Module 19: Vision: Sensory and Perception Processing
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
Transduce
Transform
How do we see?
Light travels in waves, and the shape of those waves influences what we see
Wavelength
The distance from the peak of one light or sound wave to the next

Hue
The color that is determined by the wavelength of light that we see
Intensity
The amount of energy in a light or sound wave, which influences what those with typical vision or hearing perceive as brightness or loudness
Intensity is determined by the wave’s…
amplitude (height)

Cornea
Where light enters the eye from
Purpose of the Cornea
Bends light to help provide focus
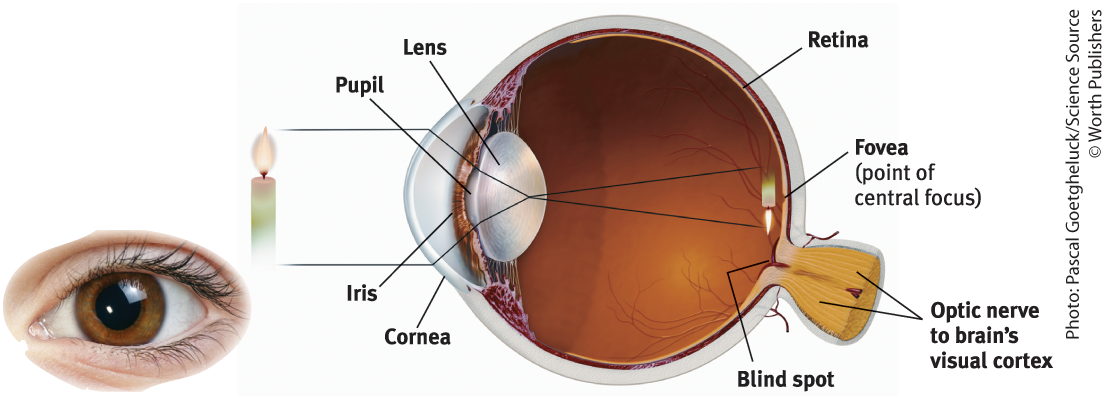
Pupil
Small adjustable opening that light passes through after it passes the cornea
