Week 1: Conception and Fetal Development
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
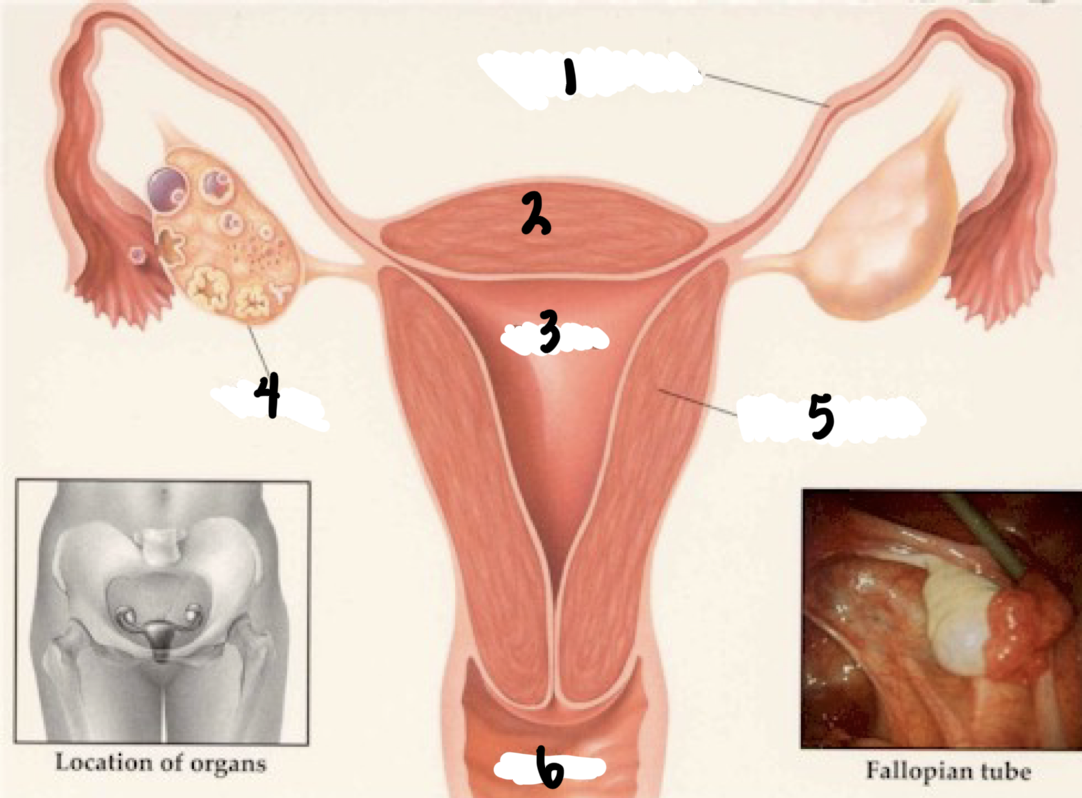
1
Fallopian tube
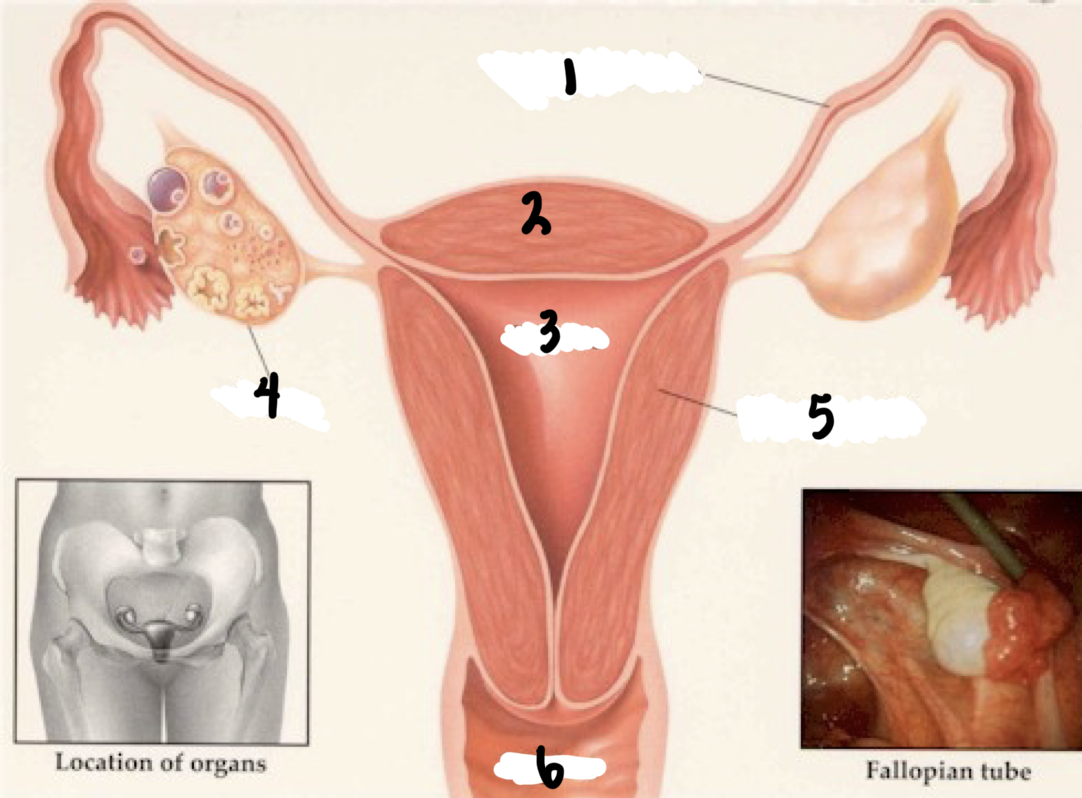
2
Fundus
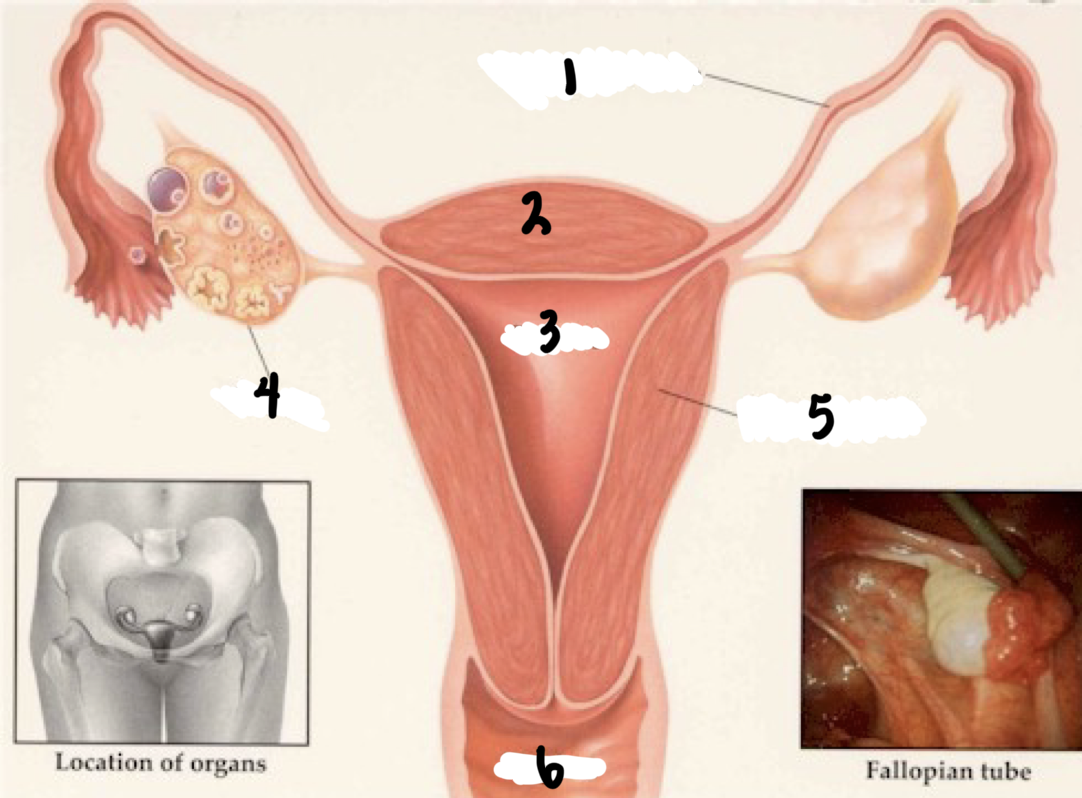
3
Uterus
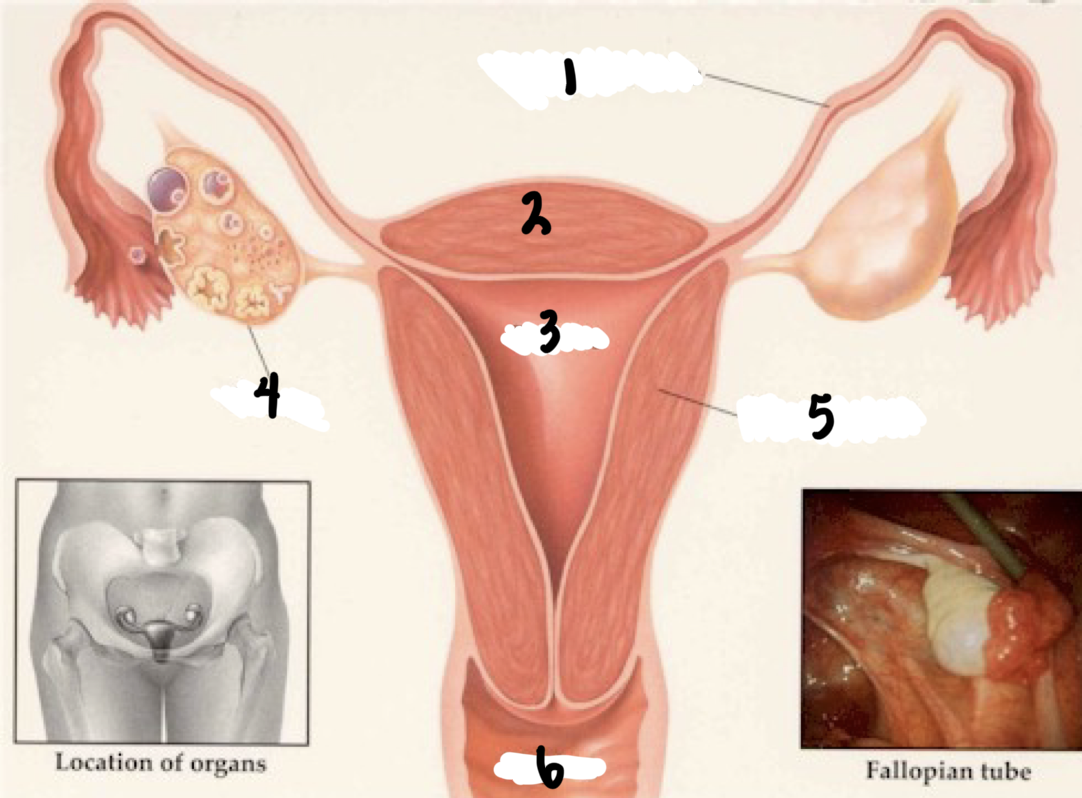
4
Ovary
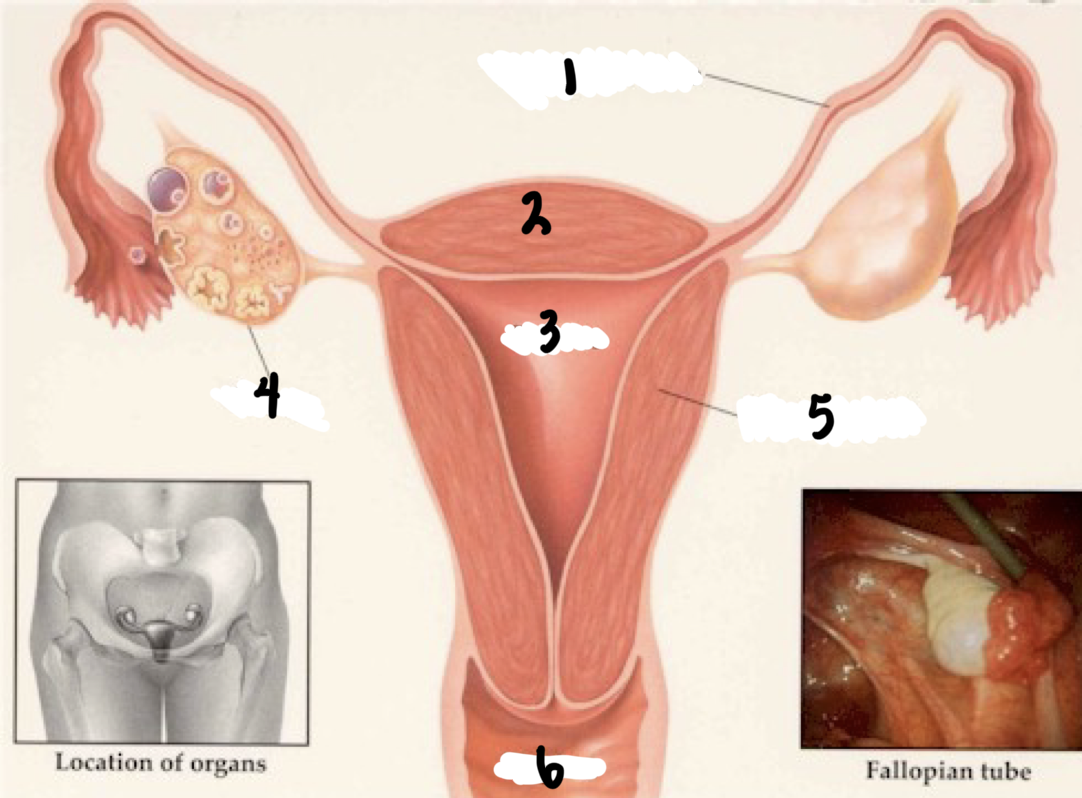
5
Uterine wall
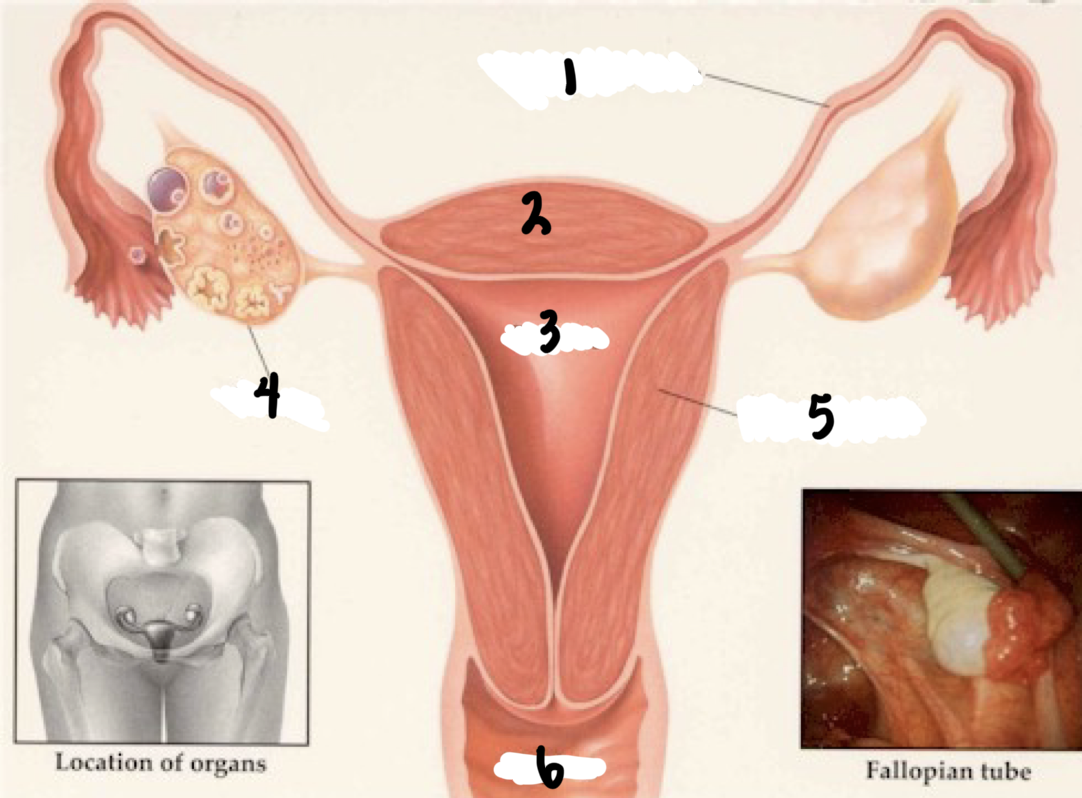
6
Vagina
Oocyte
Immature female reproductive cell
Ovum
Mature female reproductive cell
Gametogenesis—Oogenesis
the process of egg/ovum formation from an oocyte
Ovulation
Phase in the menstrual cycle where the ovary releases an ovum (egg)
one primary Oocyte matures monthly
Zygote
Ovum (egg) that is fertilized by sperm
Vaginal exam
2 fingers up cervix and examine the thickness and consistency
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
