Gen bio 1, test 2
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/71
Earn XP
Last updated 3:52 AM on 3/14/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
1
New cards
What is the first step of the Cellular Respiration cycle
glycolysis
2
New cards
what does the first step of the cellular respiration cycle do?
glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm, it breaks down glycolysis and as a product makes a 3-carbon sugar called pyruvate. This is then able to enter the mitochondria
3
New cards
what are the products of glycolysis
2 ATP, 2 NADH
4
New cards
What is ATP synthase, describe structure and function
a mechanical enzyme. Protons move through this channel through the inter membrane space, the energy is moved through the rotator shaft which is released and coupled with ADP and a high energy phosphate group to make ATP
5
New cards
What is oxidized and reduced (OIL RIG) in cellular respiration
In cellular respiration, the carbon atoms in glucose are oxidized because they lose H atoms. Oxygen is reduced because it gains H atoms.
6
New cards
what is the third step of cellular respiration, where is it located
the krebs or citric acid cycle, this occurs in the matrix of the mitochondria.
7
New cards
What is the krebs cycle
takes acetyl CoA produced by the oxidation of pyruvate and originally derived from glucose as its starting material, endures a series of reactions and a carrier remains attached to the enzyme and transfers the electrons to the electron transport chain directly. This process is made possible by the localization of the enzyme catalyzing this step inside the inner membrane of the mitochondrion.
8
New cards
what does the Krebs cycle produce?
two molecules of carbon, three molecules of NADH, one molecule of FADH2 and one molecule of ATP or GTP
9
New cards
what is the last step of cellular respiration and what does it do?
the Electron Transport Chain, this occurs in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. First NADH gives up electrons which gives it back to NAD+. then NAD+ can either be used for glycolysis or the krebs cycle. Then the high energy electrons are picked up by complex 1 which accomplished the movement of protons from the matrix to the inter membran. the lipid Q transfers the electron to the other cytochromes until it reaches cyto. A which picks up protons to join that electron to produce H2O
10
New cards
What is anaerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration is respiration using electron acceptors other than molecular oxygen.
11
New cards
what is alcohol fermentation
Alcoholic fermentation takes place in the cytosol of the cell, and releases the energy from glucose molecules into useable cellular energy called ATP. Alcoholic fermentation also creates ethanol (an alcohol) as a waste product, from which the process alcoholic fermentation gets its name
12
New cards
what is lactic acid fermentation in muscle cells
we are able to convert pyruvate into lactate, this only occurs if the electron transport chain is working at its maximum rate. B/c of this alot of pyruvate builds up and gets converted temporarily to lactate so it can be converted to NAD+
13
New cards
Describe Lactic Acid Fermentation in RBC’s
Pyruvate is converted into lactate since there are no mitochondria, the lactate is used to make 2 ATP per molecule and then released into the blood plasma which will travel to the liver
14
New cards
How can cellular respiration be inhibited
1. many poisons can bind to the electron transport chain for example, cyanide can bind to cytochrome A easily which stops the passing of electrons
2. DNP, ( used to be a diet pill) has the ability to form channels in the innermitochondrial membrane that would make it leaky to protons.
15
New cards
what is Brown fat
mainly seen in babies but it has a lot of mitochondria and lots of capillaries. Uses stored fat to generate heat rather than store excess energy.
16
New cards
Why do babies need a lot of brown fat?
1. Since they can’t shiver they have a lack of thermal insulation.
2. They have the inability to move away from cold areas and have an inability to use additional ways to keep warm
3. Nervous system is not fully developed and doesn’t respond properly to cold
17
New cards
How are proteins used to make ATP?
Proteins are converted to amino acids which are then eithier used for protein synthesis or they’ll be deanimated and used for ATP synthesis in the Krebs cycle
18
New cards
How are Lipids used to make ATP?
( also known as fatty acids) fats and phospholipids are broken down into glycerol or fatty acids, glycerol will then enter glycolysis and go through that process to make ATP while fatty acids will be converted to Acetyl CoA which is used in the Krebs cycle
19
New cards
what is the relationship between energy and wavelength
Energy is inversely proportional to wavelength
20
New cards
Would you expect a plant to grow well in only green light?
No, plants would not grow well in the green light. Plants appear to be green because they reflect this wavelength of light. Thus, plants need to encounter light except green to initiate photosynthesis.
21
New cards
In the fall leaves “change color” what do you think accounts for this
In the fall, plants slow down and finally stop production of the chlorophylls before the other \n pigments. In addition, the chlorophylls are broken down faster. As a result, we see the yellow, \n orange, red, and sometimes pink pigments. We may see a transition as these pigments break \n down at different rates.
