lab 10: ans, general senses, gustation and olfaction
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
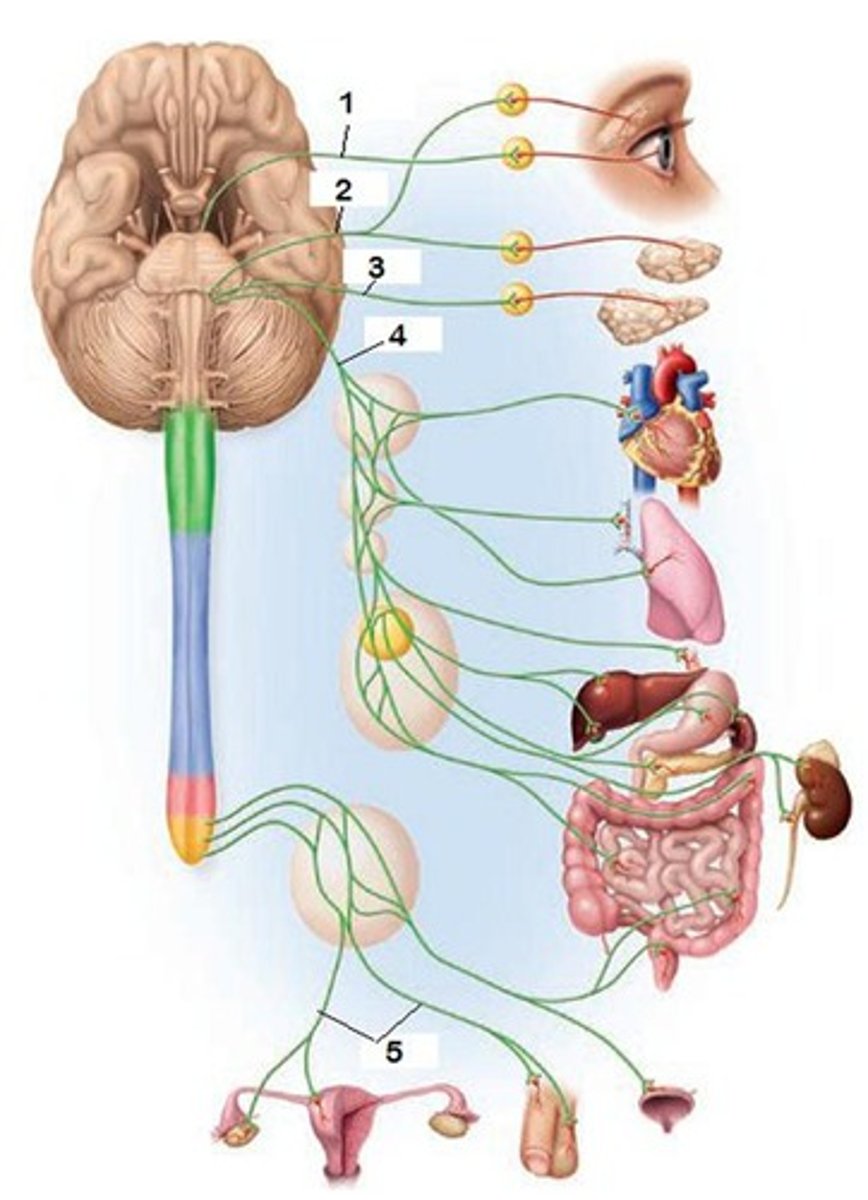
autonomic nervous system (ANS)
the part of the peripheral nervous system that controls the glands and the muscles of the internal organs (such as the heart). Its sympathetic division arouses; its parasympathetic division calms.
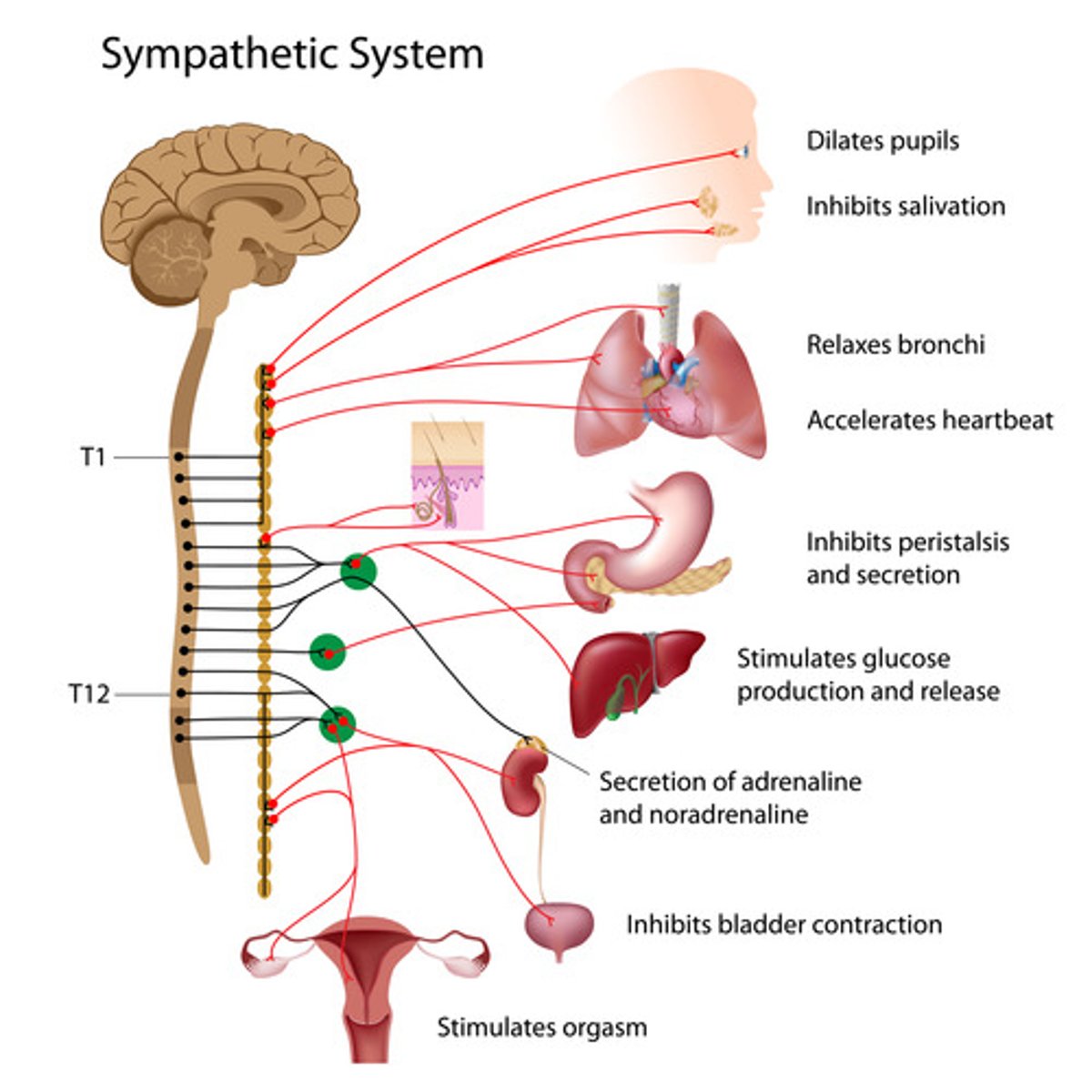
sympathetic division
adapts the body for physical activity; "fight or flight"
increases alertness, pulse, blood pressure, pulmonary airflow, blood glucose concentration, and blood flow to cardiac and skeletal muscle
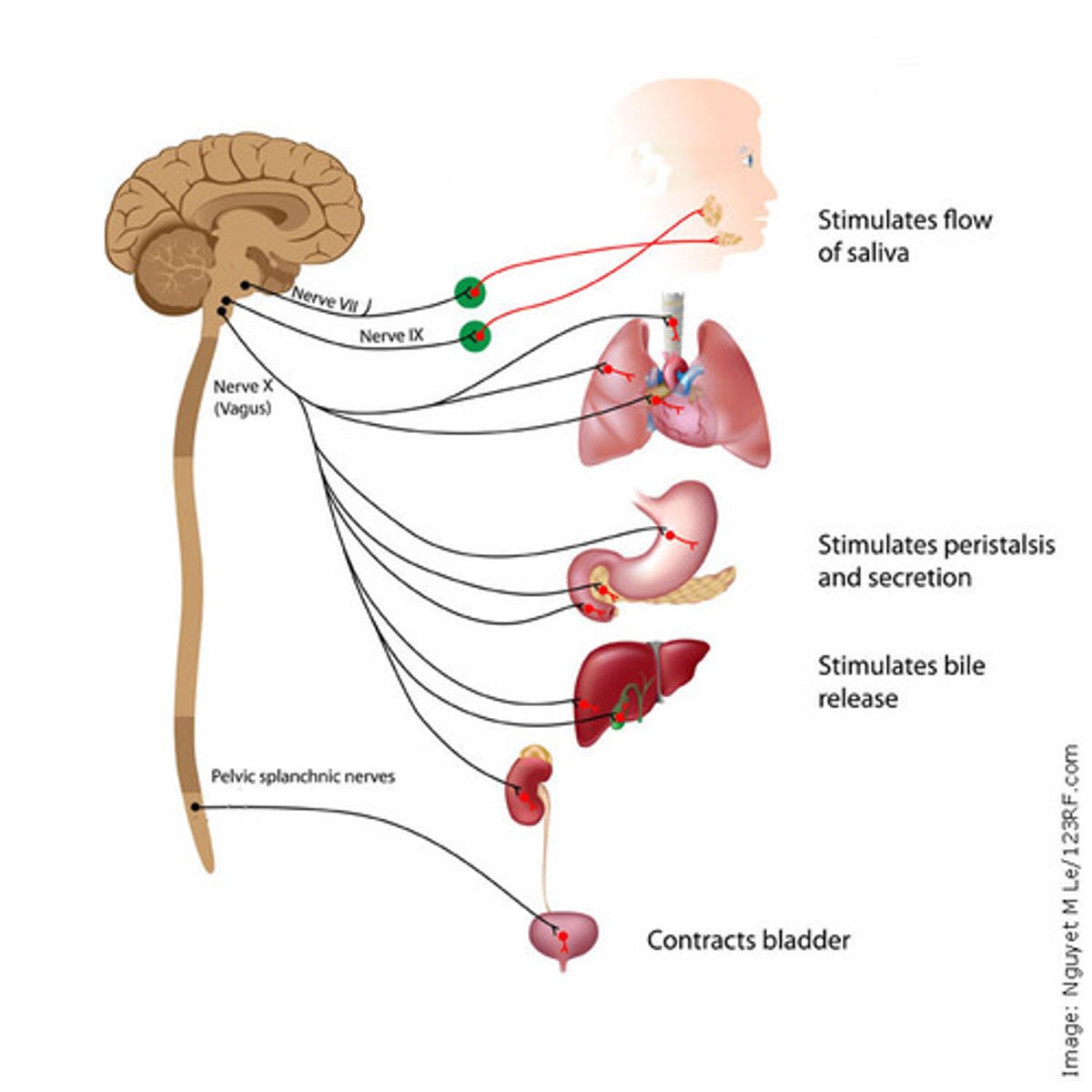
parasympathetic division
has calming effect on many body functions; associated with reduced energy expenditure and normal bodily maintenance; digestion and waste elimination
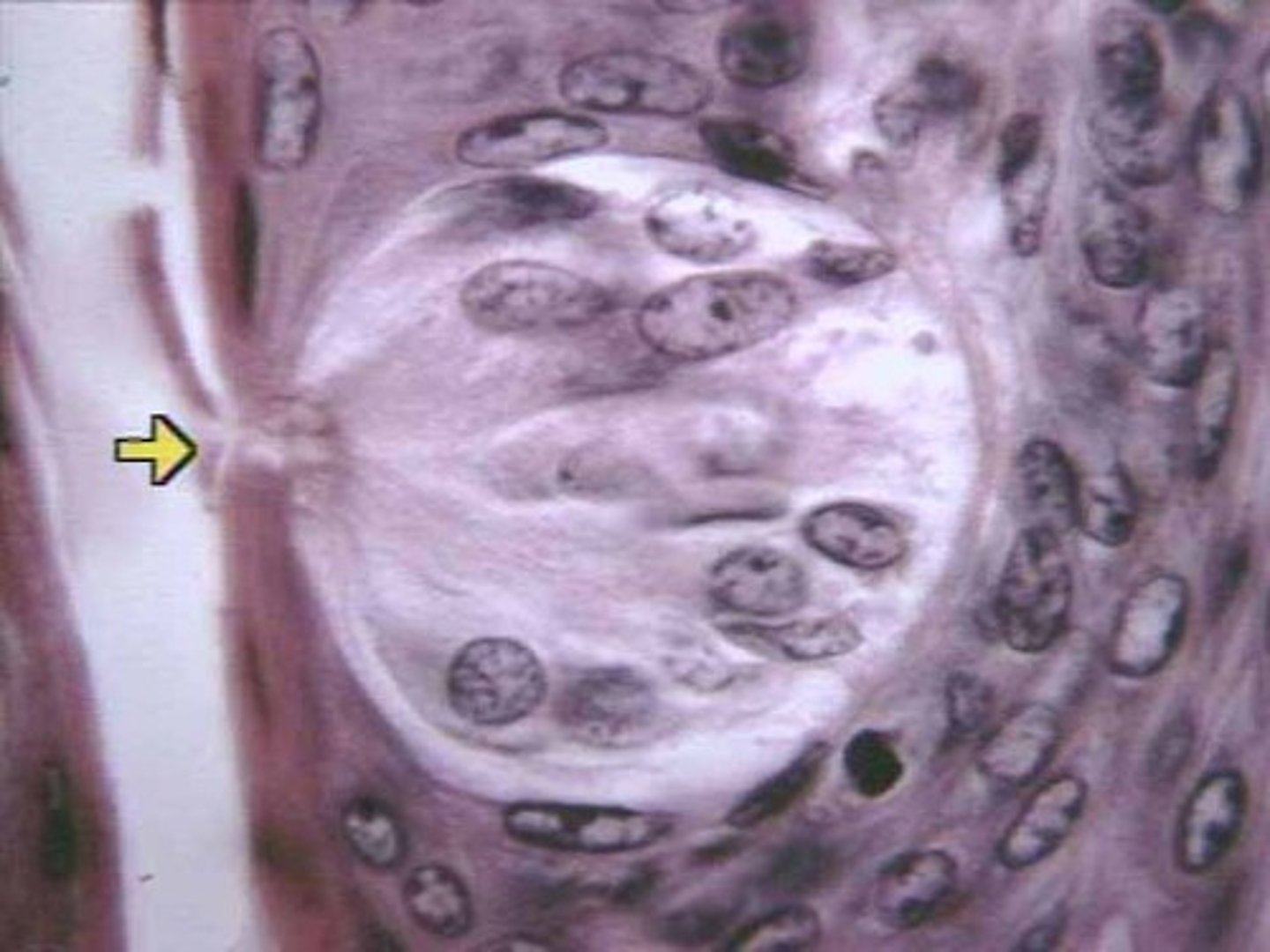
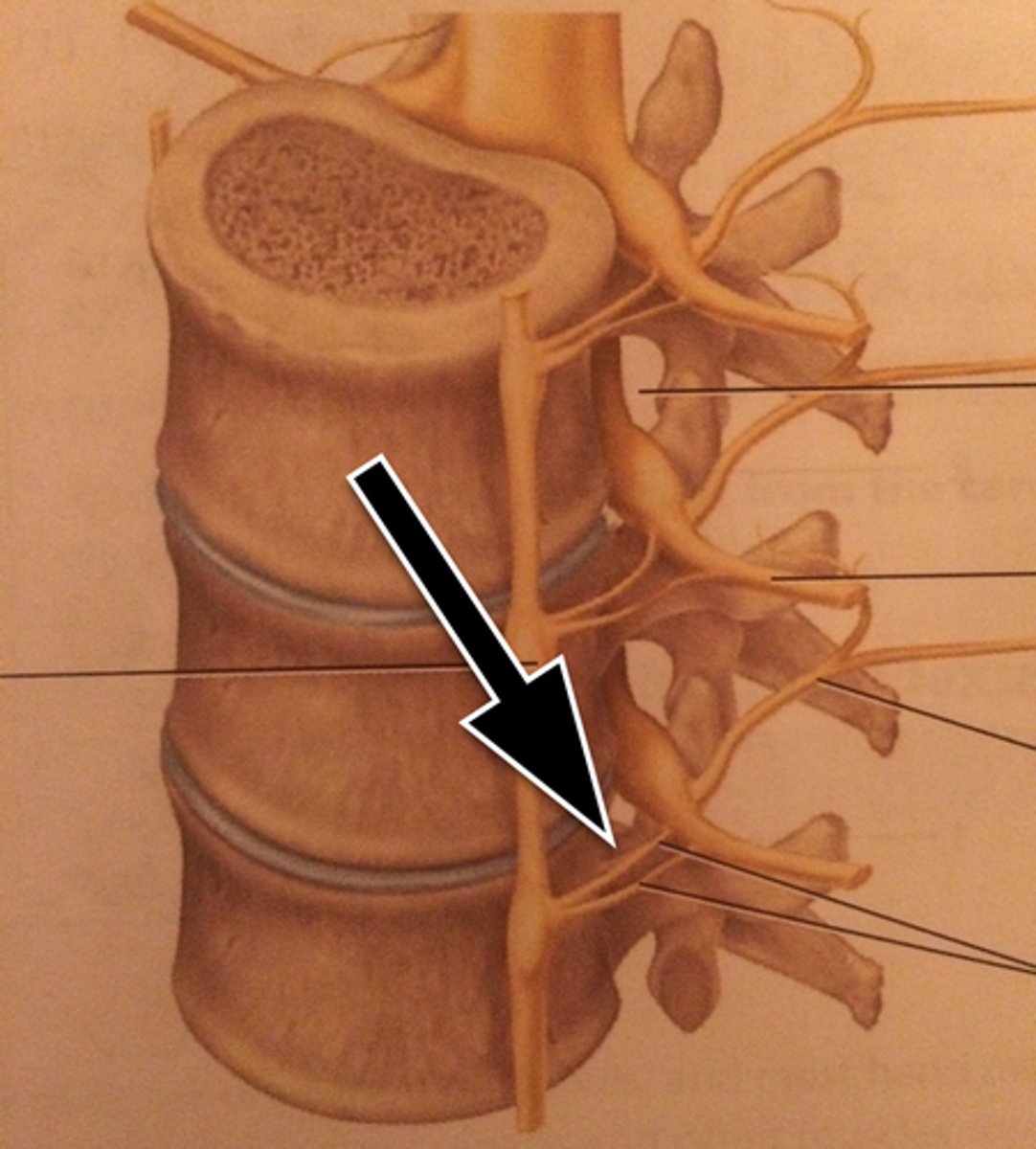
sympathetic chain ganglia
bulges on the sympathetic chain composed of neuronal cell bodies.
