Histology
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
116 Terms
bright-field microscope
light microscope
one we use
has obj lens and eye piece
electron microscope
has higher mag than bright field
Transmission EM (TEM)
shows internal structures
2d detailed
Scanning EM (SEM)
scans topography
3d surface of structures
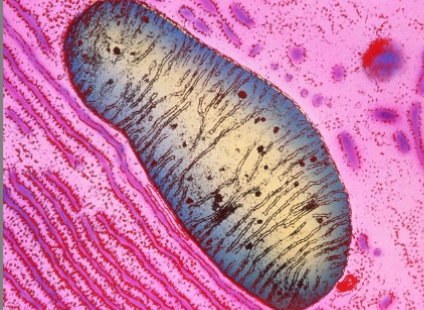
what kind of microscope is this image from
TEM

what kind of microscope is this image from
SEM
Atomic force microscope
similar to SEM but mobile
tip runs over structures, laser reflects light
Body Fluid compartments
Extracellular fluid 33%TBW
plasma 20%
interstitial fluid 80%
intracellular fluid 66% TBW
intracellular fluid
how to find total body water
0.6x body weight
Plasma membrane
function
protective barrier
regulation of transport in and out of cell
selectively permeable
features
amphipathic phospholipid bilayer
cholesterol
provides strength and rigidity →allows PM to be more fluid and not fall apart
integral proteins
peripheral proteins
glycoproteins
glycolipids
integral proteins
embedded in membrane
amphipathic
functions:
channels/pumps/carriers
receptors
linker / anchor
enzymes
structural proteins
link neighboring cells
peripheral proteins
only interact w heads
only on one side of membrane
glycoproteins + glycolipids
glycoproteins
oligosaccharides attached to integral proteins on extracellular surface
glycolipids
oligosaccharides attached to heads of membranes
function:
cell-cell identification
cell-cell signaling
attachments for intracellular interactions
Cytoplasm
fluid compartment of cell between nucleus and PM
contains membrane+ non-mem bound organelles + inclusions within cytoplasmic matrix
Cytoplasmic matrix:
water
inorganic ions
organic molecules
non-membranous organelles
cytoskeleton
centrosome
ribosome
membranous organelles
nucleus
Endoplasmic Reticulum
golgi apparatus
lysosomes
peroxisome
mitochondria
cytoskeleton
complex network of protein subunits that form internal framework of cell
helps w framework of cell and movement
3 types :
microtubules
microfilaments (actin filaments)
intermediate filaments
microtubules
features
non-branching, rigid, hollow tubes of proteins
rapidly assemble/dissasemble
originates in MTOC
main protein subunits
alpha -tubulin
beta-tubulin
uses GTP + Mg2+ to make dimer
dimers stack on top of each other to make tube
function
railway system for intracellular transport
maintain cell shape by resisting compression
move cells
move chromosomes during cell division
move organelles
examples
motile cilia/flagella
9 doublets + central pair
non-motile cilia
9 doublets
centriole
9 triplets
spindle fibers
cell division
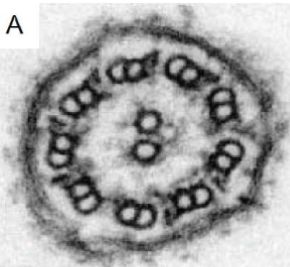
what is this and what is it made of
motile cilia / flagella
microtubules
9doublets and 1 central pair
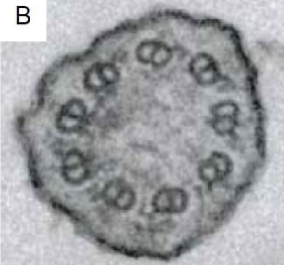
what is this and what is it made of
non-motile cilia
microtubules
9 doublets
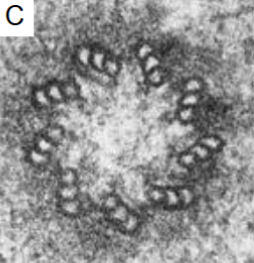
what is this and what is it made of
centriole
microtubules
9 triplets
Actin filaments (microfilaments)
features:
