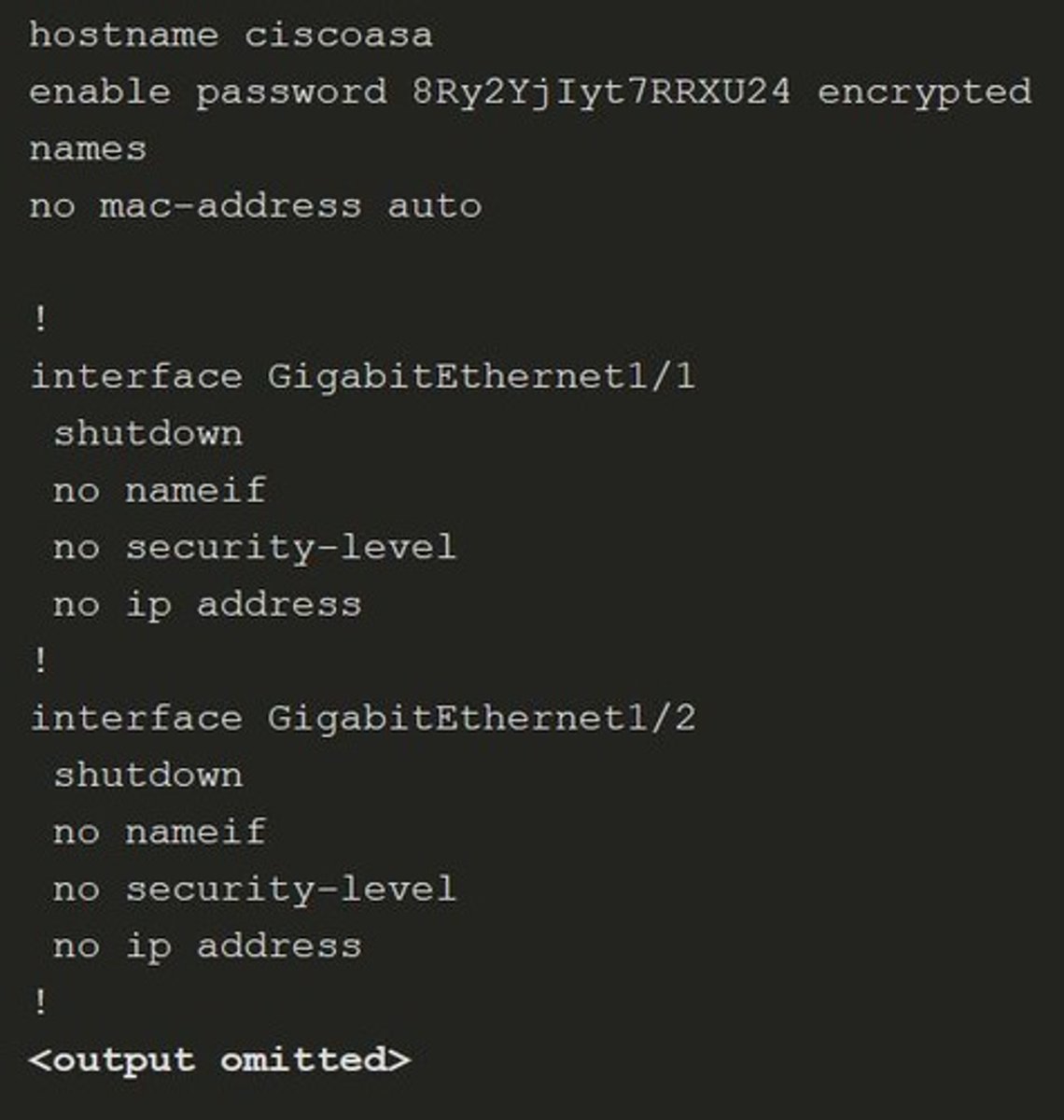
ASA Firewall Configuration and Management Overview
1/118
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
119 Terms
Objects
Reusable components for use in configurations.
Object Groups
Support objects and object groups in Cisco ASA configurations.
host
A host address.
fqdn
A fully-qualified domain name.
range
A range of IP addresses.
subnet
An entire IP network or subnet.
Service Object
Specifies an IP protocol name or number.
Object Group
Objects can be grouped together to create an object group.
Access Control Entry (ACE)
An object group can be used in an access control entry instead of having to enter an ACE for each object separately.