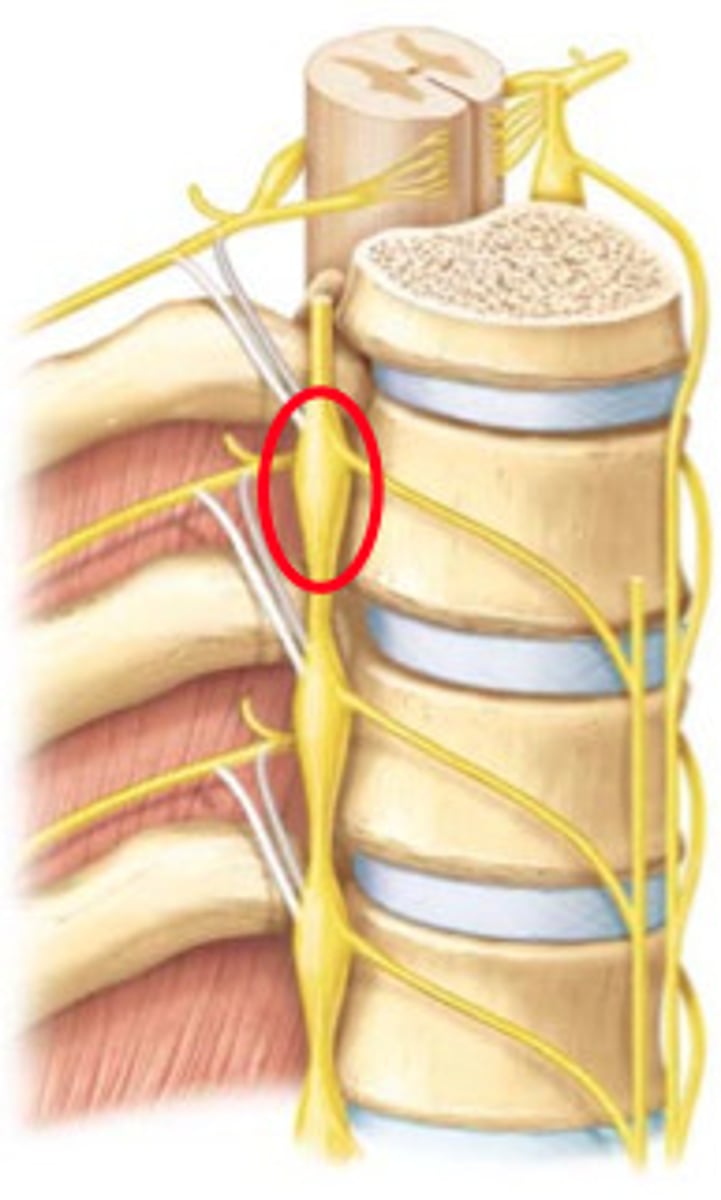
communicating rami
communicate with sympathetic chain of ganglia
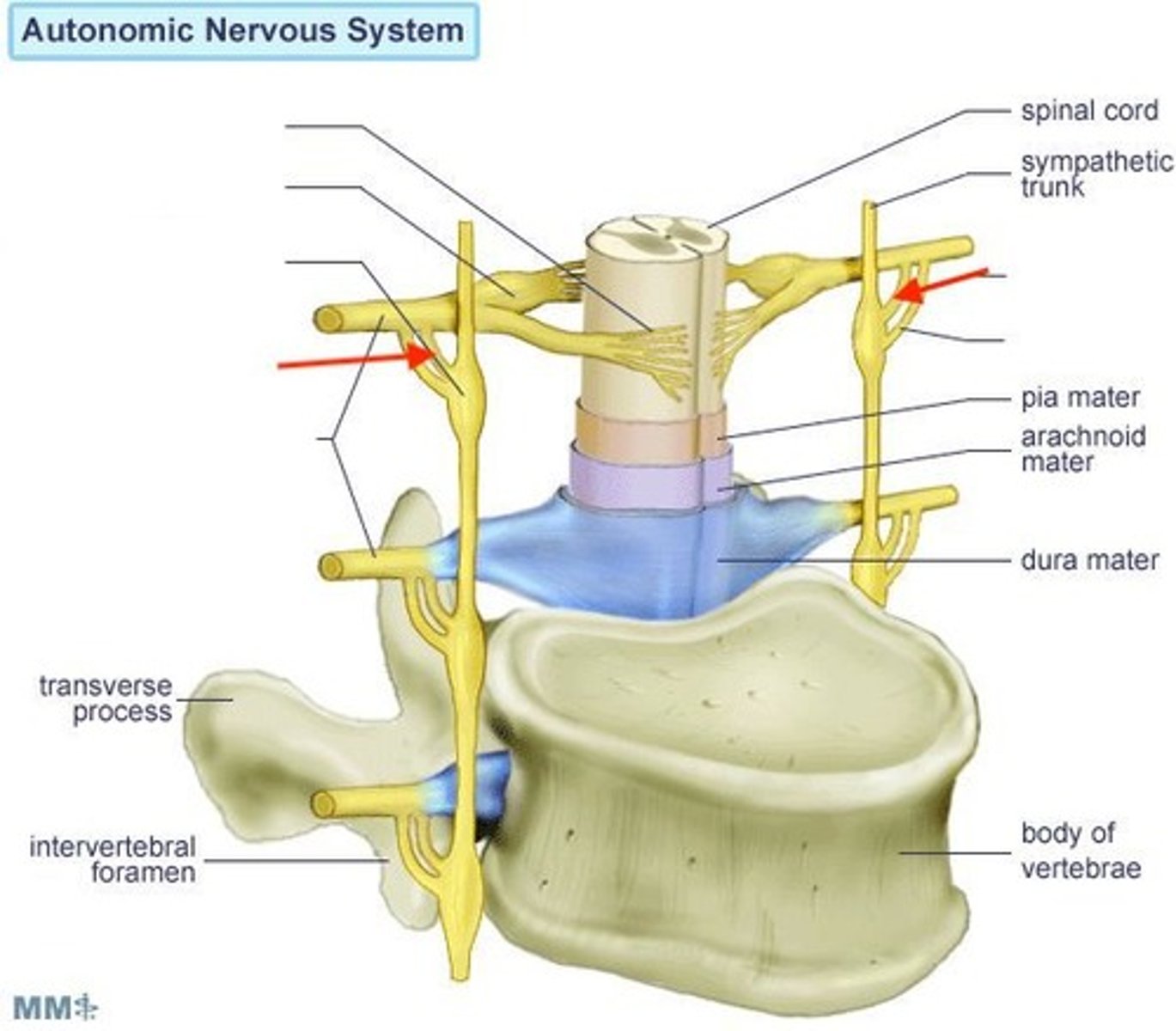
white communicating ramus
myelinated, where preganglionic fibers enter sympathetic chain of ganglia
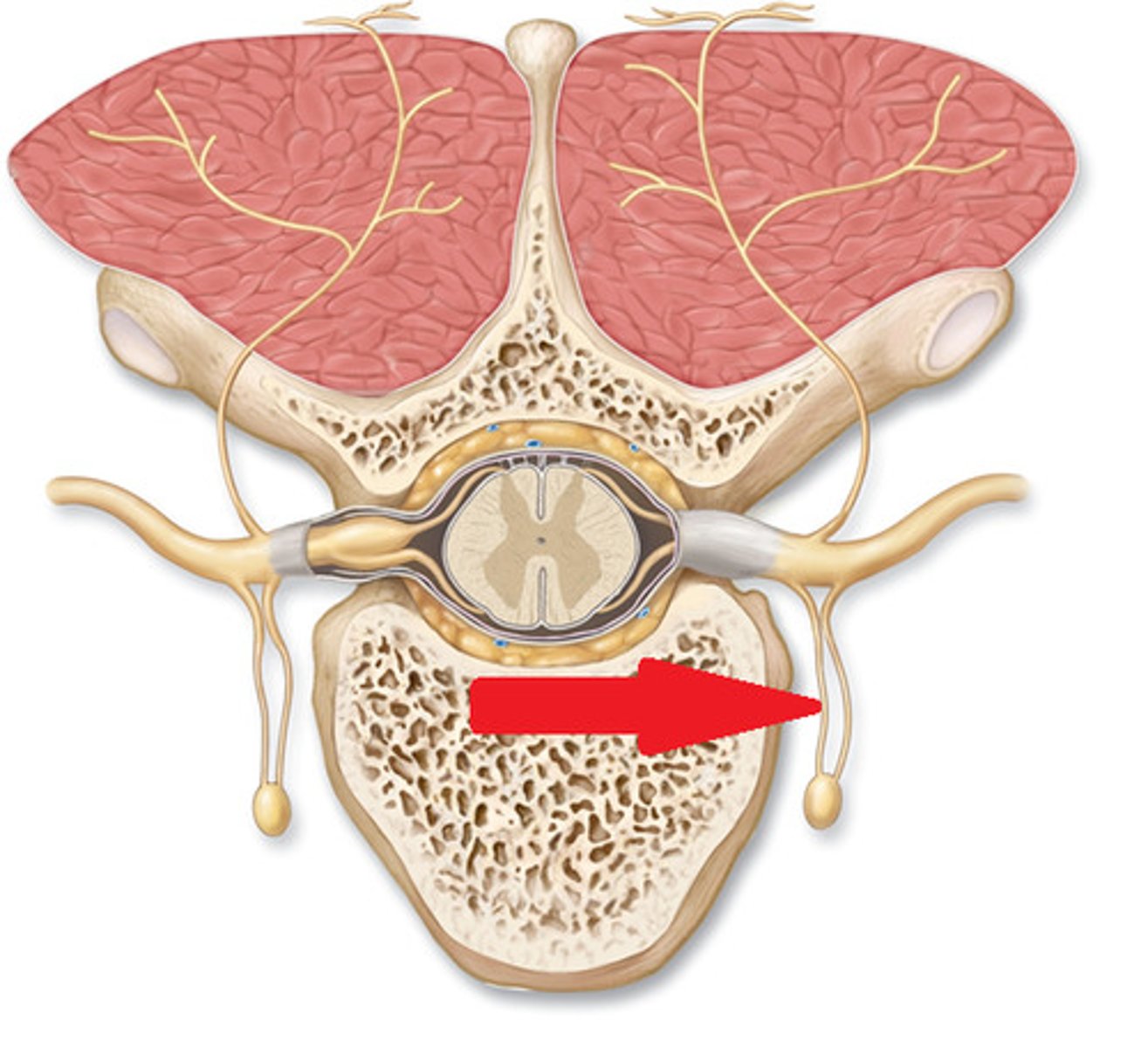
gray communicating ramus
unmyelinated, where postganglionic fibers exit the sympathetic chain
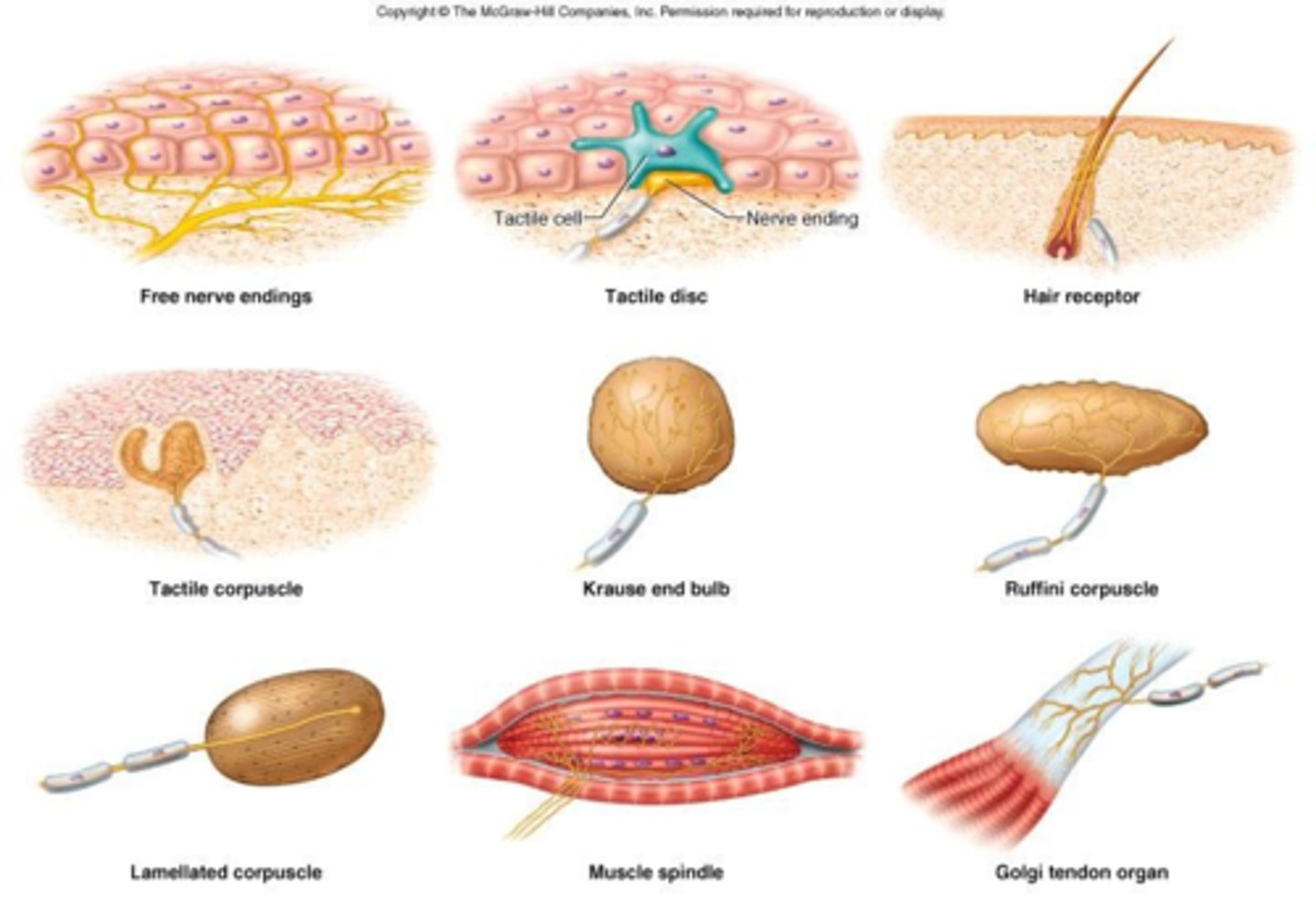
general senses
widely distributed receptors in the skin, muscles, tendons, joints, viscera; include temperature, pain, touch, pressure, vibration, proprioception
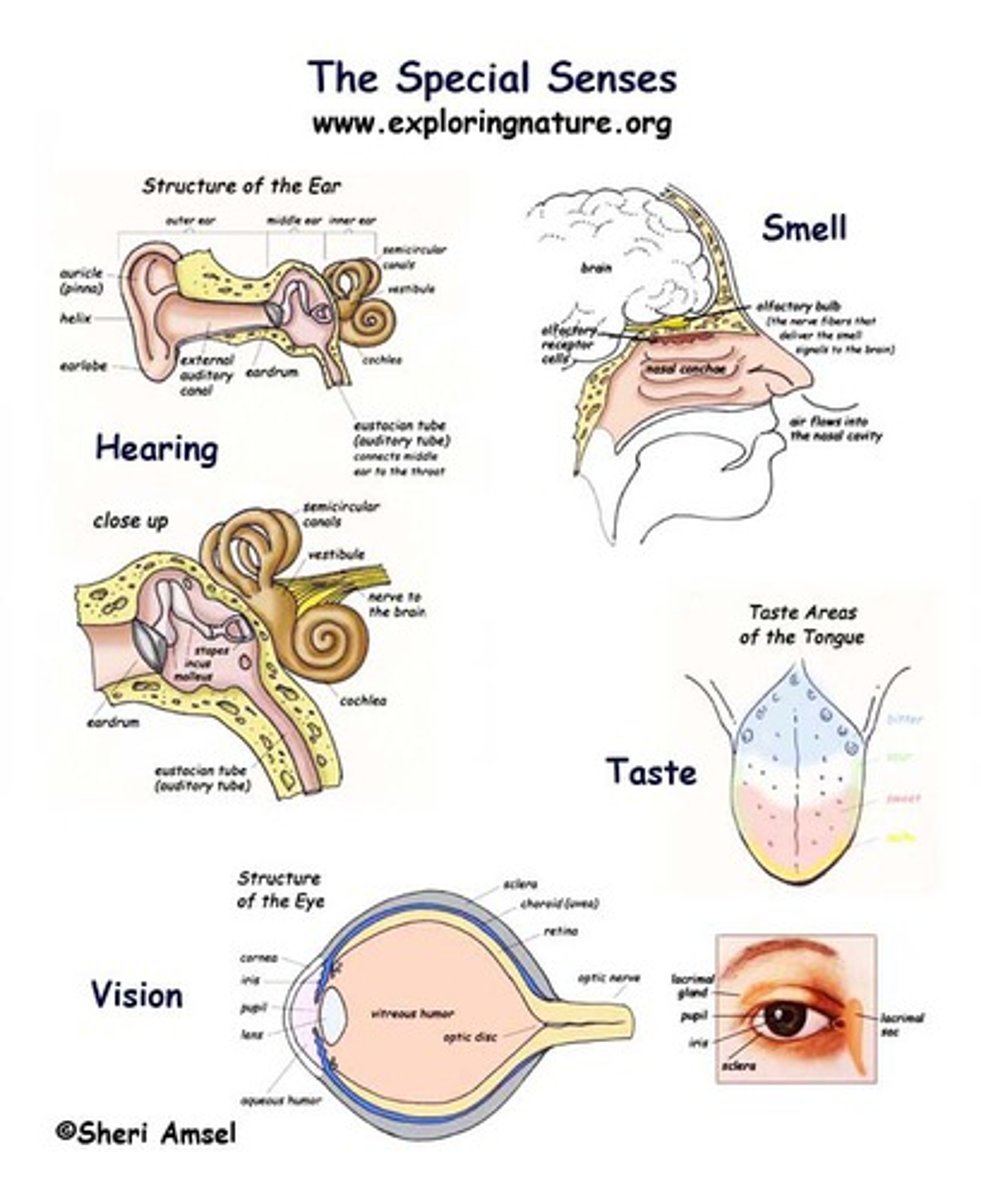
special senses
