DF6: Alkenes- versatile compounds
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
What is an alkene?
unsaturated hydrocarbon
How are alkenes named?
1. Identify the longest chain and use the appropriate prefix to indicate the number of carbon atoms.
2. Follow the prefix with 'ene' to indicate the compound is an alkene.
3. For alkenes with longer chains or branched chains, indicate the position of the double bond using the lowest number possible.
4. For cyclic alkenes, use the prefix cyclo- (e.g., cyclohexene).
What is the general formula of alkenes?
CnH2n
what are electrophiles?
positive ion or molecule with partial positive charge that is attracted to a negatively charged region and will react by accepting a lone pair of electrons to form a covalent bond
What is electrophilic addition?
reaction where an electrophile reacts with an alkene's electron-rich double bond to form a single larger molecule
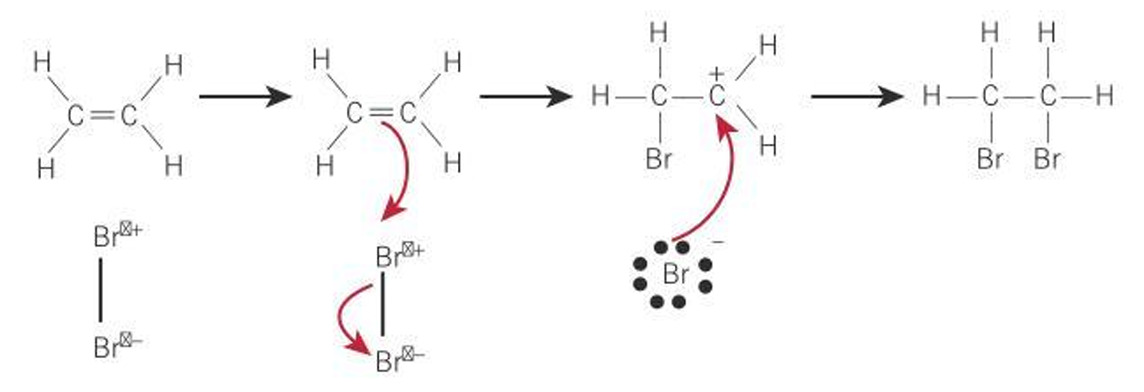
Describe the reaction of ethene with bromine.
Bromine becomes polarised as electrons are repelled by double bond
Bromine atom nearest double bond becomes slightly positive, the other slightly negative
Positive bromine atom behaves as an electrophile and reacts with alkene double bond.
One of the carbons becomes a carbocation
A pair of electrons moves from the negative bromine atom and forms a covalent bond
How many pi/sigma bonds in a single bond?
1 sigma bond
sigma bonds form in
an area of increased electron density
How are sigma bonds formed?
overlap of s orbitals
What kind of bonds in a double bond?
one sigma
one pi
one pi bond consists of ___ areas of negative charge
one ______ one _________
2
above
below
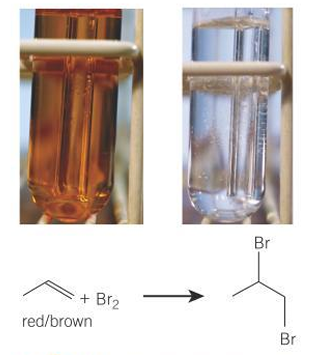
How can you identify an alkene?
brown bromine water becomes colourless
Electrophilic addition of Br2 to alkene
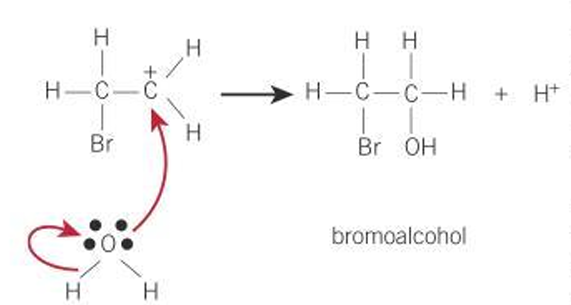
Formation of a bromo-alcohol
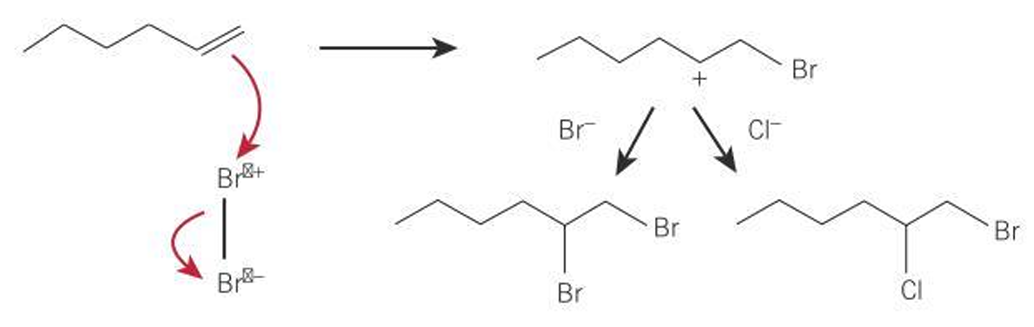
Conditions for reaction of alkene with hydrogen bromide
room temperature
polar solvent
Conditions for reaction of alkene with water
high temperature
high pressure
catalyst- phosphoric acid adsorbed on solid silica
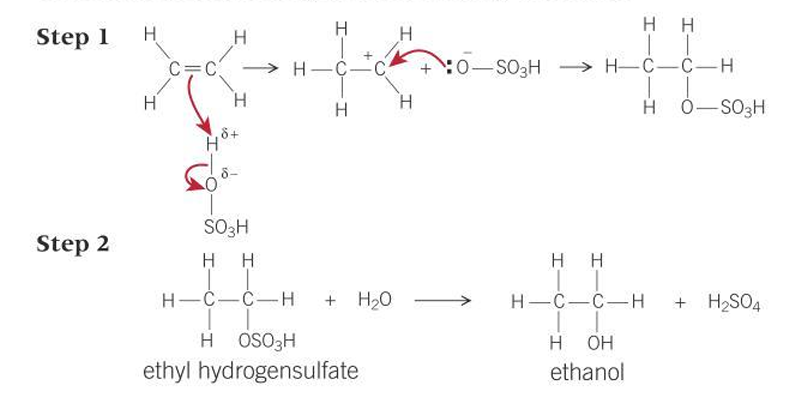
Mechanisms for reaction of ethene and water
Conditions of reaction of ethene with hydrogen
Platinum catalyst- standard conditions
Finely powdered nickel- high temperature and pressure
Why is a catalyst needed for reaction of alkene and hydrogen?
break strong H-H bonds to form H atoms