Unit 7 AP HUG Vocab words
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
88 Terms
Industrial Revolution
the rapid transformation of the economy through the introduction of machines, new power sources, and new chemical processes in Europe and the United States between 1760 and 1830
textile
fabric or cloth woven from the fibers of wool, cotton or flax
labor productivity
the average amount of goods or services produced per worker per unit of time
fossil fuels
-natural fuel derived from the fossilized remains of living organisms-coal, crude oil, natural gas
crude oils
yellowish-black liquid fossil fuel found in geologic deposits
commercial farmers
farmers who raise crops and livestock to se;; in the market at a profit rather than raising them for their own consumption
wage labor
a socioecinic relationship in which an employer pays a worker to complete a task, sometimes by the day or by the hour
working class
the people in an industrial economy who depend on wage labor to obtain the necessities of life
capitalist class
the employers who own production, paid the wages
middle class
people who are either salaried professionals (lawyers, educators, physicians) or office wage workers (bank tellers, store clerks) also managerial class
labor unions
associations of workers in particular industries established to collectively bargain with capitalists
mass production
the machine manufacture of large quantites of identical products
assembly line
system of manufacturing in which parts and procedures are added one step at a time through a series of workstations until a finished product is assembled (fordism)
mass Consumption
the purchase of large amounts of mass-produced goods by large numbers of people
international division of labor
the situation in which the labor forces of different countries and world regions play complementary roles in interdependent global economy
economic sectors
the different categories of economic activity within an economy, including primary (extracting raw materials), secondary (manufacturing), and tertiary (services) sectors.
primary sector
"extractive"industries that extract natural resources from the environment-phisyical skill workers, not high paying, US has small % of these workers-fishing, hunting, farming, logging, oil, mining, foresting-farmer, fisherman, forest worker, gold miner
secondary sector
"manufacturing"-Industries that process the raw materials extracted by primary industries, transforming them into finished, usable forms-ore to steel, logs to lumber, fish to cans,-can be light and heavy like furniture vs automobile-wages vary greatly-washing machine manufacturer, paper production worker, textile factory worker
tertiary Sector
-transportation/common services, producer and consumer services-industries that provide services to businesses and consumers, including all the diff types of work needed to transport and deliver goods/resources-automobile salesperson, grocery store clerk, refrigerator repair person, mechanic, jewelry seller
quaternary sector
The portion of the economy dedicated to intellectual and informational services, such as scientific research & development-scientific research, patterns of new goods & procedures, computer software development & biomedical research-small % employees-advanced edu, increased wages
quinary sector