limited to the head and innervated by the cranial nerves; include vision, smell, taste, hearing / equilibrium
nociceptors
pain receptors
thermoreceptors
respond to changes in temperature; heat and cold
mechanoreceptors
respond to physical deformation of a cell or tissue caused by vibration, touch, pressure, stretch, or tension
tactile receptors
lamellated corpuscles, tactile corpuscles, ruffini corpuscles
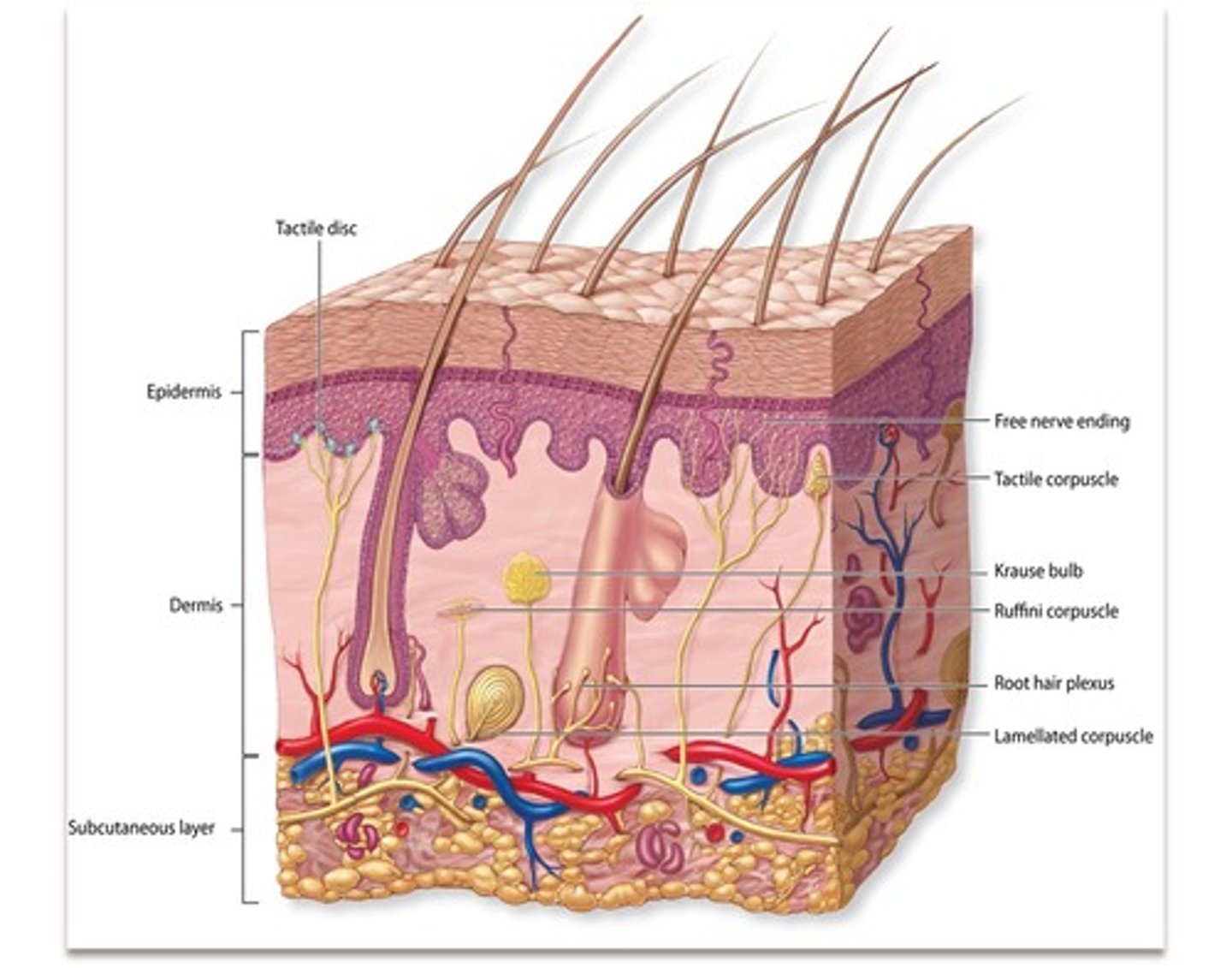
lamellated corpuscles
nerve endings that are sensitive to pressure
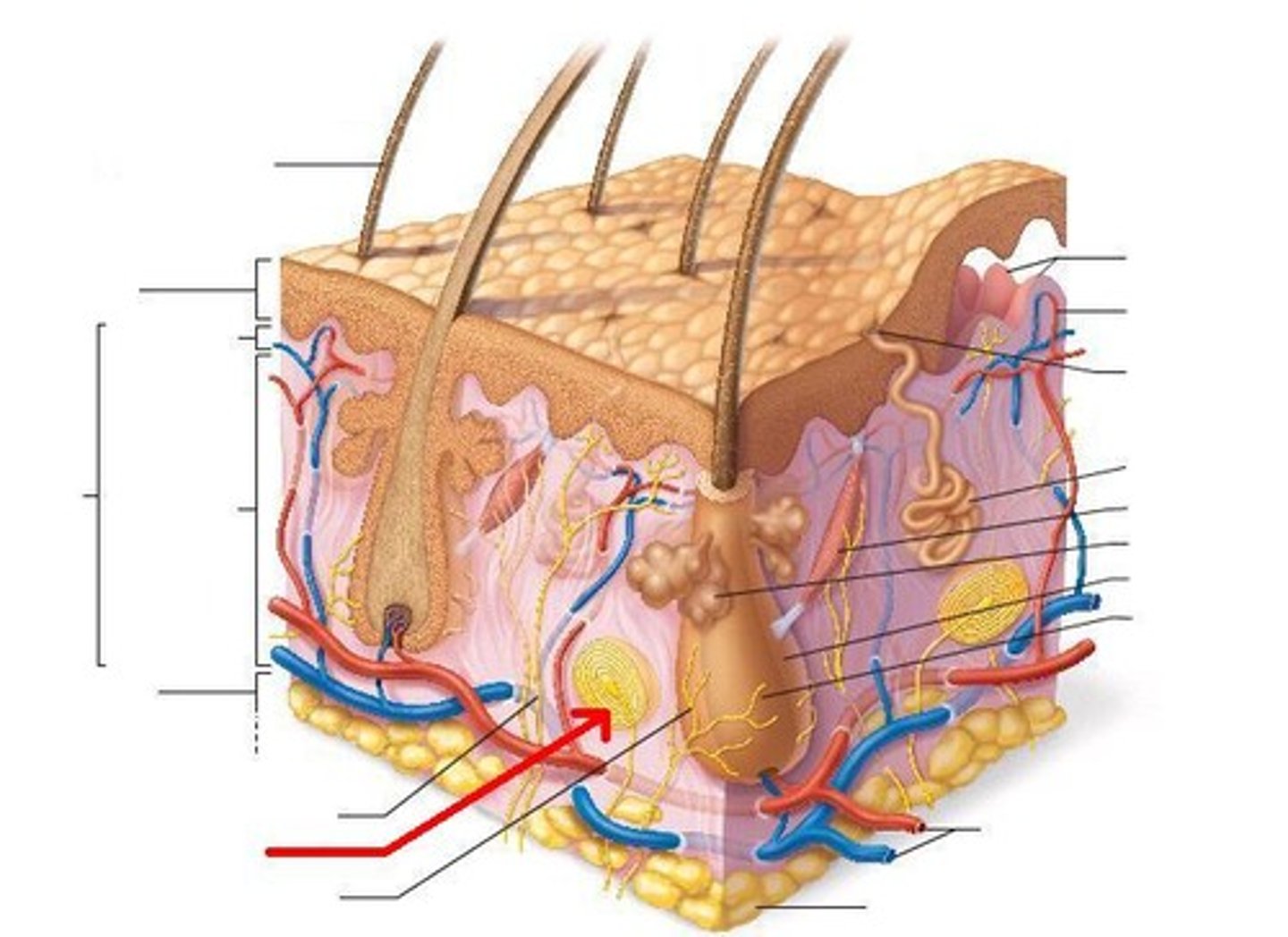
tactile corpuscles
small epidermal structures with nerve endings that are sensitive to touch and pressure
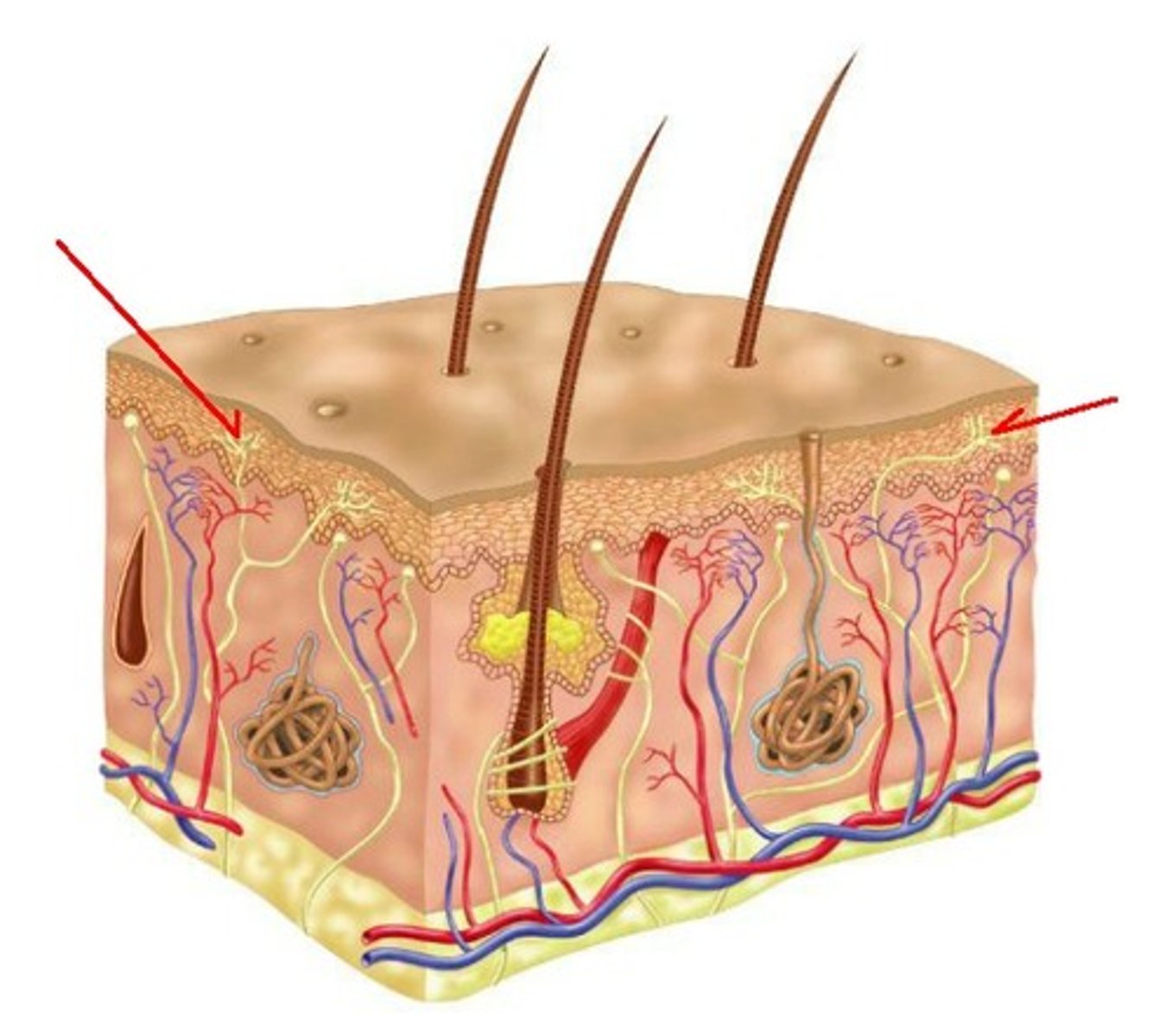
ruffini corpuscles
