Neisseria Species and Moraxella catarrhalis Overview
1/99
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
100 Terms
Neisseriaceae
Family including Neisseria, Kingella, Eikenella, Simonsiella, Alysiella.
Neisseria
Aerobic, capnophilic, gram-negative diplococci.
N. elongata
Catalase-negative, rod-shaped Neisseria species.
N. bacilliformis
Catalase-negative, rod-shaped Neisseria species.
N. weaveri
Catalase-positive, rod-shaped Neisseria species.
Normal flora
Non-pathogenic bacteria in upper respiratory, urogenital tracts.
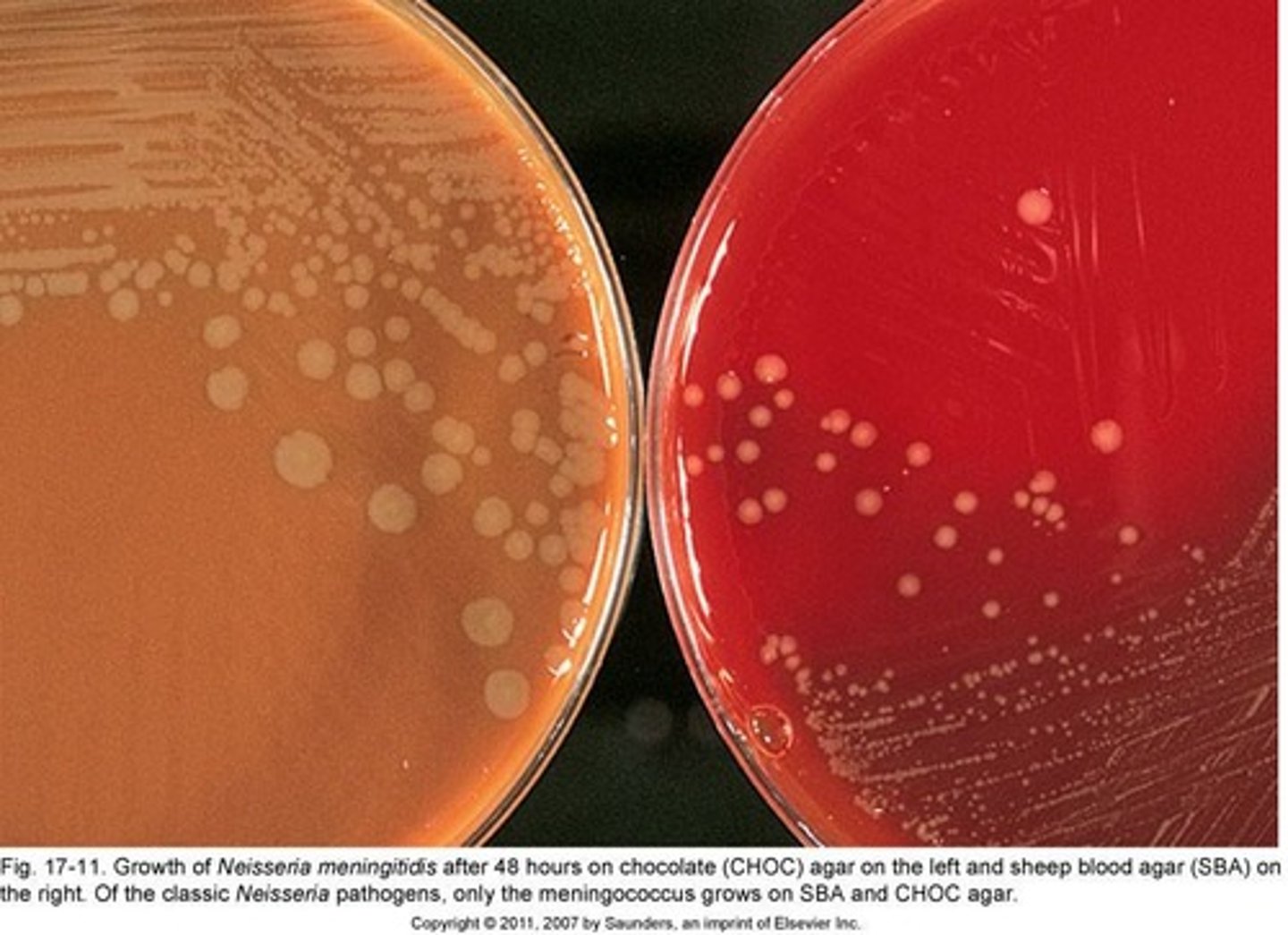
N. meningitidis
Commensal inhabitant, can cause meningitis.
