Marketing Exam 2
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
92 Terms
Strategic Planning
A "Matching" Process between Internal and External
Internal: Organization's Goals & Capabilities
External: Marketing Opportunities
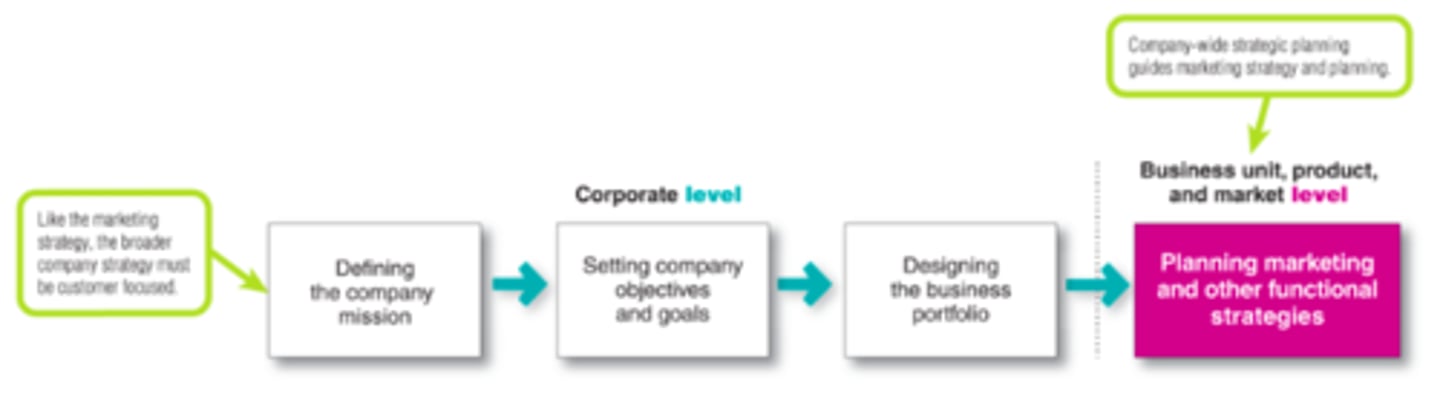
Steps in Strategic Planning
Marketing Process Model (5)
Mission Statement
A statement of the organization's purpose (not part of the marketing plan)
Take into account:
What is our business?
Who is the customer? What do they value?
What are our core competencies?
What should our business be?
Good Mission Statements Are
Market-oriented
Realistic
Specific
Motivating
Illustrative of distinctive competencies
What is our competitive advantage?
Mission statement leads to
Detailed supporting objectives for each level of management
Must be measurable
Designing the Business Portfolio (def, 3 objectives, alternate name)
A combination of businesses that has the potential to reach objectives.
Which businesses to enter?
Which to exit?
How much to invest?
"Businesses" may be called Strategic Business Units (SBUs), divisions, markets, product lines, etc.
BCG Growth Share Matrix

Some Criticisms of the BCG Matrix
Limited number of variables used
Ignores interrelationships between businesses. (e.g., some Disney movies are dogs)
The placement of a business in the matrix is highly dependent on definition of market
Product/Market Expansion Grid
*Used to identify growth opportunities
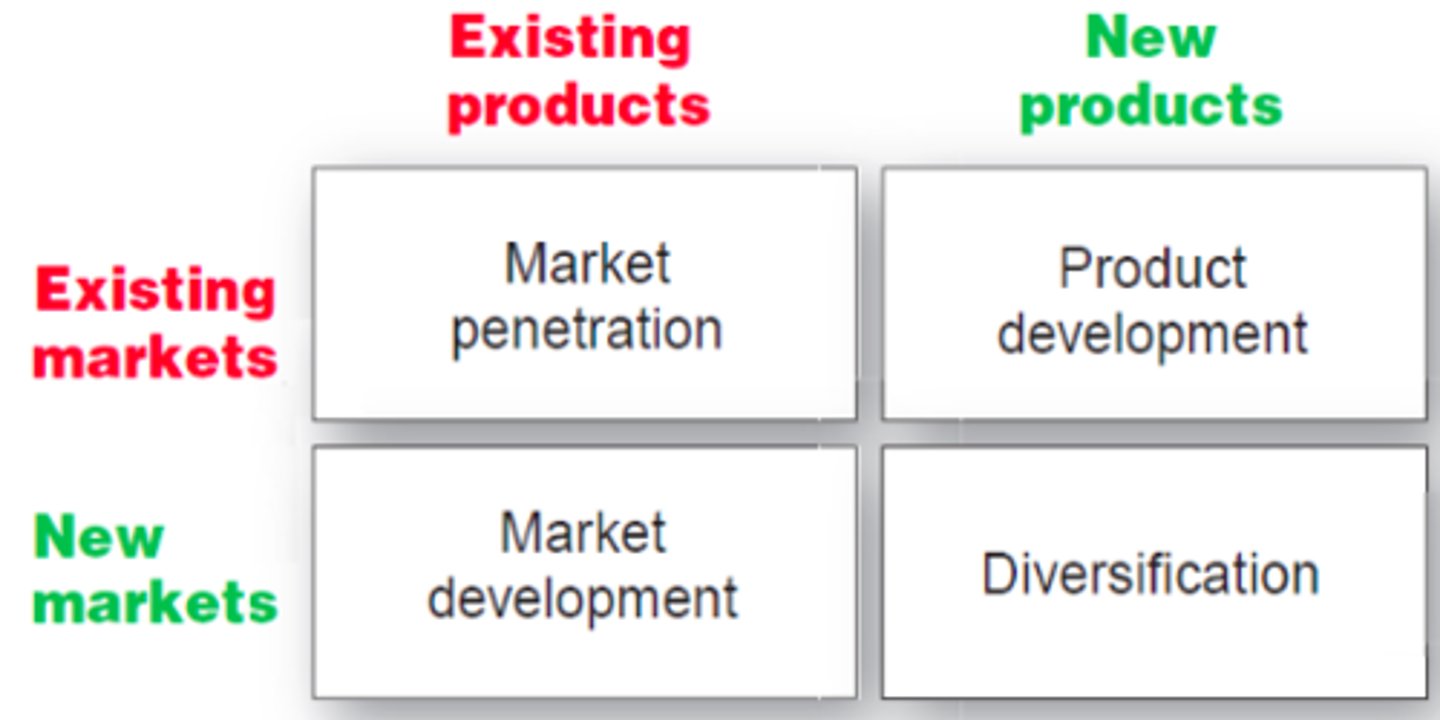
Market Penetration
Strategy: to increase sales to current customers without changing the products being sold
Can be achieved by:
Price
Place
Promotion
ex: Coupon to come back to a coffee company
Market Development
Strategy: identify and develop new markets (geographic or demographic) for current products
Product Development
Strategy: offering modified or new products to current markets.
Diversification
Strategy: start up or buy businesses outside of current products and markets.
Strategy Formulation Steps
1) What do we know?
2) What do we want to accomplish?
3 & 4) How will we do it?
