Homology and Analogy
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
morphological
visible anatomical traits
homology
trait that is present in two groups because it was present in a common ancestor and maintained over time is a
analogy
a trait that is not present in a common ancestor of two groups but evolved independently (as a result of convergent evolution) in two groups is an
convergent evolution
natural selection promoting similar adaptations in unrelated taxa subject to similar environmental conditions.
when does convergent evolution happen
It occurs when organisms evolve similar traits independently as a result of living in similar environments and being subject to similar selective pressures.
A trait that _ in two groups because of common ancestry is a homology. A trait that _ in the common ancestor and evolved independently in two groups is an analogy.
is not present; is not present
is not present; is present
is present; is not present
is present; is present
is present; is not present
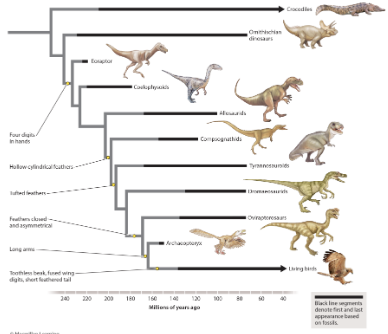
evolutionary biologists place traits on tress to indicate when the traits evolved. How many traits have been placed on this tree?
zero
one
two
four
six or more
six or more
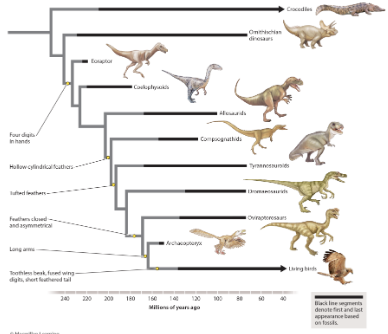
evolutionary biologists place traits on tress to indicate when the traits evolved. Traits that are visible anatomical traits, such as having hollow cylindrical feathers , are referred to as _ traits.
developmental
morphological
molecular
morphological
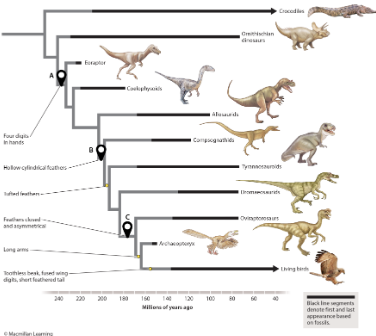
a trait that was present in the common ancestor of two groups and has been maintained or modified over time is a homology. Which labeled marker represents a trait that is homologous in eoraptors and allosaurids?
A
B
C
A
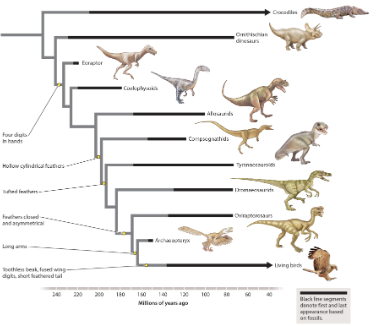
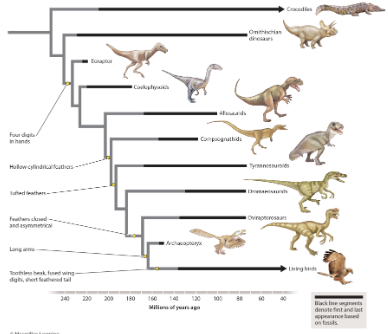
a trait that was present in the common ancestor of two groups and has been maintained or modified over time is a homology, and a trait that is not in the common ancestor but evolved independently in two groups by convergent evolution is an analogy. Which of the trait(s) listed here is/are homologous in tyrannosaurids and oviraptorosaurs? select all that apply.
four digits in hands
no traits are homologous
long arms
tufted feathers
four digits in hands and tufted feathers
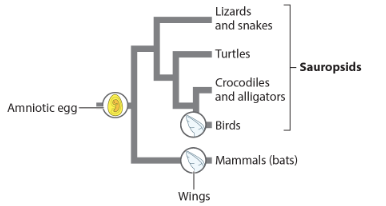
the amniotic edd is a(n) _ trait because it is a trait that evolved once in the common ancestor of sauropsids and mammals.
analogous
homologous
homologous
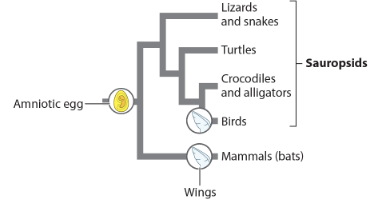
the wing is a(n) _ trait because it evolved independently in birds and bats (mammals) and was not present in their common ancestor.
analogous
homologous
analogous
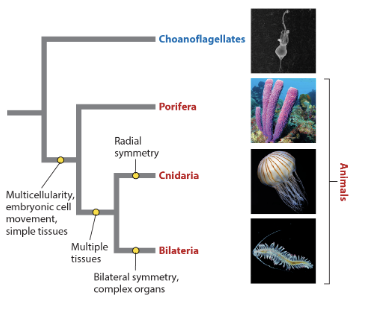
multicellularity in a(n) _ trait because it is a trait of porifera, bilaterians, and cnidarians and their common ancestor.
analogous
homologous
homologous
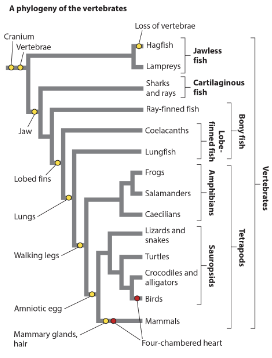
analogous traits evolve more than once independently in different groups. homologous traits evolve once in the common ancestor and are maintained. Which of these statements are true? Select all that apply.
lungs are an analogous trait of lungfish and salamanders.
walking legs are a homologous trait of tetrapods.
four-chambered heart is an analogous trait of birds and mammals.
walking legs are a homologous trait of tetrapods and four-chambered heart is an analogous trait of birds and mammals
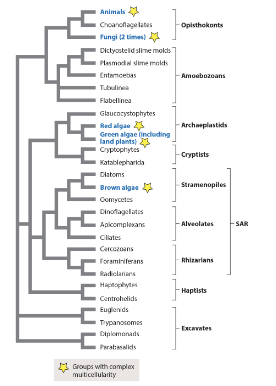
complex multicellularity is a(n) _ trait of some of the organisms on this tree.
analogous
homologous
analogous
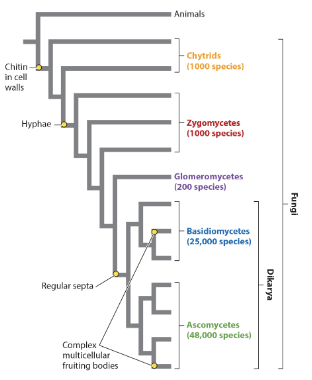
regular septa is a(n) _ trait of the Dikarya group.
analogous
homologous
homologous
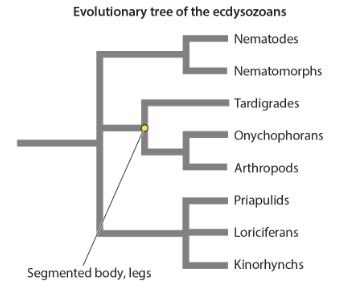
the segmented, legged body of tardigrades, onychophorans, and arthropods is a(n) their trait because it was present in
analogous; convergent ancestor
homologous; common ancestor
homologous; convergent ancestor
analogous; common ancestor
homologous; common ancestor