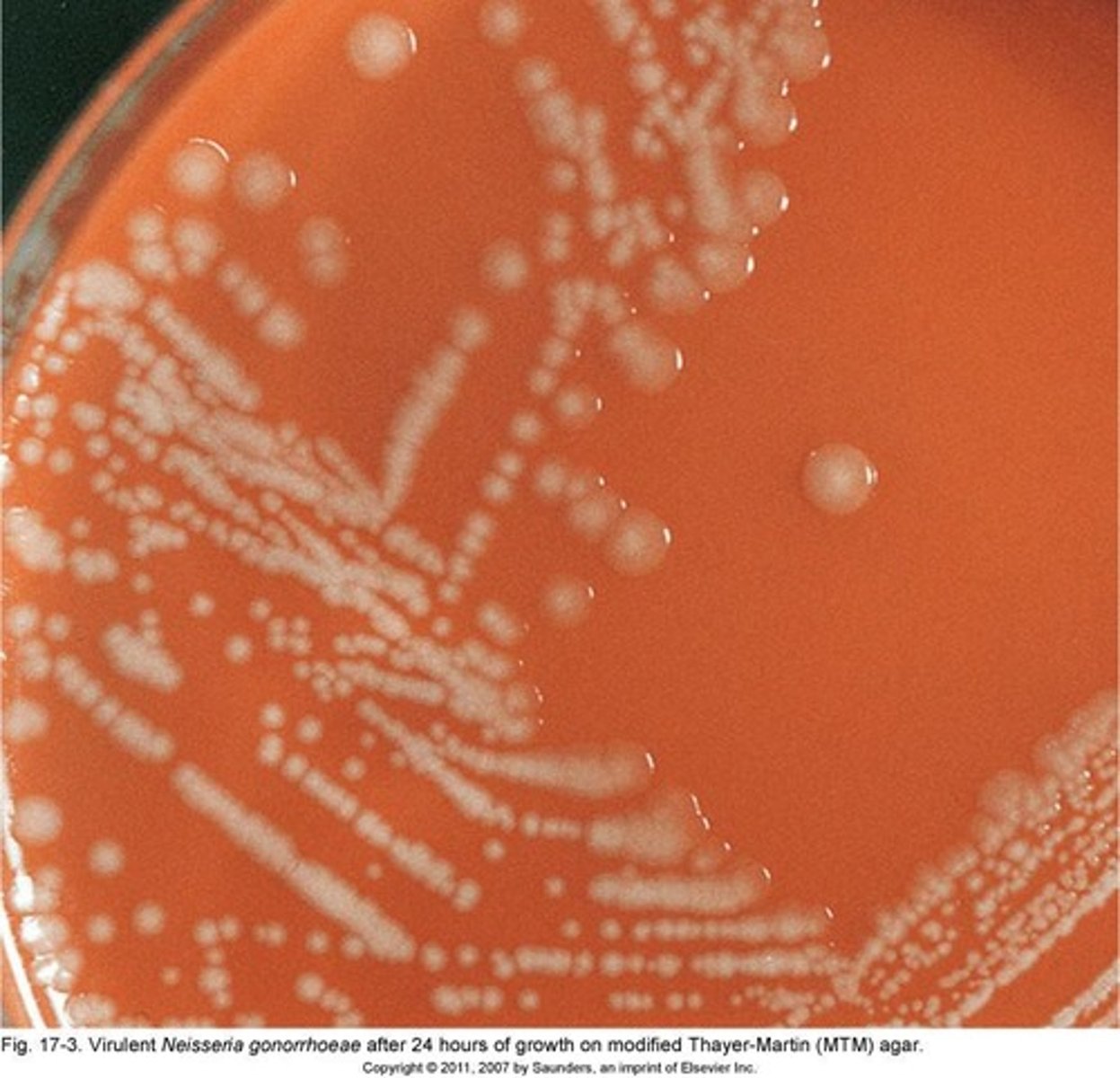
N. gonorrhoeae
Primary pathogen causing gonorrhea, only human host.
