3 - Molecules of Life
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Organic
A compound that consists mainly of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
Hydrocarbon
Compound that consists only of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
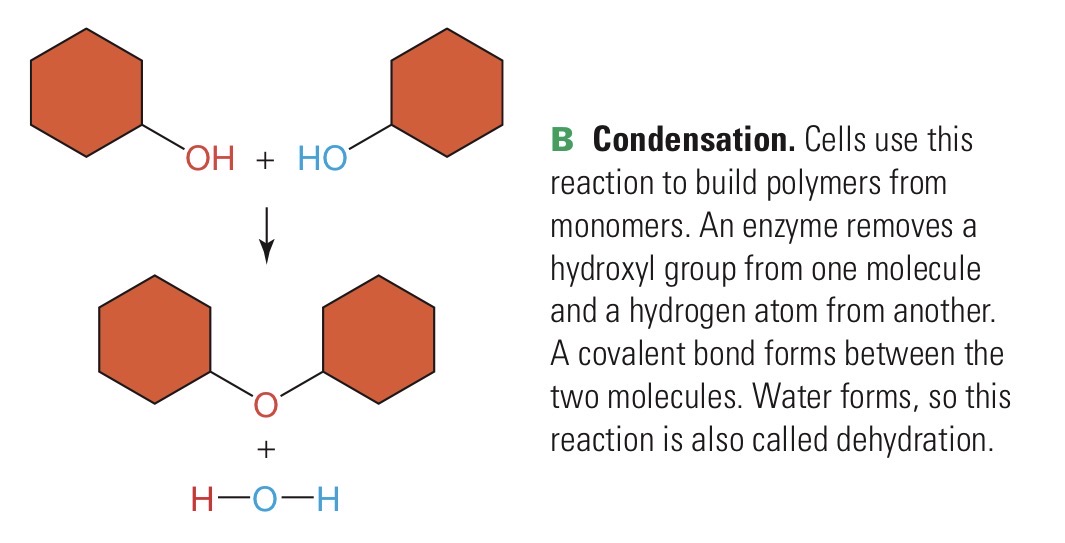
Condensation
Chemical reaction in which an enzyme builds a large molecule from smaller units and water is formed
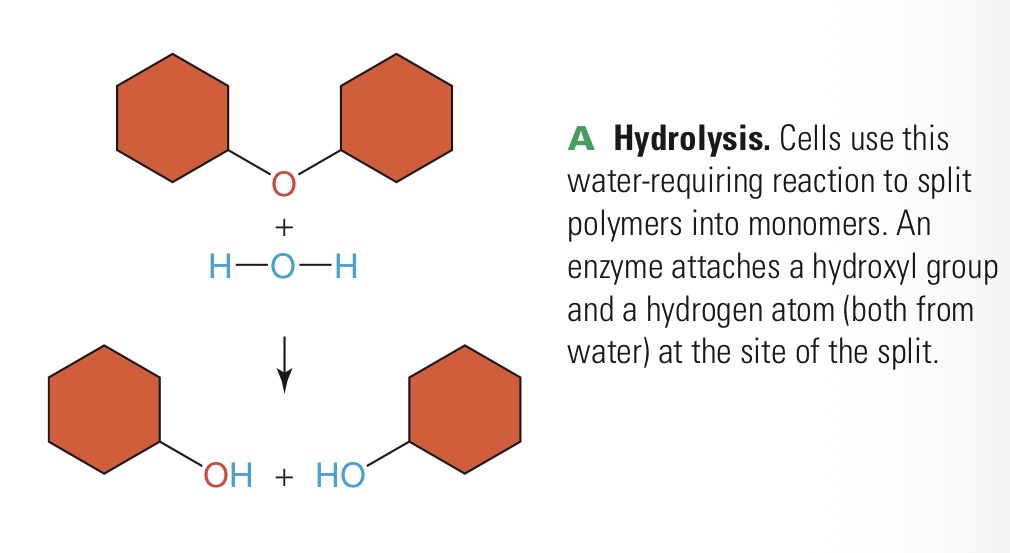
Hydrolysis
Water-requiring chemical reaction in which an enzyme breaks a molecule into smaller subunits
Carbohydrate
Molecule that consists primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms in a 1:2:1 ratio
Monosaccharides
Simple sugar; consists of one sugar unit so it cannot be broken apart into monomers
Examples of monosaccharides