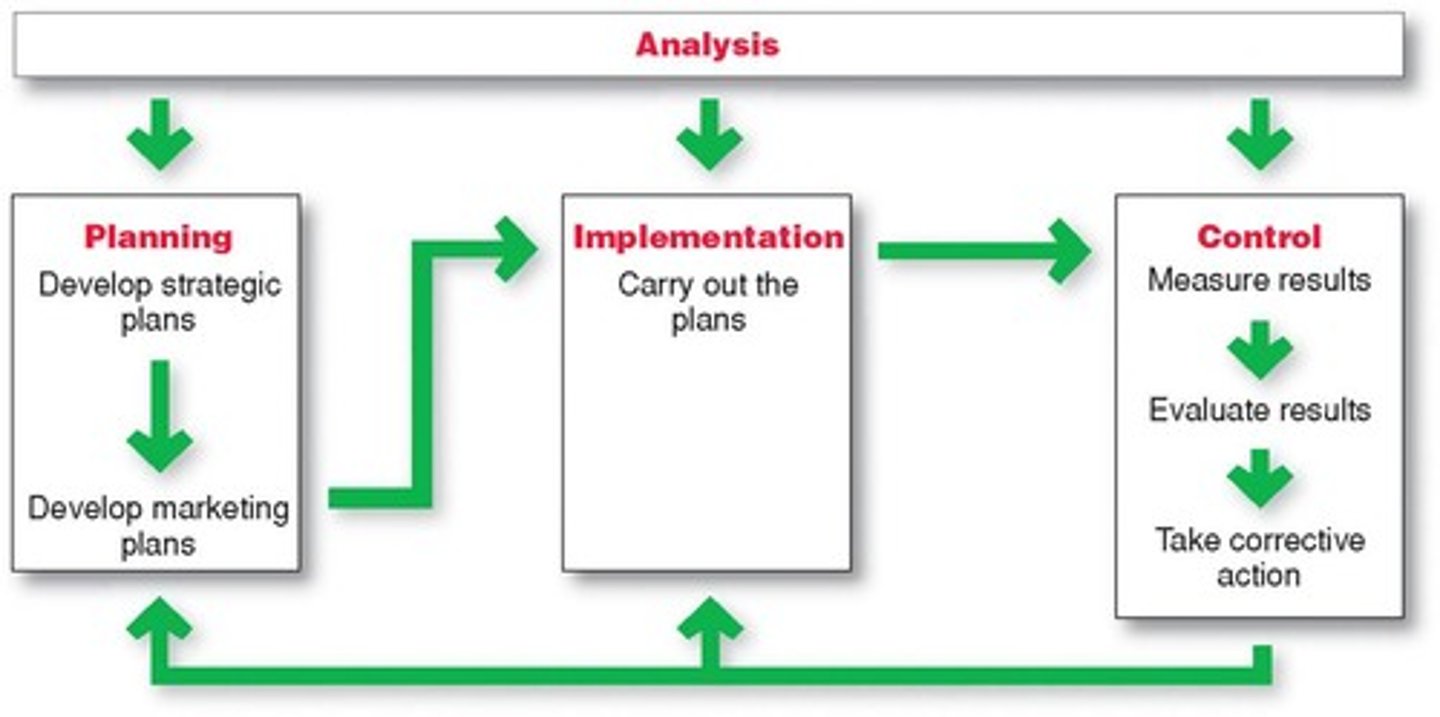
Marketing Management
Marketing Plan (8 steps)
1. Executive Summary
2. Current Marketing Situation
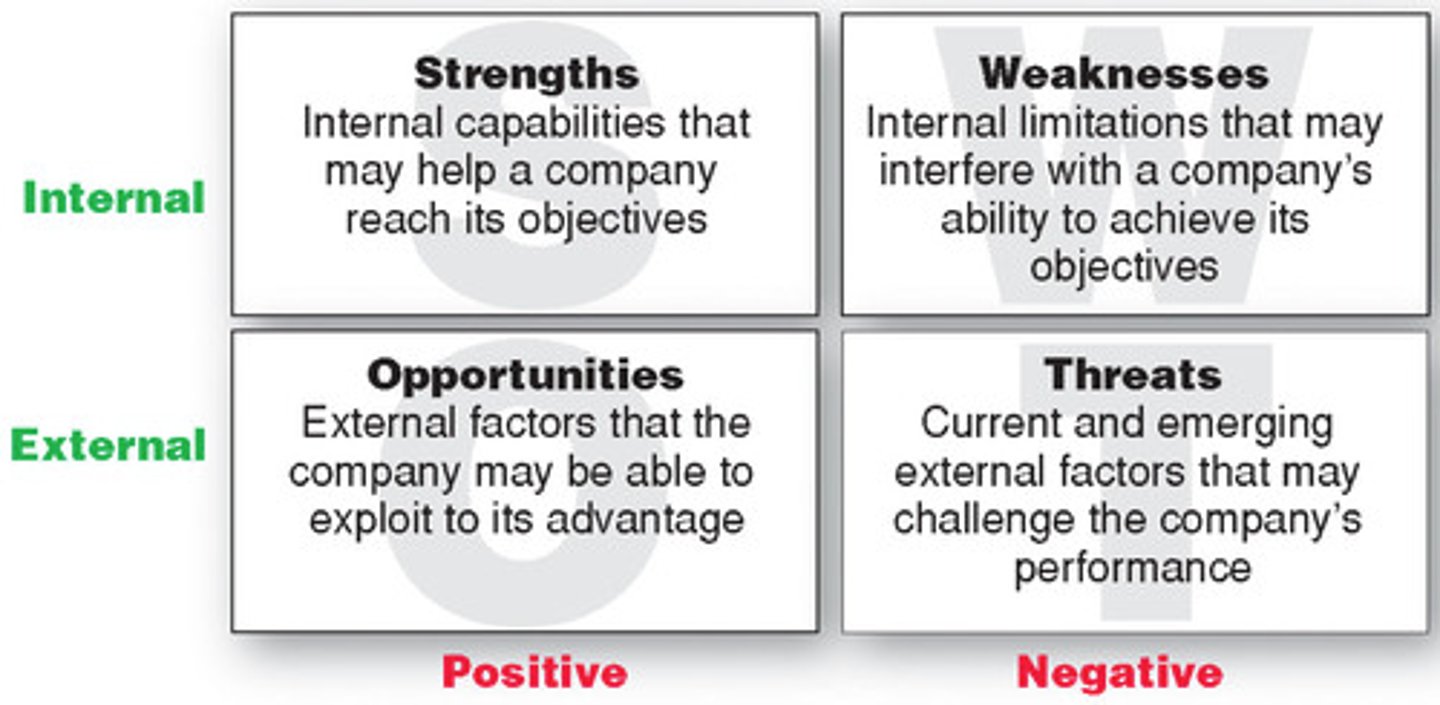
3. SWOT Analysis
4. Objectives
5. Marketing Strategy:
a. Segmentation, Targeting & Positioning (STP)
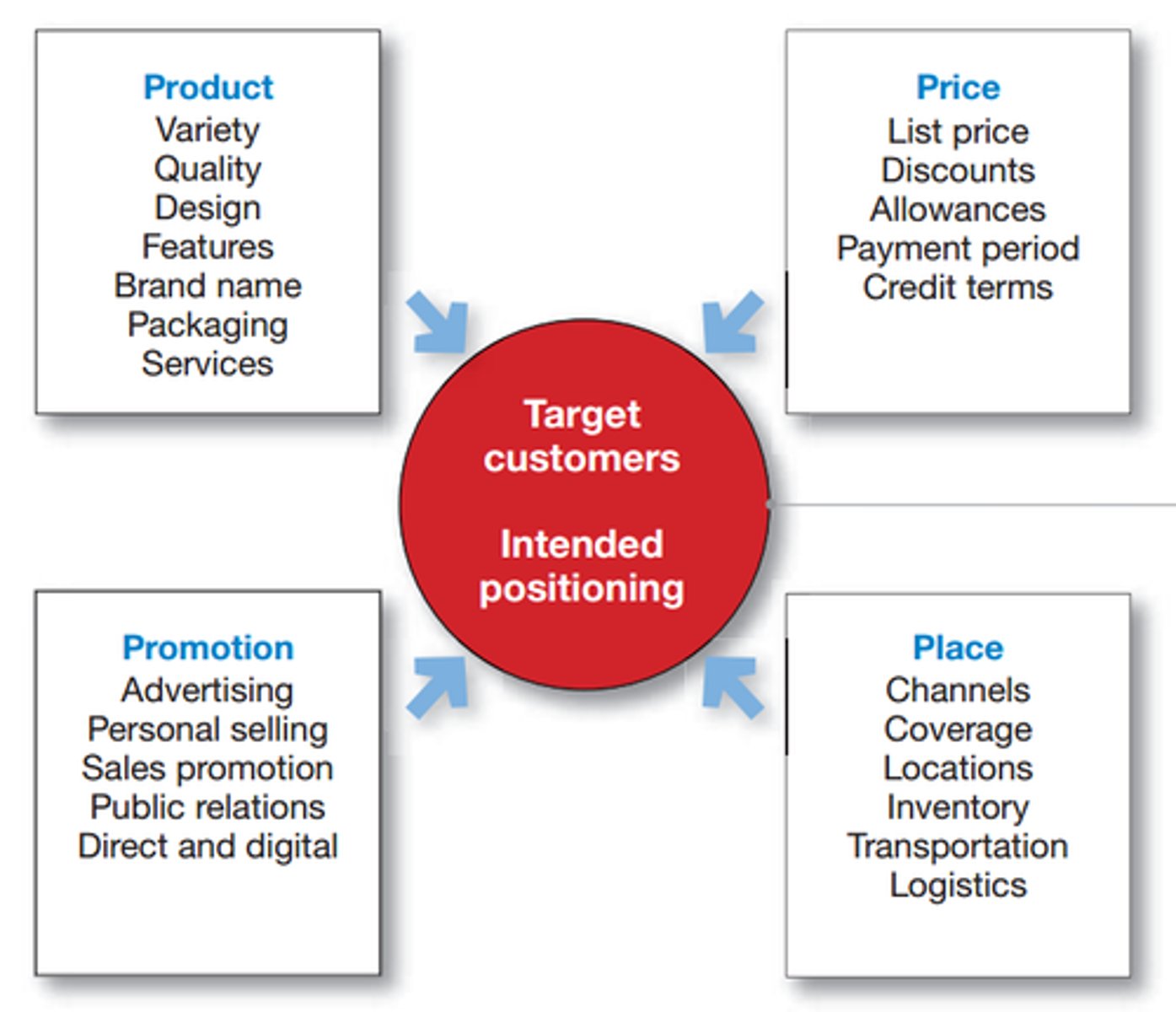
b. The 4 Ps of the Marketing Mix
6. Action Programs
7. Budgets
8. Controls
SWOT Analysis
The Four Ps of Marketing
Marketing Implementation
Successful implementation depends upon (5)
The execution of a plan is usually the hardest part.
Successful implementation depends upon:
Company culture
Employees' shared beliefs and values
Organizational structure
Reward systems
Implementation often ends up being more about personal relationships and/or luck than plans took into account.
Marketing Control
Evaluate the results of marketing strategies and plans
- Set marketing goals
- Measure actual vs. expected performance on goals
- Take corrective action to close goals between goals and performance
Steps in STP
Segmentation
Targeting
Positioning

Segmentation
Dividing a market into smaller groups that:
- Have distinct needs, characteristics, or behaviors
- Respond similarly to marketing efforts, and therefore,
- Might require their own products and marketing (4 Ps)
If you’re segmenting and you want segmentation to be differentiable, you have to distinguish the markets from each other
Types of Segmentation (5)
Geographic
Demographic
Psychographic
Behavioral
Intermarket
Geographic Segmentation
Dividing a market into different geographic units (e.g., country, country region, city size)
McDonald’s in different countries has different products
McDonald’s in Germany has beer
McDonald’s in New England has lobster rolls
Demographic Segmentation
Dividing a market based on demographic variables (e.g., age, gender, family size, family life cycle, race, generation)
Easier to measure than most other types of variables