Network Object Group
A network-based object group specifies a list of IP host, subnet, or network addresses.
User Object Group
Locally created, as well as imported Active Directory user groups can be defined for use in features that support the identity firewall.
Service Object Group
A service-based object group is used to group TCP, UDP, or TCP and UDP ports into an object.
ICMP-Type Object Group
The ICMP protocol uses unique types to send control messages (RFC 792).
Security Object Group
A security group object group can be used in features that support Cisco TrustSec by including the group in an extended ACL.
ACEs
ACEs are applied to a protocol, a source and destination IP address, a network, or the source and destination ports.
Sequential Processing of ACLs
ACLs are processed sequentially from top down.
Criteria Match
A criteria match will cause the ACL to be exited.
Implicit Deny
There is an implicit deny any at the bottom of an ACL.
Remarks in ACLs
Remarks can be added per ACE or ACL.
Time-Based ACLs
ACLs can be enabled/disabled based on time ranges.
Network Mask in ASA
The ASA uses a network mask (e.g., 255.255.255.0) and not a wildcard mask (e.g. 0.0.0.255).
Named ACLs
ACLs are always named instead of numbered.
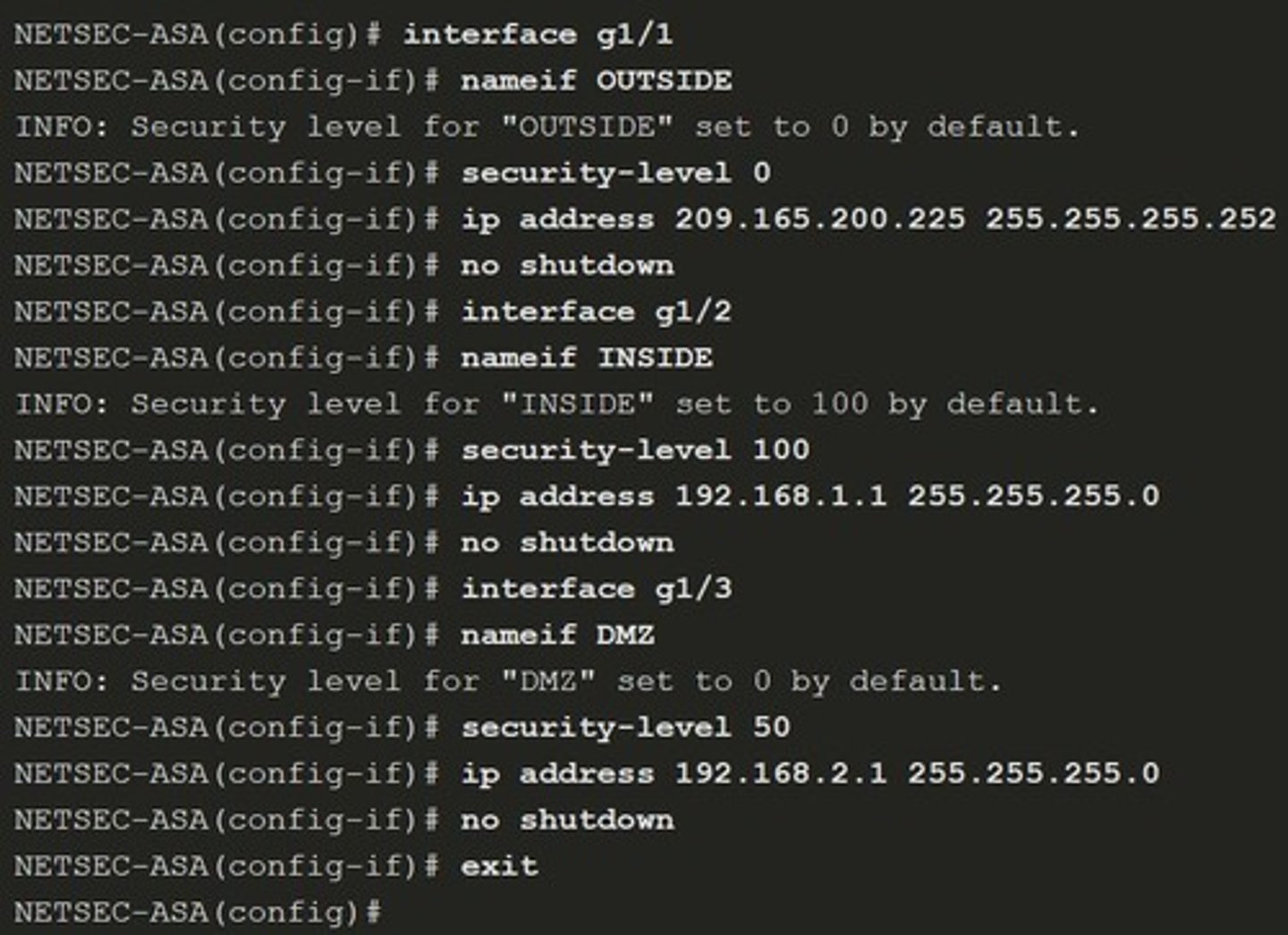
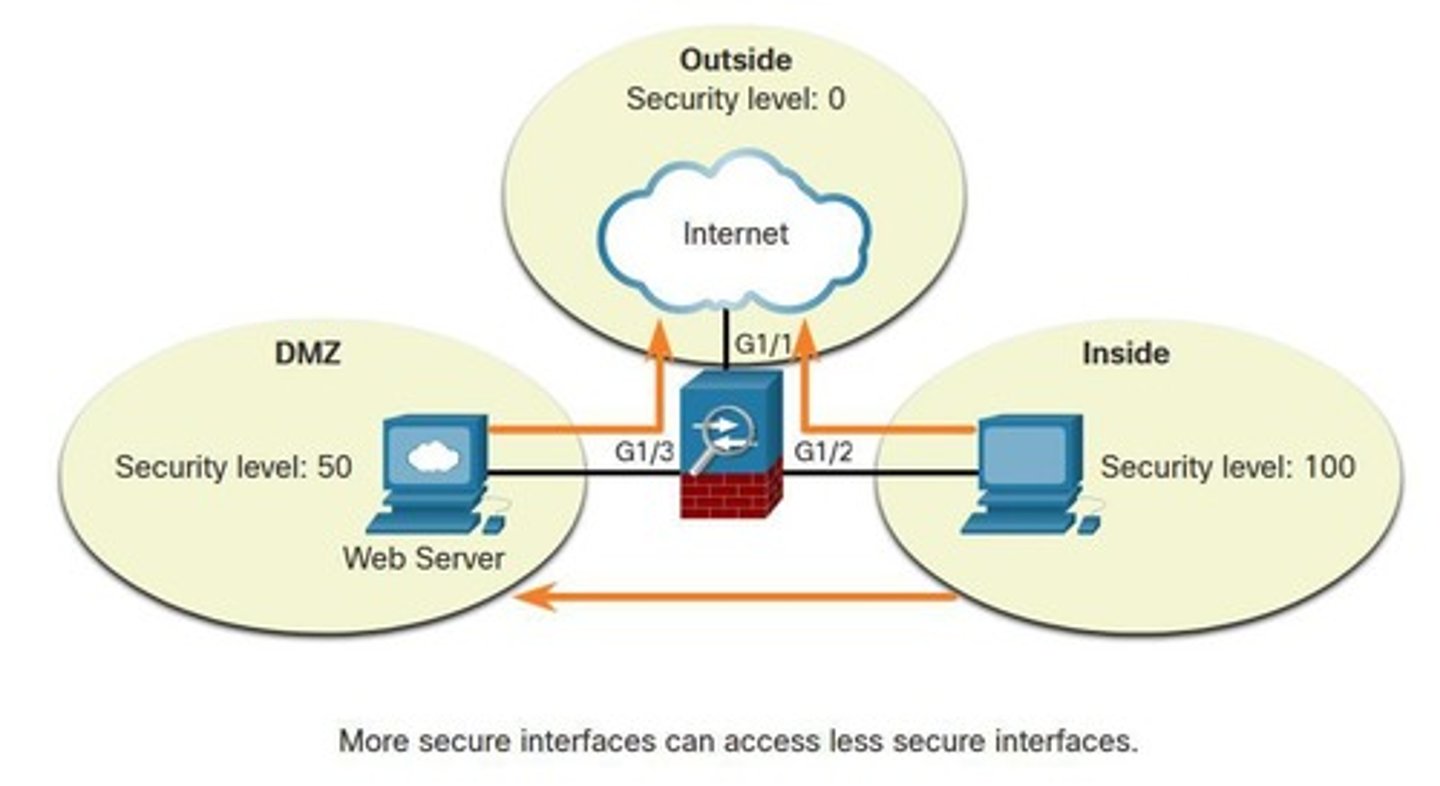
Default Security Levels
By default, interface security levels apply access control without an ACL configured.