22
New cards
Why do some pigments move up the paper at a faster rate than others?
the pigments move with the solvent. Some move faster than others because some have more polarity than others, the more polar it is the more it will stick to the cellulose in the paper making it slower
23
New cards
The spinach leaf looks green, but your chromatogram demonstrated that other pigments are in the leaf as well. Why can you not readily see the other pigments in the leaf?
The two chlorophylls are more abundant and reflect more light (are brighter).
24
New cards
what is the importance of the Chloroplast
helps maintain the leaf’s structure. Has an outer layer that secretes a wax to waterproof it, this prevents water loss and the exchange of gasses which is essential to photosynthesis
25
New cards
What is the stomata
tiny pores where the plants breathe takes in carbon dioxide, and releases oxygen. It also assists in monitoring the movement of water via transpiration.
26
New cards
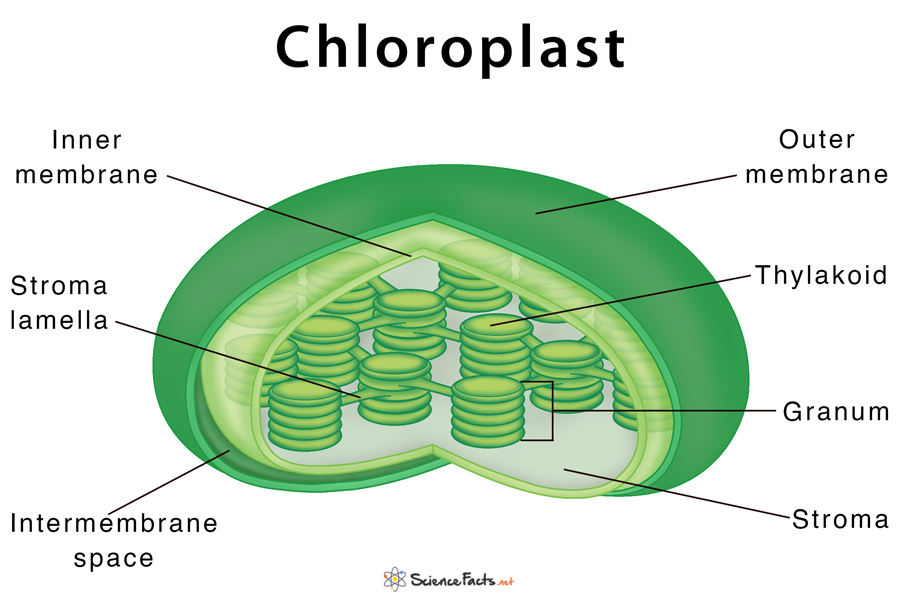
name what is located in the thylakoid space, the thylakoid membrane and the Inner membrane
Thylakoid Space- a continuous fluid in the thylakoid
Thylakoid membrane- Where the photosynthetic pigments are
Inner membrane- Protects the Stroma from the cytosol
Thylakoid membrane- Where the photosynthetic pigments are
Inner membrane- Protects the Stroma from the cytosol
27
New cards
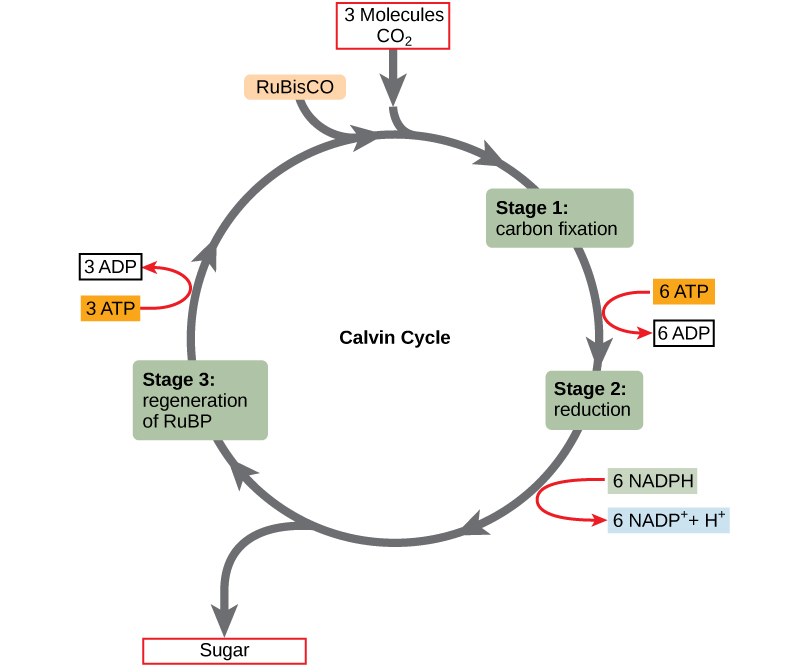
What is the goal of the calvin cycle
a progression of reactions that happens in the stoma of chloroplasts in a plant cell. The chemical reactions convert carbon dioxide into glucose with the assistance of ATP and NADPH to overall make sucrose
28
New cards
describe the steps of the calvin cycle
Rubisco takes co2 and adds it to a 5-carbon sugar ( the carbon of co2 is being fixed) with each cycle it spits out 1 3-carbon sugar (G3P) this then gets connected to other 3-carbon sugars to make glucose and fructose which are combined to make sucrose (reducing CO2)
29
New cards
What is carbon Fixation
Carbon fixation is the process of adding a carbon to a 5-carbon sugar. It is the first step of the Calvin \n Cycle and involves the enzyme rubisco.