Gonorrhea
Acute pyogenic infection of urogenital tract, pharynx.
Disseminated infections
Less common infections from N. gonorrhoeae.
Public health issue
Gonorrhea is nationally reportable STD.
Chlamydia
Most reported STD, gonorrhea is second.
Ceftriaxone
Injectable cephalosporin for gonorrhea treatment.

Azithromycin
Oral antibiotic used in dual therapy.
Pili
Aid attachment, prevent phagocytosis, exchange genetic material.
Colony types
Five types: T1-T2 virulent, T3-T5 non-virulent.
Capsule
Virulence factor preventing phagocytosis.
Outer membrane proteins
Cause antigenic variation, useless antibody production.
Porin proteins
Major outer membrane proteins for nutrient transport.
por A and por B
Genes expressed in N. meningitidis, only por B in N. gonorrhoeae.
Sex pili
Transfer antibiotic resistance genes between bacteria.
Acute pyogenic infection
Infection characterized by pus formation.
Conjunctiva infection
Eye infection caused by N. gonorrhoeae.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Causative agent of gonorrhea, a sexually transmitted infection.

Virulence Factors
Characteristics that enhance pathogen's ability to cause disease.
Protein II (Opa)
Facilitates adherence to phagocytic and epithelial cells.
Protein III (Rmp)
Blocks host serum bactericidal action against Neisseria.
Lipooligosaccharides (LOS)
Major virulence factor, mediates tissue damage.
IgA protease
Cleaves IgA at mucosal surfaces, aiding infection.
Primary Infection Sites
Urethra, endocervix, anal canal, pharynx, conjunctiva.
Incubation Period
2 to 7 days before symptoms appear.
Male Symptoms
Dysuria, purulent discharge, often symptomatic.
Complications in Males
Epididymitis, urethral stricture, prostatitis.
Female Symptoms
Burning urination, vaginal discharge, abdominal pain.
Asymptomatic Females
50% of infections show no symptoms.
Complications in Females
Pelvic inflammatory disease, sterility, ectopic pregnancy.
Disseminated Gonococcal Disease
Acute form with fever, chills, and skin lesions.
Gonococcal Arthritis
Result of disseminated gonococcal bacteremia.
Ophthalmia Neonatorum
Eye infection in newborns from infected mothers.
Extragenital Infections
Includes pharyngitis and anorectal infections.
Anorectal Infection Rate
30%-60% of women with genital infection concurrent.
Laboratory Diagnosis
Requires specific media for isolation of Neisseria.
Specimen Collection
Proper techniques for urethral and endocervical samples.
Treatment for Neonates
Antimicrobial eye drops to prevent infection.
Pharyngitis Symptoms
Chief complaint in oropharyngeal infections.
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Bacterial pathogen causing gonorrhea in humans.
Susceptibility to Drying
Neisseria is sensitive to drying and cold temperatures.
Direct Inoculation
Transfer to room temperature plate if possible.
Transport Media
Transgrow, JEMBEC, Amies used for specimen transport.
Capnophilic Atmosphere
Special media requiring increased CO2 levels.
Plating Time
Specimens should be plated within 6 hours.
