Plant Anatomy Lab
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
Parallel
Monocots have leaves that have _____ veins.
Netlike
Dicots have leaves that have ____ veins.
Taproot
Dicots usually have what type of root?
Fibrous
Monocots usually have what type of root?
Dicots
What type of plant is it common to have secondary growth?
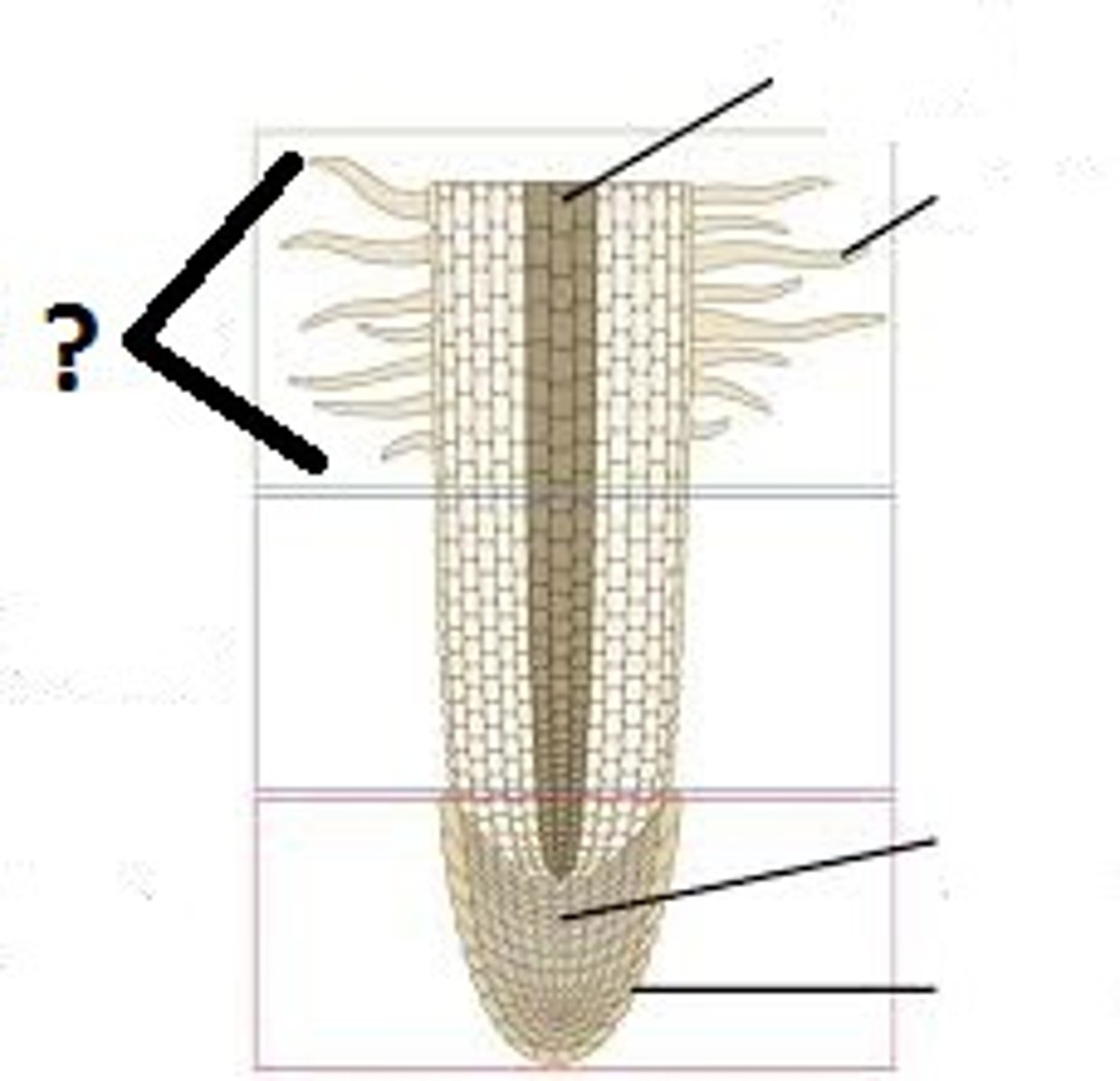
Root cap
Structure labeled yellow?
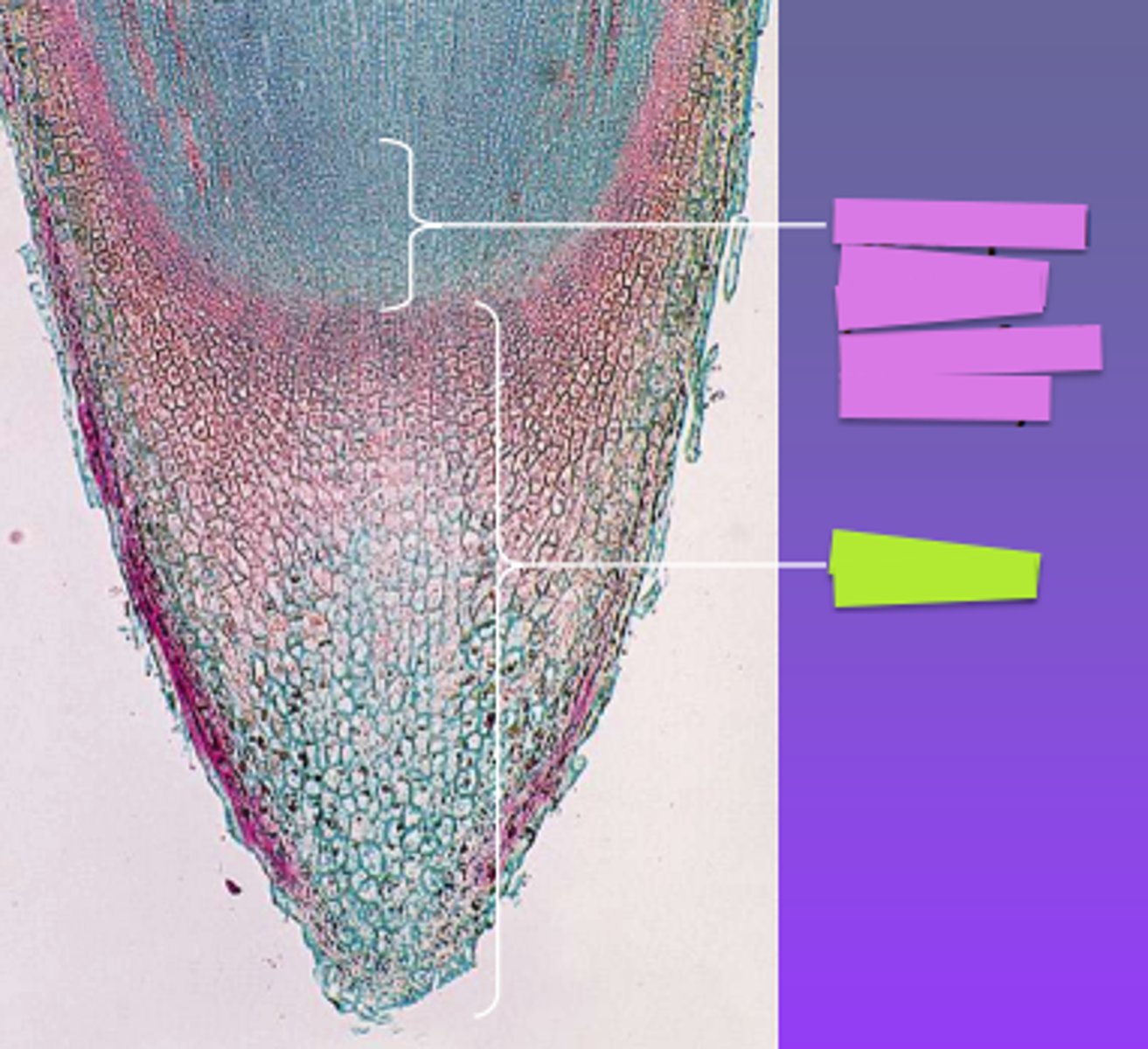
Apical meristem
Structure labeled pink?
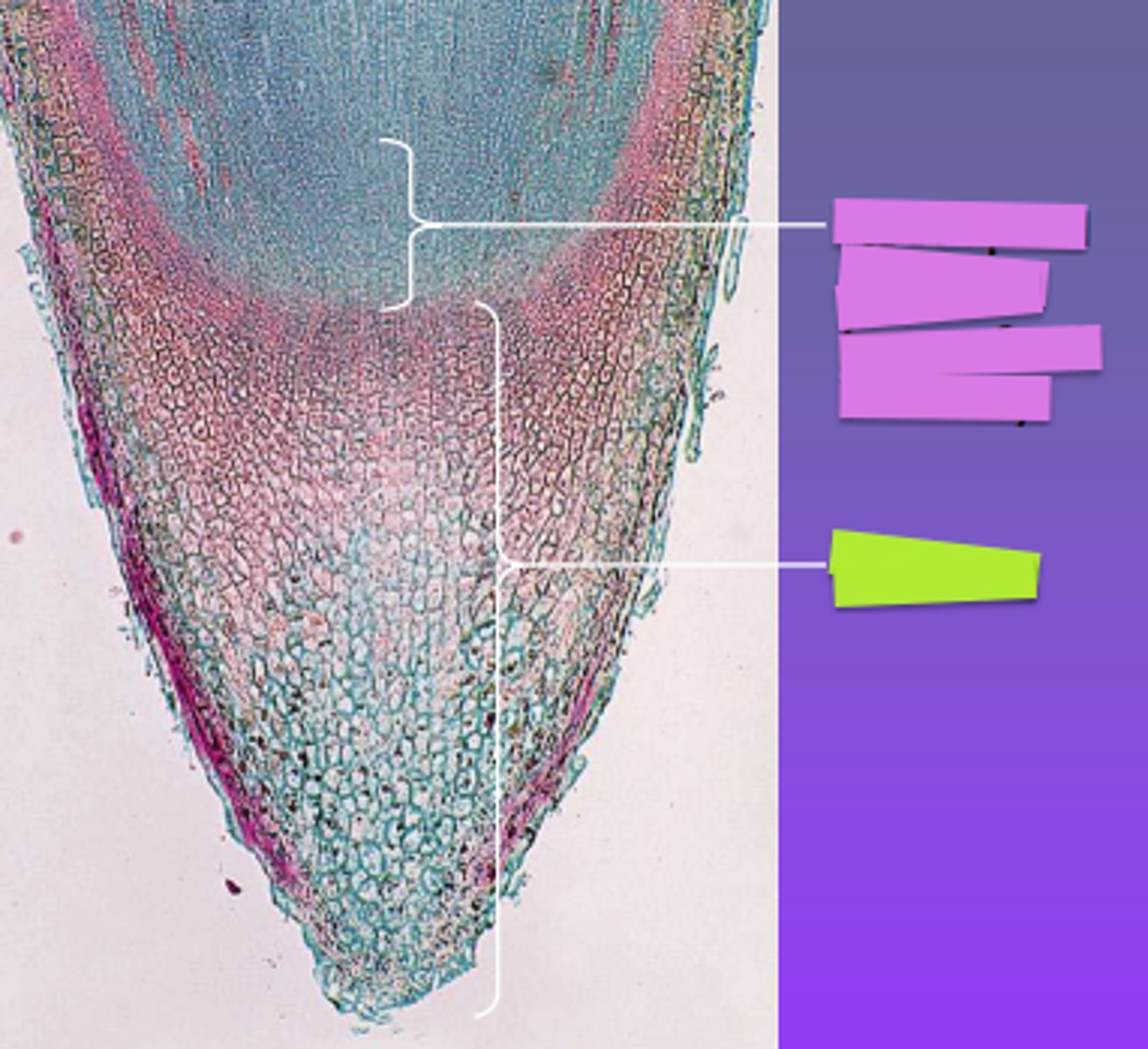
Elongation
Area at ?
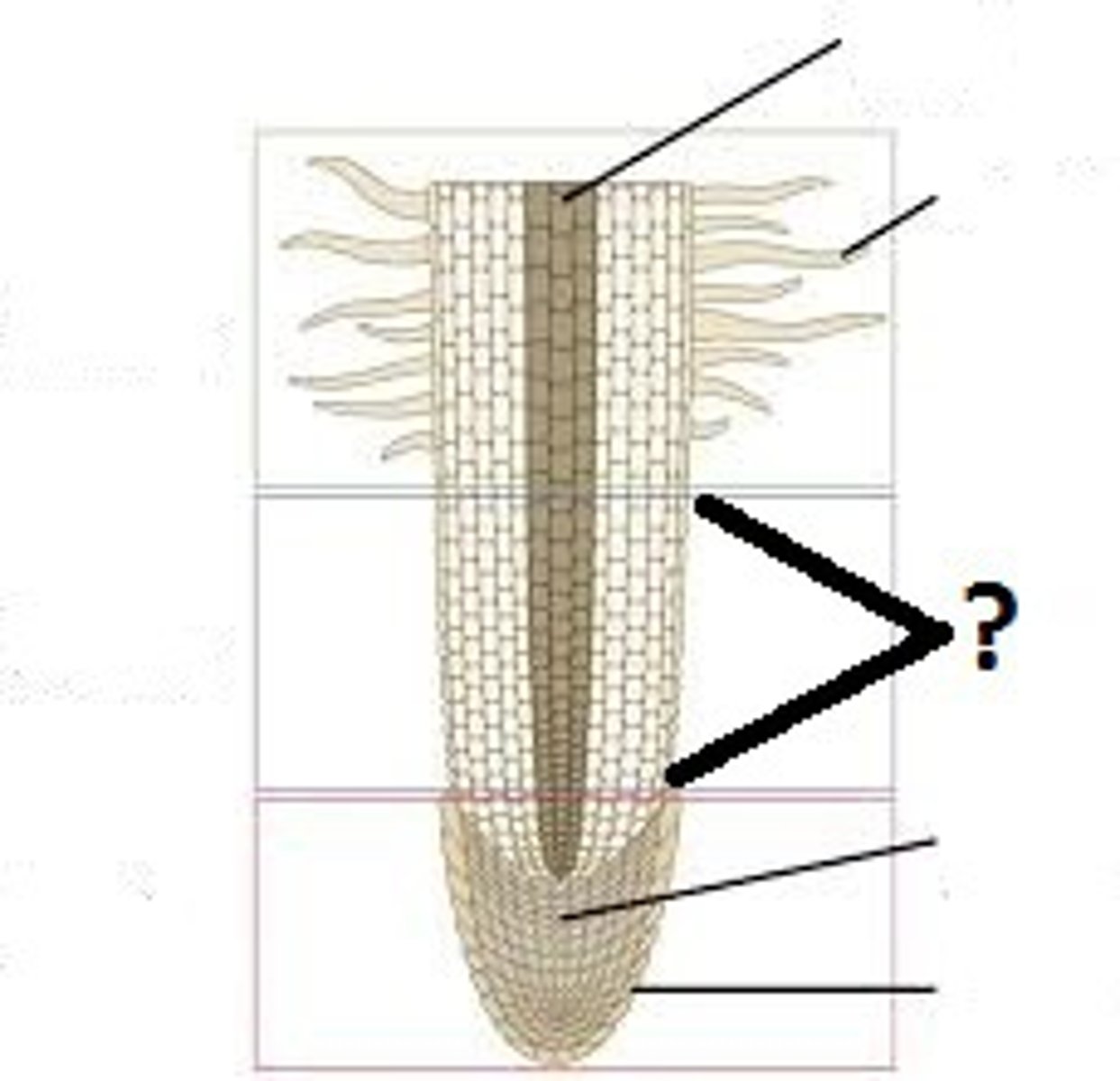
Maturation
Area at ?
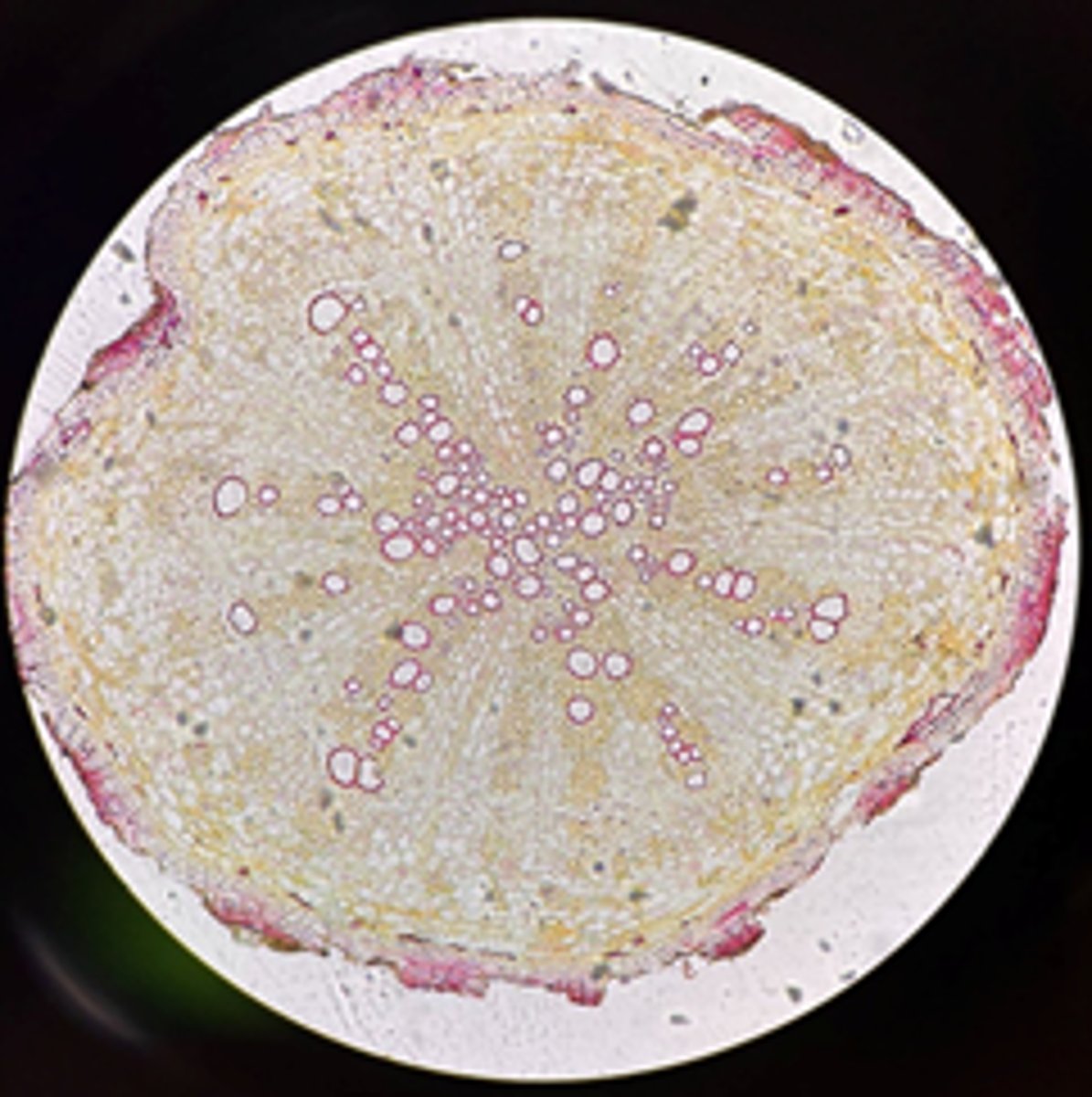
Monocot
Is this Medicago root a Monocot or Dicot?
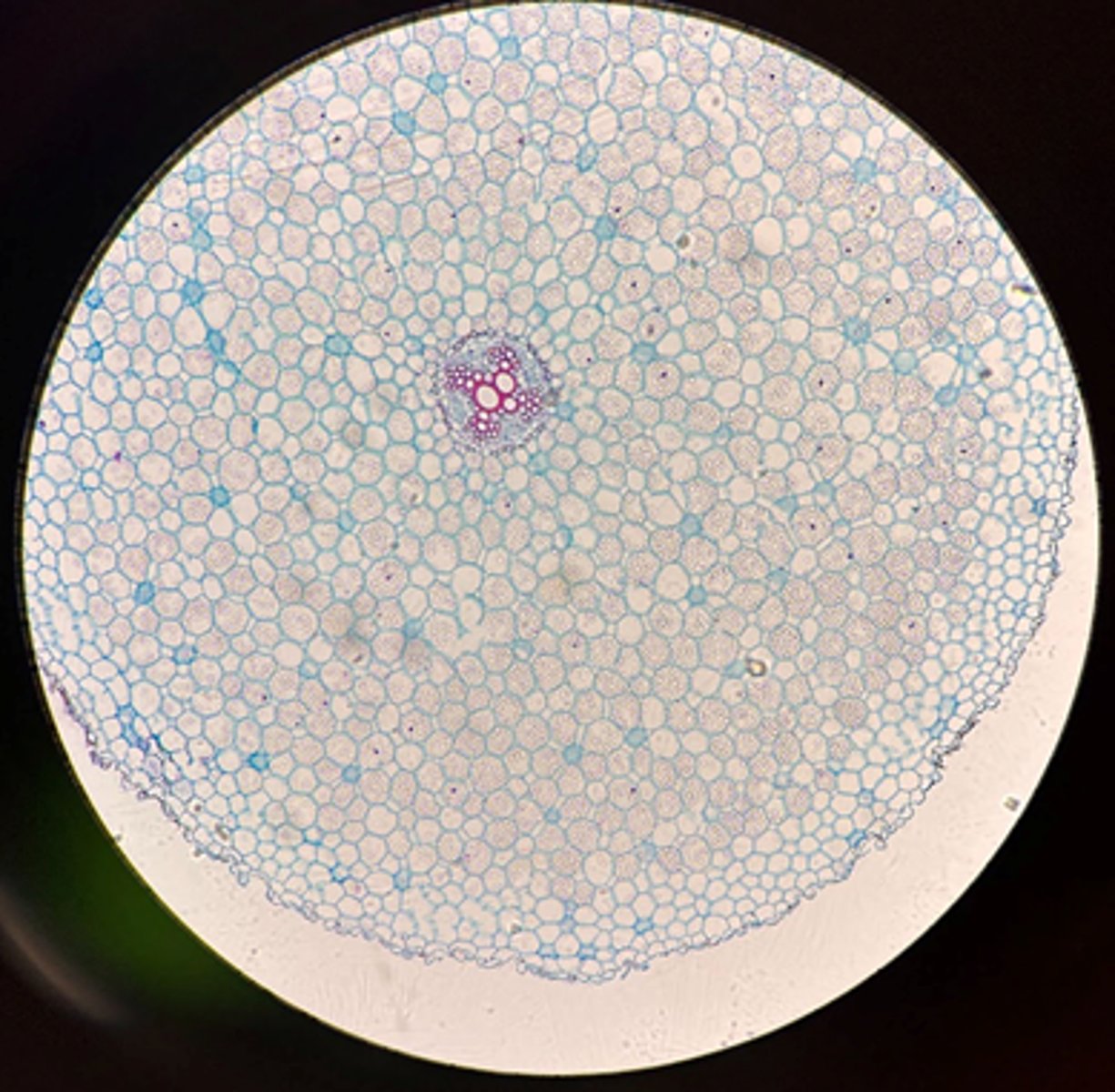
Dicot
Is this Buttercup root a Monocot or Dicot?
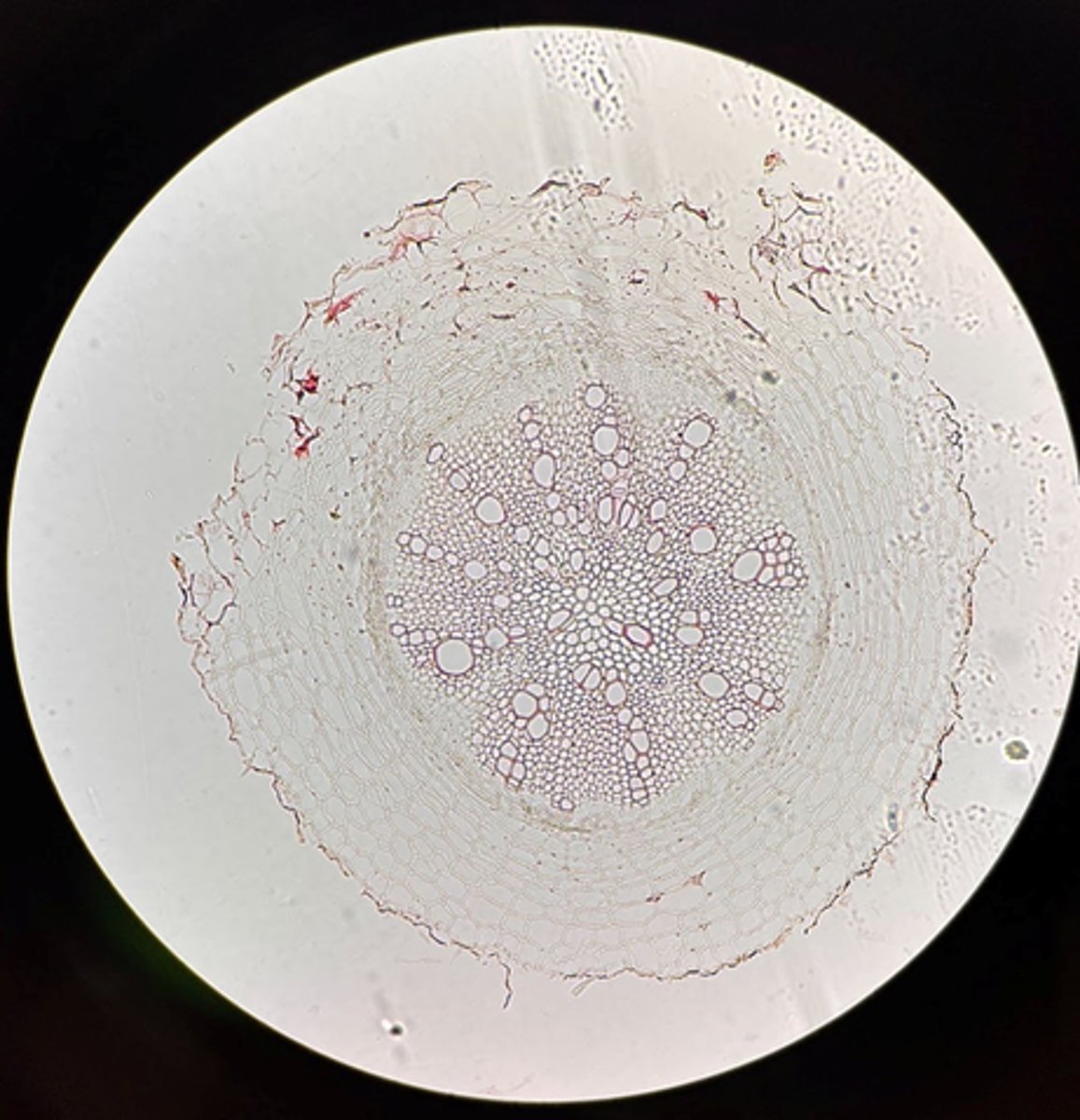
Dicot
Is this Helanthius root a Monocot or Dicot?
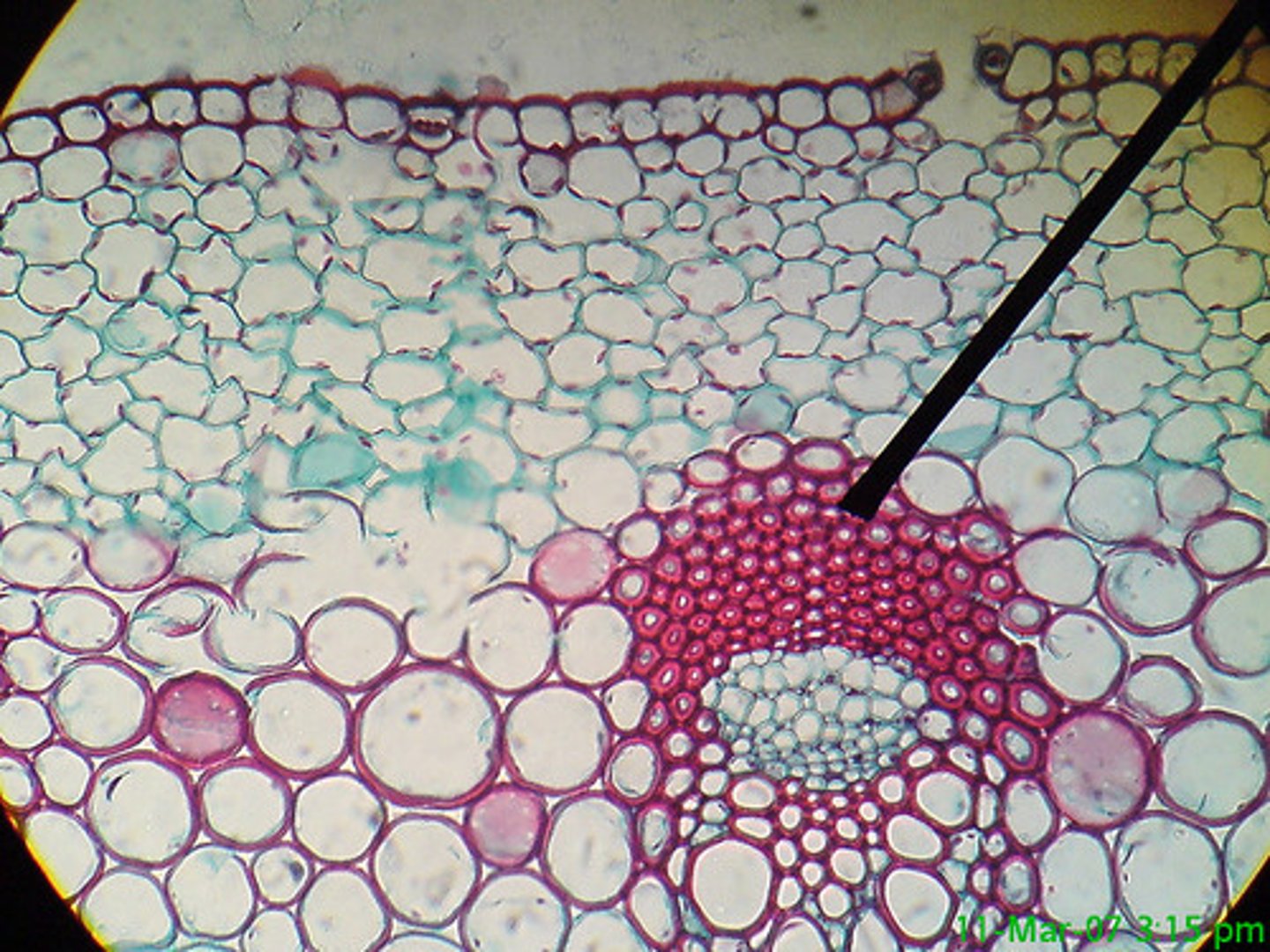
Epidermis
A?
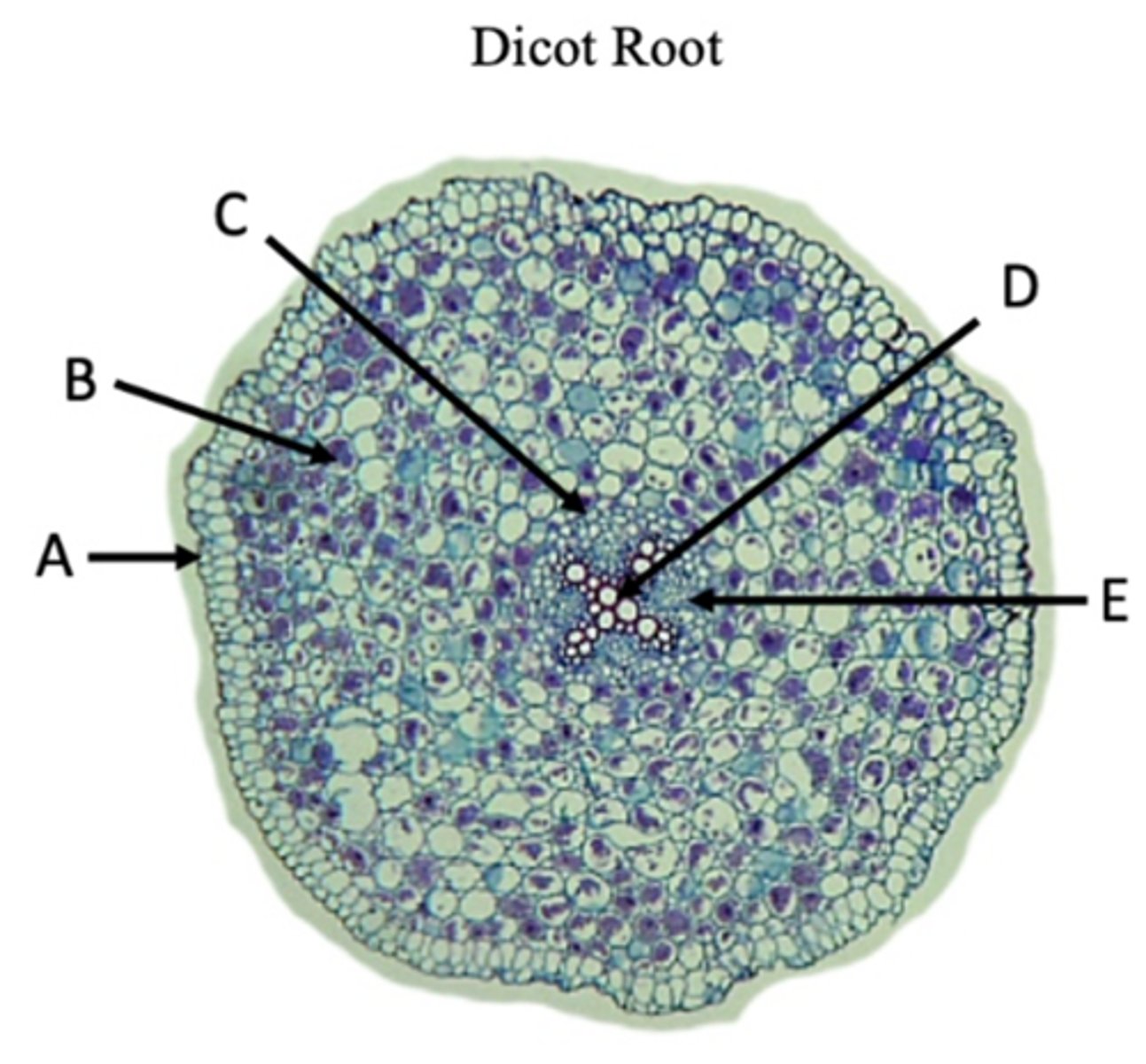
Cortex
B?