thin, short, flexible protein structures
in all cell types
rapidly assemble and disassemble
main protein subunits
G-actin (globular) proteins
spherical
free actin proteins in cell
F-actin (filamentous) proteins
actin protein polymerized into filaments
multiple G-actin come together to make dimer→trimer → multiple F-actin → actin filaments
require ATP + K+ + Mg2+
function
maintain cell shape by resisting tension
move cells
cell division
move organelles / cytoplasm
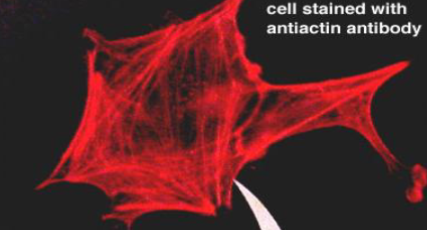
what is this made of
Actin filaments
Intermediate filaments
features
tough insoluble, rope-like protein structures
fixed assembly
2 helical monomers coil → coiled-coil dimer → 2 coiled coil dimers twist → staggered tetramer
main protein subunits
class 1+2 = keratins
epithelial cells
mechanical strength
class 3= vimentin
class 4= neurofilaments
class 5= lamins
class 6= beaded filaments
functions
maintain cell shape by resisting tension
anchor nucleus and other organelles
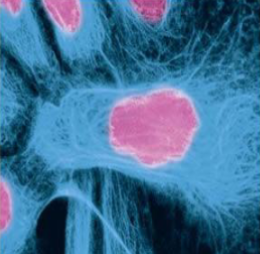
what makes up the blue part
actin/microfilaments
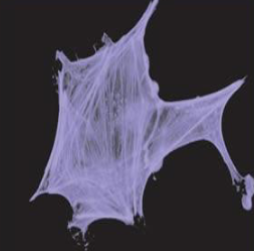
what is this made of
intermediate filaments
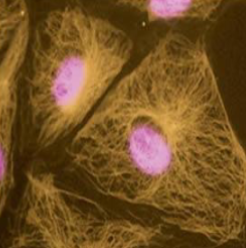
what are the gold structures made of
microtubules
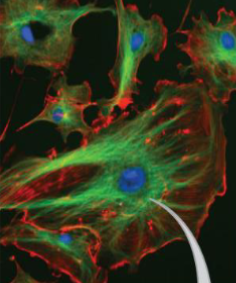
what are the red and green parts made of
green - microtubules
red - actin filaments
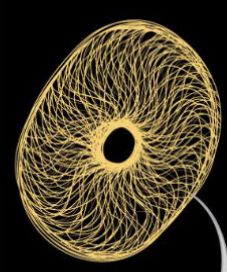
what is this made of
intermediate filaments
centrosome
made of
2 centrioles arranged at right angles
surrounded by pericentriolar material (PCM)
function
Microtubule organizing center
stabilize chromosomes during mitosis

what are these
a centrosome made of 2 centrioles
Ribosomes
features
2 subunits made from rRNA
60S= large subunit
40S= small subunit
80S= whole ribo
bound to enzymes
rRNA strands fold → subunits in nucleolus
located unbound in cytoplasm or bound to Rough ER
function
protein synthesis via translation of mRNA → amino acid sequences → proteins
what does S stand for in 60S
Svedburg unit - measures sedimentation rate
Endoplasmic Reticulum
membrane bound network of cisterns continuous w outer envelope of nuclear envelope
rough ER (granular)
has ribos
protein synthesis
new proteins fold in lumen of rER → package into vesicles → golgi
Smooth ER (agranular)
no ribos
detoxify toxins of GI tract
stores intracellular Ca2+
make lipids, phospholipids, steroids
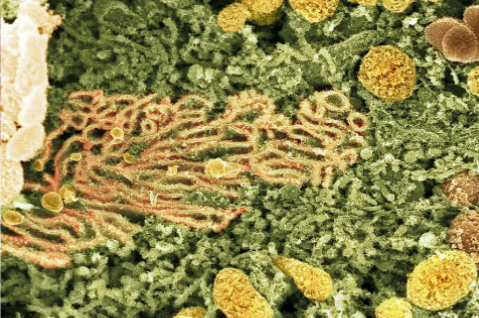
where is this from
smooth ER
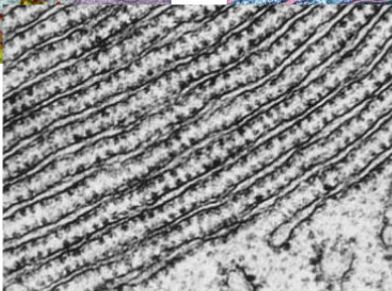
where is this from
Rough ER
golgi apparatus
network of membrane enclosed discs
2 main networks
cis golgi network (CGN)
toward ER
trans golgi network (TGN)
toward cell membrane
functions
post-translational modification of new proteins delivered from rER
proteins get modified to increase variability of function
package and delivery of proteins
types of transport from ER→ golgi
Anterograde Transport
new proteins from rER → CGN
COP II surrounds transport vesicles
Retrograde Transport
proteins transported from CGN → rER to be recycled
COP I
