AP Psych - Unit 0 Vocab
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Hindsight Bias
The tendency people have to view events as more predictable than they really are.
Confirmation Bias
The tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one’s pre-exisiting beliefs or hypotheses.
Falsifiable
The logical possibility that an assertion, hypothesis, or theory can be shown to be false by an observation or experiment.
Operational Definition
A clear and specific explanation of how a concept or variable is measured or observed in a study.
Case Study
A research method used to investigate a particular individual, group, or situation in depth.
Meta-Analysis
An objective examination of published data from many studies of the same research topic.
Survey
A systematic method of collecting data from individuals, typically through standardized questions or interviews.
Social desirability bias
The tendency for people to present themselves in a generally favorable fashion.
Self-report bias
When people report experiences that are considered socially acceptable or preferred.
Experimenter Bias
When a researcher affects the data, participants, or results of an experiment due to their expectations or biases.
Sampling Bias
When a sample does not accurately represent the population being studied.
Random Sample
A group of people selected from a larger population in a way that gives each person an equal chance of being chosen.
Convenience Sampling
When data is collected from an easily accessible and available group of people.
Representative Sample
A group that closely matches the charactersitics of its population as a whole.
Experimental Methodology
Manipulating one variable to determine if this causes changes in another variable.
Non-Experimental Methodology
Research that lacks the manipulation of an independent variable
Correlation Coefficient
A statistical measure that quantifies the strength and direction of the linear relationship between two variables; often expressed as “r” and ranges from -1 to +1.
Illusory Correlation
Perceiving a relationship between variables even when no such relationship exists.
Regression Toward the Mean
Where if one sample of a random variable is extreme, the next sampling of the same random variable is likely to be closer to its mean.
Experimental Group
The group of test subjects who are exposed to the independent variable in an experiment.
Control Group
The group that does not recieve the experimental treatment or intervention.
Independent Variable
The cause, manipulated by the researcher in an experiment.
Dependent Variable
The effect, measured outcome that changes in response to manipulations of the independent variable.
Random Assignment
The practice of assigning participants to experimental groups in a study in an unbiased way.
Single-Blind Procedure
When participants are unaware of the experimental conditions under which they are operating.
Double-Blind Procedure
When neither the subjects or the administraters know the critical aspects of an experiment.
Confounding Variable
An external factor that interferes with the relationship between an experiment’s independent and dependent variable.
Quantitative Research
A method of research that relies on measuring variables using a numerical system.
Qualitative Research
The process of collecting, analyzing, and interpreting non-numerical data
Likert Scales
A rating scale that consists of a statement or a question, followed by a series of five or seven answer statements.
Institutional Review
The evaluation of research proposals by a committee to ensure that they comply with ethical standards and regulations.
Informed Consent
Consent given by individuals who have reached the legel age of consent.
Informed Assent
The agreement of someone not able to give legal consent
Confidentiality
The responsibility of professionals to keep client information private
Research Confederates
Individuals who seem to be participants but are actually part of the research team.
Debriefing
The procedure for revealing the true purpose of a psychological study to a participant after deception.
Descriptive Statistics
A set of techniques used to summarize and display data.
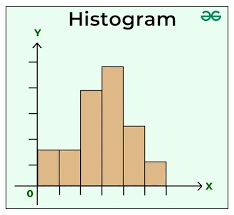
Histogram
A graphical display of a distribution
Measure of Central Tendency
A single value that represents the center point of a dataset. (Mean, median, and mode)
Mode
Most often occurring number in a data set
Mean
Average value of a set of numbers
Median
Midpoint in a data set
Percentile Rank
The percentage of scores in a distribution that are lower than a given score
Measures of Variation
The spread of scores in a distribution (range, interquartile range, standard deviation, etc.)