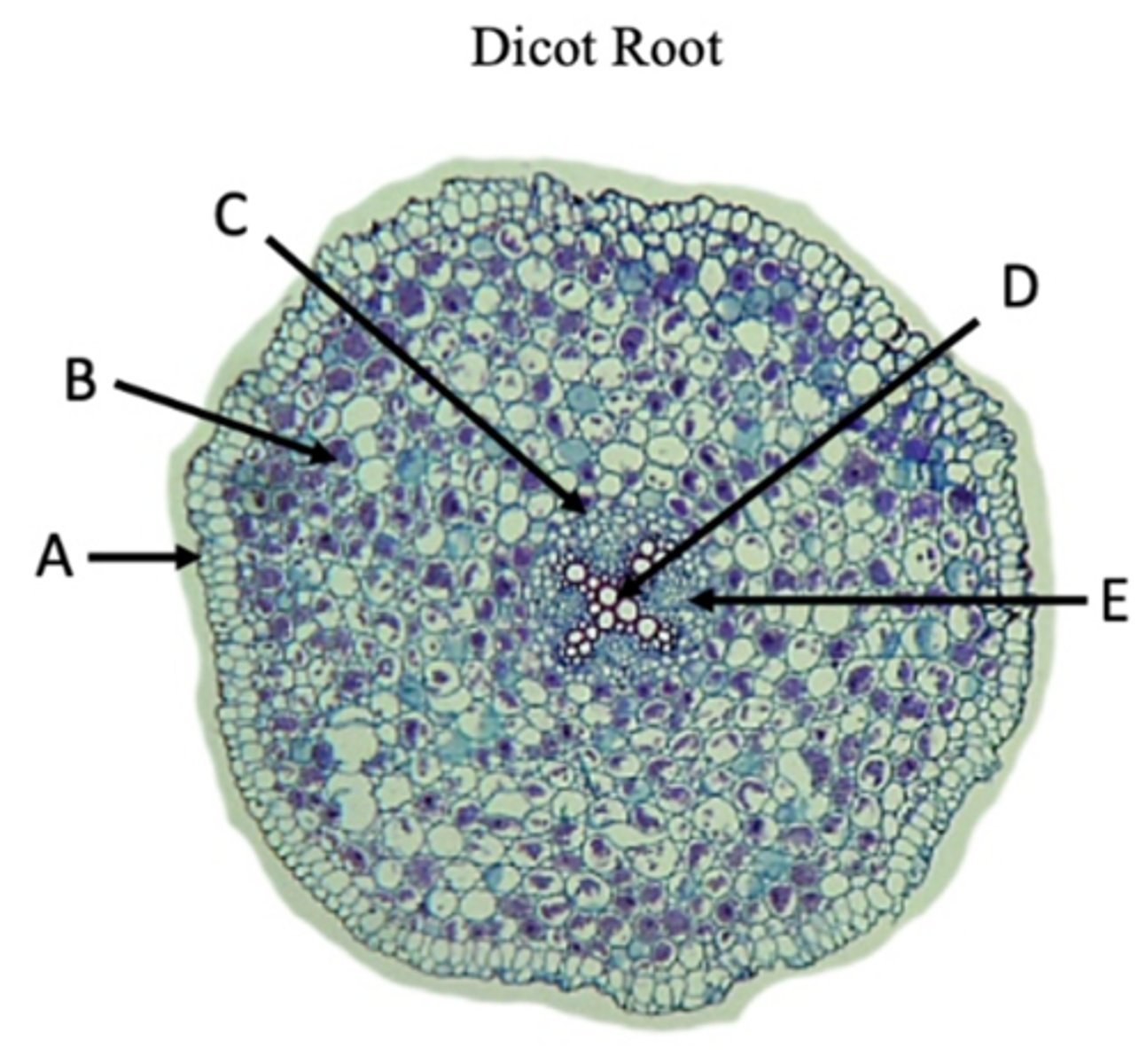
Endodermis
C?
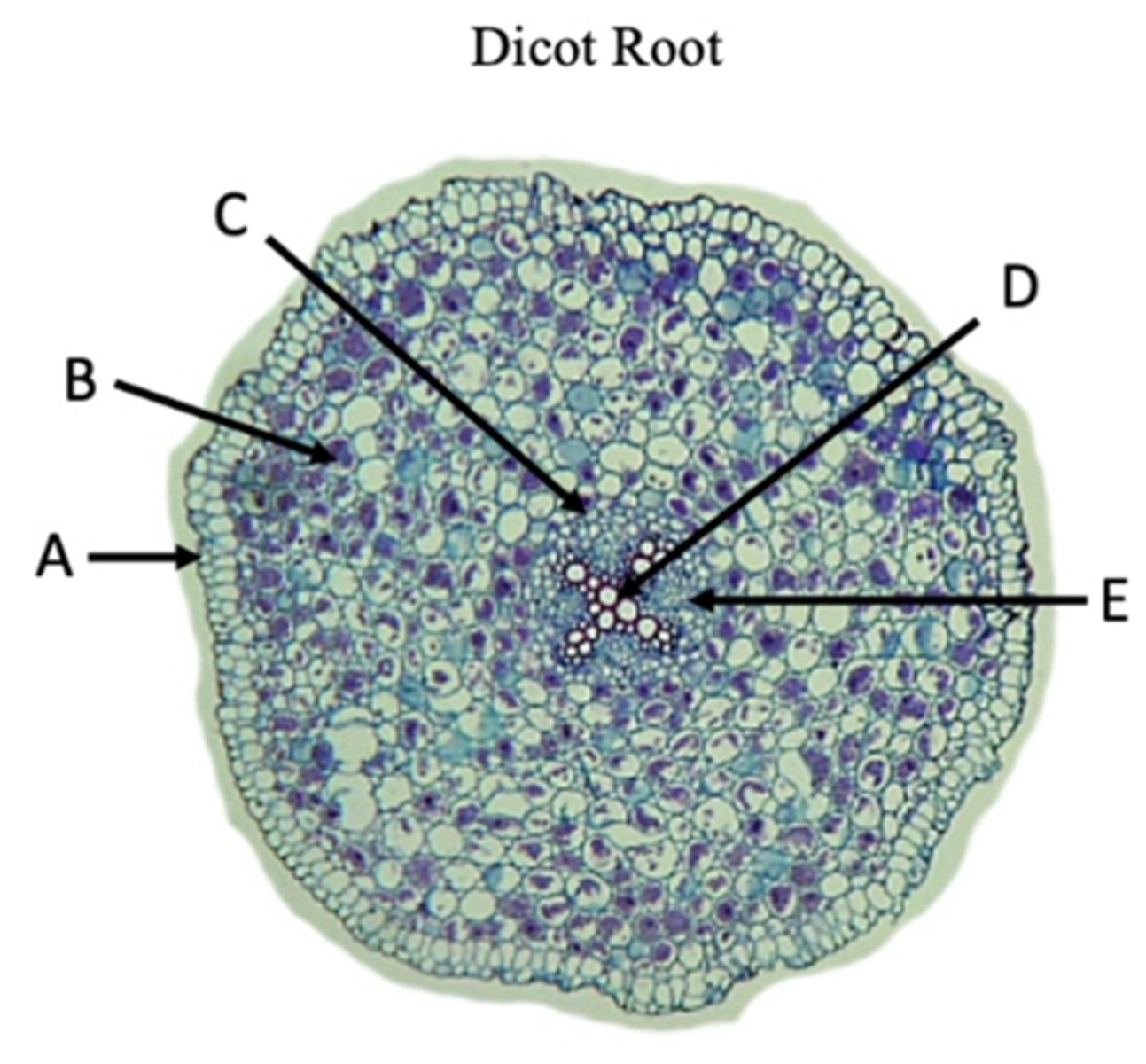
Pericycle
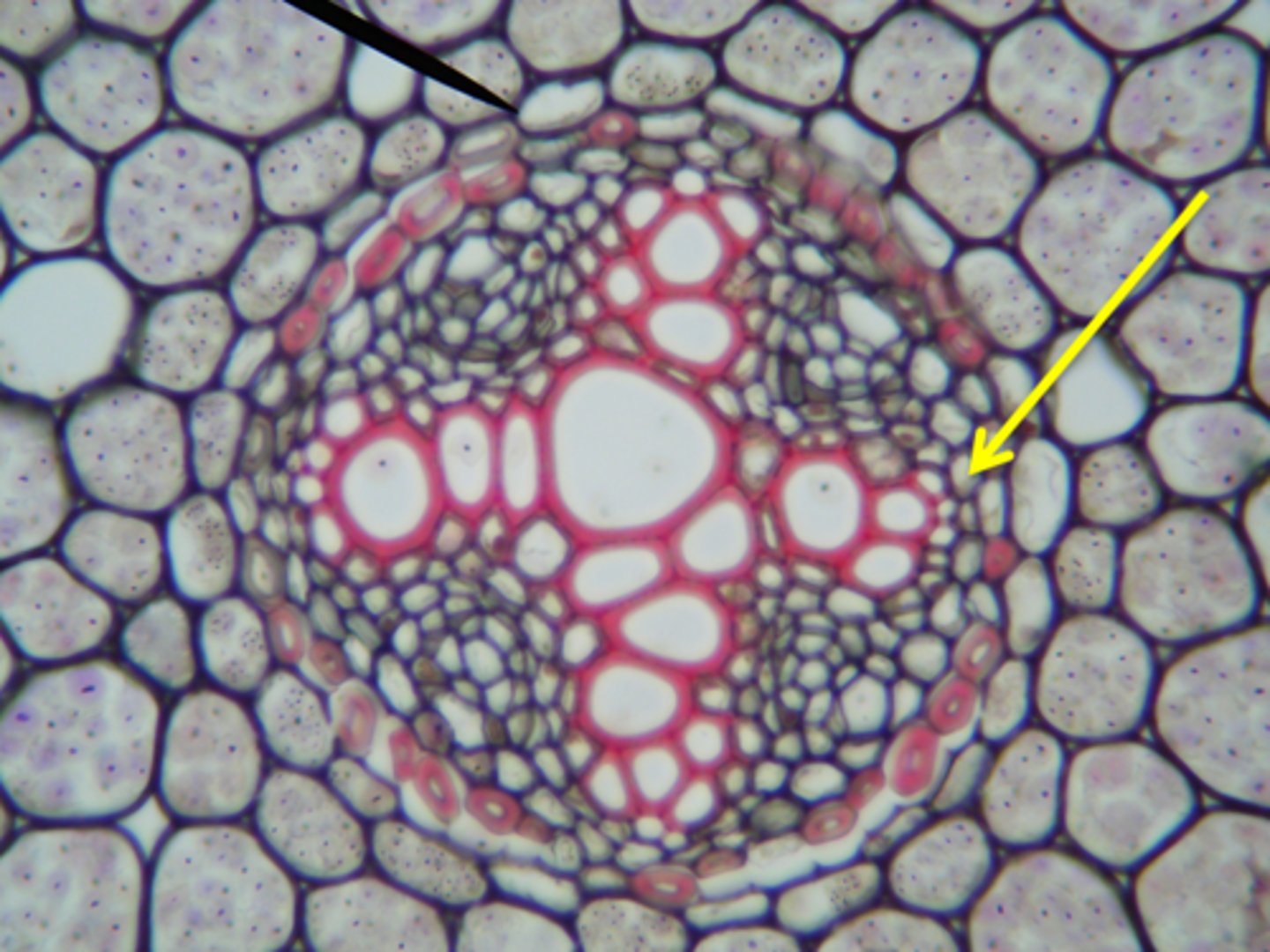
Name of structure at arrow.
Xylem
D?
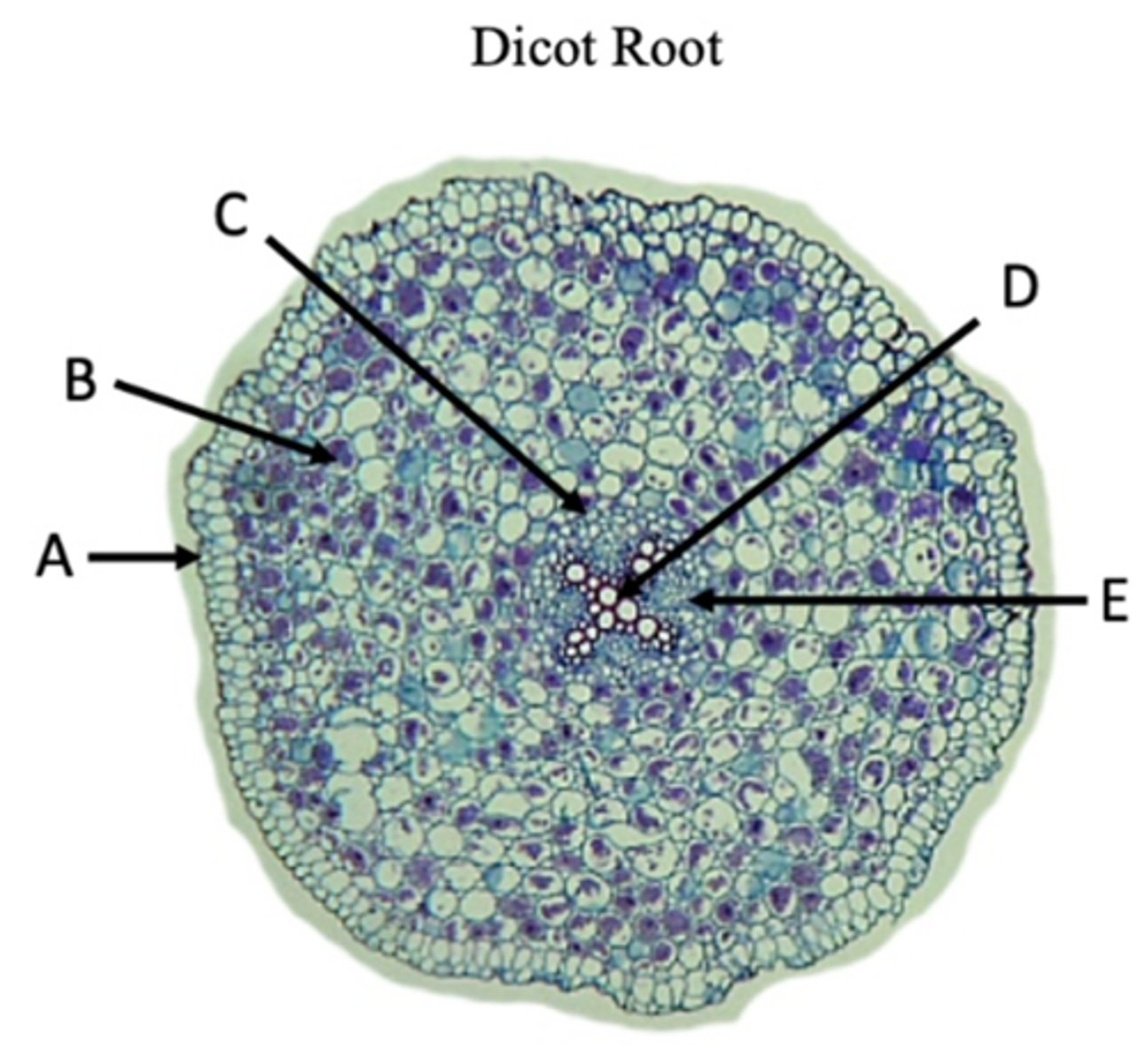
Phloem
E?
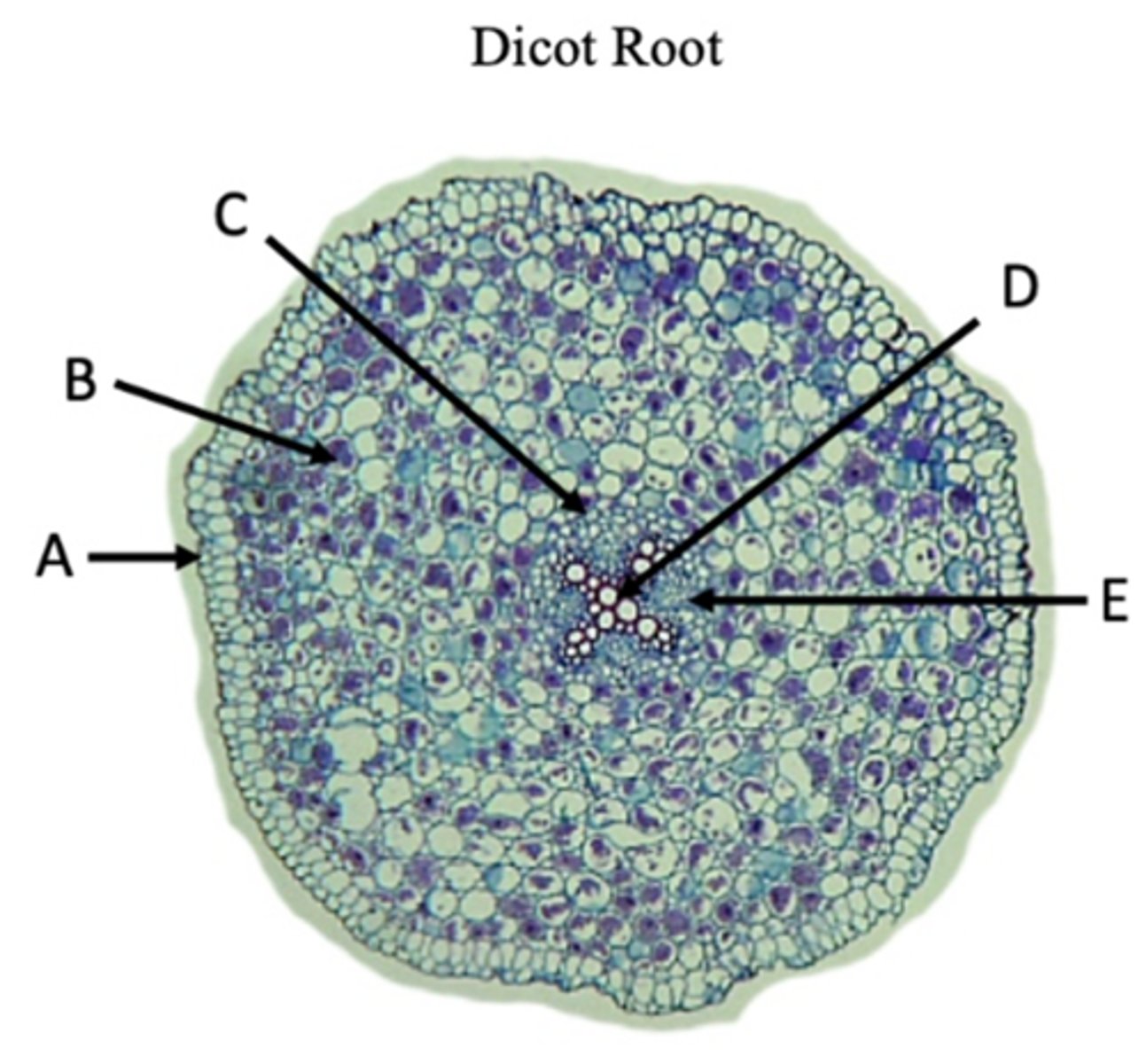
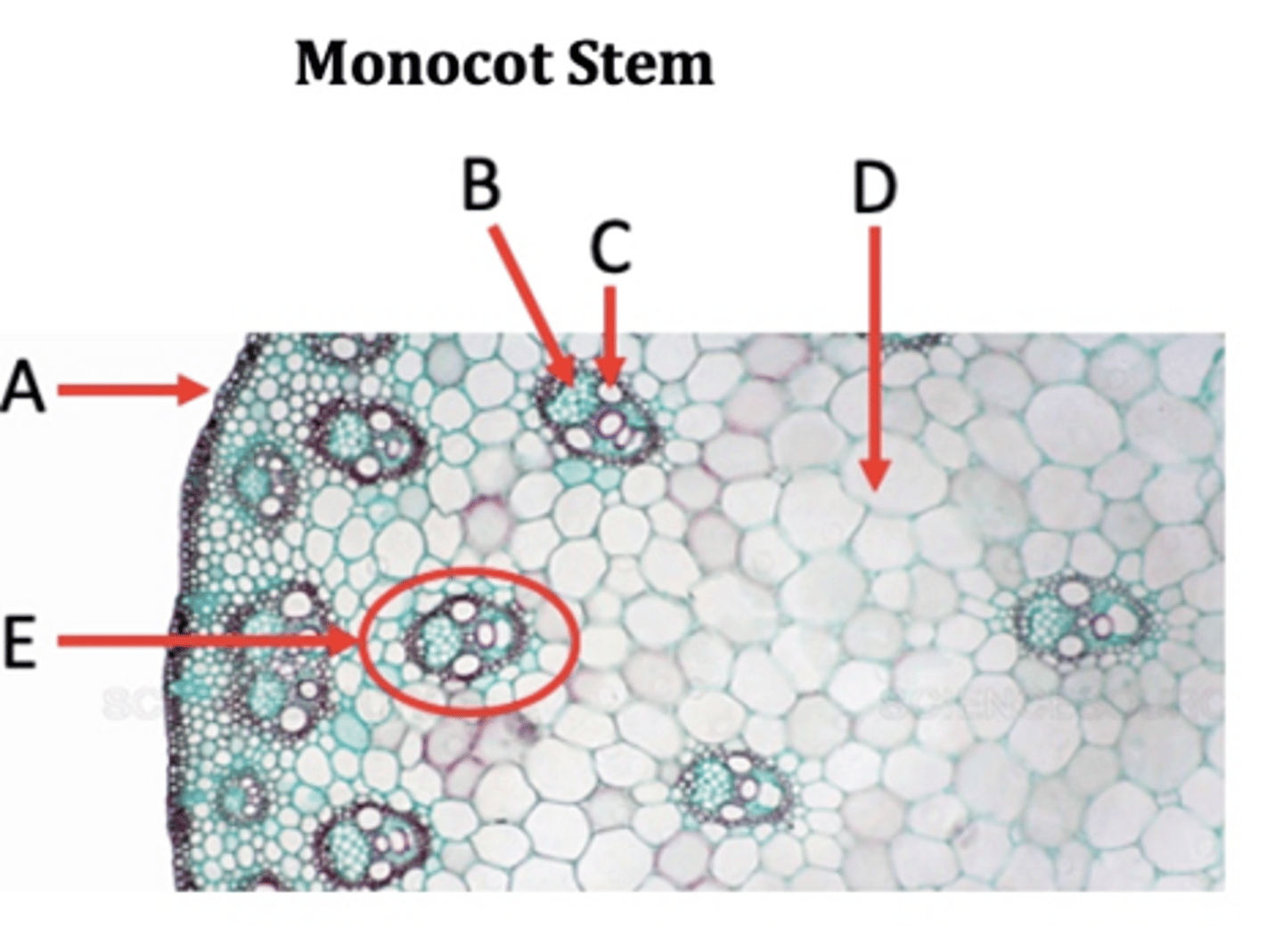
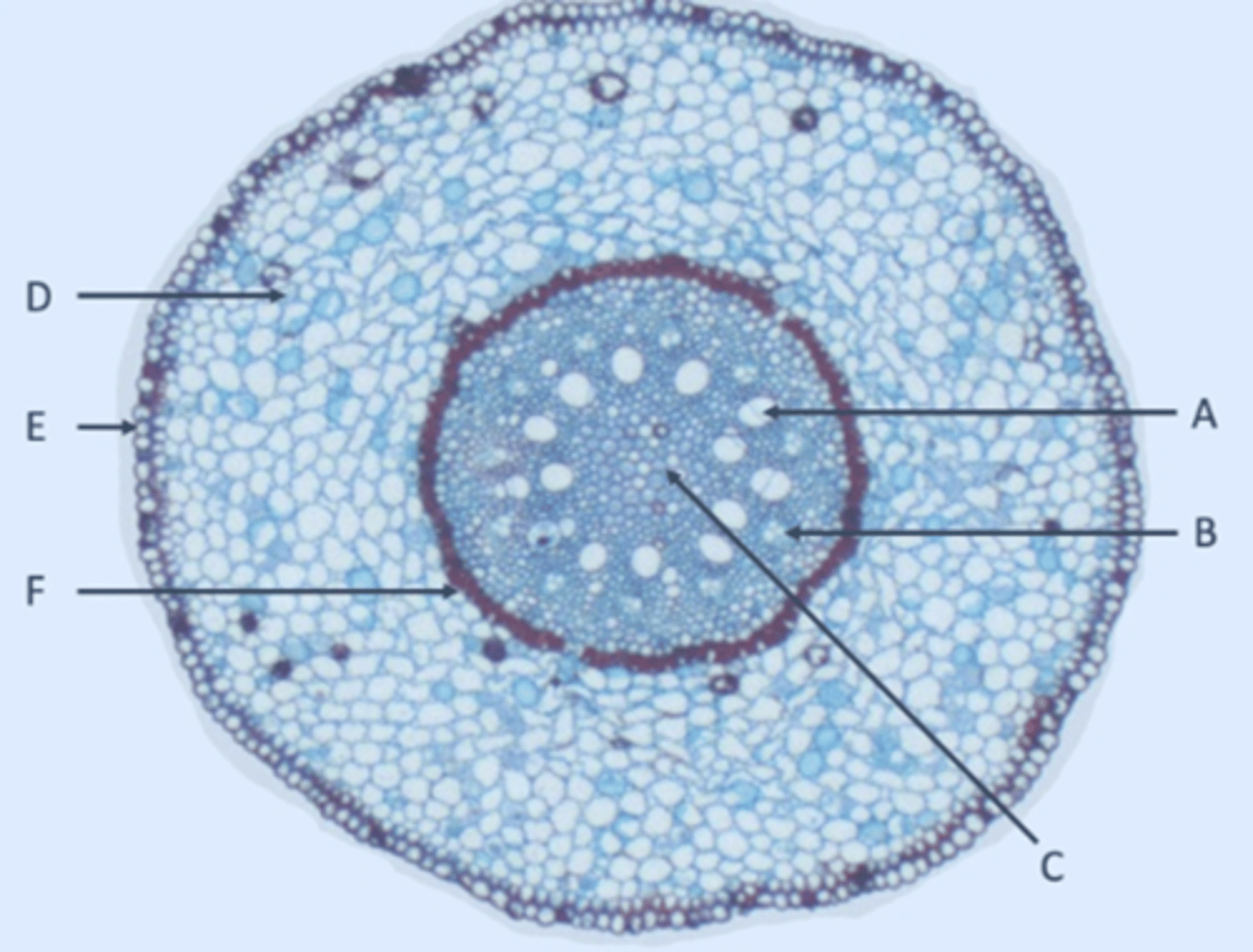
Epidermis
A?
Phloem
B?
Xylem
C?
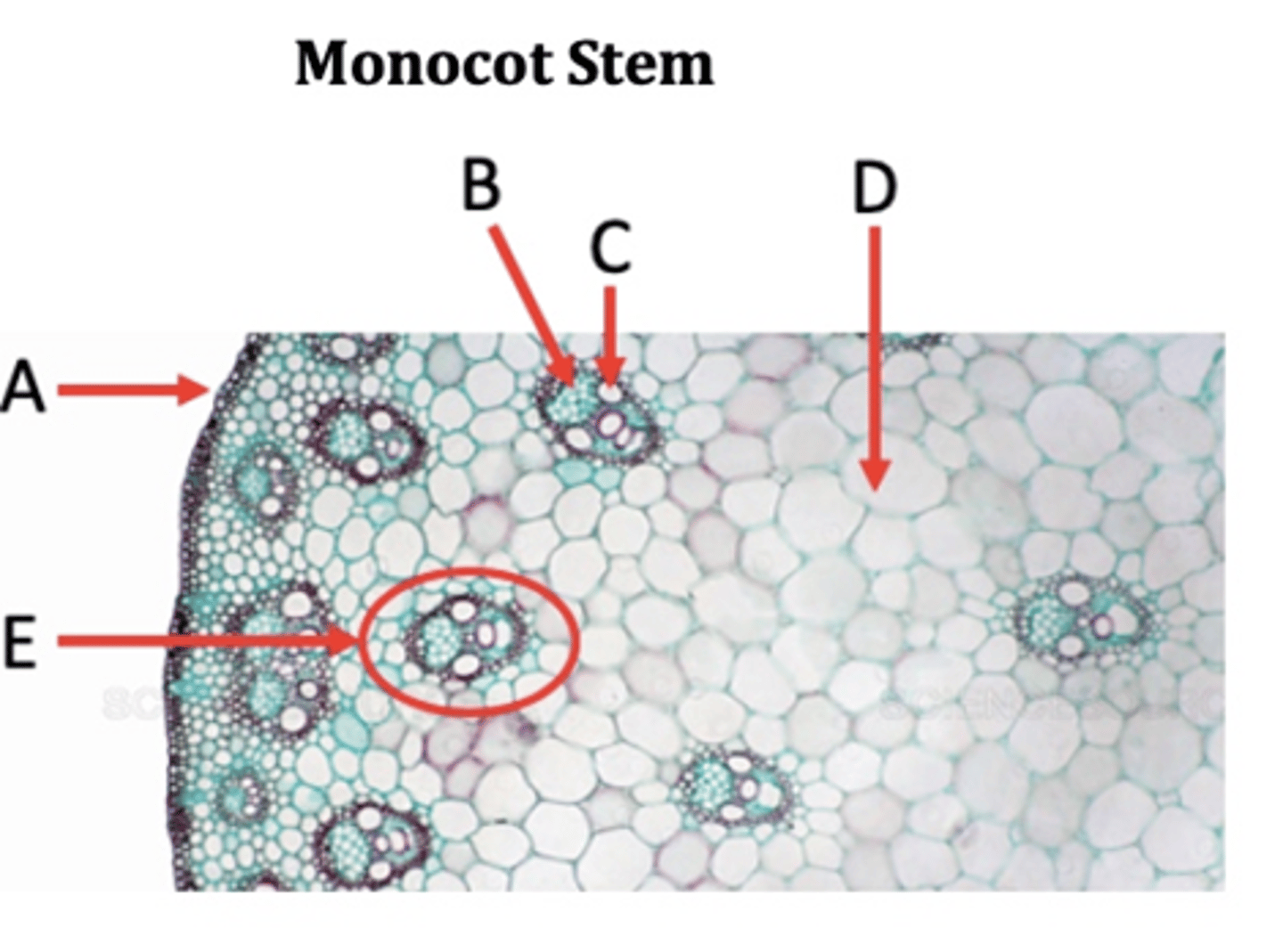
Ground tissue
D?
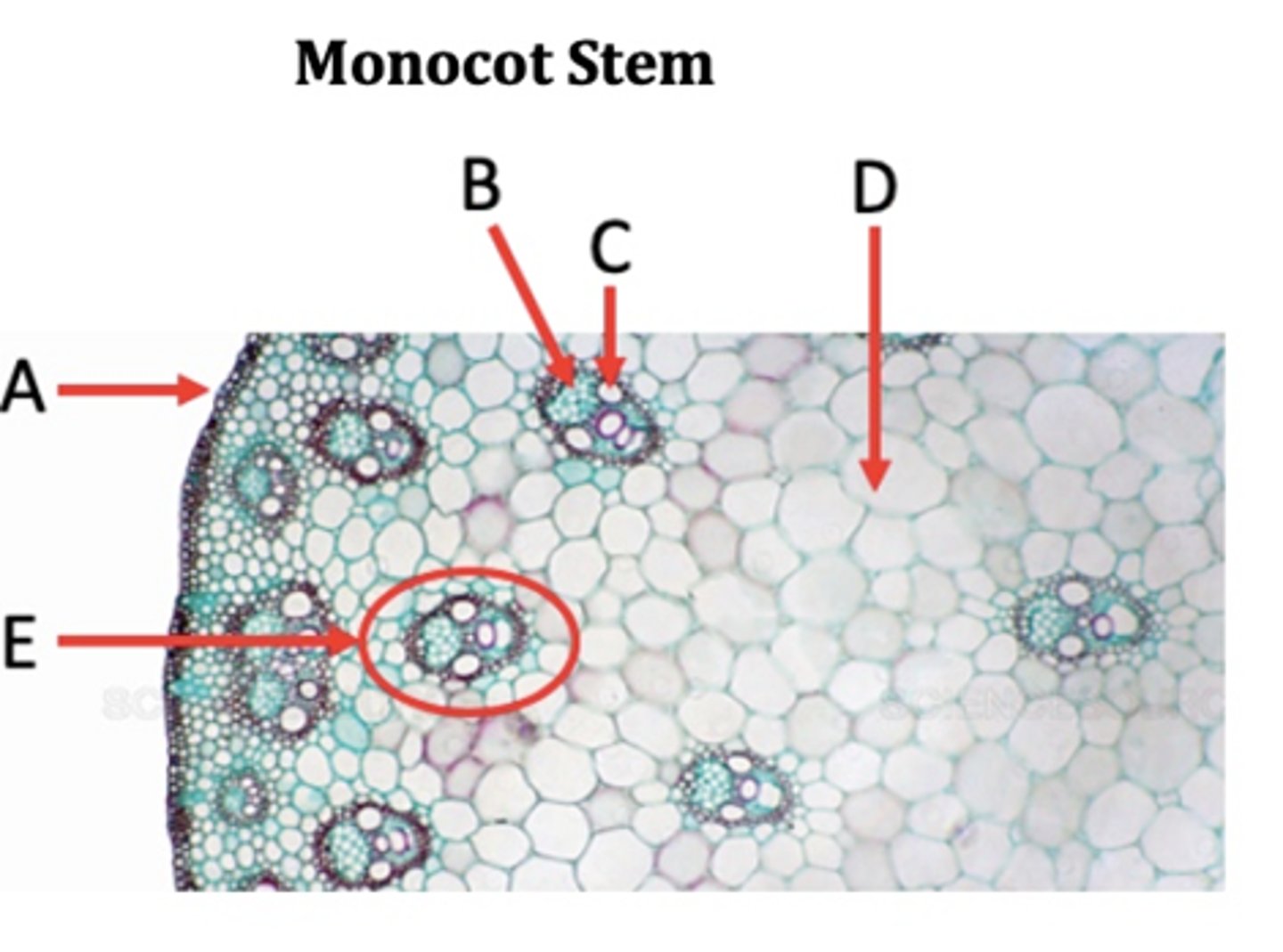
Vascular bundle
E?
