Olfaction and Gustation
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
where are special sensory receptors located?
within a special sensory organ or a distinct part of epithelium
what are the special senses?
olfaction, gustation, audition, equilibrium, vision
what are the types of general senses?
touch, pain, temperature
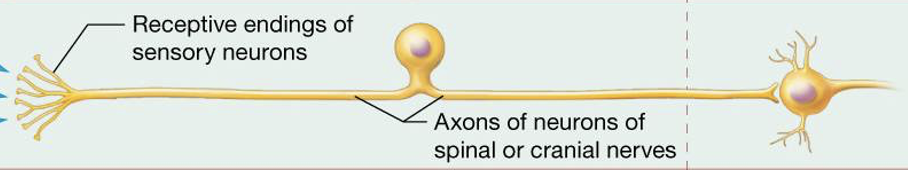
what type of senses are associated with this neuron?
general senses
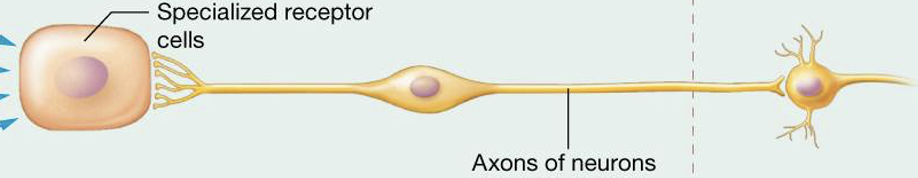
what type of senses are associated with this type of neuron?
taste, light, sound, head movement
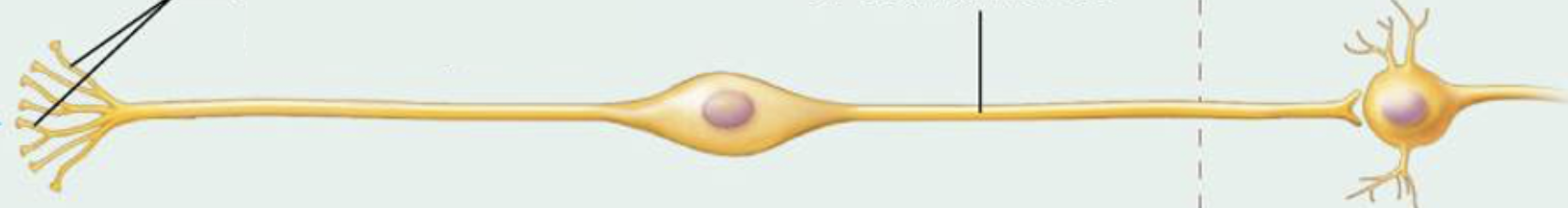
what sense is associated with this type of neuron?
smell
what is olfaction?
sense of smell
what are olfactory receptors?
chemoreceptors
what do olfactory receptors respond to?
chemicals in solution
what is the solution that chemicals are dissolved in to allow us to smell?
fluids of the nasal mucous membrane
due to location, what does sniffing do?