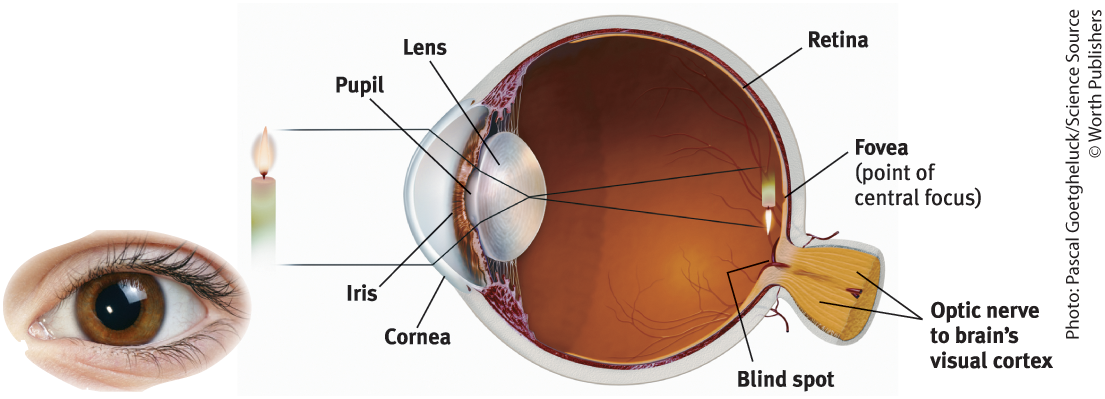
Iris
Surrounds the pupil and controls its size, colored muscle that dilates or constricts in response to light intensity, also responds to cognitive and emotional states
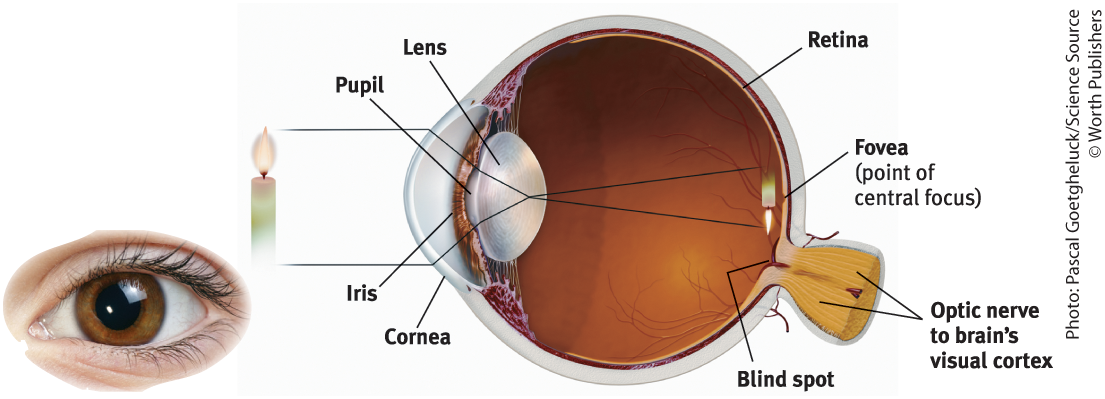
Lens
The transparent part of the eye that the light hits after passing through the pupil, then focuses the light rays into an image on our retina
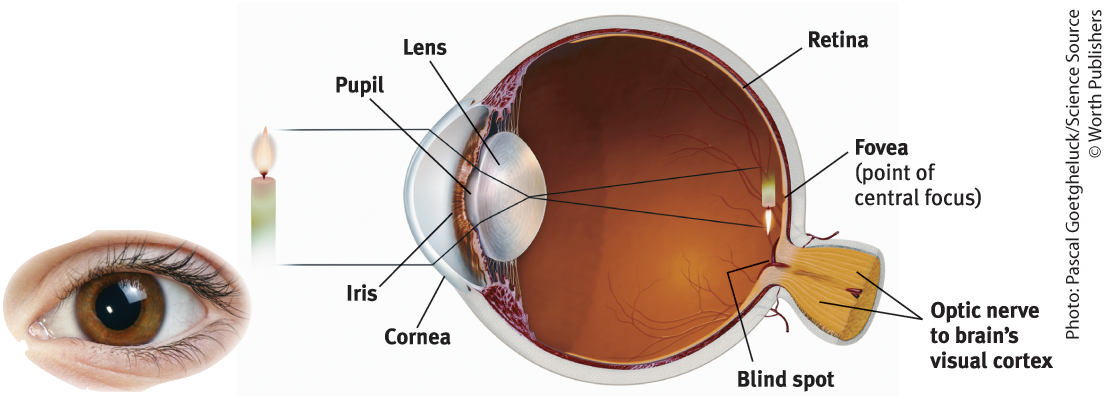
Retina
The light-sensitive back inner surface of the eye, containing the receptor rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
Accomodation
A process where the eye's lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina
Myopia
Nearsightedness, seeing near objects clearly but not distant objects
How do we understand the world?
