Introduction to Living Things and Key Biological Concepts
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Characteristics of Life
Essential traits defining living organisms.
Homeostasis
Maintaining stable internal conditions in organisms.
Metabolism
Chemical processes for energy use in organisms.
Heredity
Transmission of genetic traits to offspring.
Evolution
Change in species over time through adaptation.
CHONPS
Key elements: Carbon, Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen, Phosphorus, Sulfur.
Proteins
Molecules made of amino acids, essential for structure.
Carbohydrates
Organic compounds for energy, includes sugars and starches.
Amino Acids
Building blocks of proteins, 20 types exist.
Cellulose
Plant fiber, important for structure and support.
Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA, carriers of genetic information.
Lipids
Fats and oils, energy storage and membrane structure.
Enzymes
Proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions.
Heterotrophs
Organisms that consume others for energy.
Autotrophs
Organisms that produce their own food from sunlight.
Photosynthesis
Process converting sunlight into chemical energy.
Cellular Respiration
Process converting sugar and oxygen into ATP.
Fermentation
Anaerobic process producing energy without oxygen.
Prokaryotes
Single-celled organisms without a nucleus.
Eukaryotes
Organisms with cells containing a true nucleus.
Osmosis
Diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane.
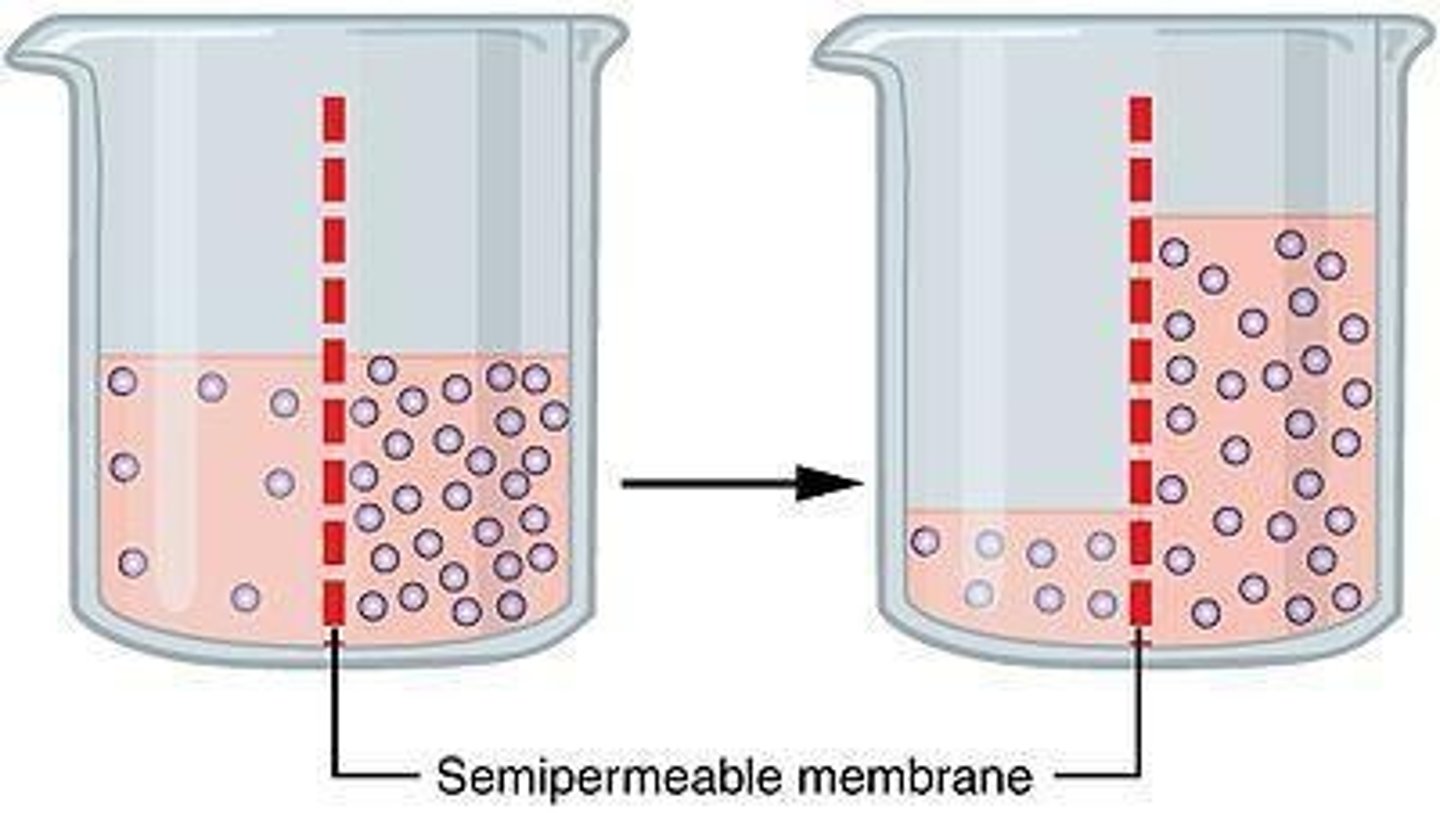
Concentration Gradient