30
New cards
How do plant cells that lack chloroplasts make ATP?
They would make ATP through the electron transport chain moving protons from the mitochondrial \n matrix to the inner membrane space. The protons would be allowed to move through ATP synthase and \n this would create ATP inside the matrix.
31
New cards
Describe the first step of light reactions
1. photooxidation occurs in photosystem 2, it takes the electrons from water to replace the ones that have been excited and then moves them to the primary acceptors
32
New cards
Describe the second and third step of light reactions
2. The electrons are passed to the plastoquinone ( a mobile carrier) which passes the high-energy electrons and moves the proton against the gradient
3. Then photosystem 1 passes on the high-energy electron onto a coenzyme of high-energy electrons. this makes NADP to NADPH for the calvin cycle (makes o2 during the first step in photosystem 2)
33
New cards
what is S-phase in the cell cycle
(synthesis of DNA) we get an exact replica of each chromosome made
34
New cards
what occurs in G2 of the cell cycle
They do proof reading to make sure all the chromosomes are the same as well as protein synthesis
35
New cards
what occurs in G1 of the cell cycle
biosynthesis, prepares to make 2 cells which makes it almost double in size
36
New cards
what are the 2 checkpoints in G1 and G2
to pass the G1 checkpoint the cell has to almost be double to size and has to have room to grow. To pass the G2 checkpoint it needs to go through proof reading and if it has to many mistakes/mutations it’ll be sent to die.
37
New cards
Why are these checkpoints needed (G1 and G2)
is a cell passes through the G2 checkpoint without being properly proofread it could potentially produce cells with mistakes in their DNA
38
New cards
What happens after the G2 checkpoint, describe what happens
it then enters prophase the longest phase of mitosis. the chromosomes begin to condense, the mitotic spindle begins to form and the nuclear envelope begins to move away from the chromosomes.
39
New cards
name the cell cycle phases in order.
1.G0
2. G1
3. S-phase
4. G2
5. mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase)
2. G1
3. S-phase
4. G2
5. mitosis (prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase)
40
New cards