Destinations for modified proteins from TGN
secreted out of cell
clathrin coated secretory vesicles fuse w PM → exocytosis
integral / peripheral proteins
non-clathrin coated vesicles fuse w PM
lysosomal enzymes
clathrin-coated vesicles containing mannose-6-phosphate receptors fuse w lysosomes that have mannose-6-phosphate on them
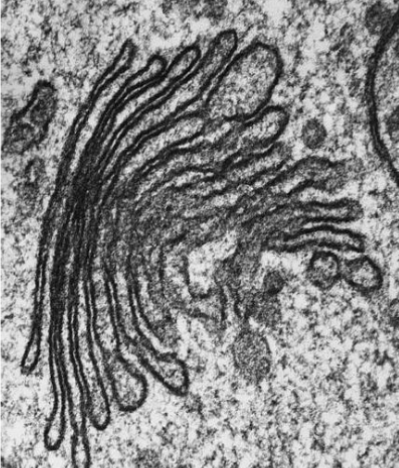
what is this
golgi apparatus
lysosomes
features
small-large
contains digestive enzymes
pH of lysosome = acidic (4.5-5)
functions
digest external structures
fusion w phagosomes → form phagolysosomes
autophagy
digest old or damaged organelles through direct fusion w organelles
apoptosis
programmed cell death
immune system tells lysosome if cell is beyond repair → enzymes in lysosome break down rest of cell
Peroxisome
features
looks sim to lysosome
contains enzymes for specialized metabolic activities
functions
alpha+beta oxidation
break down of long chain fatty acids → shorter fatty acids → eventual ATP prod
production of plasmlogen
detoxification
converts reactive oxygen species to hydrogen peroxide to o2 and water
ethanol metabolism
ethanol → acetaldehyde (toxic)→ acetic acid → acetyl CoA → water +CO2
Mitochondria
features
double membrane
outer-smooth
inner- folded into cristae+ surrounds matrix
intermembrane space
space between 2 membranes
intermatrix space
inside space
in all cells except RBC
functions
synthesis of ATP thru aerobic cellular respiration
Nucleus
contains genetic material
DNA
DNA strands wrap around histones
tightly coiled → chromatin
heterochromatin
highly condensed chromatin
euchromatin
loosely packed chromatin
protected by nuclear envelope
double membrane separated by perinuclear (cisternal) space
nuclear pores
nucleolus
non-membranous
surrounds transciptionally active DNA → codes for rRNA
function
primary site for ribo production and assembly
Functions of membrane transport
obtain nutrients
excrete waste
maintain electrochemical gradient
regulate osmolality +tonicity
types of membrane transport
passive — no energy req
simple diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
active — req energy
primary
secondary
bulk vesicular transport —- large quantities
exocytosis
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated endocytosis
diffusion
solutes will randomly move apart from each other
high conc→ low conc
net diffusion rate
measures suration at which the conc of sulutes reaches quilibrium across membrane
affected by
concentration gradient of solute
permeability of membrane
surface area of membrane
temp of solution
simple diffusion
features
small , non-polar , hydrophobic, lipid soluble solutes
gases, cholesterol, steroids
high→ low conc
across permeable membrane
no energy expenditure
rules
membrane must be permeable to solutes
concentration gradient for solutes must exist across membrane
facilitated diffusion
features
small, charged, polar solutes
ions, glucose, amino acids
high→ low conc
across permeable membrane
no energy expenditure
must be facilitated by channels (ions) or carriers (polar compounds)
rules
membrane must be permeable to solutes