hormone produced in the hypothalamus that stimulates the the anterior pituitary gland to release luteinizing hormone (LH) and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH)
Hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland that stimulates the growth, development, and maturation of ovarian follicles that contain the egg
Luteinizing hormone (LH)
hormone produced by the anterior pituitary gland that is essential for reproduction, triggering ovulation and progesterone production in women
Progesterone
Released during menstruation and promotes thickening of the uterine lining and creating a good environment for a fertilized egg to implant
Progesterone = Pro-gestation
Order of hormone elevation during menstrual cycle
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone
Follicle-stimulating hormone
Luteinizing hormone
Progesterone
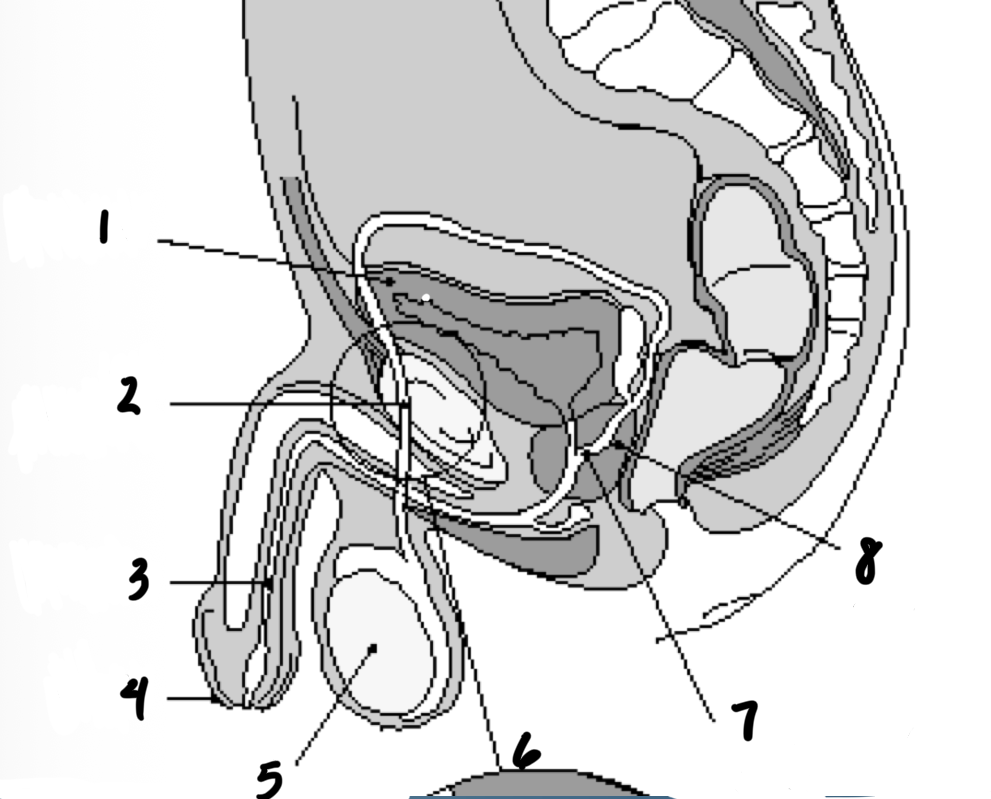
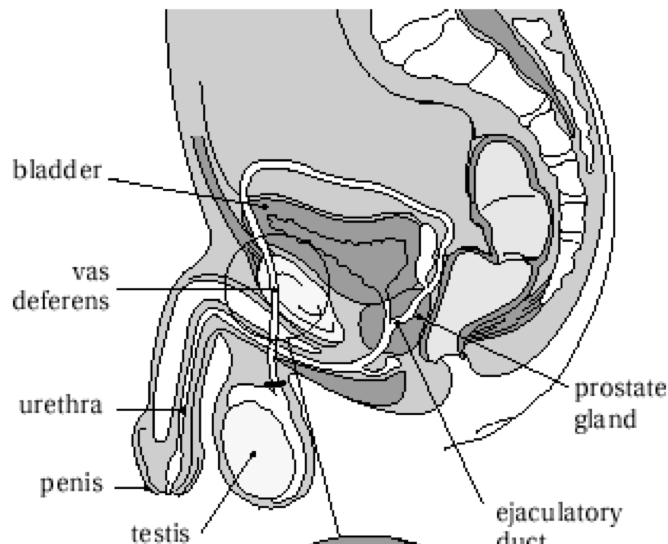
1
Bladder
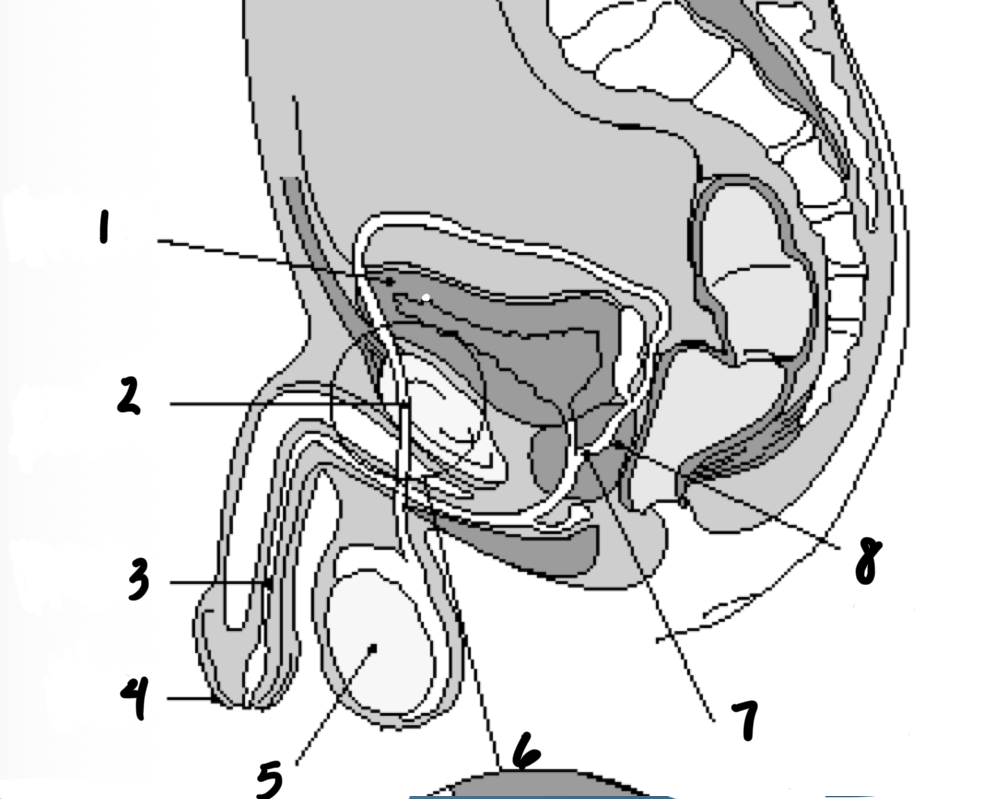
2
Vas deferens
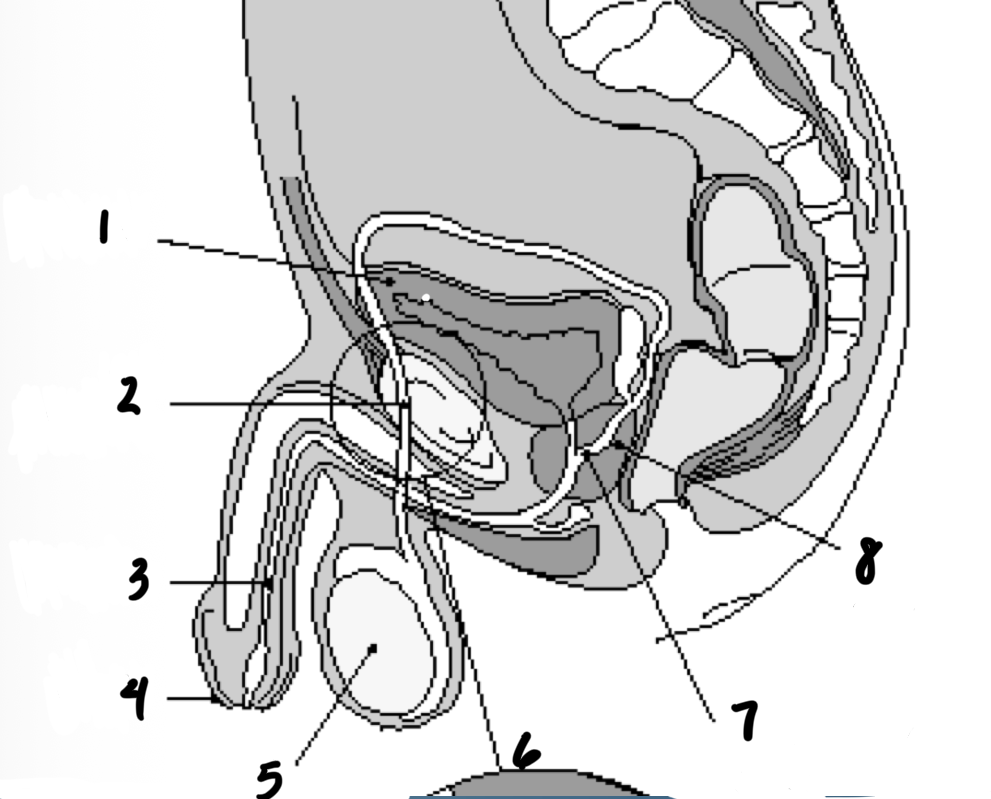
3
Urethra
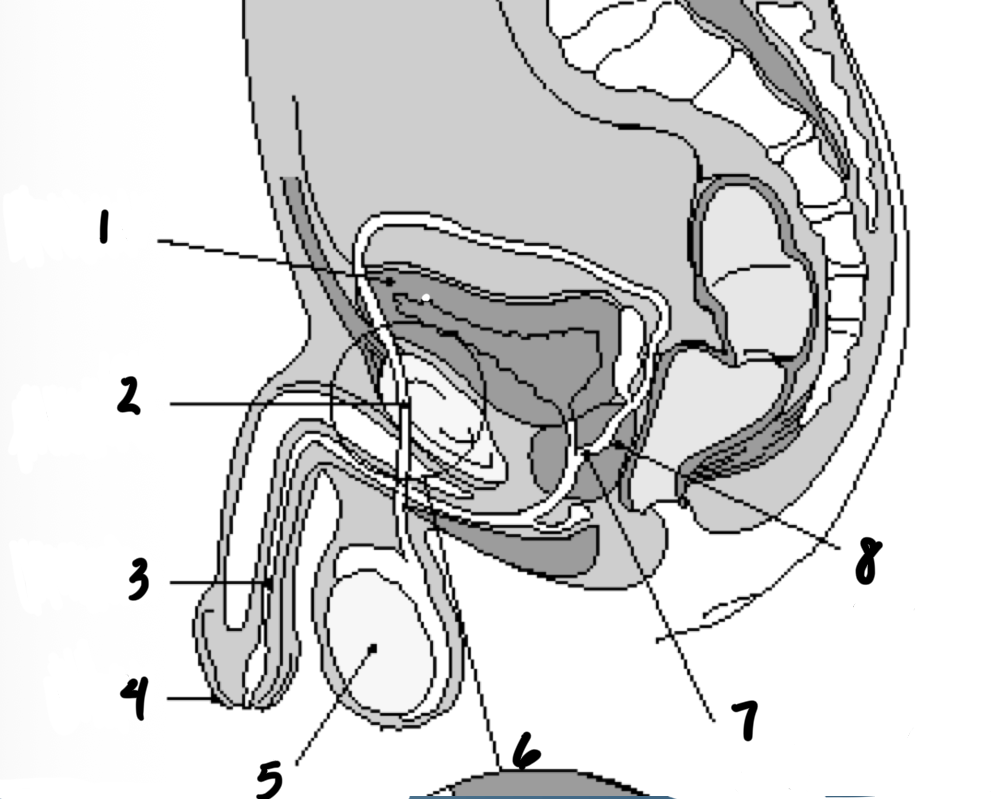
4
penis
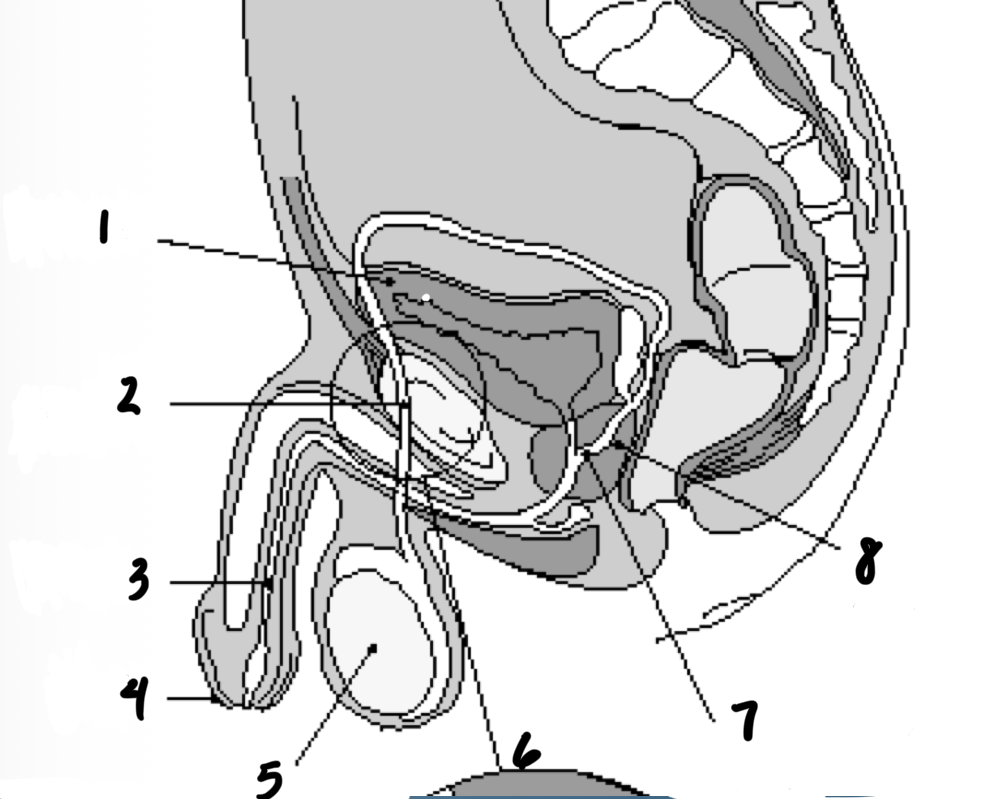
5
testes
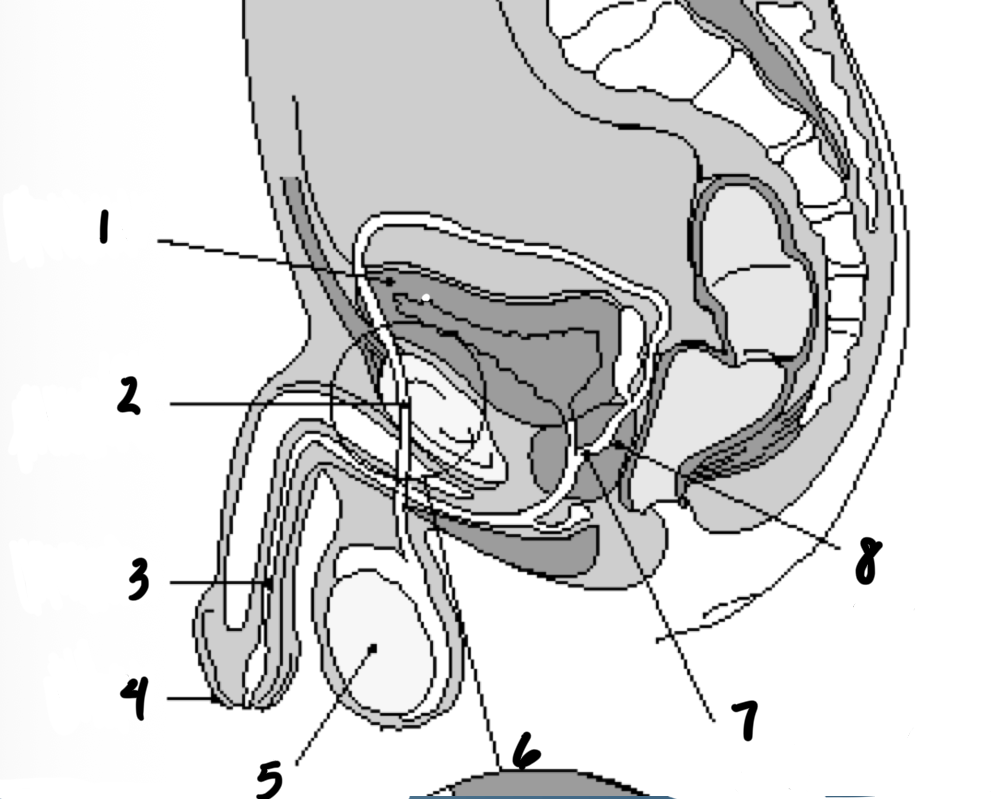
7
Ejaculatory duct
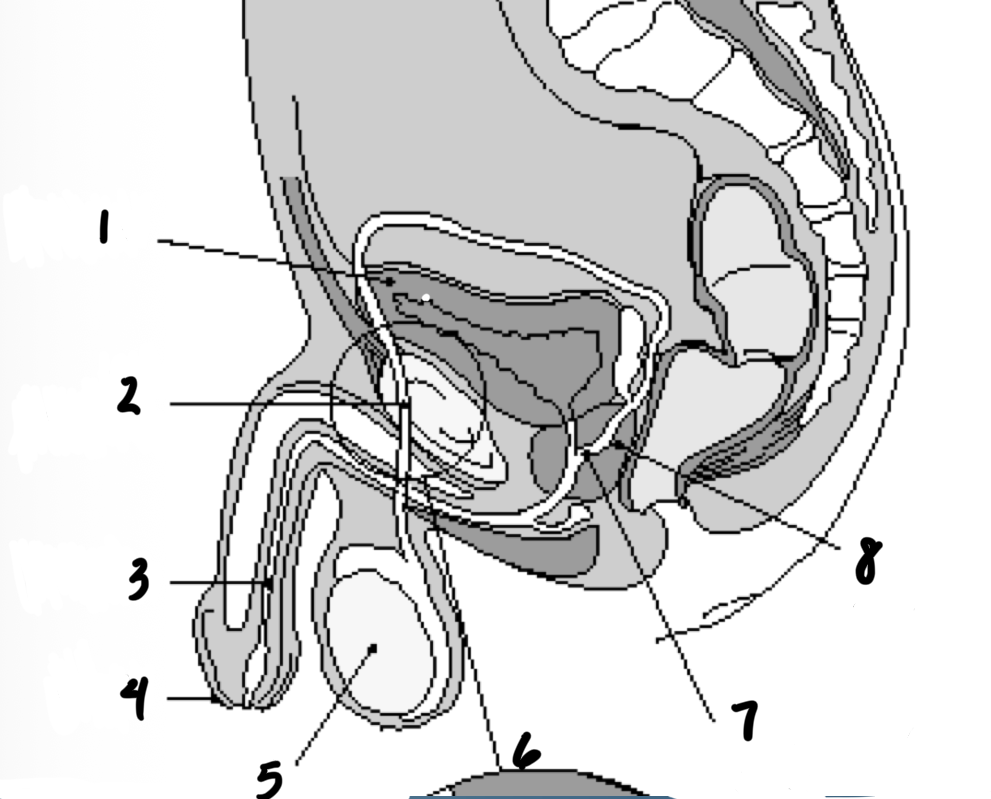
8
prostate gland
Structures in order of sperm’s path until ejaculation
Epididymis
Prostate
Testes
Urethra
Vas deferens
Seminal vesicles
3 - Testes
1 - Epididymis
5 - Vas deferents
6 - Seminal vesicles
2 - Prostate
4 - Urethra
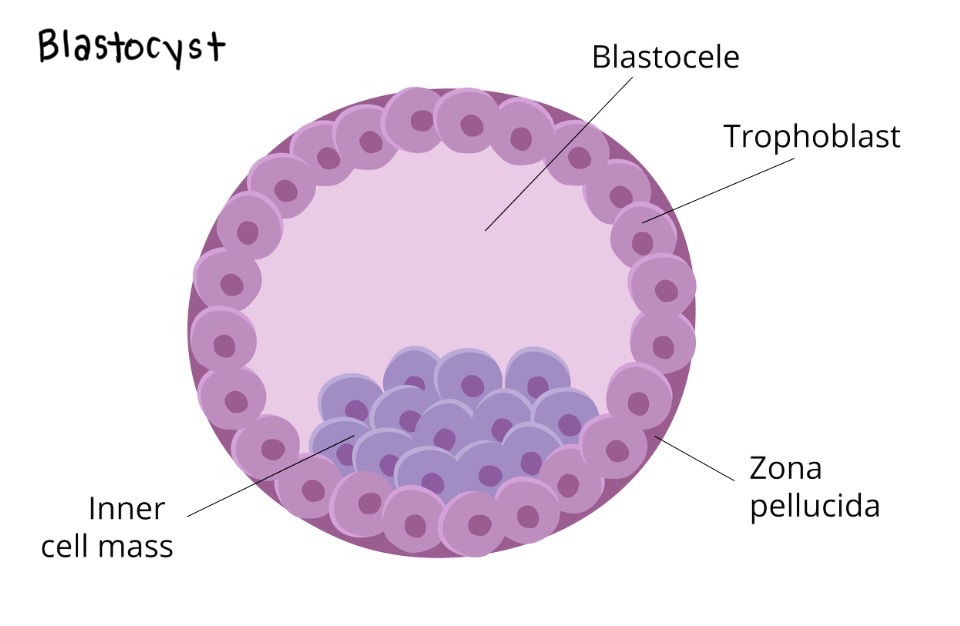
Zona pellucida
Plasma membrane around an ovum that binds to sperm and engulfs it and prevents other sperm from binding by releasing chemicals