Difference in solute concentration across a membrane.
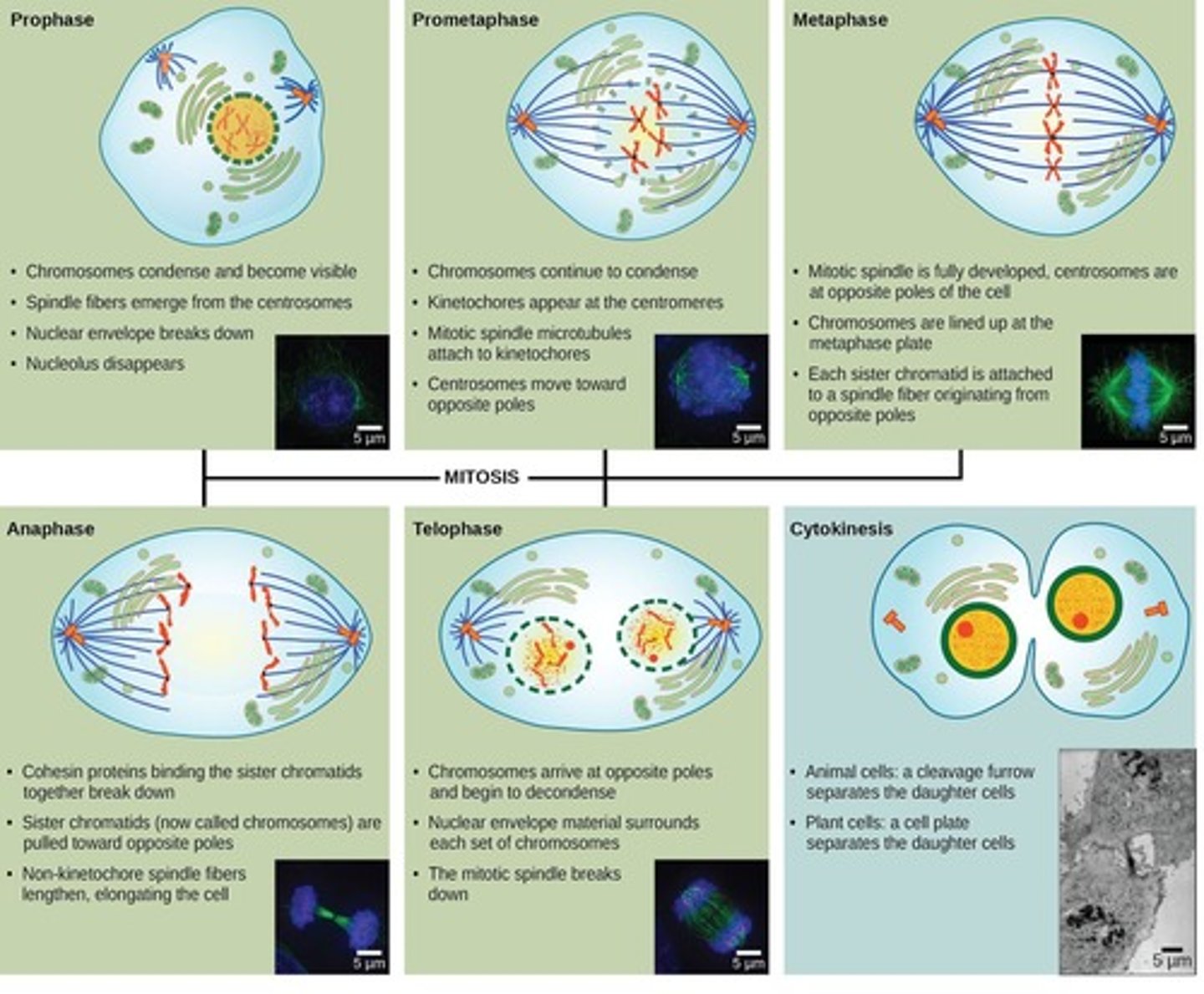
Mitosis
Cell division resulting in two identical daughter cells.
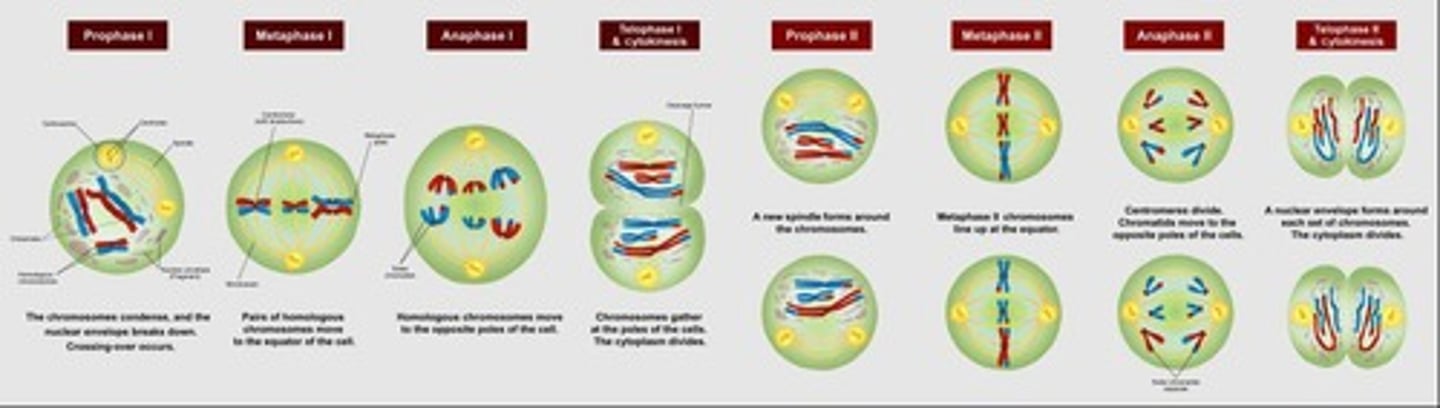
Meiosis
Cell division producing gametes with half chromosome number.
Asexual Reproduction
Reproduction without the fusion of gametes.
Growth
Increase in cell number from fertilized egg.
Repair & Renewal
Replacement of cells due to damage or aging.
Homologous Chromosomes
Paired chromosomes with matching genes.
Diploid
Cell with two sets of chromosomes (2n).
Interphase
Phase where the cell prepares for division.
Mitosis
Process producing two identical daughter cells.
Zygote
Fertilized egg formed from sperm and egg.
Meiosis
Cell division reducing chromosome number by half.