Glucose, fructose, galactose
Oligosaccharide
Short chains of covalently bonded monosaccharides
Disaccharide
Carbohydrate that consists of two monosaccharide monomers
Examples of disaccharides
Sucrose: glucose+sucrose
Lactose: glucose+galactose
Maltose: glucose+glucose
Polysaccharide
Carbohydrate that consists of hundreds or thousands of monosaccharide monomers
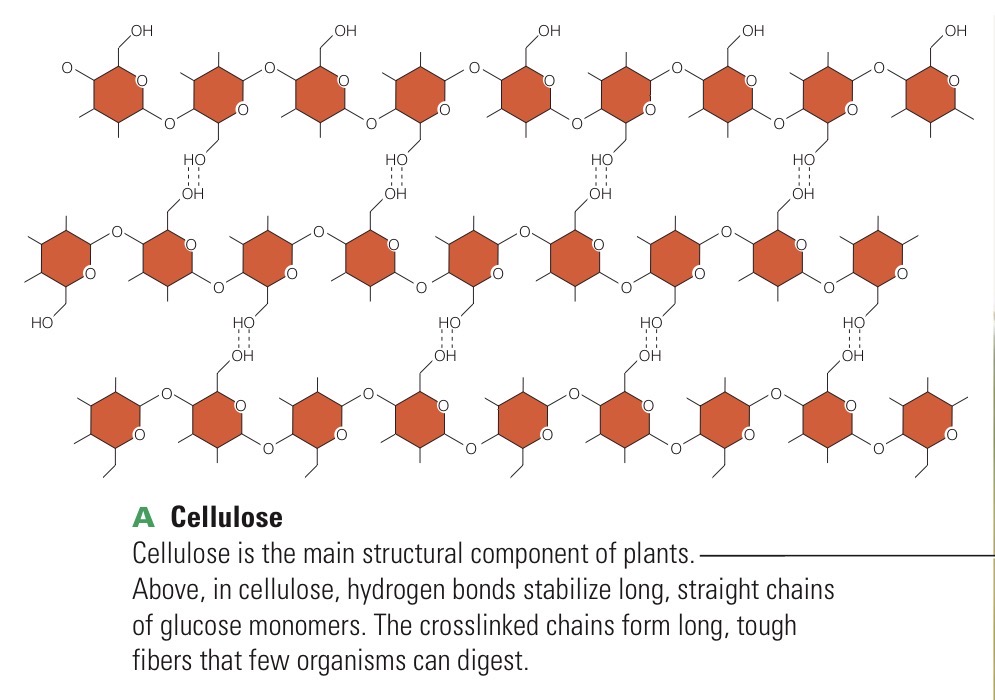
Cellulose
Crosslinked polysaccharide of glucose monomers; the major structural material in plants
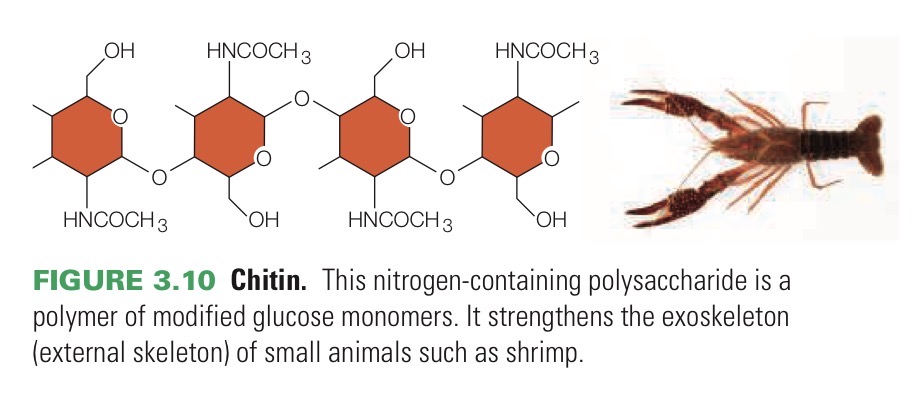
Chitin
Nitrogen-containing polysaccharide that composes fungal cell walls and arthropod exoskeletons
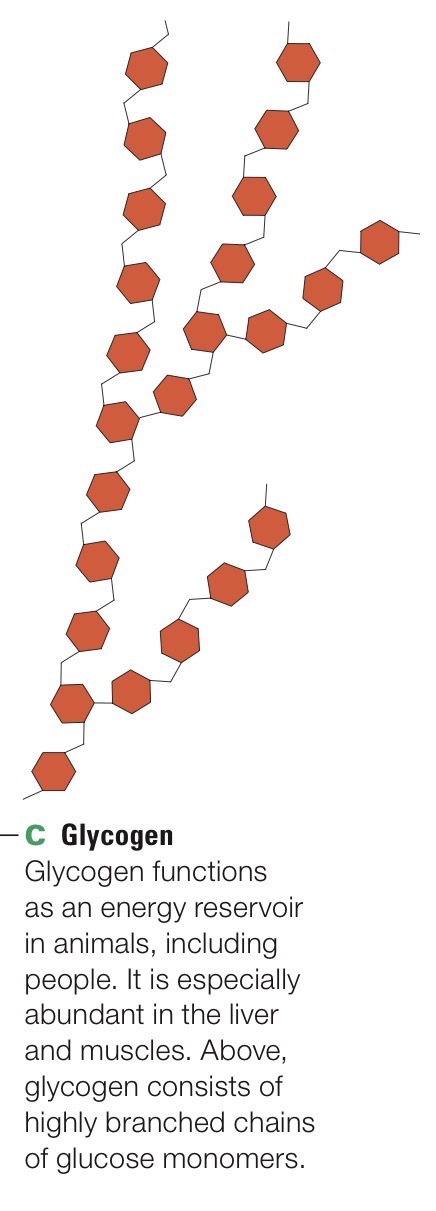
Glycogen
Highly branched polysaccharide of glucose monomers. Principal form of stored sugars in animals.