Psychographic Segmentation
Dividing the market based on:
Social class
Ex: upper, middle, working class, lower classes
Lifestyle
Ex: Hollister - California, high school/college, surfer look
Personality
Ex: luxury travelers
Nike: everyone’s an athlete
Under Armour: fierce and intense
Adidas: creative
Behavioral Segmentation
Based on behaviors such as:
Benefits sought
Usage occasion
User status
Usage rate
Loyalty status
Intermarket Segmentation
Segments of consumers who have similar needs and buying behavior even though they are located in different countries
consumers use our products the same way, so we don’t have to change our product
Requirements for Effective Segmentation
Measurable
- can be identified and measured
Accesible
- can be reached and served
Substantial
- large and profitable enough
Differentiable
- separate from other segments
Actionable
- can be marketed to by our company
Targeting
Choosing the segment that is most attractive to your organization
companies selecting a specific age group to pursue
Evaluating Market Segments
Internal
Does the segment fit with our objectives and resources?
External
How big is the segment? What is its growth potential?
What is the competitive climate like? Are there lots of substitute products?
How much power do suppliers and customers hold?
Target Marketing Strategies
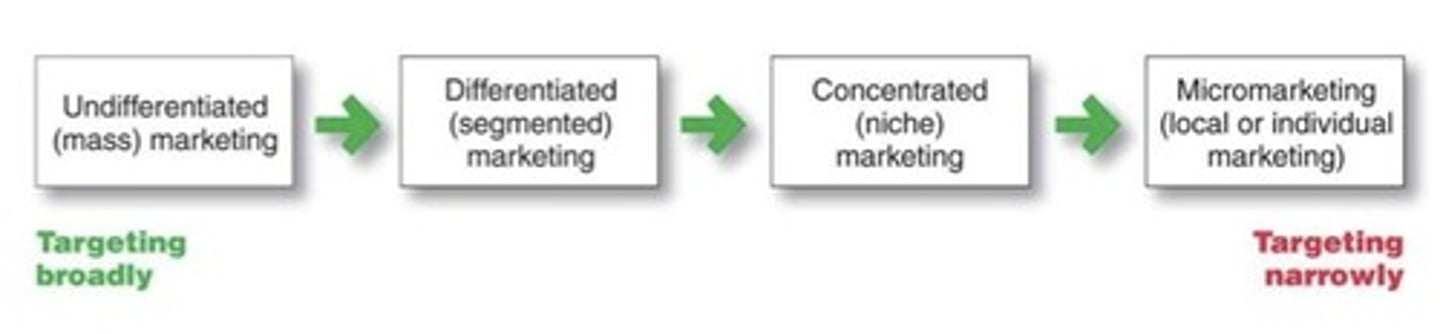
Differentiated (Segmented) Marketing
Targets several market segments and designs separate offers for each
Concentrated (Niche) Marketing
Targets a large share of one or a few small segments or niches
TetraMin fish food - main go-to for fish food
Southwest Airlines - used to be specifically in the Southwest
Etsy - someone can sell their crocheted llamas and be THE crochet llama seller
Coca-Cola has so many different flavors, which goes after a small niche
Micromarketing
Tailoring products and marketing programs to suit the tastes of specific locales and/or individuals.