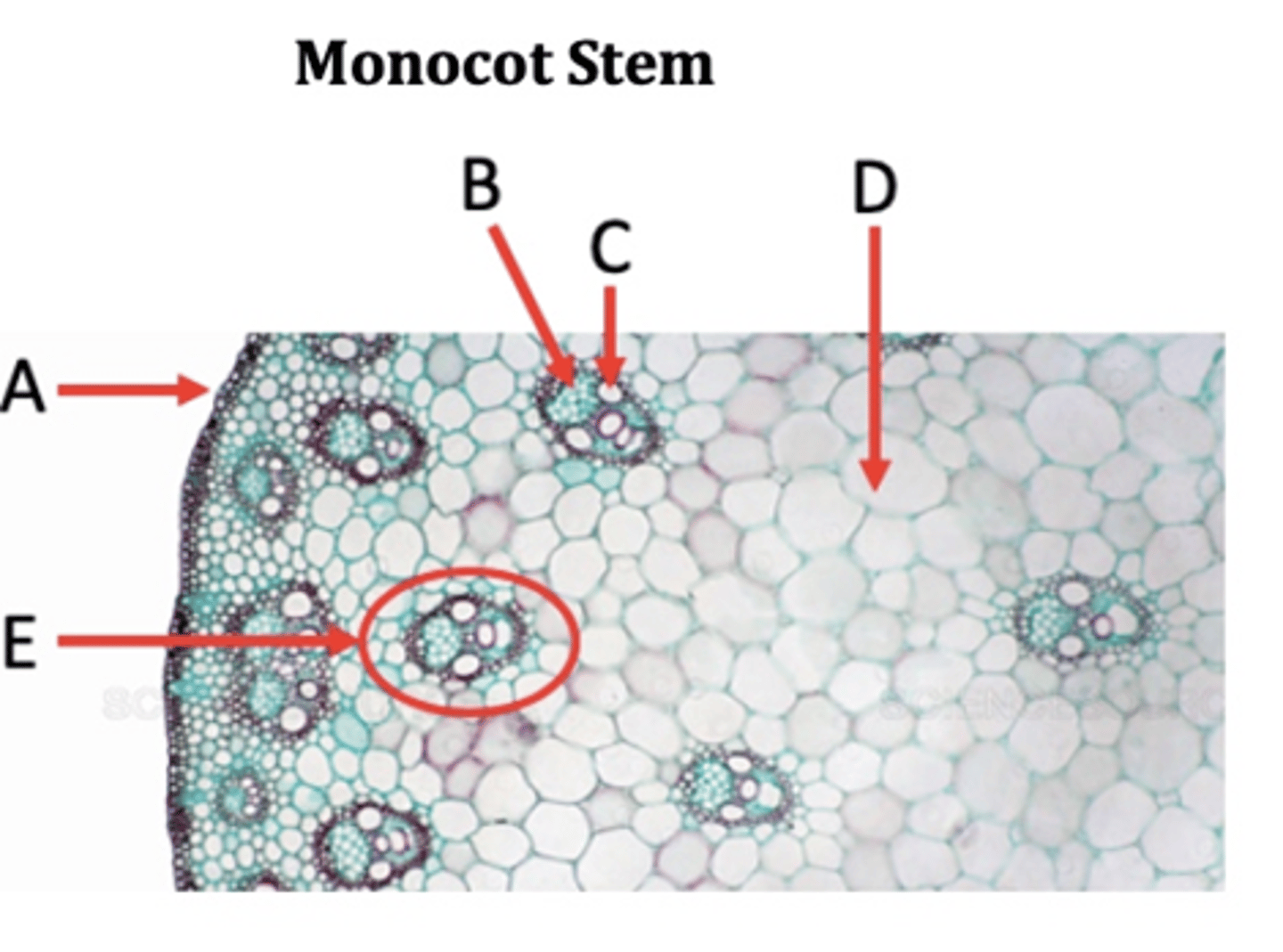
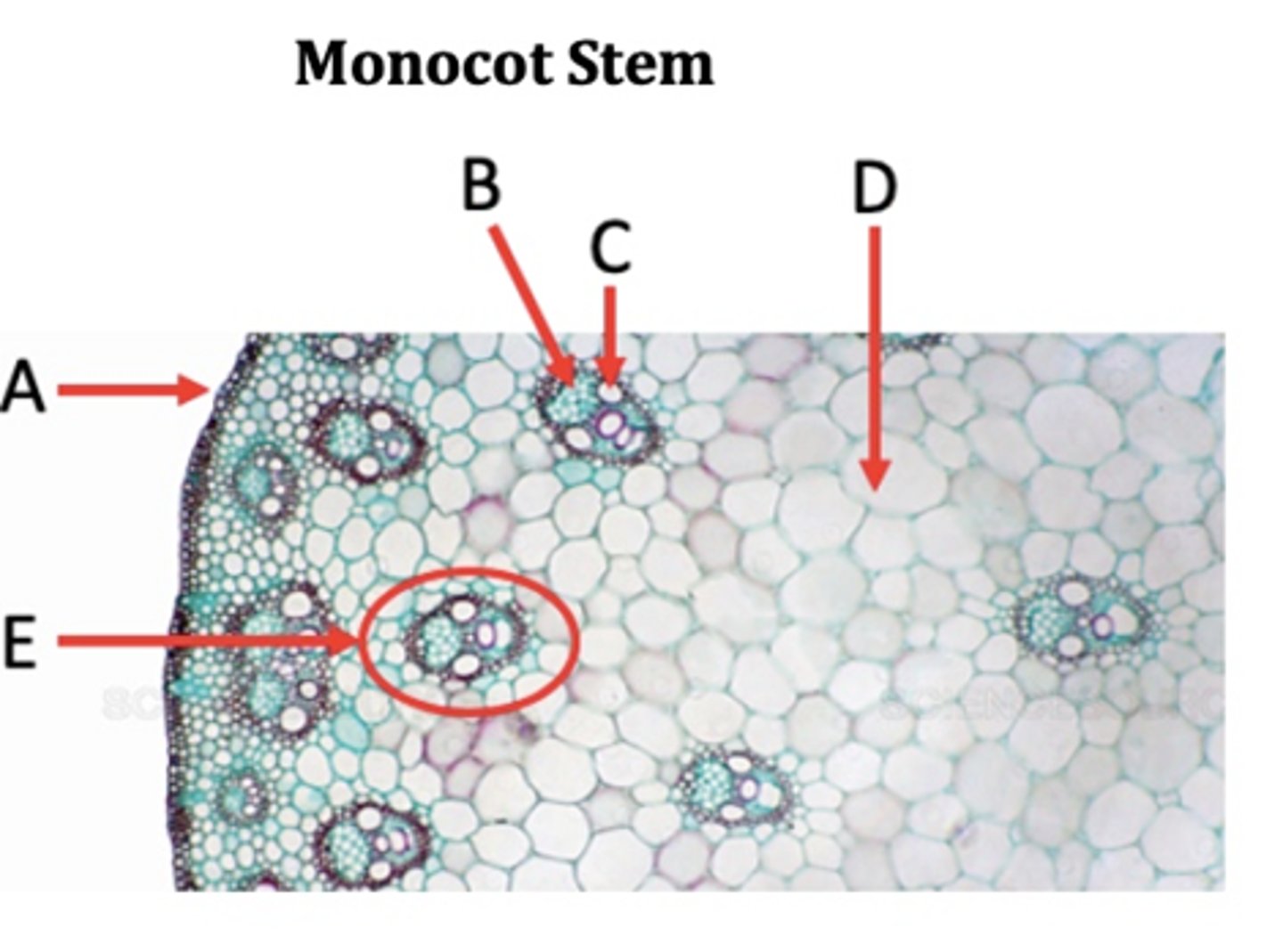
Vascular bundles
A?
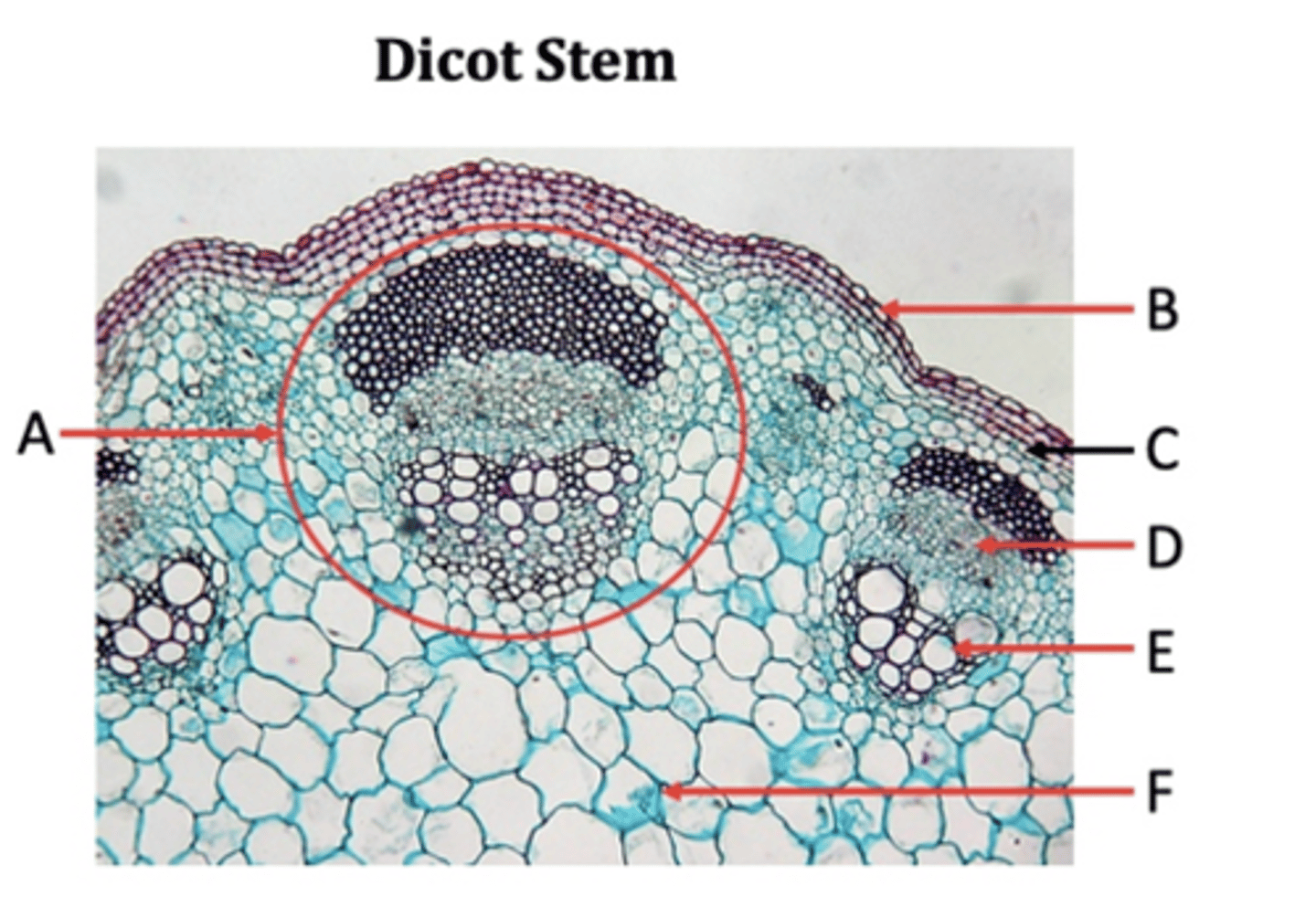
Epidermis
B?
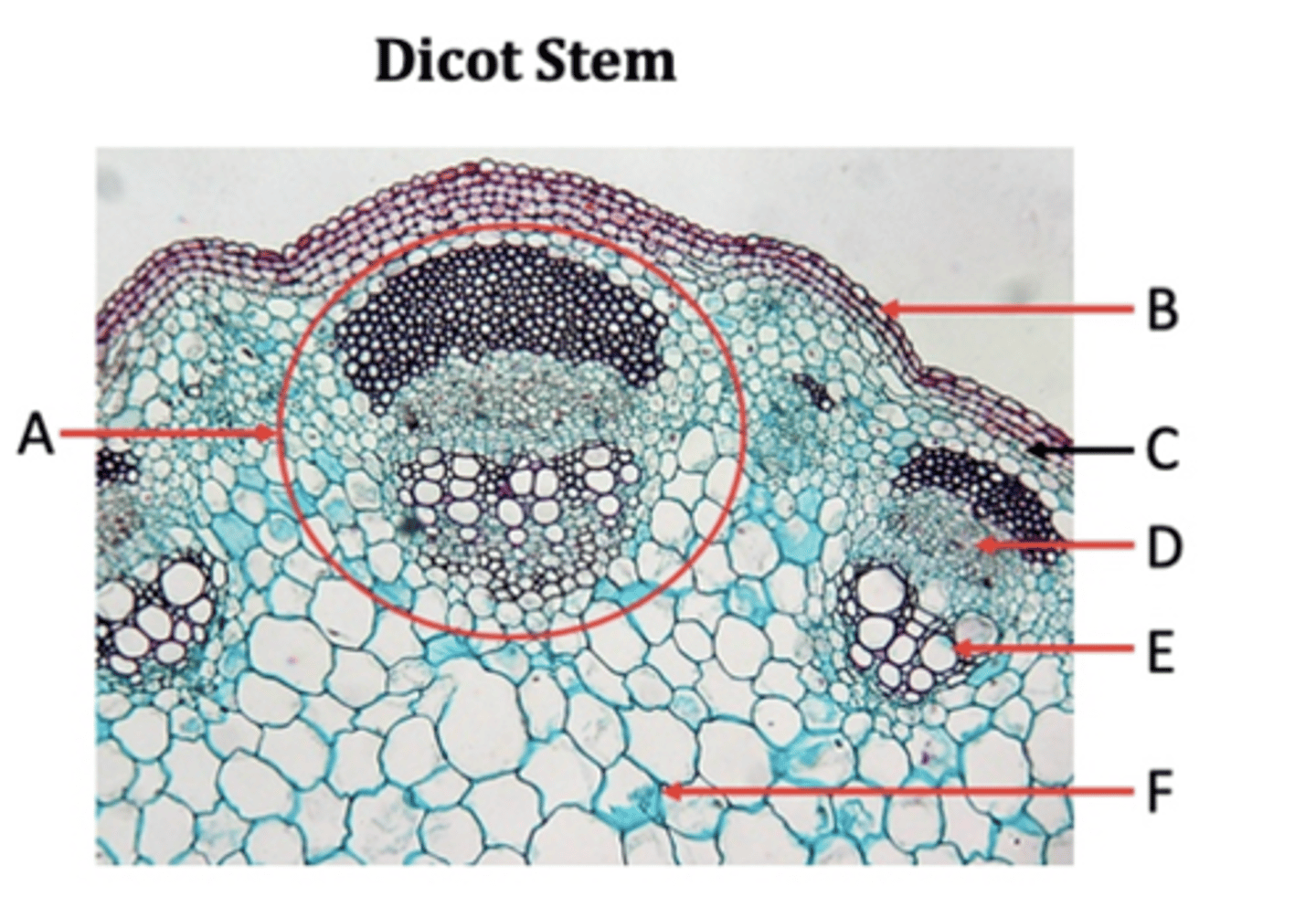
Collenchyma
C?
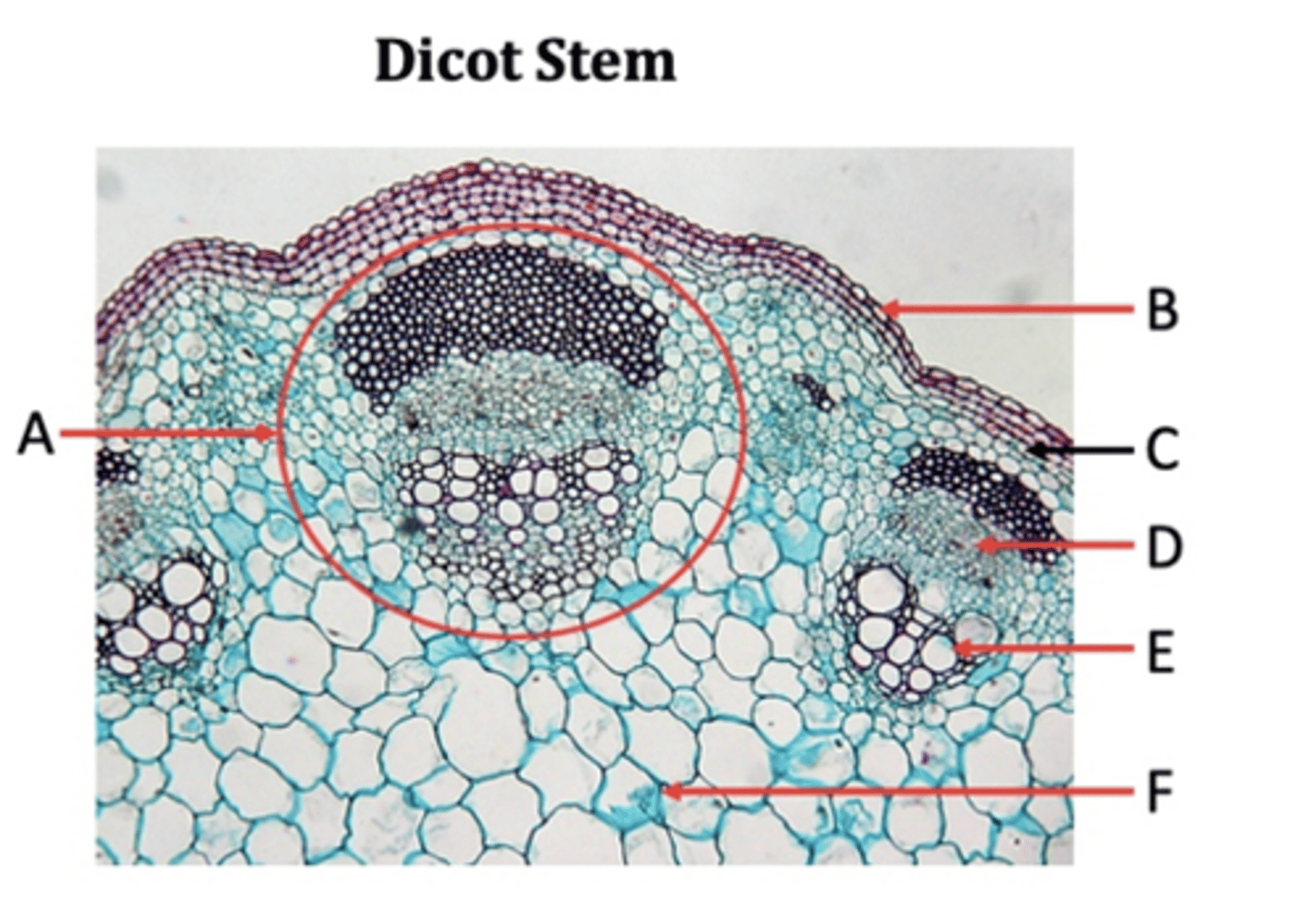
Phloem
D?
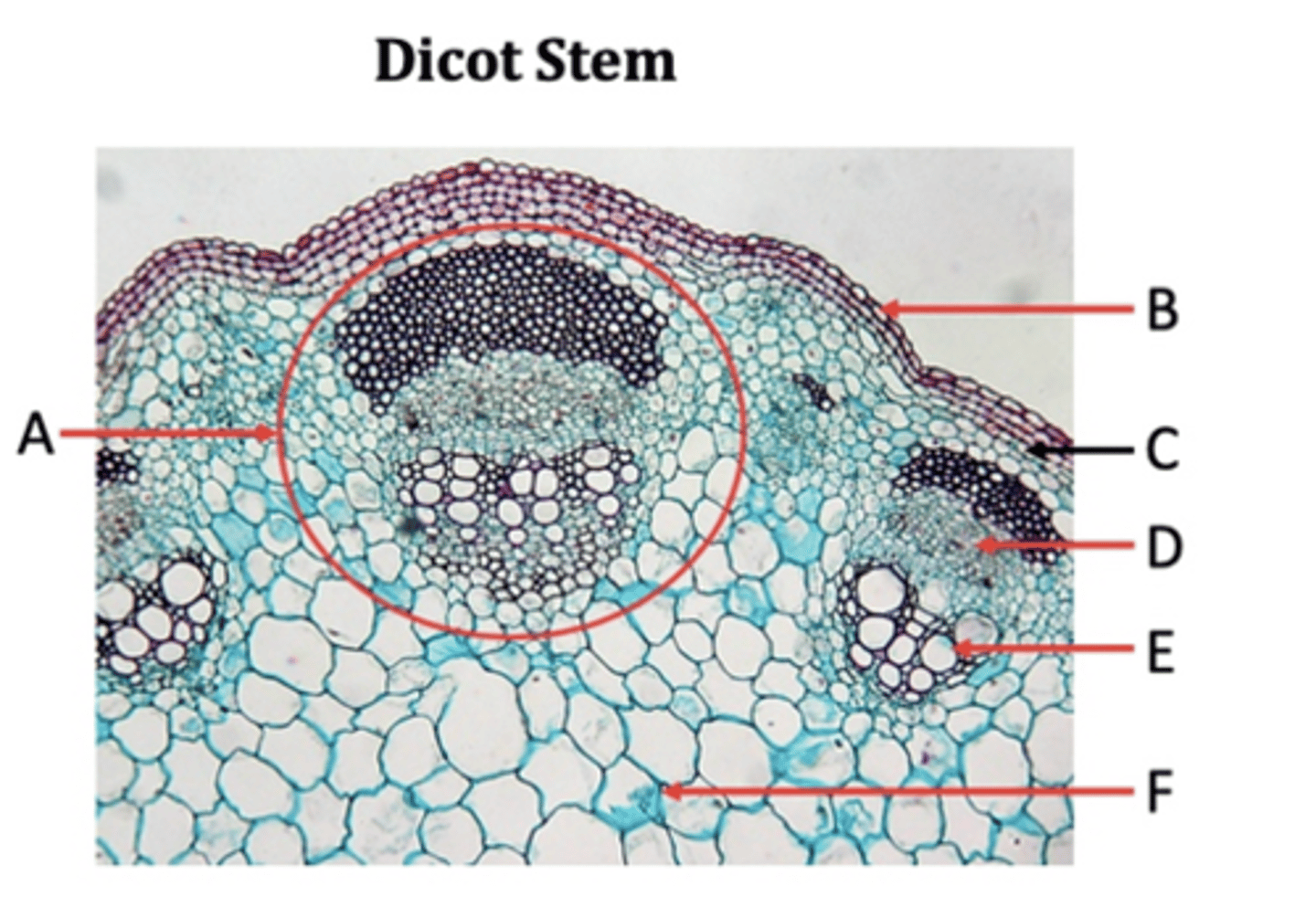
Xylem
E?
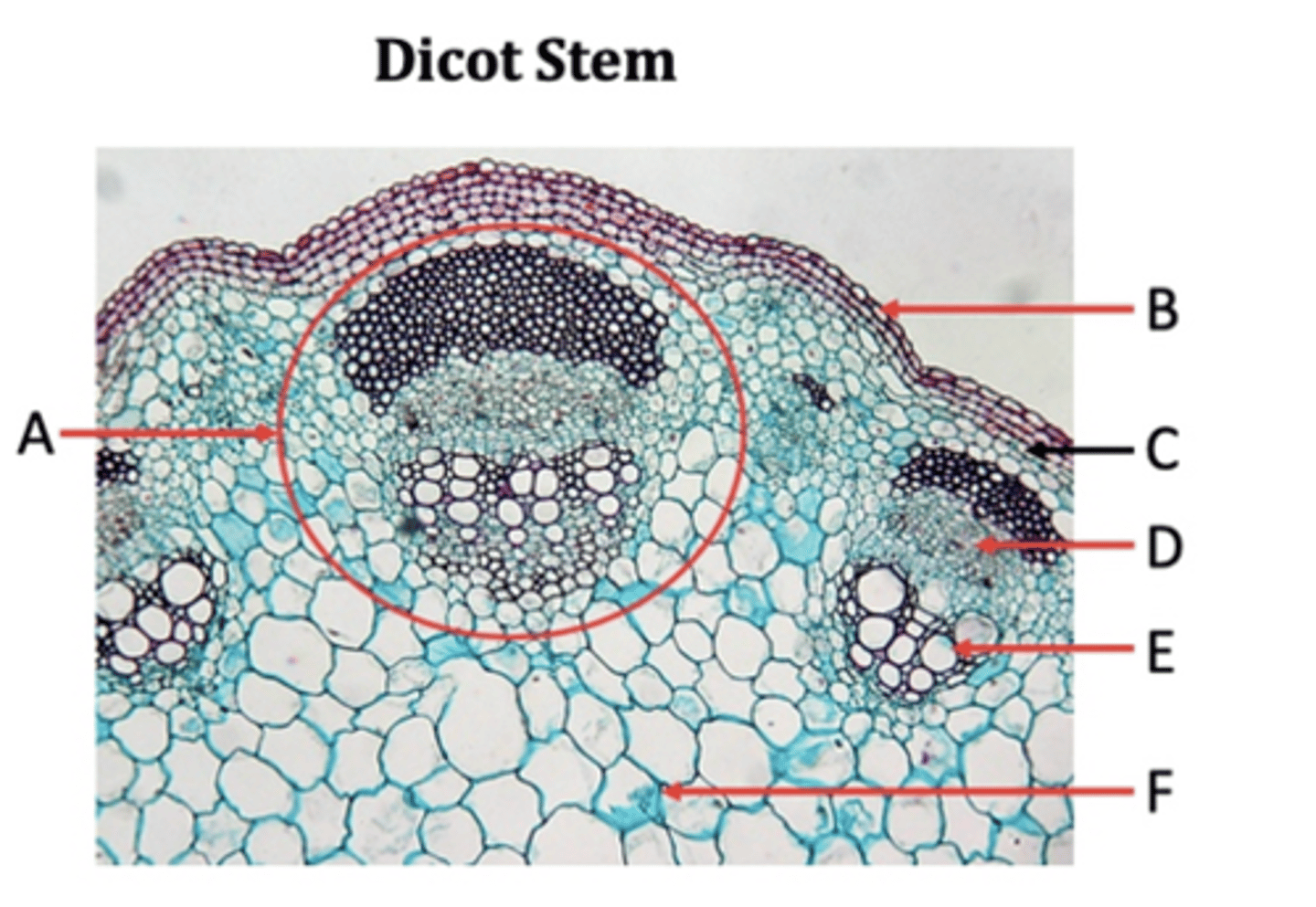
Pith
F?
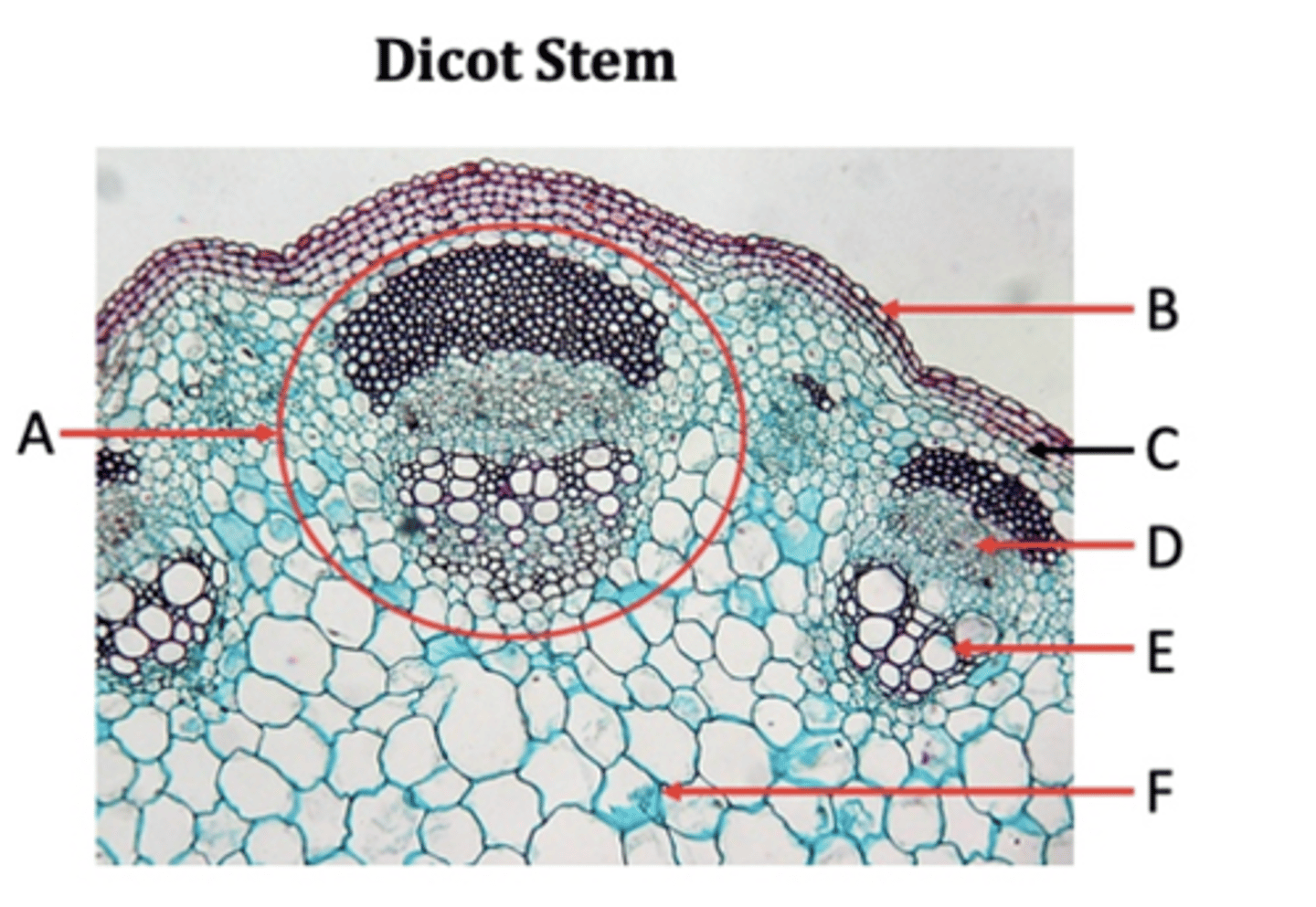
Parenchyma
In monocots, the ground tissue is primarily consisted of _____ cells.
Dicot
Vascular tissues in stems are in a ring. Monocot or Dicot?
Pith
Monocots to not have a ____.
Monocot
Vascular tissues in stems are scattered. Monocot or Dicot?
Casparian strip
What is the name of the water-impermeable seal that fills space between cells of root endodermis and forces water and minerals to pass through plasma membrane rather than cell walls?
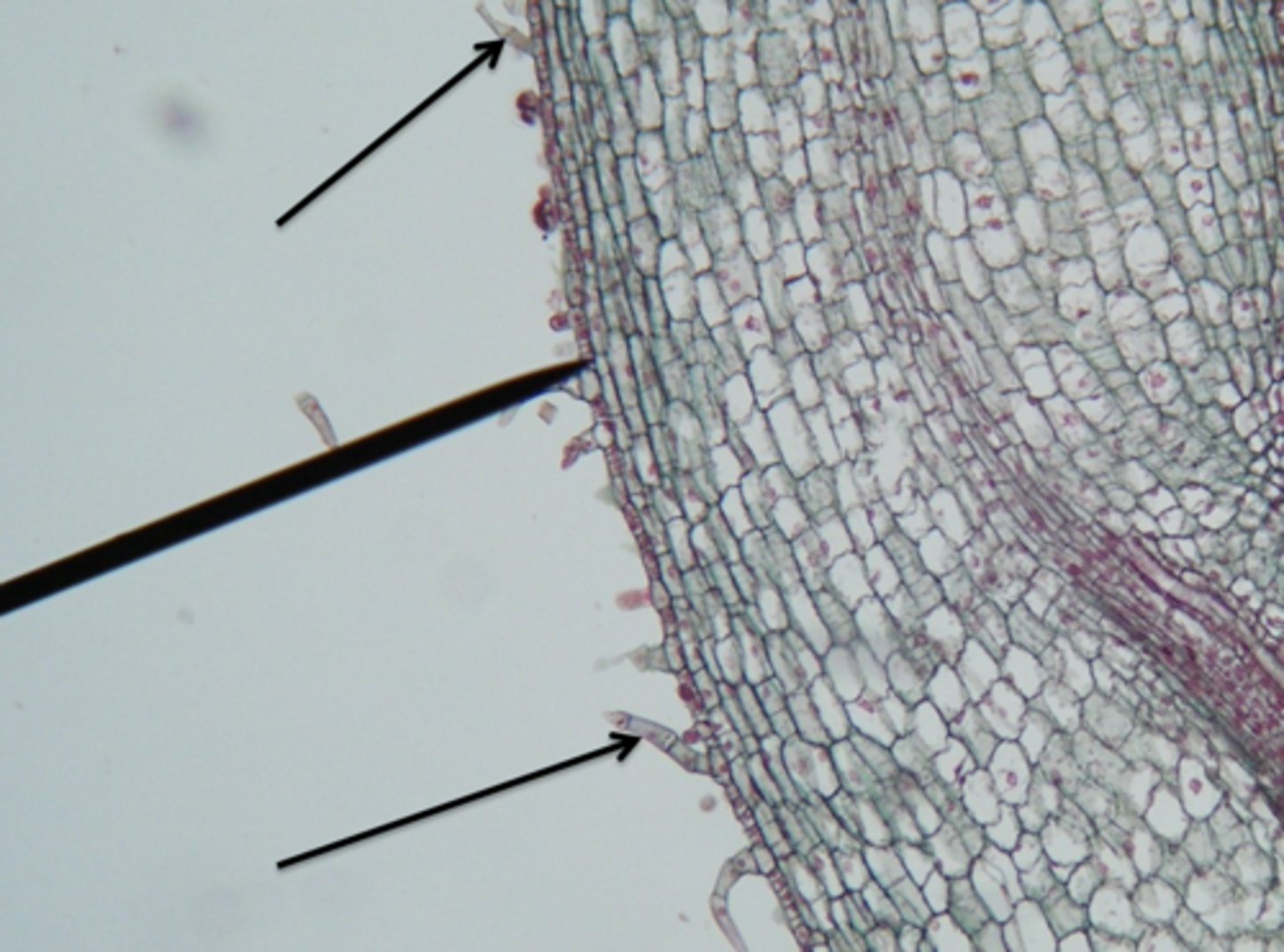
Root hairs
What is the name of the organ in plants whose function is to uptake water and minerals?