depends on presence and activity of channels/carriers
conc gradient for solutes must exist across membrane
mechanism
solute attach to binding site on carrier → carrier changes conformation → release solute to other side
subject to
specificity
1 carrier only lets specific things through
competition
solutes want a spot to move
saturation
specific to carrier
limited number of binding site to polar compounds
osmosis
diffusion of water molecules across a permeable membrane without the expenditure of energy
water can slowly diffuse through cell membrane but mainly through aquaporins
directly influenced by the concentration of the solutes in solution
rules:
concentration gradient of solutes must exist
the membrane must be impermeable to solutes
membrane must be permeable to water
water moves from low to high concentration of solutes
net movement equalizes the dilution of the solutions → total volume of solution increases
hydrostatic pressure
pressure of water pushing against wall/membrane
think blood pressure on vessel
osmotic pressure
the minimum amount of pressure required to stope the net movement of solvent
high solute conc difference = high osmotic pressure
higher Osm = higher osmotic pressure
pulling of fluid in
the more water wants to come in → higher osmotic pressure
tonicity
compares osm of extracellular environment to the osm of the intracellular environment
isotonic
osmolality is equal
water moves in and out equally
ideal environment
hypotonic
Osm of the extracellular environment is less than that of the intracellular environment
water moves into cell→ can cause cell to lyse
hypertonic
osm of extracellular environment is greater than that of the intracellular environment
water goes out → can cause cell to shrivel/crenate
Primary Active transport
movement of ions/ polar compounds across a permeable membrane from an area of low solute con → high solute conc using carrier proteins with the expenditure of energy (ATP)
carrier protein = enzyme (ATPase) to hydrolyze ATP → ADP+Pi
the energy released by breaking ATP used to drive movement of solutes against conc gradient
Na+/ K+ ATPase
ATPase open to inside and 3 Na+ bind to pump
the binding of the Na+ promotes hydrolysis of ATP → ADP+Pi
this phosphorylated the pump
phosphorylation causes pump to change shape and releases Na+ to outside
2 K+ from outside binds
K+ binding → release of phosphate → returns pump to og position (inside open)
ATP attaches and releases K+ and repeat
in all living cells in our bodies
helps maintain electrochemical gradient for action potentials
since 3 Na+ out and 2+ in makes the inside more neg
Secondary Active transport
movement of ions/ polar compounds across a permeable membrane from an area of low solute concentration to an area of high conc using carrier proteins, without direct energy expenditure
powered by conc gradient created by Na/K ATPase with Na more on the outside
use diffusion energy to move other solutes against their gradients
carrier protein act as co-transporter (symport/antiport)
Bulk (vesicular transport