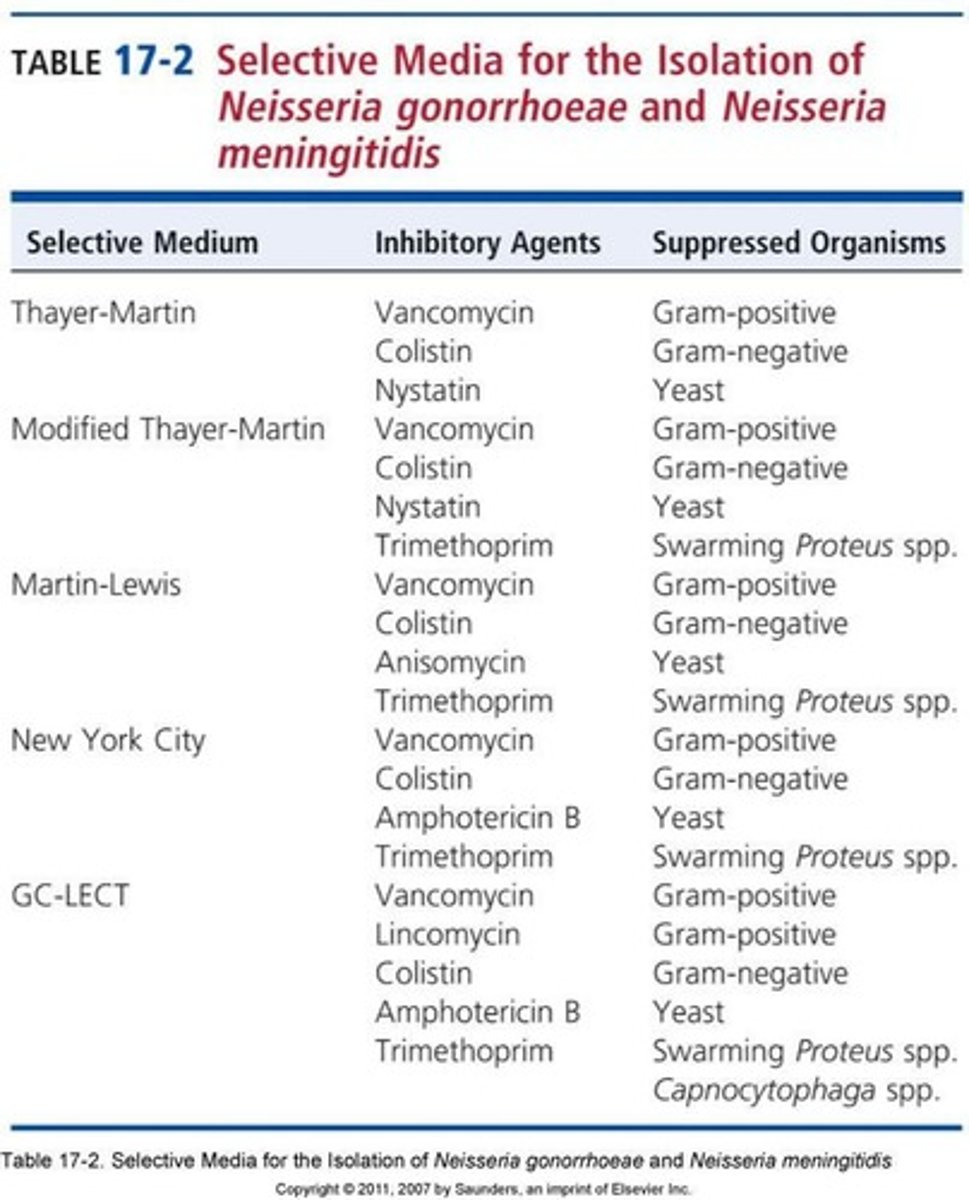
Selective Media
Chocolate agar with inhibitors for unwanted flora.
Colony Morphology
Small, gray to tan, translucent colonies observed.
Incubation Temperature
Culture media incubated at 35°C with CO2.
Incubation Duration
Incubate for up to 72 hours.
Candle Extinction Jar
Used to maintain humidity during incubation.
BioBag CO2
Environmental chamber for CO2 incubation.