Root hairs
Tubular extensions of epidermal cells are the origin of what plant organ?
Lateral roots
What plant organ originated from the pericycle opposite to protoxylem poles and is endogenous?
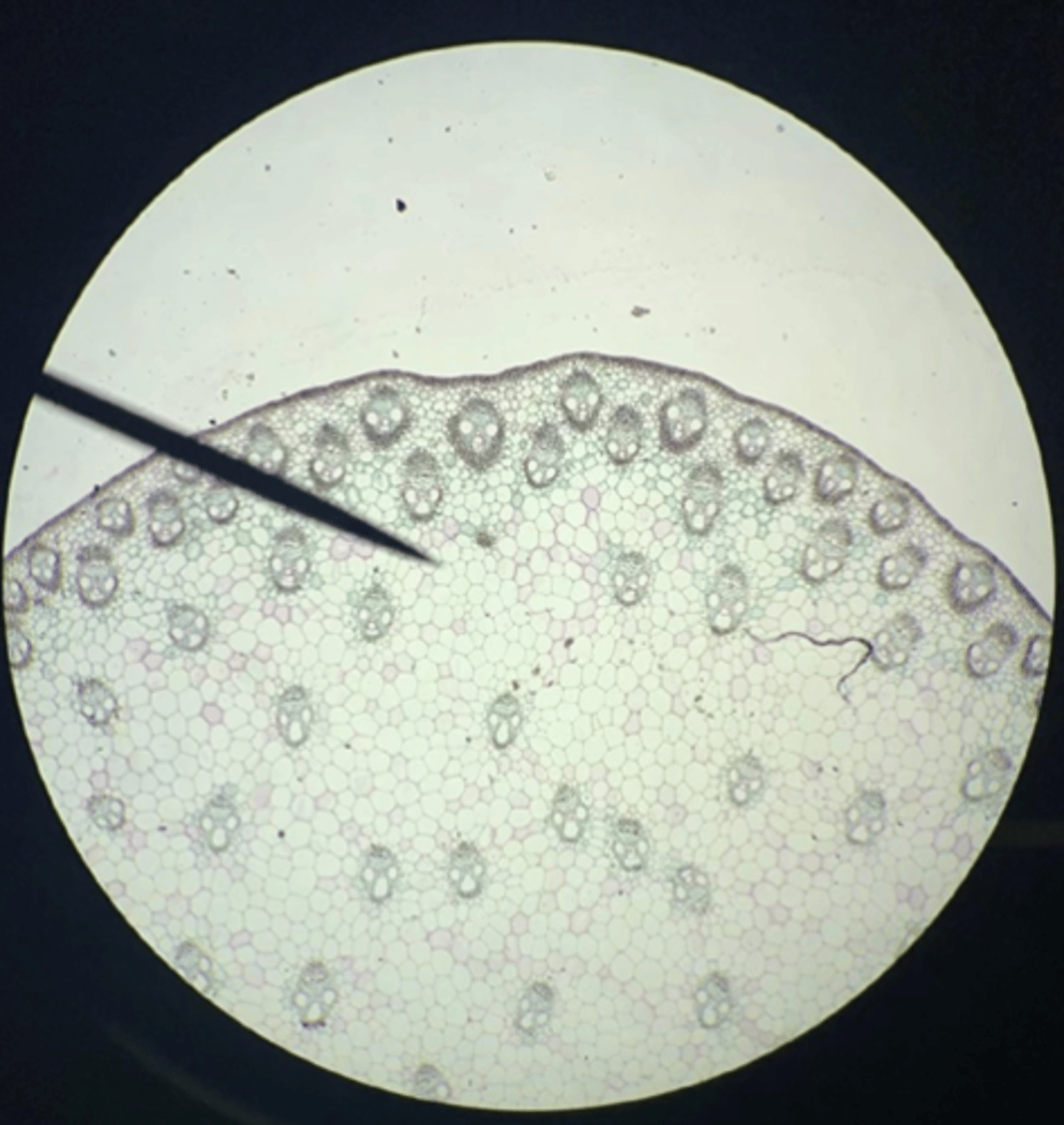
Monocot
Is this Zea stem a Monocot or Dicot?
Monocot
Is this Zea root a Monocot or Dicot?
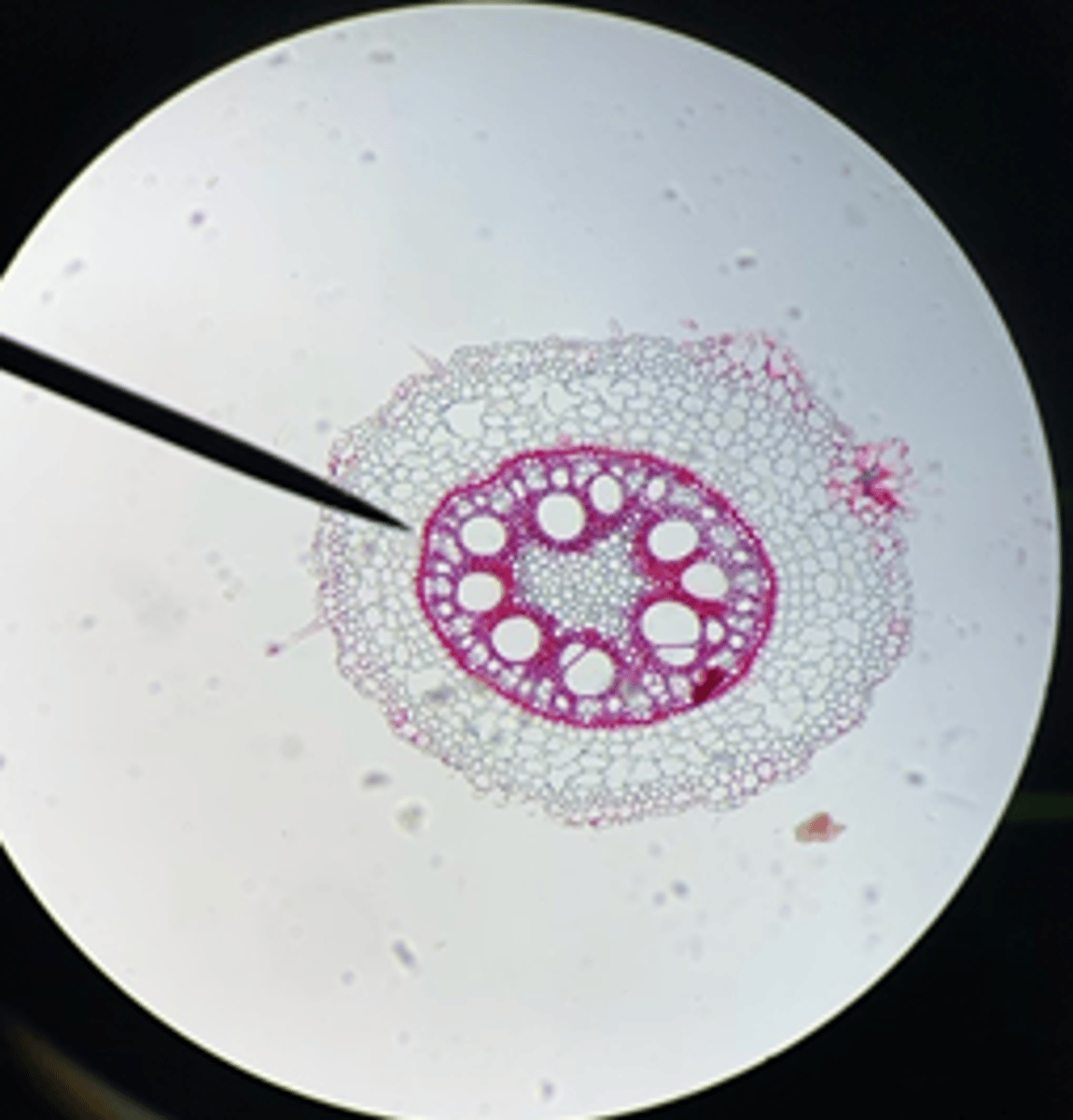
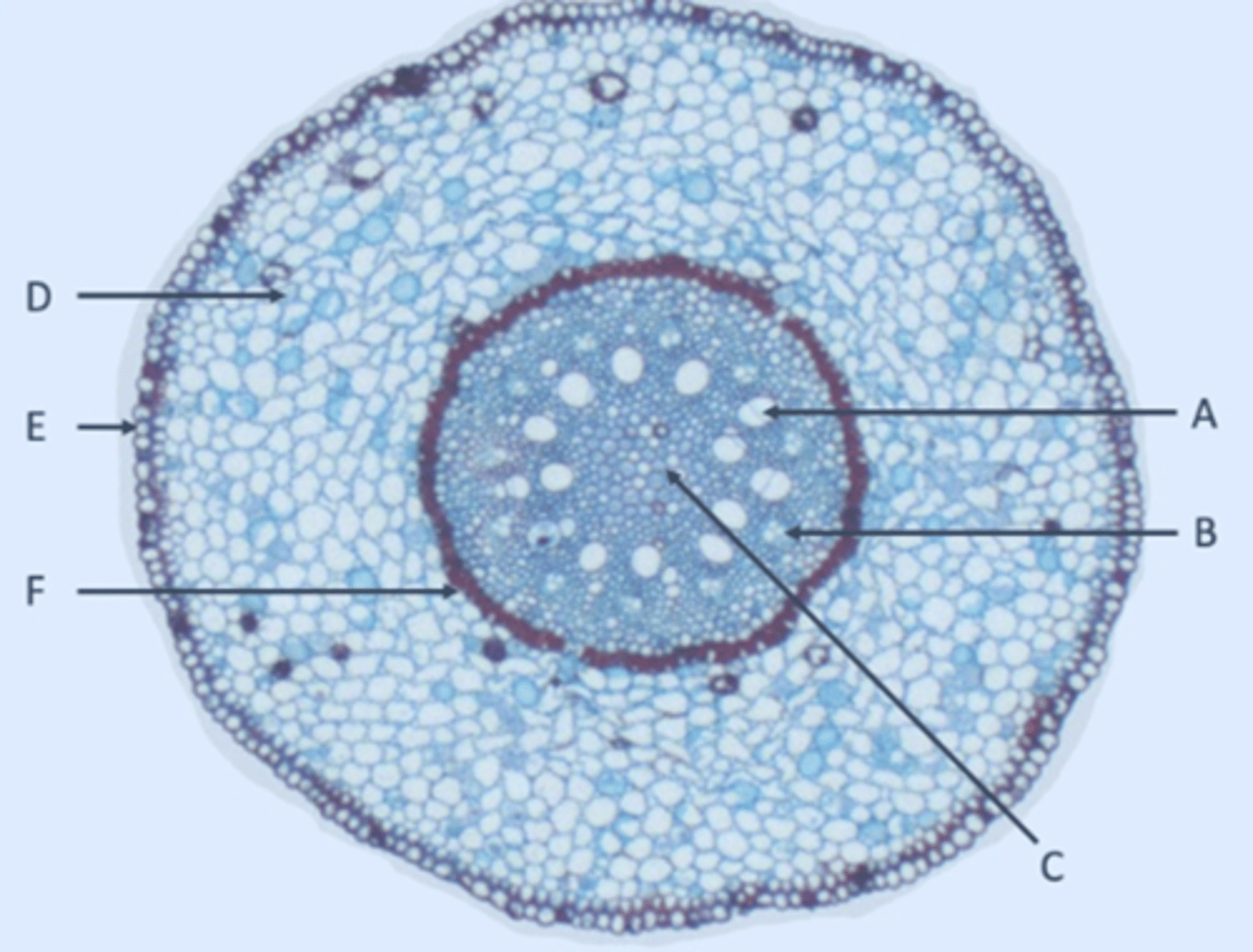
Xylem
A?
Phloem
B?
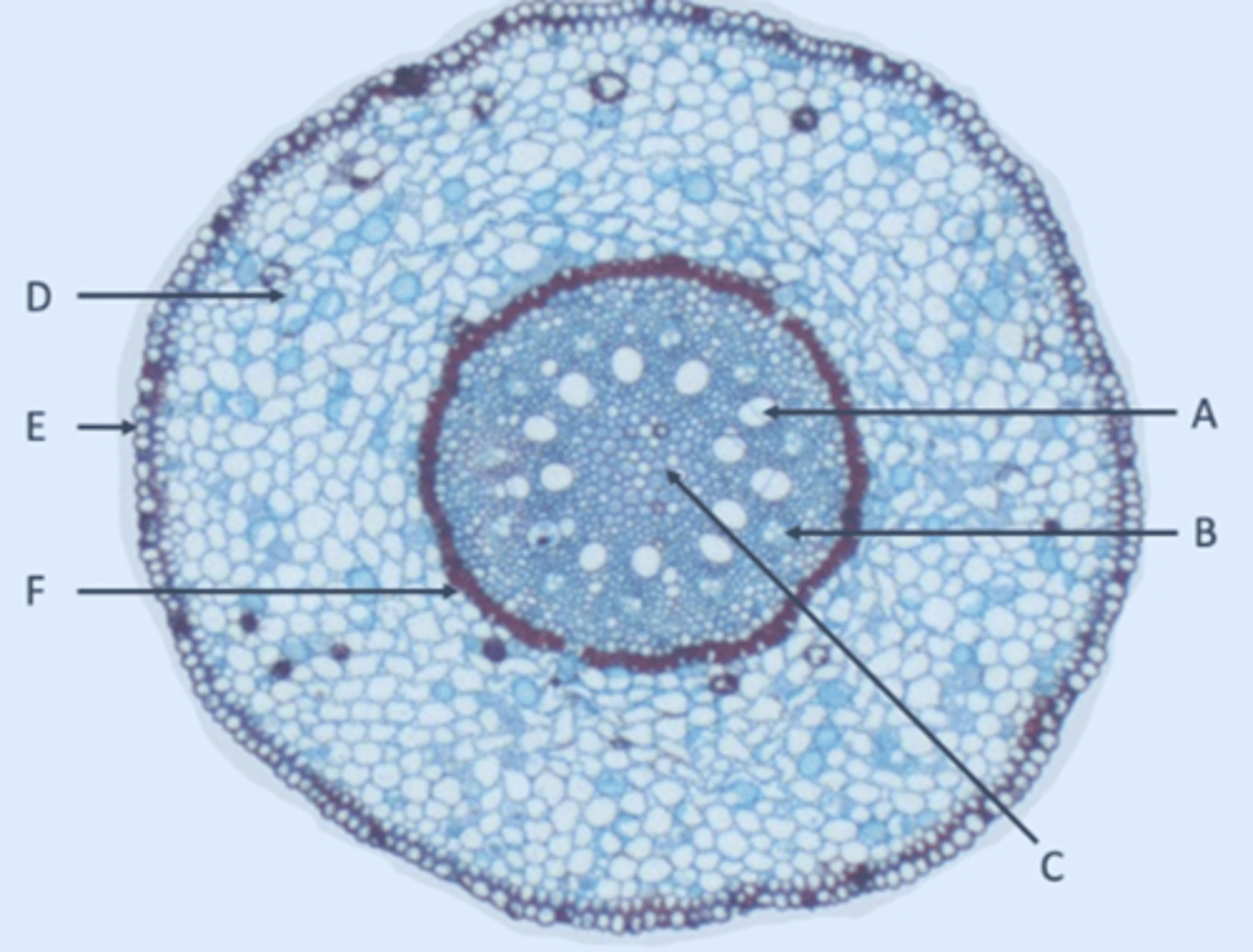
Pith
C?
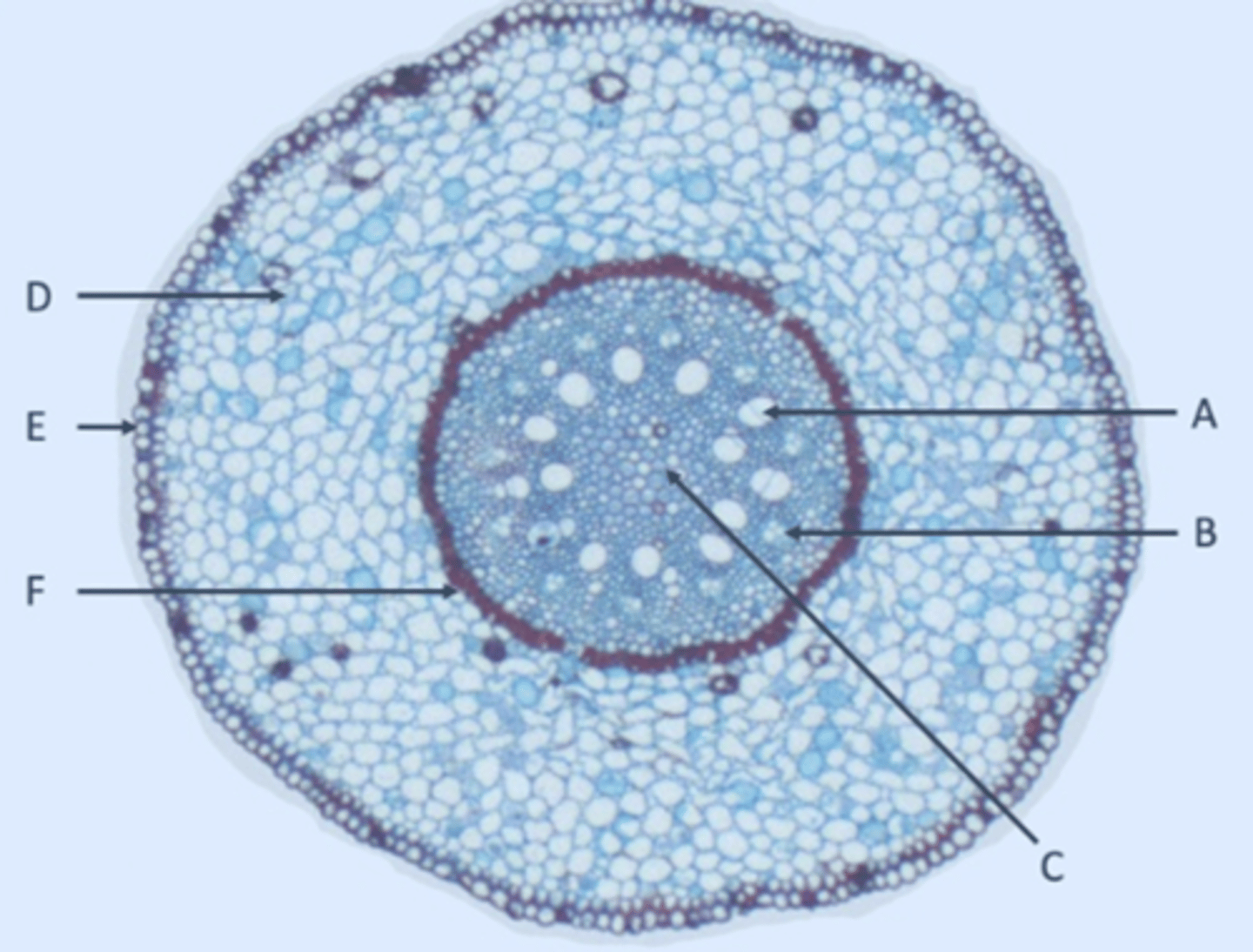
Parenchyma
D?
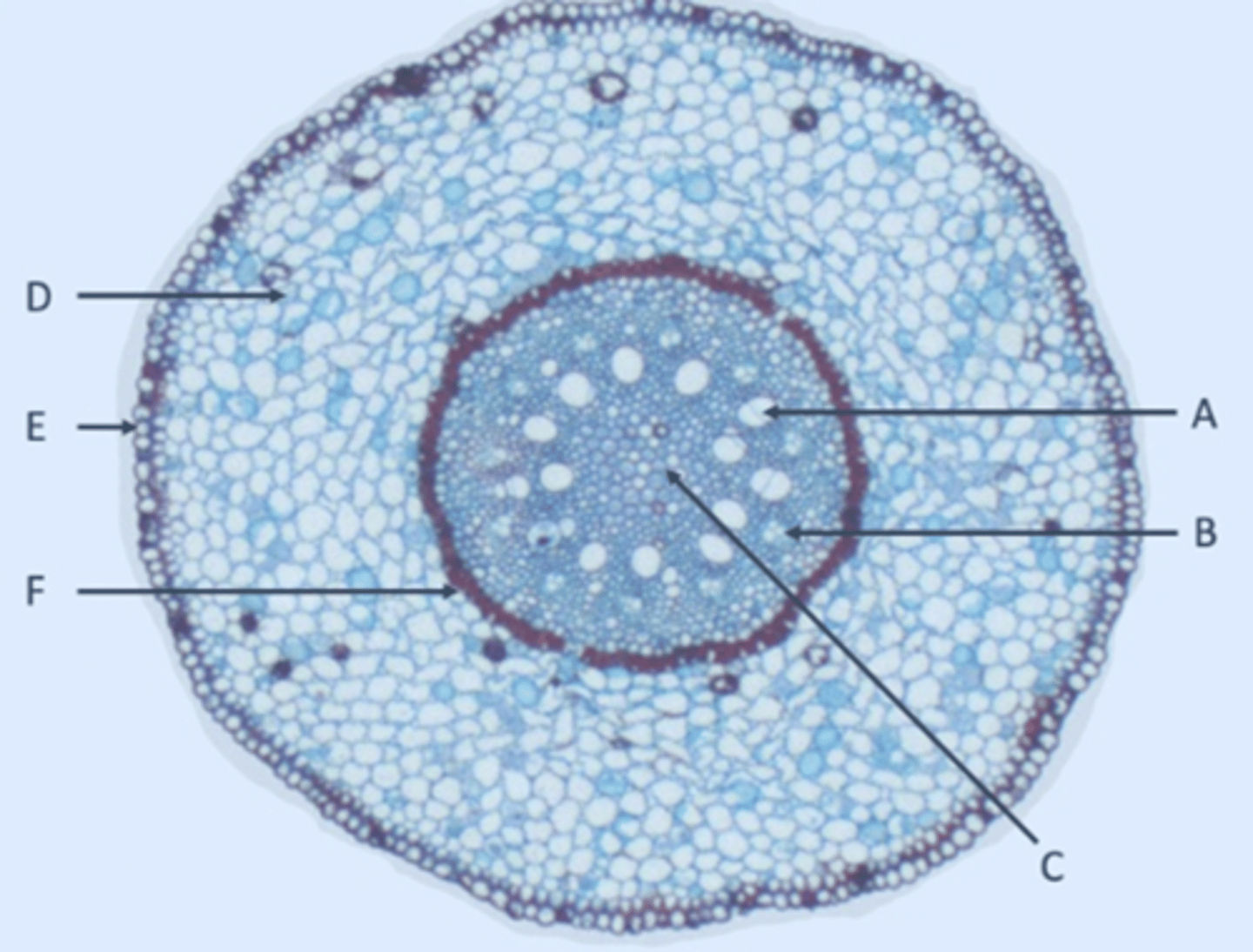
Epidermis
E?
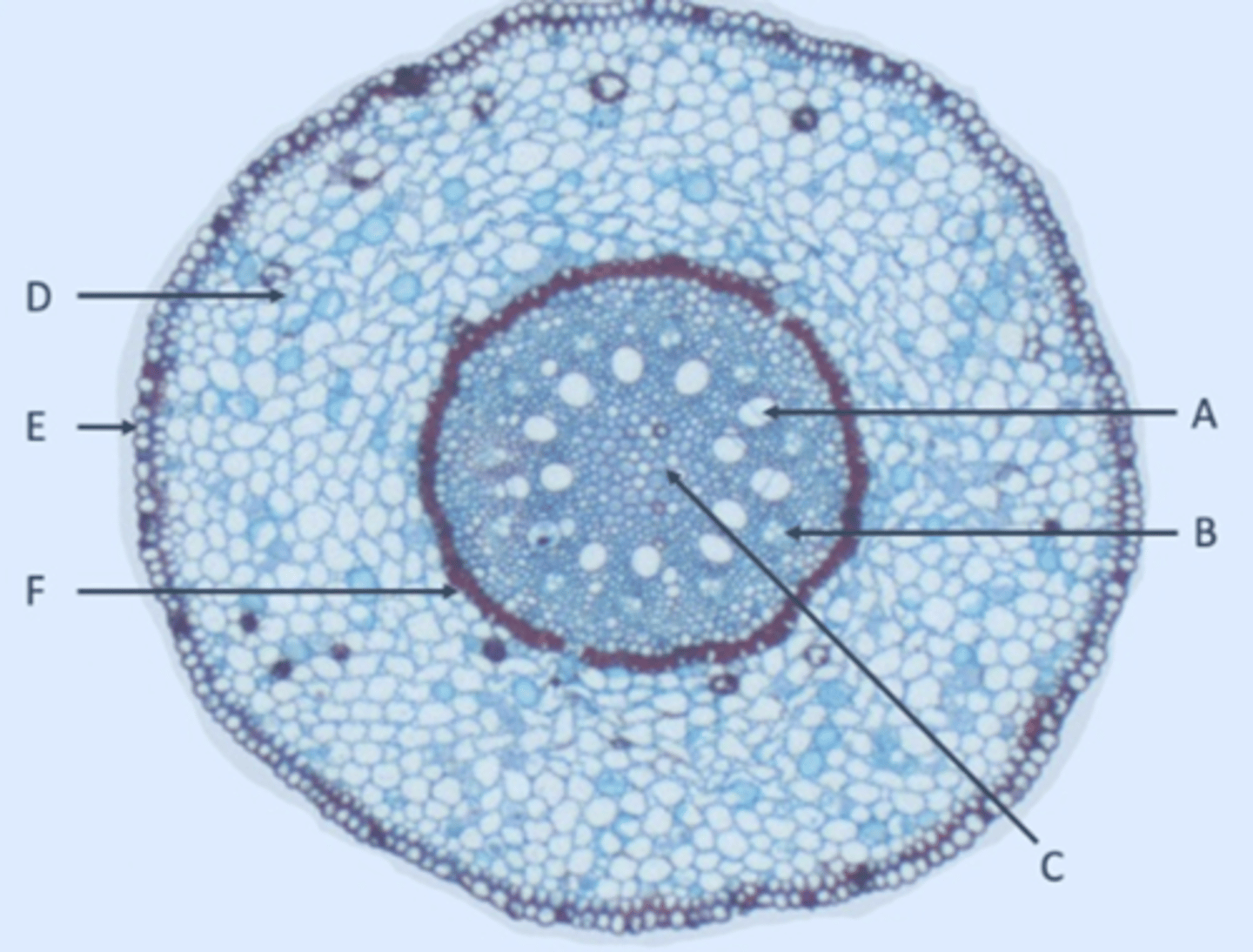
Endodermis
F?
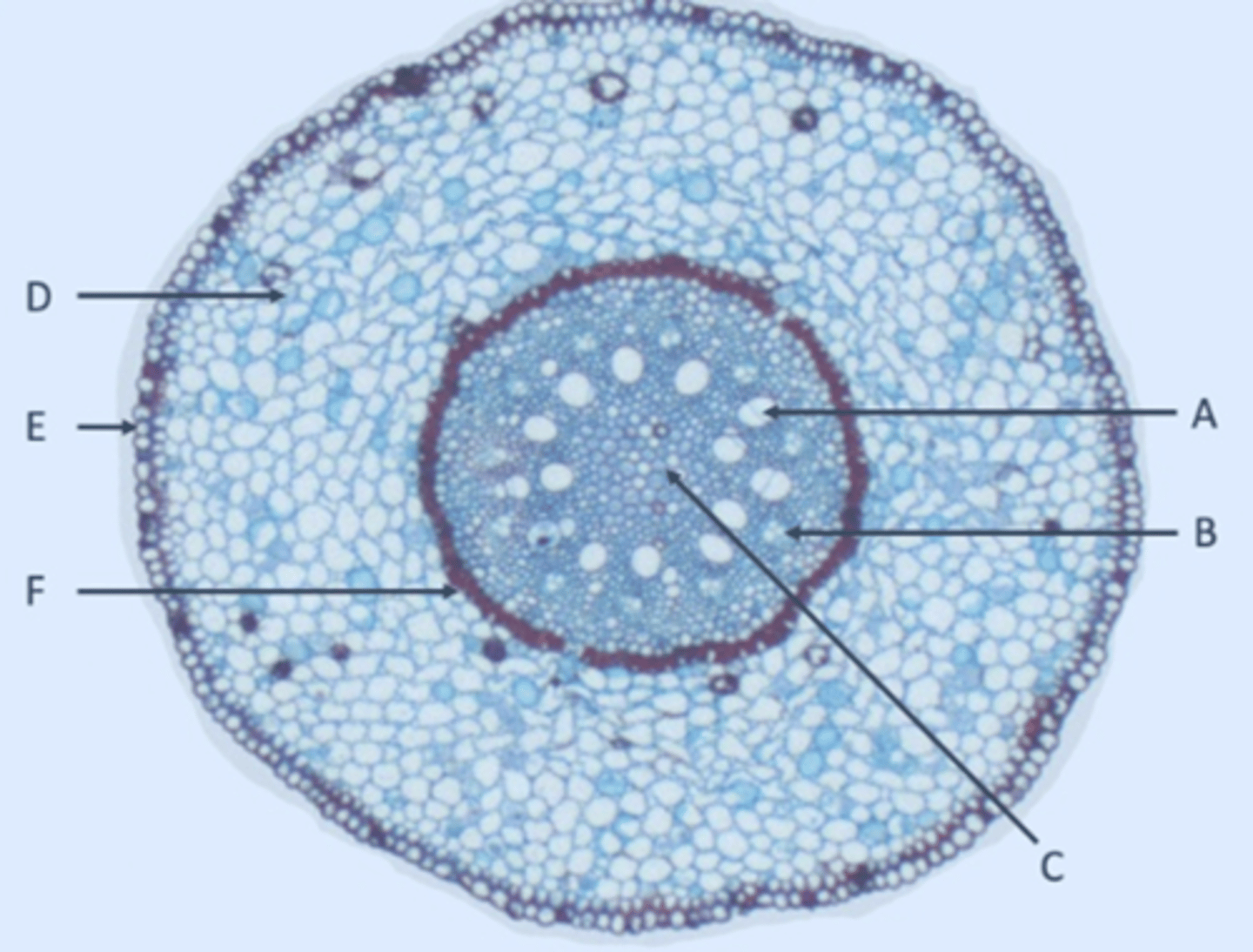
Pericycle
Inside edge of F?
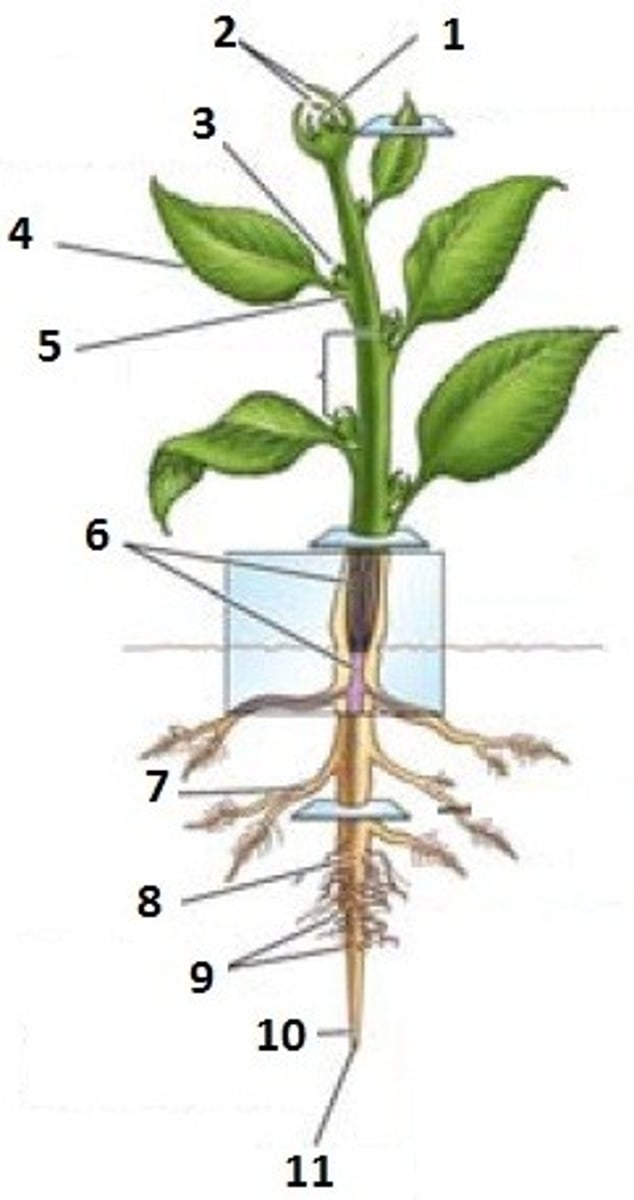
Leaf primordial
A?