The retina does not ‘see’ a whole image. Its millions of receptor cells convert the particles of light energy into neural impulses to forward those to the brain, which reassembles them, right side up, into what we perceive
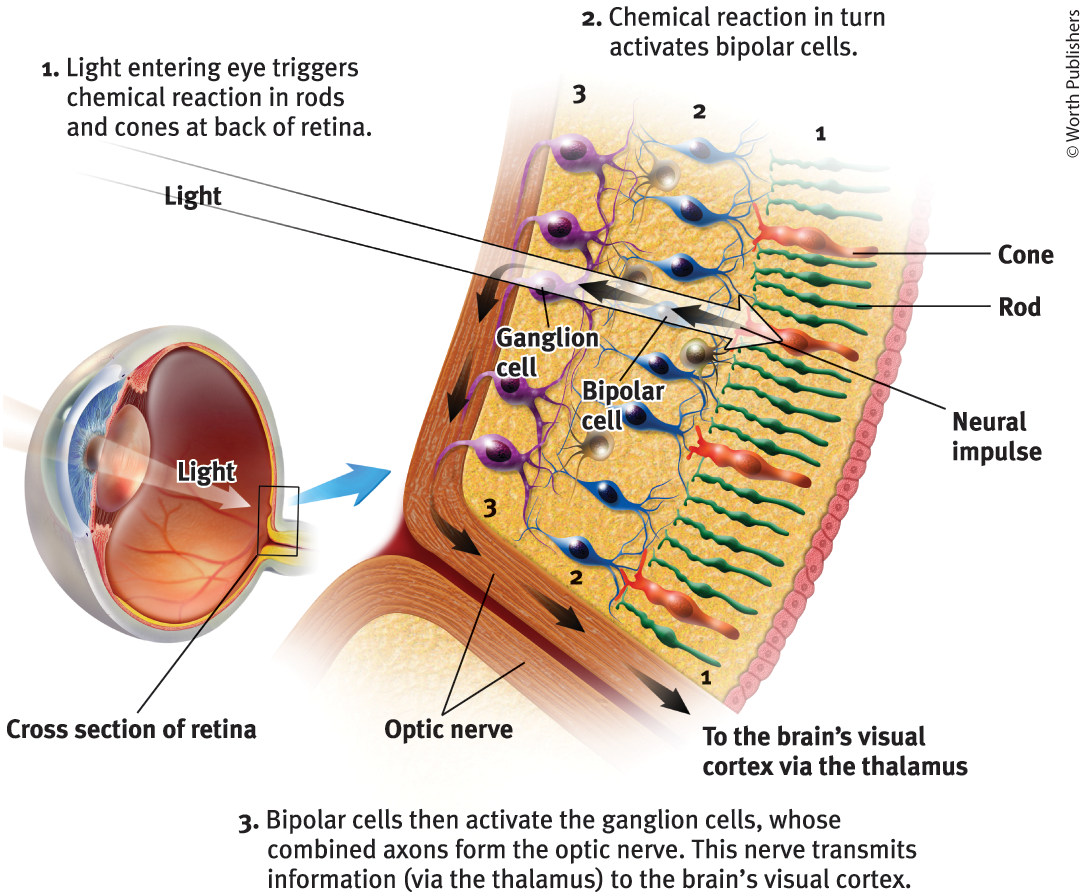