Gametes
Reproductive cells (sperm and egg).
Genetic Diversity
Variation in genetic traits among offspring.
Fertilization
Union of sperm and egg to form zygote.
Chromosome Reduction
Halving chromosome number from 46 to 23.
Cell Cycle
Sequence of phases in cell division process.
Mitosis
Single division producing genetically identical daughter cells.
Meiosis
Two divisions producing genetically different gametes.
Haploid
Cell with one set of chromosomes (1n).
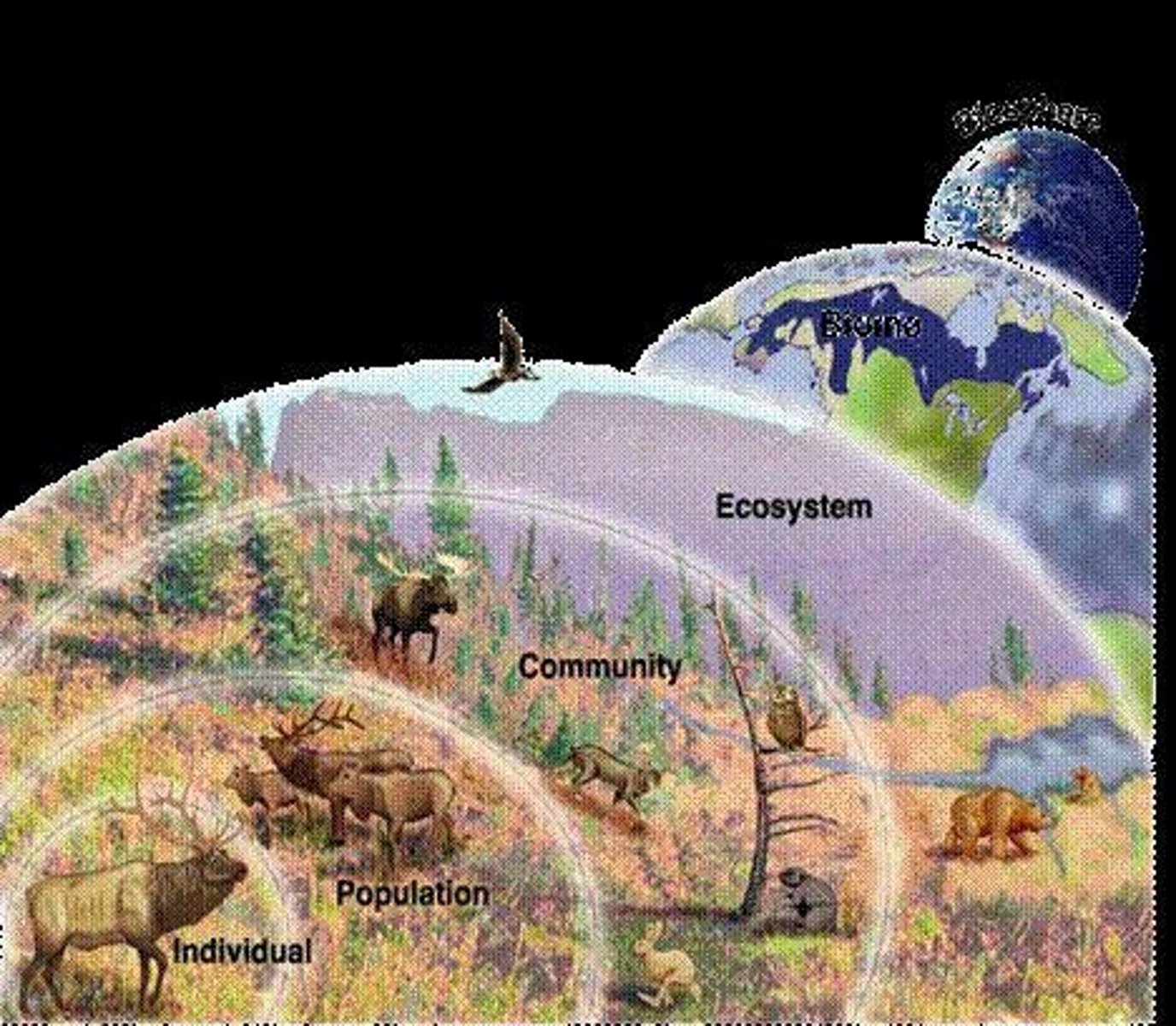
Ecosystem
Natural unit of living and non-living interactions.