enhances smell
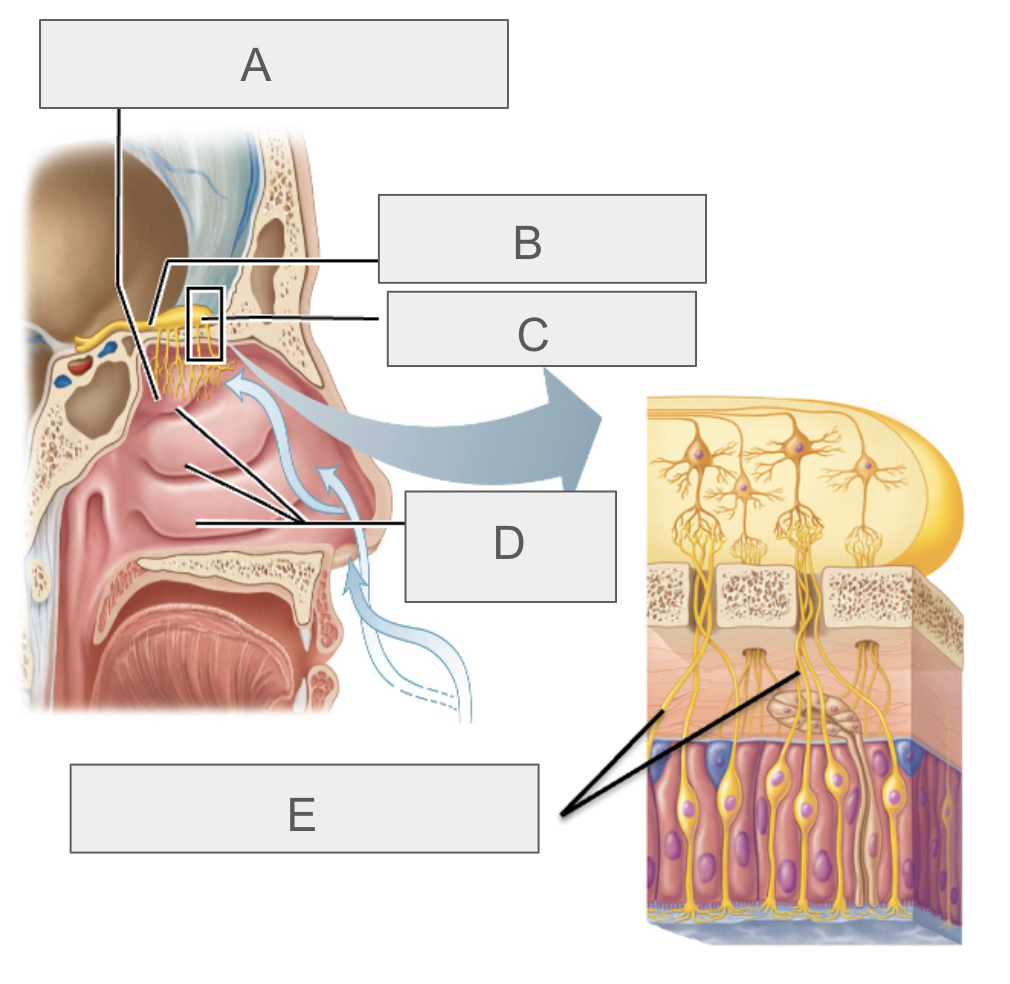
what is A?
olfactory epithelium