deep pressure and stretch
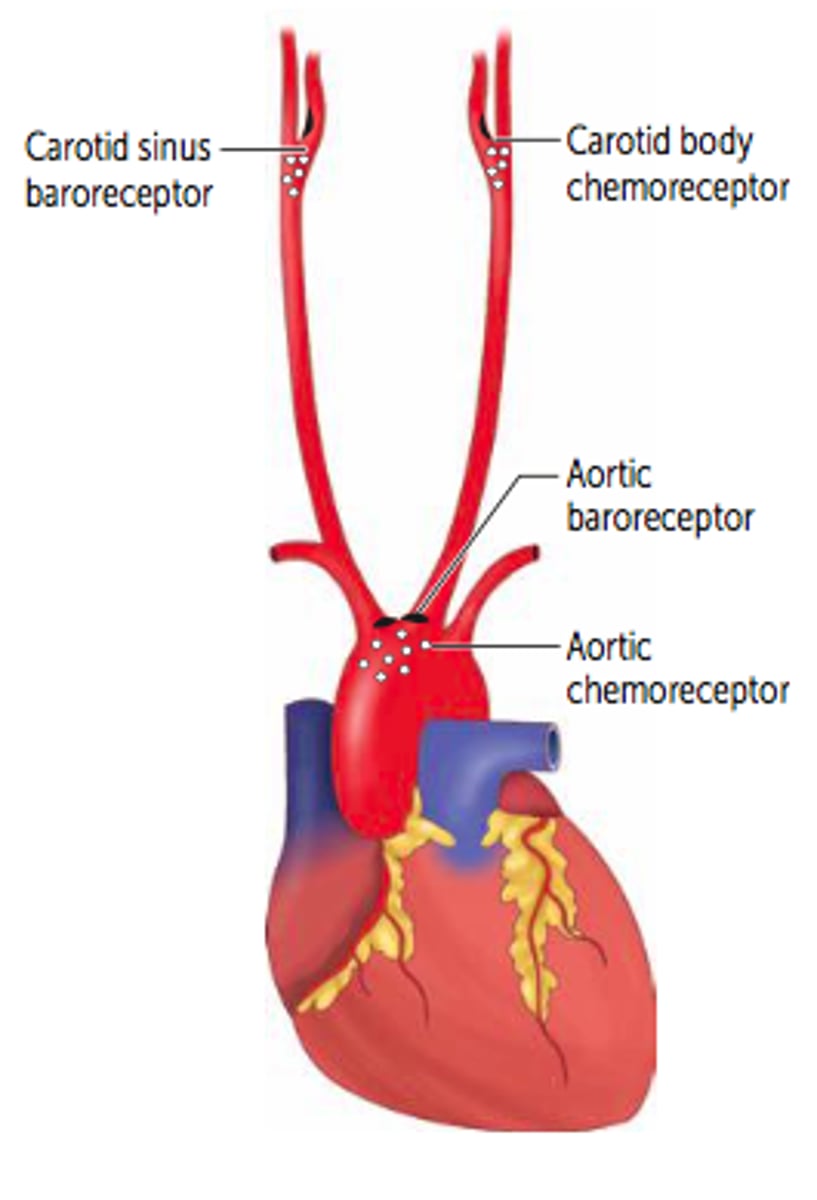
baroreceptors
detect changes in blood pressure
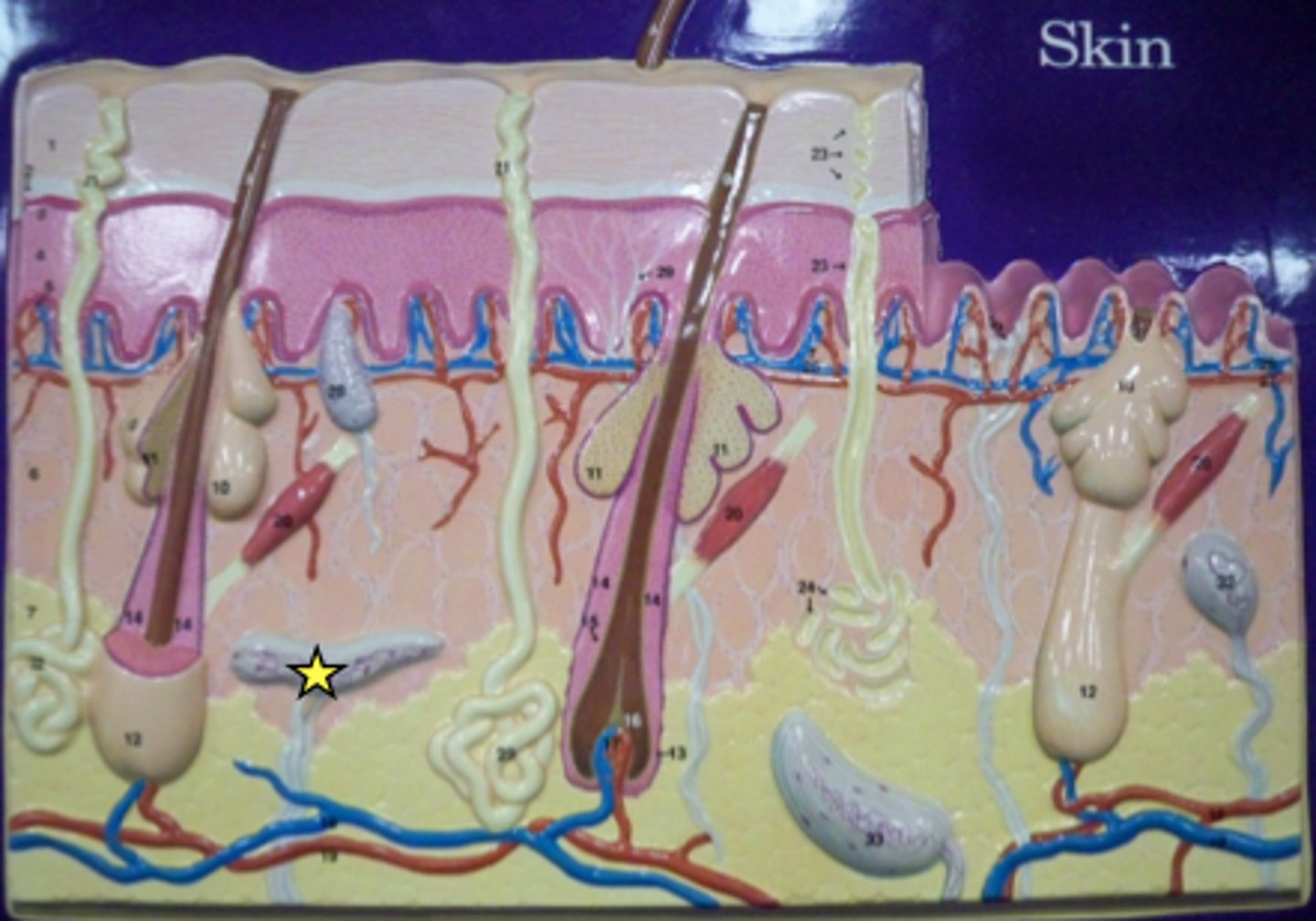
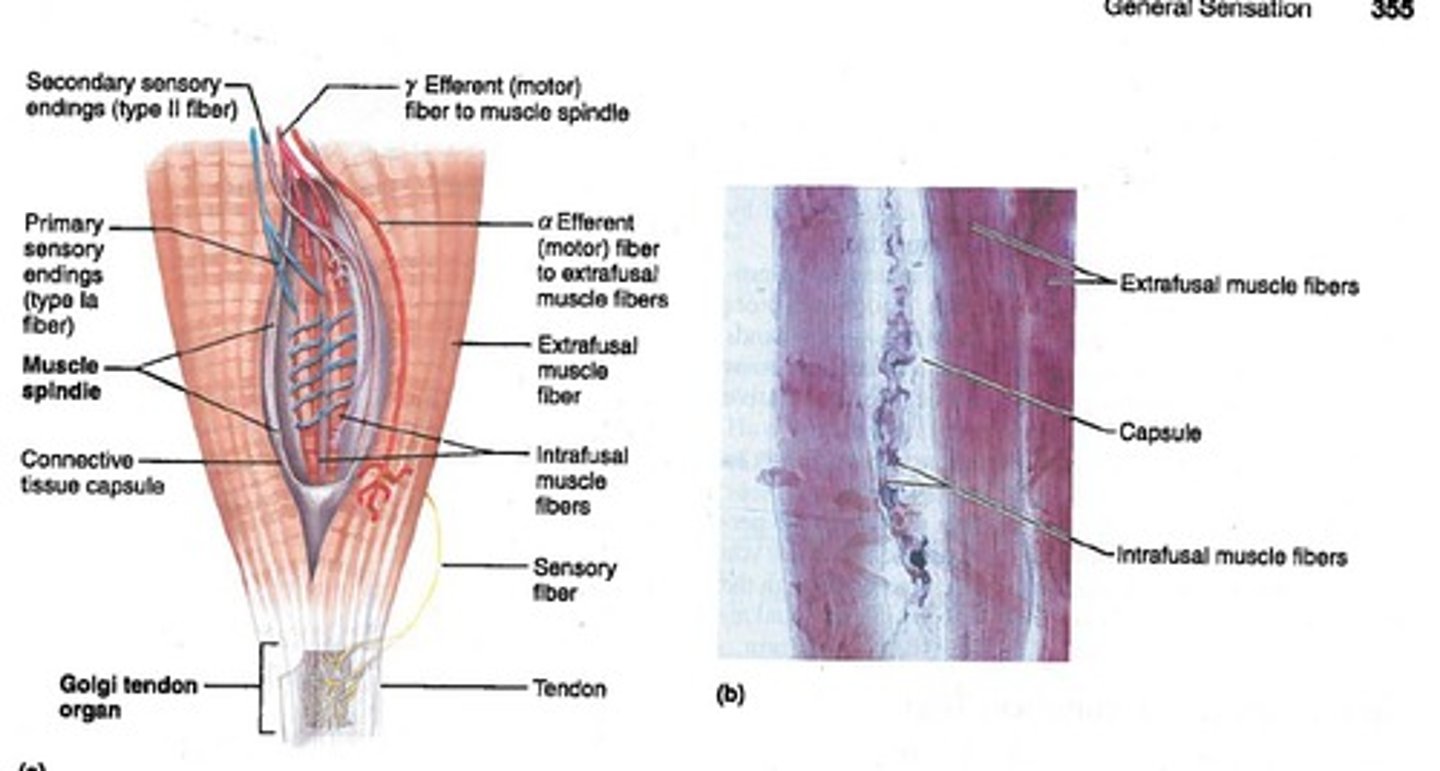
proprioceptors
monitor body position and include muscle spindles and golgi tendon organs
free / naked dendritic endings
dendrites with no connective tissue wrapping; thermoreceptors and nociceptors
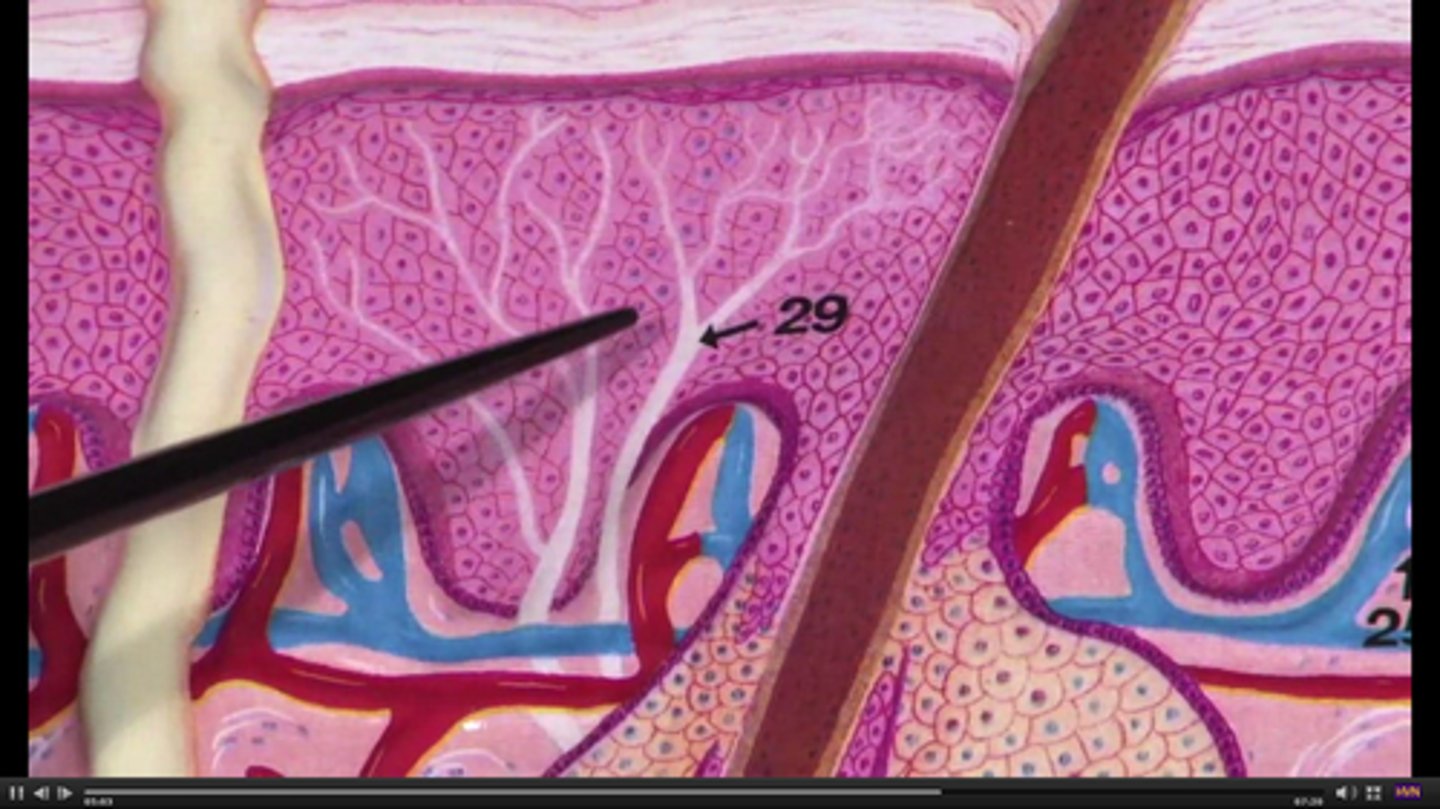
tactile (merkel) discs
function as light touch receptors; located in deeper layers of epidermis
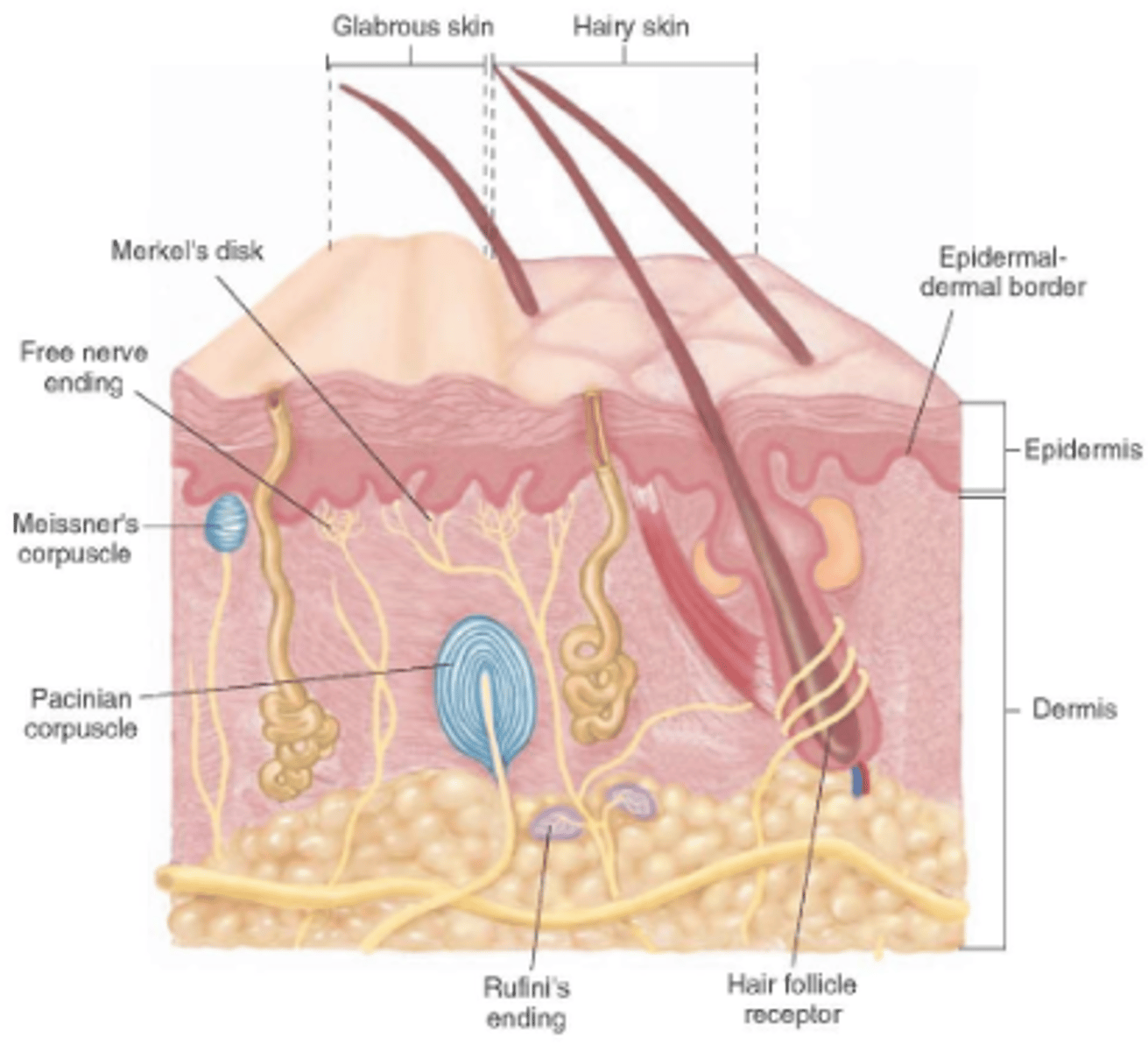
root hair plexus
sensory nerves surrounding the base of each hair follicle and detects the movement of the shaft.