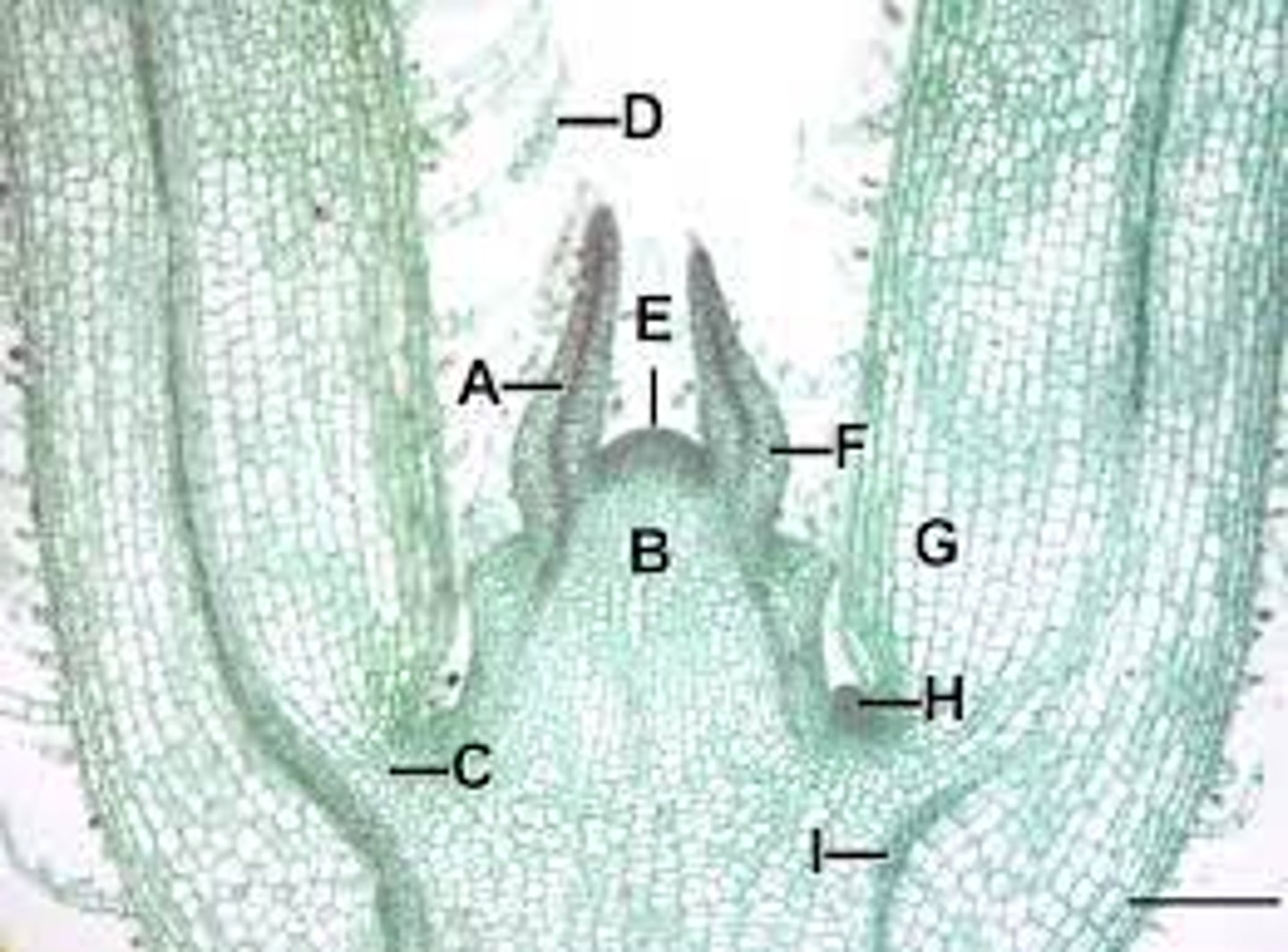
Apical meristem
E?
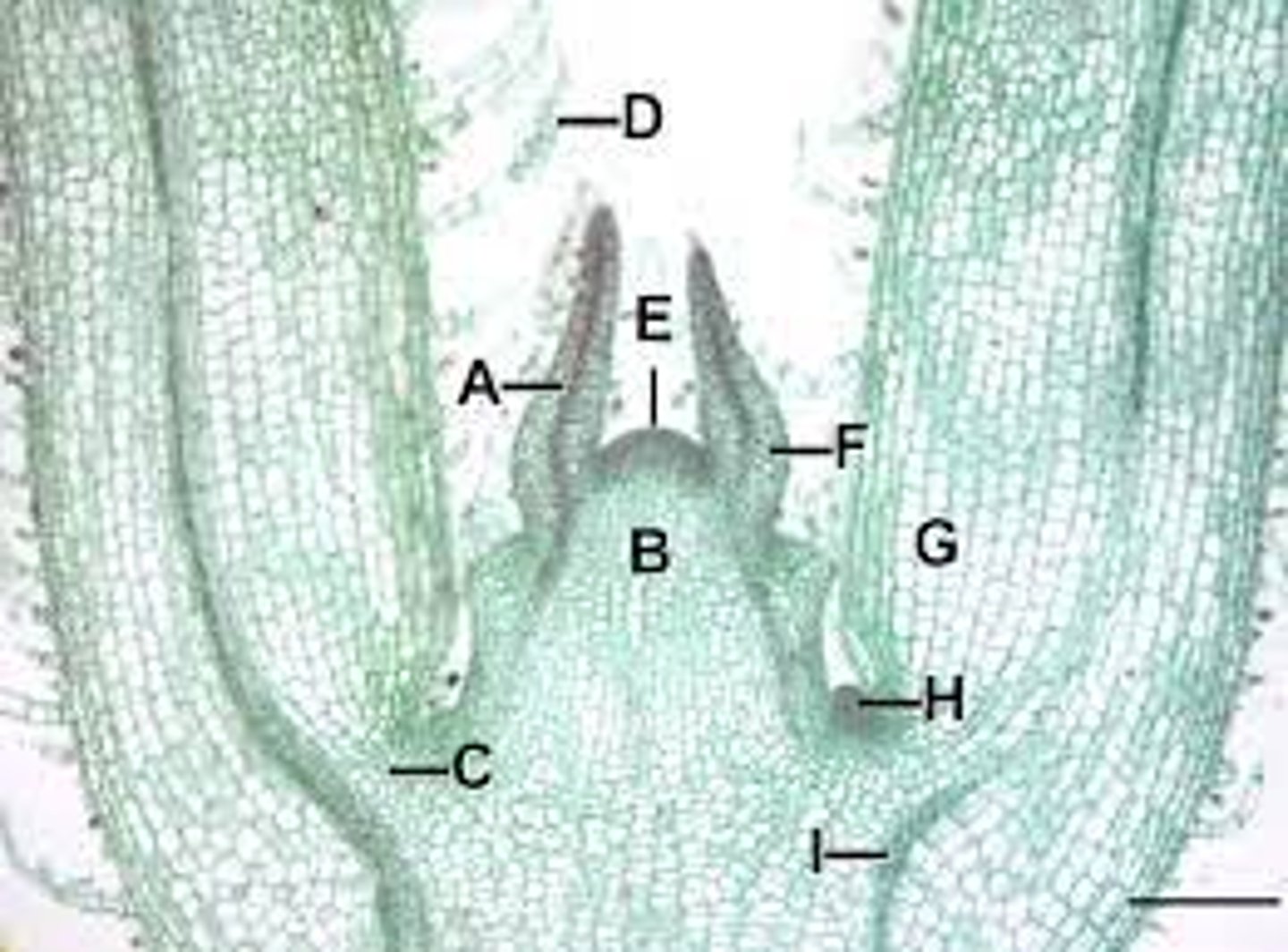
Lateral bud
H?
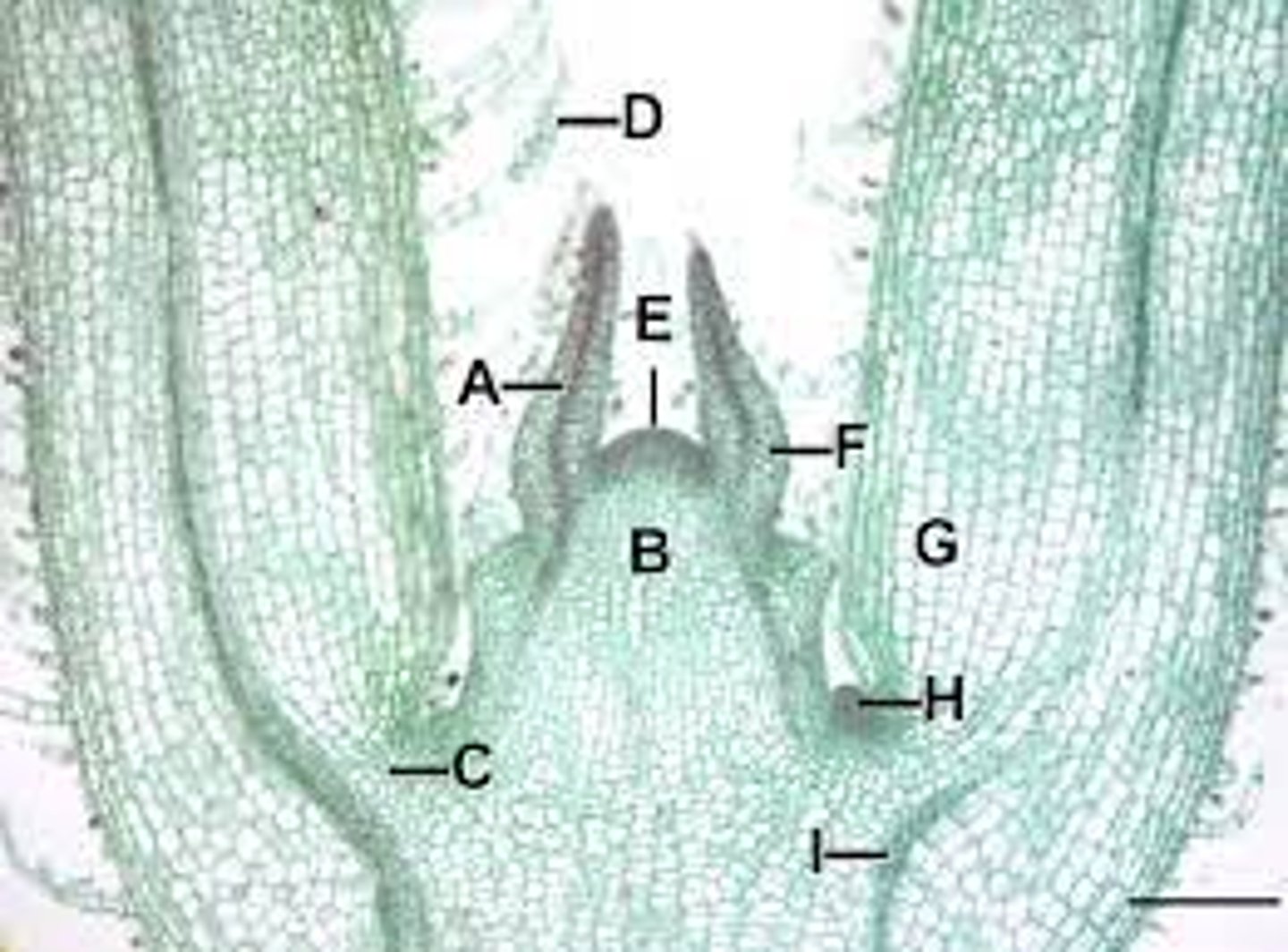
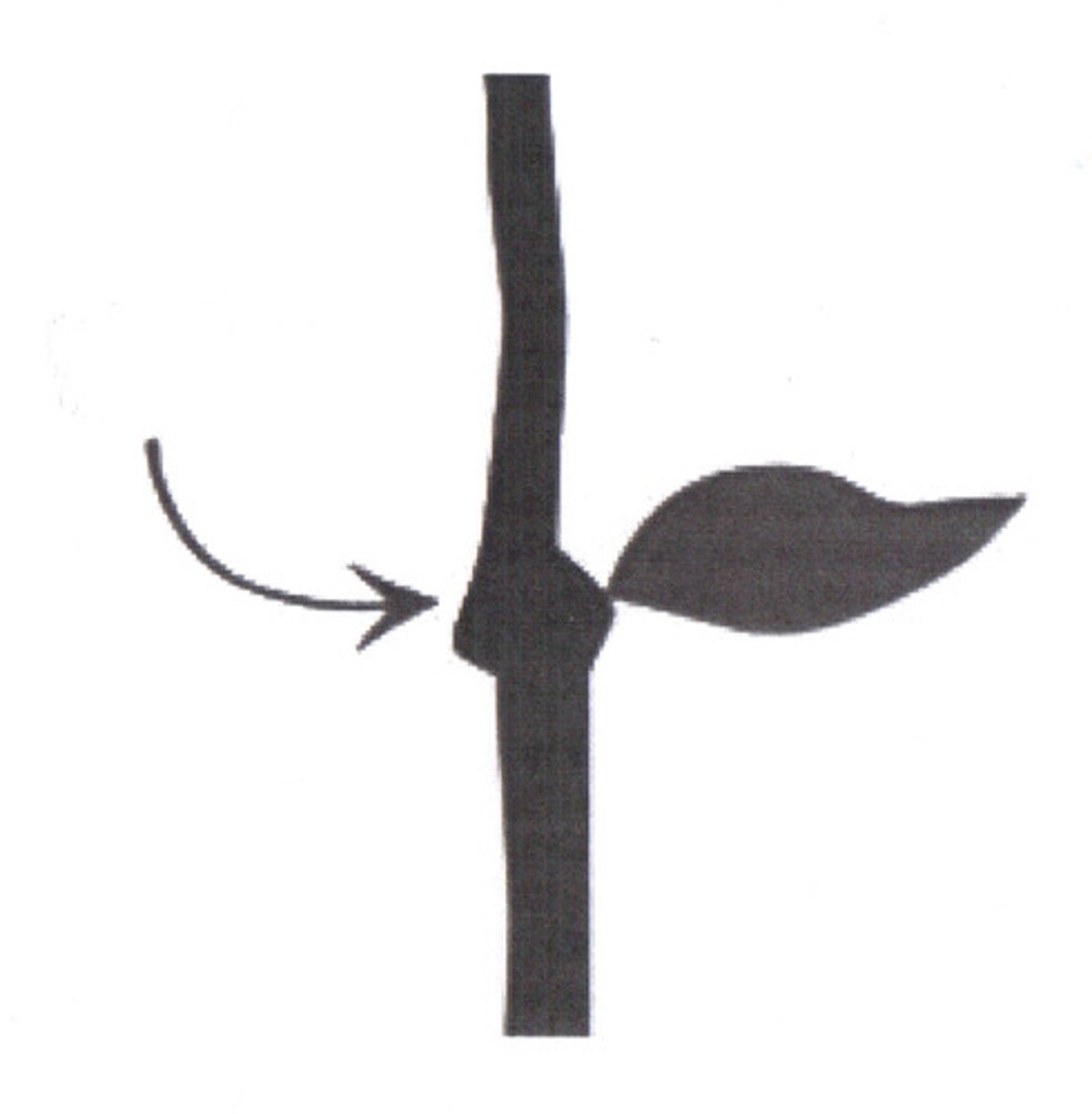
Node
What is the name of the organ at the arrow?
Pith
1?
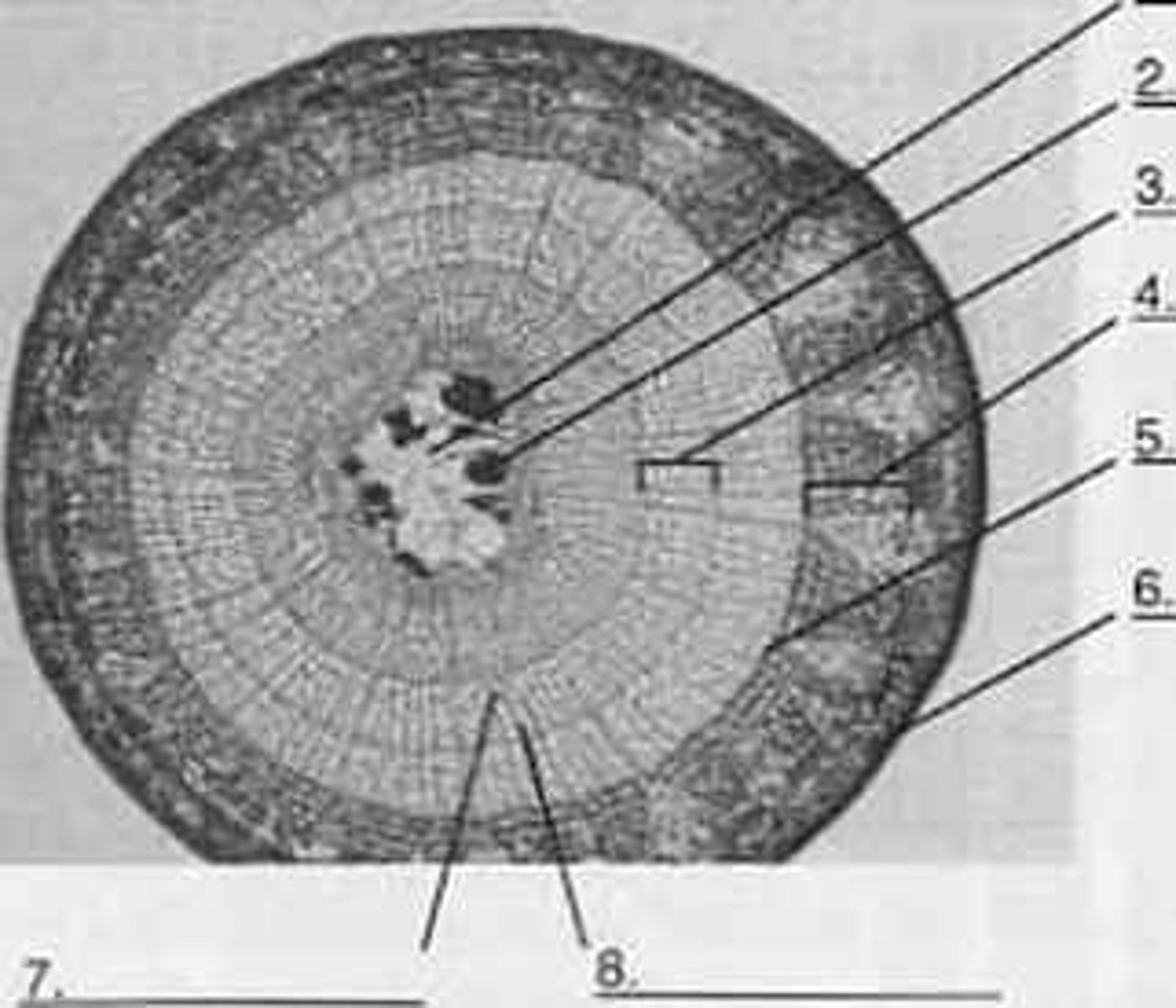
Secondary Xylem
3?
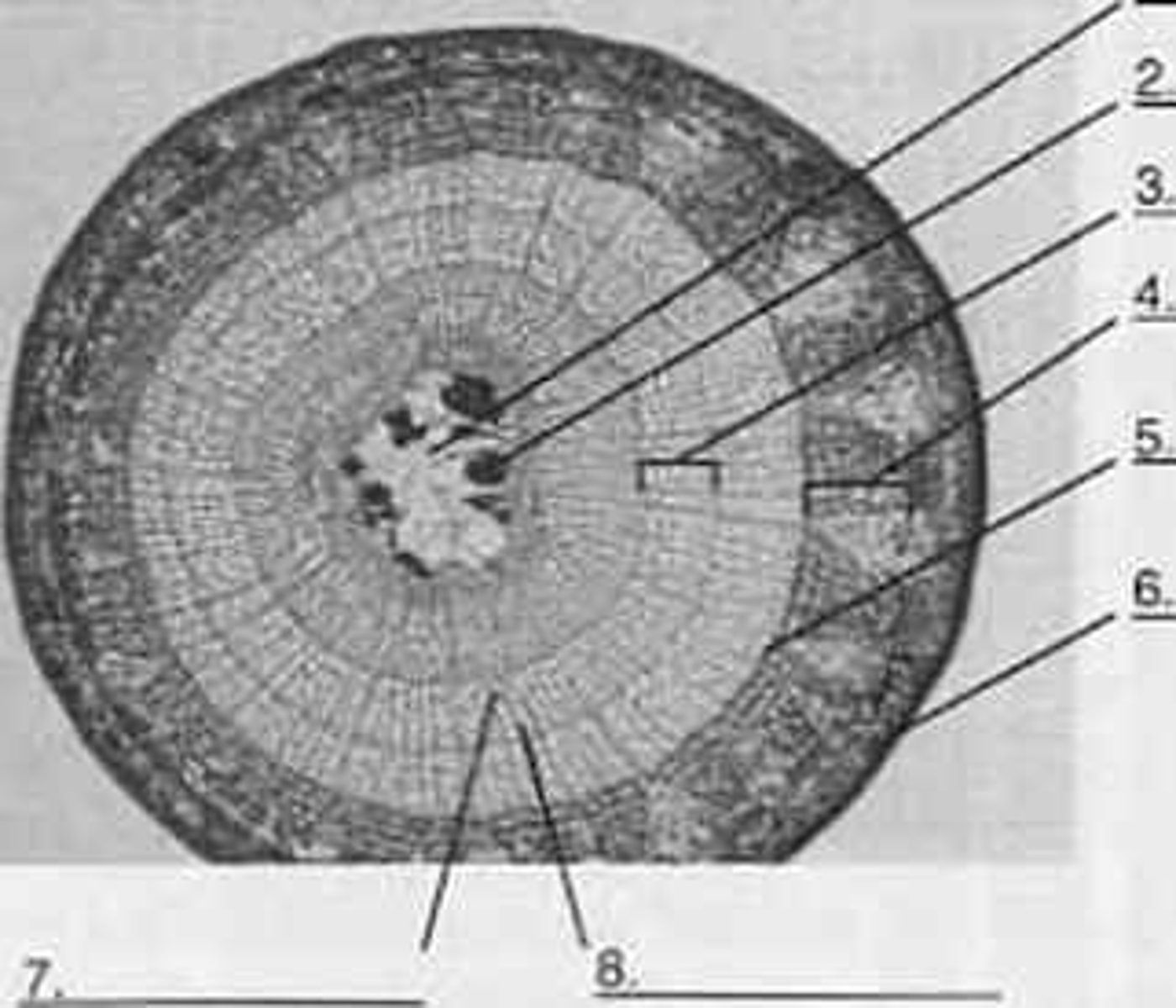
Secondary Phloem
4?
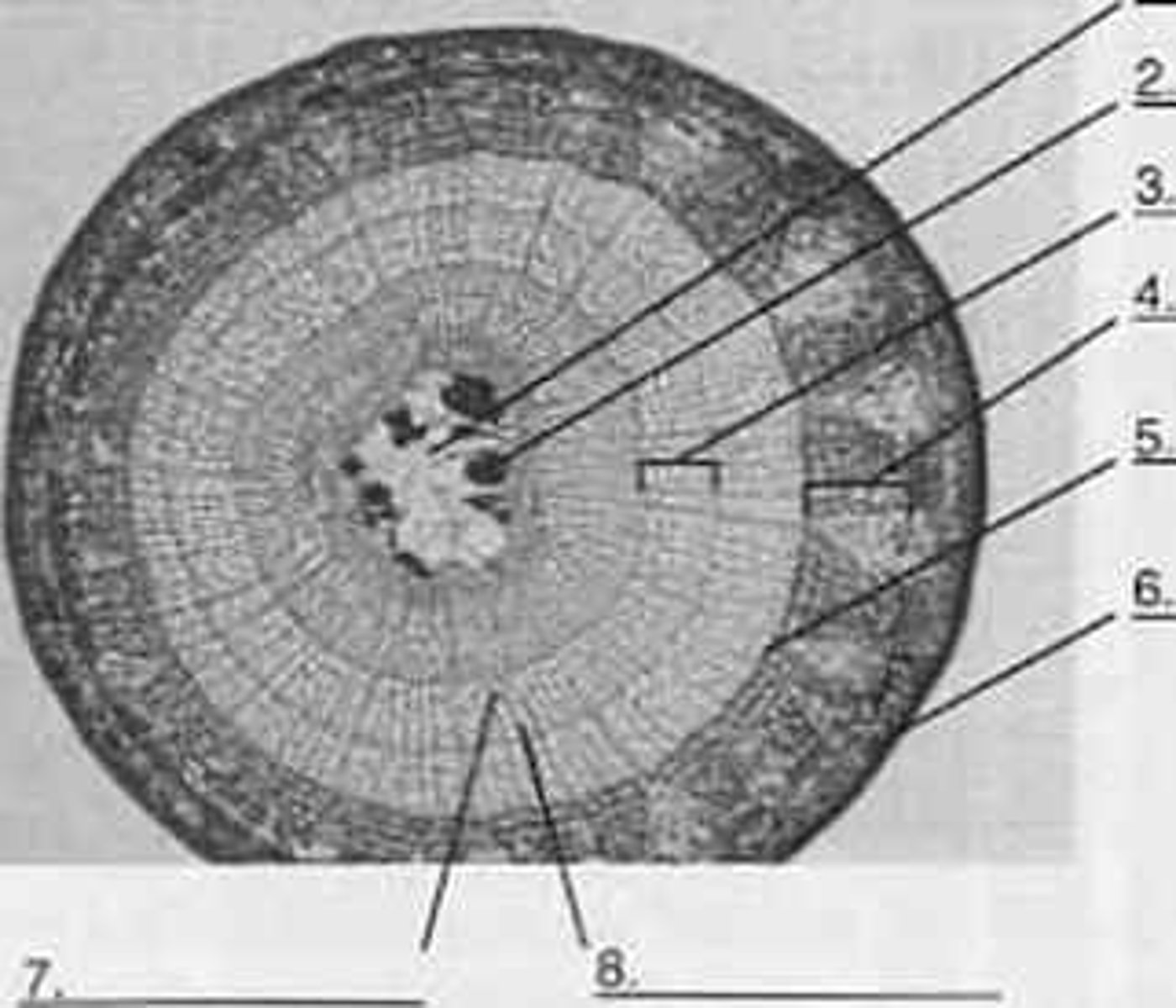
Periderm
6?
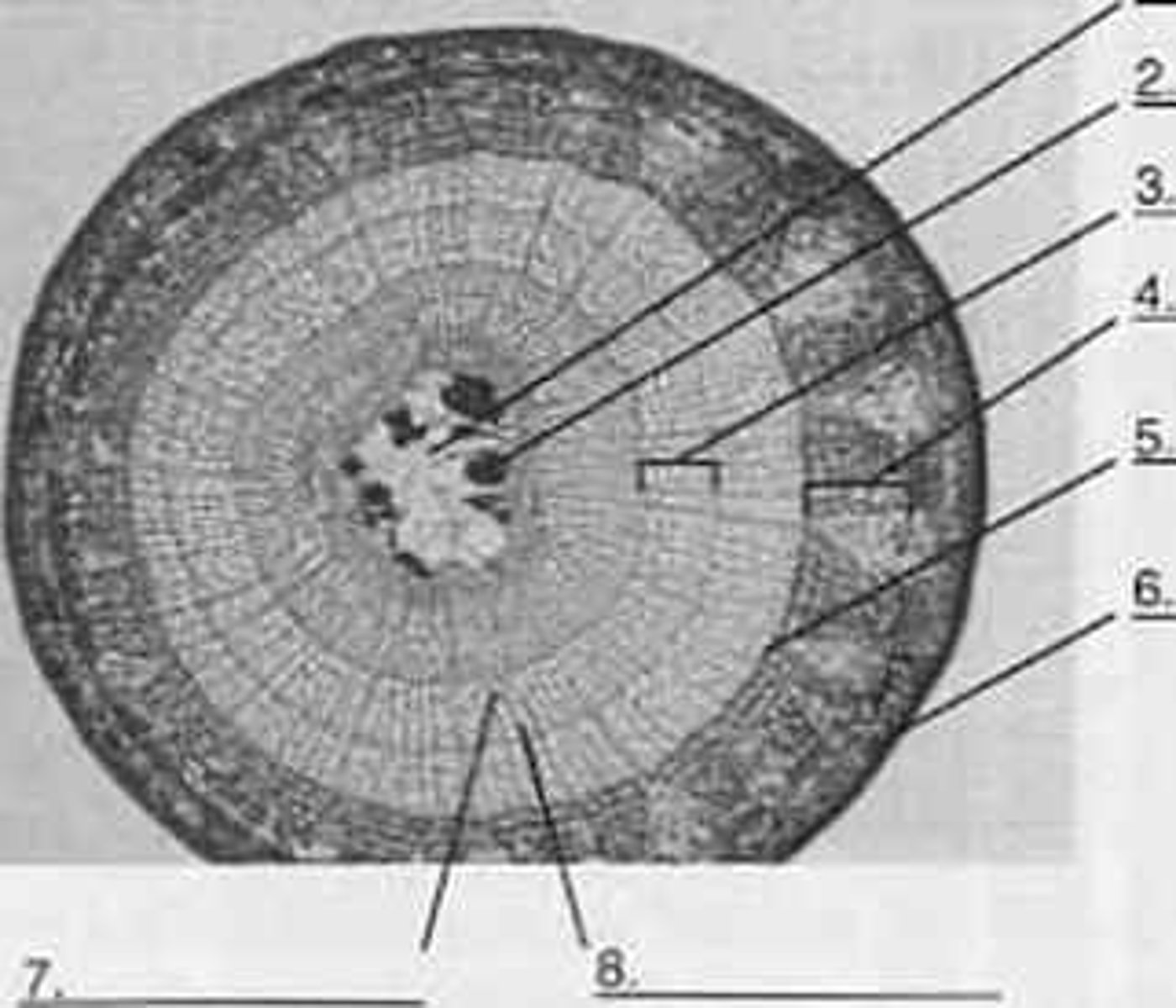
Stops
Cutting off the apical meristem _____ the growth/elongation.
Apical meristem
To retain water in arid climates or soil conditions and to conduct photosynthesis are purposes for cutting of what?
Apical meristem
1?
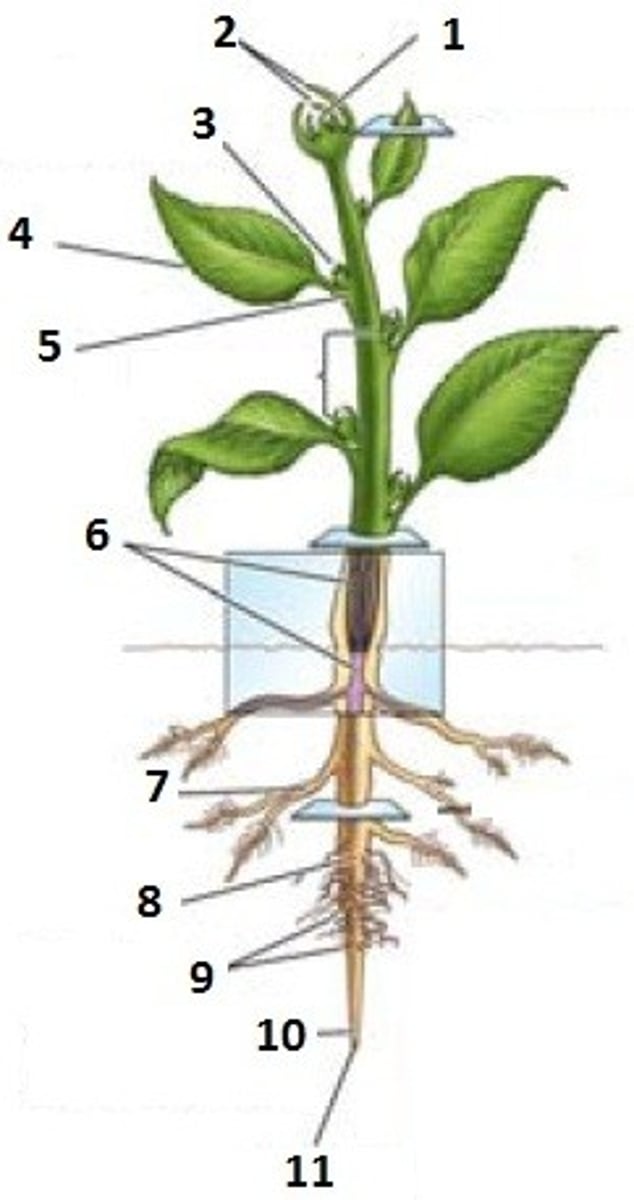
Node
5?
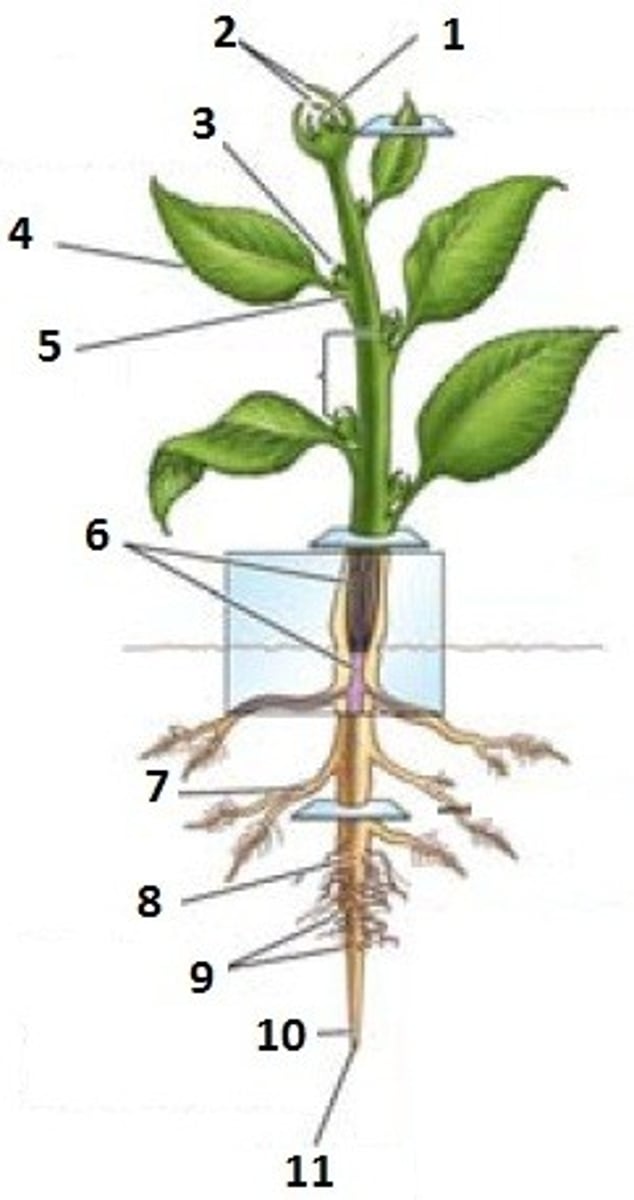
Internode
B?