Range
The difference between the highest and lowest values in a dataset
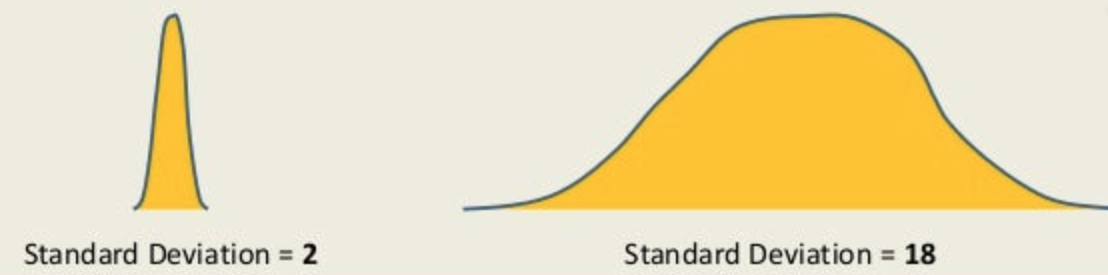
Standard Deviation
A number that describes how scores in a distribution are spread out from one another
Longitudinal Study
When data is collected from the same subjects repeatedly over a long period of time.
Cross-Sectional Study
Observational studies that analyze data from a population at a single point in time.
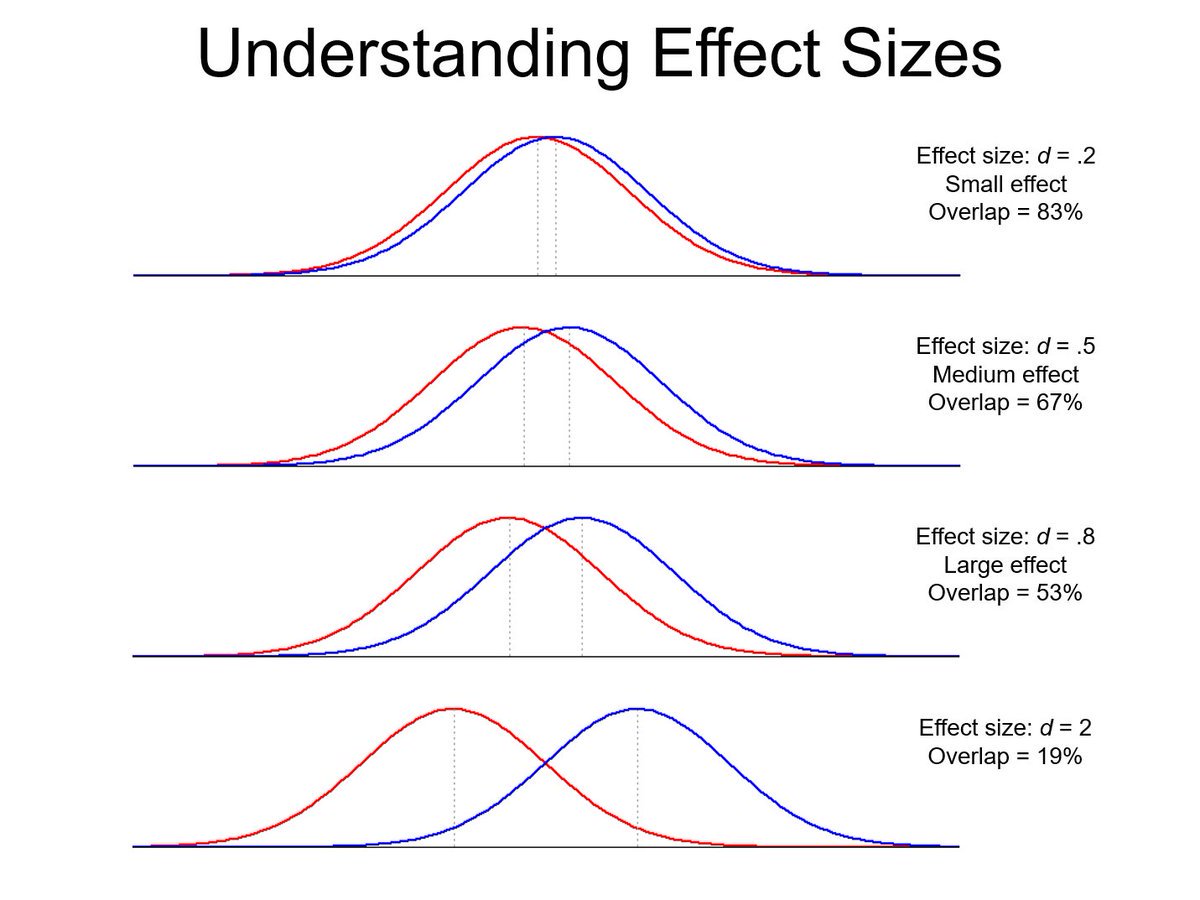
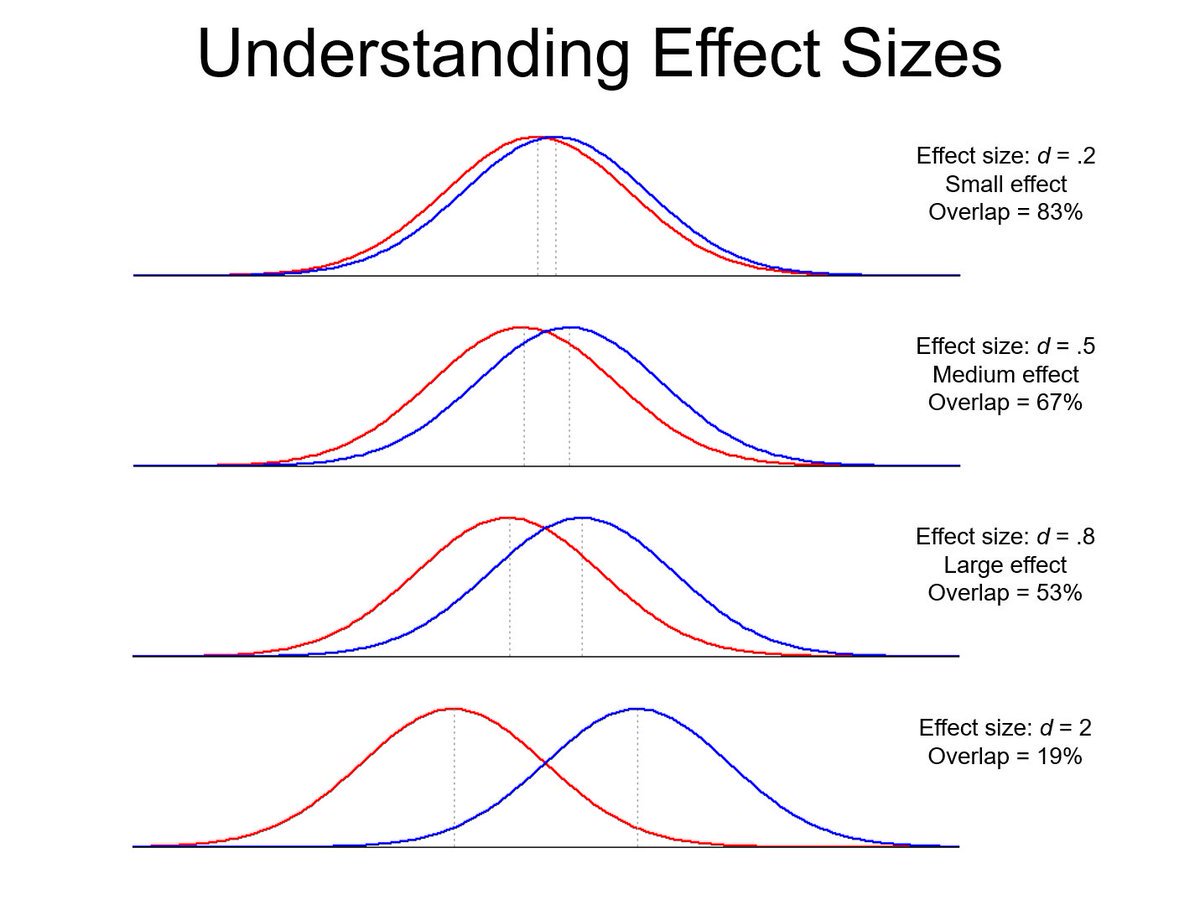
Effect Size
The strength of the relationship between two variables, or the difference between groups.
Statistical Significance
The likelihood that observed results are not due to random chance, but rather represent a real effect or relationship.
Skewness