- Local Marketing
- Individual Marketing
ex: making your own pizza, custom products
Individual Marketing
a.k.a. Markets-of-One Marketing or One-to-One Marketing
Main tool: mass customization
Positioning
The key concept to be communicated to the target consumer
The place the product occupies in the consumer's mind relative to competing products
the stage companies focus on the messaging
"The Battle for the Mind"
"Products are created in a factory, but brands are created in the mind."
Walter Landor
Competitive Advantage
Differentiate your brand based on:
Product
Services
Channels
People
Image
Two Types of Differentiation
Vertical Differentiation:
- One product is clearly better
- 5 star hotel vs 1 star hotel
Horizontal Differentiation:
- "Better" is a matter of opinion
- Nike vs Adidas
Positioning Statement
A statement that summarizes company or brand positioning
Slogans are based on positioning
To (target segment) who (need) (brand) is (concept) that (point-of-difference).
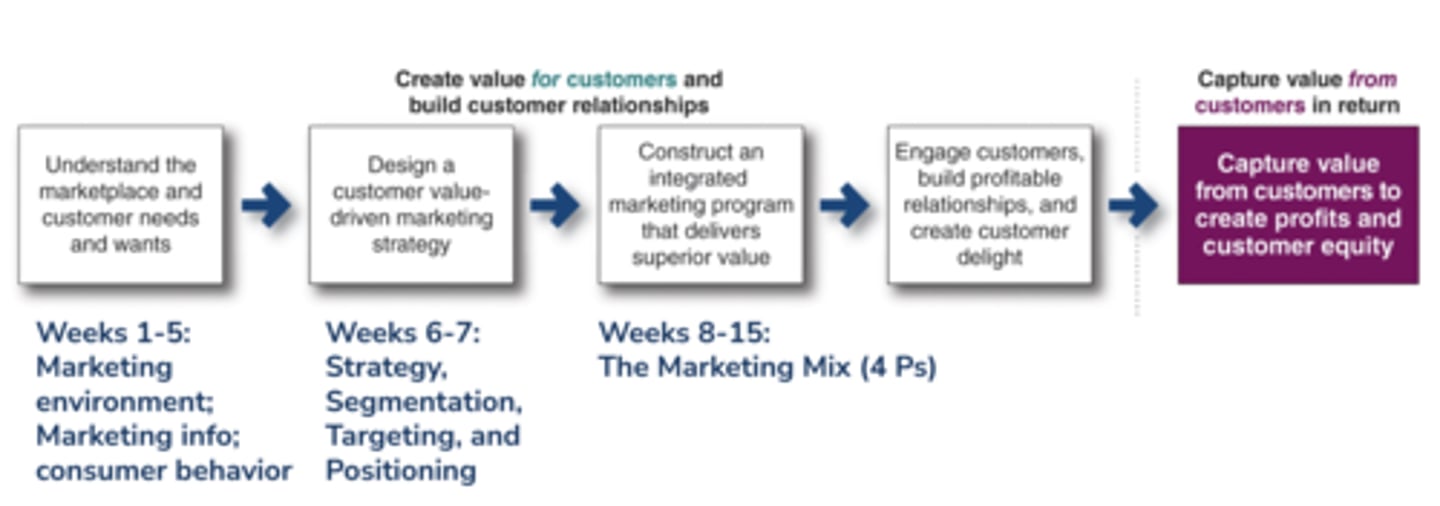
Marketing Process Model (3)
Core Customer Value
Actual Product
- Brand name, Quality, Features, Packaging
Augmented Product
- Delivery, Product support, Warranty, After-sale service
Product decisions are driven by:
Customer Behavior
Marketing Information
Microenvironment
Macroenvironment
Strategy
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Types of Consumer Products
Convenience
Shopping
Specialty
Unsought
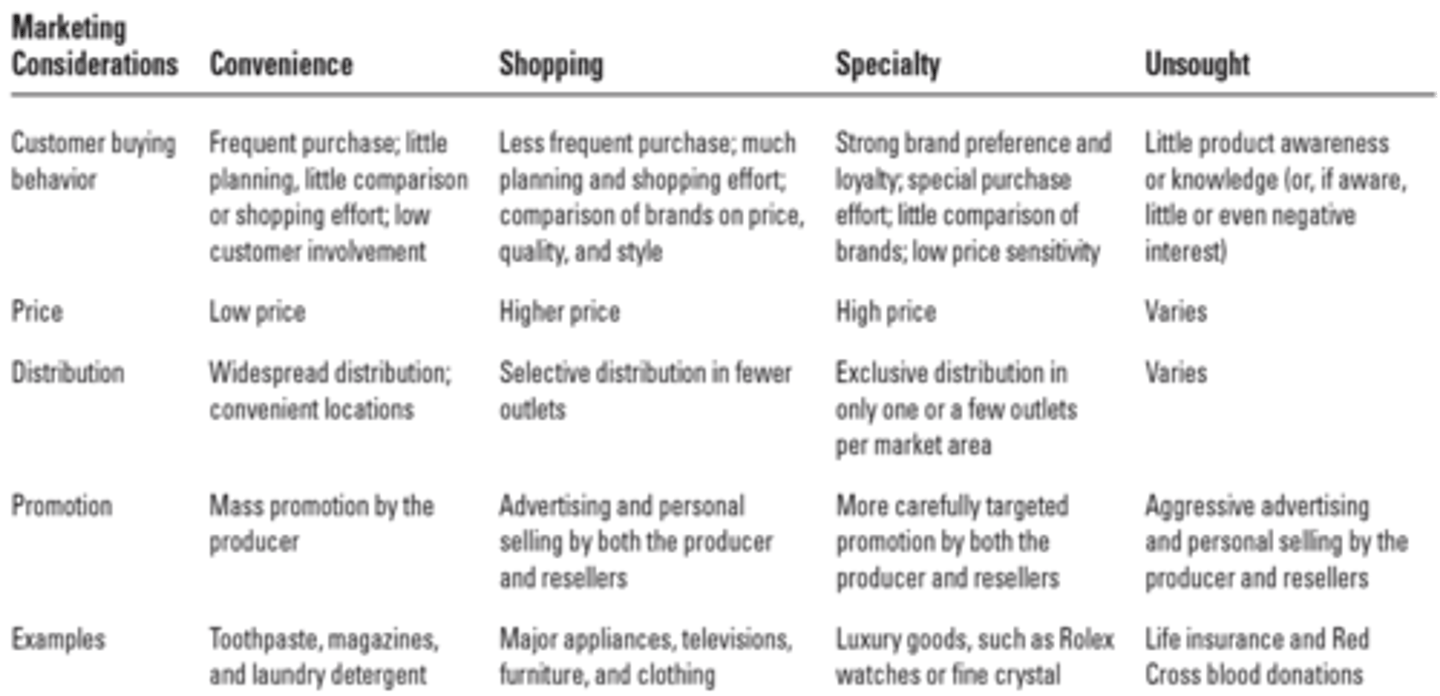
Convenience Consumer Products
Frequent purchase, little planning, little comparison/effort
Low price
Widespread distribution; convenient locations
Mass promotion by the producer
Ex. Toothpaste, paper towels, detergent, toilet paper, etc
Consumer Products - Shopping
Less frequent purchase; much planning and shopping effort, comparison of brand price, quality, and style
Higher price
Selective distribution in fewer outlets
Advertising and personal selling by both producer and resellers
Ex. Airpods, Beats Headphones, North Face jackets, Major appliances, tv, furniture, clothing
Specialty Consumer Products
Strong brand preference and loyalty; special purchase effort; little comparison of brands; low price sensitivity
High price
Exclusive distribution in only one or a few outlets per market area
More carefully targeted promotion by both the producer and resellers
don’t have wide distribution strategies
Ex. Luxury goods, like Rolex, Bentley, diamond jewelry stuff over $1000
Unsought Consumer Products
Little product awareness or knowledge (or, if aware, little or even negative interest)
Price varies
Distribution varies
Aggressive advertising and personal selling by the producer and resellers
Ex. Life insurance, Red Cross blood donations, Free food, butter spreader, dictionaries
Other "Products"
Industrial products
Organizations: For-profit (businesses) and nonprofit (schools, churches, etc.)
