MATE EXAM 3
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
Hydrogen bonding
adds/shares on electron with another to fill its shell; sigma bond
hydrogen molecule
rotational motion about bond and axis - s orbitals
Carbon-Carbon bonding
pi - p orbitals; no coincident with axis and no rotational motion
sigma - 2s² and 2p²; shares valence electrons to form an octet
polymer bonding
molecular solids with major bond rotational motion as long as there are no pi bonds

polyethylene (PE)
homopolymer with only C backbone and H
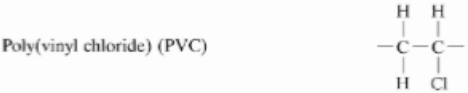
Poly(vinyl chloride) (PVC)
homopolymer with Cl

Polypropylene (PP)
homopolymer - with CH3

Polytetrafluorothylene (PTFE)
copolymer - includes F

Polystyrene (PS)
copolymer including a nylon
molecular chemistry
no single rule; logic required
Molecular shape
based on molecular weight, degree of polymerization, and physical length
molecular size
physical outline - influences rotation and chain flexibility
less flexible = higher modulus = stiffer polymer
molecular structure
mer unit arrangment:
linear = single chain (PE, PVC, PS, nylon)
branched: side chains off main
cross-linked: linear joined by covalent bonds
networked: 3D networks (PE, PTFE, epoxies)
thermoplastic polymer
soft when heated, hard when cooled
linear or branched
bonding diminished, movement between chains increases
thermosetting polymers
permanently hard when cross-linked/networked
no melting, held by primary bonds, disintegrate/burn
chain folded model
platelets/lamellar/interwoven chains folding in on themselves
spherulites
bulk polymers crystallized from melt; semi-crystalline
ductile and brittle polymers
weaker and softer - time/temp sensitive
ductile/brittles effected by
strength of inter-molecular secondary bonding
ease of rotational motion
ductile/brittles behaviors
elastic primary bond stretching <1%
elastic chain reorientation »1%
plastic primary bond breakage ~1%
plastic chain slippage »1%
brittle
little to no chain slippage:
bond stretch
bond break
ducrtile
some chain mobility:
elastic primary bond stretch & chain reorientation
plastic primary breakage & chain slippagesome chain mobility: allows deformation before fracture, characterized by both elastic and plastic responses.
viscoelasticity
applied stress in instantaneous elastic strain followed by viscous
viscoelasticity behaviors
brittle at low temps
viscous at high temps
Creep
time-dependent strain
stress relax
time-dependent stress
FIllers
sand, glass, clay:
improve tensile/compressive strengths, abrasion resistance & toughness
plasticizers
small molecules occupying positions between polymer chains to increase distance between chains/decrease interactiosn
increase flexibility and ductilitysta
stabilizers
prevent degradation/burning
UV absorbers enhance UV resistance
Thermoplastics
formed above Tg; recyclable, flash reusedt
thermosetting polymers
prepare linear polymer, curing/hardening of crosslinking
not recyclable
molding
injection: 1+ molds
extrusions: constant cross-sections through die
blow
casting
spinning
fabrication of fibers: molten/solution state pumped through spinnert with small holes, rapidly solidifes
films
makes sheets, bags, films, molten extrusion molding through die and calendaring
natural composites
bone: tough protein/collagen particles of brittle mineral
artificial composites
concrete: aggregate particles mixed into cement
particle matrix phase
continuous, surrounding dispersion phase
disperesed phase
discontinuous, imbedded din matrix
large composies
particles increase the modulus over matrix
A composite found in high-performance applications
lower modulus material is the glue
fiber composite structure
high strength polymers used in composites/textile threads
natural fiber
wood:flexible cellulose fibers held by stiff lignin
artifical fiber composite
fiber-glass: glass fibers mixed into polyester
fiber composite structures
Ef>Em
Lf>Lc
fiber composite behaviors
large particle L<Lc
discontinuous L<15 Lc
continuous L> 15 Lc
general tensile fiber composite
1) fiber and matrix deform elastically
2) matrix yields plastically but fiber continuous elastically3) ultimate tensile strength is determined by the fiber's strength and the fiber-matrix bond quality.
fiber composite longitudinal failure
fiber failure → matrix failure → composite failure
electrochemical corrosion
anode loses ions + oxidizes
cathode gains electrons + reduces
rate-controlling variables
temp: higher = faster rxn
conc: higher=faster
viscosity: faster=further corrosion
galvanic corrosion
basic
two dissimilar metals
crevice corrosion
concentration difference of oxygen
erosion corrosion
combined chemical + mechanical abrasion
stress corrosion
stressed material corrodes by forming cracks
thermal expansion
solid materials expand with heat, contract with cooling
caused by assymetry of potential energy curve
metal heats = decreased density
thermal stress
material unable to undergo expansion/contraction from temp; internal stress develops
conductivity
heat transported from high to loe temps
must have free elctrons
resistivity
property limiting current in a material; length and cross-sectional area relation
electronic band rules
No two electrons in closed system with same energy state OR only two have the same energy
Image shelves on shelves or highway analogy
Last band = valence; first empty band = conduction
Band gap energy E(g) in insulators & conductors is associated with bond strength
electronic bands of metals
In metals electrons conduct in valence band
electronic bands in semiconductors/insulators
In semiconductors/insulators, electrons conduct in conduction band
In semiconductors/insulators, electrons must be promoted from valence band to conduction band to conduct
In semiconductors/insulators, valence band is full
recombination
excited electrons losing energy and dropping back to empty state
thermal vibration
move off perfect equilibrium sites, constantly scattering, always thermal vibrations
conduction in metals
large electron concentrations in partially full band - easy excitation
affected by purity of alloys and temperature
conduction in semiconductors
Orbitals become bands,
Completely full valence band
Conduction band is completely empty
Elemental/compound materials have better covalent bonds – Silicon
intrinsic
electrons concentration equal to hole concentration
extrinsic
derived from impurities/dopants
donor: 1+
acceptors: 1-
n-type extrinsic
small dopant
p-type extrinsic
large dopant