what happens in metaphase (cell cycle)
all the chromosomes are aligned in the center plane of the cell

41
New cards
what happens in anaphase (cell cycle)
The kinetochore fibers shorten and non kinetochore fibers lengthen to move chromosomes to opposite poles.
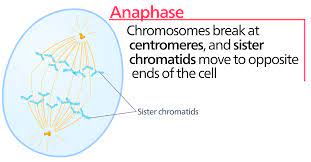
42
New cards
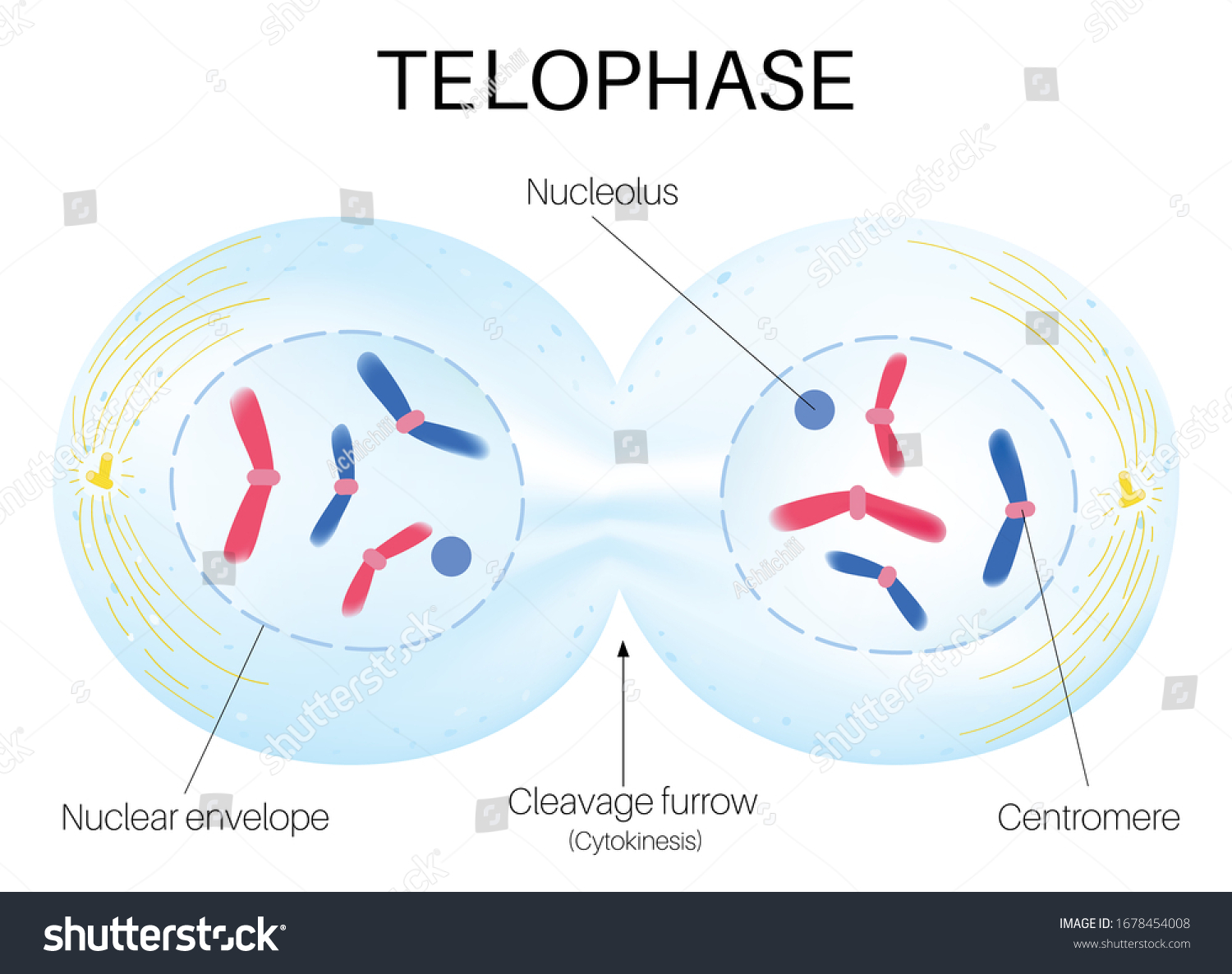
what happens in Telophase (cell cycle)
Dissolves the spindle apparatus, decondensed DNA, and reforms the nuclear envelope.
43
New cards
what is meiosis
its purpose is to generate haploid genetically unique gammates. ( to produce unique offspring
44
New cards
What happens in prophase 2 of the life cycle
the chromosomes condense, the nuclear envelope pulls away so that the apparatus spindle can have access to chromosomes.
45
New cards
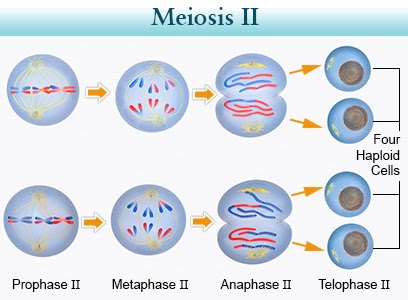
What happens in Meiosis 2 ( life cycle)
the chromosomes get attached to the spindle apparatus which will grow and line them up on the center plane. Then they are separated at the centromere making 4 genetically unique cells
46
New cards
how many chromosomes does a human cell have in prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase
prophase- 46 metaphase-46 anaphase-92 telophase-92
end of mitosis-46
end of mitosis-46
47
New cards
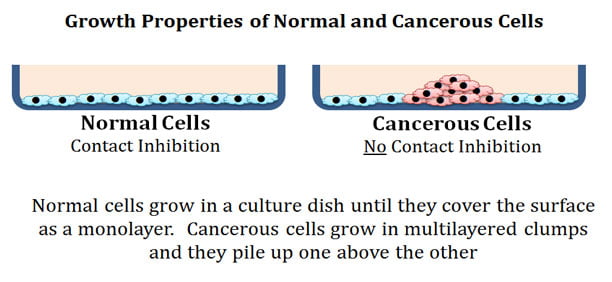
what is contact inhibition
Contact inhibition enables noncancerous cells to cease proliferation and growth when they contact each other
48
New cards
what are fibroblast cells and why are they important
Fibroblasts play a critical role in normal wound healing.These cells produce the proteins that hold vessels, tissues, muscles, and other structures in place
49
New cards
What is mendels blending hypothesis
stated that the offsprings traits are an average of its parents, which isn't true
50
New cards
What is mendel’s law of segregation
only one of the two gene copies present in an organism is distributed to each gamete (egg or sperm cell) that it makes, and the allocation of the gene copies is random.
51
New cards
What is mendels law of independent assortment
the alleles of two (or more) different genes get sorted into gametes independently of one another. In other words, the allele a gamete receives for one gene does not influence the allele received for another gene.