movement of large or numerous particles into or out of cell using transport vesicles
exocytosis - out of cell
endocytosis - into cell
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor-mediated endocytosis
Exocytosis
vesicle has a V-SNARE and migrates to meet the PM that has a T-SNARE
V-SNARE and T-SNARE twist
pore opens
contents secreted to outside of cell
Phagocytosis
cell -eating
only certain cells like WBC can do this
single large particle being eaten
microbe adheres to phagocyte
phagocyte forms pseudopods that engulf particle
form a phagocytic vesicle containing microbe = phagosome
eventually fuses w lysosome to make phagolysosome
Pinocytosis
cell drinking
large amount of non-specific solutes
PM invaginates and forms a pounch to bring in large quantities of non-specific, small solutes dissolved in extracellular solution
pouch pinches off PM → pinocytotic vesicle
eventually fuse w lysosome
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
extracellular molecules bind to receptors onPM
PM sinks inward and forms a clathrin coated pit
pit pinches off PM and forms clathrin-coated endocytotic vesicle that
cell signaling function
growth and development of cell
enhance tissue repair
facilitate immune activities
maintain homeostasis
types of signaling
local signaling
paracrine
synaptic
autocrine
juxtacrine
long-distance signaling
endocrine
Paracrine signaling
local cell-cell communication
signals are released out of cell to nearby target cells
synaptic
between neurons only
autocrine signaling
self stimulating
regulatory pathway
juxtacrine
cell-cell contact
signal molecule is membrane bound and receptor is on the touched cell
signal does not go out of cell
gap junctions
integral proteins
endocrine signaling
Signal molecules (hormones) secreted into blood to stimulate distant cells
Signal reception
ligand gated receptors
G-protein coupled receptors
transduction of ion channels
voltage gated ion channel
mechanically gated ion channel
Ligand -gated receptors
signal (ligand) binds to ligand-gated receptor
channel opens
ions flow across membrane
G-protein coupled receptor
signal binds
G-protein activated
made of alpha, beta, gamma subunits
assembled using GTP
one of the subunits breaks off to effector protein or ion channel
ion channel opens
ions flow across membrane
Hematoxylin + eosin stain
hematoxylin = basic dye
react w anionic part of cells/ tissues
dark blue stain that is positive
eosin = acidic dye
reacts w cationic part
red/pink stain that is negative
4 primary tissues
epithelial tissue
lining of surface or body cavities
glandular secretion
connective tissue
support and protect tissues /organs
nervous tissue
transmission of nerve impulses
muscular tissue
strong contraction
body movements
zygote
sperm cell fertilizes ovum
eventually develops into 3 embryonic germ layers
3 embryonic germ layers
ectoderm (outer)
epidermis
nervous system
mesoderm (middle)
collagen + fibroblasts in matrix
muscle
bone
blood
cartilage
Endoderm (inner)
mucus membrane
digestive
respiratory system
Epithelial tissue
closely adhering cells