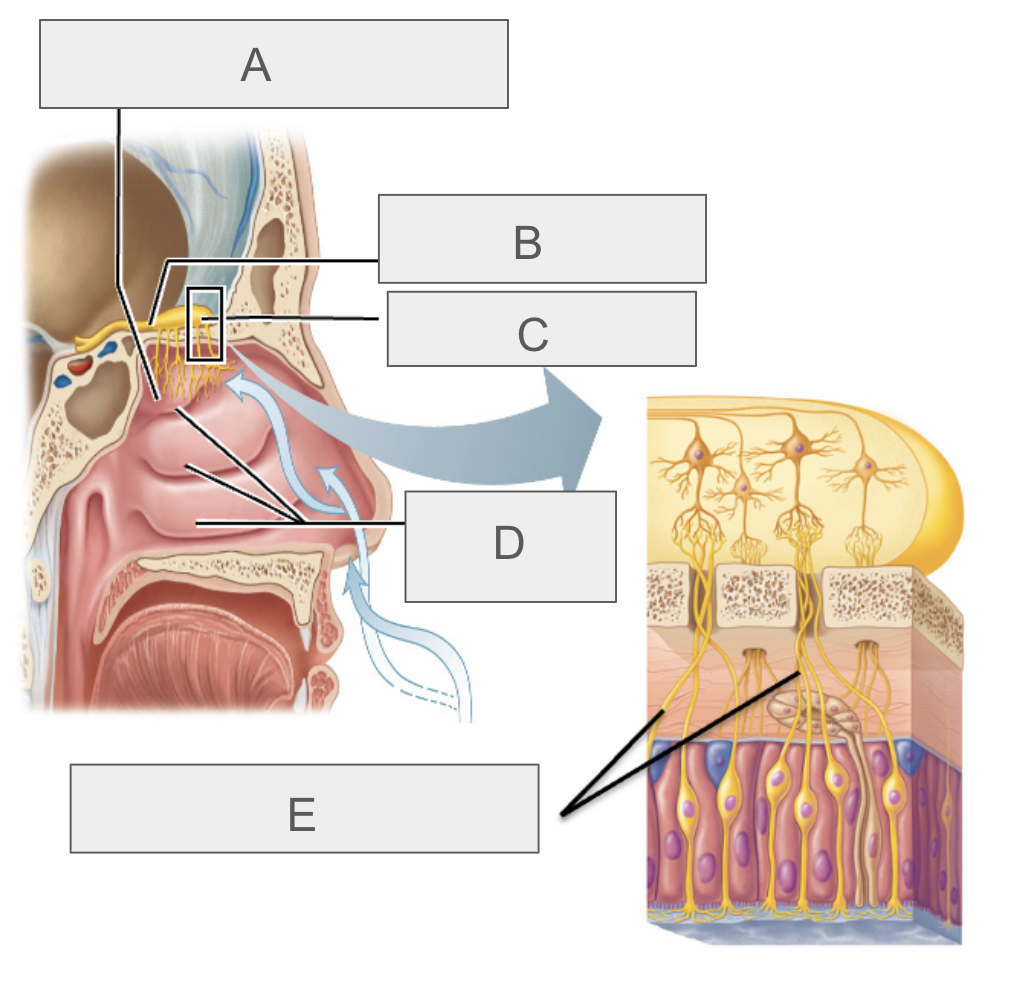
what is B?
olfactory tract
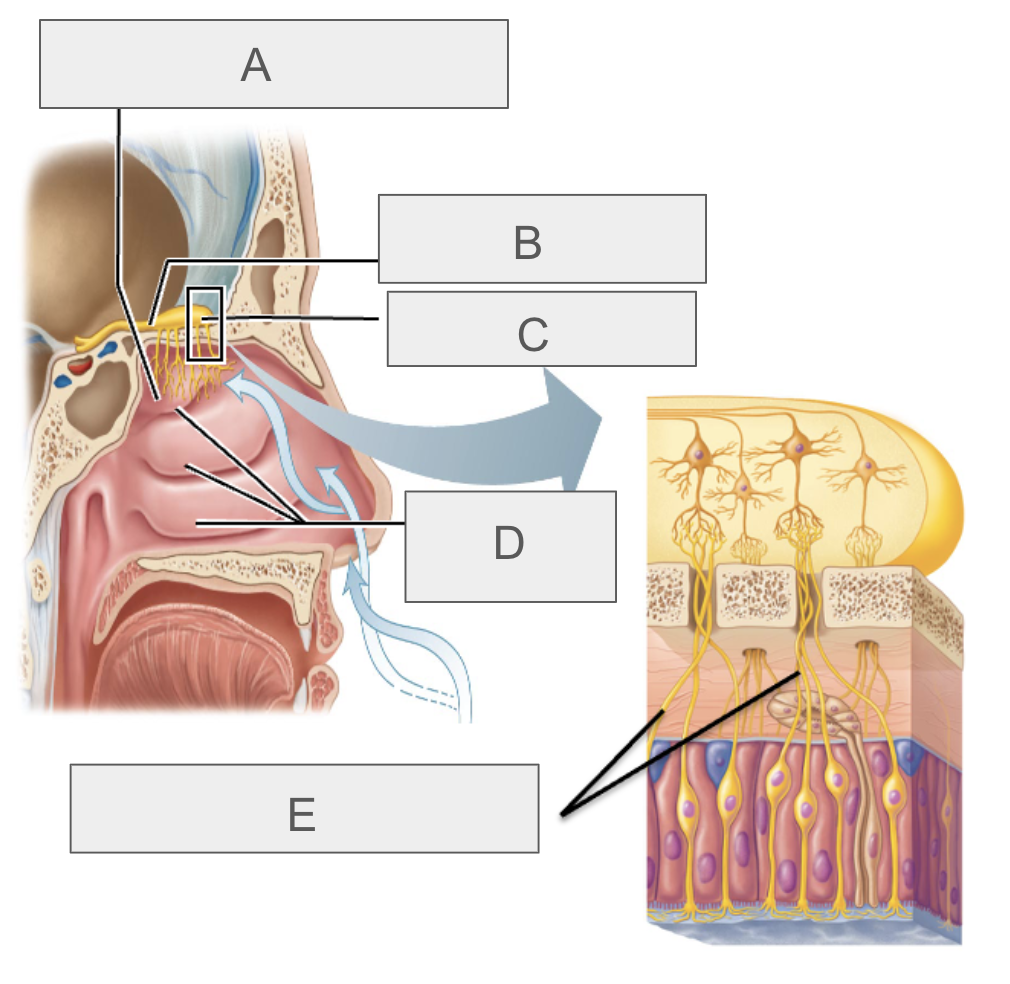
what is C?