People ("Persons"): Politicians, entertainers, pro athletes, doctors, lawyers, etc.
Places: Tourism, country-of-origin, immigration, etc.
Ideas (social marketing): Public health campaigns, environmental campaigns, family planning, human rights, etc.
Performance vs Conformance Quality
Performance Quality
- how well it performs its intended function and meets customer expectations (ex: “Lexus is so well-built”)
Conformance Quality
- the degree to which it meets established specifications and requirements (ex: “Honda is reliable”)
Levels of Product Decisions
Individual product decisions
Product line decisions
Product mix decisions
Individual Product Decisions
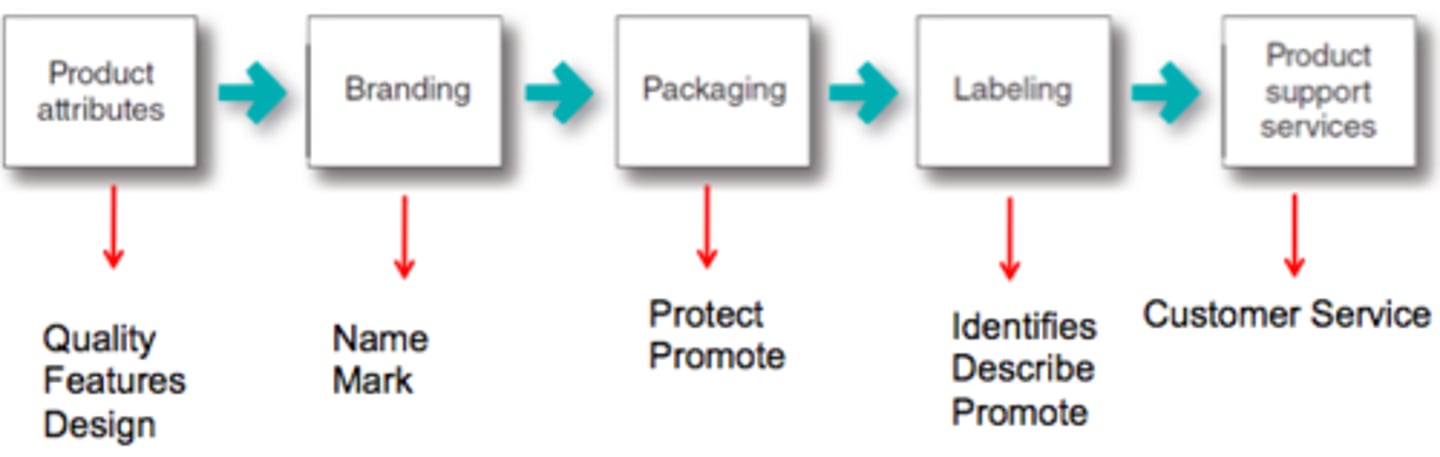
Labeling
Identifies the product or brand
Supports the brand's positioning
Adds personality to the brand
Product Line Decisions
The number of items in a product line
Apple has iphone, airpods, macbook, ipad product lines
Adjust length by:
Stretching
Downward
Apple releasing a $200 phone for kids with 1 hr battery life
Upward
Apple releasing a $3000 phone with unlimited storage that will never break
Both directions
Filling
iPhone coming in two different sizes, colors, and different amounts of storage
Product Mix
All of the product lines and items that a particular seller offers
Product mix dimensions:
Width - the number of different product lines carried
iPhone, AirPods, MacBook, iPad: 4 product lines for Apple
Length - the number of items in a line
Depth - The number of versions offered of a product in a line
We add to depth by filling
Consistency - how closely related various lines are
Product Line & Mix Example
Product Mix: Smeal College of Business (all of it)
Product Lines: Smeal ETM classes, Smeal majors, Smeal major-specific classes (specific lines as part of the product mix)
What is a brand?
A marker of identification for a product
A promise to the customer
Brand identity and brand consistency lead to feelings of trust
Brand Equity
The positive effect that knowing the brand name has on customer response to the product.