***Travel in fallopian tube to implantation in uterus
zygote
Cleavage
Morula
Blastocyst
Zygote — fertilized egg that is in the fallopian tubes
Cleavage
Morula
Blastocyst
Morula
16-cell cluster of cells formed through cell division that occurs after the formation of a zygote through fertilization
Blastocyst
an embryo that has developed for five to seven days after fertilization that is a spherical structure with a fluid-filled cavity
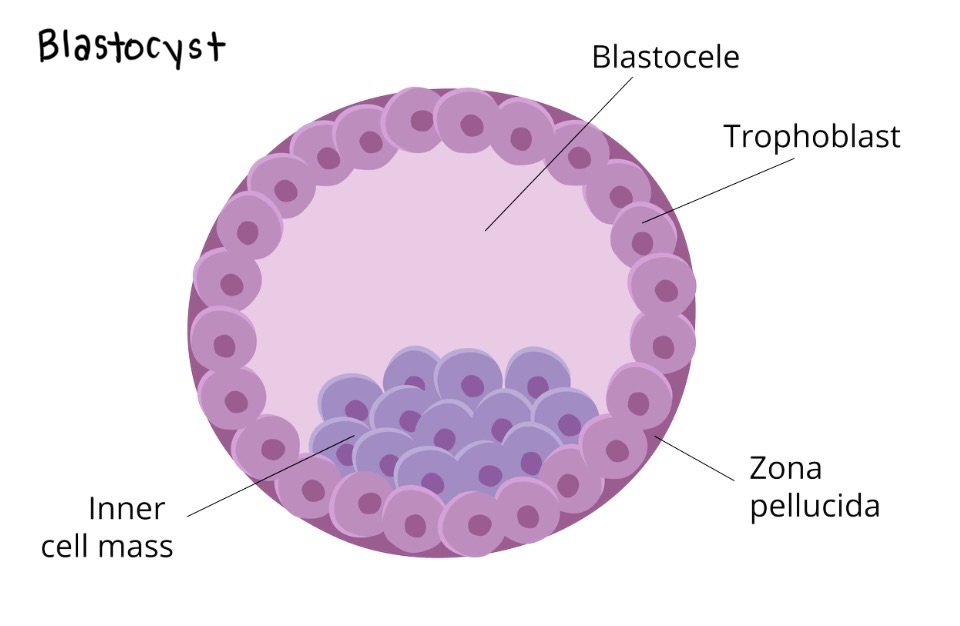
Trophoblast
blastocyst's outer layer, forming the placenta
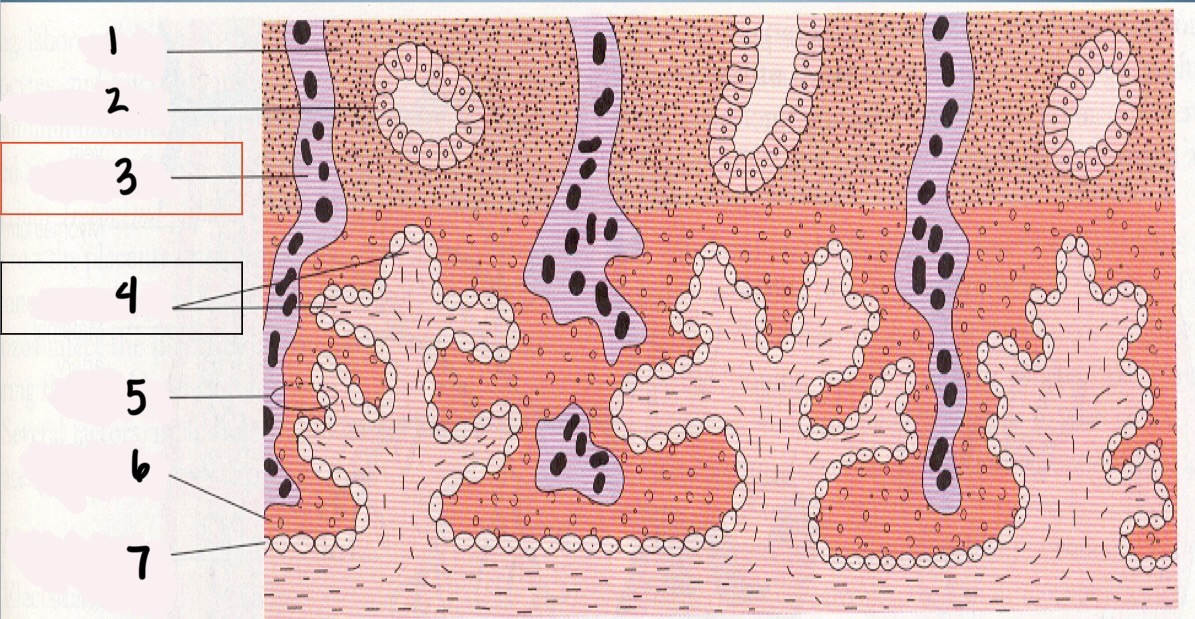
1
Decidua
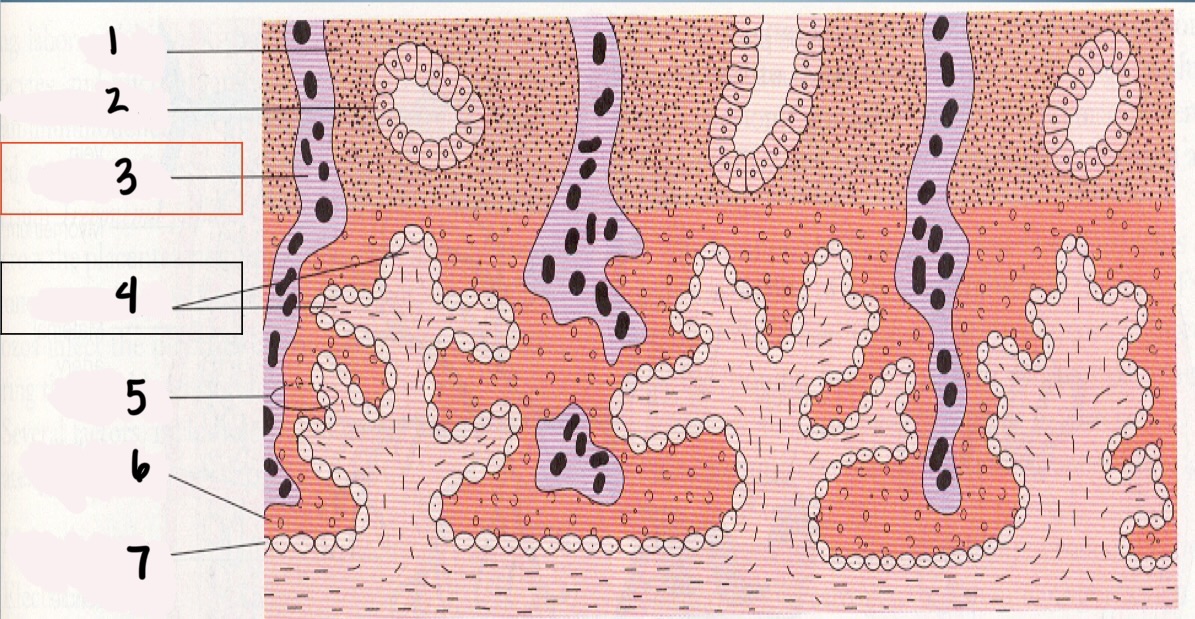
2
Endometrial gland
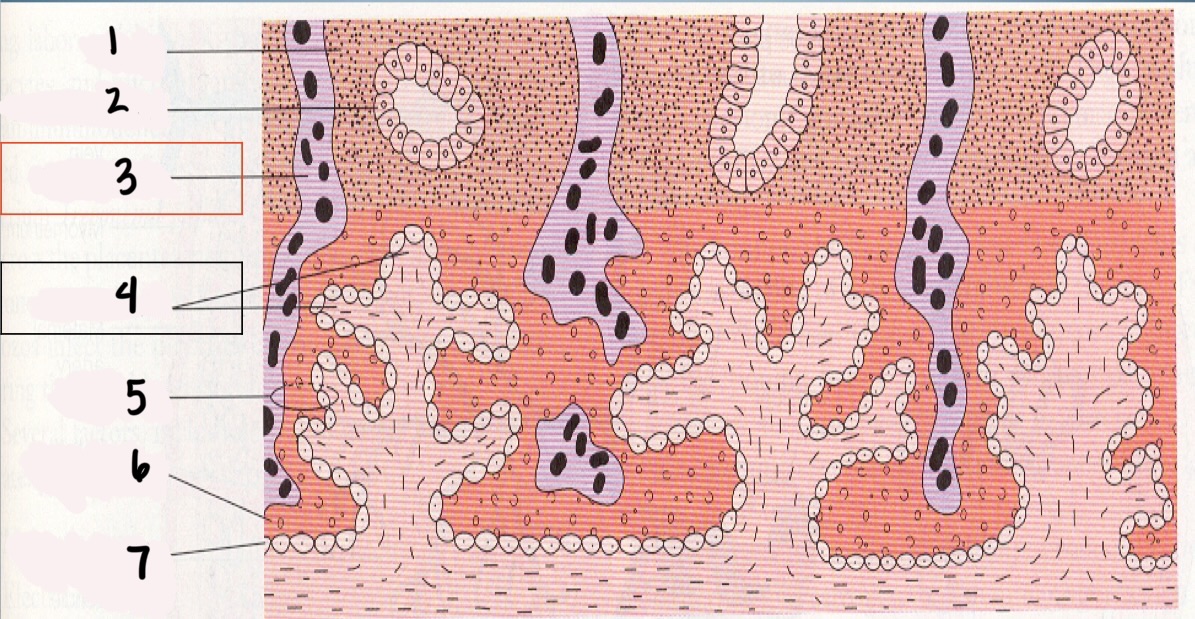
*3
Maternal vessel
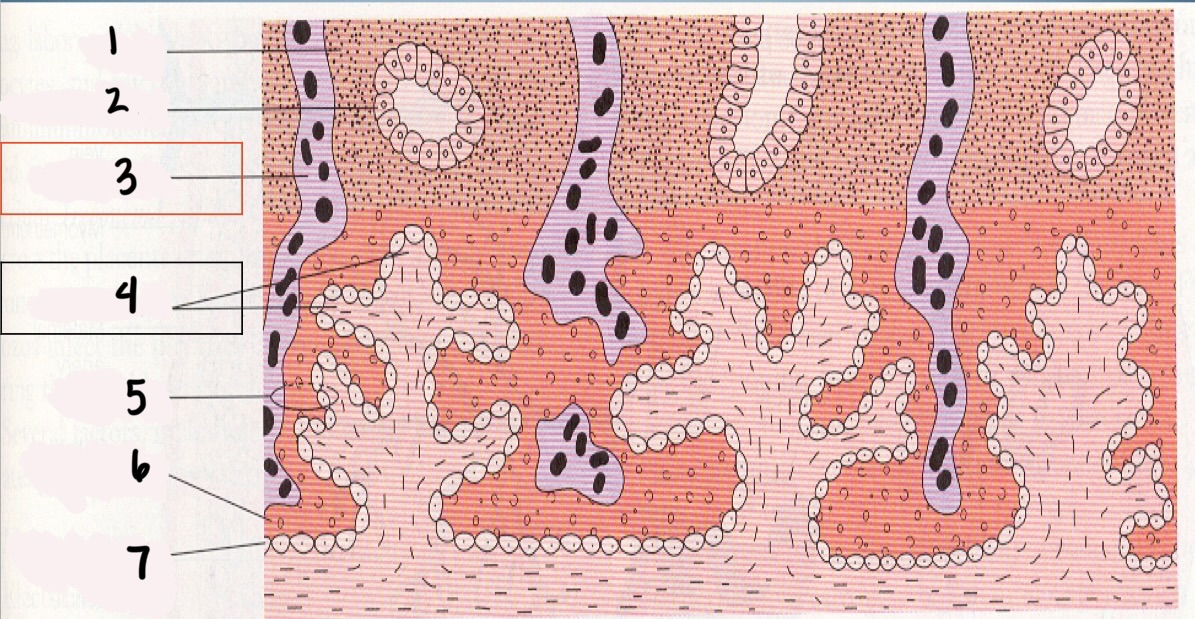
*4
Chorionic villi
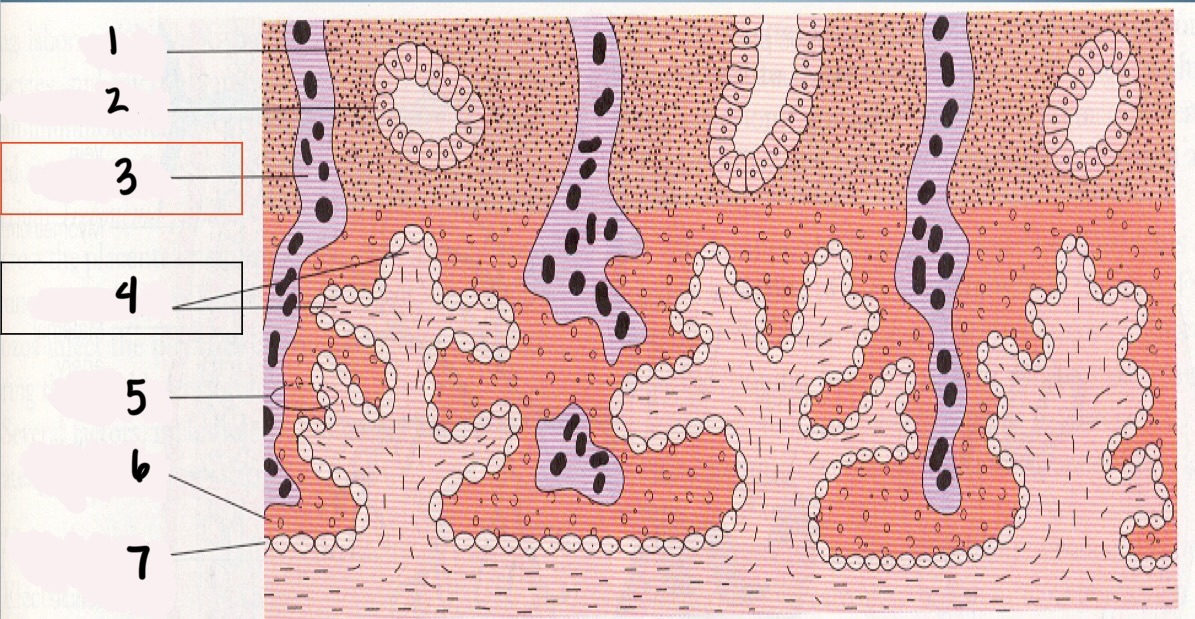
5
Trophoblast
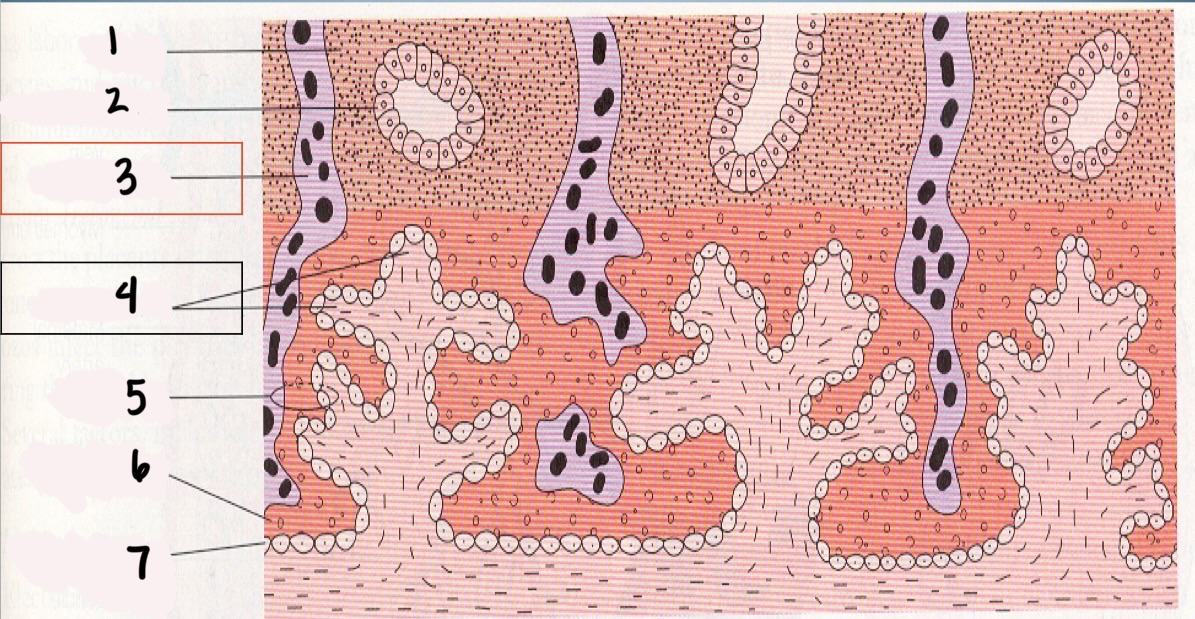
6