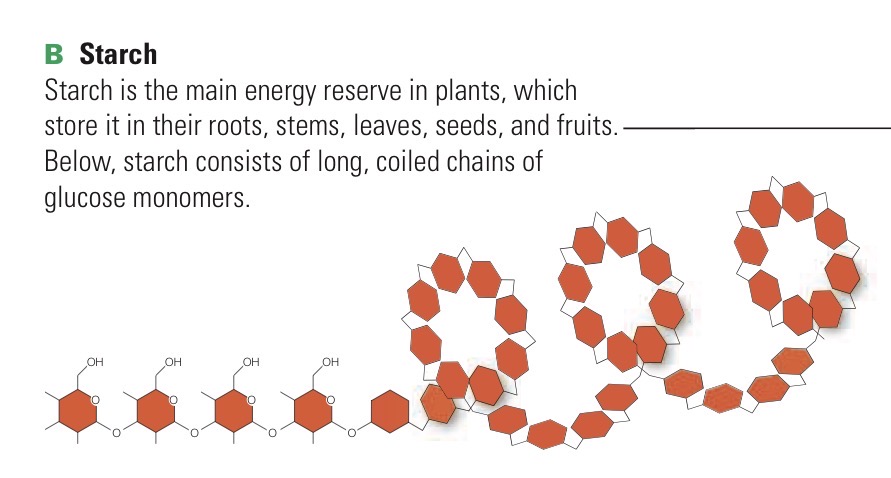
Starch
Polysaccaride - energy reservoir in plant cells
Lipid
Fatty, oily, or waxy organic compound
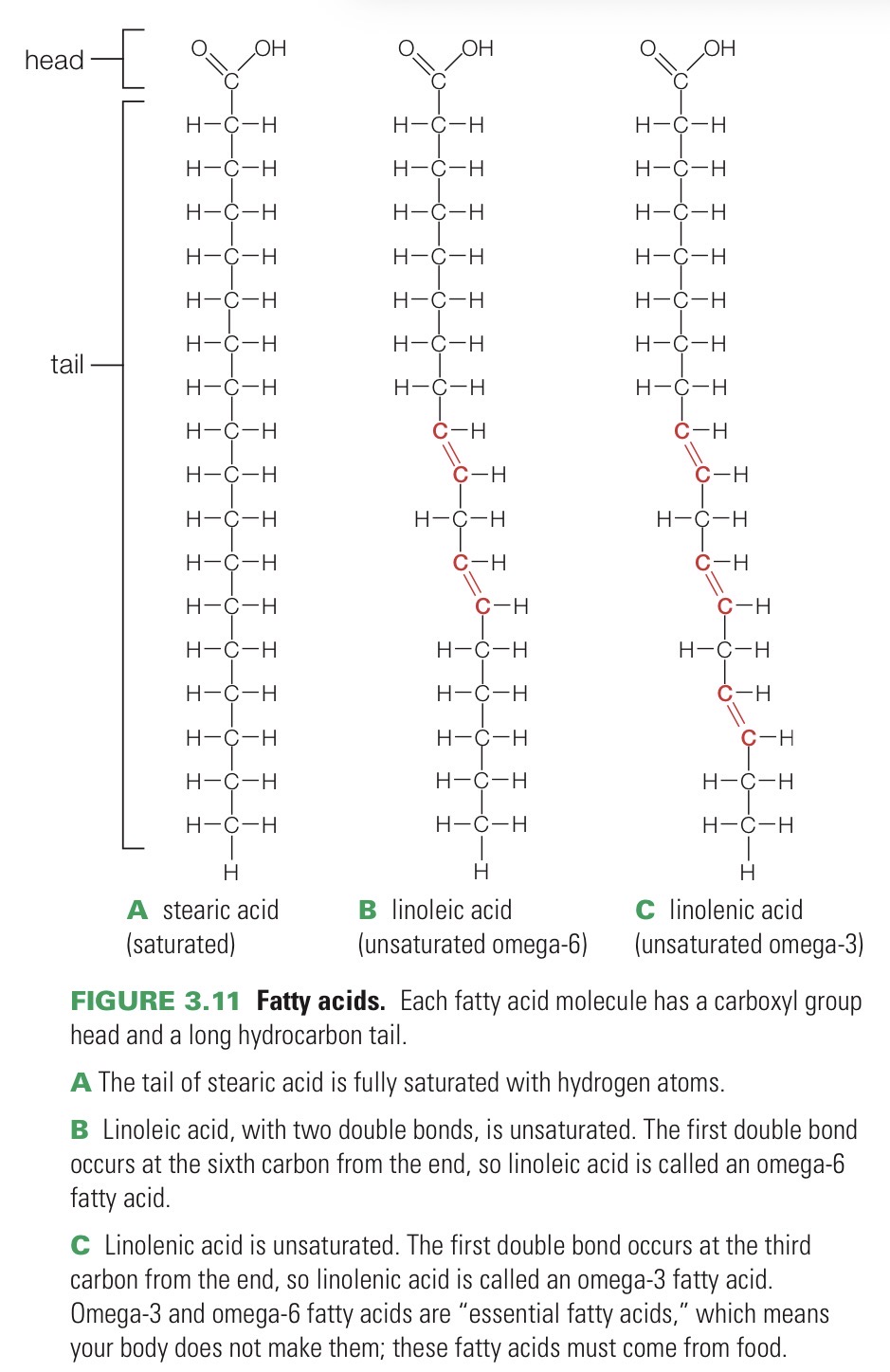
Fatty acid
Lipid that consists of an acidic carboxyl group “head” and a long hydrocarbon “tail”
Triglyceride
A molecule that is entirely hydrophobic and therefore does not dissolve in water. Most abundant and richest energy source in your body and is more energy-dense than carbs.
Has three fatty acids bonded to a glycerol.
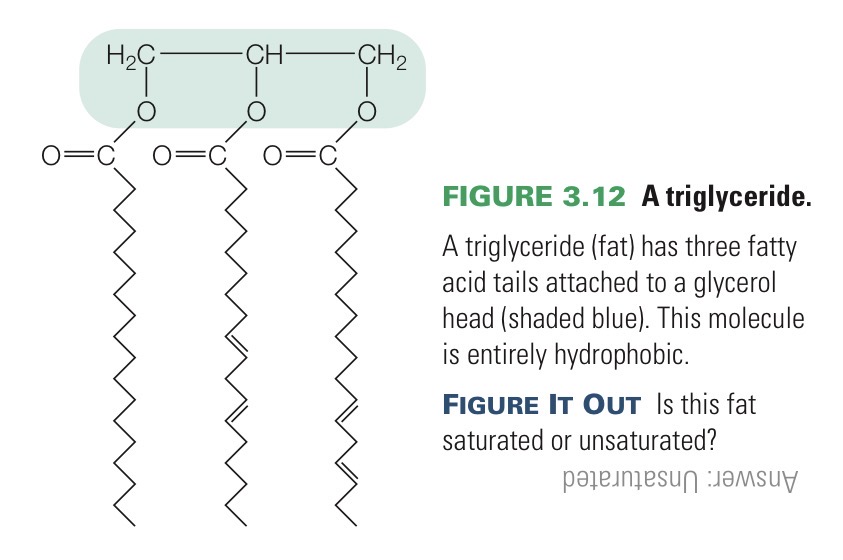
Fat
A triglyceride molecule
Saturated fat
Triglyceride molecule with three saturated fatty acid tails.
Their floppy tails pack together tightly, so they are sold at room temperature.
They only have single bonds linking the carbons in their tails.