Biotic factors
Living components of an ecosystem.
Abiotic factors
Non-living components like water and air.
Population density
Number of individuals per area.
Exponential growth
Rapid population increase in J-shaped curve.
Logistical growth
Population growth with carrying capacity in S-shaped curve.
Carrying capacity
Maximum population an environment can support.
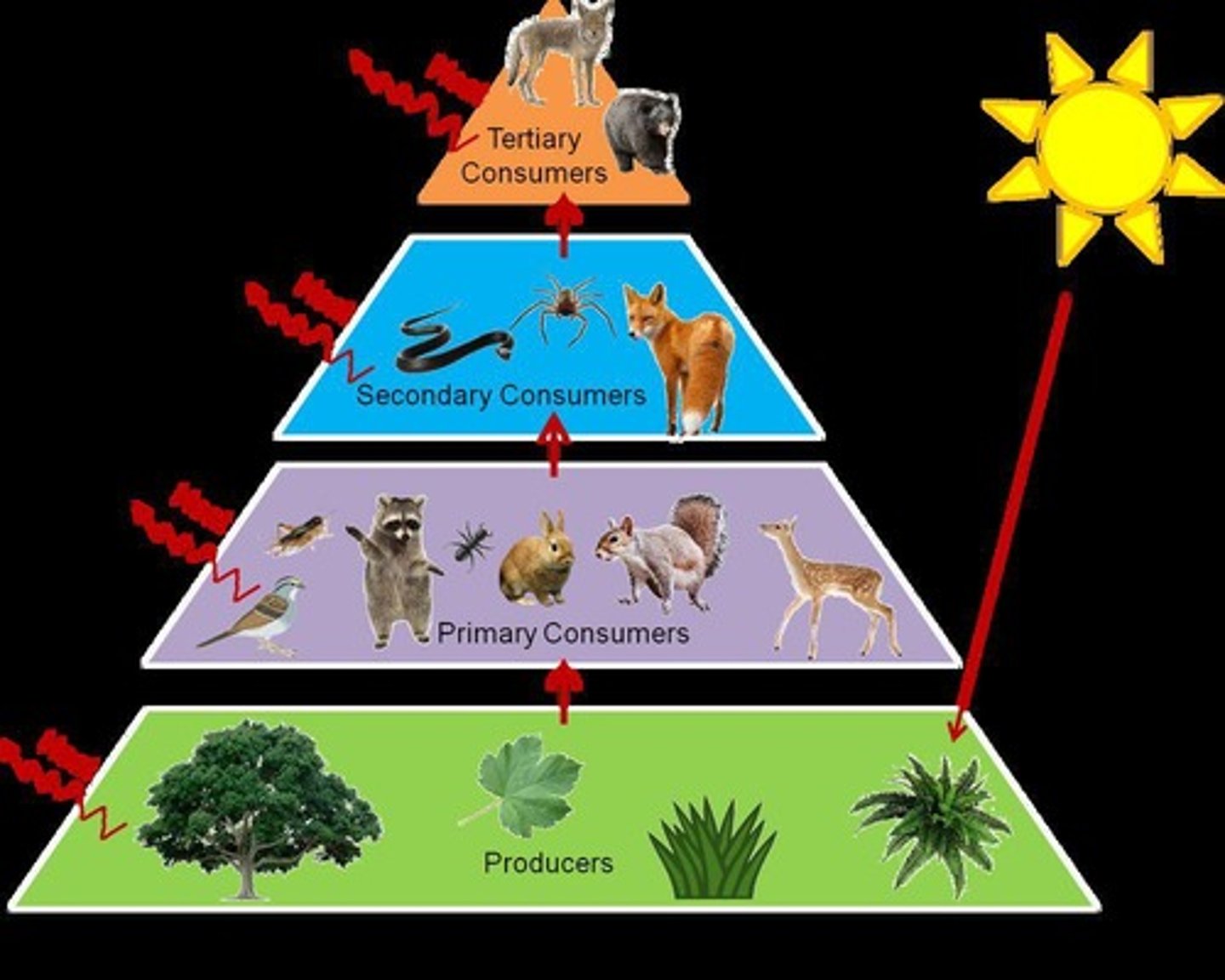
Producers
Autotrophs that create their own food.