Syncytium layer
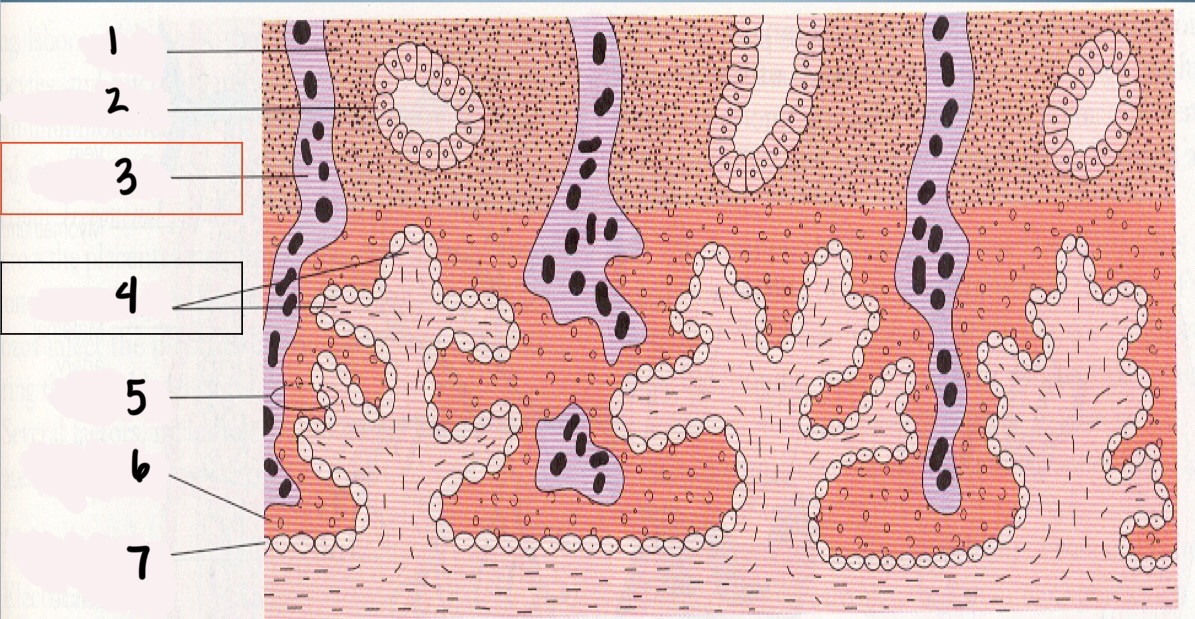
7
Cytotrophoblastic layer
Chorionic Villi (CV)
fingerlike projections that extend into the endometrium
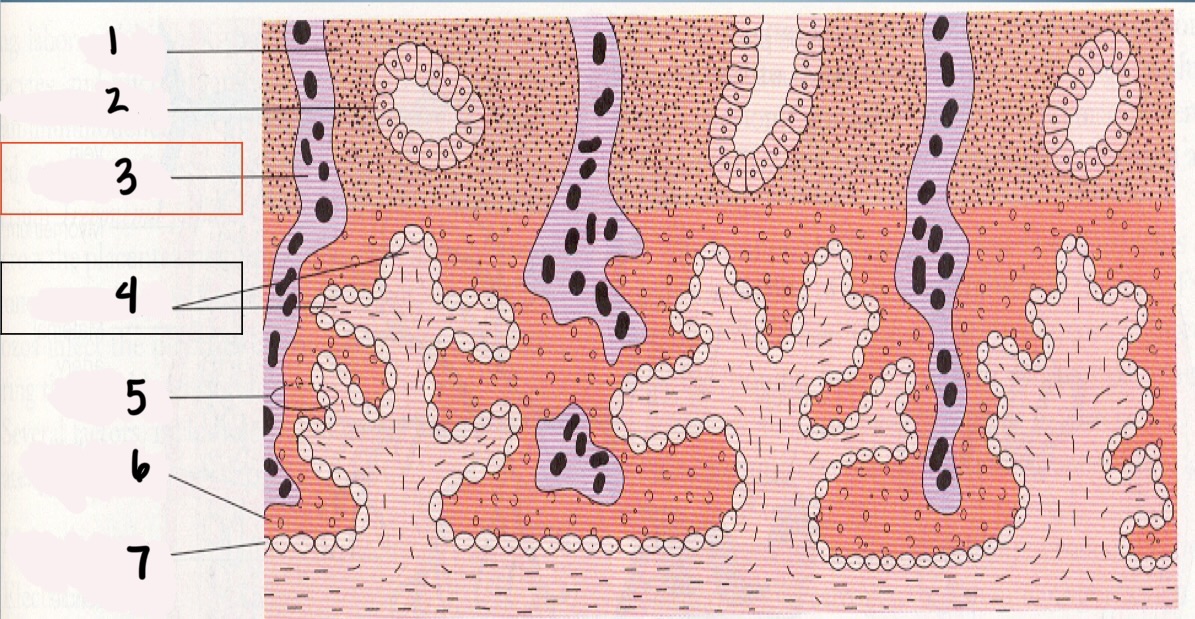
Chorionic villi functions
Obtain oxygen and nutrients from maternal blood stream
Dispose of CO2 and waste products into maternal blood stream
3 stages of fetal development
Germinal (weeks 1-2)
Embryonic (weeks 3-8)
Fetal (week 9 to birth)
When is the most important time during development of organ systems and main external features?
embryonic
by the end of the embryonic period, all organ systems and external structures are present
Teratogen
agent that acts directly on the developing fetus, causing abnormal embryonic or fetal development
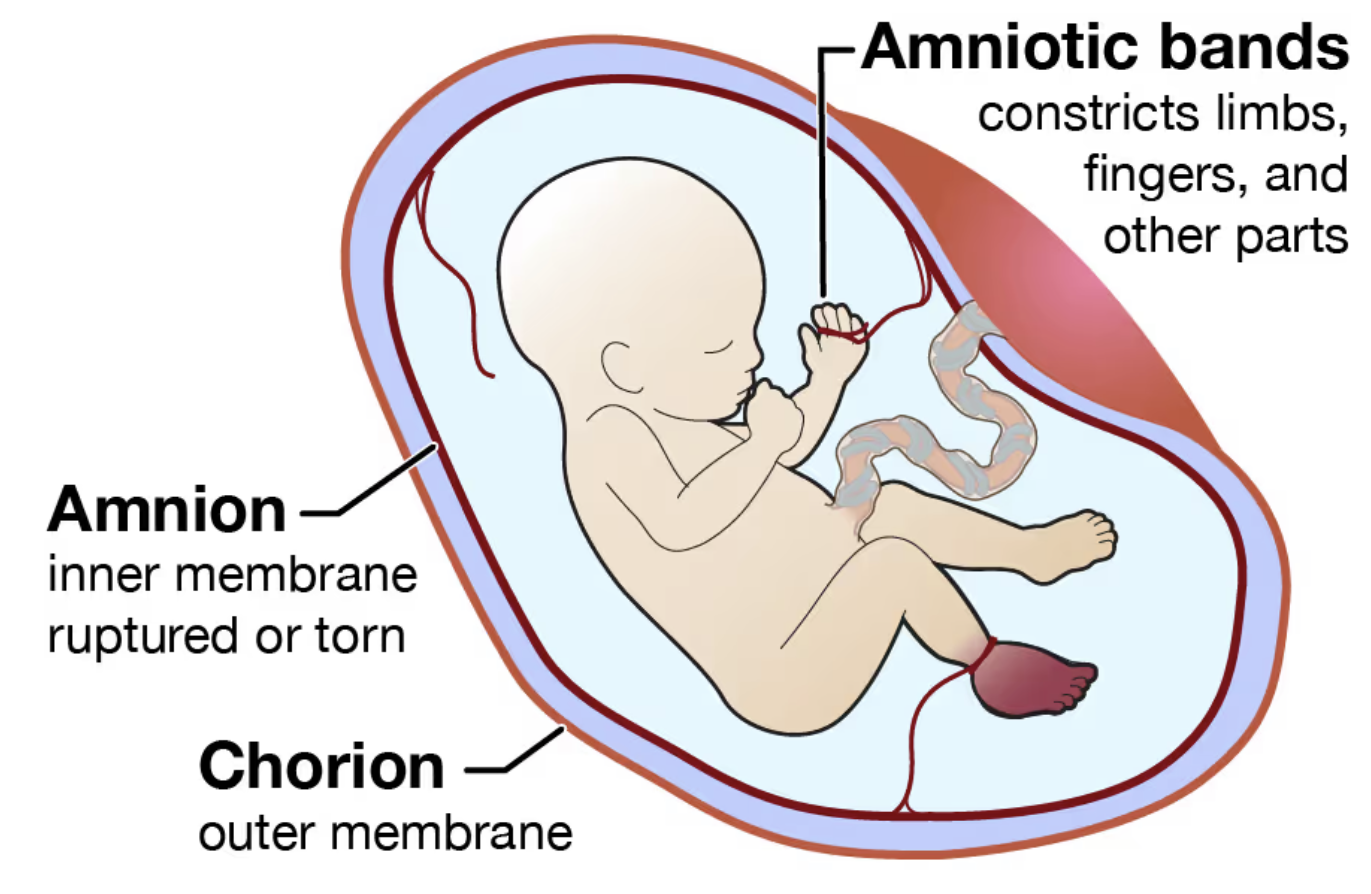
Chorion
the outer cell membrane of the fetal membrane that forms the amniotic sac