Rods
Retinal receptors that detect black, white, and gray, and are sensitive to movement
What are rods responsible for when cones don’t respond?
Peripheral and twilight vision
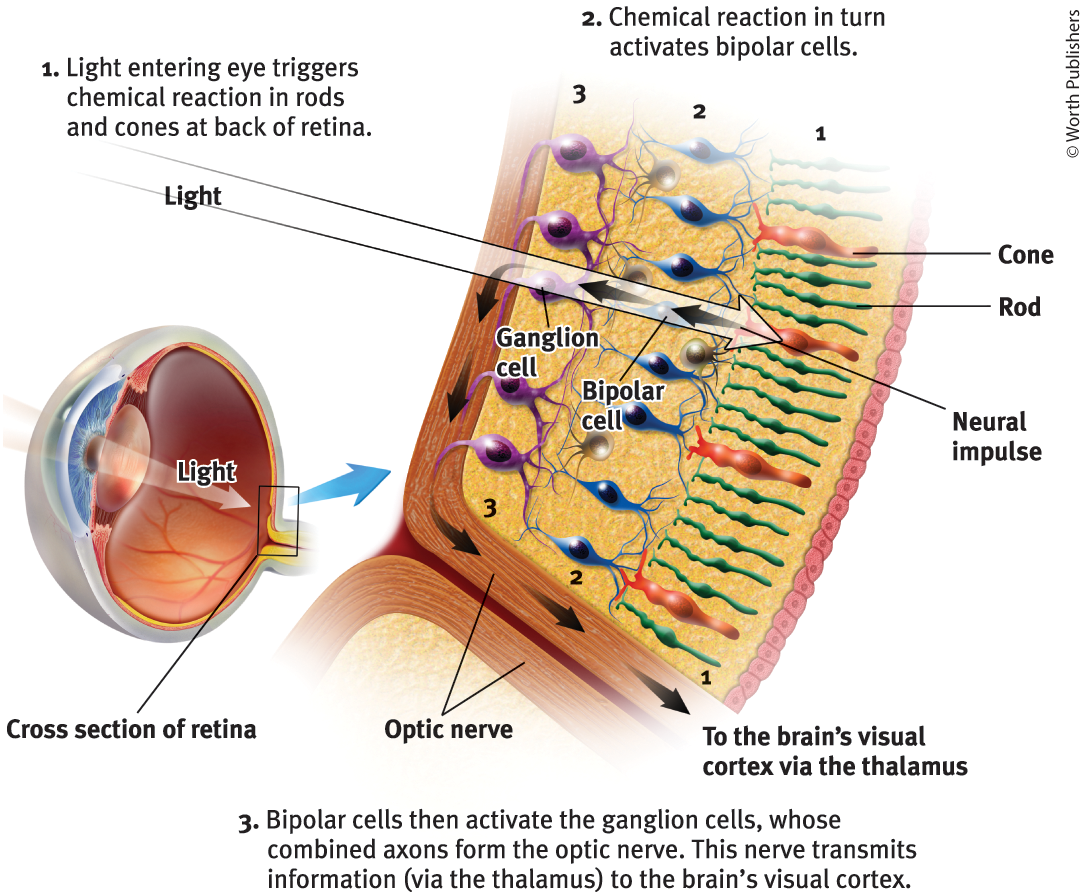
Cones
Retinal receptors that are concentrated near