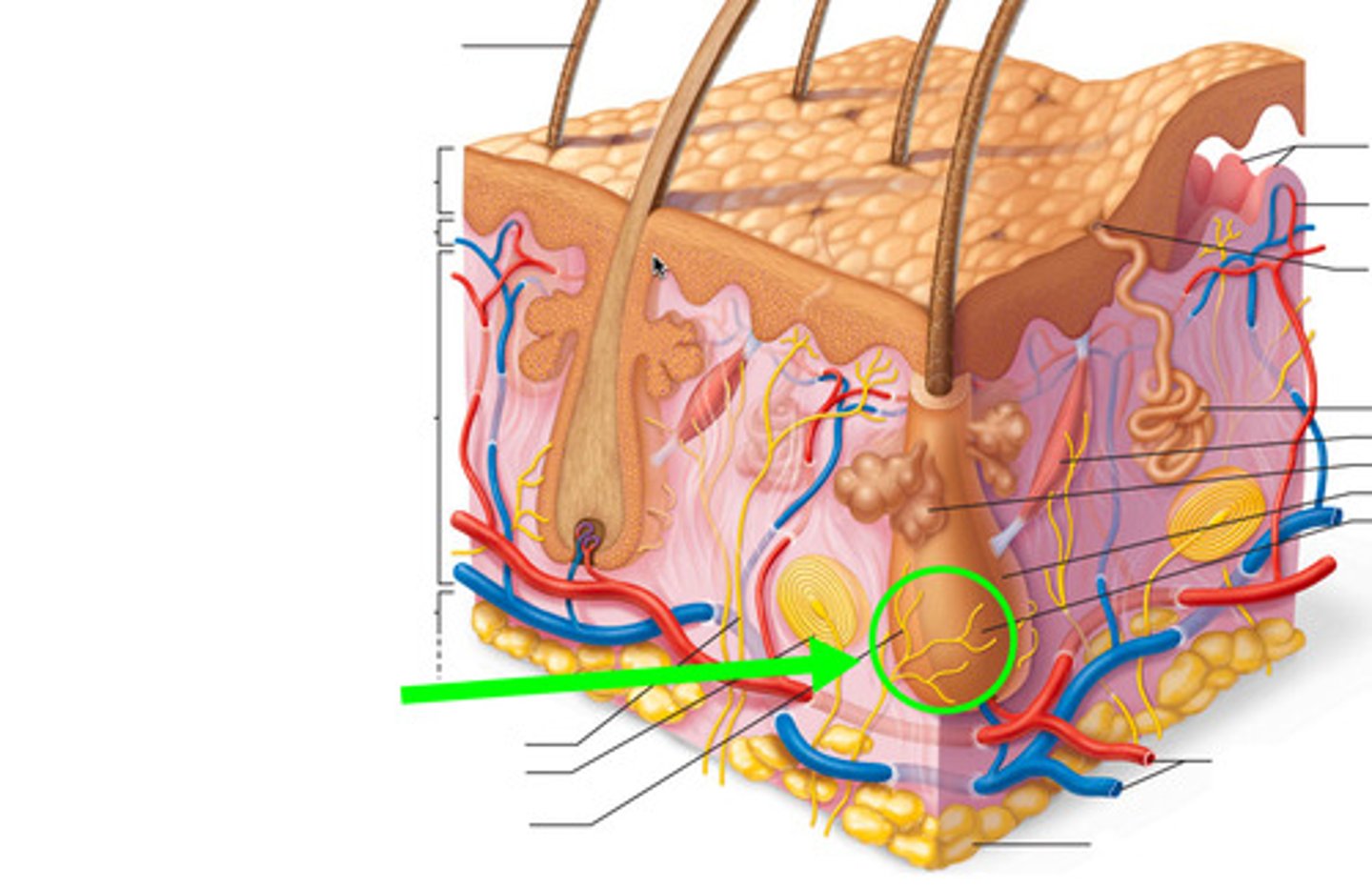
olfaction
sense of smell and is detected by olfactory neurons in the olfactory mucosa
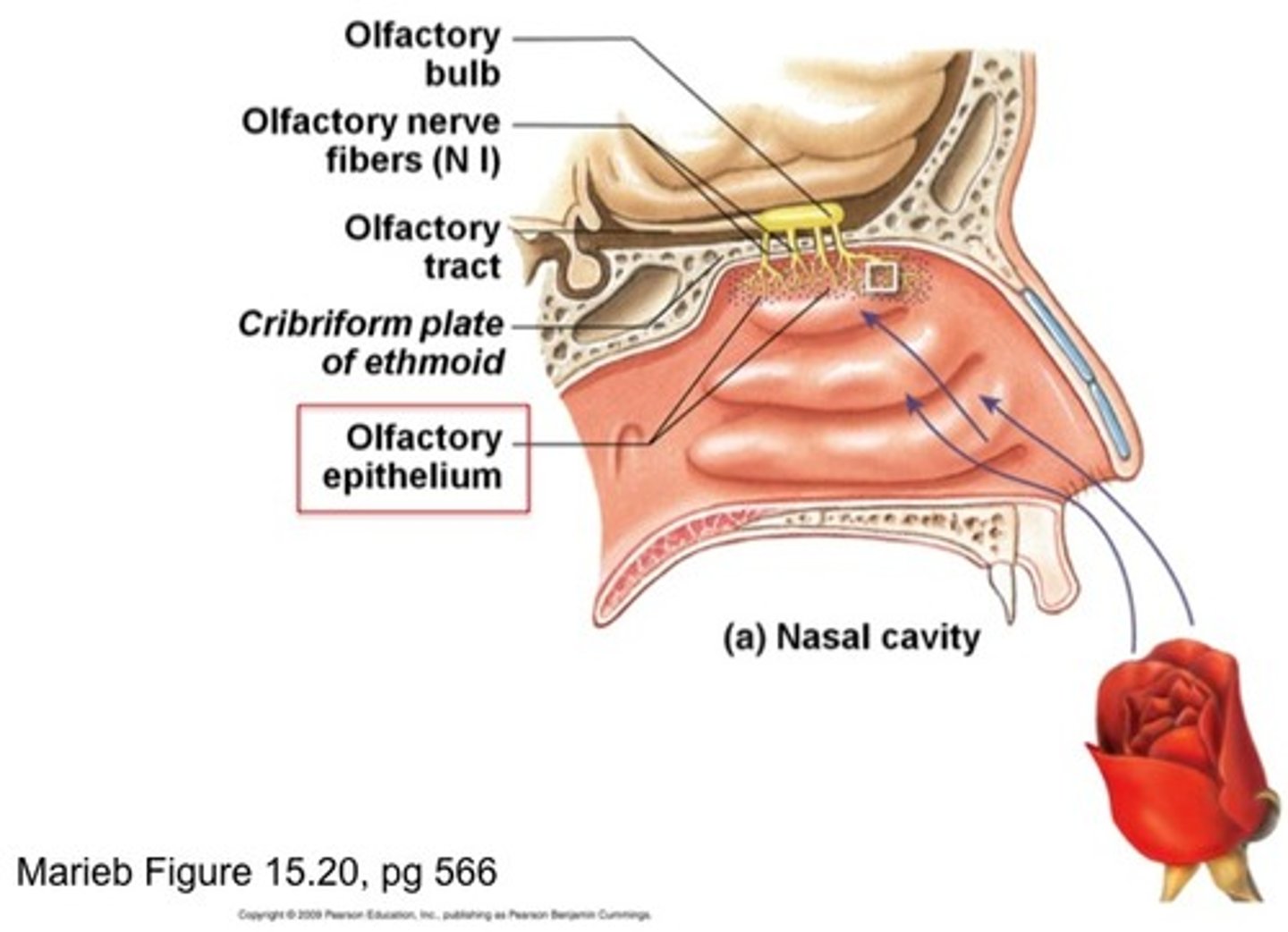
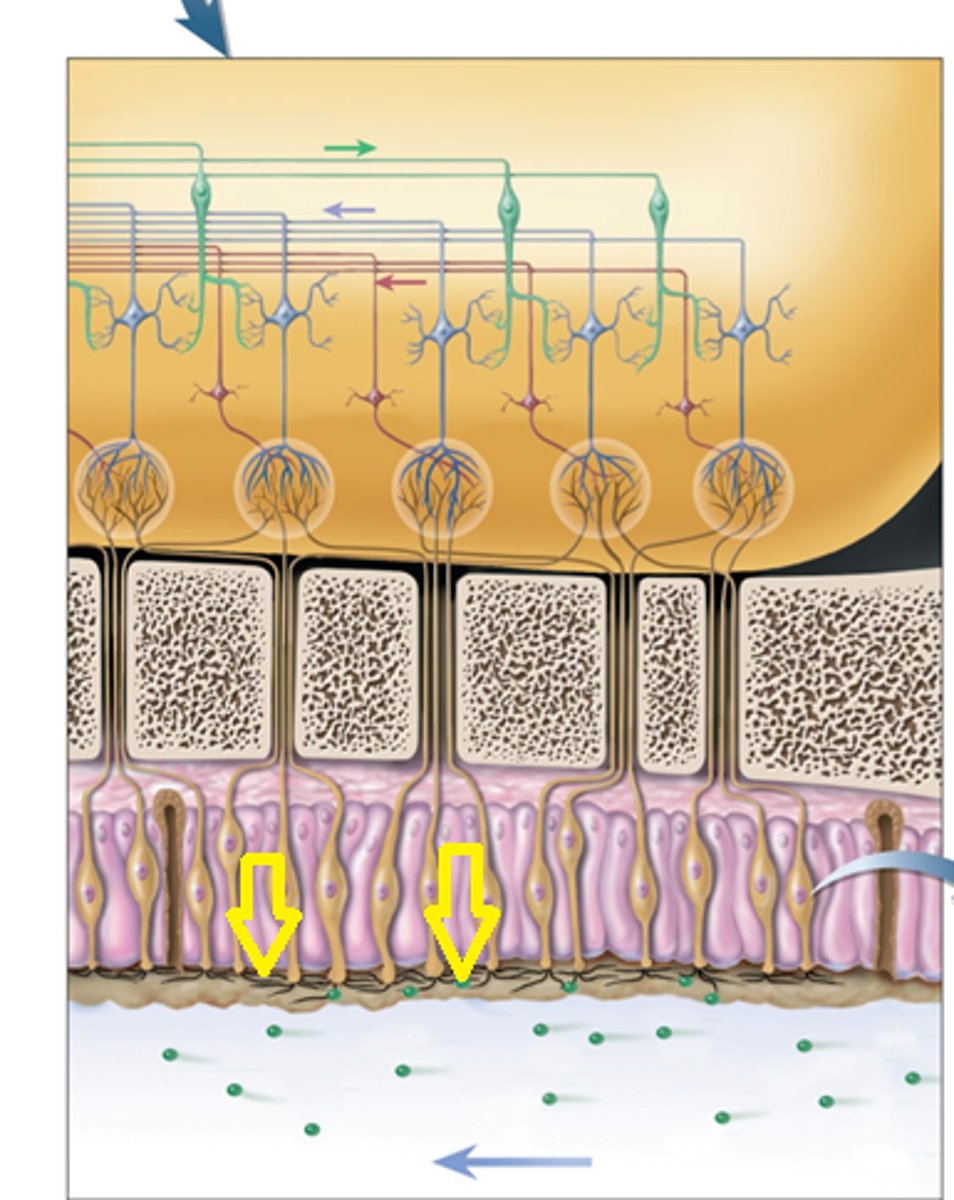
olfactory neurons
receptors for the sense of smell; shaped like bowling pins and contain olfactory hairs
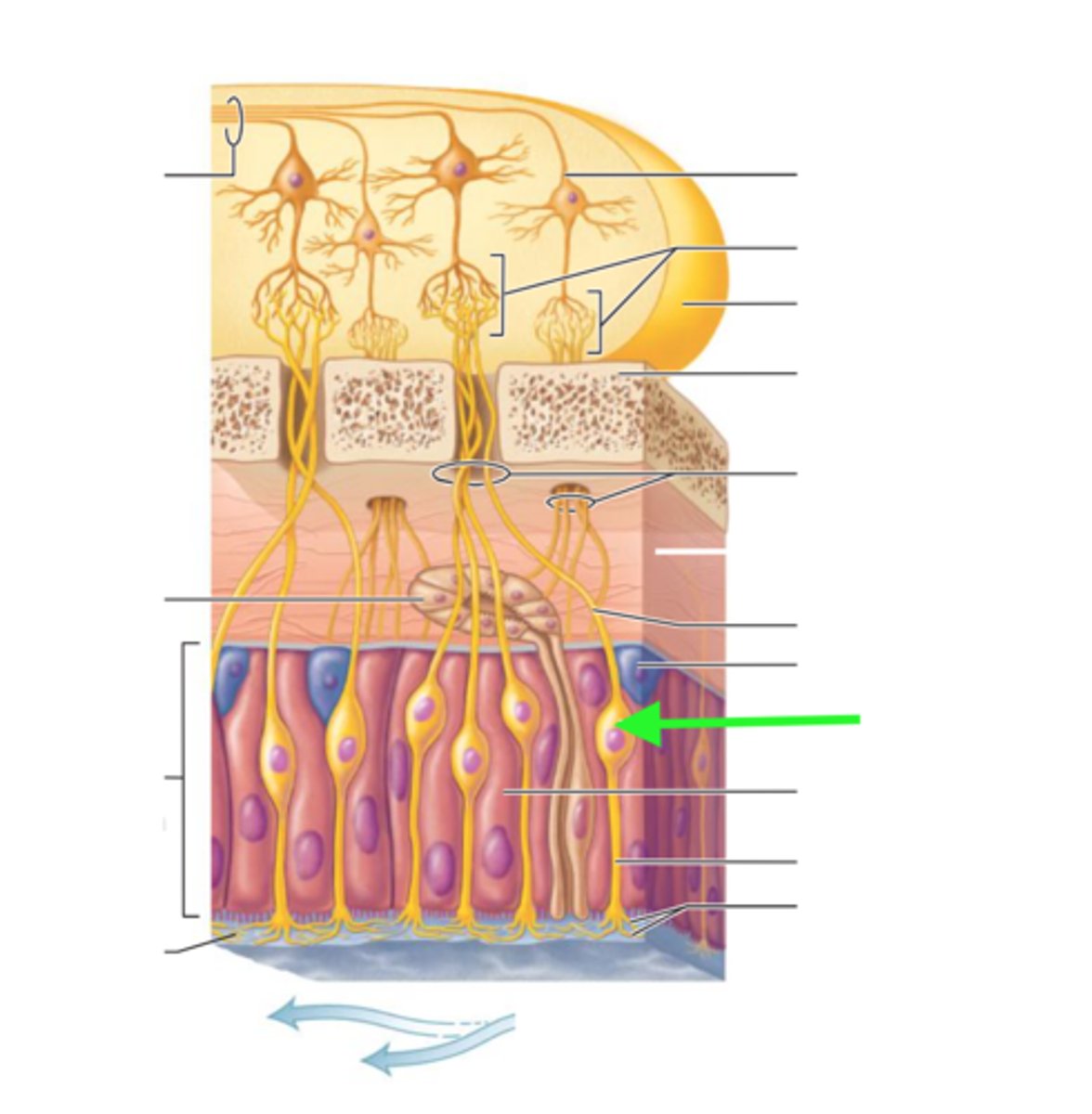
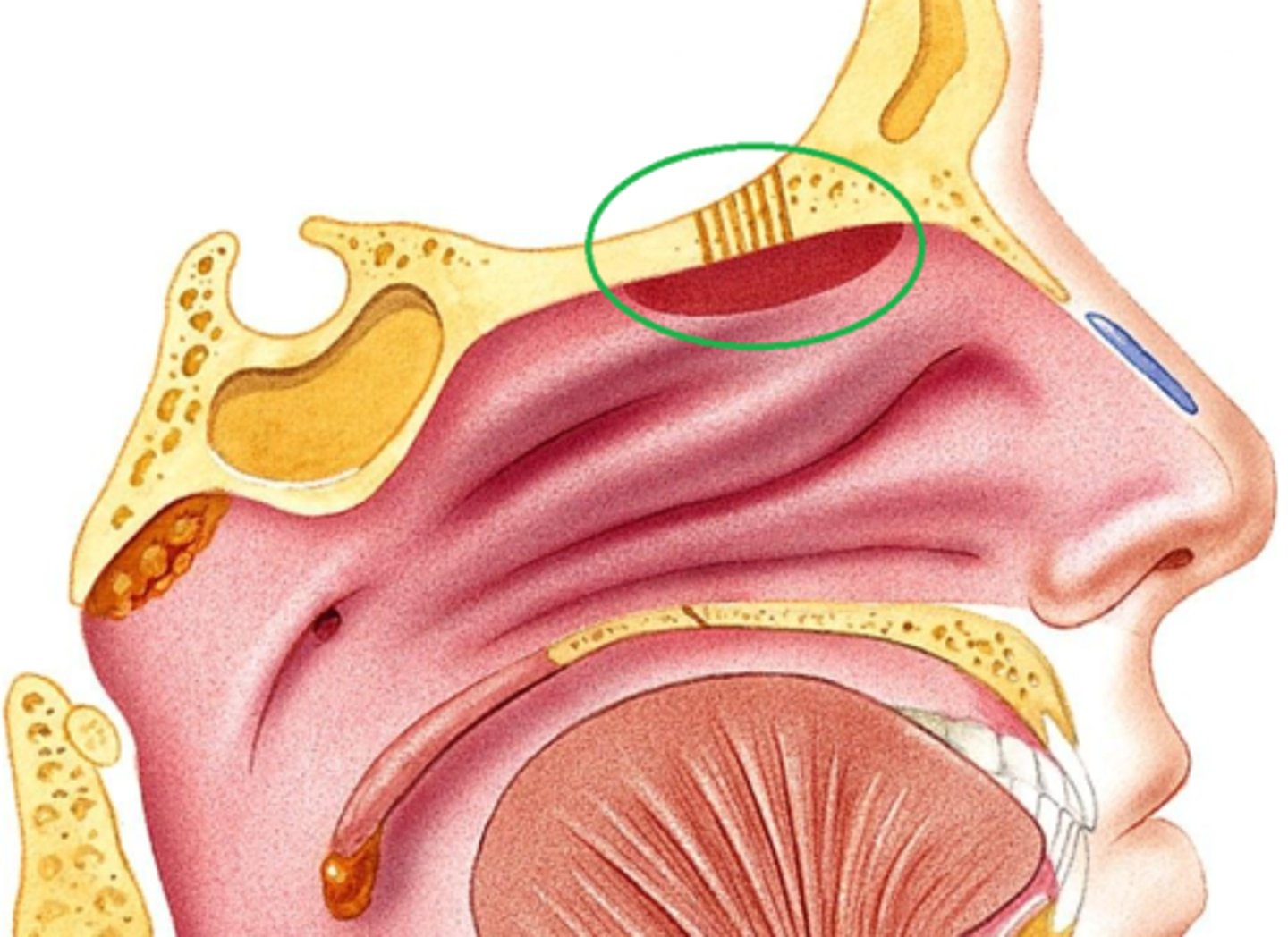
olfactory mucosa
lines the superior nasal cavity and contains smell receptors
olfactory hairs
immobile cilia that have binding sites for odor molecules
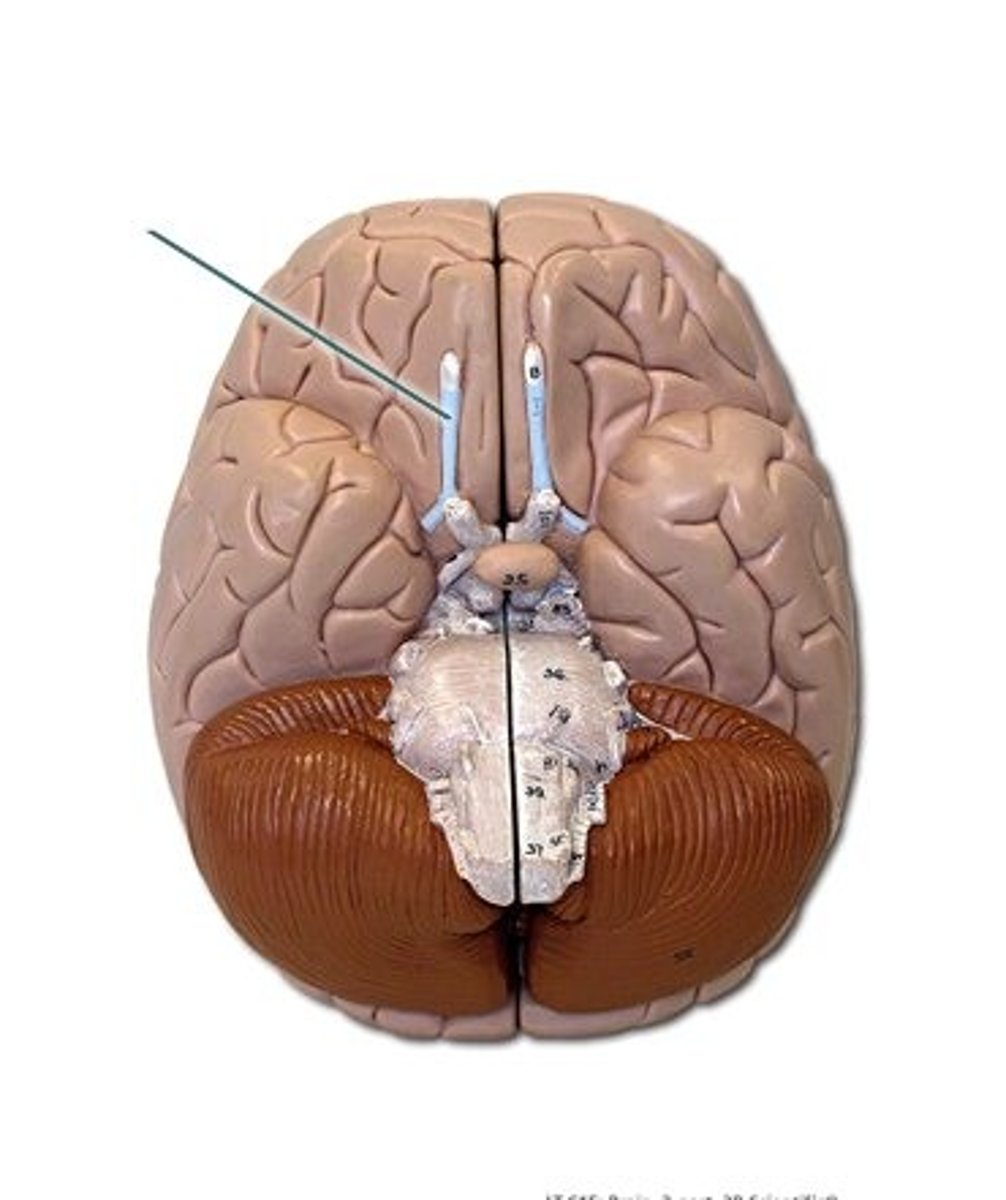
olfactory bulbs