-portion of economy where highest-level management decisions are made in the areas of business, government, education, & science-chief exec officer, ceo of software firm overseas everything by workers in quaternary sector-president, state governor, us senator
base industry
an industry of disproportionate economic importance and on whose existence other industries and employment sectors depend-over time, it attracts new industries in secondary & tertiary sectors to the core area. Also moves ppl into core area to expand workforce-example: steelmaking which attract businesses that will help steel industry run, and those that use steel for their business
semi-periphery
countries that contain aspects of both core and periphery
break of bulk point
a location where cargo is transferred from one of transportation to another
shipping containers
standardized, stackable, intermodal metal boxes used to transport goods by ship, railroad, or truck
containerization
the system of intermodal freight transport using shipping containers
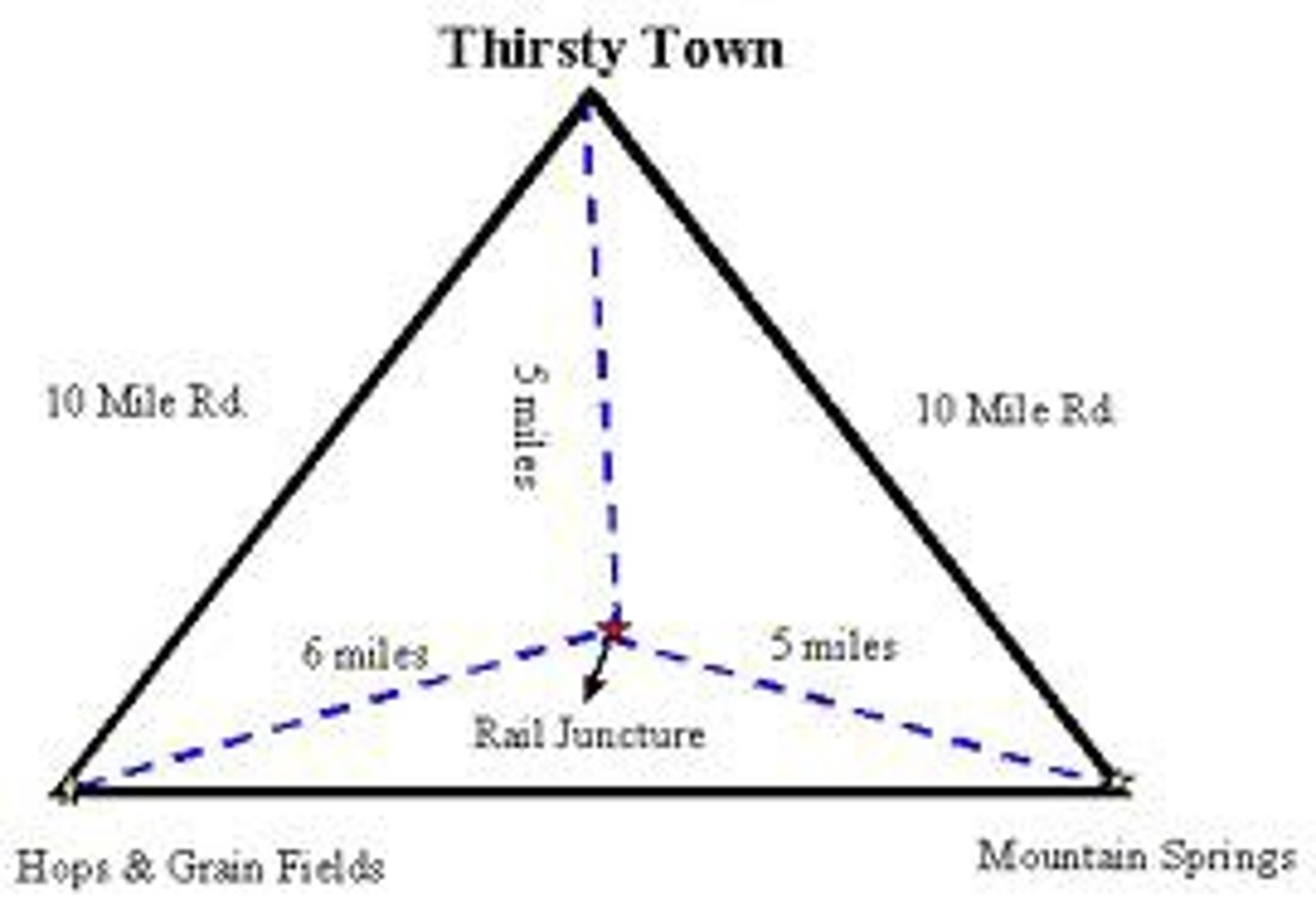
least cost theory
-location triangle with two locations for materials sources, and one for market location-manufacturing would be at spot with LOWEST costs of transportation
world systems theory
regards world history as moving through a series of socioeconomic systems, culminating in the modern world system by about the year 1900
dependency theory
the theory that the periphery is poor because it was economically dependent on the core in a disadvantageous relationship originally established under colonialism and imperialism
commodity dependence
economic dependence on exports of agricultural and mineral raw materials
gross national imput (GNP)
measures the total value of all the goods and services made by a country's residents and businesses in a specific time period, regardless of the country or location in which they were made-does not count value produced within a country by foreign residents or businesses
gross domestic product (GDP)
the total value of all goods and services produced within a country over a specific period, regardless of the producer's national origin-confined to country's boundaries
gross national income (GNI)
total income of a country's residents and businesses, including investment income, regardless of where it was earned, as well as money received from abroad such as foreign investment and development aid-measures total income rather than the total value of goods and services produced
GDP per capita
accounts for population when calculating the total amount of goods and services produced by a country-compares how wealthy or poor average brazillian would be
purchasing power parity (PPP)
measures how much a common basked of good costs locally in the currency of each country being compared
Gender Inequality Index (GII)
a statistical measure of gender inequality that combines data on reproductive health, empowerment, and labor-market participation-reproducitve health: measured by maternal mortality ratio and adolescent birth rates
Human Development Index (HDI)
created by world bank as tool to measure non-economic aspects of human life
informal sector
off the books, black market, under the table-part of any economy that is not officially recorded, monitored, or taxed by the government
formal sector
part of economy that is officially recorded with the government.