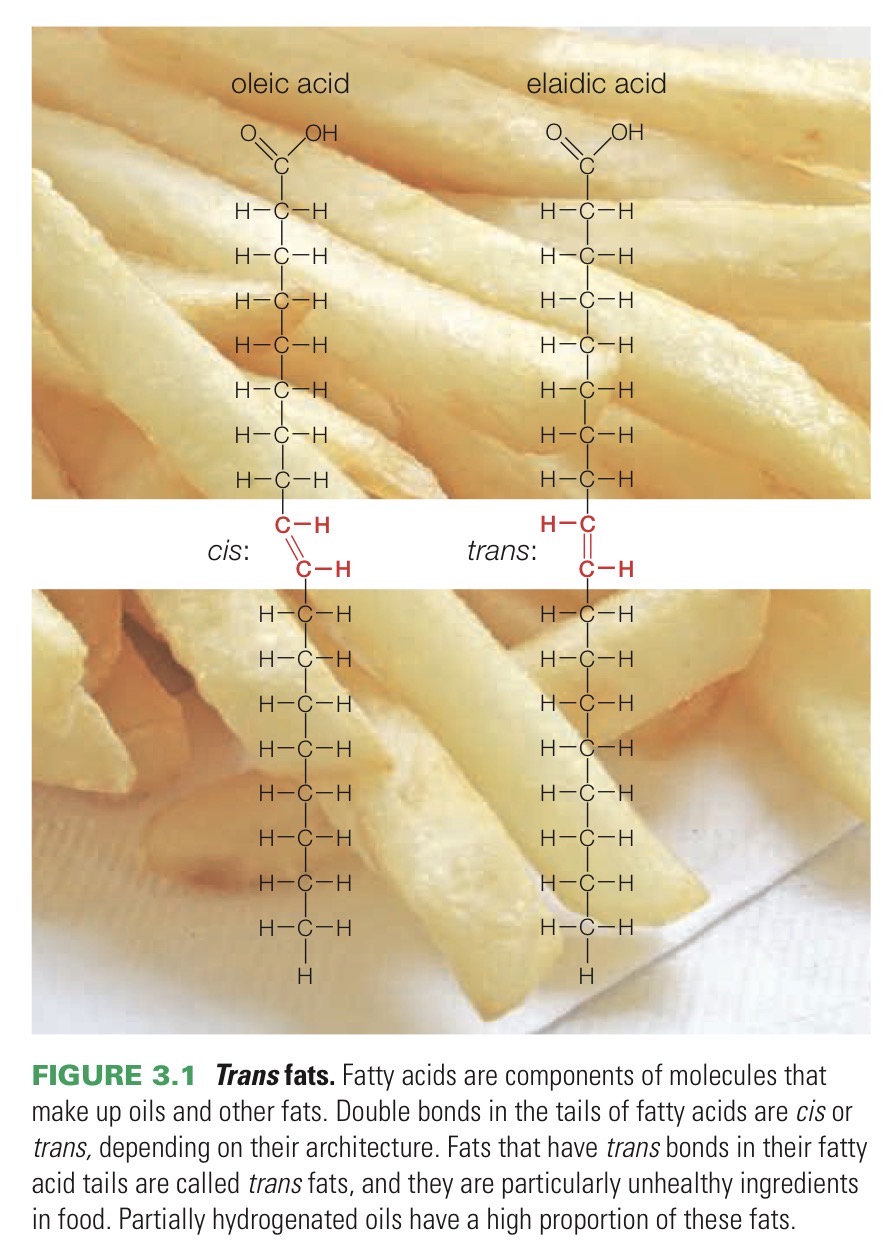
Unsaturated fat
Triglyceride molecule with one or more unsaturated fatty acid tails.
Double bonds between carbons kink the tail of an unsaturated fatty acid and limit its flexibility. This is why undaturated fats are liquid at room tempearture.
Monounsaturated fat
Has one double bond among its three tails
Polyunsaturated fat
Has two or more double bonds among its three tails
Trans fat
A type of unsaturated fat, but solid at room temperature because of a special trans double bond that keeps the tails straight.
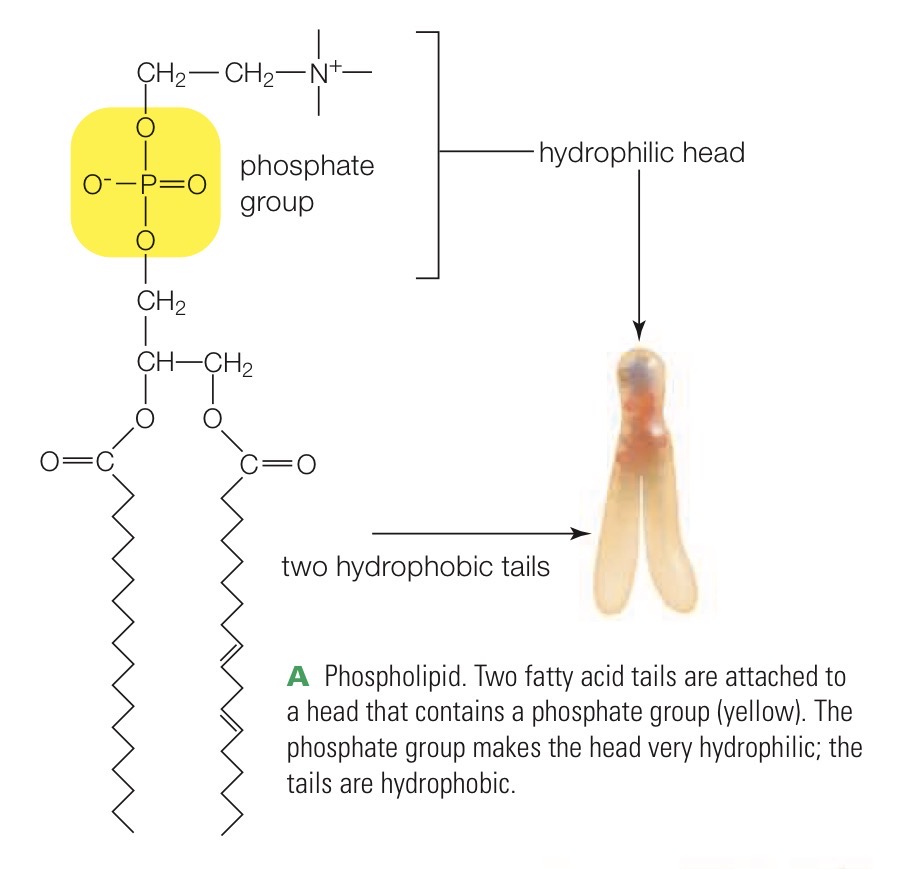
Phospholipid
A lipid with two hydrophobic fatty acid tails and a hydrophilic phosphate group in its head
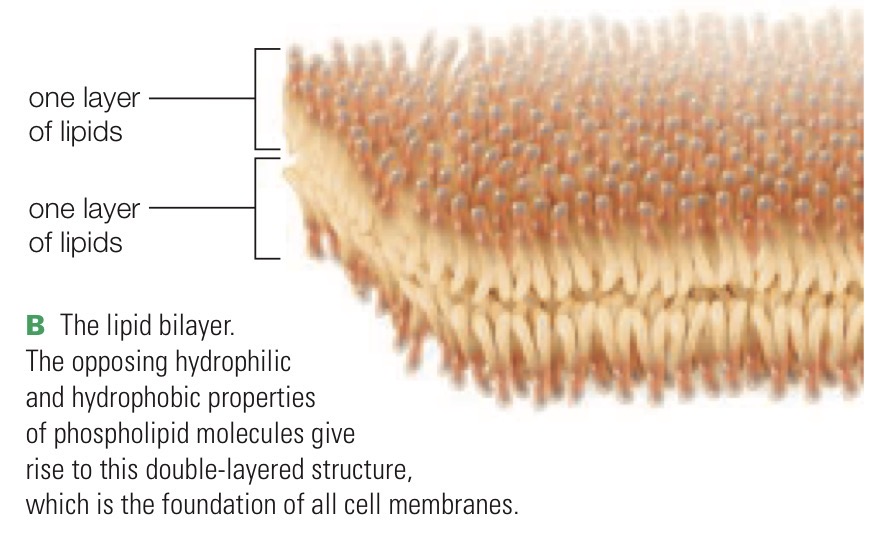
Lipid bilayer
Formed by phospholipids; double layer of lipids arranged tail-to-tail and structural foundation of cell membranes
Steroids