two projections just under the front of the brain that receive information from the receptors in the nose located just below
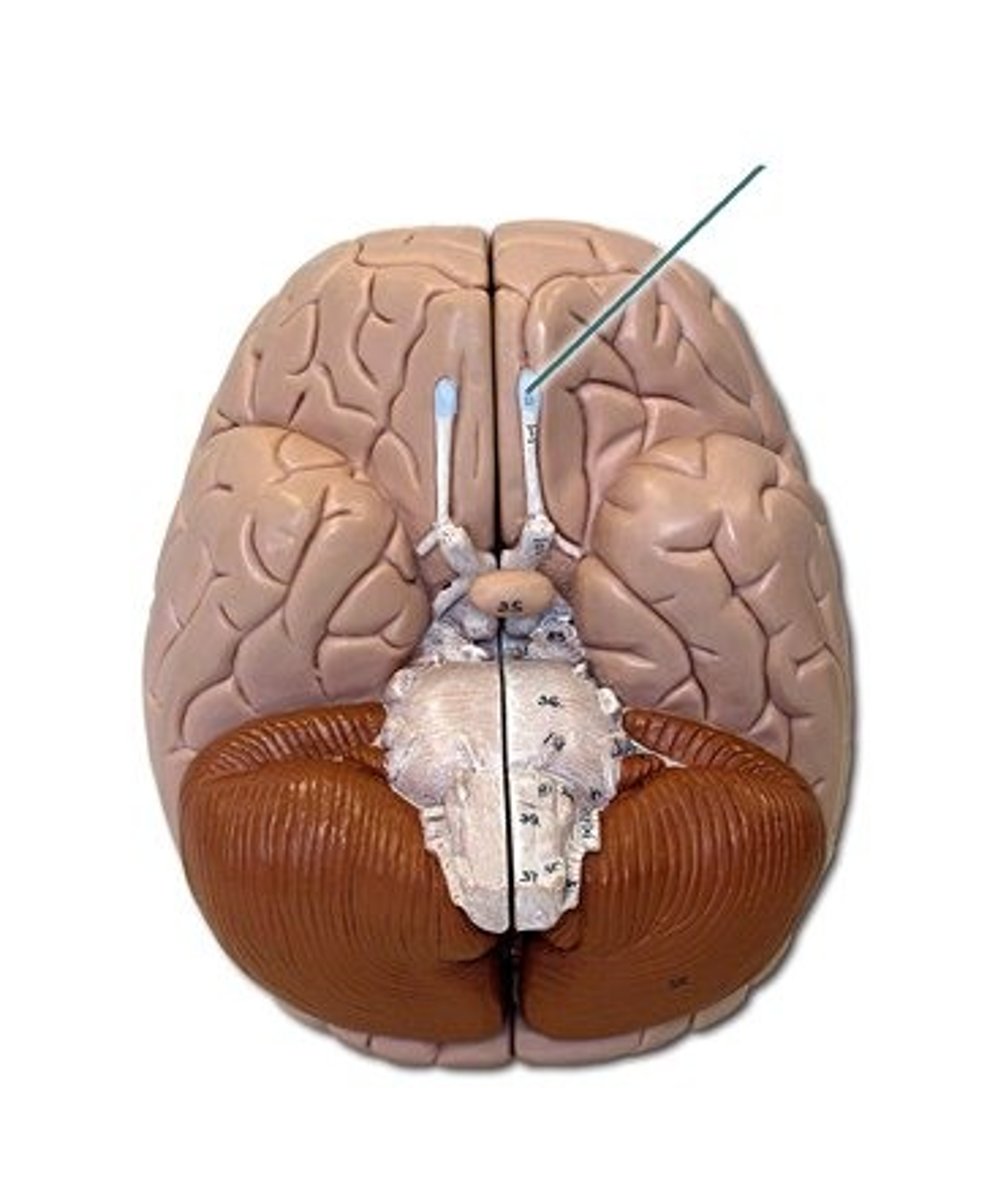
olfactory tracts
a bundle of axons connecting the cells of the olfactory bulb to several target regions in the brain
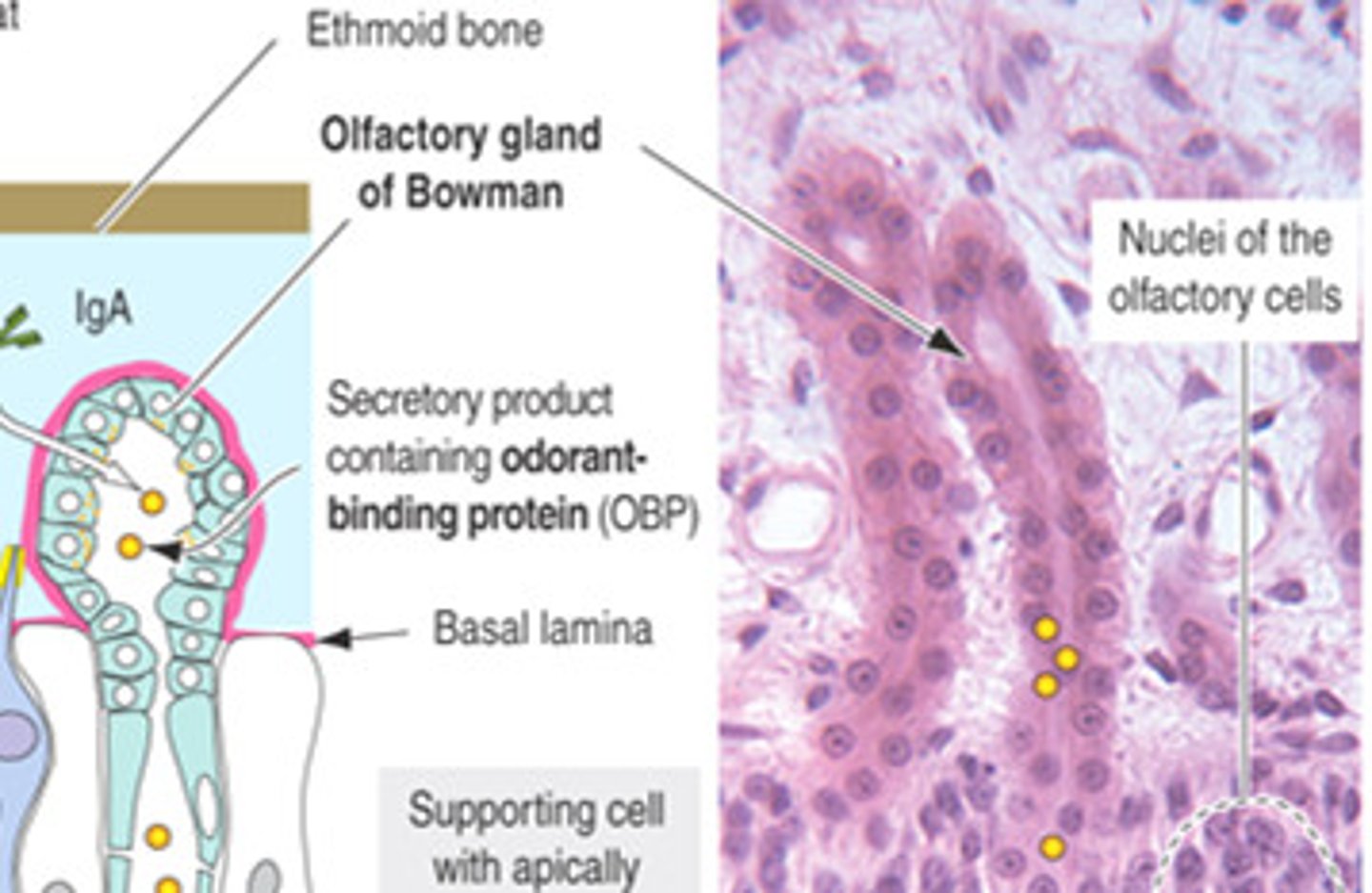
olfactory (bowman's) glands
produce mucus that dissolves odorants so they can stimulate receptors
gustation
sense of taste; begins with chemical stimulation of sensory cells in about 4000 taste buds
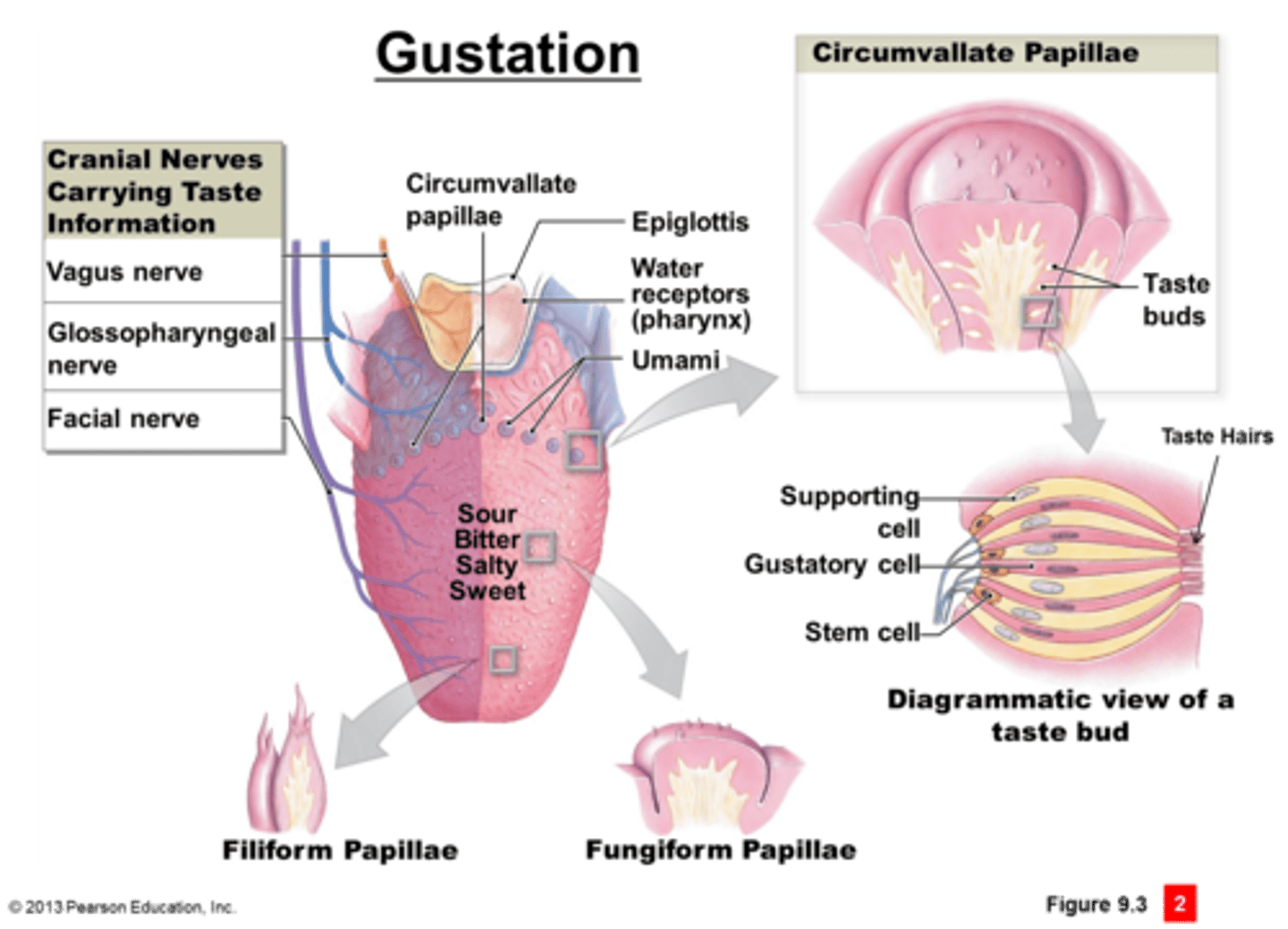
taste buds
sensory organs in the mouth that contain the receptors for taste; most are on the tongue but can also be found on cheeks, soft palate, pharynx, epiglottis