the center of the retina and function in well-lit conditions, detect fine detail and give rise to color sensations
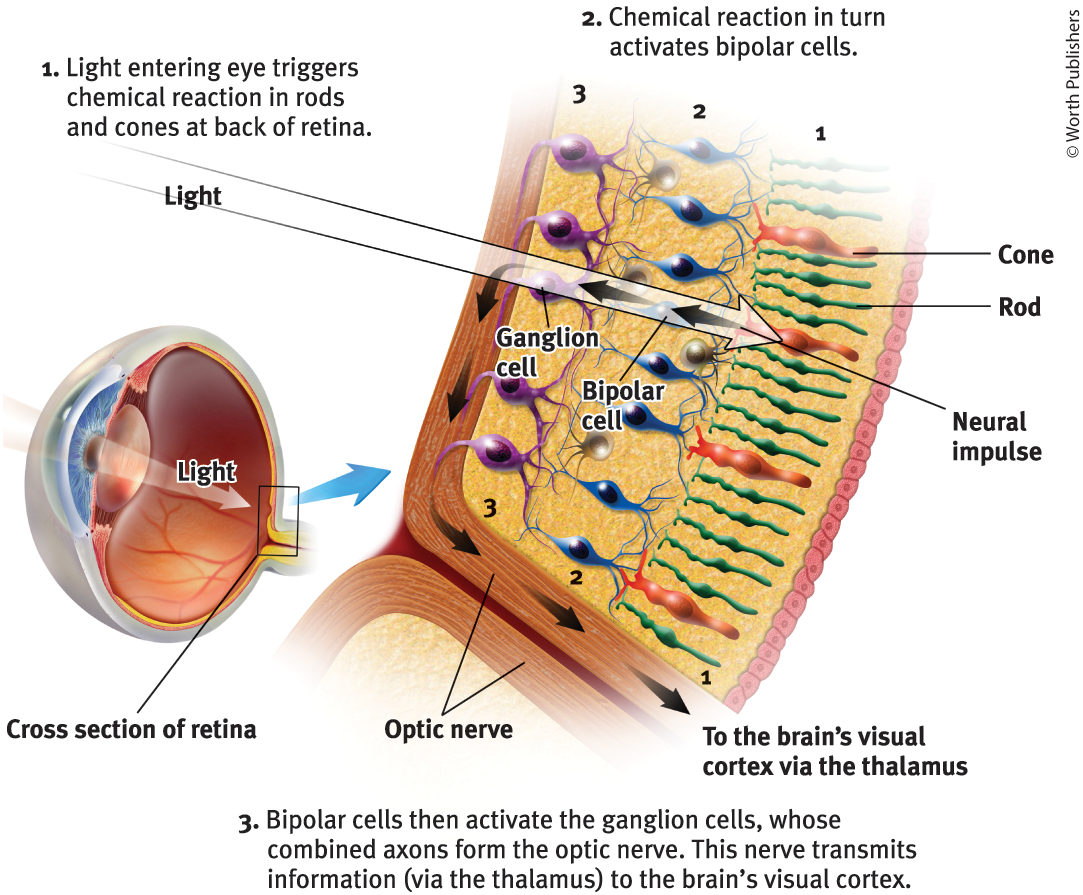
Bipolar Cells
Retinal neurons that carry signals from photoreceptors (rods + cones) to ganglion cells