toward the uterus that develops from the trophoblast
becomes the covering of fetal side of the placenta
contains major umbilical BVs
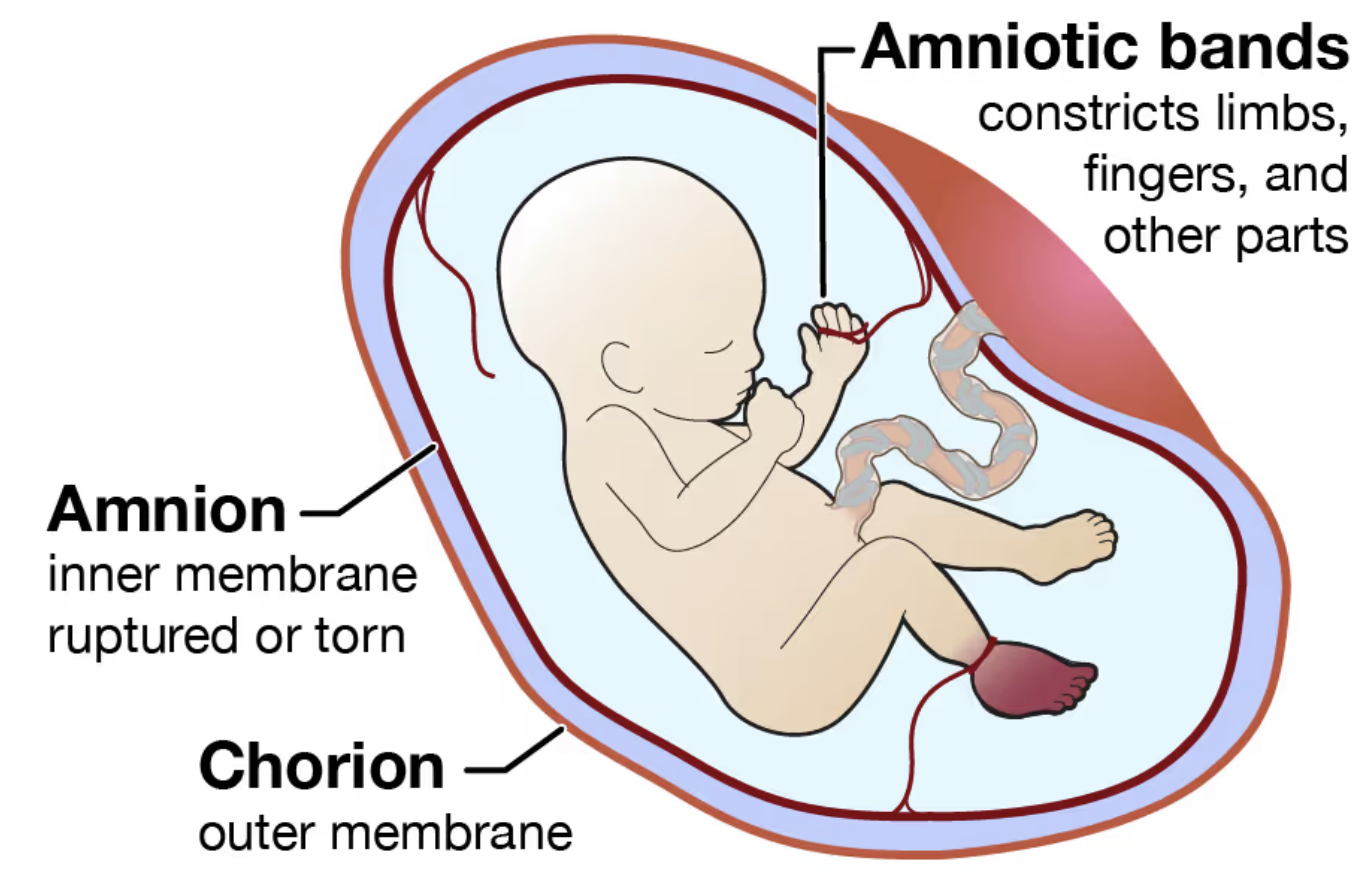
Amnion
inner cell membrane of the fetal membrane that forms the amniotic sac
develops from interior cells of the blastocyst
becomes the covering of the umbilical cord
covers chorion of the fetal surface of the placenta
Amniotic fluid functions
Maintains temp
Is a source of oral fluid
Is a repository for waste
Protects fetus from trauma
Allows for freedom of movement assisting musculoskeletal development
Placenta
Flattened circular organ in the uterus of females, nourishing and maintaining the fetus through the umbilical cord
Placenta functions
produce hormones and metabolic functions
Hormones produced by the placenta
hCG — human chorionic gonadotropin