tastants
chemicals that stimulate gustatory receptor cells
lingual papillae
bumps and projections on the tongue that are the sites of the taste buds; four types
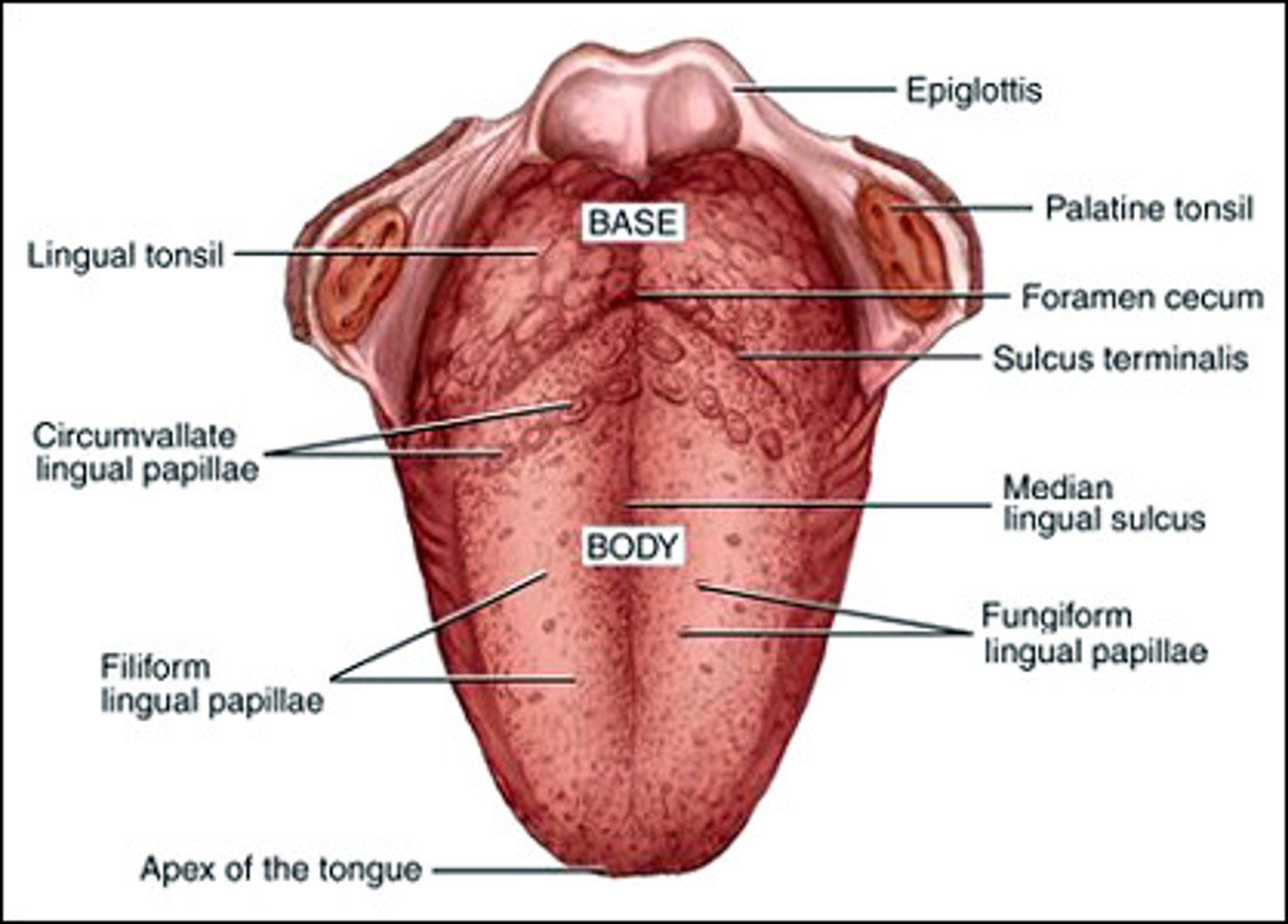
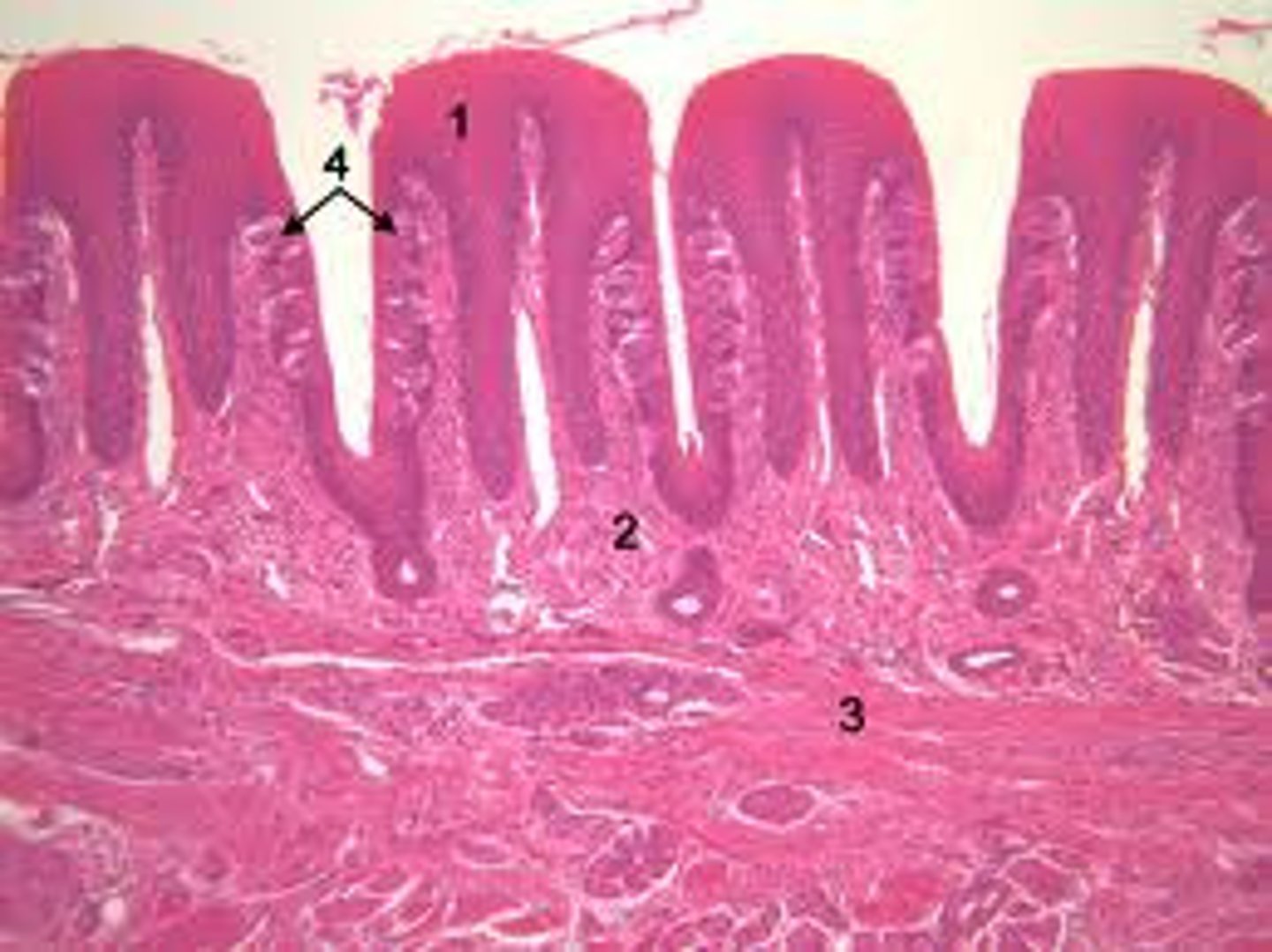
filiform papillae
sharp with no taste buds; most abundant on human tongue and serve in sense of texture of food

foliate papillae
form parallel ridges on sides of tongue about 2/3 of way back from tip; most taste buds degenerate by age 2-3
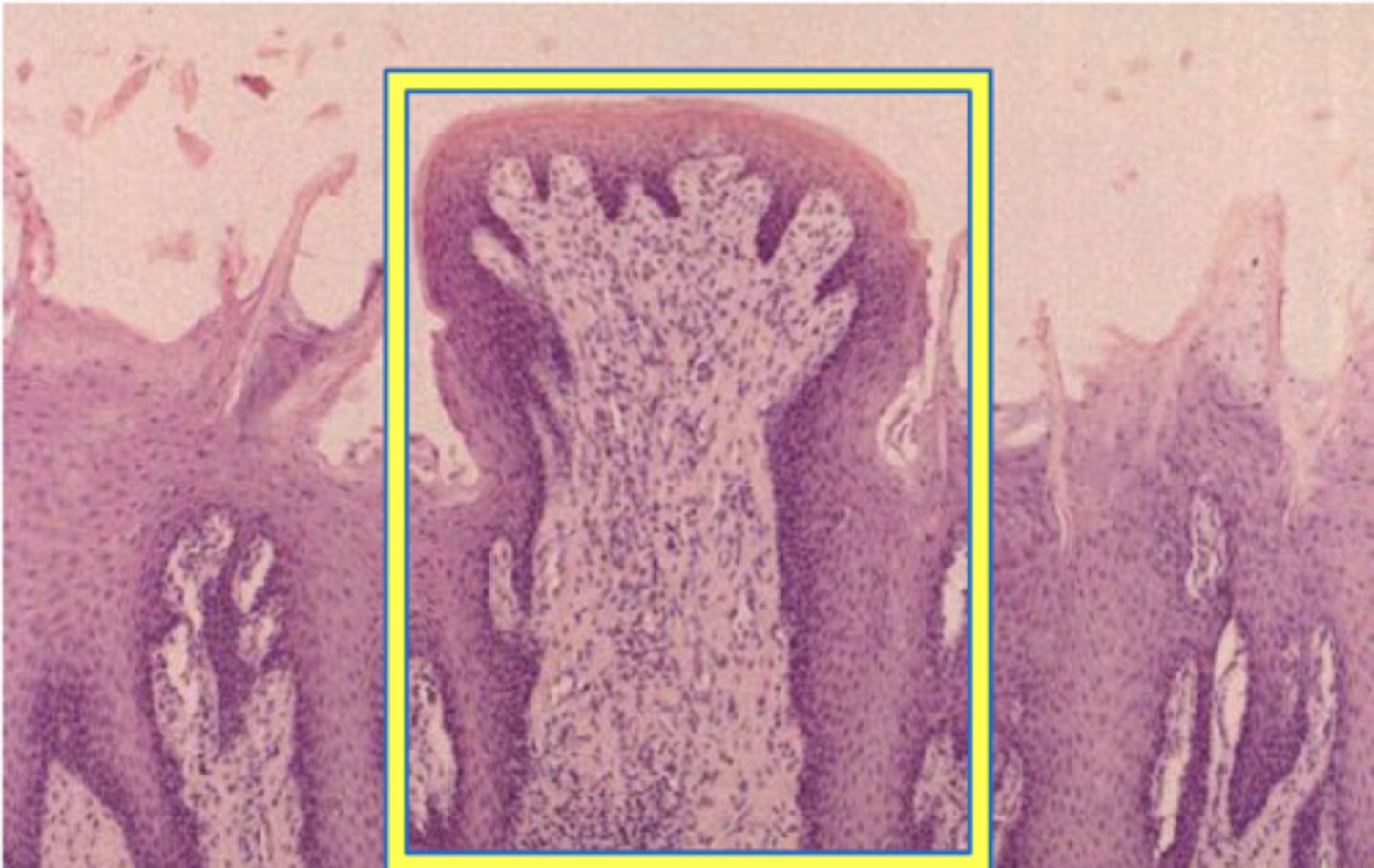
fungiform papillae
shaped like mushrooms and are found at the tip and sides of the tongue; respond to texture