Consumers
Heterotrophs that eat producers for energy.
Primary consumers
Herbivores that eat plants.
Secondary consumers
Carnivores that eat herbivores.
Omnivores
Organisms that eat both plants and animals.
Decomposers
Break down dead matter, recycling nutrients.
Food chain
Linear sequence showing energy transfer between organisms.
Food web
Complex network of interconnected food chains.
Energy flow
Energy moves unidirectionally from sun to consumers.
Carbon-Dioxide-Oxygen Cycle
Cycle of gas exchange between plants and animals.
Major land biomes
Distinct ecological areas like tundra and rainforest.
Tundra
Cold biome with permafrost and low vegetation.
Temperate Deciduous Forest
Moderate climate with trees that shed leaves.
Tropical Rainforest
High biodiversity, warm climate, and heavy rainfall.
Desert
Hot, dry biome with drought-resistant plants.
Water cycle
Process of evaporation, condensation, precipitation, transpiration.
Nitrogen cycle
Conversion of nitrogen gas into usable nitrates.
Succession
Gradual ecosystem development to a stable community.
Pioneer species
First organisms to colonize barren areas.
Climax community
Mature, stable ecosystem at succession's end.
Primary succession
Occurs on previously uninhabited surfaces like rock.
Secondary succession
Reestablishment in disrupted areas with existing soil.
Non-renewable resources
Resources that cannot be quickly replaced.
Renewable resources
Resources that can be replenished naturally.
Greenhouse effect
Heat trapping by Earth's atmosphere.
Global warming
Increase in Earth's temperature due to CO2.
Genetics
Study of heredity and trait variation.
Trait
Inherited characteristic of an organism.
Gene
DNA segment determining specific traits.
DNA
Molecule containing genetic information in cells.
Nucleotide
Building block of DNA, includes base and sugar.
Adenine
Nitrogen base pairing with thymine in DNA.
Guanine
Nitrogen base pairing with cytosine in DNA.
DNA replication
Process of DNA self-duplication.
RNA
Single-stranded nucleic acid involved in protein synthesis.
mRNA
Carries genetic information from DNA to ribosomes.
tRNA
Transfers amino acids during protein synthesis.
DNA transcription
Synthesis of mRNA from DNA in the nucleus.
DNA translation
Process of synthesizing proteins from mRNA.
Mendelian genetics
Study of inheritance patterns established by Mendel.
Alleles
Different forms of the same gene.
Law of Dominance
One allele is expressed over another in traits.
Law of Segregation
Alleles separate during meiosis for fertilization.
Probability
Likelihood of a specific genetic outcome.
Punnet Square
Chart showing possible gamete combinations.
Incomplete dominance
Heterozygous phenotype is a blend of traits.
Codominance
Both alleles are fully expressed in phenotype.
Linked genes
Genes inherited together due to proximity on chromosomes.
Sex-linked genes
Genes located on sex chromosomes, often X-linked.
Nondisjunction
Failure of chromosomes to separate properly during meiosis.
Aneuploidy
Abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell.
Trisomic
Condition with three copies of a chromosome.