can have 1 or more cell layers
avascular
depend on blood vessels of basement membrane for nourishment and waste removal
attached to basement membrane (loose CT)
functions:
interacts w external and internal environment of the body
diffusion
filtration
secretion
absorption
covers body surface and lines body cavities
forms the external and internal linings of organs
constitutes most glands
what is the surface that interacts the with the outside of epithelial tissue
apical surface
Basement membrane of epithelial cells
technically a part of the CT
secreted by the basal epithelial layer
anchors epithelium to the CT below it
consists of
basal lamina
Type IV collagen
laminin + fibronectin adhesive glycoproteins attach to integrins at hemidesmosomes
proteins and proteoglycans cross-link laminin to collagen network that control porosity of BL
reticular lamina
type III collagen network bound to BL by type VII collagen
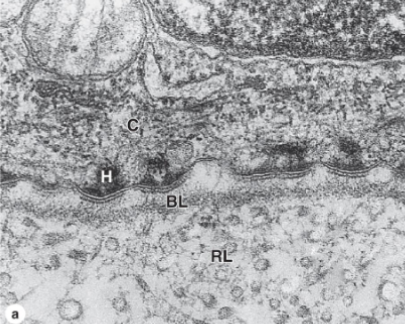
identify the parts of this epithelial tissue
H= hemidesmosome
BL= basal lamina
RL= reticular lamina
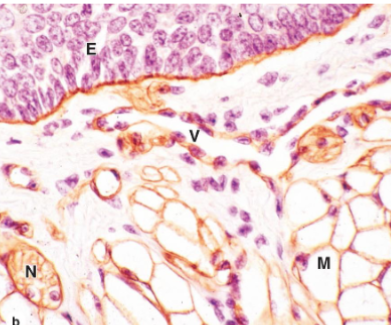
identify the parts of the epithelial tissue
brown = Basal lamina
E = epithelium
Intercellular junction
features
connections btwn 1 cell and another
all cells (except RBC and metastatic cancer cells) are anchored to each other or their matric by intercellular jxns
function
provide adhesion (resist stress)
allow for communication between cells
epithelial cells can adhere strongly to neighboring cells
5 main categories
tight junction (zonula occuludens)
adherent junction (zonula adherens)
desmosome (macula adherens)
hemidesmosome
gap junction
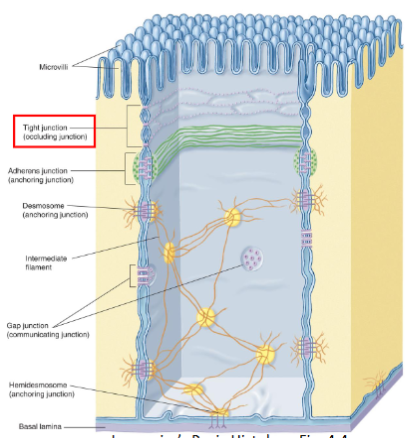
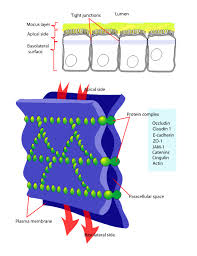
Tight junction / zonula occludens
region where adjacent membranes sealed together by linker proteins (transmembrane proteins) making a lateral perimeter around cell
claudin
occludin
closest to apical surface
Functions
seals off space between cells to prevent compounds from passing between instead of through the cell
restricts movement of membrane lipids and protein of apical surface to other areas of cell
issues:
toxin from food poisoning bacteria binds to claudin and weaken tight junctions and allows tissue fluid to leak into intestinal lumen
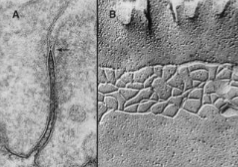
what kind of intercellular jxn is this
tight junction
close to apical surface
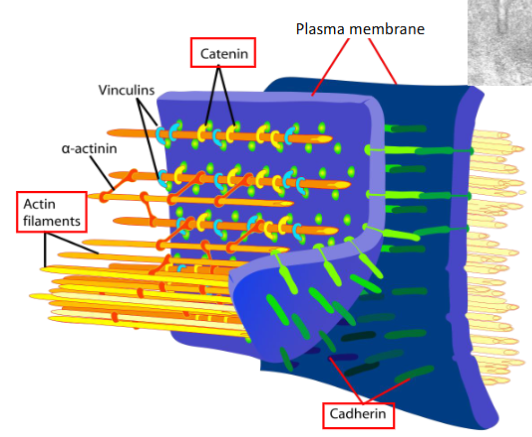
Adherent junctions / zonula adherens
region where adjacent cells are bround together by transmembrane proteins (cadherins) in the presence of Ca2+
on cytoplasm side:
cadherins bound to catenin proteins which link actin filaments to form terminal web
creates lateral perimeter
function
stabilize and strengthen zonula occludens/tight junctions
Desmosomes/ macula adherens
Transmembrane proteins (desmoglein+ desmocollins - part of cadherin fam) join neighboring cells together
cytoplasmic side:
desmoglein+desmocollins are bound to thick plaque protein which are linked to intermediate filaments
function:
