Test: We the People - Unit 2
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Test over lessons 7 through 10 in "We the People."
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Great Compromise
An agreement reached during the Constitutional Convention that established a two-house legislature, balancing the interests of both large and small states by creating the House of Representatives and the Senate.

Senate
The upper house of the U.S. Congress, consisting of two representatives from each state.

House of Representatives
The lower house of the U.S. Congress, consisting of representatives based on state population.

Abolish
To formally put an end to something.

Slave Trade
The buying and selling of humans for forced labor, primarily associated with the buying of people in Africa and selling them to landowners in the American South.
Three-fifths Clause
A constitutional provision that counted each enslaved person as three-fifths of a person for representation and taxation purposes.

The American Civil War
A conflict between Northern states and Southern states from 1861 to 1865, primarily over issues of slavery and states' rights. It resulted in the preservation of the Union between North and South as well as the abolition of slavery.

Fair
Impartial and just, without favoritism or discrimination.

Equal
Being the same in quantity, size, degree, or value.

Constitutional Convention
Another name for the Philadelphia Convention given by modern-day historians. It was the gathering of delegates in 1787 to draft the Constitution of the United States.

Interests
A specified common concern of a person or group of people.

Federal
In the United States, relating to the national government.

Preamble
The introductory statement of the Constitution that outlines its purposes and guiding principles.

Articles of the Constitution
The sections of the Constitution that detail the framework of government, including the legislative, executive, and judicial branches.

Constitutional Amendments
Changes or additions to the U.S. Constitution that modify its original text or laws.

Bill of Rights
The first ten amendments to the U.S. Constitution, which guarantee individual liberties and protect citizens from tyranny.

Roger Sherman
Founder and architect of the Great Compromise, which helped shape the legislative branch of the U.S. government.

George Washington
1st President of the United States and commander-in-chief of the Continental Army during the American Revolution.

Taxes
Required payments to a government.

Tyranny
Cruel and oppressive government rule.

Slave
A person who is the legal property of another person and is forced to obey them against their will.

Natural Rights
The idea that all humans are born with rights, which include the right to life, liberty, and property.

Consent to be Governed
The idea that government derives its authority from the people it governs.

Social Contract
An agreement between the people and their government signifying their consent to be governed.

Direct Democracy
A form of government in which citizens rule directly and participate in all aspects of government.

Representative Democracy
A system of government in which citizens elect representatives to make decisions and laws for all people.

Constitution
A set of rules and laws that explain how a government is organized and how it will run.

Limit
A point beyond which something cannot go.

Shay’s Rebellion
An armed protest in November 1786 by more than 1000 angry farmers against the state of Massachusetts. It showed the weakness of the Articles of Confederation.

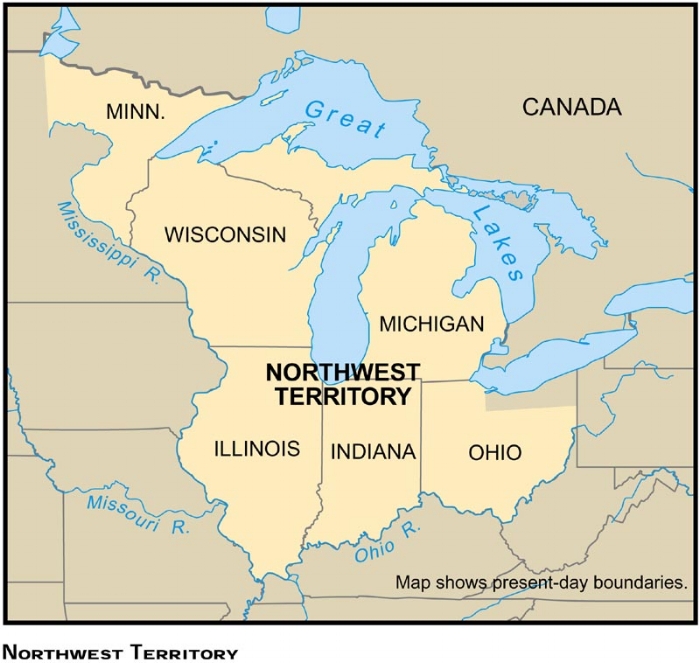
Northwest Ordinance of 1787
A plan for adding new states to the United States. Allowed people in the Northwest Territories to organize their own governments.
Philadelphia Convention
A meeting in 1787 where delegates from twelve U.S. states convened to address the problems of the Articles of Confederation, ultimately leading to the drafting of the U.S. Constitution.

James Madison
A key Framer and the fourth President of the United States, known as the "Father of the Constitution" for his role in drafting the U.S. Constitution and the Bill of Rights.

Benjamin Franklin
An influential Founder, Framer, inventor, and diplomat. Key in securing French support during the American Revolutionary War and a signer of the Declaration of Independence.

Articles of Confederation
The first plan for government in the United States. Set up a loose union of states with equal powers and a weak national government.

Confederation
A union of sovereign statesthat work together for common goals while maintaining their independence.

Delegate
An individual chosen or elected to represent a group at a convention or conference.
Framer
A delegate involved in drafting the Constitution of the United States at the Philadelphia Convention.

Inalienable
Something, like a person’s natural rights, that cannot be taken away or removed.

Congress
The legislative body of the United States government, consisting of two chambers: the Senate and the House of Representatives.

Revolutionary War
A conflict from 1775 to 1783 in which the Thirteen Colonies fought for independence from British rule.