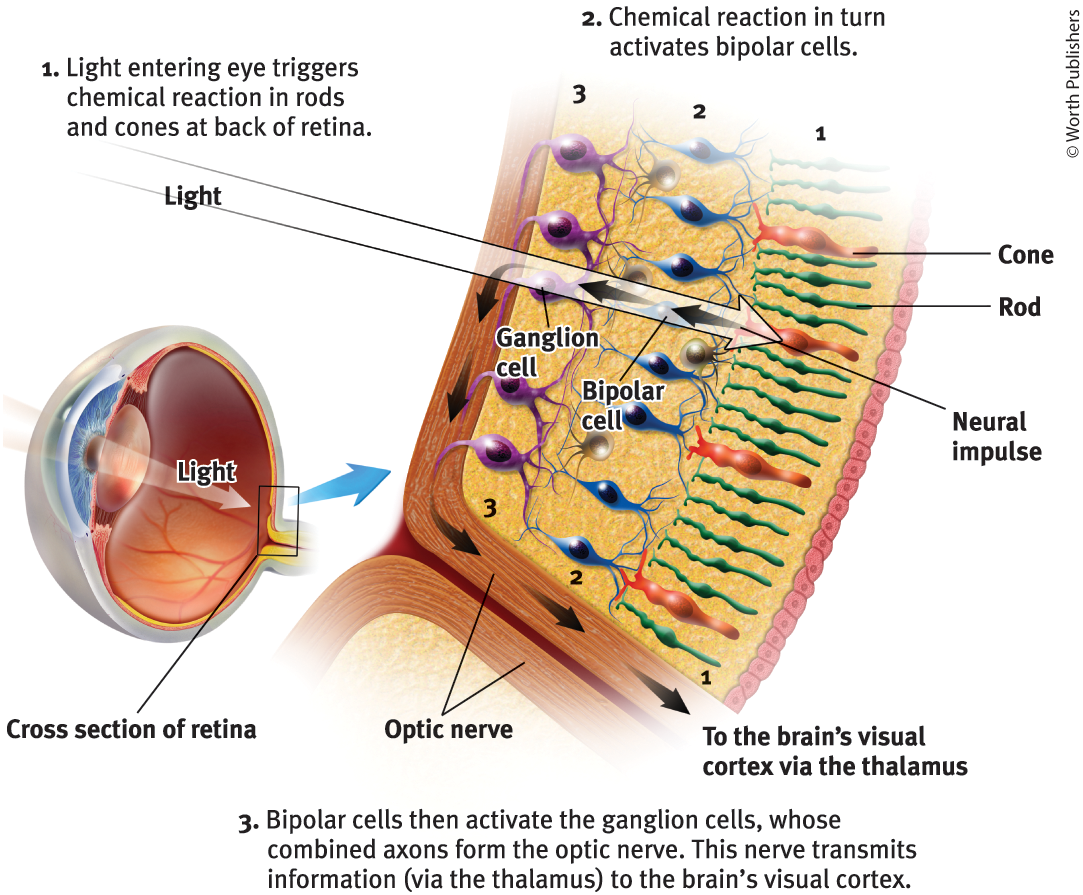
Ganglion cells
Neurons that are essential for vision, activated by bipolar cells
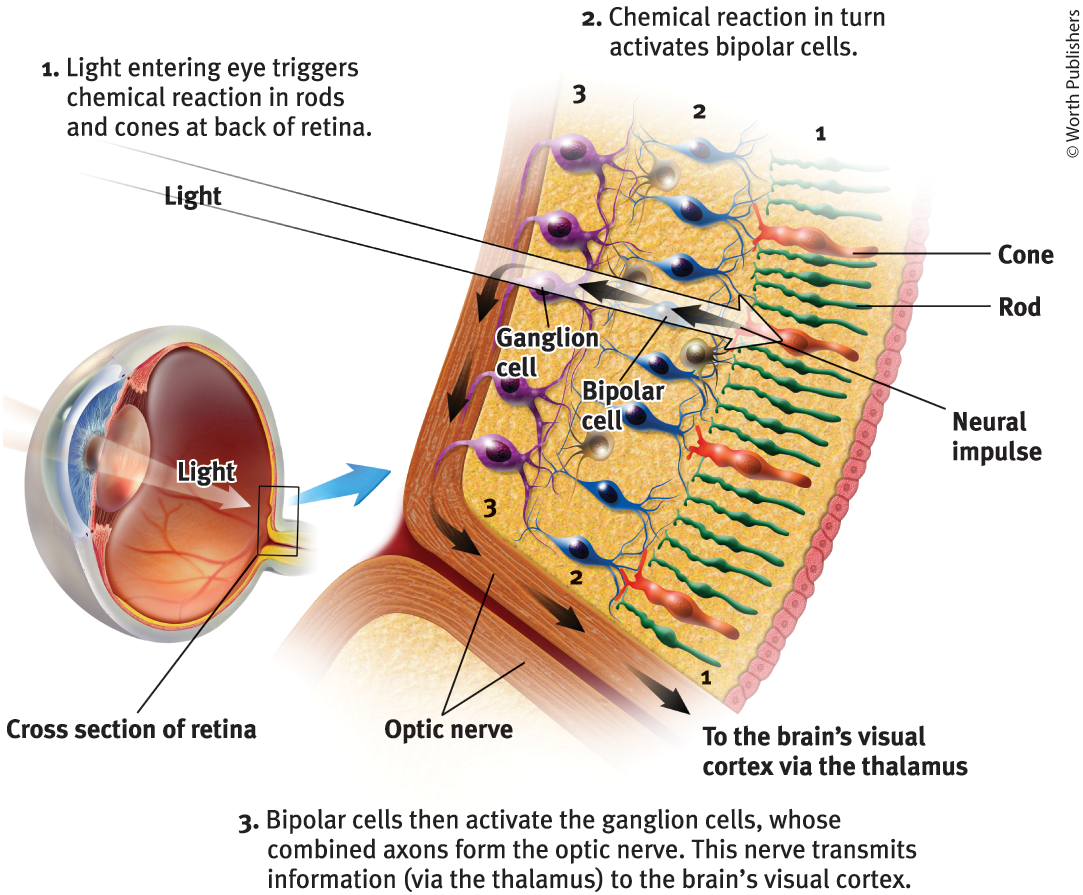
Optic nerve
The nerve that carries neural impulses from the eye to the brain
How is an optic nerve formed?