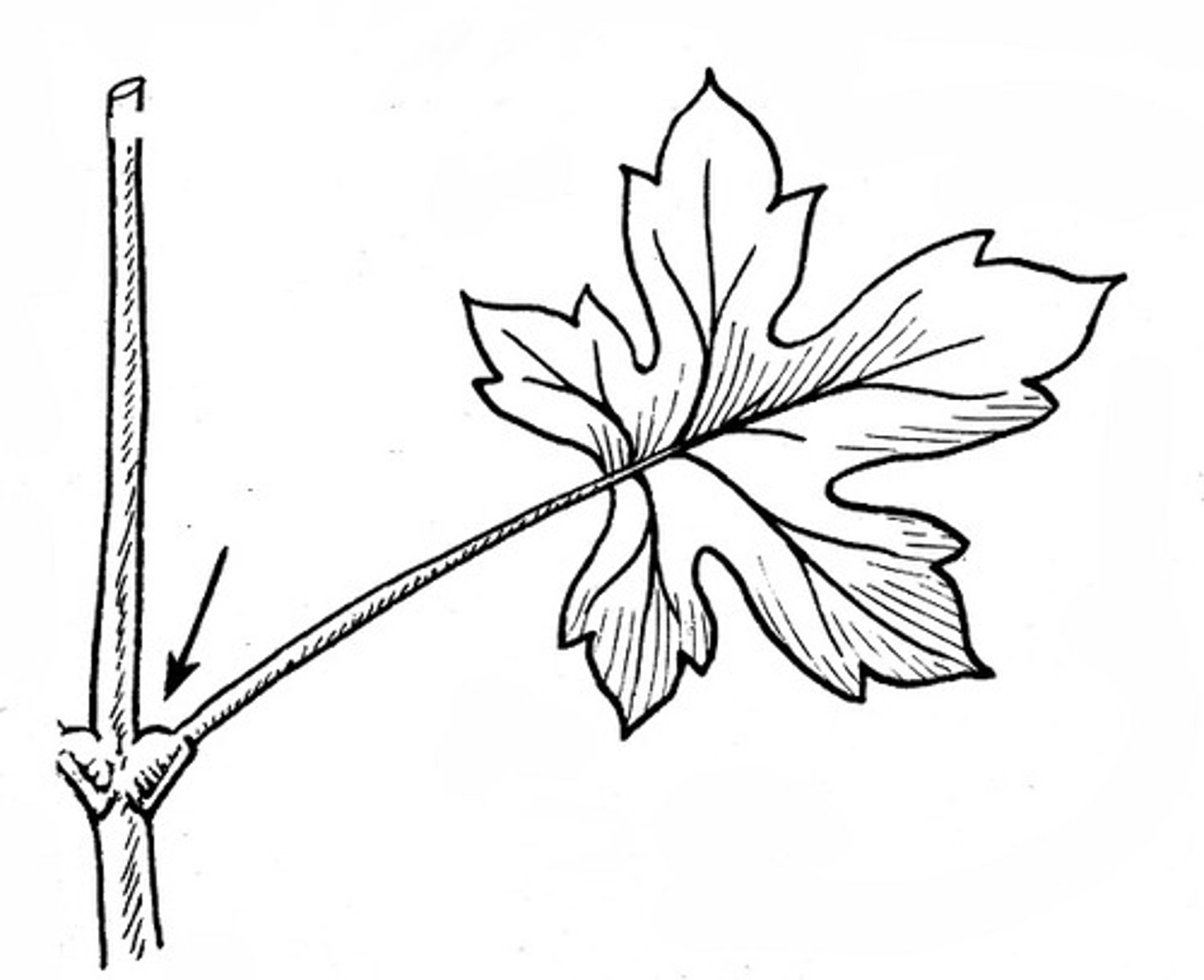
Bud
3?
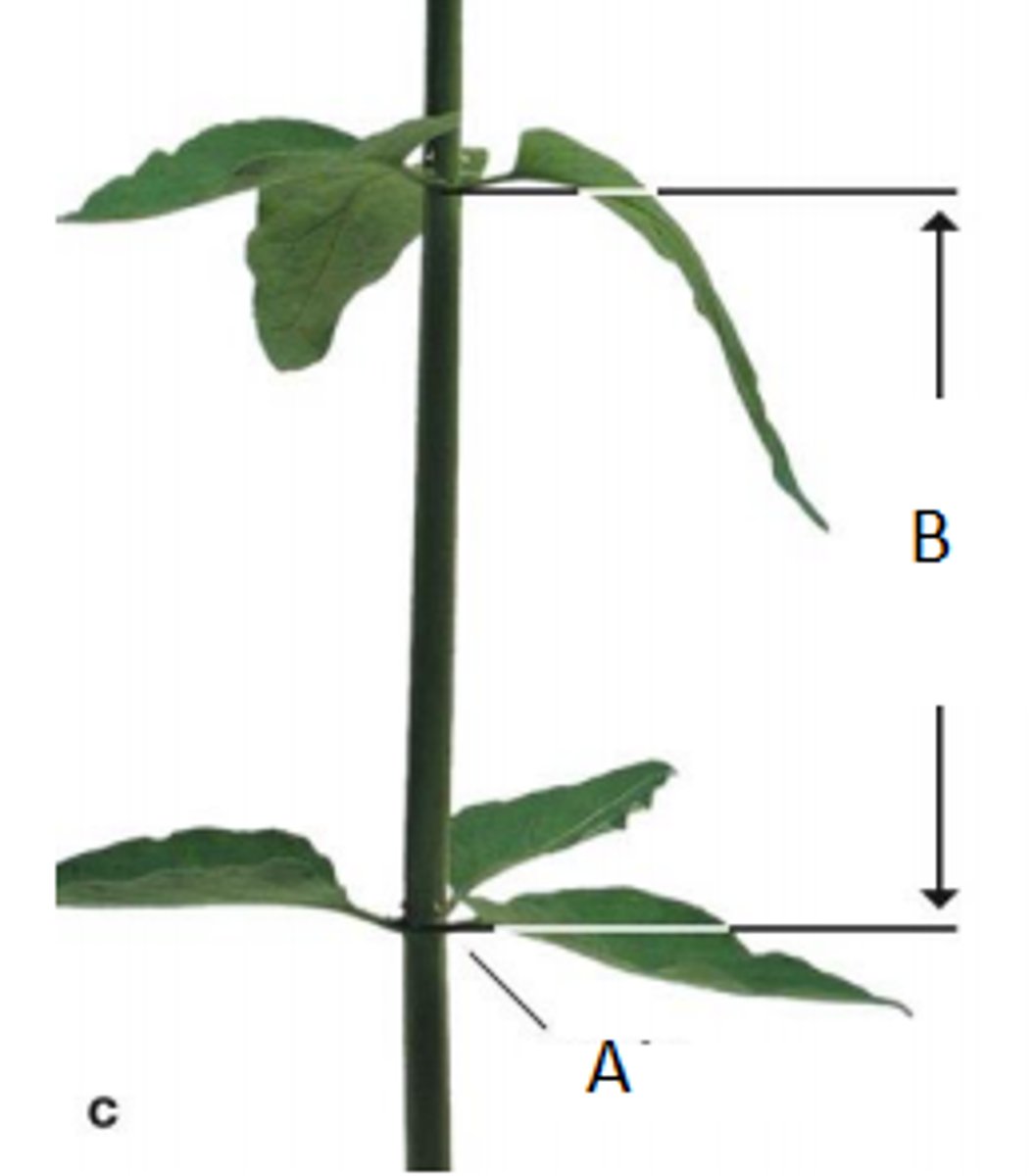
Axil
The angle between petiole and stem?
Primary vein
A?
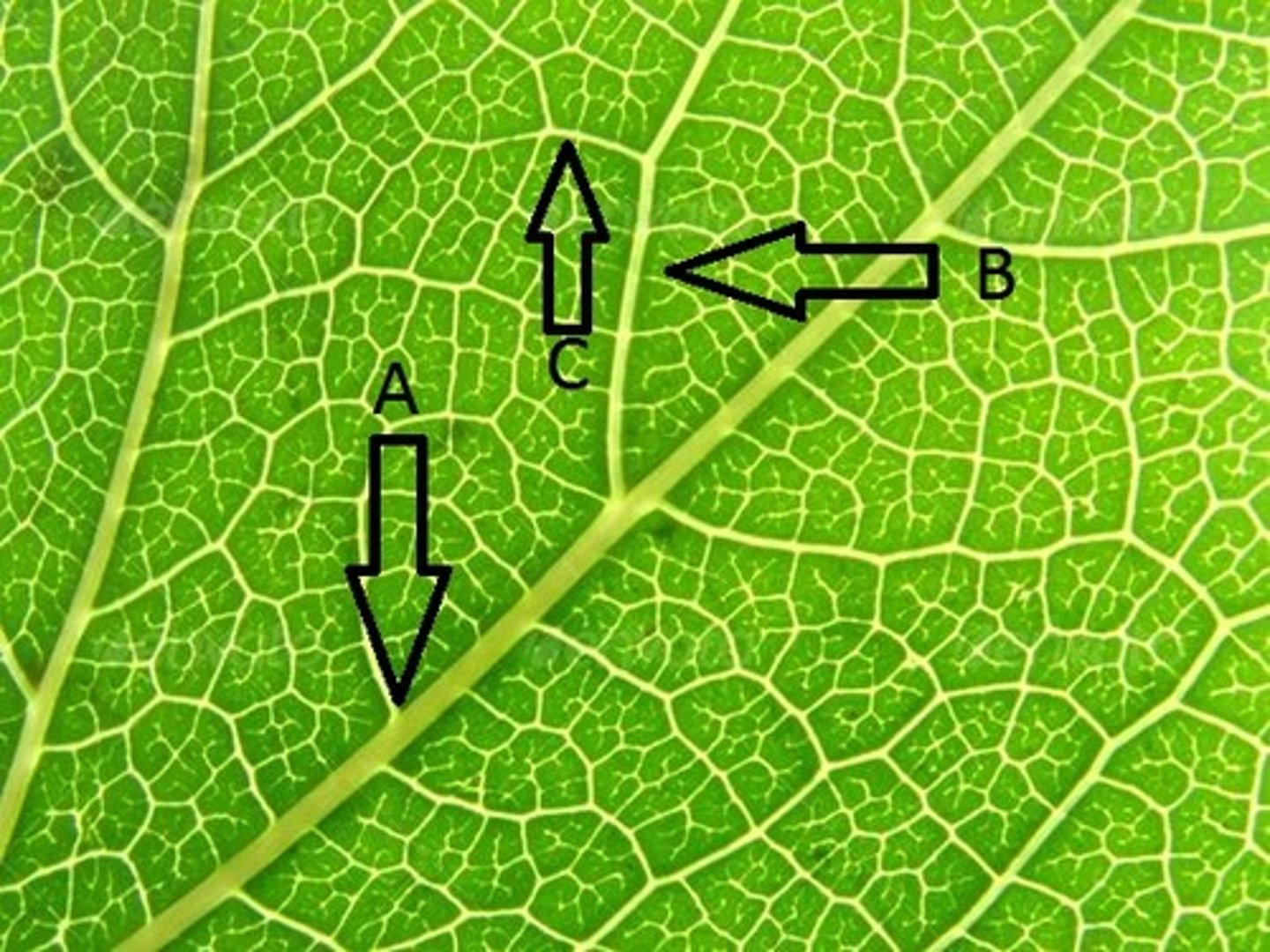
Secondary
B?
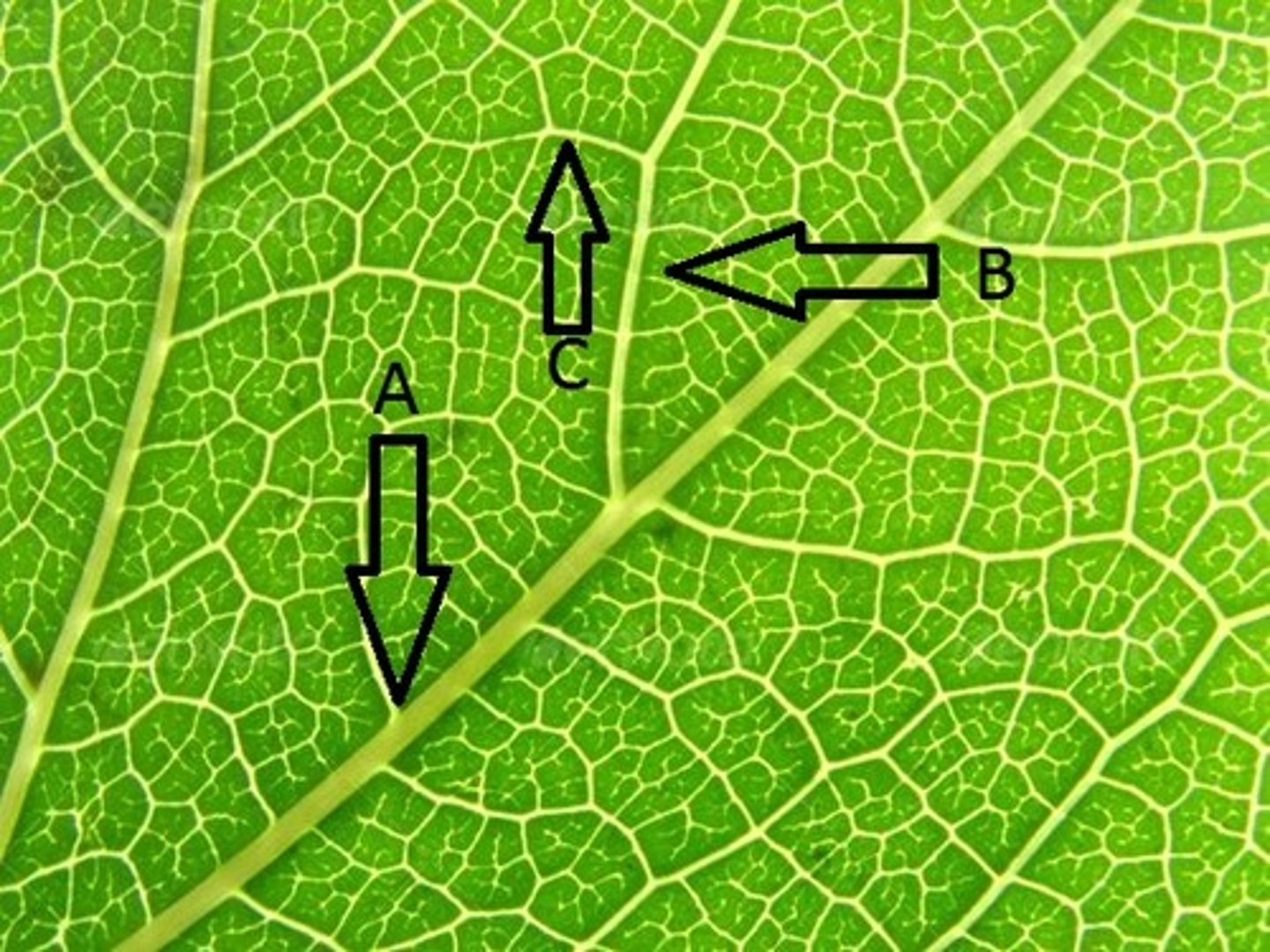
Tertiary
C?
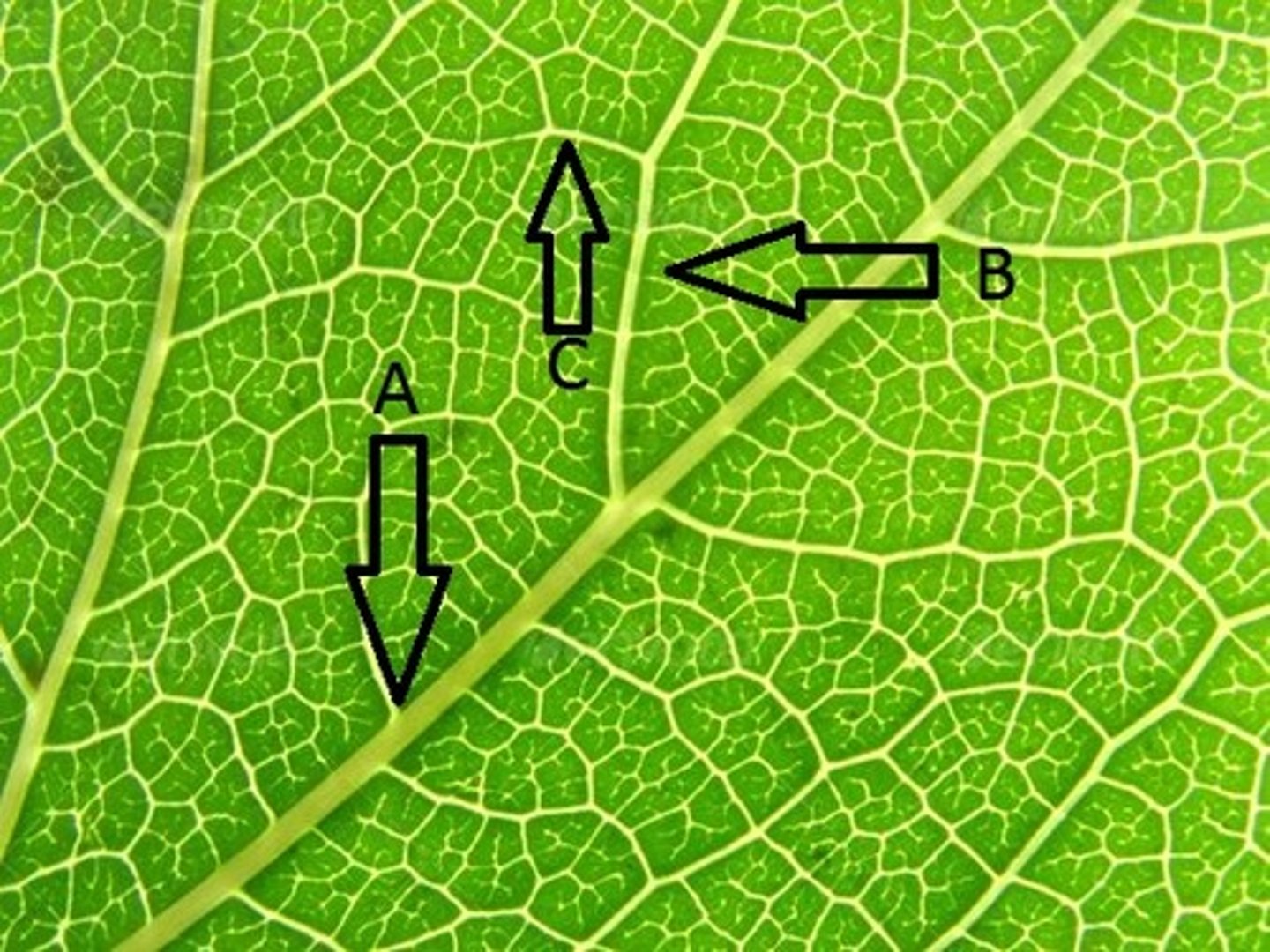
Quaternary
After the tertiary vein, the next branched vein is?
Xeromorphic
What type of habitat?
Xeromorphic
All of the following are characteristics of what kind of habitat?
- thicker cuticle
- multi layered epidermis
- arid environments (dry)
- numerous stomata for higher gas exchange
Mesomorphic
All of the following are characteristics of what kind of habitat?
- thin cuticle
- single layer epidermis
- not wet or dry environments

Hydromorphic
All of the following are characteristics of what kind of habitat?
- no cuticle
- single layer epidermis
- very wet environments
- needs lots of water
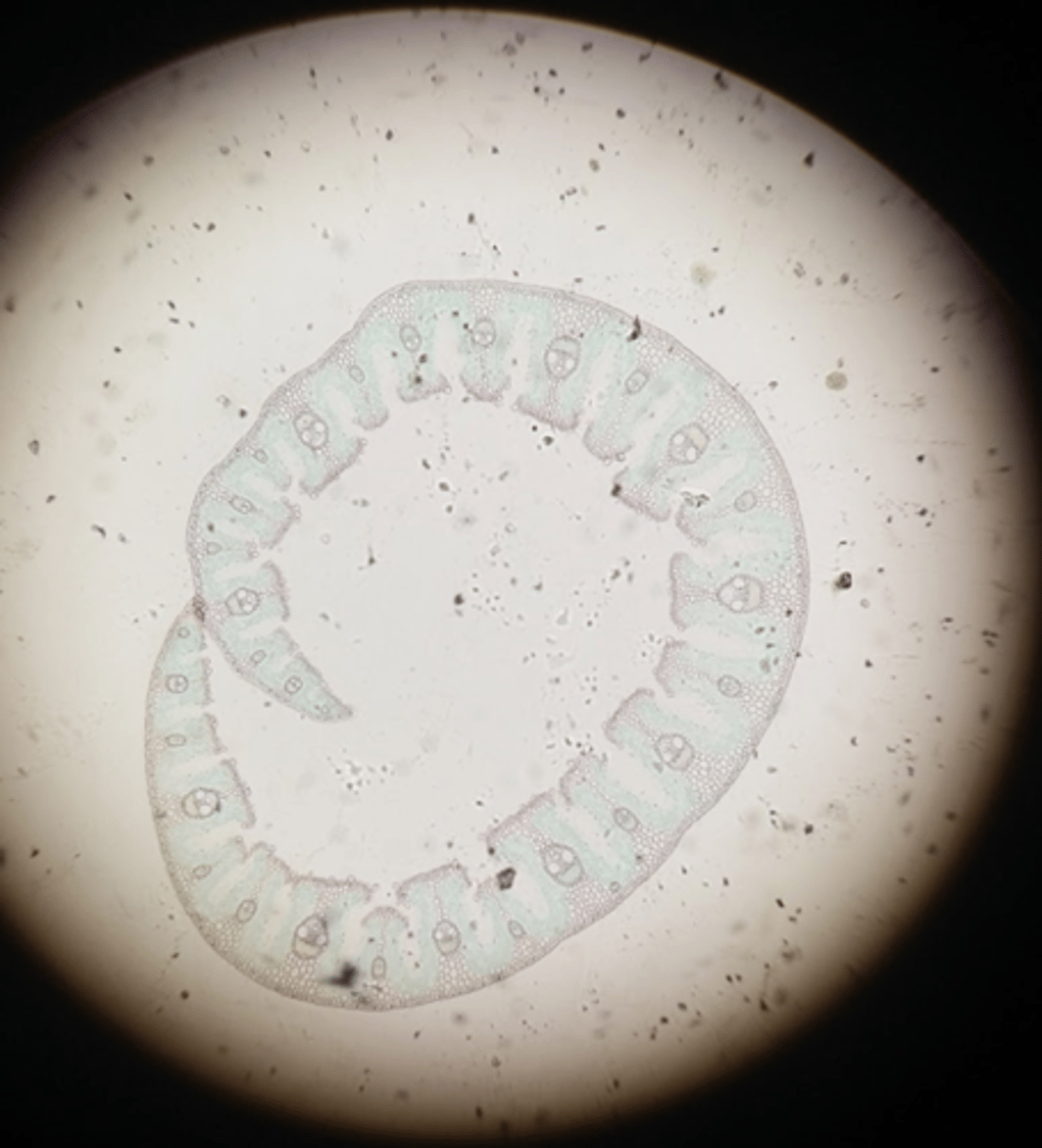
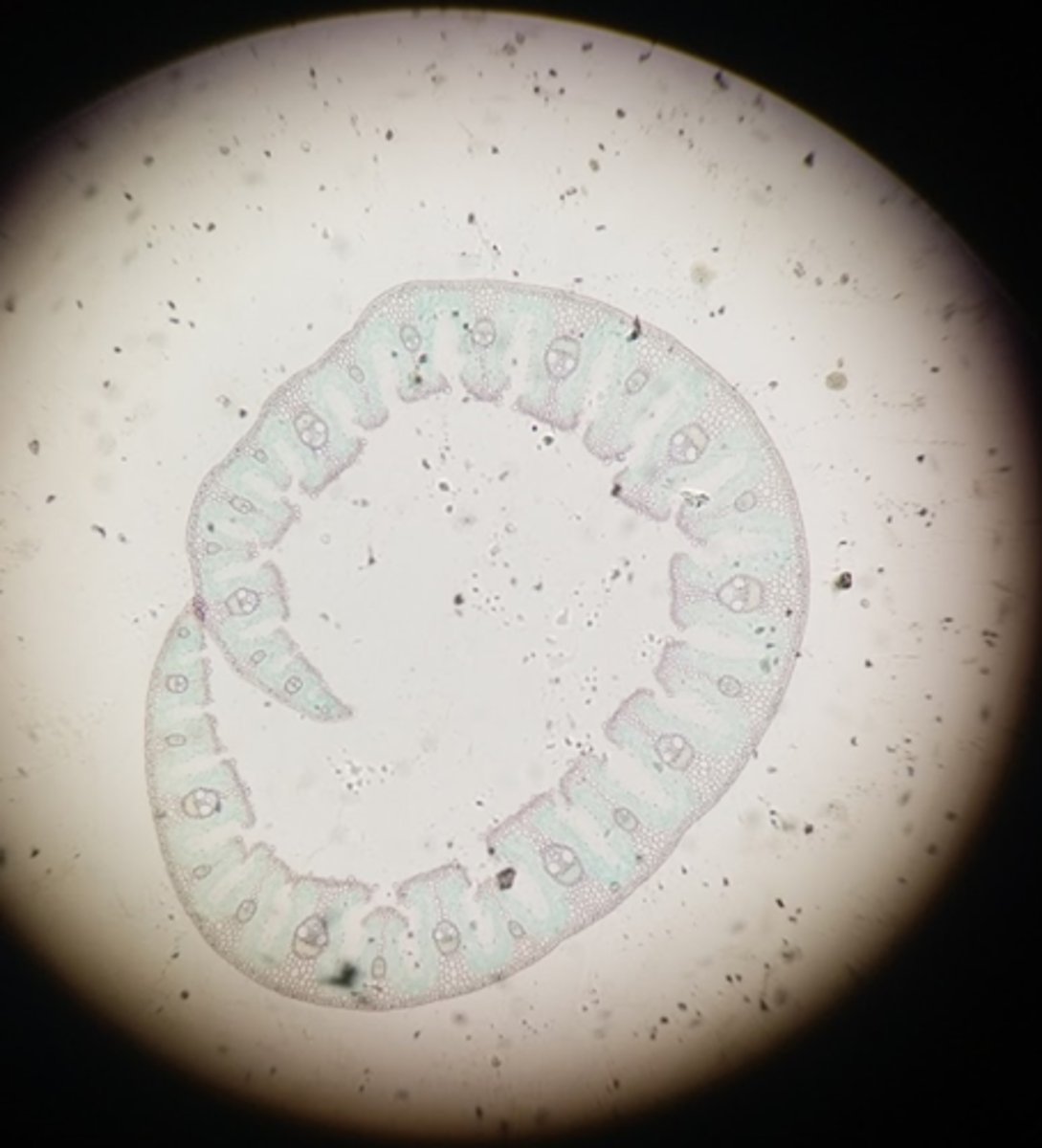
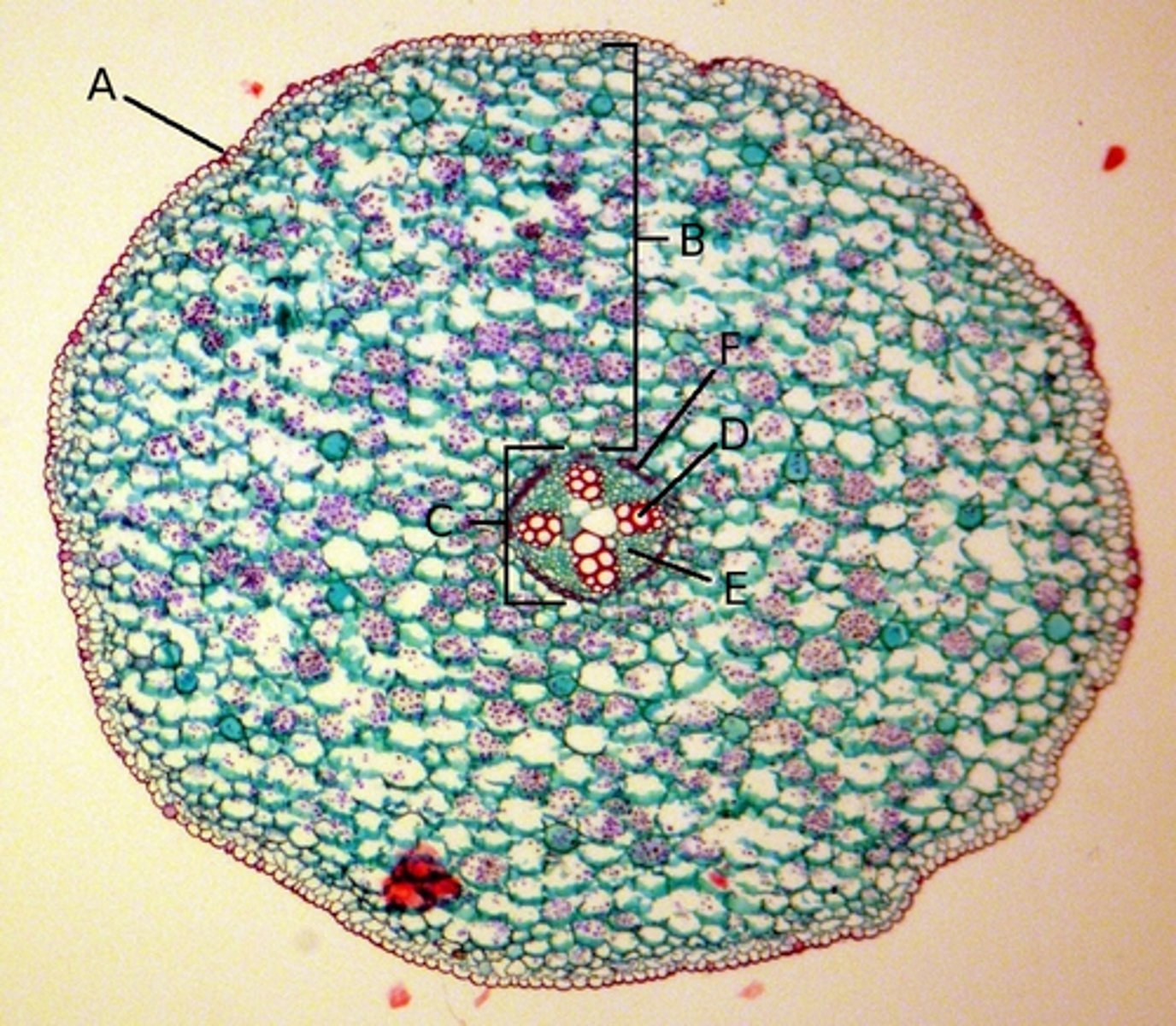
Root
This cross section is of what part of a dicot plant?
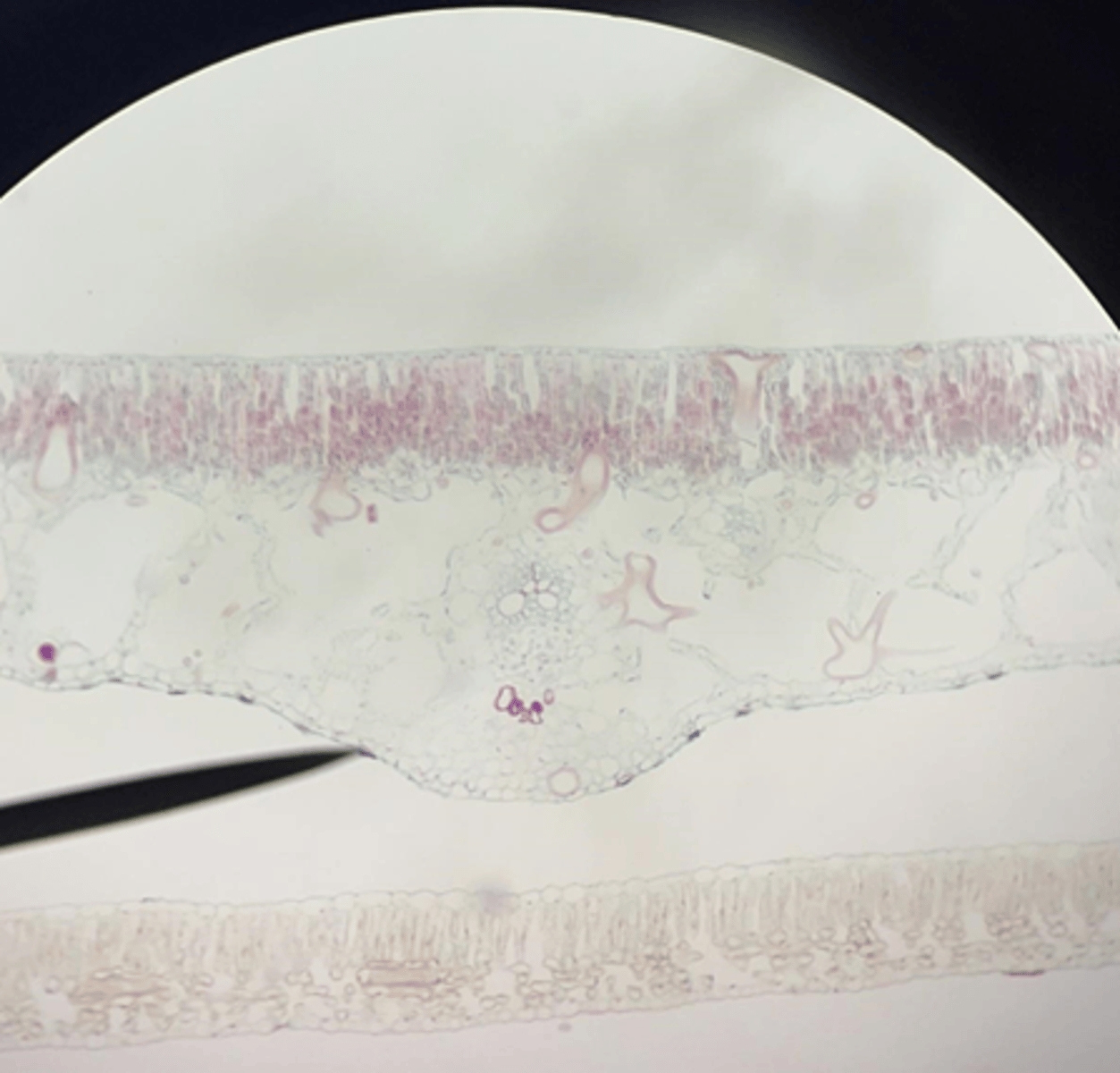
Stem
This cross section is of what part of a dicot plant?