Through-Traffic Filtering
Traffic passing through the ASA from one interface to another interface.
To-the-Box-Traffic Filtering
Management access rule that applies to traffic that terminates at the ASA.
Extended Access List
The most common type of ACL.
Standard Access List
ASA standard ACLs are used to identify the destination IP addresses.
EtherType Access List
An EtherType ACL can be configured only if the security appliance is running in transparent mode.
Webtype Access List
Used for filtering for clientless SSL VPN traffic.
IPv6 Access List
Used to determine which IPv6 traffic to block and which traffic to forward at router interfaces.
Control Network Access for IP Traffic
The ASA does not allow any traffic from a lower security interface to a higher security interface unless it is explicitly permitted by an extended access list.
Identify Traffic for AAA Rules
AAA rules use access lists to identify traffic.

Identify Addresses for NAT
Policy NAT lets you identify local traffic for address translation by specifying the source and destination addresses in an extended access list.
Establish VPN Access
Extended access list can be used in VPN commands.
Modular Policy Framework (MPF)
A framework that uses class maps to identify traffic for features such as TCP, general connection settings, and inspection.
Standard ACLs
Access lists that include only the destination address and can control the redistribution of OSPF routes.
VPN filters
Filters traffic for LAN-to-LAN (L2L), Cisco VPN Client, and the Cisco AnyConnect Secure Mobility Client traffic.
ACL id
The name of the ACL.
Action
Can be permit or deny.
Protocol number - Source