52
New cards
What is complete dominance, give an example
a condition where in the dominant allele completely masks the effect of the recessive allele. EX: Brown eyes are a trait that exhibits complete dominance: someone with a copy of the gene for brown eyes will always have brown eyes. Blue eyes, on the other hand, are recessive: if a copy of the gene for brown eyes is present, the blue-eyed gene will be completely masked
53
New cards
What is incomplete dominance
e occurs when neither trait is truly dominant over the other. This means that both traits can be expressed in the same regions, resulting a blending of two phenotypes. EX:If a white and black dog produce a gray offspring,
54
New cards
What is co-dominance
exemplified by a plant that bears flowers with two distinct color phenotypes. For instance, a white-spotted red flower could be caused by a cross between a red flower and a white flower.
55
New cards
What is epistasis
The effect of one gene being dependent on the presence of one or more 'modifier genes'. Epistasis occurs when one gene interacts with another to affect its function. EX: a man may have the gene for a widows peak but could also have the gene for being bald so the widows peak gene isn’t important because it depends on the bald gene
56
New cards
Describe the role of the Y chromosome in sex determination. Distinguish between sex \n determination and sexual identity.
The Y chromosome contains a "male-determining gene," the SRY gene, that causes testes to form in the embryo and results in the development of external and internal male genitalia. Sex determination is solely based on the X and Y chromosomes ( female and male genitalia) while sexual identity refers to the total expression of who you are as a human being
57
New cards
how does tay sachs disease exhibit incomplete dominance
incomplete dominance is when a dominant allele, or form of a gene, does not completely mask the effects of a recessive allele. In this case, the normal allele for the gene produces an enzyme responsible for breaking down lipids. A defective allele for the gene results in the production of a nonfunctional enzyme.
58
New cards
give an example of incomplete dominance
A child heterozygous for a recessive disease has a phenotype unlike either of his homozygous parents
59
New cards
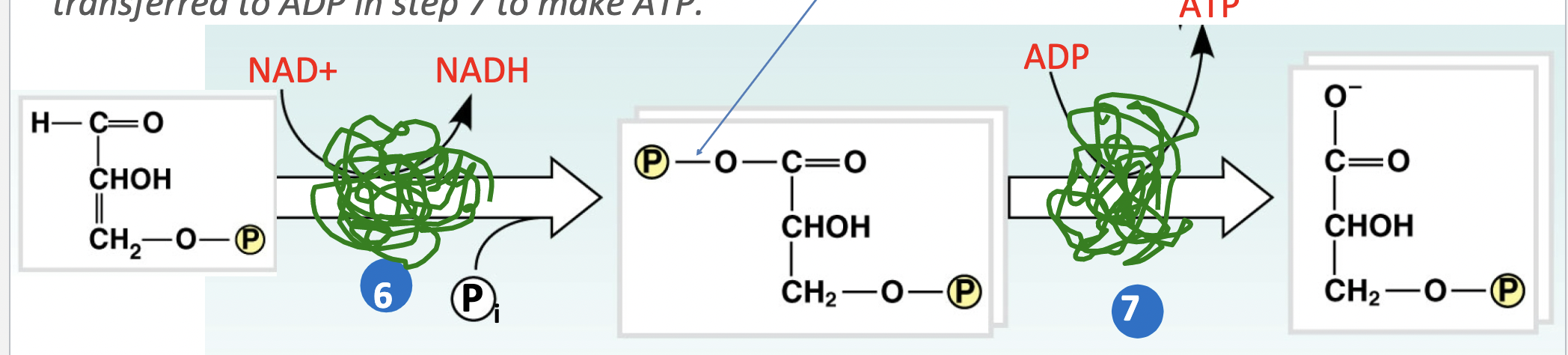
what is the intermediate step of cellular respiration (steps 6 and 7)
the oxidation/reduction step.
In step 6 the sugar is oxidized and NAD+ is reduced. \n This reaction is coupled to the synthesis of a high energy phosphate bond which is transferred to ADP in step 7 to make ATP. ( 4 ATP is made here)
In step 6 the sugar is oxidized and NAD+ is reduced. \n This reaction is coupled to the synthesis of a high energy phosphate bond which is transferred to ADP in step 7 to make ATP. ( 4 ATP is made here)
60
New cards
What is the role of Hexokinase, and why are glucose-6-phosphate and fructose-6-phosphate not considered true intermediates.