Made up of ganglion cells whose axons twine together like rope

Blind Spot
The point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a ‘blind spot’ because no receptor cells are located there
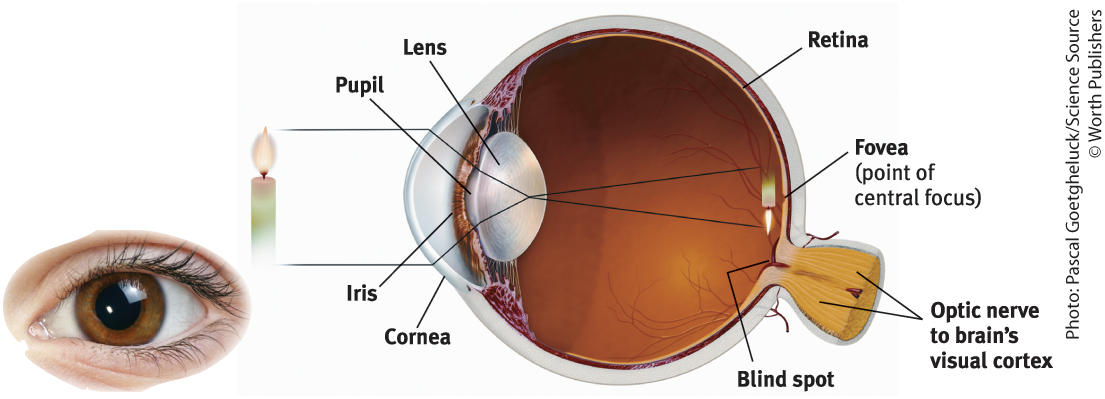
Fovea
The central/main point in the retina where the eye’s cones cluster
How are messages transmitted from the eye to the brain?
One cone transmits a message to one bipolar cell, which relays the message to the visual cortex
Why are connections so direct (ONE cone connects to ONE bipolar cell)?
These direct connections preserve the cone’s precise info, making them better able to detect more detail
Color processing
When we see a specific color, that color is being reflected, while all other colors are being absorbed
Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic (three-color theory)
The theory that the retina contains three different types of color receptors: one most sensitive to red, one to green, and one to blue (when stimulated in combination, can produce the perception of any color)
Color-Deficient Vision
Cones don’t work properly, causing difficulty seeing or distinguishing certain colors
Opponent-Process Theory
Theory that opposing retinal processes (red-green, blue-yellow, white-black) enable color vision
Some cells are inhibited by red and stimulated by green, meaning we can’t see colors that are reddish-green. This is an example of the…
Opponent-process theory
Feature Detectors
Nerve cells in the brain’s visual cortex that respond to specific features of the stimulus, such as shape, angle, or movement
Supercell Clusters
Groups of cells that respond to more complex patterns of information
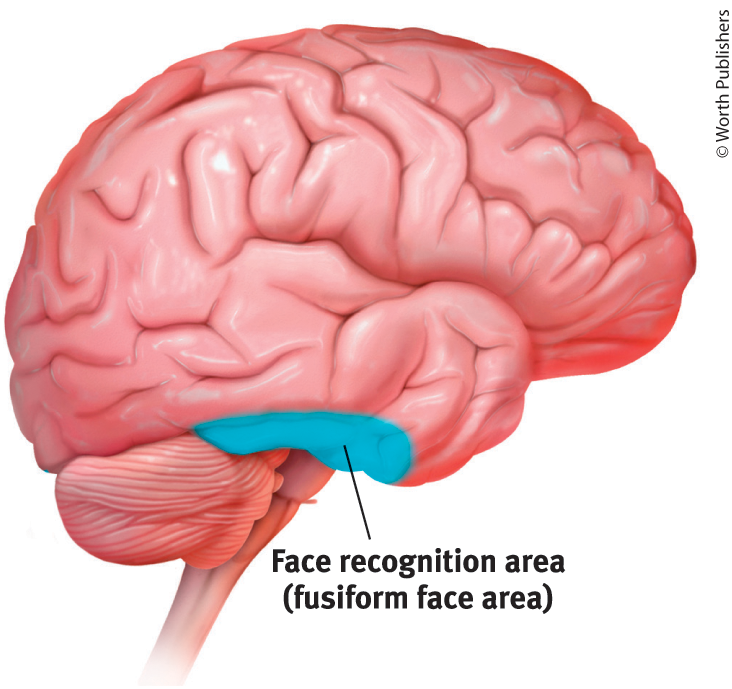
Fusiform Face Area
A region in the temporal lobe that responds to faces and is crucial for face perception and recognition
Parallel Processing
Processing multiple aspects of a stimulus or problem simultaneously
Gestalt
An organized whole/our tendency to put together pieces of information to form a meaningful whole
Figure-ground
The organization of the visual field into objects (figures) that stand out from their surroundings (ground)
Grouping
The perceptual tendency to organize stimuli into logical groups
Depth-Perception
The ability to see objects in three dimensions, although the images that strike the retina are two-dimensional
We are able to judge distance because of…
Depth perception
Visual Cliff
A laboratory device for testing depth perception in infants and young animals
Binocular Cues
A depth cue, such as retinal disparity that depends on the use of two eyes
Retinal Disparity
A binocular cue for perceiving depth: comparing retinal images from the two eyes, the brain computes distance
The greater the disparity (difference) between the two images, the… the object
closer
Monocular Cues
A depth cue available to either eye alone
Interposition
A monocular cue where one object that is partially blocking another is perceived as being closer
Linear Perpective