Can be IP for all traffic, or the name/IP protocol number (0-250) including icmp (1), tcp (6), udp (17), or a protocol object-group.
Source
Identifies the source and can be any, a host, a network, or a network object group.
Source port operator
(Optional) Operand used in conjunction with the source port, valid operands include lt (less than), gt (greater than), eq (equal), neq (not equal), and range for an inclusive range.
Source port
(Optional) Can be the actual TCP or UDP port number, select port names, or service object group.
Destination
Identifies the destination and can be any, a host, a network, or a network object group.
Destination port operator
(Optional) Operand used in conjunction with the destination port, valid operands are the same as the source port operands.
Destination port
(Optional) Can be the actual TCP or UDP port number, select port names, or service object group.
Log
Can set elements for syslog including severity level and log interval.
Time range
(Optional) Specify a time range for the ACE.
access-group
Keyword used to apply an ACL to an interface.
in
The ACL will filter inbound packets.
out
The ACL will filter outbound packets.
interface
Keyword to specify the interface to which to apply the ACL.
if_name
The name of the interface to which to apply an ACL.
per-user-override
Option that allows downloadable ACLs to override the entries on the interface ACL.
ACLs
Access Control Lists used to filter traffic.
ACE
Access Control Entry, a single rule in an ACL.
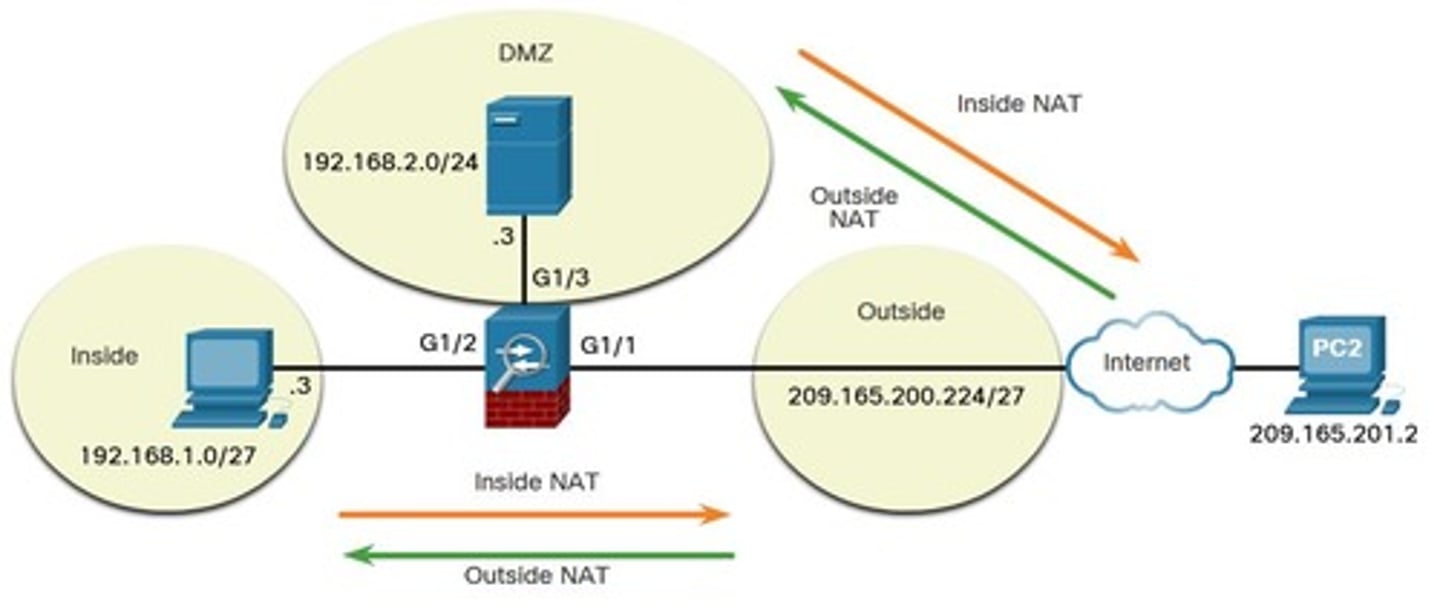
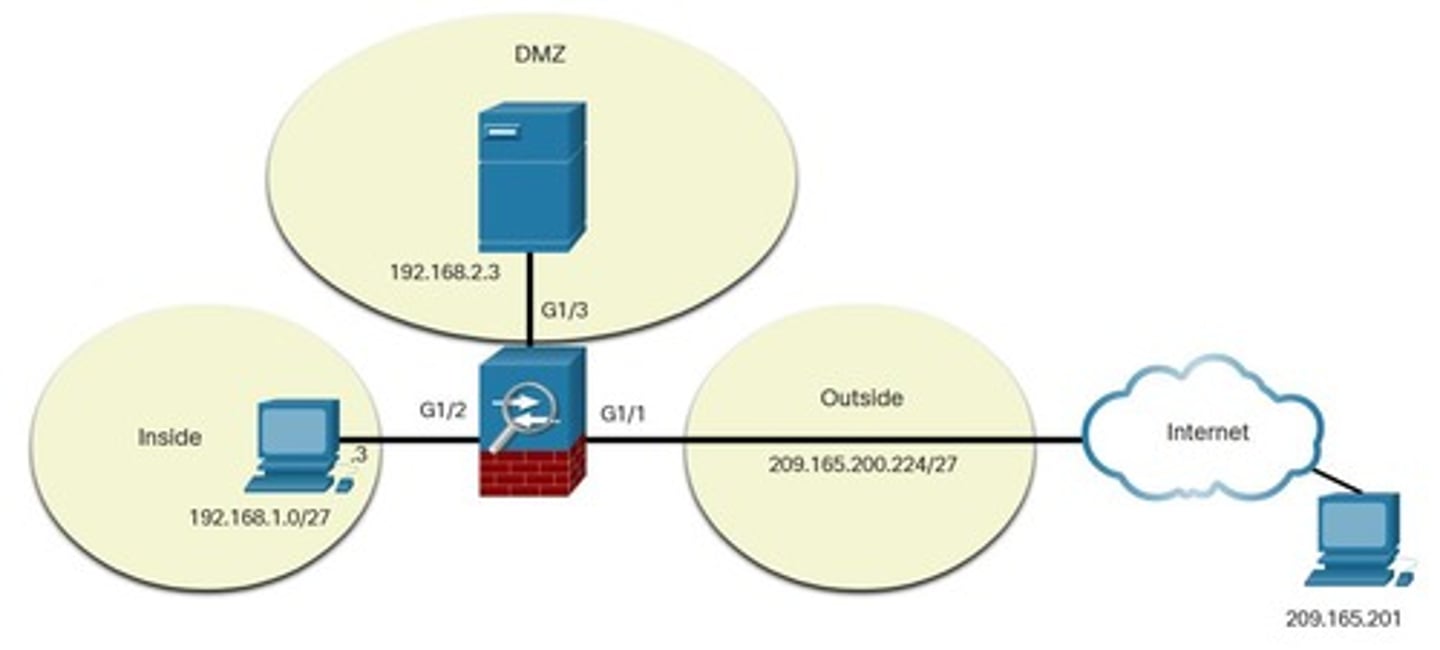
Inside NAT
NAT configuration where internal addresses are translated to external addresses.