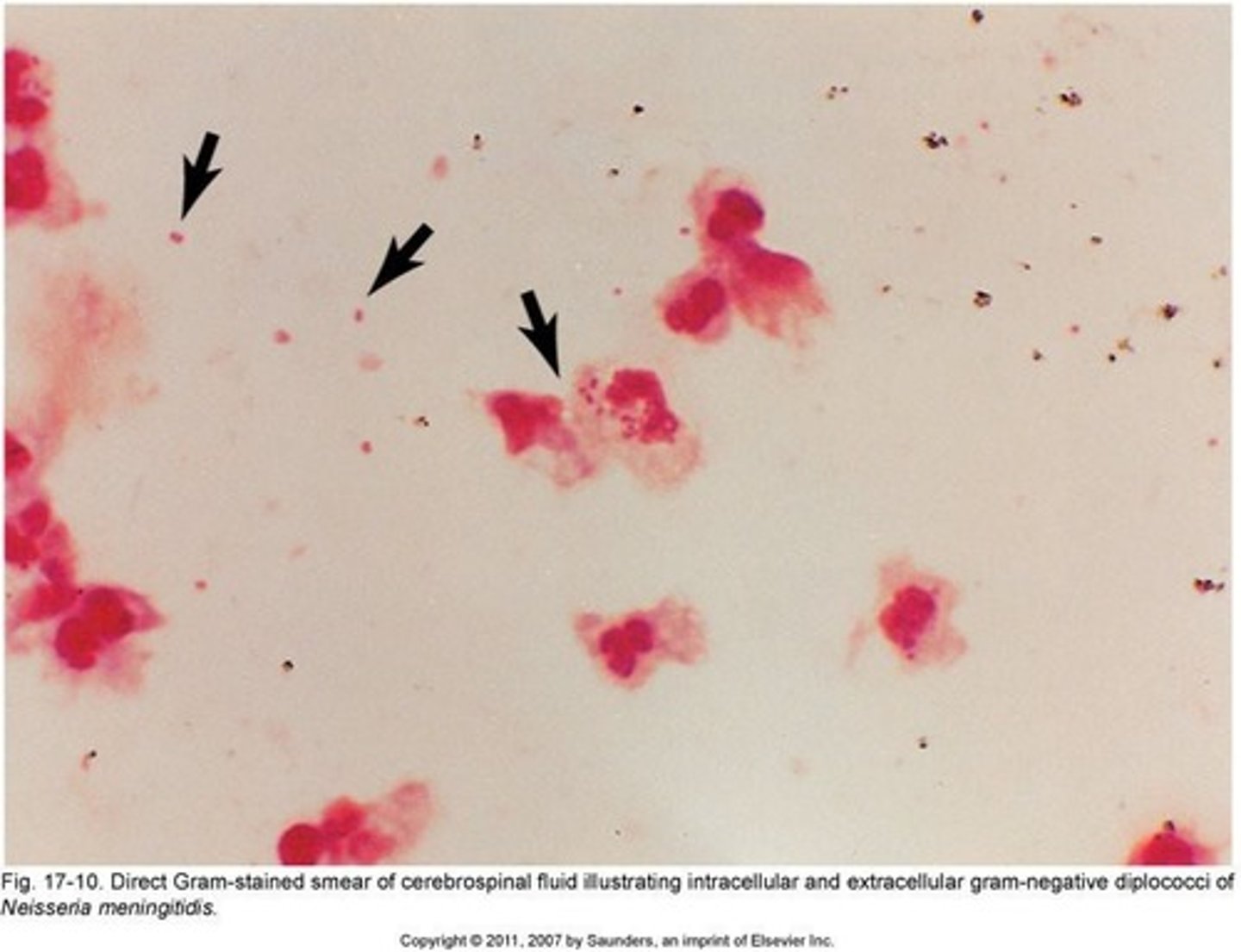
Gram-negative Intracellular Diplococci
Diagnostic feature in male urethral discharge.
Polymorphonuclear Neutrophils (PMN)
>5 PMN suggests nongonococcal urethritis.
Vaginal Commensal Microbiota
Resembles gonococci, complicating diagnosis in women.
Direct Gram Stain
Used to identify N. gonorrhoeae in specimens.
