AP Biology Unit 3A
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
biological catalysts of enzymes
proteins; facilitation of chemical reactions; and highly specific
function of the bio catalyst “facilitation of chemical reactions”
increases rate of reaction without being consumed or degraded
reduces activation energy
doesn’t change free energy released or required
required for most bio reactions
function of the bio catalyst “highly specific”
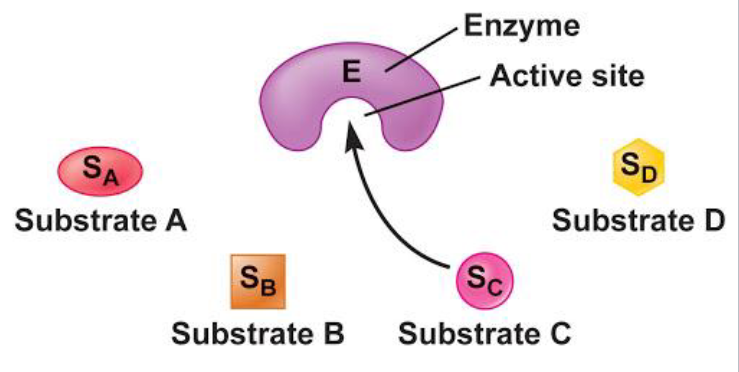
enzyme and substrate binding is highly specific
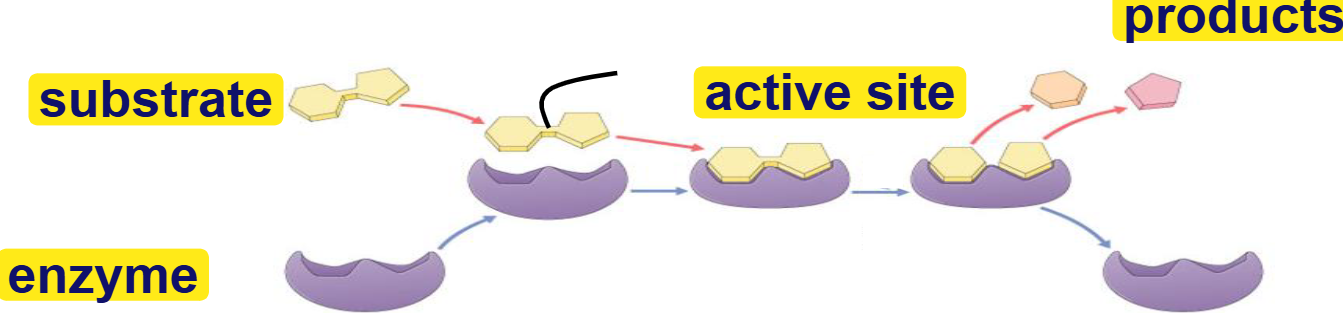
substrate
reactant that binds to enzyme(s)
enzyme-substrate complex: temporary association
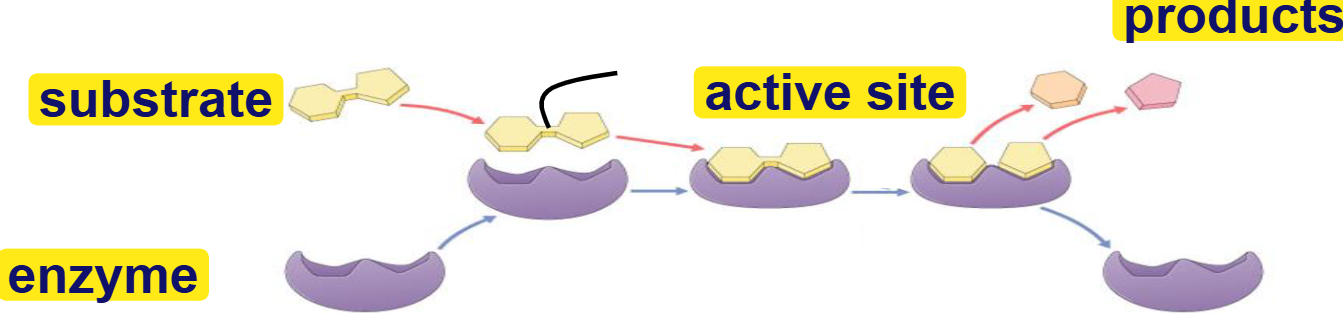
product
end result of reaction
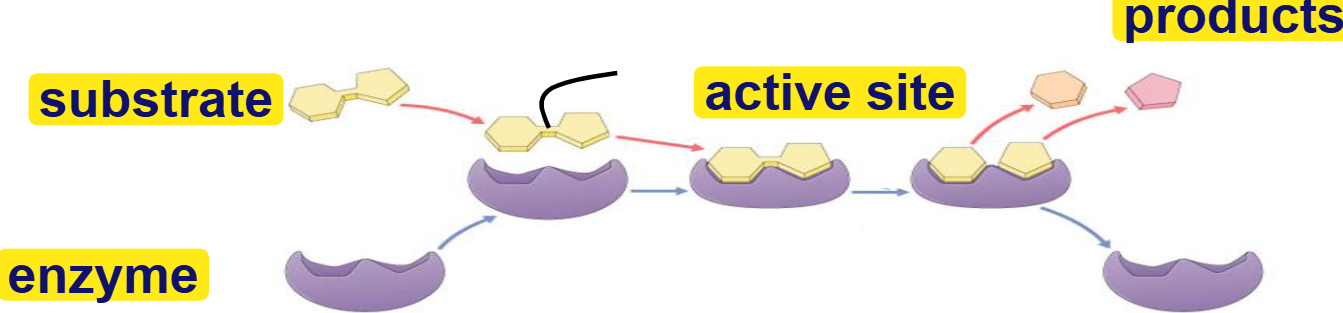
active site
binding site for substrates
induced fit
substrate binding causes active site to change in conformation change (slightly)
does not change primary/secondary/tertiary structure
properties of enzymes
reaction specific
not consumed in reaction
affected by cellular condition
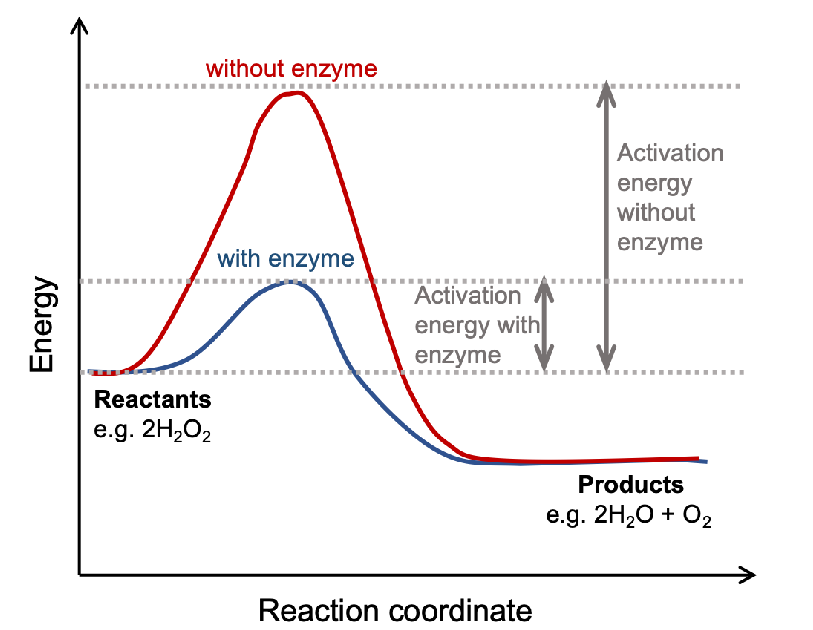
How do enzymes affect the rate of bio reactions
enzymes are biological catalysts that facilitate chemical reactions in cells by lowering the activation energy
how do enzymes lower the EA barrier
enzyme-substrate complex stabilizes the transition state
enzymes do not
affect the change in free energy
enzymes do
speed up reactions by lowering activation energy
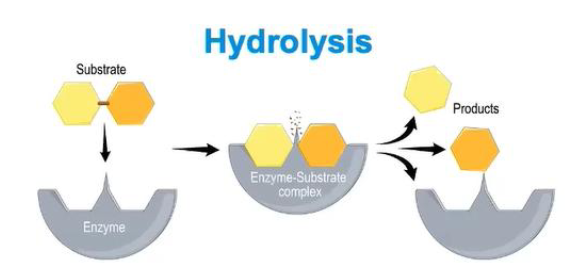
how is hydrolysis relevant in enzymes
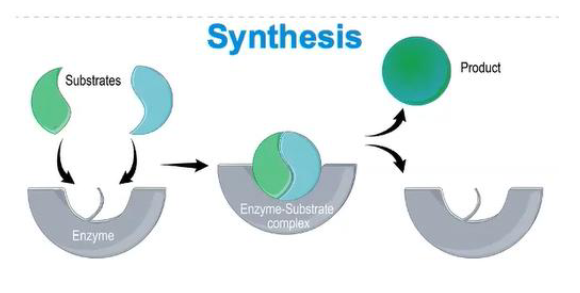
how is synthesis relevant in enzymes
catalysts are chemical agents that speed up reactions without being
consumed by the reaction
facts that affect enzyme function
Salt concentration
enzyme concentration
pH levels
in a fixed substrate concentration
increase in enzymes = increase in reaction rate
more enzymes = more collisions with substrate
reaction rate levels off (horizontal line on graph)
[enzymes] = [substrates]
substrate becomes limiting factor