Outside NAT
NAT configuration where external addresses are translated to internal addresses.
Bidirectional NAT
NAT configuration that allows translation in both directions.
Dynamic PAT
A many-to-one translation method, also known as NAT with overload.
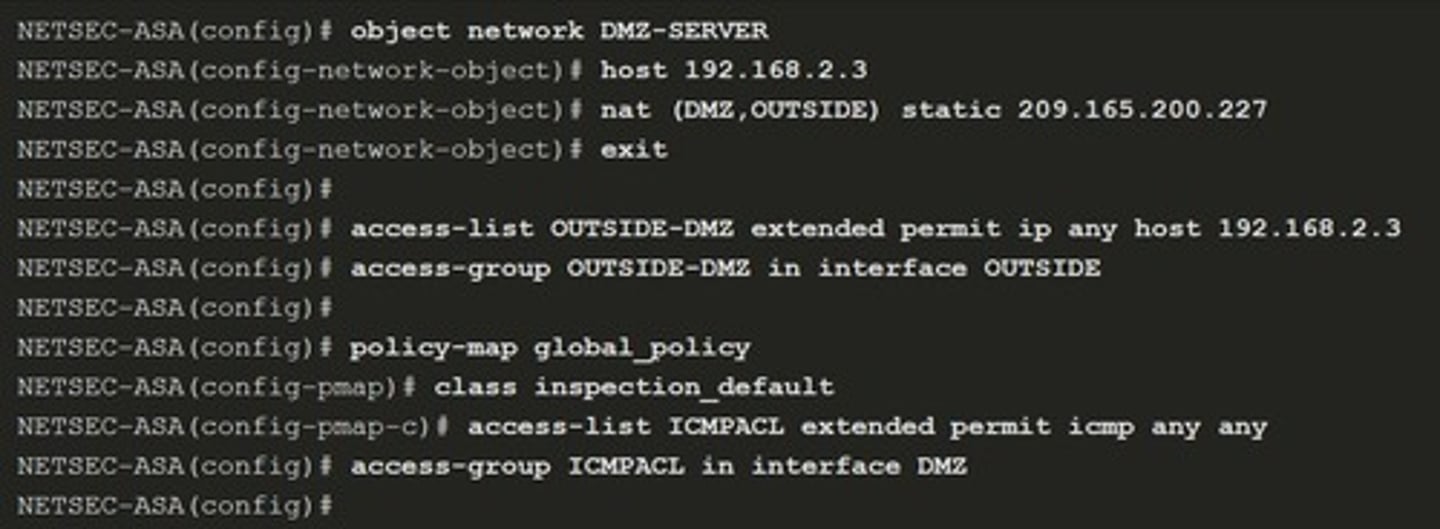
Static NAT
A one-to-one translation method mapping an outside address to an internal server.
Policy NAT
NAT based on a set of defined rules.
Identity NAT
A NAT configuration where a real address is translated to itself.
Dynamic NAT Configuration
Requires two network objects: one for public IP addresses and one for internal addresses.
AAA
Authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) provides an extra level of protection and user control.
Authorization
Authorization controls access, per user, after users are authenticated.
Accounting
Accounting tracks traffic that passes through the ASA, enabling administrators to have a record of user activity.
Modular Policy Framework (MPF)
A Modular Policy Framework (MPF) configuration defines a set of rules for applying firewall features, such as traffic inspection and QoS, to the traffic that traverses the ASA.
Class Maps
Class Maps define what are we looking for in the traffic.
Policy Maps
Policy Maps define what shall we do with the identified traffic.
Service Policy
Service Policy defines where do we apply the policy.
Class Map
A configuration mode used to create a class map and identify traffic to match.
DHCP
A service that automatically assigns IP addresses to devices on a network.
Static NAT
A type of NAT that maps a private IP address to a public IP address.
ACLs
Access Control Lists that filter traffic based on defined rules.
Network Objects
Entities that represent host addresses, subnets, ranges of addresses, and FQDNs.
Service Objects
Entities that refer to different network services and protocols.
Object Groups
Collections of related objects used to simplify configurations.