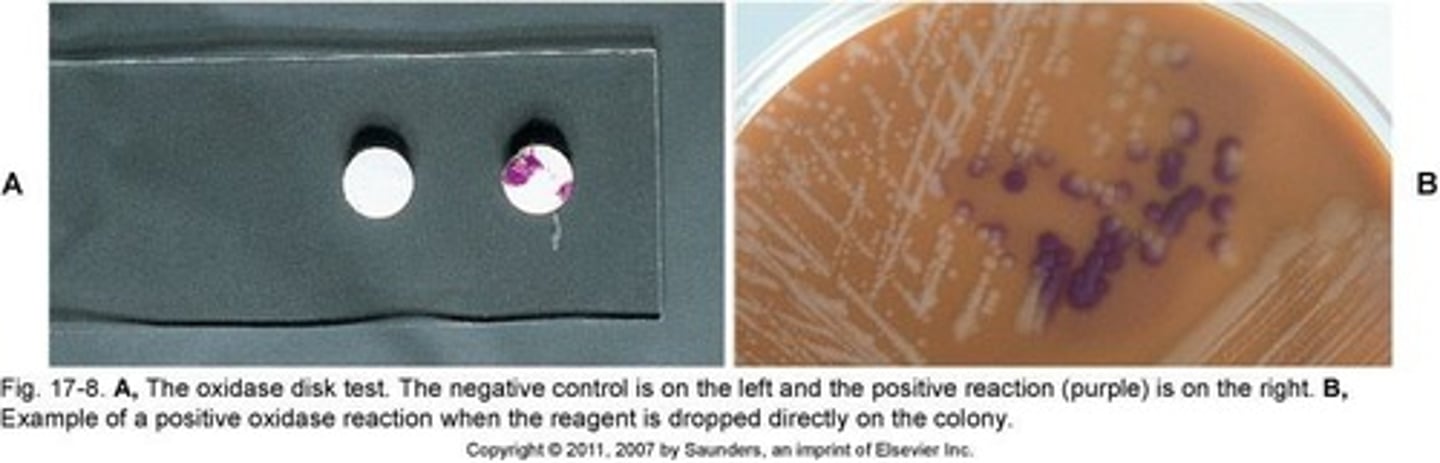
Oxidase Test
Identifies oxidase-positive bacteria using specific reagents.
Positive Oxidase Reaction
Purple color develops within 10 seconds.
Subculture Requirement
Colonies must be subcultured before oxidase testing.
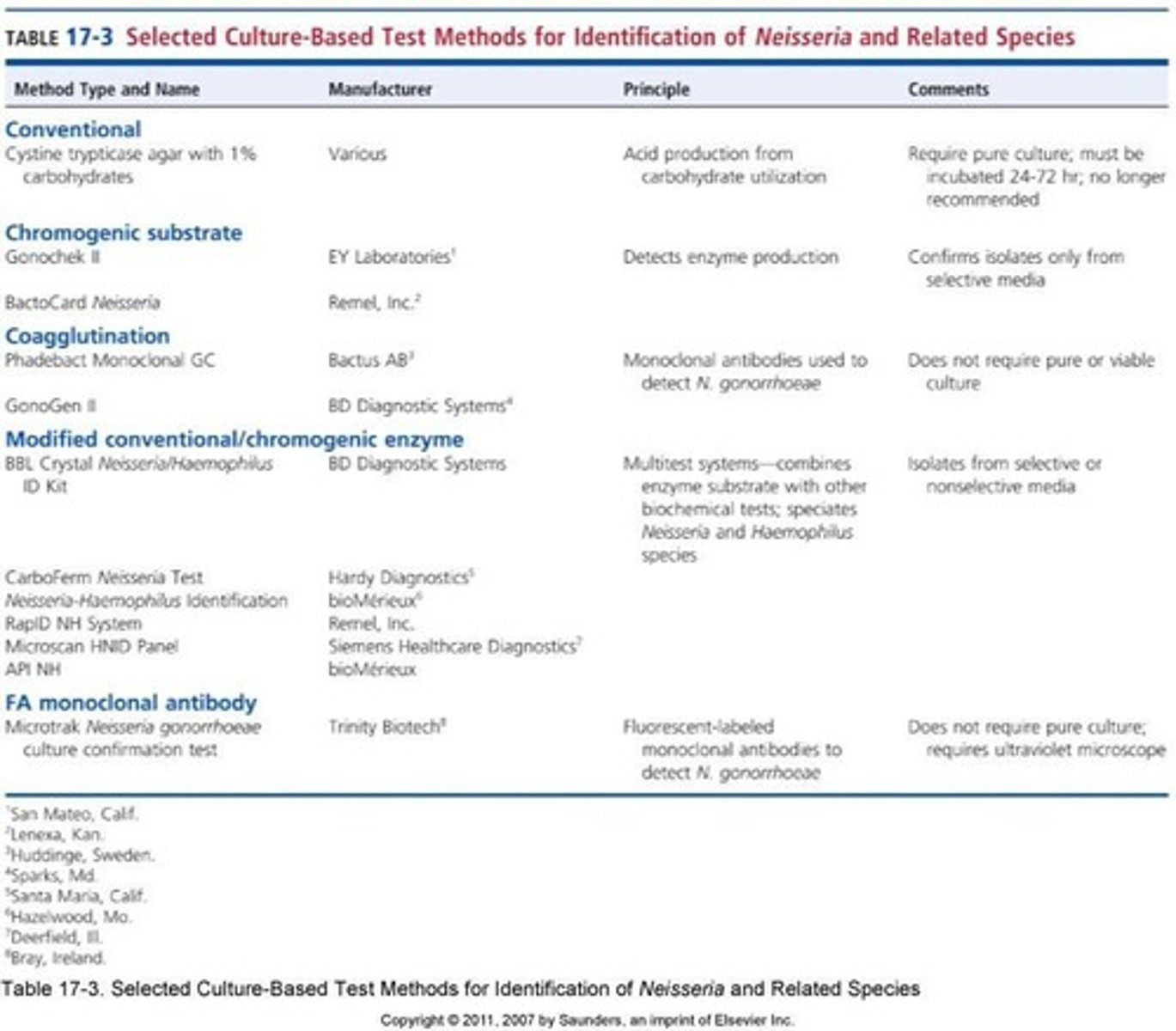
Definitive Identification
Multiple methods used to confirm N. gonorrhoeae.
Demographic Profile
Consider patient demographics for testing methods.
Sensitivity and Specificity
Choose methods based on test accuracy.
Definitive Identification
Process of accurately identifying microorganisms.
Cystine Trypticase Agar (CTA)
Medium for traditional Neisseria identification.
Carbohydrate Utilization Test
Tests organism's ability to ferment carbohydrates.
Phenol Red
pH indicator used in carbohydrate tests.
Acid Production
Result of carbohydrate fermentation in tests.
N. gonorrhoeae
Only ferments glucose in carbohydrate tests.
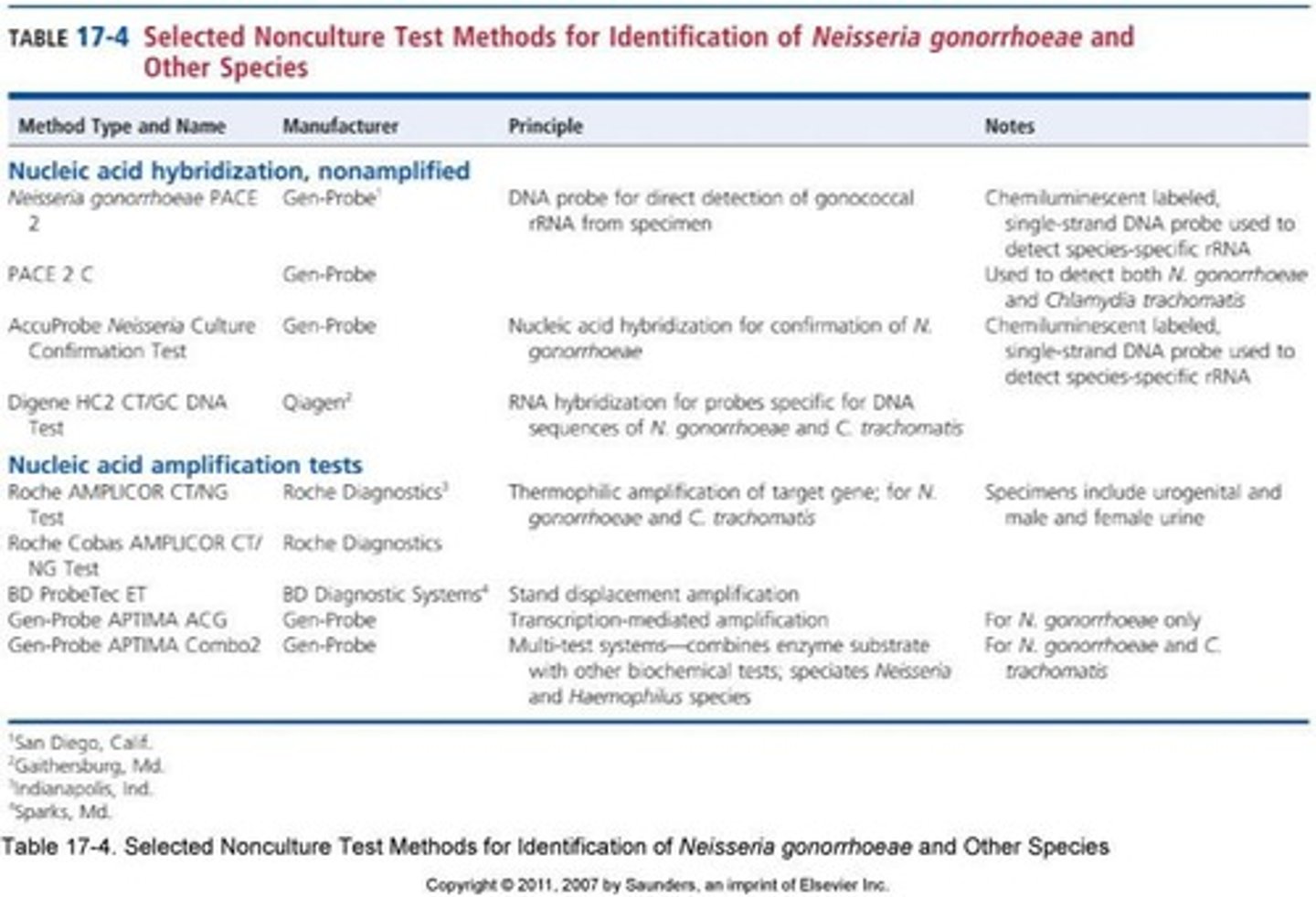