in a fixed enzyme concentration
increase in substrates = increase in reaction rate
more substrates = more collisions with enzyme
reaction rate levels off
enzymes become limiting factor
all active sites are occupied
initial velocity
higher frequency of substrate binding to enzyme’s active site
the reaction decreases over time because product to substrate ratio increases
rate of reaction can be measured by
product formation
disappearance of substrate
overtime reaction decreases because
product to substrate (P/S) ratio increases; substrates slowly decrease as product increases
units for rate of reaction
M/sec
rate of reaction can be calculated using what formula
slope formula; using two points
substrates can be
consumed, denatured, broken, etc.
but NOT enzymes
the best temperature for an enzyme is where on the graph
the peak of the graph
if you keep increasing heat, the reaction will decline. why?
the proteins are fragile and will denature due to high temperature
the best pH for an enzyme is where on the graph
the peak of the graph; the enzyme will start to denature past the peak
enzymes can be renatured in temp/pH levels by
putting it back in the most optimal temperature/pH level
once active site is denatured, the substrate
will no longer fit to the active site
positive control is
something that will give indicate a reaction
negative control is
something that will not indicate a reaction
denatured proteins can be used as
negative controls
competitive inhibitor molecules
(irreversibly or reversibly) binds to the active site, but does not cause a reaction like a normal substrate would
increase in substrate can reduce inhibition because it increases the chance the substrate will bind to the enzyme
structurally identical to the enzyme/active site
noncompetitive inhibitor molecules
binds to the allosteric site, changing the activity of the enzyme, causing the substrate to no longer fit to the active site
enzyme changes shape (conformation)
increasing substrates does not reduce inhibition
irreversible