Lipids with no fatty acid tails. Instead they have four carbon rings.
Eg cholesterol, steroid hormones.
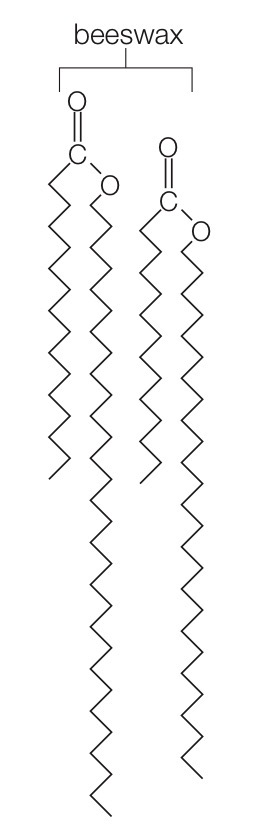
Wax
A water-repellent substance that consists of a complex, varying mixture of lipids with long fatty acid tails bonded to long-chain alcohols.
Waxes are waterproof because they pack together very tightly.
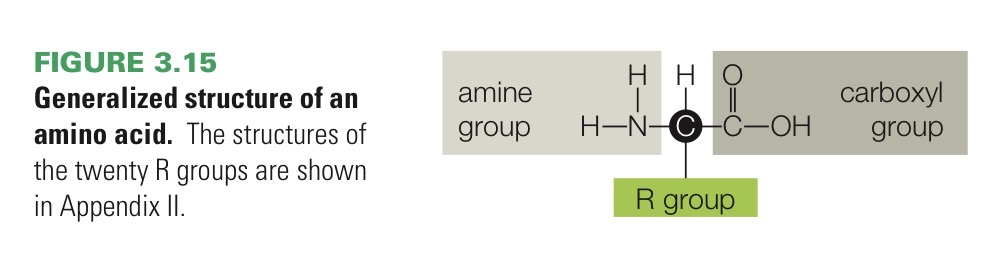
Amino acid
Small organic compound that is a monomer of proteins. Consists of an amine group (—NH2), a carboxyl group (—COOH, the acid), and one of 20 “R” groups that defines the kind of amino acid, all typically bonded to the same carbon atom.
Peptide
Short chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
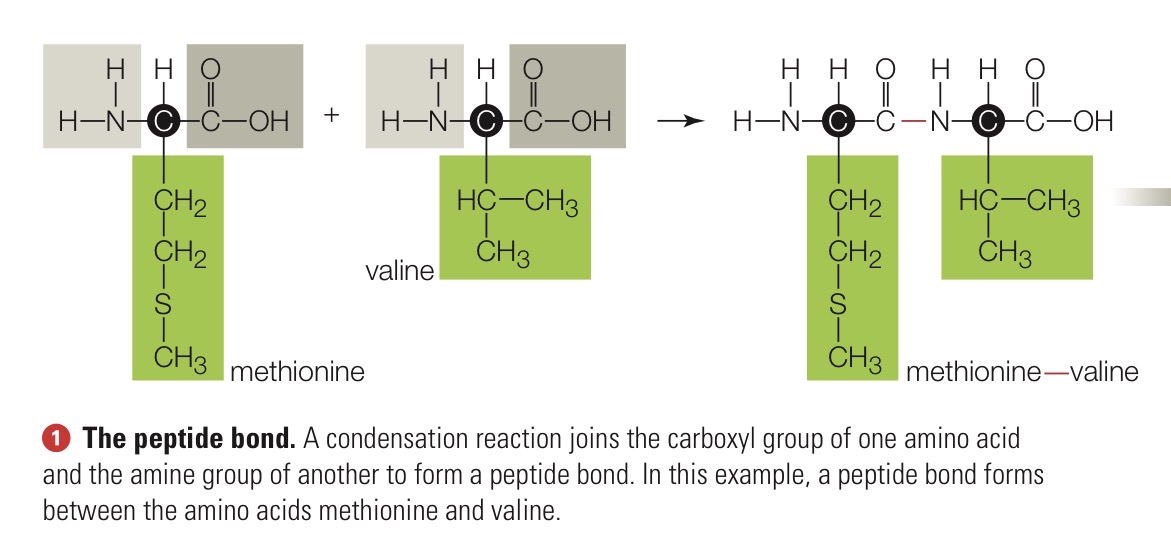
Peptide bond
The covalent bond that links amino acids in a protein. Joins the amine group of one amino acid and the carboxyl group of another.