Human placental lactogen
Progesterone
Estriol (estrogen)
Metabolic functions of the placenta
Respiration
Nutrition
Excretion
Storage
Progesterone function in placenta
helps keep uterine smooth muscle loose to prevent contractions and miscarriage
Estrogen function in placenta
Promotes uterine growth
Increases BF to uterus — BV dialation
Supports fetal organ development
Placental angiogenesis
Viability
ability of the fetus to survive outside the uterus
legally viable is when the baby is born < 20 weeks and < 500 g
Umbilical cord
2 arteries deliver deoxygenated blood to placenta
Single vein returns oxygenated blood to fetus
Why are there holes in fetal hearts?
To increase BF and O2 to the brain
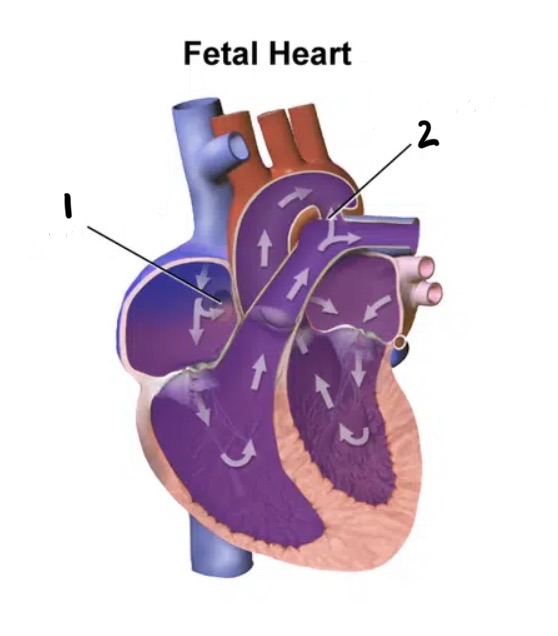
Holes in the fetal heart
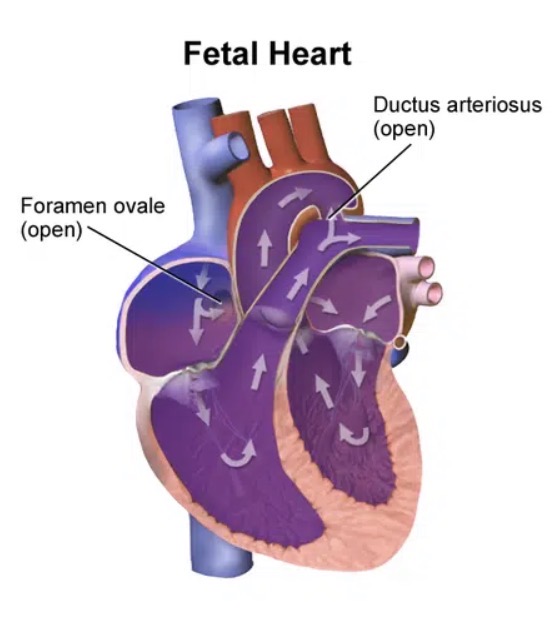
The liver is bypassed by the _____ _____