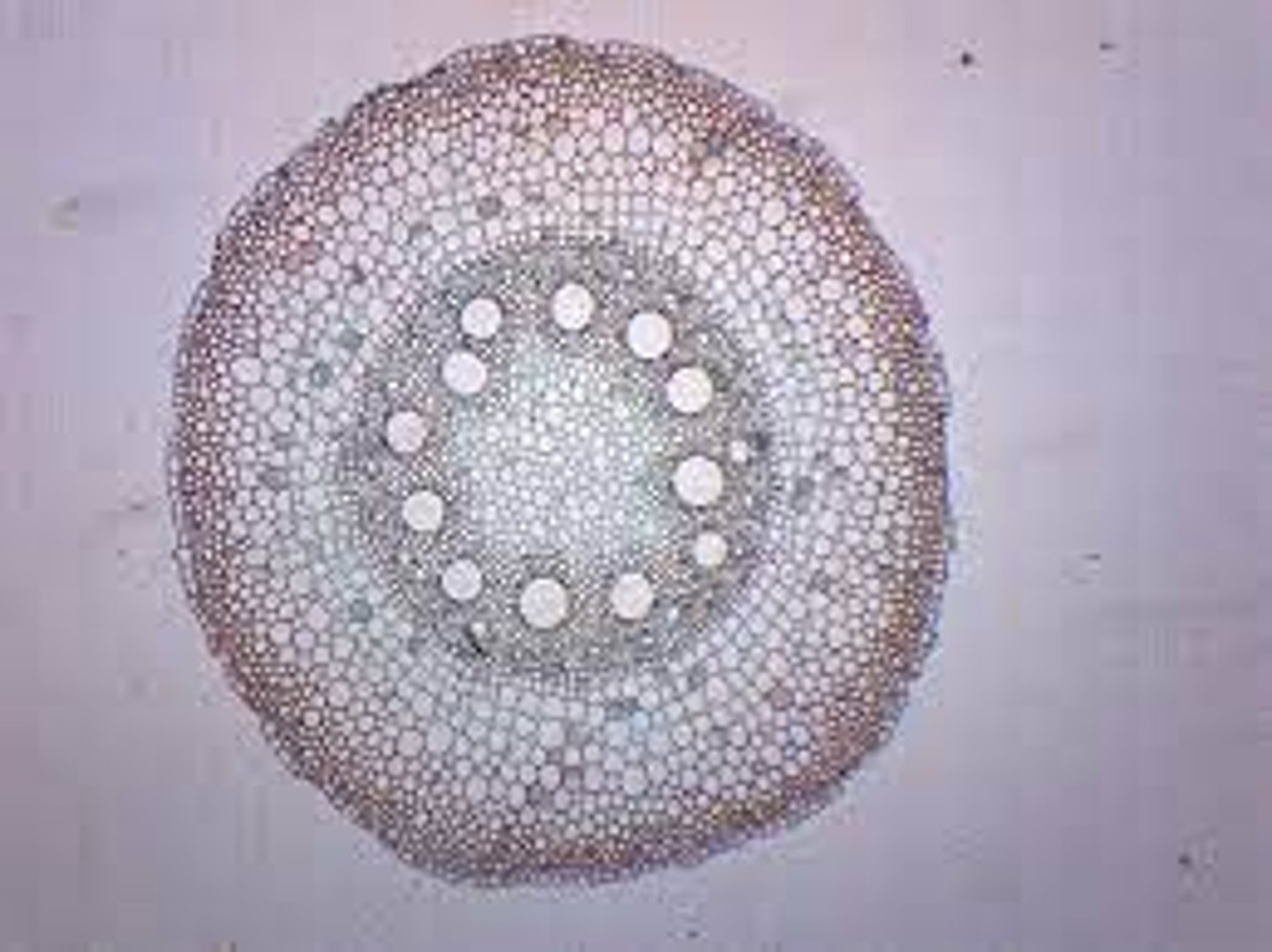
Root
This cross section is of what part of a monocot plant?
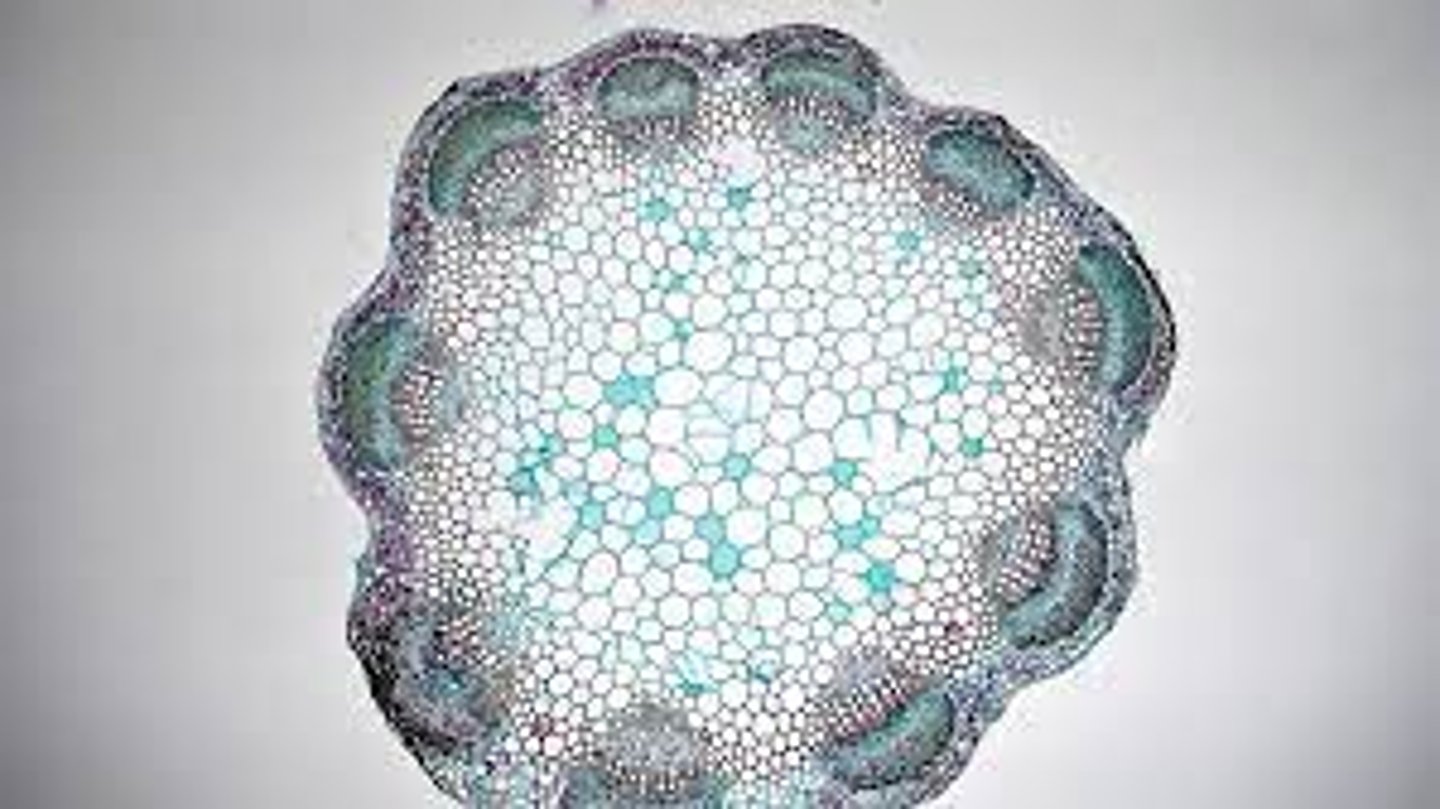
Stem
This cross section is of what part of a monocot plant?
Mesomorphic
What type of environment?

Hydromorphic
What type of habitat?
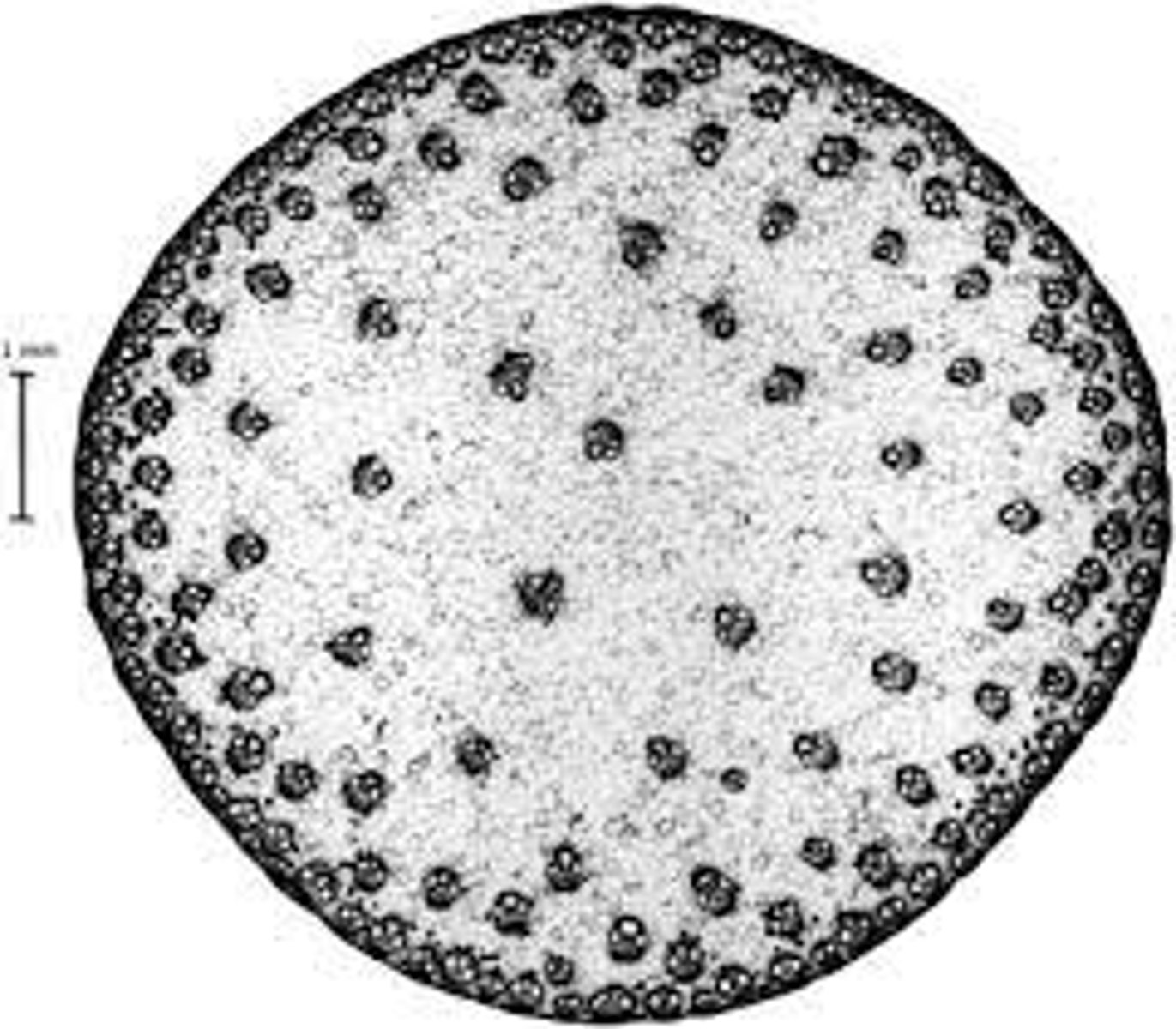
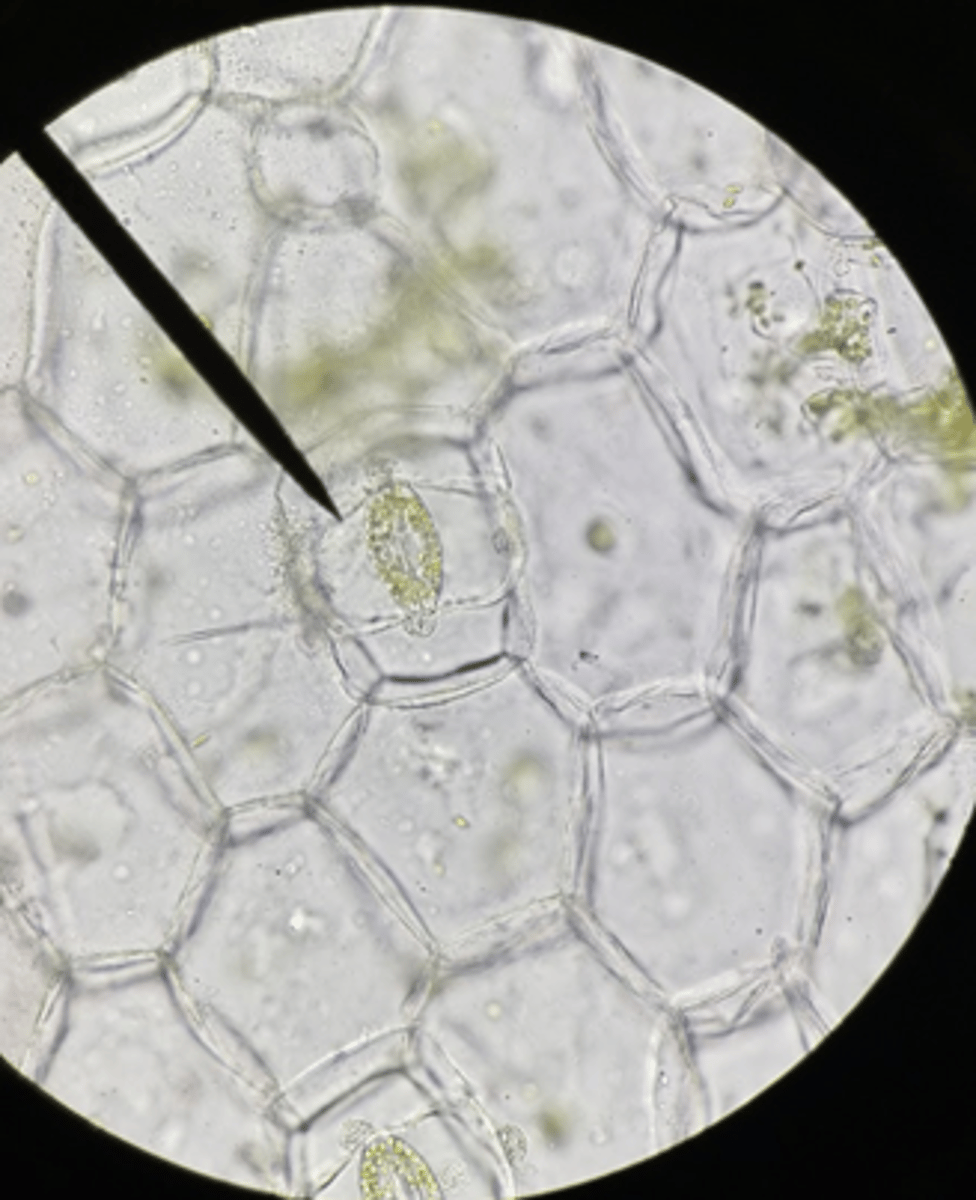
Stomata
Structure at point?

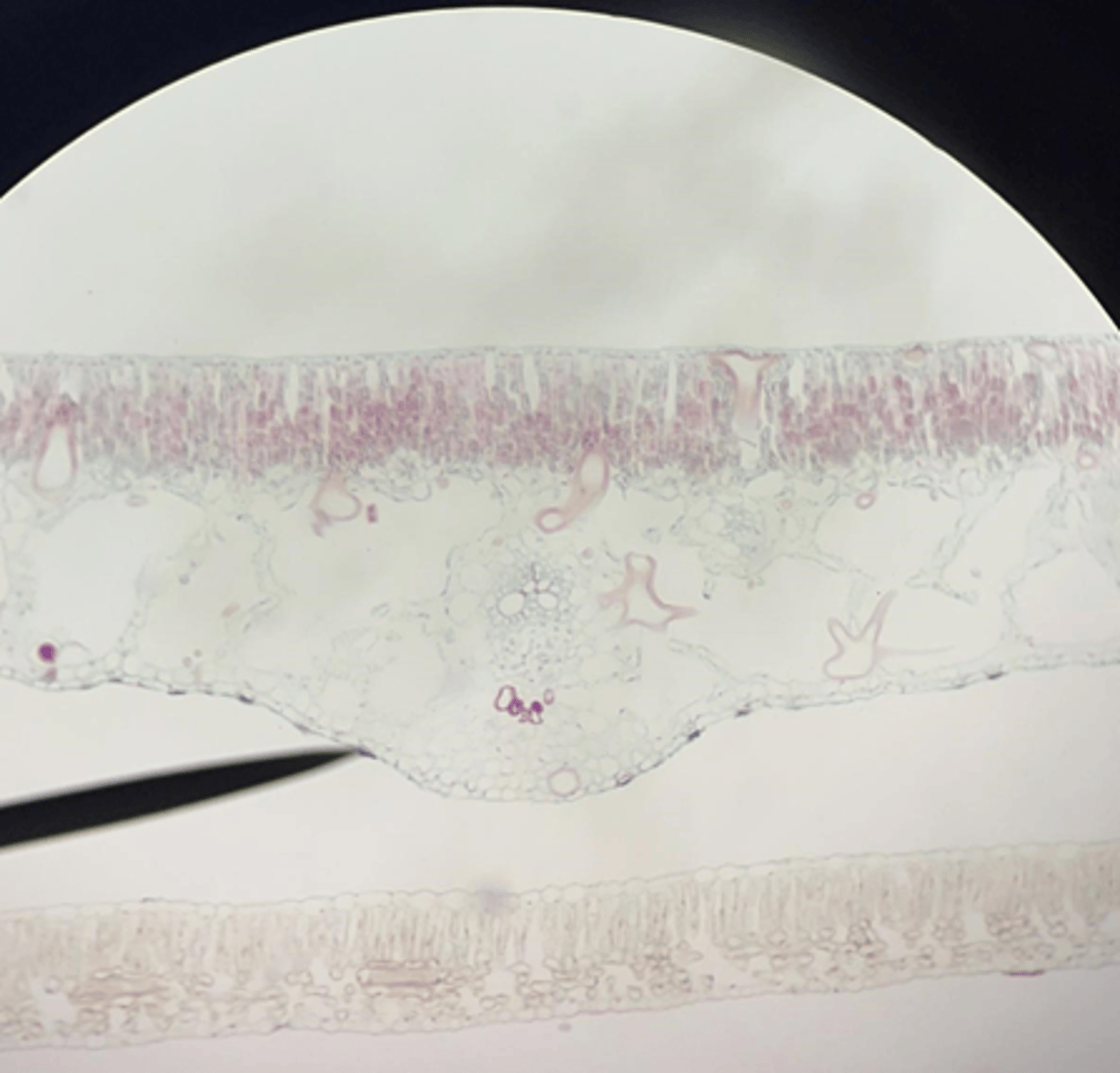
Sun
Sun or shade leaf?
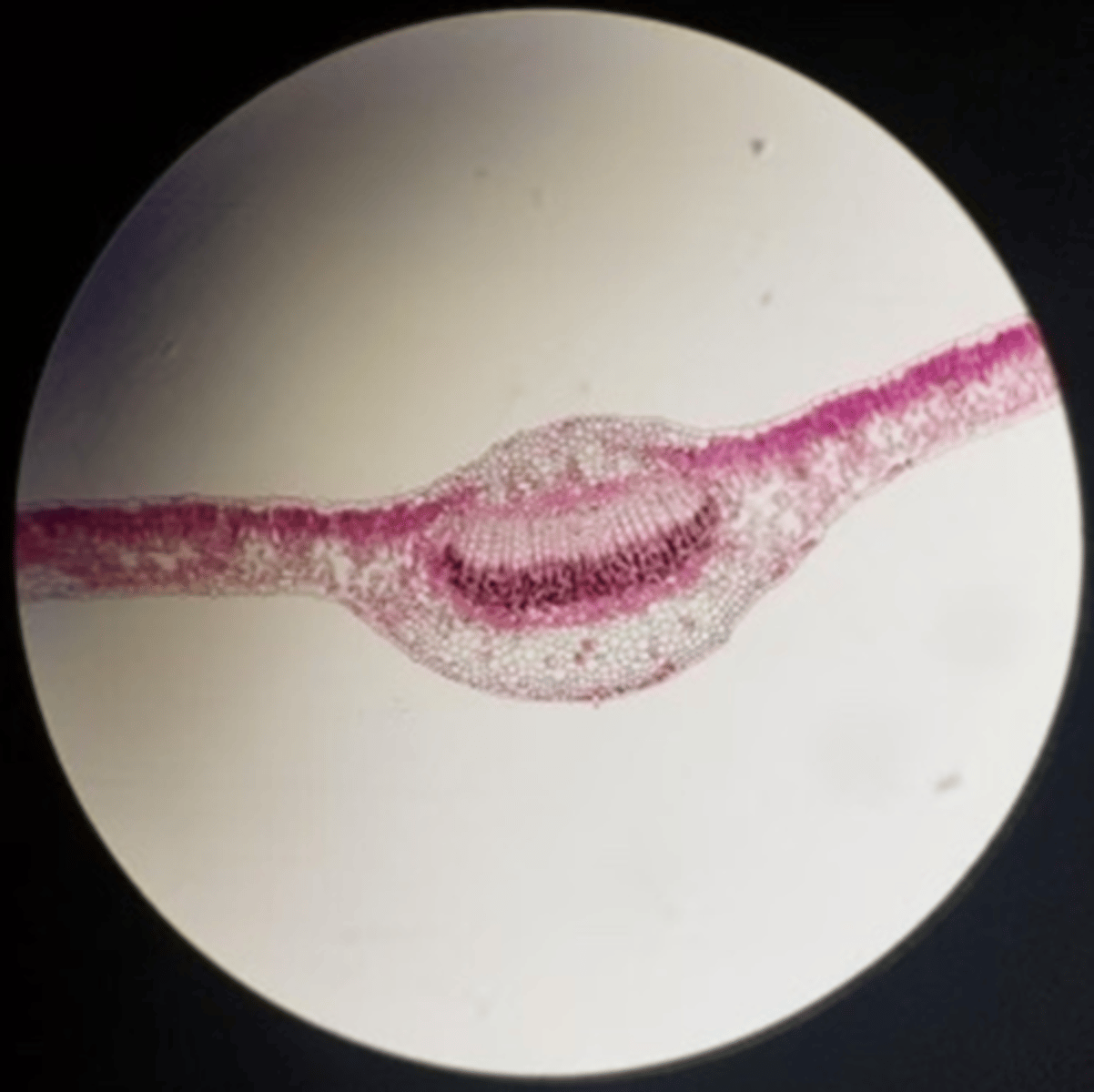
Shade
Sun or shade leaf?
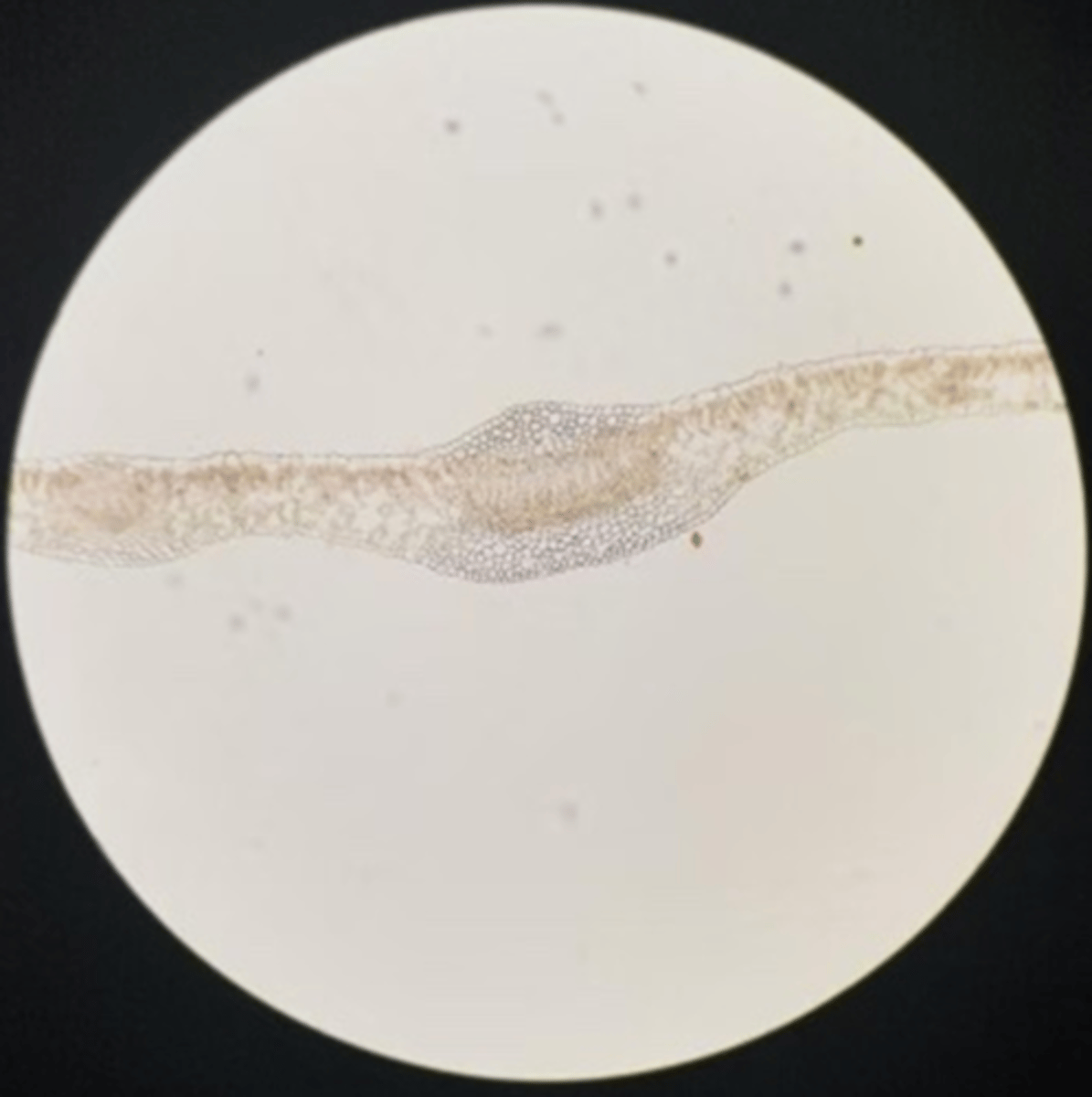
Sun
All of the following are characteristics of a shade or sun leaf?
- small thick leaf
- 2 to 3 layers of palisade parenchyma
- abundant number of veins
- large veins
- thick cuticle
Shade
All of the following ae characteristics of a shade or sun leaf?
- large thin leaf
- 1 layer of palisade parenchyma
- small veins
- thin cuticle
Monocot
Is this Zea mays leaf Monocot or dicot?
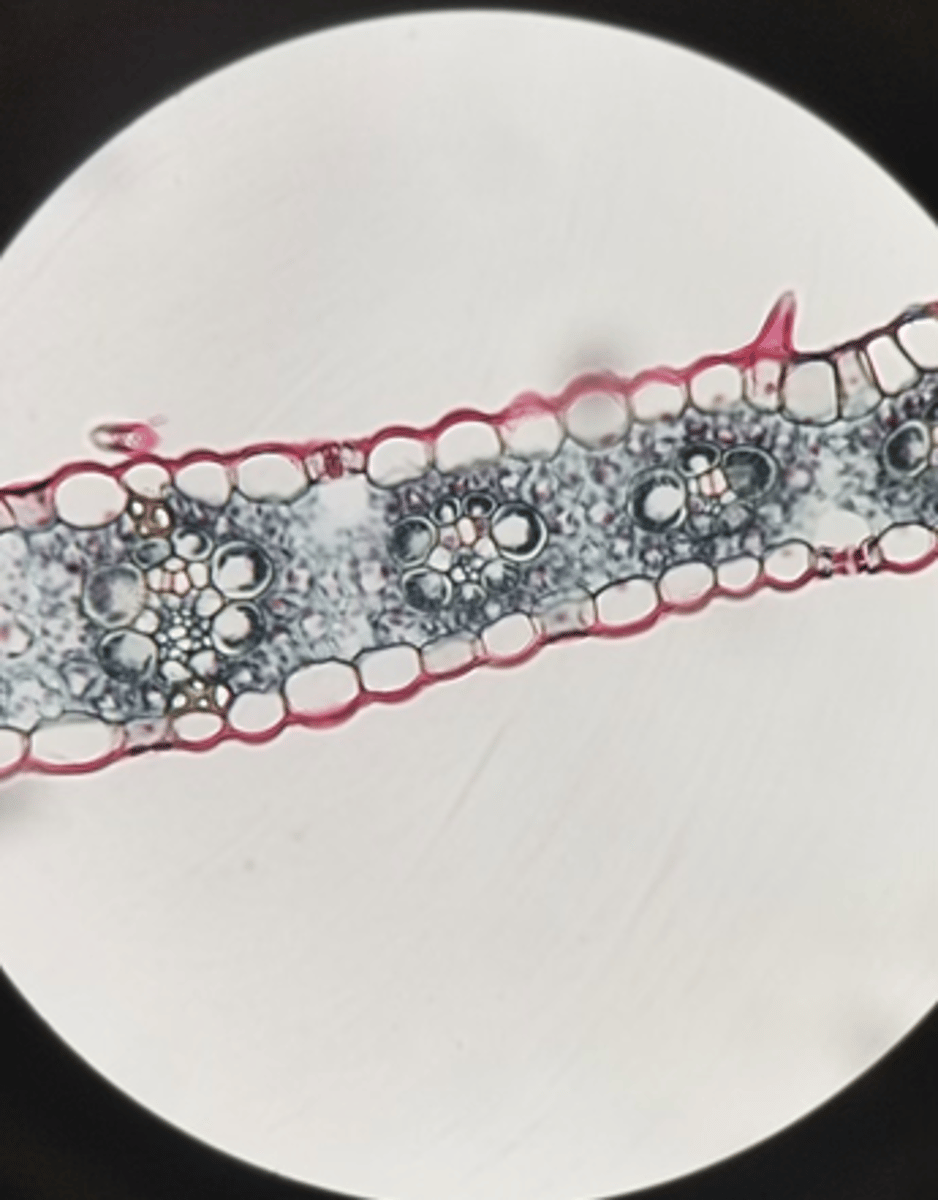
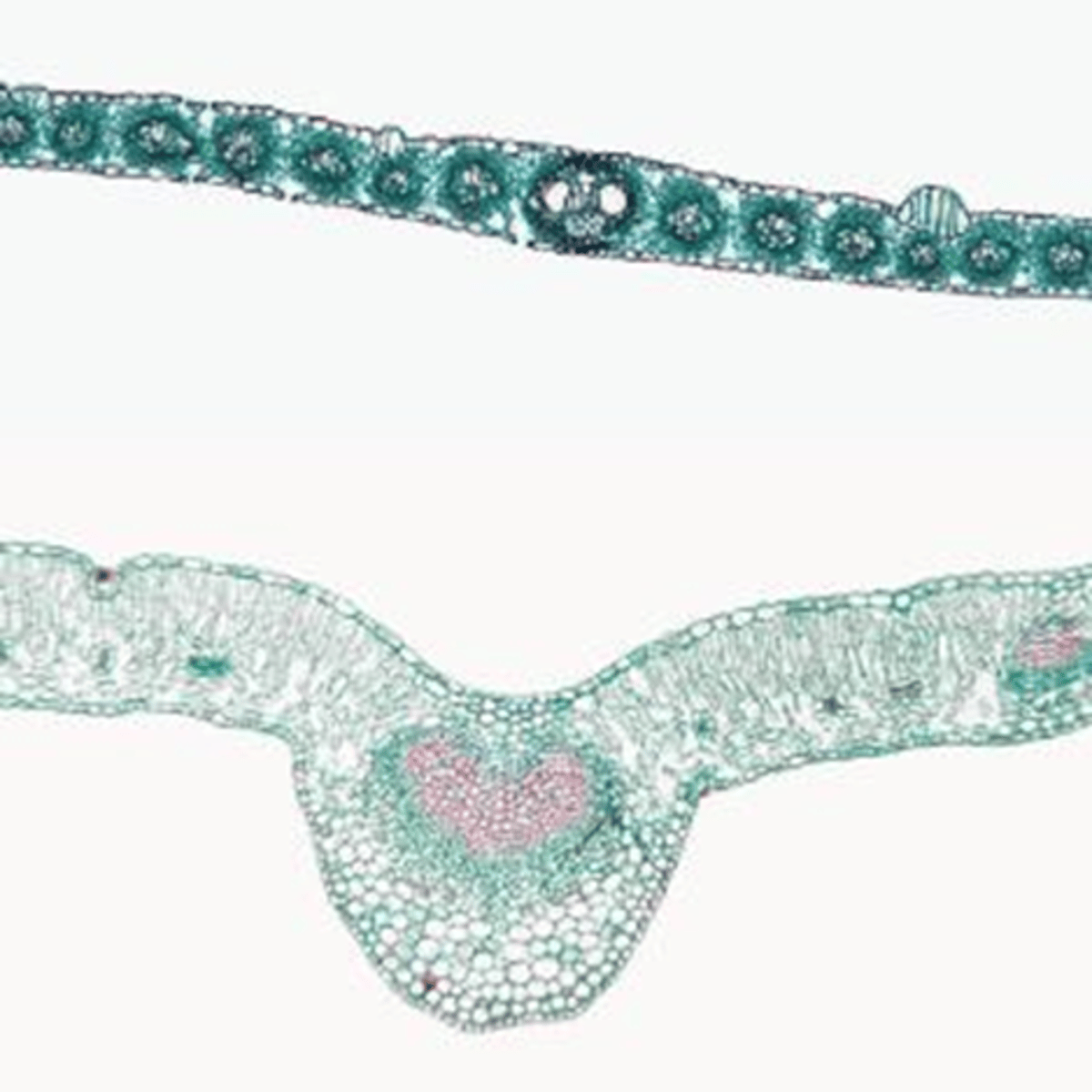
Monocot
Top leaf monocot or dicot?