High brand equity provides:
Greater awareness and loyalty
Basis for strong, profitable customer relationships
Willingness to buy over competitors and/or willingness to pay a premium for the brand
Brand Positioning
Based on:
- Product attributes
- Benefits
- Beliefs and values (ex: Dove)
Brand Name Selection
Desirable qualities:
- Suggests product's benefits and qualities
- Easy to pronounce, recognize, and remember
- Distinctive
- Extendable, not limited to one particular product
- Translates easily into foreign languages
- Capable of being registered and legally protected
- Rhyme
- Alliteration
- Repetition
Brand Name Protection
Genericization voids trademark’s legal protection
Genericization - when a brand name becomes the common, generic term for a type of product
Must include the registered trademark symbol
Some include the word “brand” for added protection
Examples: Tabasco, Jell-O, Band-Aid
The Law of Shape (Ries and Ries*)
The ideal shape for a logo is Horizontal
Brand Development Strategies
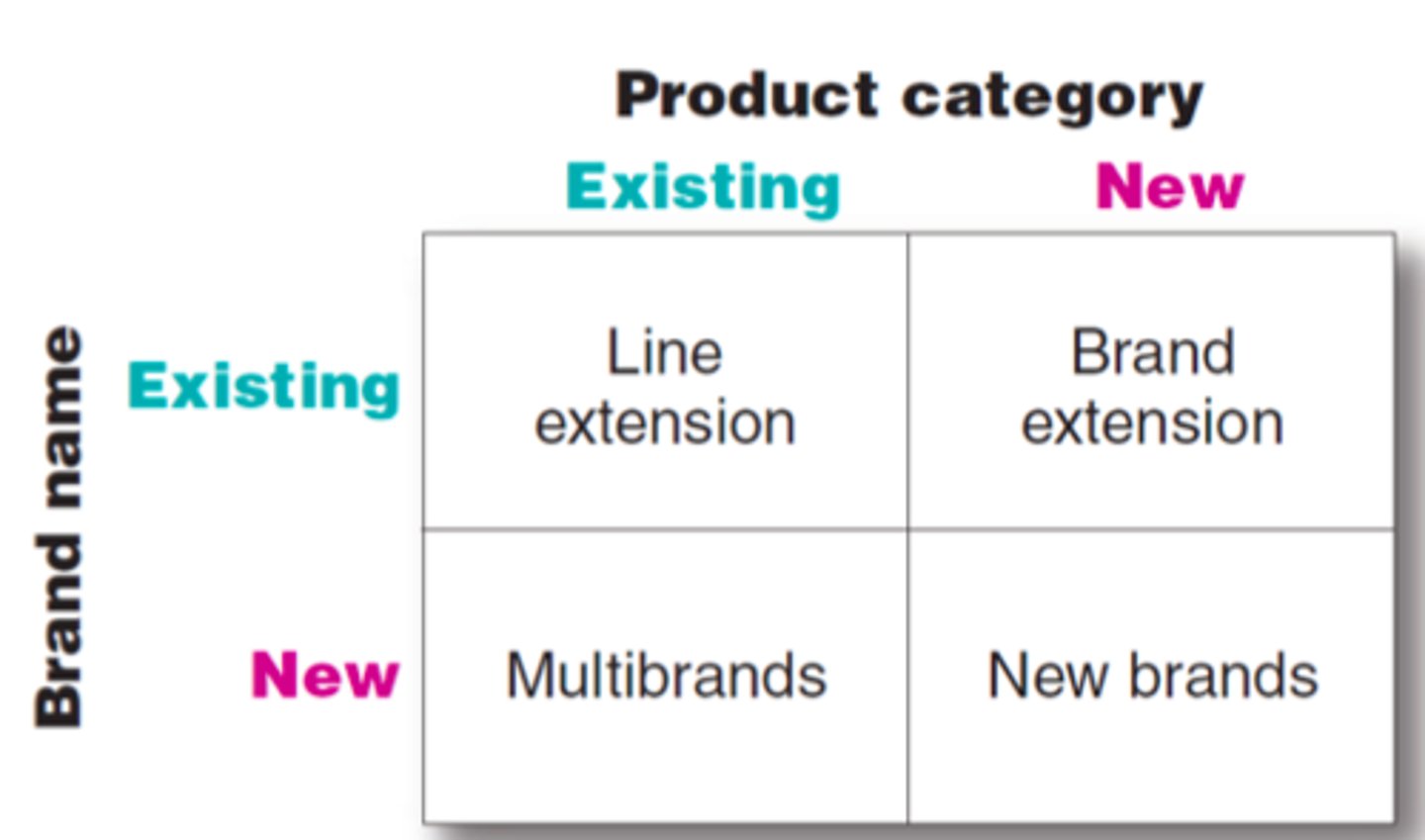
Line Extension
Introduction of additional items within the current product category under the same brand name (e.g., new flavors, forms, colors, ingredients, or package sizes)
- Ex. Bud Light Lime, Cherry Coke, Golden Oreo
Cannibalization
Killing the sales of the original product after a new line extension
(Avoid Cannibalization)
Brand Extension
Using a successful brand name to launch a product in a new category
Apple using its successful brand name to launch watches
Mr Clean creates a car wash
There is instant credibility when a successful brand name creates new products
Customers accept the products faster
Multibranding
Multiple brands by the same company in the same product category
Yum! Brands owns A&W, KFC, Long John Silver’s, Pizza Hut, Taco Bell
Pepsi owns Pepsi, Mountain Dew, Mug, Sierra Mist
New Brands
Used when existing brand names are either unsuitable for brand extension or the company doesn't want to dilute them
The Law of the Word (Ries and Ries*)
a brand should aim to own a single, powerful word in the consumer's mind.
ex: Mercedes-Benz may own the word "prestige" in the minds of consumers (22 Immutable Laws of Branding)
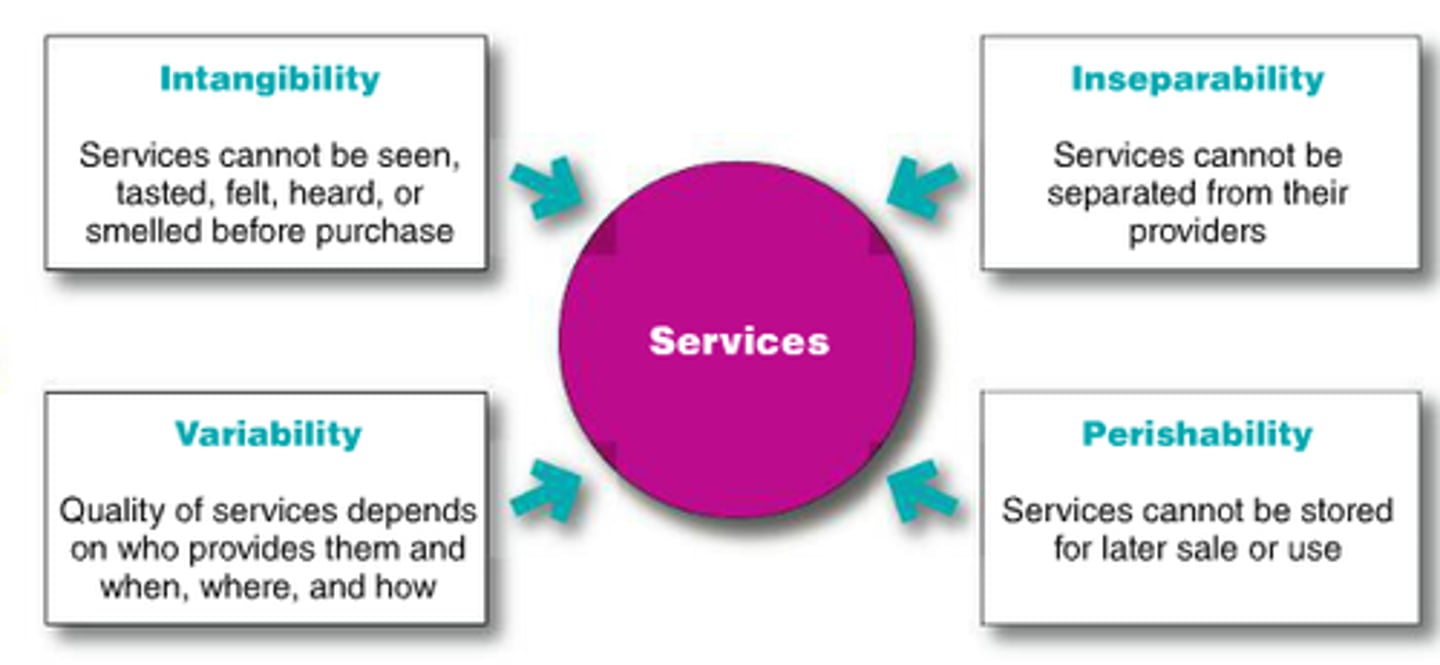
Four Service Characteristics
New Product Development, (Why new products?)