resist mechanical stress to keep cells from pulling apart
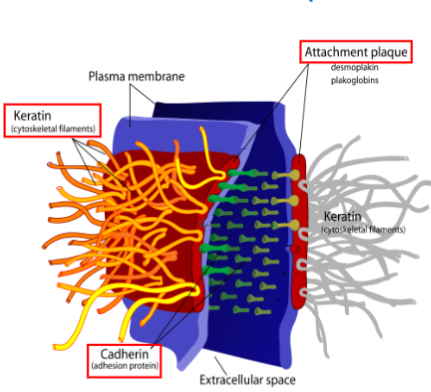
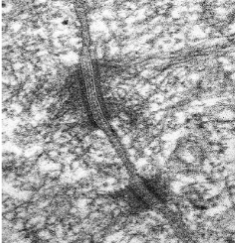
what kind of intercellular junction is this
desmosome
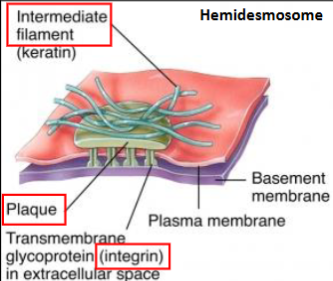
Hemidesmosomes
transmembrane protein= integrins , attach to laminin in BL of basement membrane
on cytoplasmic side: integrins bound to plaque proteins which are linked to intermediate filaments
intermediate filaments link hemi-hemi-desmo
function
anchor the basal surface of cells to basement membrane
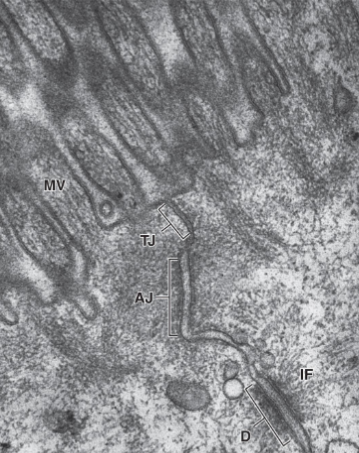
identify the structures
MV= microvilli
TJ= tight junction
AJ= adherent junction
D = desmosome
IF = intermediate filament
Gap junctions
6 transmembrane proteins (connexin) arranged next to each other → form aqueous channel (connexon) that connects lateral surfaces of neighboring cells
function:
allow ions, glucose, polar compounds, amino acids, water, and other small (<1.5 nm) solutes to pass from one cell to another
rapid cell to cell communication
can open and close and is tightly regulated
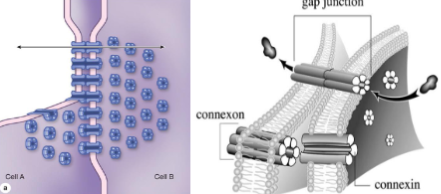
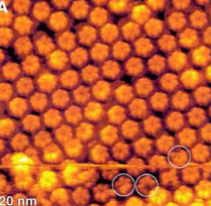
what kind of intercellular junction is this + what microscope
gap junction
atomic force
compare simple epithelium and stratified epithelium
simple:
1 layer of cells
named by shape of cells
all cells attached to basement membrane
stratified
more than 1 layer of cells
named by shape of apical layer
some cells rest on tope of others and are not attached to the basement membrane
epithelial cell shapes
squamous
oval and flattened nucleus
flat shaped cell
cuboidal
width=height
round + central nucleus
columnar
tall>wide
nucleus stretched vertically and closer to basal surface
epithelial cell classes
simple
1 layer
pseudostratified columnar
technically 1 layer, but looks like multiple
stratified
multiple layers
simple squamous epithelium
single row of squamous cells attached to basement membrane
found in serous and synovial membranes
serous: surrounds organs + makes serous fluid
synovial: joints + synovial fluid
secrete fluid that lubricate tissue
locations
lungs (alveoli)
kidneys (glomerulus + tubules)
internal layer of BV (endothelium)
functions
rapid diffusion, filtration, absorption of gases, nutrients, wastes
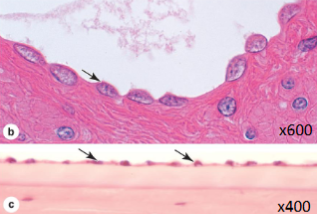
what kind of epithelium is this
simple squamous
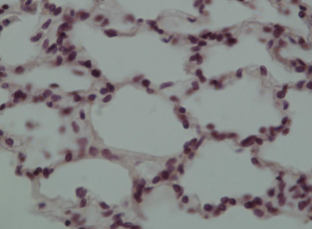
what kind of epithelium is this made of
simple squamous - lungs /alveoli
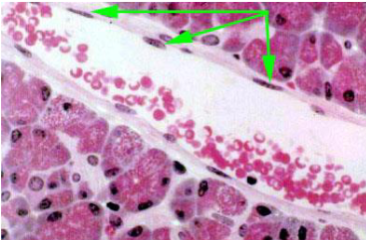
what kind of epithelium is this made of
simple squamous - BV
simple cuboidal epithelium
single layer of cuboidal cells attached to basement membrane
found as secretory cells of exocrine and endocrine glands
tubes and ducts usually = cuboidal
minor ducts = simple cuboidal
major ducts = stratifies cuboidal
functions
diffusion
reabsorption
secretion
locations
collecting tubules of kidneys
thyroid follicles
outer surface of ovaries
salivary glands
simple ducts
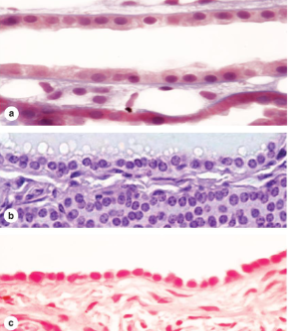
what kind of epithelium are these
simple cuboidal