A monocular cue that tricks the brain in perceiving depth and distance in flat (2D) images
Motion Perception
Shrinking objects are retreating and enlarging objects are approaching
Phi Phenomenon
An illusion or movement created when two or more adjacent lights blink on and off in quick succession
Perceptual Constancy
Perceiving objects as unchanging (having consistent color, brightness, shape, and size), even as illumination and retinal images change
Relative Luminance
The amount of light an object reflects relative to its surroundings
Shape Constancy
Those with typical vision perceive the form of familiar objects as constant even while the retinas receive changing images of them
Size Constancy
Those with typical vision perceive an object as having an unchanging size, even while distance from it varies
For sensory and perceptual development, there is a… where exposure to certain stimuli or experiences is required
critical period
Perceptual Adaptation
The ability to adjust to changes sensory input, including an artificially displaced or inverted visual field
Proximity
Gestalt principle where we group nearby objects together as a unit, seeing relatedness in closeness
Similarity
Gestalt principle where we group things that look alike (color, shape size)
Closure
Gestalt principle where we mentally fill in gaps or incomplete information
Texture Gradient
A monocular depth cue where surfaces close to us appear detailed, and when they are farther the texture seems smoother
Relative Motion
A monocular depth cue where closer objects seem faster and farther objects seem to be slower or not moving
Light and Shadow
A monocular cue where shading suggests depth and dimension
Relative Size
A monocular cue where when two objects are similar, the one casting a smaller image on our retina is perceived as farther away
Lightness Constancy
The ability to see an object with the same brightness even when the lighting around you is different
Sclera
The outer layer of the eye that is white and smoothly transitions to the cornea
Astigmatism
A disorder of the curvature of the cornea or lens that results in difficulty seeing fine detail
Conjunctiva
The thin layer of mucous membrane that covers the outer eye and inside the eyelids for protection
Aqueous Humor
Clear fluid located near the front of the eye that supplies nutrients to the eye, removes waste, and maintains the shape of the eye
Cataract
A condition where the lens of the eye is cloudy. Can affect vision due to aging, injury, or disease
Vitreous Humor
Clear gelatinous fluid that fills the area behind the lens to the back of the eye
Choroid
A bunch of blood vessels that keep the eye healthy by providing oxygen and nutrients
Height in Plane
A monocular depth cue where objects higher up in our visual field are perceived as farther away, and vise versa
Monochromatism
A type of color blindness where the person sees everything in the shade of one color
Convergence
A binocular cue for depth perception where your eyes turn inward (converge) to focus on nearby objects