New products are crucial for the health of the enterprise
- Rejuvenate
- Grow
Tied to higher stock values and internal motivation for employees
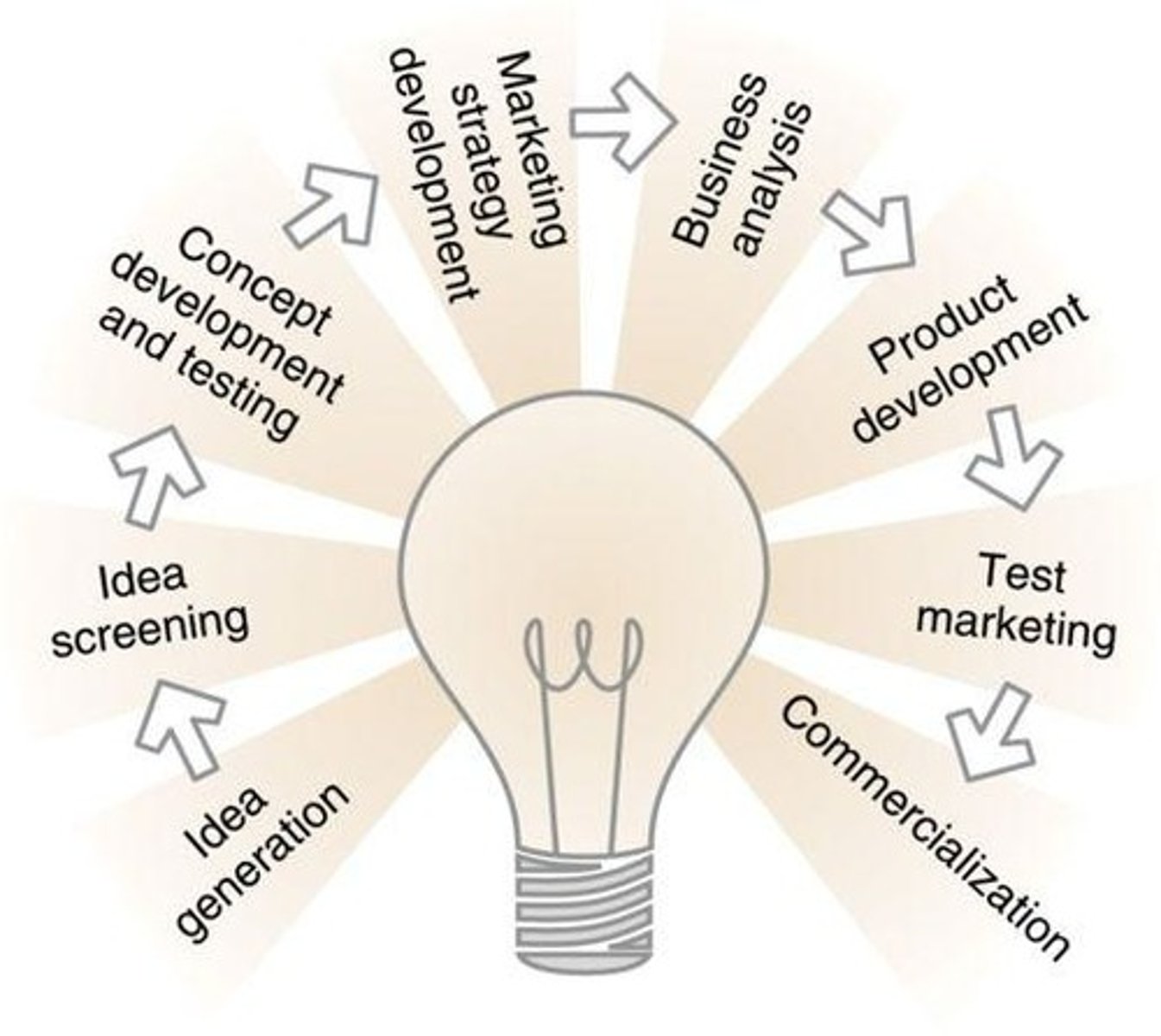
NPD Process (9)
Idea generation
Idea Screening
Concept Development
Concept Testing
Marketing Strategy Development
Business Analysis
Product Development
Test Marketing
Commercialization
*Having skill sets for one point in the process does not mean you're also good at the others.
Idea Generation
The systematic search for new product ideas.
Internal sources:
Company employees at all levels
External sources:
Customers, competitors, distributors, suppliers, outsourcing partners
Idea Screening
Screening process to reduce # of ideas by spotting good ones and dropping poor ones.
Describe product, target market, and competition
Estimate market size, product price, development time and costs, manufacturing costs, and rate of return
Evaluate against a set of company criteria for new products
Concept Development
Translate your product idea into a detailed concept stated in meaningful consumer terms (i.e., what will the consumer get out of this product?)
E.g., A (descriptor of product) that provides (benefit/feelings/results)
E.g., A convenience restaurant that provides high-quality, fresh, made-to-order food
Sheetz changed their logo because they were adding decent food to their array of products
Concept Testing
Do this with a group of target consumers to find out level of appeal
In doing so, describe the product and elicit responses to the product
Sample Testing:
Do you understand the concept behind the product?
Is this concept believable?
What are the major benefits of this product?
How does it compare with other similar products?
What improvements might you suggest?
What factors might affect your decision to buy this product?
Marketing Strategy Development
An initial marketing strategy is designed for the new product, consisting of:
Target market and initial objectives
Target market, planned product positioning, and goals for sales, market share, and profit for the first few years. Usually first-year market is higher than other years
Launch tactics
Price, distribution, and marketing budget for the first year
Long-term objectives
Long-run sales and profit goals, marketing mix (4Ps) to be used
Business Analysis
Does the idea make business sense?
Involves a review of the sales, costs, and profit projections to assess fit with company objectives
Assess risk under various scenarios
If results are positive, project moves to the product development phase
Product Development
Develop from concept into actual product ("_").
Investment increases considerably: moving from idea into realm of reality.
Product testing often happens alongside development.
Test Marketing
Product & marketing program introduced in a limited setting
Can be expensive and time consuming, and shows your plans to competitors
New Product Failures
- Only 10% of new consumer products are still on the market and profitable after 2 years.
- Less than 2% are considered "truly successful."
Failure is due to:
- Problems at any stage of the marketing process
Commercialization
LAUNCH!!
Must decide when and where to initially introduce the product
Ex: Sheetz Card
Must develop a market rollout plan
Where to go next?