NAT Deployment Methods
Three methods: inside NAT, outside NAT, and bidirectional NAT.
Dynamic NAT with Overload
A type of NAT that allows multiple devices to share a single public IP address.
Modular Policy Framework (MPF)
A configuration that defines rules for applying firewall features to traffic.
Class Maps in MPF
Used to identify the traffic that will be processed by MPF.
Policy Maps in MPF
Define actions to be taken on identified traffic.
Service Policies in MPF
Identify which interfaces the policy map should be applied to.
Interface Grouping for ACLs
ASA ACLs must be grouped with an interface to take effect.
Local User Database
A database used for authenticating access
External Server Authentication
An option for authenticating access on Cisco ASAs using an external server.
Stateful Packet Inspection
A firewall service that monitors the state of active connections and determines which network packets to allow through the firewall.
Zone-Based Policy Firewall (ZPF)
A firewall configuration method that applies security policies based on zones rather than individual interfaces.
Throughput
The maximum amount of traffic that can be processed by a firewall model, varying between different ASA models.
Manageability
The ease with which a firewall can be configured, monitored, and maintained.
Next-Generation Firewall (NGFW)
A firewall that provides advanced features such as integrated threat defense and malware protection.
Identity-based firewall services
These services enhance the existing access control and security policy mechanisms by allowing users, or groups, to be specified in place of source IP addresses.
Advanced Inspection and Prevention (AIP)
The ASA uses the Advanced Inspection and Prevention (AIP) modules.
Content Security and Control (CSC) module
Antimalware capabilities can be deployed by integrating the Content Security and Control (CSC) module.
Next-generation IPS (NGIPS)
An advanced threat and malware detection capability included in the ASA 5500-X with FirePOWER Services.
Advanced Malware Protection (AMP)
An advanced threat and malware detection capability included in the ASA 5500-X with FirePOWER Services.
Application control and URL filtering
An advanced threat and malware detection capability included in the ASA 5500-X with FirePOWER Services.
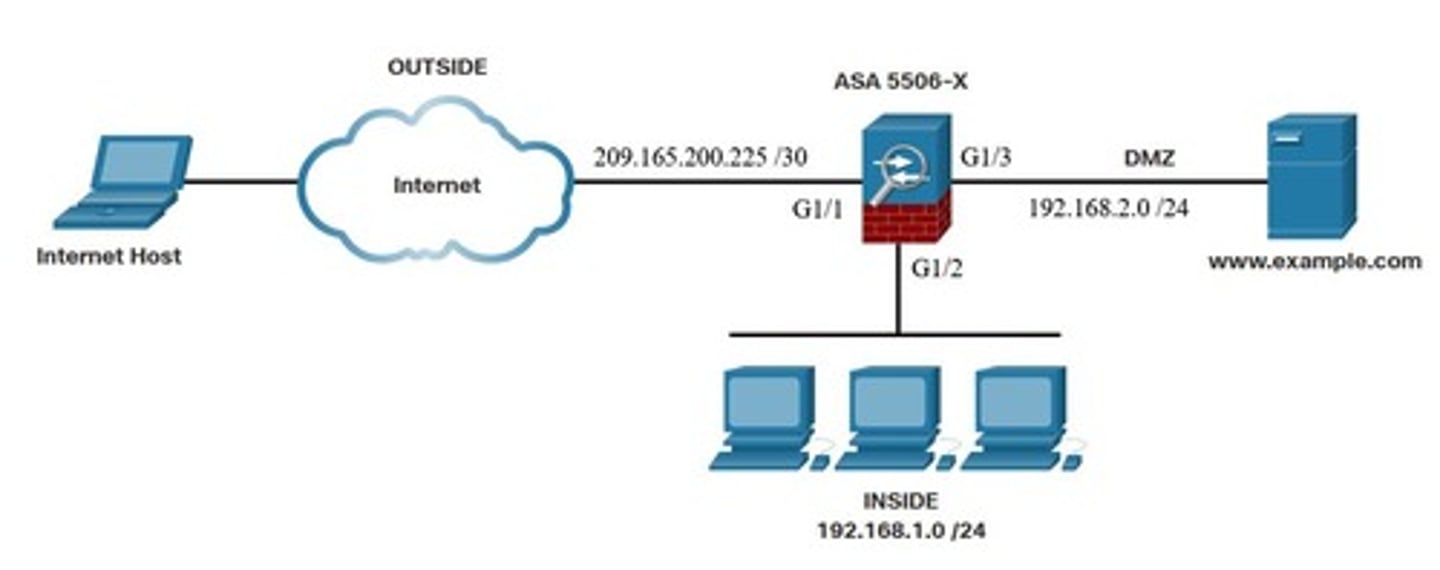
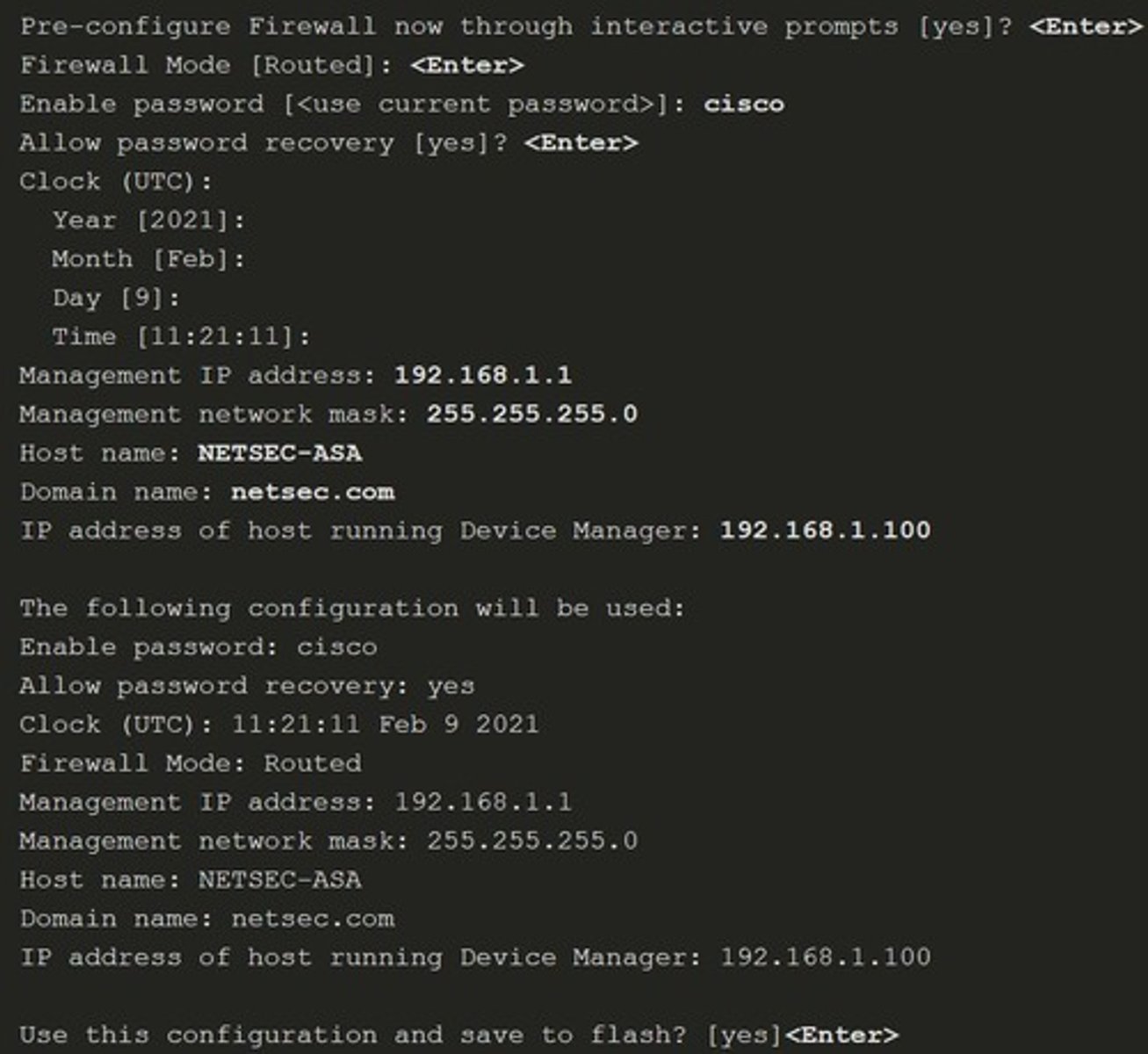
Outside network
The network/zone that is outside the protection of the firewall.
Inside network
The network/zone that is protected and behind the firewall.