Unit 5: Heredity
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Meiosis
cell division that reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in four genetically diverse gametes.
→ Sexual Reproduction
→ happens in 2 stages goes from 46 chromosomes to 23
→ ends up with 4 genetically unique haploid cells with HALF of the genetic info, getting the other half from the other parent during fertilization
Crossing over
exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes
→ occurs in prophase I of meiosis and increases genetic variation in gametes.
The law of independent assortment
Alleles on different genes will sort into gametes independently of one another during meiosis
→ This means that the inheritance of one trait will not affect the inheritance of another trait. It is one of the principles that explains genetic variation.
Allele
A form of a gene:
→ Blue eyes is an allele // Eye color is the gene
Gene
The basic unit of heredity that carries genetic information and determines traits in organisms.
Law of Segregation
The principle stating that during gamete formation, the two alleles for a trait separate, ensuring that offspring receive one allele from each parent. This explains how traits are passed down through generations.
Anaphase I
Separates Homologous Pairs
Anaphase II
Separates sister chromatids
Mitosis Functions
Growth and repair
Asexual Reproduction
creates 2 identical daughter diploid cells
only goes through one round of PMAT
separation of sister chromatids is the ONLY form of genetic variation
Meiosis Functions
makes gametes for sexual reproduction
4 Genetically unique haploid cells
two rounds of PMAT
independent assortment in metaphase I
crossing over in prophase I
separation of homologous pairs in anaphase I
separation of sister chromatids in anaphase II
Haploid
A cell that contains one complete set of chromosomes, typically half the number found in diploid cells - Meiosis
Diploid
A cell that contains two complete sets of chromosomes, one from each parent, typically found in somatic cells - Mitosis
Incomplete dominance
Neither Allele is demonstrated physically, instead a mix between the two of them resulting in a phenotype that is a blend of the parents' traits
→ Ex: red and white flowers producing pink flowers
Co-Dominance
Scenario where both alleles are expressed and neither is dominant
→ Ex) AB blood type in humans
Phenotypic Plasticity
Ability in organisms to change phenotype depending on environmental conditions without altering genotype
Genotype
Probability of an organisms allele combo
Phenotype
Likelihood of inheriting and expressing characteristics based on genotype and environment
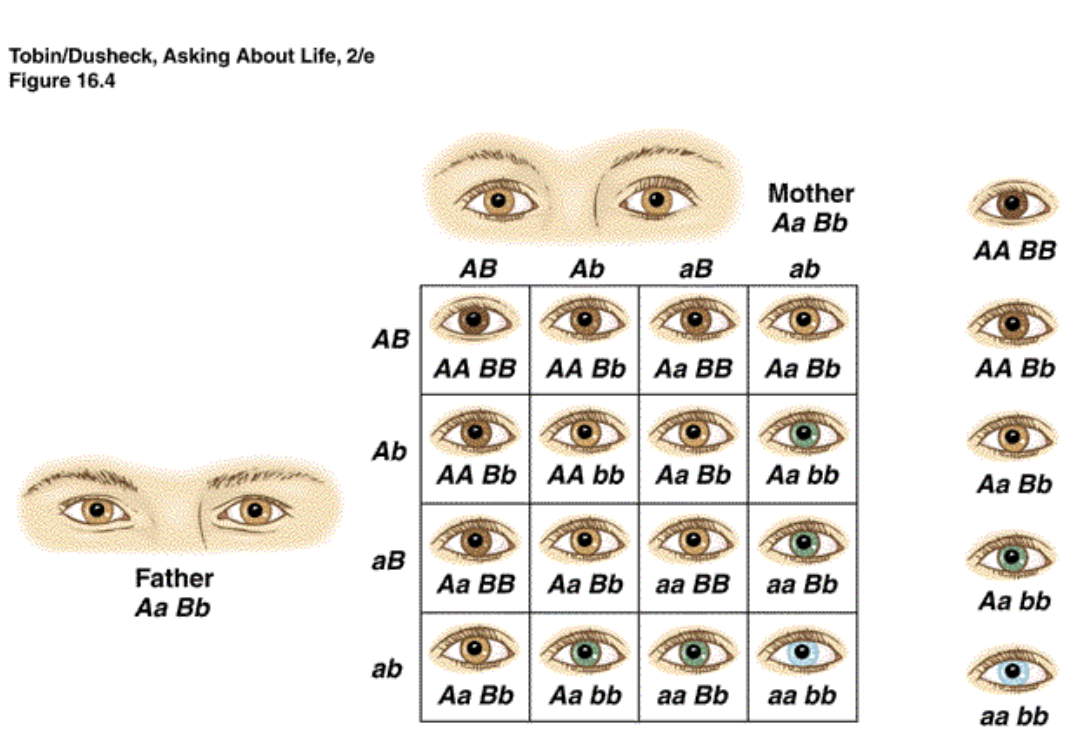
Di Hybrid crosses
if both parents are heterozygous, answer is most likely in the 9:3:3:1 ratio given by filling out crosses
→2N explains the heterozygous amounts in the equation
Ex): 22=4 meaning there will be 4 possible genotypic and phenotypic expressions ( AaBb x AaBb)
A- Brown hair // a- Blonde hair // B- Brown eyes // b- blue eyes
If 2 parents are both AaBb the possible expressions will be
AB- 9
Ab- 3
aB- 3
ab- 1
Autosomal Chromosomes
Chromosomes that are not Sex chromosomes and are involved in determining most of an individual's traits and characteristics
Sex-Linked
Traits associated with either the X and Y chromosomes that are inherited differently based on the sex of the individual, often showing different expression patterns in males and females.