1. To trap glucose in the cell (Glucose-6-Phosphate can’t leave the cell). It is the first step in converting glucose into gylcogen. (first step of glycolysis)
2. Both are precursors for glycogen synthesis.
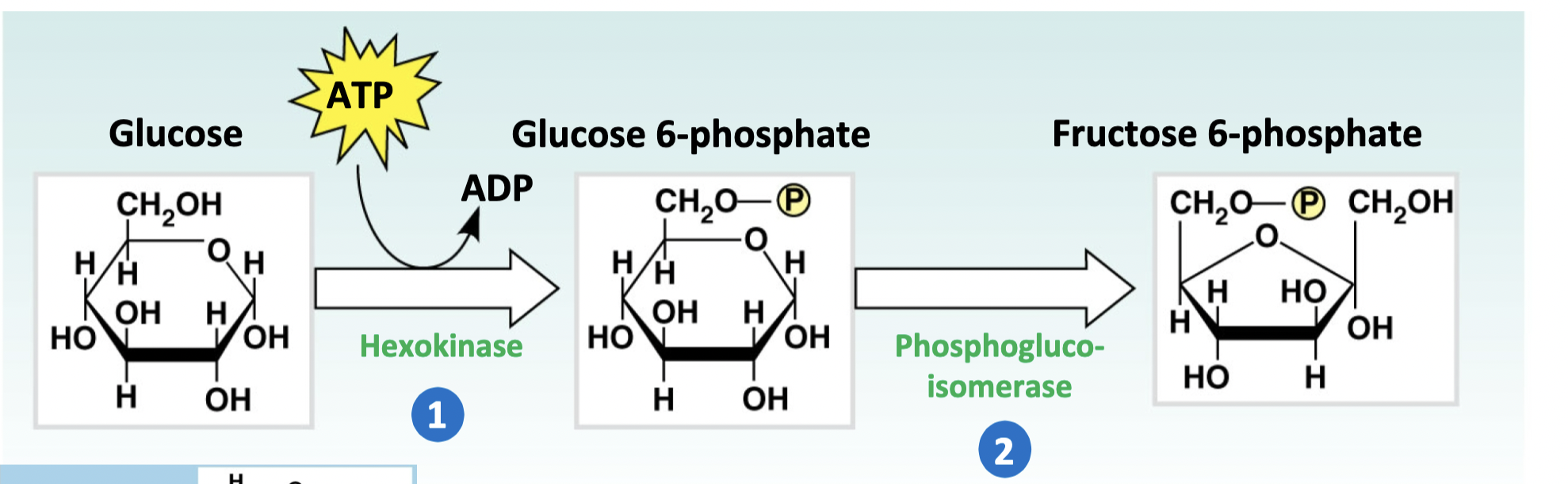
61
New cards
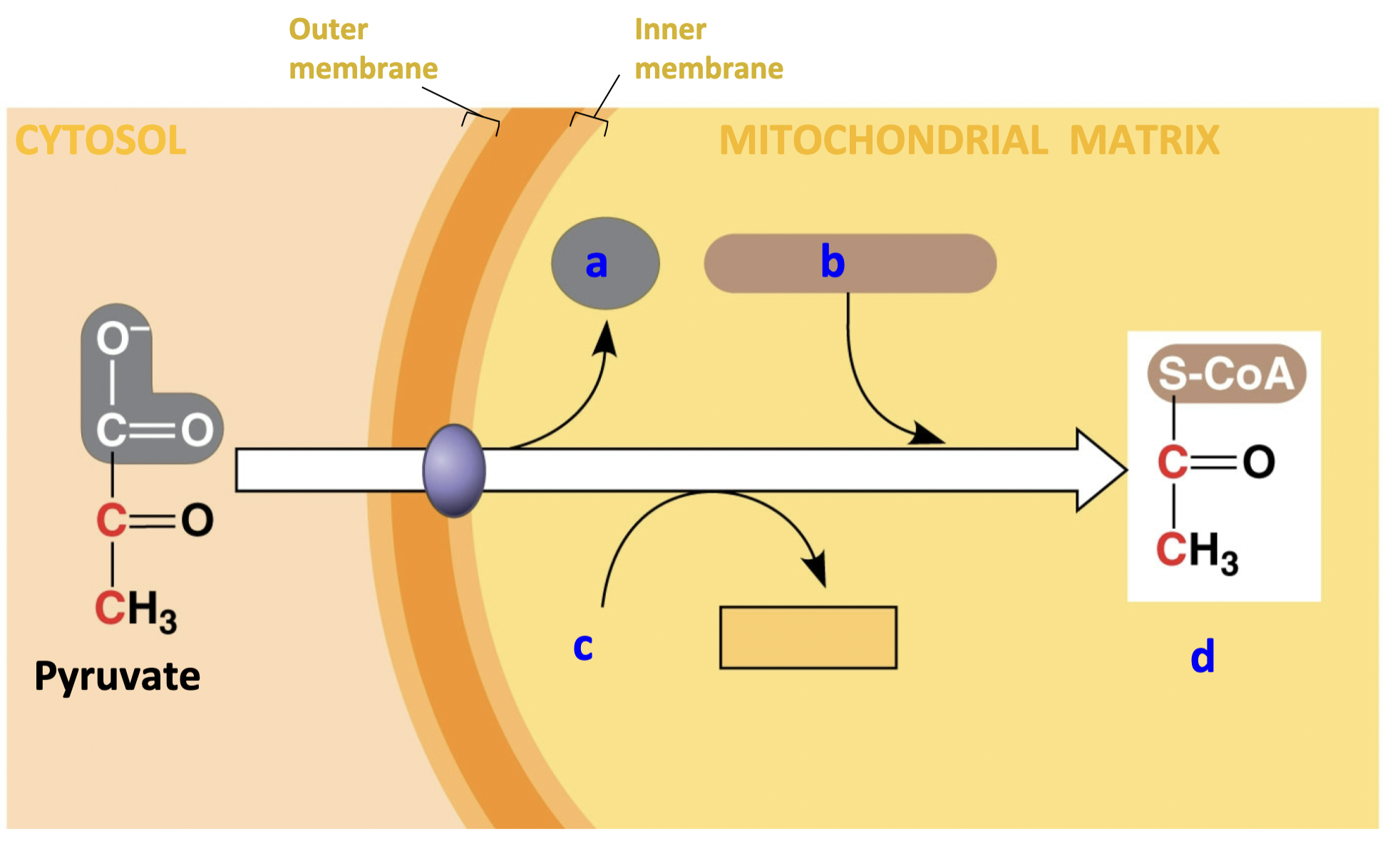
label the blank thingys
shown in picture
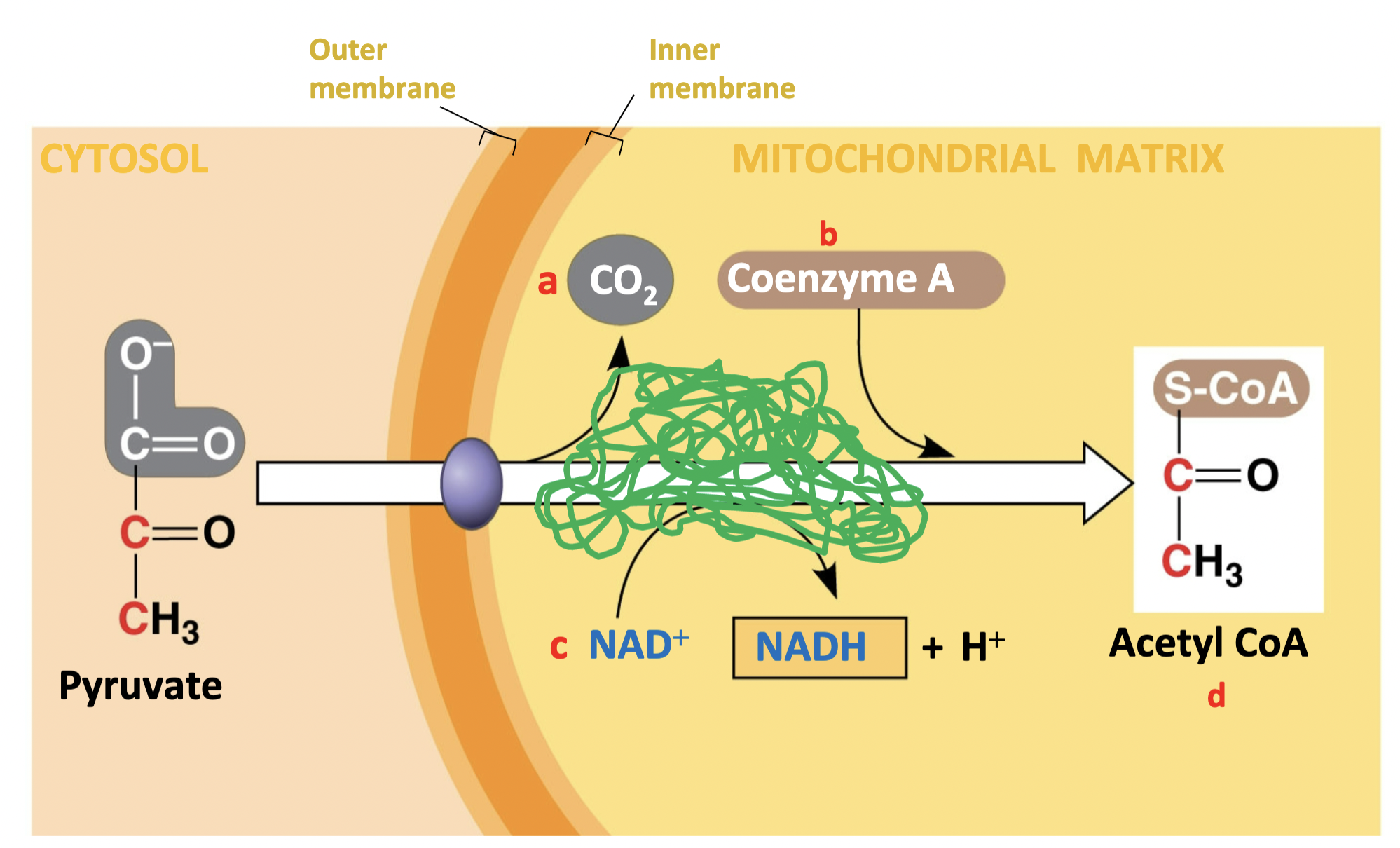
62
New cards
A particular cell has half as much DNA as some of the other cells in a mitotically active tissue. The cell in question us most likely in
G1
63
New cards
Spindle fibers attach to kinetochores during
prophase
64
New cards
What is incorrect about crossing over
Crossing over plays a role in both ssexual and asexual reproduction
65
New cards
What is substrate-level phosphorylation
production of ATP from ADP by a direct transfer of a high-energy phosphate group
66
New cards
Distinguish between an allosteric inhibitor and a competitive inhibitor.