Polypeptide
Long chain of amino acids linked by peptide bonds
Protein
Organic molecule that consists of one or more polypeptides folded into a specific shape
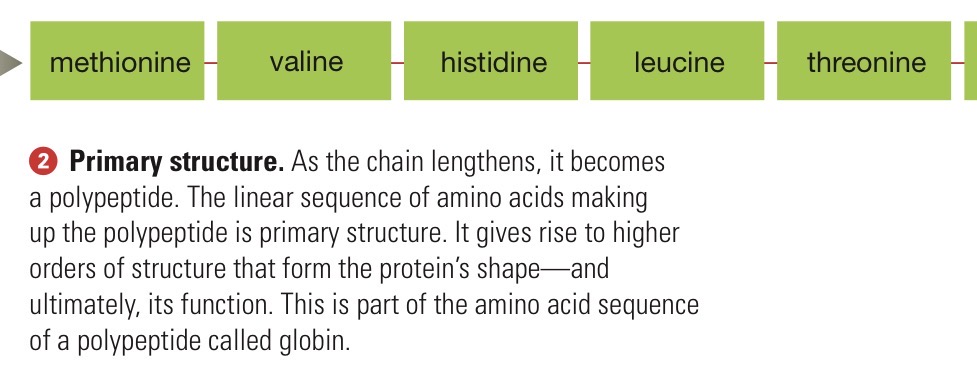
Protein primary structure
Linear sequence of amino acids.
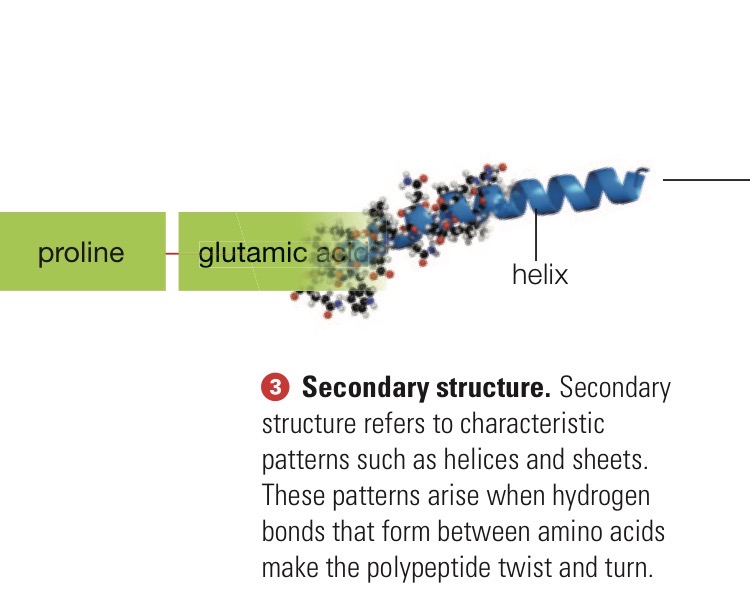
Secondary structure
Helices and sheets. These patterns arise when hydrogen bonds that form between amino acids make the polypeptide twist and turn.
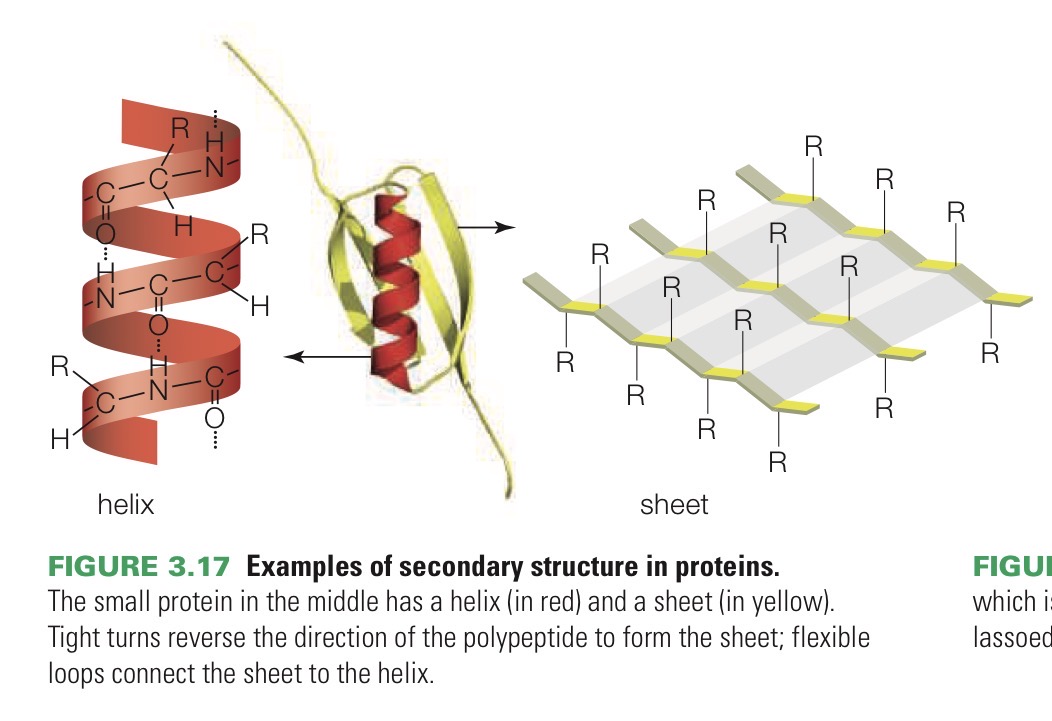
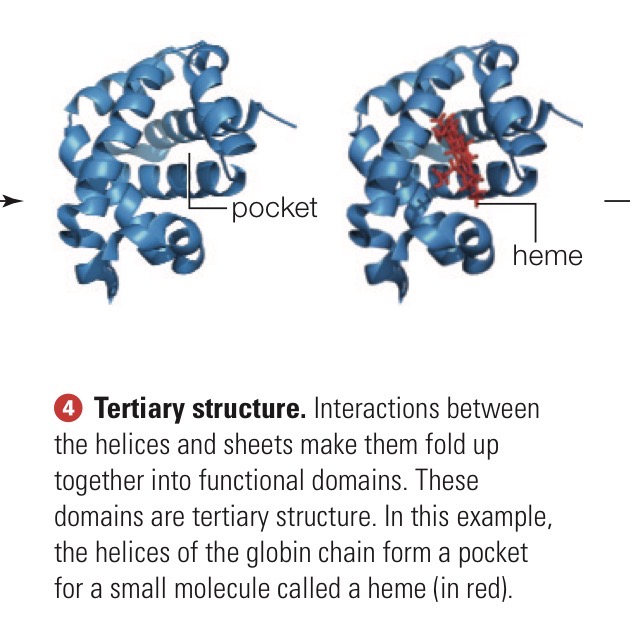
Tertiary structure
Functional domains formed by interactions between helices and sheets that make them fold up together.