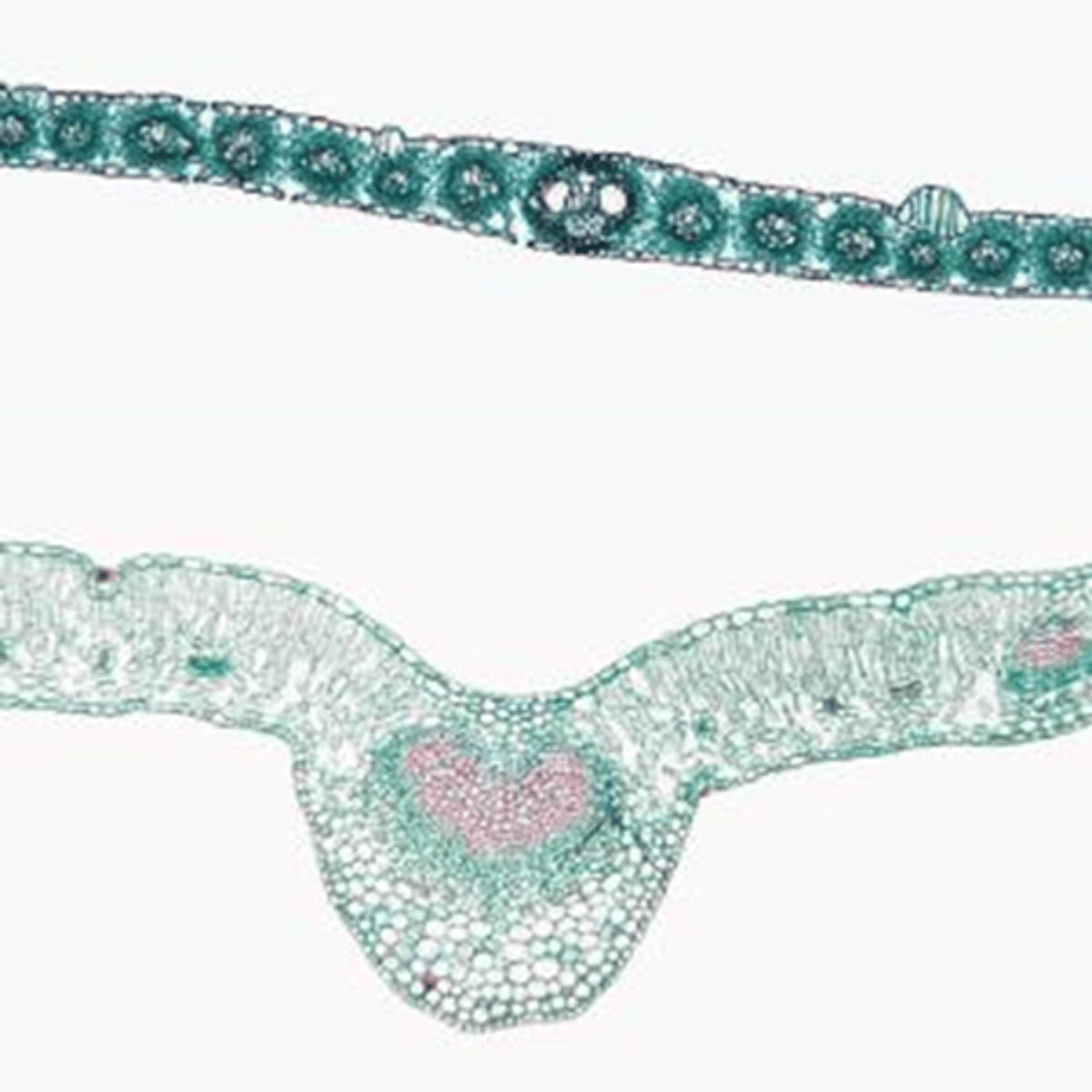

Dicot
Bottom leaf monocot or dicot?

Spongy mesophyll
A?
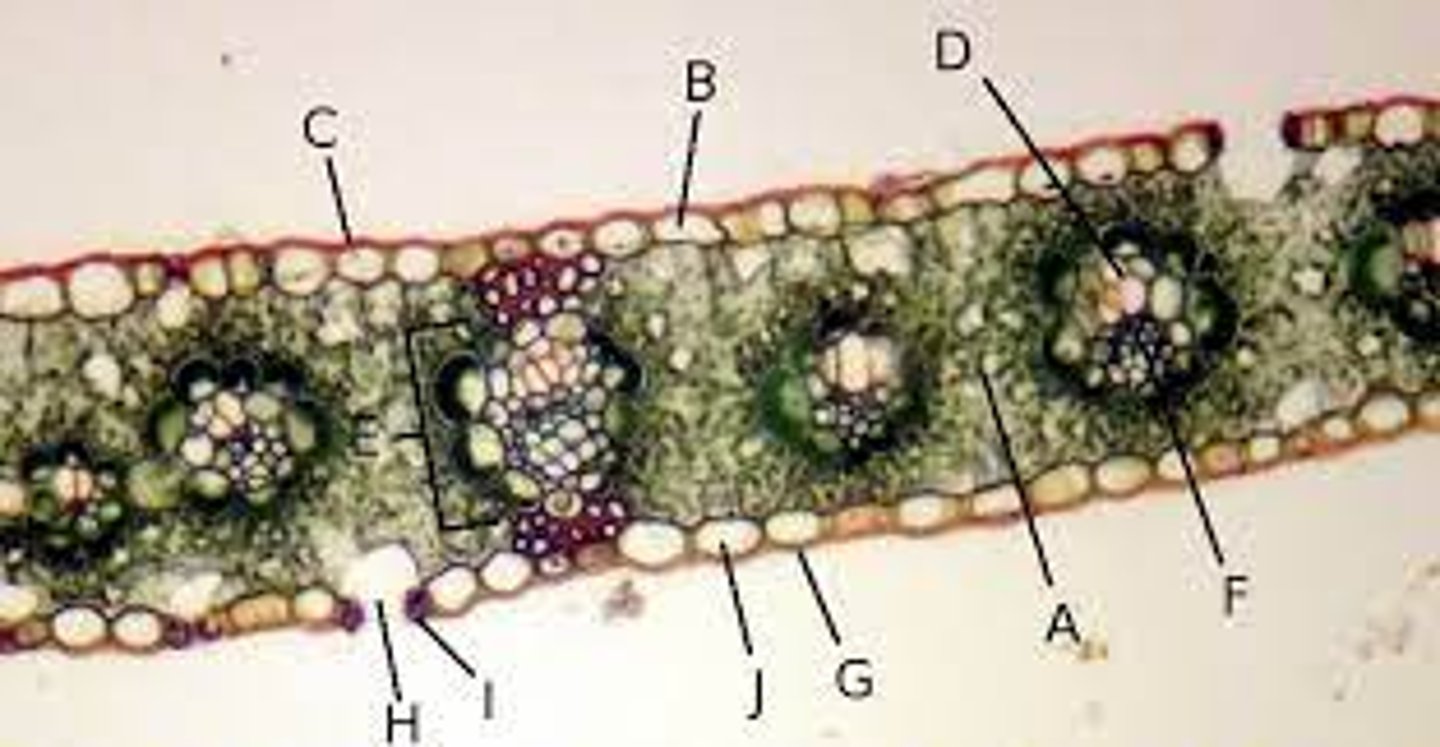
Xylem
D?
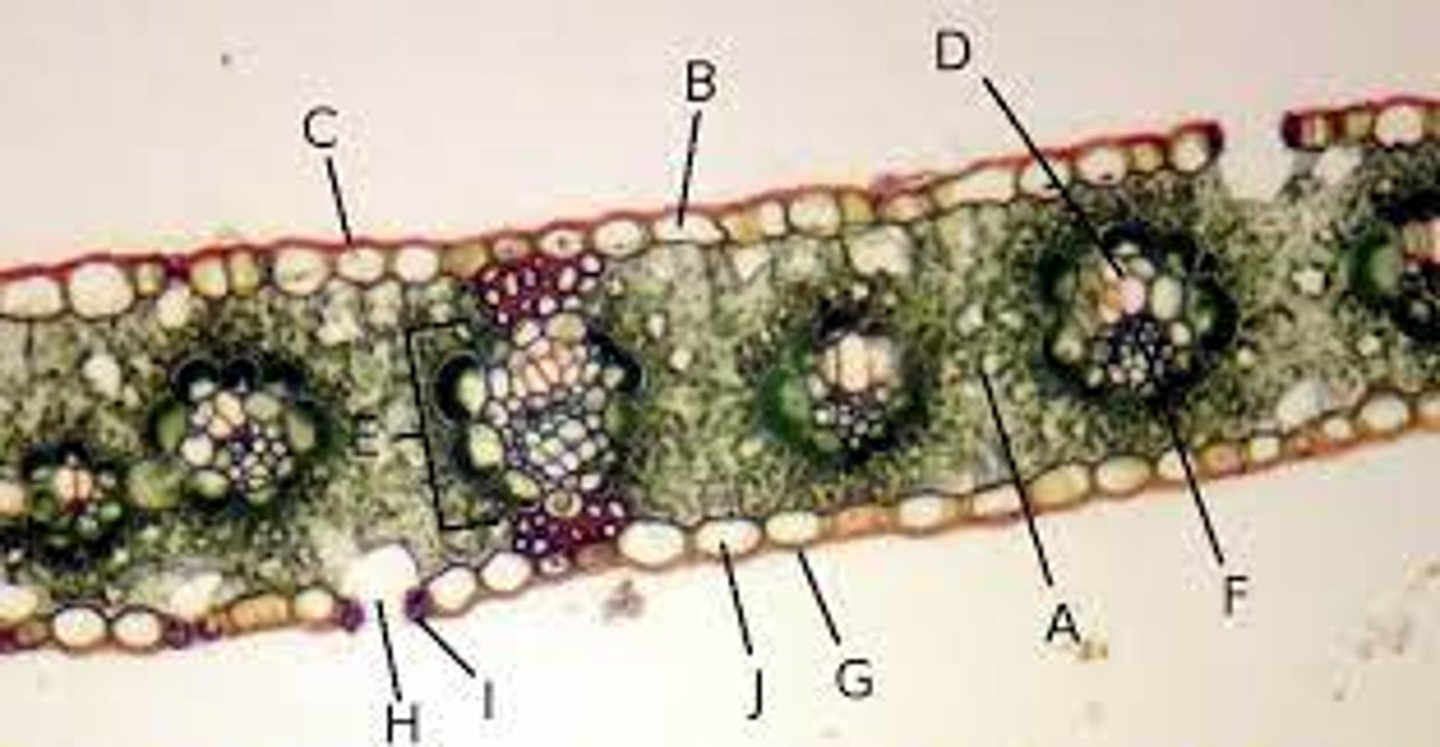
Phloem
F?
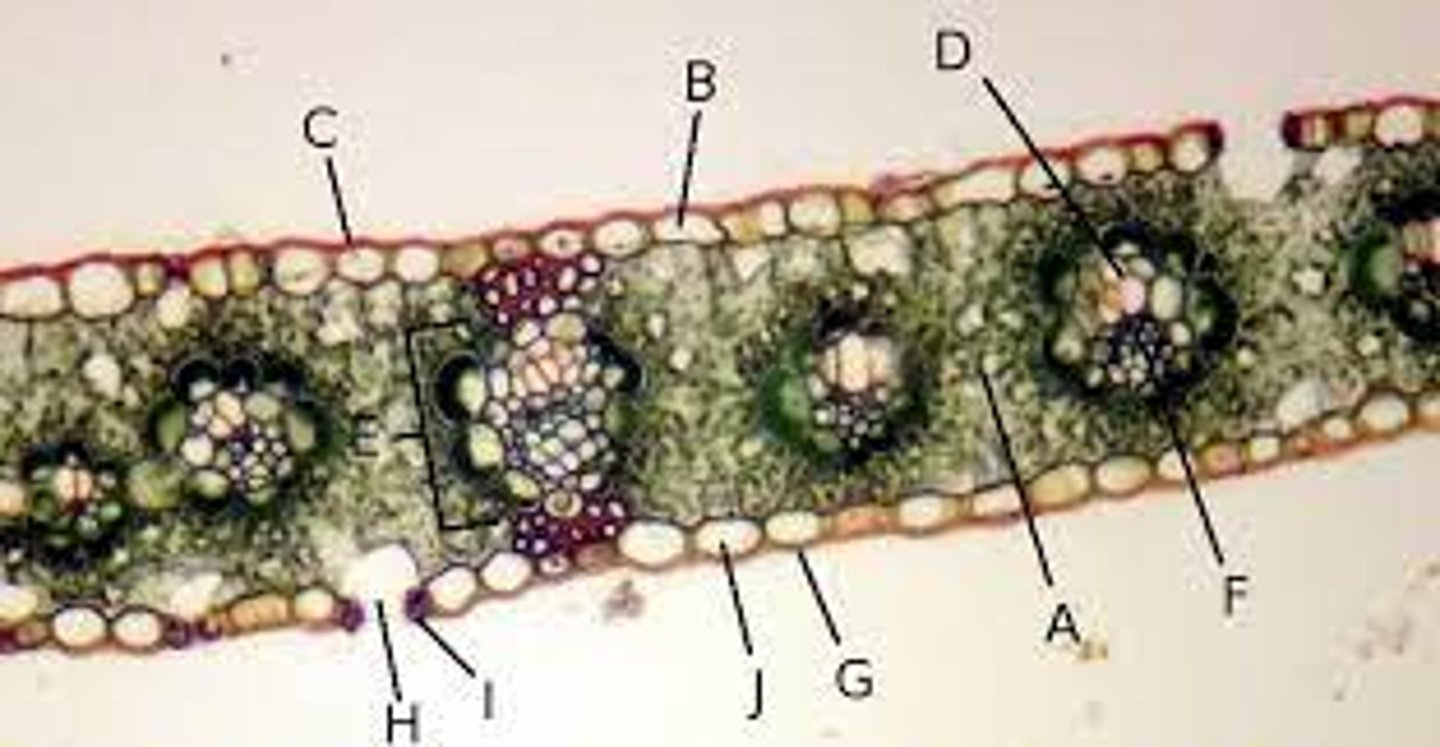
Cuticle
G?
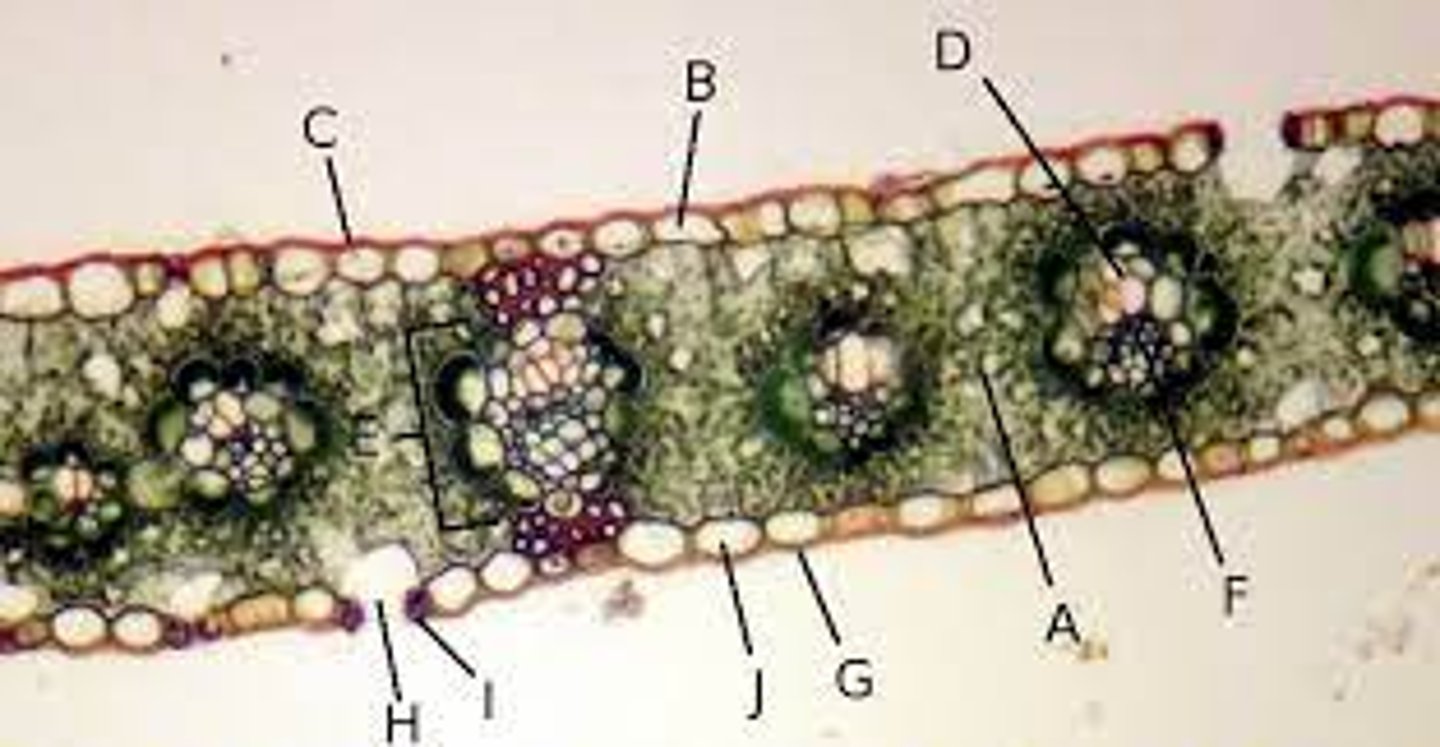
Epidermis
J?
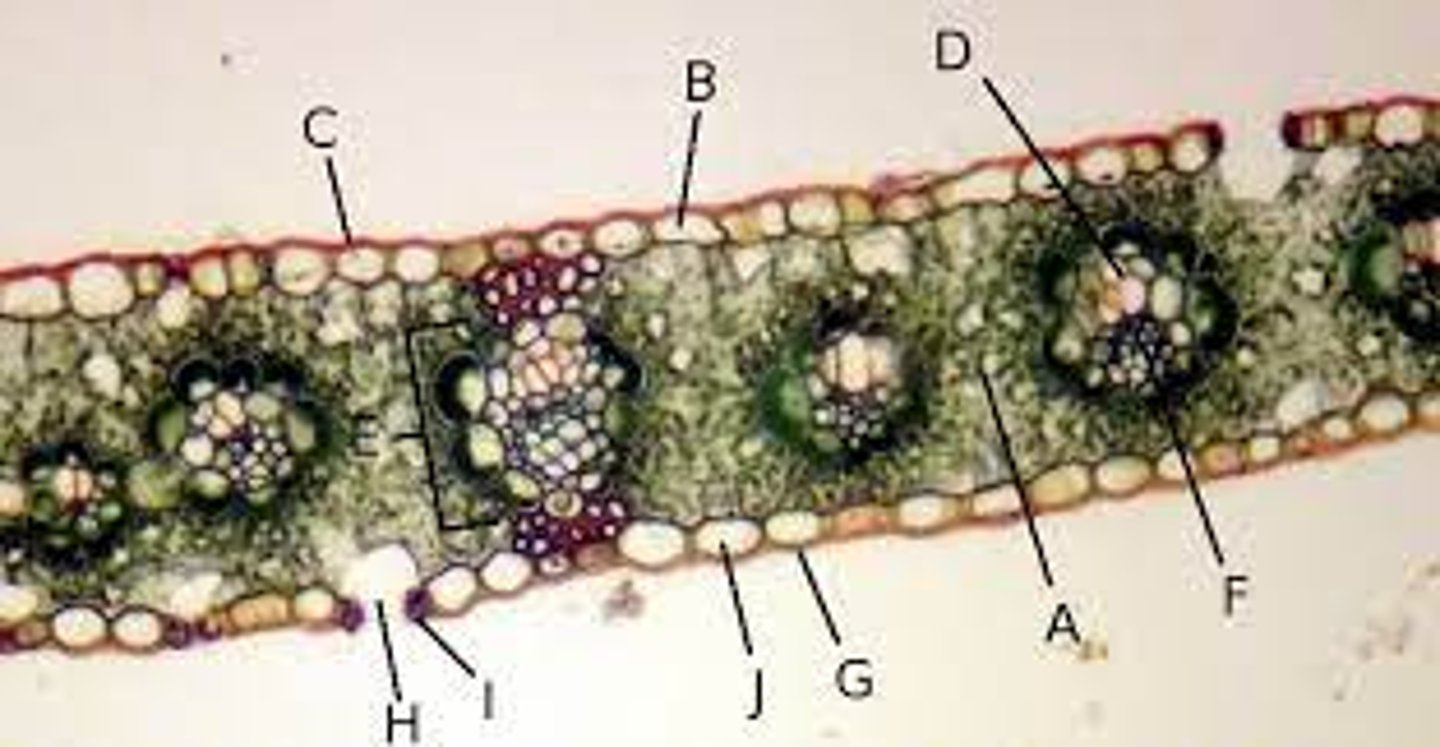
Vascular
Xylem and phloem are what type of tissue?
Ground
Spongy mesophyll is what type of tissue?
Trichomes
All of the following describe the function of what?
- increased reflection of solar radiation
- lower leaf temperatures
- lower rate of water loss
- deterrence of pests
- exude salts
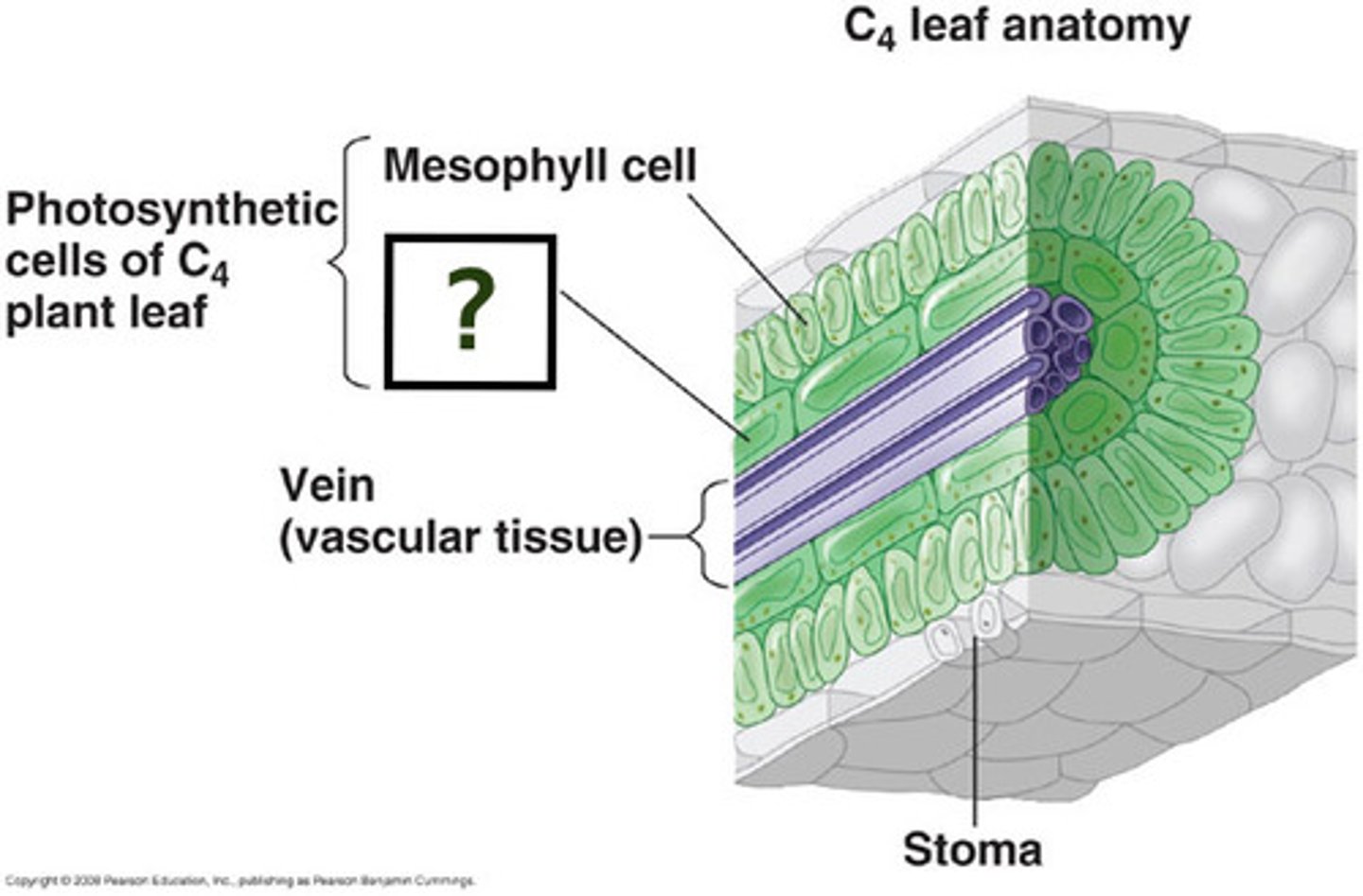
bundle sheath
A protective covering around a leaf vein, consisting of one or more cell layers, usually parenchyma.
spongy mesophyll
Loose tissue beneath the palisade layer of a leaf; has many air spaces between its cells
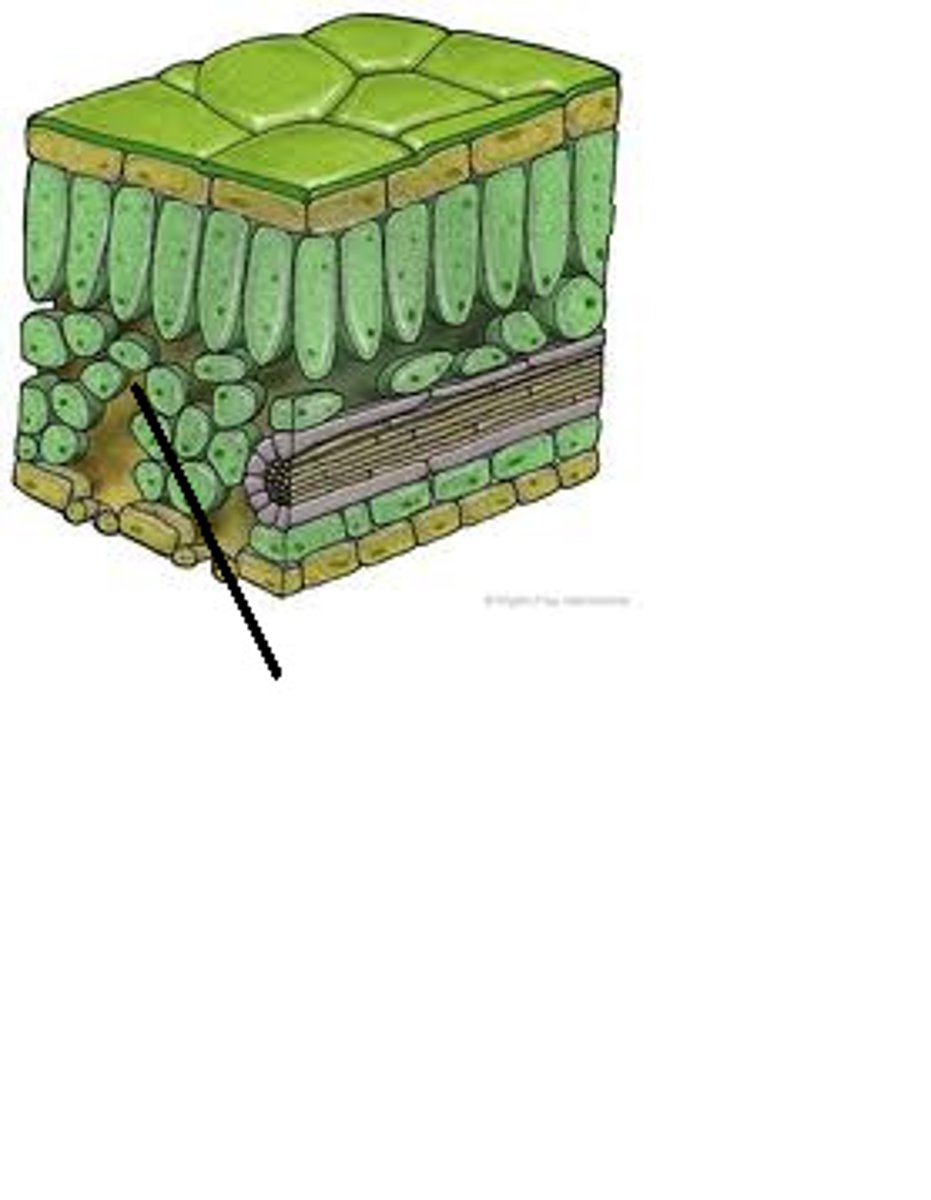
Dermal
The cuticle, stomata, and trichome are types of what tissue?
Epidermis
outermost cell layer
Periderm
replaces epidermal tissue on the roots & stems of woody plants
Ground
Parenchyma tissue, Collenchyma tissue, and Sclerenchyma tissue are types of what tissue?
Parenchyma
Metabolic processes such as respiration, secretion, and photosynthesis; storage and conduction; wound healing and regeneration (chloroplasts)
Throughout the plant body (cortex, pith, xylem, phloem)
Collenchyma
Support in the primary plant body (elongated irregularly thickened walls)
Beneath epidermis in young elongating stems (ribs along veins)
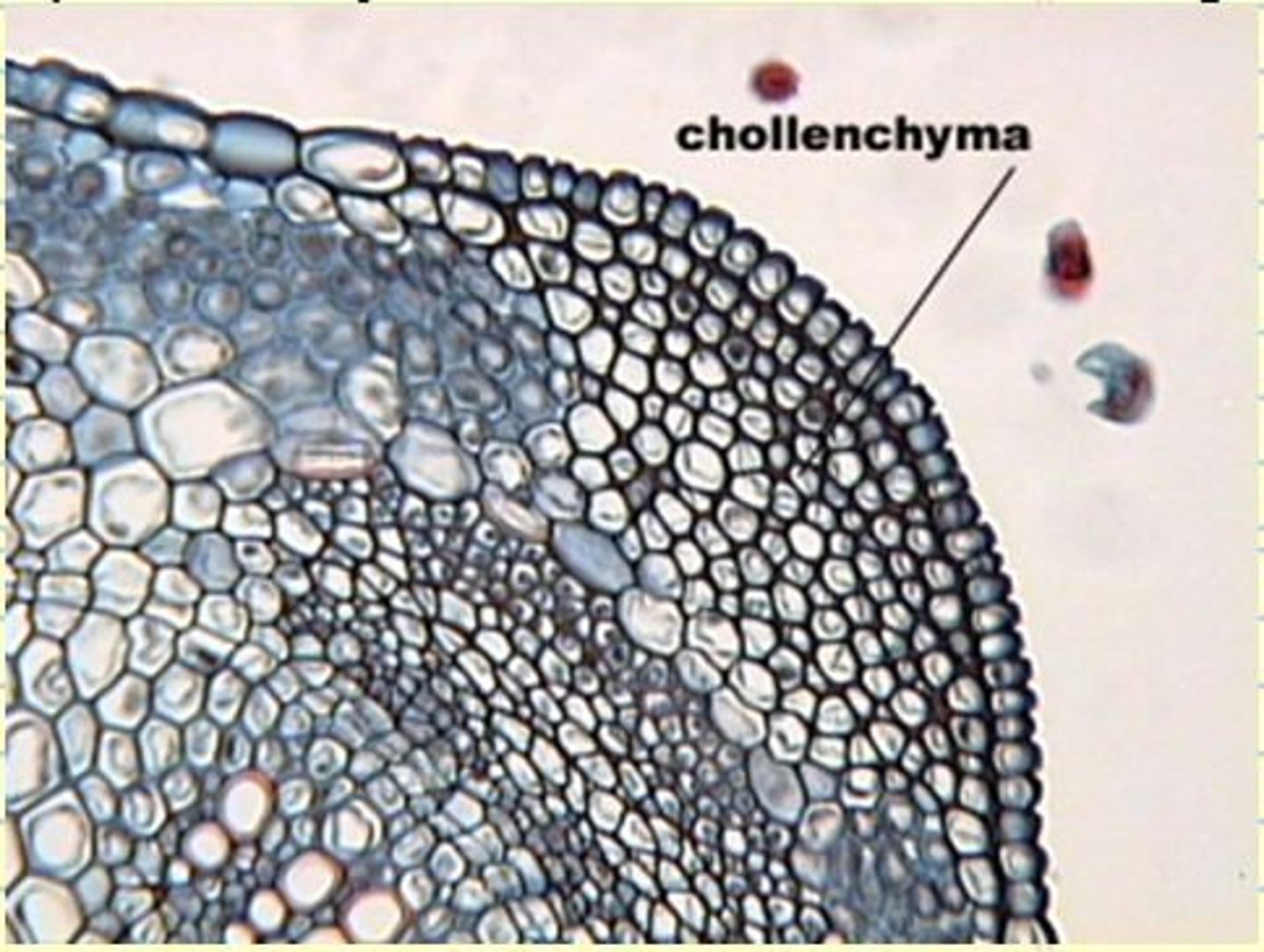
Sclerenchyma
Support; storage (very thick cell walls containing lignin)
In the cortex and stems of monocots (xylem and phloem)