“Allosteric” literally means “other site”. These inhibitors bind to a regulatory site away from the active site and in so doing change the shape of the enzyme so that it is less complementary to the active site. Competitive inhibitors compete with substrates for the active site, thereby slowing the reaction down.
67
New cards
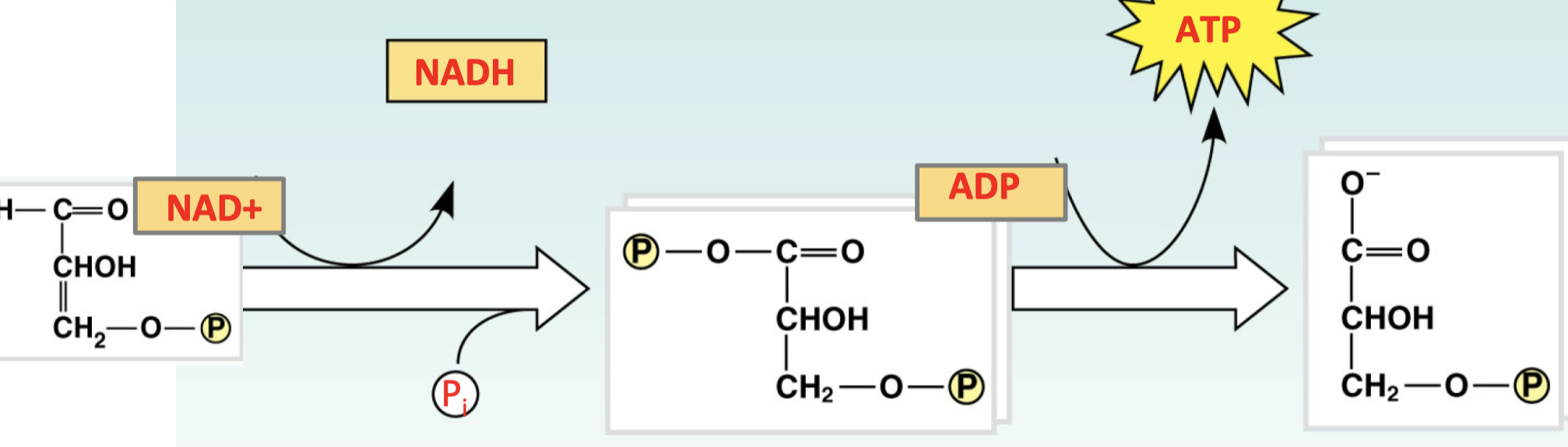
A- what is this first type of reaction called
\
B- what is the second part of the reaction called
\
B- what is the second part of the reaction called
A- oxidation/reduction B-substrate level phosphorylation
68
New cards
What two products of the Dark reactions are needed for the Light reactions?
ATP & NADPH
69
New cards
What would be the immediate effect of a poison that allows protons to leak across the \n outer mitochondrial membrane?
A-Would the electron transport chain still function?
B-Would you expect O2 consumption to increase, decrease, or remain the same?
A-Would the electron transport chain still function?
B-Would you expect O2 consumption to increase, decrease, or remain the same?
\n Reduces the H+ gradient so less ATP can be synthesized.
A-Yes, it would speed up to try to make up for loss
B-O2 consumption would increase in an attempt to rebuild the proton gradient.
A-Yes, it would speed up to try to make up for loss
B-O2 consumption would increase in an attempt to rebuild the proton gradient.
70
New cards
The chemotherapeutic drug taxol, suppresses the disassembly of kinetochore fibers at \n the kinetochore plate (attached at centromere). A cell treated with taxol would therefore be \n arrested at what stage of mitosis
Metaphase
71
New cards
How do the products of meiosis differ from those of mitosis?
Meiosis produces 4 genetically unique haploid cells, mitosis produce two genetically identical diploid cells
72
New cards
magine an organism with a diploid number of 12. \n • How many homologous pairs are present in a somatic cell? \n • How many chromosomes are present in a cell in anaphase 2?
6, 12