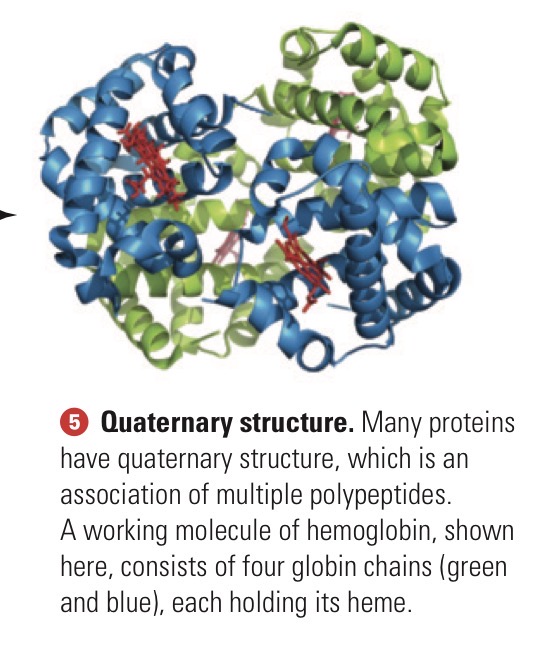
Quaternary structure
An association of multiple polypeptides.
Denaturation
When a protein has its hydrogen bonds, which maintain the shape of a protein, disrupted by shifts in pH or temperature or by exposure to detergents or salts, and a protein loses its secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structure.
Eg. When you cook an egg, you denature the protein in the egg white.
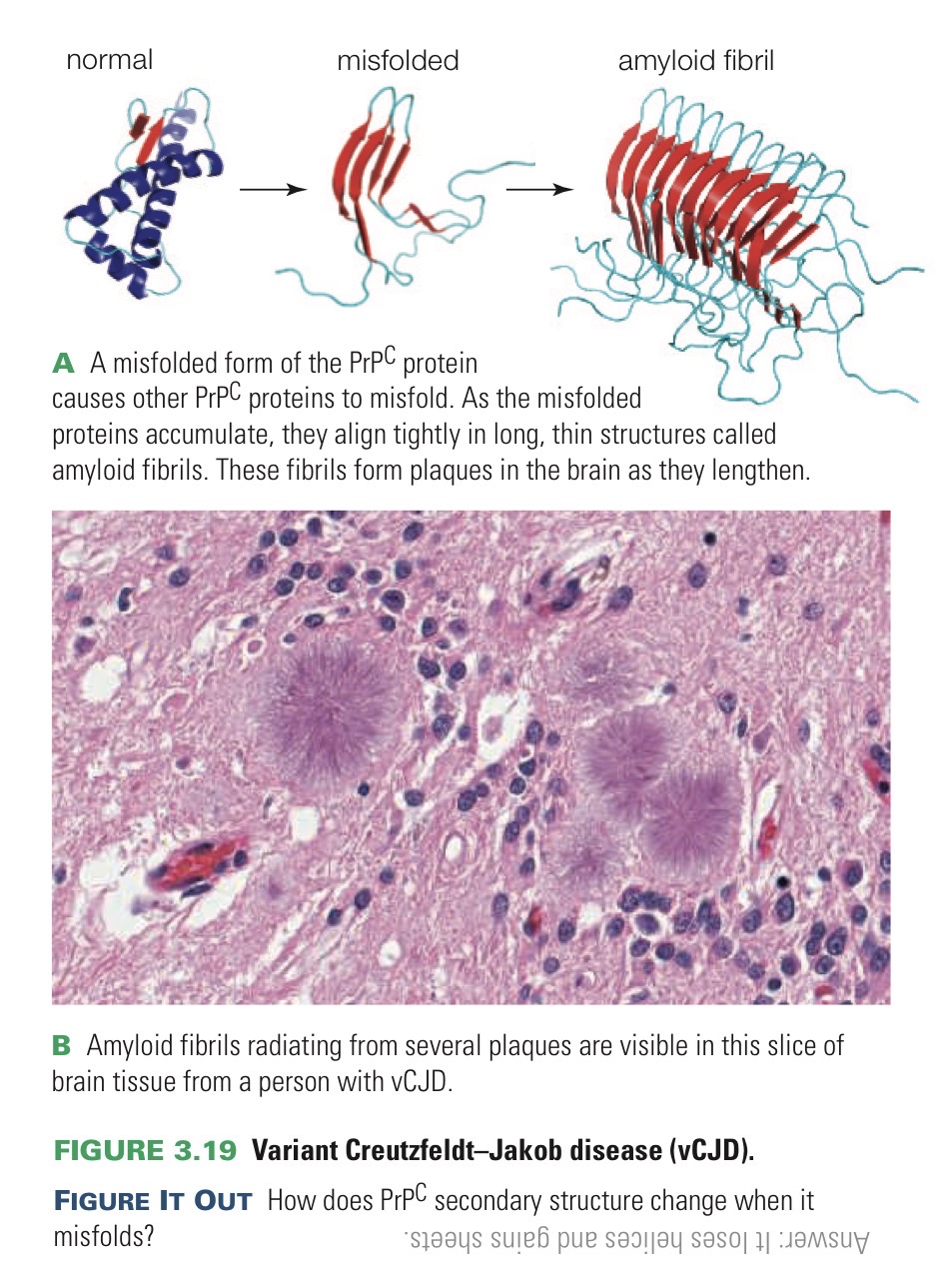
Prion
Infectious protein that causes other normally folded proteins to misfold too.