Product Life Cycle (PLC)
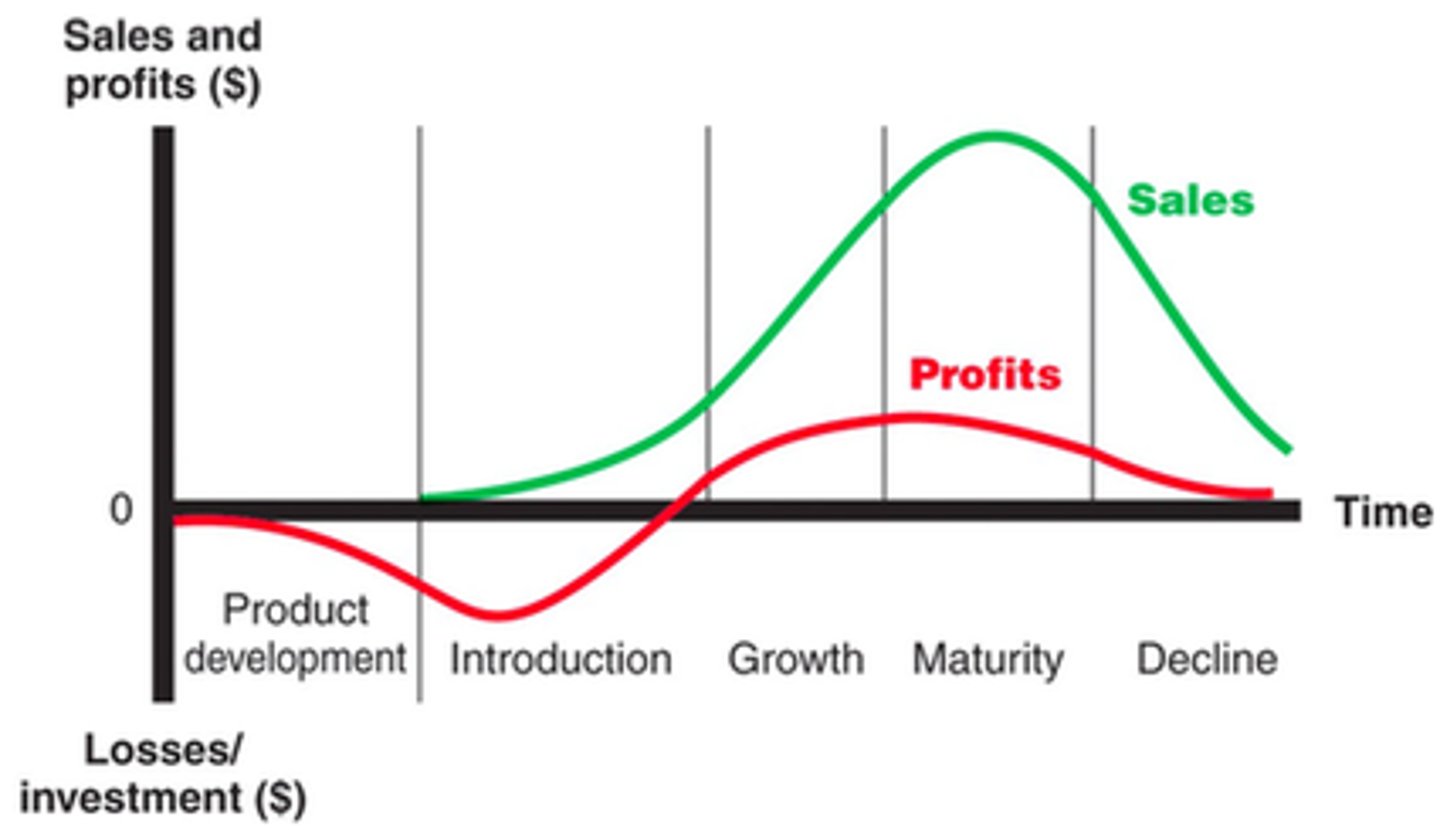
Introduction Stage
Product is first launched
Cost of informing & acquiring customers is high, and sales (as well as sales growth) are usually slow
Profits are usually negative
Objective: Create product awareness and trial
Growth Stage
If the product gains traction, sales start growing rapidly
Higher unit sales lead to lower average costs per unit sold, and profitability can be achieved
Objective: Maximize market share. The growth in sales will lead to a number of competitors entering the market, fighting over initial customers
Maturity Stage
Sales level off
Many people already have the product; some are re-buying or upgrading
Production costs are usually low, so those with high market share can still make good profits
Objective: Defend market share. Try to get customers to switch to your product
Ways to Grow during "Maturity"
Modify the Market
Target new segments OR increase usage among current customers
Modify the Product
Deliver an improved product to get new or repeat customers
Modify the rest of the Marketing Mix
Add services, cut prices, change distribution, change promotion
Decline Stage
Sales fall, as people do not need to buy the product anymore
Unit sales and prices fall; difficult to remain profitable despite low production costs
Some niche products may do well when competitors exit the market
Objective: Reduce expenses to stay profitable, milk the product and invest elsewhere. If able to, "restart" PLC, otherwise look for a way out on time
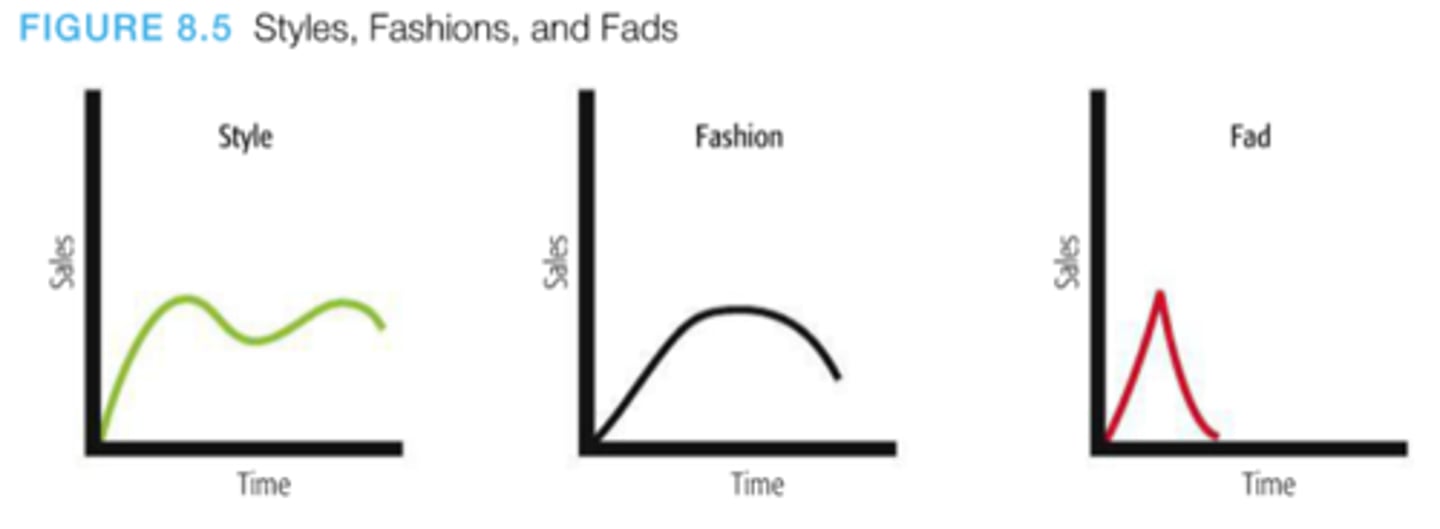
Styles, Fashions, Fads
Style is a basic but distinctive mode of expression (e.g., formalwear vs casualwear, country music, leather and denim jackets, a colonial house, hip-hop music)
Fashion is a popular style in a given field (e.g., Uggs, white Air Force 1s, Beats headphones, lululemon cross bags, big teased hair, Jay-Z, athleisure)
Fad is a fashion that enters quickly, is adopted quickly, and declines fast (e.g., pet rocks, silly bands, Webkinz, Gangnam Style, Rubik's Cube, fidget spinners, Pokémon Go, dab, Snapchat dog filter)
Practical Problems of the PLC Model
Reality is never as "clean" and clear as the PLC curve
It can be hard to even identify which stage of the PLC a product is really in
Hard to forecast the length of each stage of the PLC
Strategy is both a result and a cause of the PLC