Interference (Part-V)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Reflection Phase Change (Fixed Boundary)
ΔΦ = π (180°)
The reflected wave is inverted
Reflection Phase Change (Free Boundary)
ΔΦ = 0
The reflected wave is not inverted
Incident–Reflected Amplitude (Ideal Boundaries)
A_R = A_I
For both fixed and free boundaries, the reflected wave has the same amplitude as the incident wave (ideal case).
Principle of Superposition
yR(x, t) = y1(x, t) + y2(x, t)
Linear Wave Equation
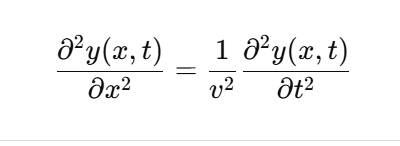
Traveling Wave Solution
y(x, t) = f(x ± vt)
Any function of x ± vt satisfies the linear wave equation.
Sinusoidal Wave Function
y(x, t) = Asin(kx - ωt + Φ)
Wave Number
k = (2π)/λ
Wave Speed (Sinusoidal Wave)
v = ω/k = fλ
Two Identical Waves with Phase Difference
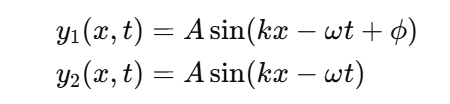
Trigonometric Identity for Superposition
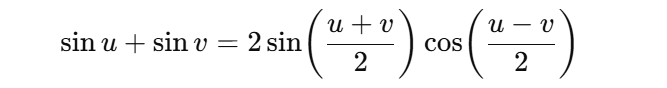
Resultant Wave from Two Identical Sinusoids
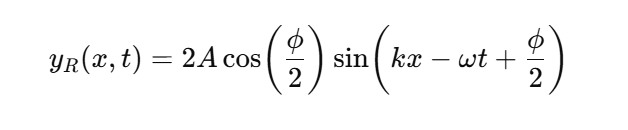
Resultant Amplitude (Phase Dependent)
A_R = 2Acos(Φ/2)
Constructive Interference Condition
If Φ = 0, then A_R = 2A
Destructive Interference Condition
If Φ = π, then A_R = 0
Partial Interference
If 0 < Φ < π
then 0 < A_R < 2A
Phase difference (Φ)
What Determines Interference Type?
λ, f, ω, and k
What Does NOT Change During Interference?
Linear Restoring Force → Linear Wave Equation → Valid Superposition
Why Small Amplitudes Matter?
Angular Frequency
ω = 2πf