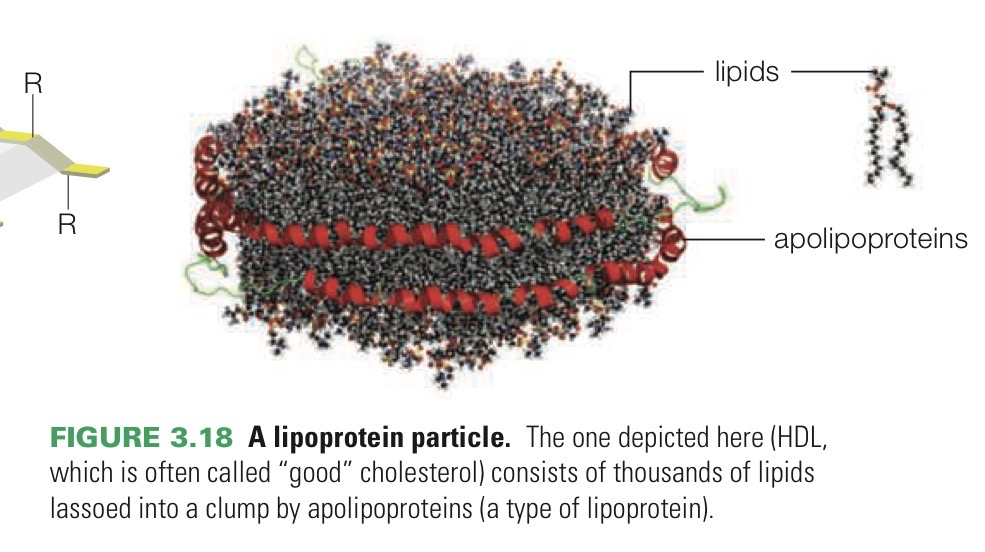
Lipoprotein
Protein that can bind to lipids. They form particles that allow fats and other hydrophobic molecules to move through watery fluid into cells and bodies.
Glycoprotein
A protein with one or more oligosaccharides attached to it. They allow a tissue or a body to recognize its own cells.
Nucleotides
Small molecule with a five-carbon sugar, a nitrogen-containing base, and phosphate groups. Monomer of nucleic acids.
Function as energy carriers, enzyme helpers, chemical messengers, and subunits of DNA, and RNA.
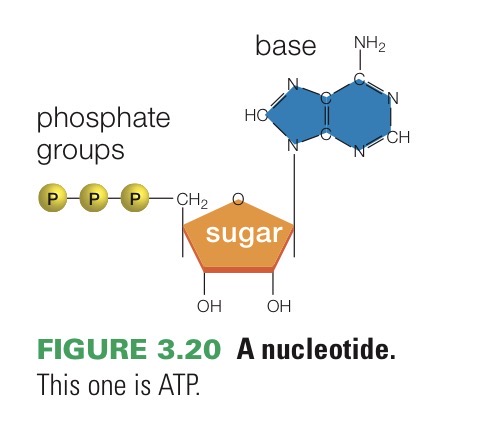
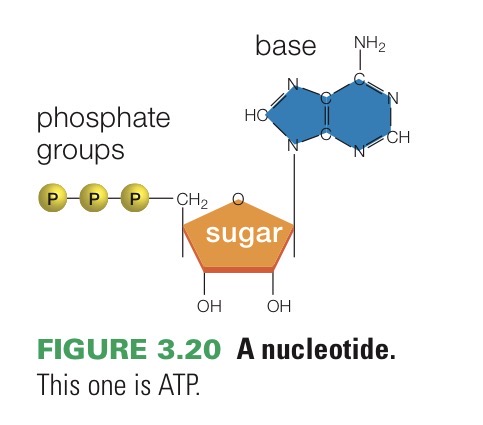
ATP
Adenosine triphosphate. Nucleotide monomer of RNA and an important energy carrier in cells.
Nucleic acid
Polymer of nucleotides. DNA or RNA.
Sugar of one nucleotide is joined to the phosphate group of the next.
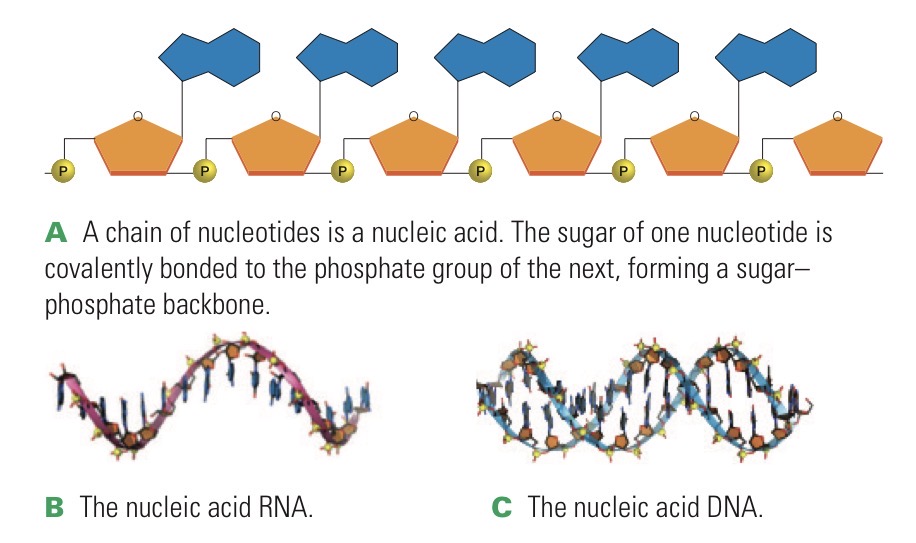
RNA
Ribonucleic acid. Single chain of nucleotide monomers. Carries out protein synthesis
DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid. Nucleic acid that carries hereditary information.