Rapid Tests
Provide results in 2-4 hours for identification.
Preformed Enzymes
Enzymes present before bacterial growth in tests.
Weak Acid Production
Issue with some N. gonorrhoeae strains.
Misidentification
Incorrectly identifying N. subflava as N. meningitidis.
Chromogenic Methods
Detect enzymes producing colored end products.
Selective Media
Inhibits nonpathogenic species to avoid false positives.
Multitest Methods
Combines enzyme tests with biochemical tests.
N. meningitidis
Ferments glucose and maltose in tests.
Coagglutination
Uses monoclonal antibodies for identifying N. gonorrhoeae.
Fluorescent Antibody Testing
Uses fluorescent tags for pathogen identification.
MALDI-TOF MS
Identifies pathogens by unique protein signatures.
Ionization Process
Vaporizes proteins for mass spectrometry analysis.
Nucleic Acid Assays
Rapid tests for detecting genetic material.
False Positives
Incorrect positive results due to contamination.
Nonamplified Probe Test
Marginally sensitive compared to cervical culture.
Low Prevalence Populations
Non-culture methods unsuitable for children or abuse cases.
Selective Gonococcal Media
Cultures specimens for accurate gonococcus identification.
Biochemical Procedures
Two different tests recommended for definitive ID.
Nucleic Acid Assays
Tests detecting DNA or RNA in samples.
Advantages
Benefits of nucleic acid assays include rapid results.
Sensitivity
Ability to detect low levels of target nucleic acids.
Urine Samples
Nucleic acid assays can utilize urine for testing.
Nonamplified Probe Test
Marginally more sensitive than cervical culture.
FDA Approval
Not approved for pharyngeal or rectal specimens.
Susceptibility Testing
Recovery of organisms for testing is not possible.
Children and Sexual Abuse Cases
Nucleic acid assays cannot be used in these cases.
False Positives
Result from laboratory cross-contamination of nucleic acids.