ductus venosus
Ductus venosus
a shunt that allows oxygenated blood in the umbilical vein to bypass the liver and is essential for normal fetal circulation
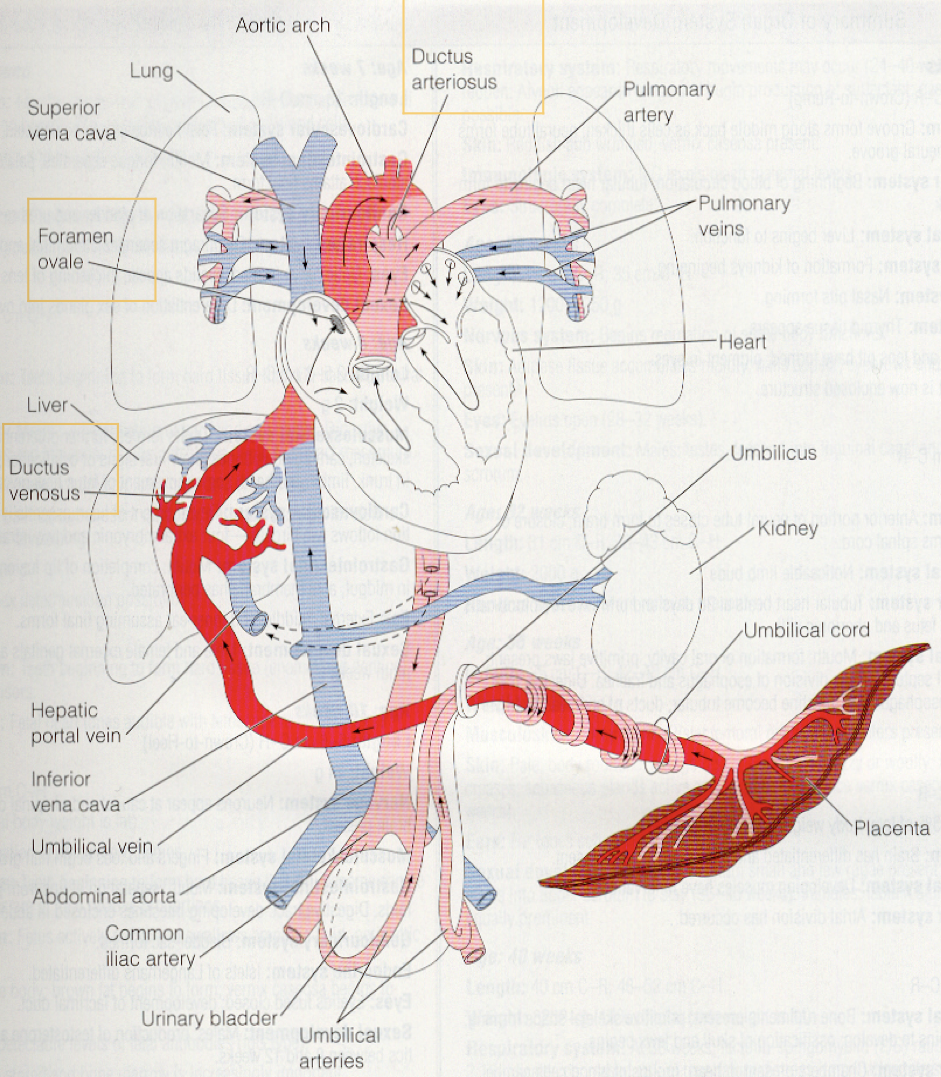
The lungs are bypassed by the ____ ____ and ____ ____
foramen ovale and ductus arteriosus holes in the heart
Hematopoietic system
Process of blood cell development in fetus that begins in liver in 6th week
Pulmonary surfactants
Lecithin (L)
Sphingomycin (S)
Lecithin surfactant
most critical surfactant required for postnatal lung expansion
Proper Lecithin (L)/Sphingomyelin (S) (L/S) ratio
2:1 is considered mature
about 35 weeks gestation
How can L/S be tested?
testing amniotic fluid
Hepatic system
Renal system
Neurological system
Endocrine system
Reproductive system
Musculoskeletal system
Integumentary system
Immunologic system