anatomy quiz one
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
sensory information
from the enviorment to the brain (afferent)
motor information
processed in the brain that leads to more movement in the muscles (efferent)
afferent
conducts information into the brain
efferent
conducts information out of the brain
automatic
involuntary responses or activiation patterns
*reflective
*skeletal or smooth
*if its smooth its automatically automatic
volitional
purposeful or goal directed responses or activation patterns
*control
*skeletal
feedback control
when a system iterates plans based on the real time sensory information caused by executing og the processing plan
feed foward control
a system executes a plan using a predictive information rather than relying on real time feedback
centeral sulcus
aka rolandic fissure *divides parental and frontal lobes
lateral solcus
(slyvian fissure) *divides temporal frontal, parental
superior longitudinal fissure
divides left and right hemisphere
brocas area
expressive language
frontal lobe
planning, decison making, motor control is localized in the primary motor cortex (M1)
homunculus “little man”
regions of the body served by motor cortex, size of the strip represents degree of innervation and importance
-contralaterally organized
somatosensory homunculus (left lateral view)
where we process sensory input pain, temp
each body part is localized on somatosensory strip
cerebellum
the primary structure responable for coordination of the fine movement
Which is more distal, your wrist or your elbow?
wrist
What is directly anterior to your bottom teeth?
bottom lip
The tongue is made of several bands of muscle. These muscles must both be able to move quickly (to make rapid articulation changes) and be able to stay contracted for long periods of time (so that it can help position foods that take a lot of time to chew/break down). What type of muscle fibers do you think the tongue is mostly made up of?
both type 1 and type 2 muscle fibers
With a lot of training, you can shift the balance of mostly one type of muscle fiber in a muscle to the other type, but there is a limit to how much you can change the muscle fiber composition of the muscle based on the function of the muscle and the unique way your body metabolizes and uses energy, true/false?
true
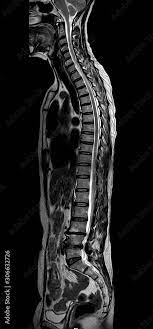
the image below depicts an MRI scan of the spine. On what plane has this image been taken?
sagittal plane
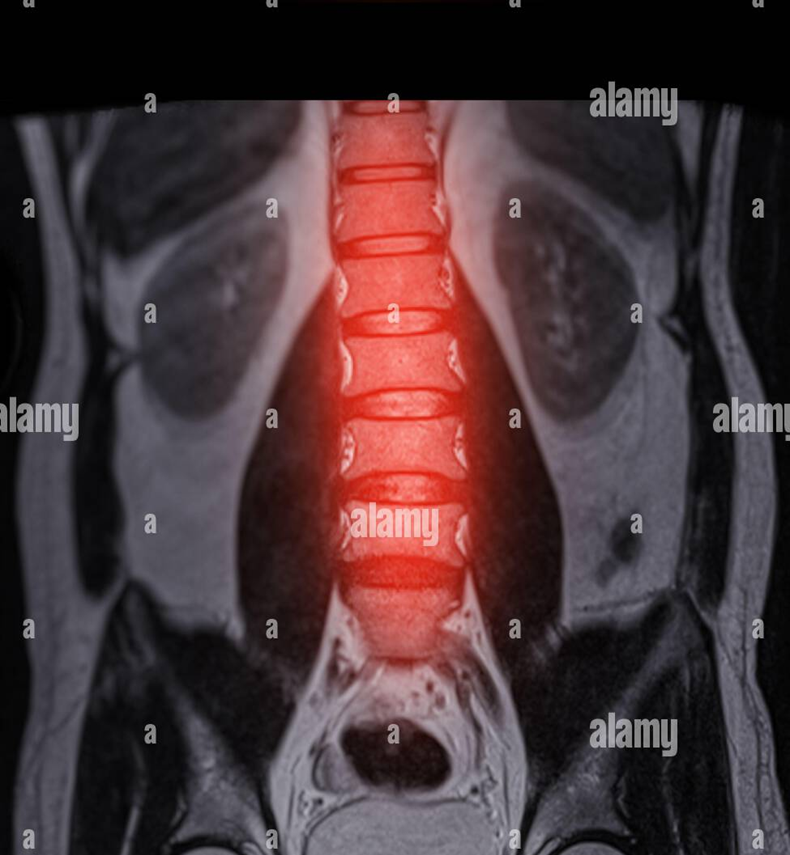
The image below depicts an MRI of the spine (shown in red). On what plane was the image taken?
coronal plane
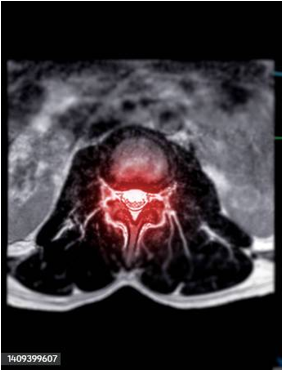
The image below depicts an MRI of the spine (shown in red). On what plane was the image taken?
transverse plane
what is the other term used to indicate the coronal plane?
frontal
what is the other term used to indicate the transverse plane?
horizontal
the image below depicts an MRI image of the spine. Though the spine itself is in the middle of the body, this particular image depicts a slightly lateral view of the spine, as indicated by the 'gaps' shown on some of the vertebrae (compare this with the other images seen in this HW). Is this image a para- or mid- sagittal image?
para-sagittal
The scalenes are muscles of the neck that help our head stay upright and balanced. They need to be able to stay contracted for a long period of time, but do not need to generate a lot of force. Would you expect them to be primarily type 1 or type 2 fibers?
he longus capitis is a muscle in the neck that helps turn the head. It needs to be able to contract quickly and forcefully so that we can turn towards stimuli that may be dangerous. Would you expect a muscle with this function to be primarily composed of type 1 or type 2 fibers?
type 2 muscle fibers
We will spend some time this semester discussing cranial nerve 12 (CN XII). The name of this nerve is the 'hypoglossal' nerve. If 'glossal' means tongue, would you expect this nerve to innervate structures above or below the surface of the tongue?
below
The muscles above the hyoid bone are called the 'infra- / supra- hyoids'.
supra
The epithelial cells shown below line the nasal passage. What is their anatomical name?
ciliated columnar epithelium
he tensor tympani is a muscle of hearing, and thus needs to be able to make well-coordinated, fine movements. Would you expect such a muscle to have a large motor unit (ex. 500 muscle fibers per neuron) or a smaller motor unit (5 muscle fibers/neuron)?
5/1, smaller