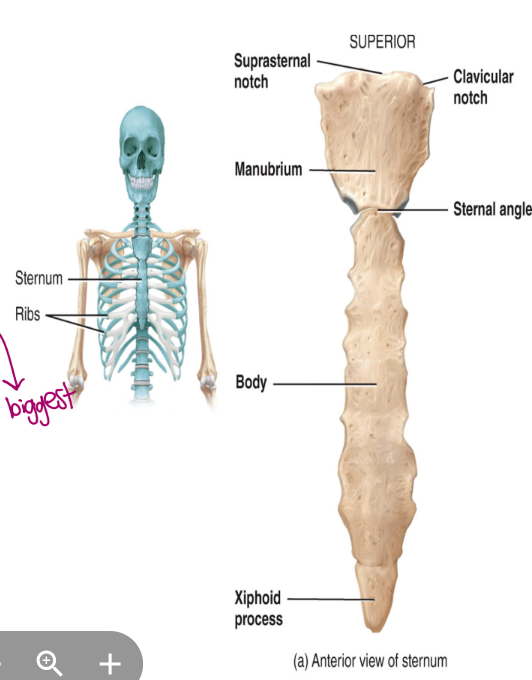
the axial skeleton: the thoracic cage, sternum
the sternum
the breast bone
the manubrium is superior
the body is portion (biggest)
the xiphoid is inferior
the axial skeleton: the thoracic cage, ribs
there are 12 pair of ribs
they articulate posteriorly with thoracic vertebrae
there are true ribs and false ribs
true ribs: attach directly to the sternum via costal cartilage (hyaline cartilage) → there are 7 pair of true ribs
false ribs: attach either indirectly to the sternum or not at all
pairs 8-10 attach indirectly to the sternum via costal cartilage
pairs 11 and 12 are not attached and are embedded in muscle → called floating ribs