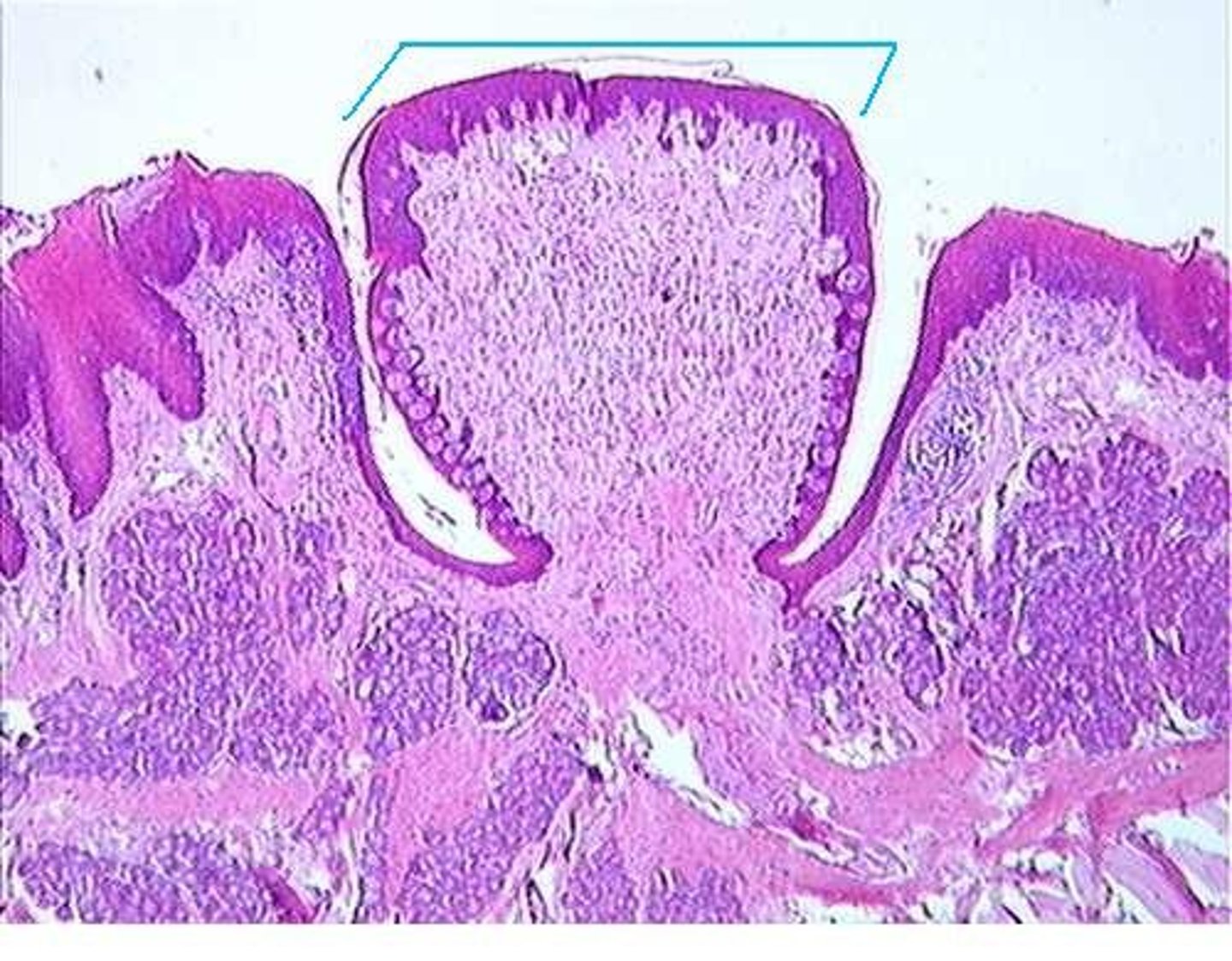
vallate (circumvallate) papillae
large and arranged in a V at the rear of the tongue; only 7 to 12 total but contain up to half of all taste buds (around 250 each)
primary tastants
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami
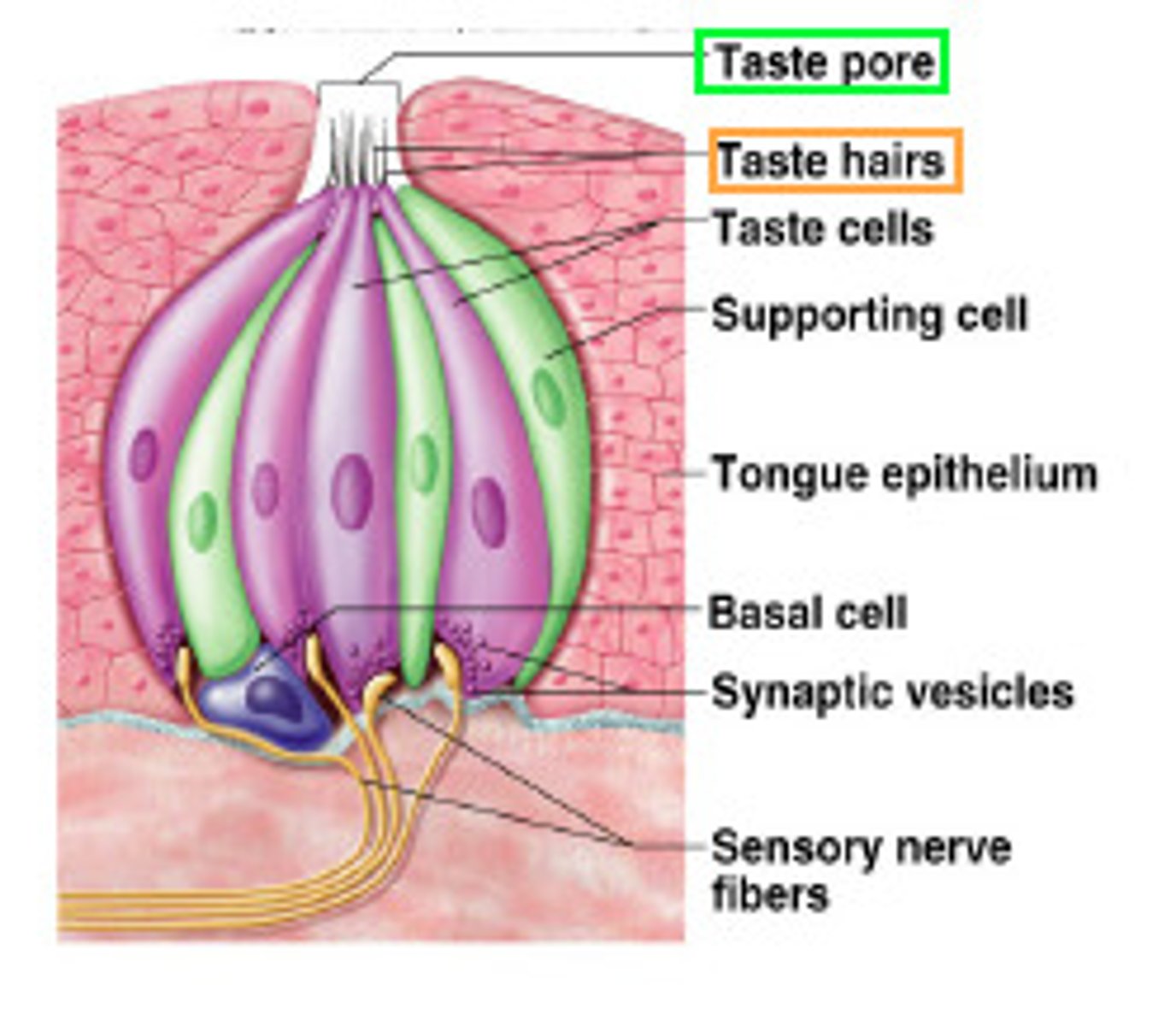
gustatory cells
banana shaped and contain apical microvilli called taste hairs
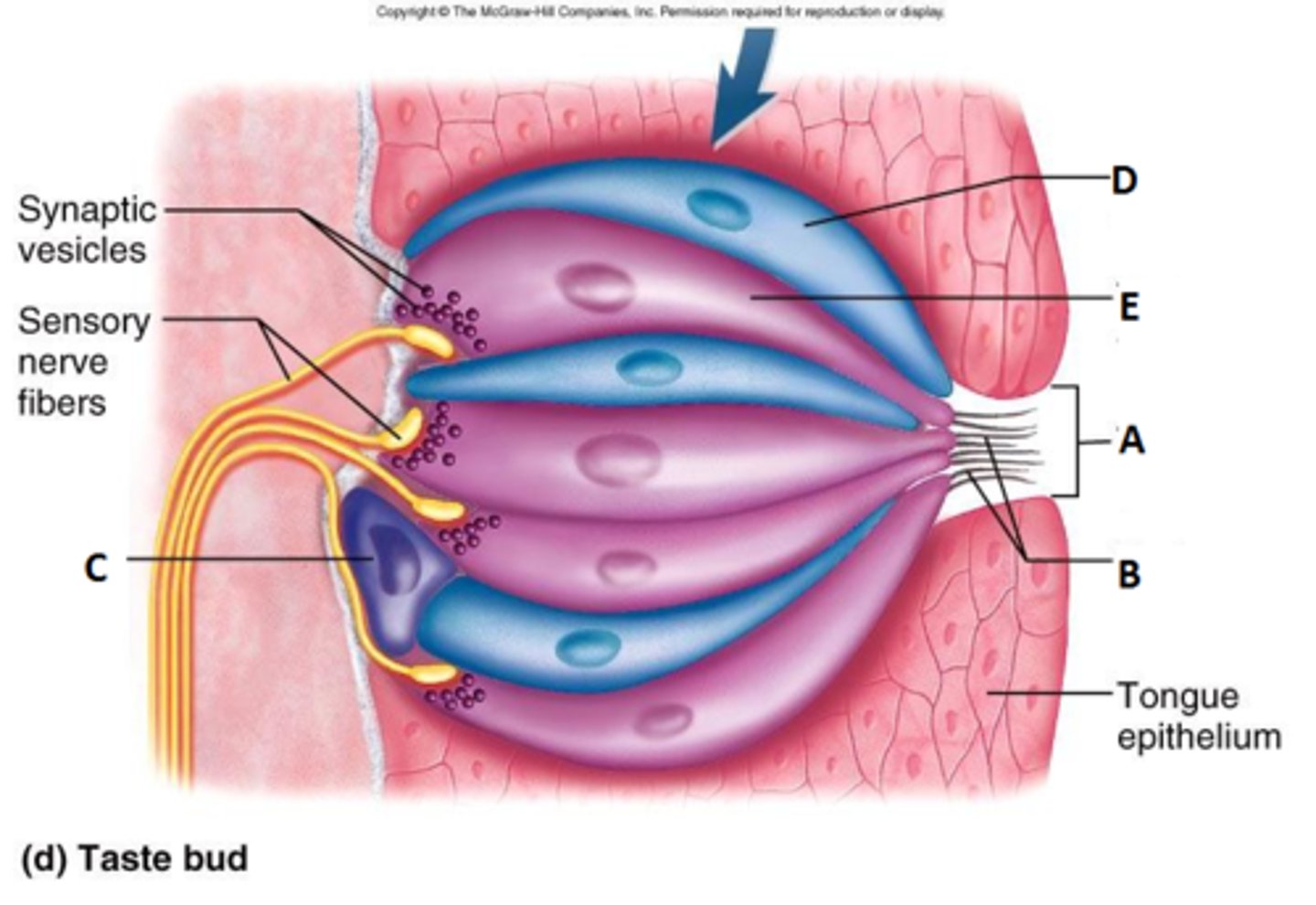
taste hairs (microvilli)
tiny hairs send messages to the brain about how something tastes
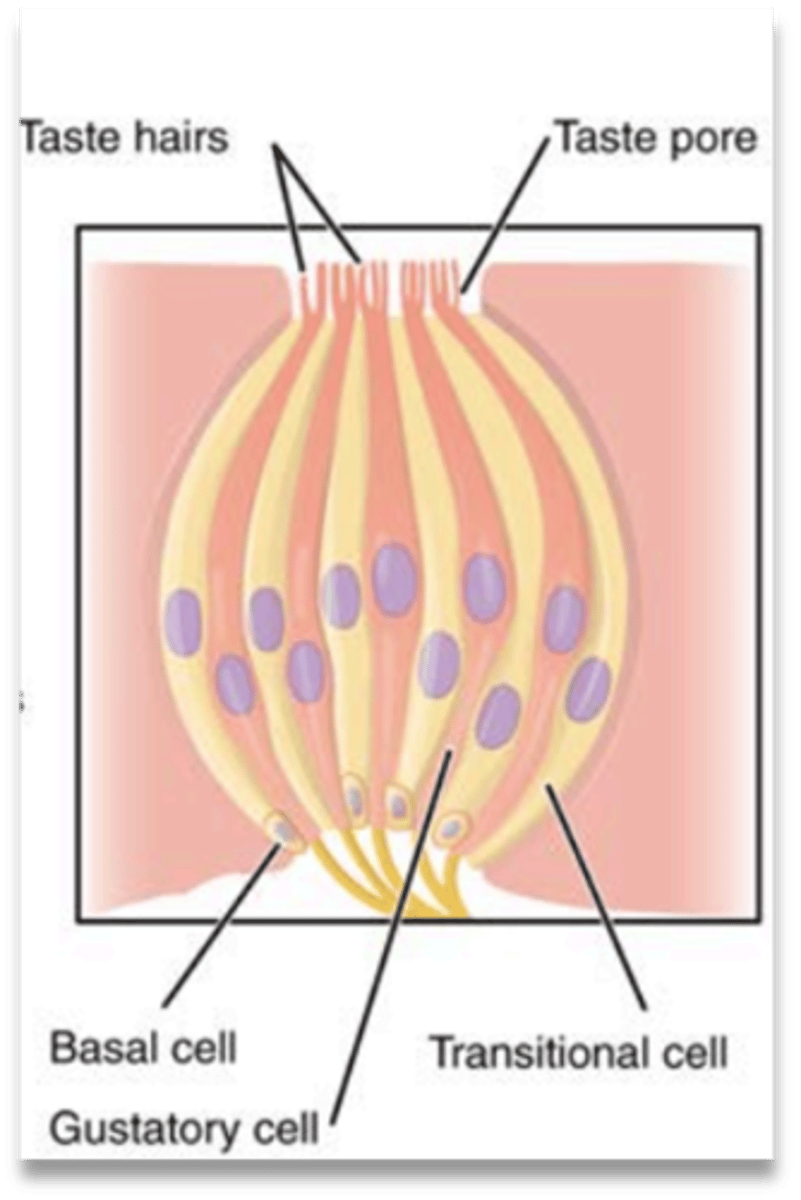
taste pore
opening in taste bud