income distribution
how a country's total GDP is distributed among the individuals in its population
GEM
made by UN-measurement of gender equality that includes the proportion of seats held by women in national parliaments, the percentage of women in economic decision-making positions, and women's versus men's share of earned income
gender parity
a way of documenting progress toward gender equality using measures such as relative access to education, average incomes for women vs men, and workforce participation-hobs labeled "women's work" tend to make less money
Microloan
a very small loan to people with little income or collateral intended to help them establish or expand a small business-part of microcredit system
Mercantilism
prevailing theory of trade in 16th century-states that each country strives to export more than it imports in order to accumulate wealth-colonialism was central to this system
protectionism
trade rules that restrict imports in order to protect domestic industries-central to mercanstilism
Absoulte Advantage
comparative advantage
a country's ability to produce a good or service more efficiently than another country
complementary
a measure of how well one country's export profile matches another country's import profile-high degree can provide the basis for successful trade
transnational corporation
a firm with the power to coordinate and control operations in more than one country, even if it does not own those operations-work to maintain competitive advantage through continuous innovation and upgrading
competitive advantage
a firm's relative ability to outperform other TNCs in its industry
Neoliberism
range of pro-market and anti-government positions on the economy, such as reducing government ownership and regulation and promoting privatization and market-based solutions
international monetary fund
international organization that seeks to foster global monetary cooperation, achieve financial stability, facilitate international trade, and promote sustainable economic growth-provides loans to countries that are so deep in debt they cannot get loans from private banks
world bank
an international financial organization that provides funding and expertise to promote sustainable economic growth in developing countries
world trade organization
an international organization that regulates trade among 184 member states, providing a framework for negotiating trade agreements and resolving trade disputes
free-trade organization
a treaty between 2 or more countries that reduces tariffs and promotes foreign investment-ex./USMCA (US-Mexico-Canada) agreement formally known as NAFTA. Eliminated some, but not all tariffs and trade barriers among all 3 countries and increased international trade volume among all 3 countries but unevenly
tariff
tax on imported goods and services
customs union
type of regional trade agreement-a free trade agreement among 2 or more member countries, combined with a single, common external trade policy for nonmembers
mercosur
spanish acronym for the southern common market, a south american customs union that includes argentina, brazil, paraguay, and uruguay as its full members
OPEC
an international trade agreement designed to regulate the output of oil-founded in 1965 by oil-producing countries: Iran, Iraq, Kuwait, Saudi Arabia, and Venezuela to coordinate oul production and avoid trade competition among members
Trade embargo
an official ban on trade with a specific country or of a specific good-usually imposed during periods of heightened political conflict
financial market
marketplace where financial instruments are traded; stock markets, bond markets, and foreign exchange markets are all financial markets-major ones in Asia, Europe, and North America, and global trade in financial products is conducted 24 hours a day
debt crisis
occurs when a government's debts exceed its tax revenues to the point that it cannot meet its loan payments
ISI
an economic development policy intended to replace imported goods with domestically produced goods as a way to spur industrialization and reduce dependence on other countries
Fordism
the economic and social arrangement based on the mass production of standardized good, high labor union membership rates, stable and full-time manufacturing employment, and high factory wages that enable mass consumption
corporate disinvestment
a process in which companies stop investing in factory construction, equipment, and improvement and begin selling off assets, such as machinery, buildings, and land
offshoring
the relocation of manufacturing and support services from one country to another
outsourcing
cost-saving-when a firm transfers part of its internal operations to a third party
deindustrialization
the decline, and sometimes complete disappearance, of employment in the manufacturing sector core's industrial centers
Special economic zone
specific area within a country's borders where business and trade laws are different from those in the rest of the country
export processing zone
industrial zone with special incentives to attract foreign investment to places where imported materials undergo processing or assembly before being re-exported
free trade zone
specially designated duty-free area that provides warehousing, storage, and distribution facilities for goods intended for trade or re-export
new international division of labor
the spatial shift of manufacturing from developed countries to developing countries, including the global scaling of labor markets and industrial sites
Post-Fordism
refers to the shifts from manufacturing centers to spatially dispersed production sites, from standardized mass production to specialized batch production, and from a permanent workforce to temporary and contract workers
just in time manufacturing
early flexible production-the production of small batches of goods as needed by customer demand
high technology industry
an industry that develops and uses the most advanced technologies available and has the highest levels of research and development-aerospace, computers, communications and electronics, pharmaceuticals
agglomeration economies
occur where firms cluster spatially in order to take advantage of geographic concentrations of skilled labor and industry suppliers, specialized infrastructure and ease of face-to-face contact with industry participants
multiplier effects
the creation of new business and jobs in other industries as the result of investment in a different industry
growth pole
geographically pinpointed center of economic activity organized around a designated industry, commonly in the high-tech sector
sustainable development
development that meets present consumption needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their consumption needs-reduce industrialization's worst environmental effects
resources depletion
the consumption of natural resources faster than they can be replenished
environmental pollution
the contamination of the physical (air, water, earth) and biological components of the environment to the point that normal functions are negatively affected
point source pollution
any single identifiable source from which contaminants are discharged, such as a pipe or a smokestack
nonpoint source pollution
contamination originating from multiple, diffuse sources
climate change
a long-term shift in global or regional climate patterns
cogneration
producing two forms of energy from one fuel(reuse or recycle)-using the heat that is released during fuel combustion to warm buildings or power machinery
carbon neutrality
goal of those who are committed to reducing amount of co2 in atmosphere
carbon offsets
processes that remove or sequester carbon from the atmosphere to make up for co2 emissions else where
ecotourism
travel to natural areas of ecological value in support of conservation efforts and socially just economic development