olfactory bulb
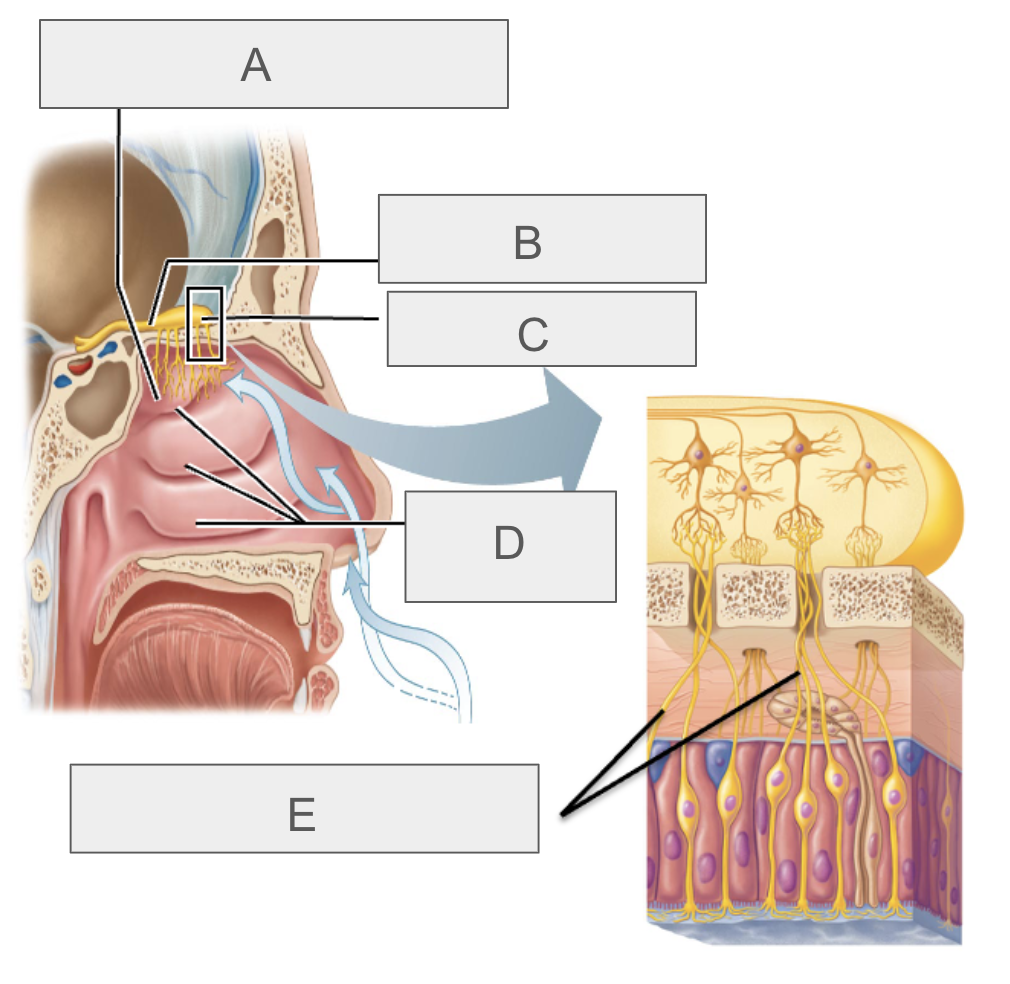
what is D?
nasal conchae
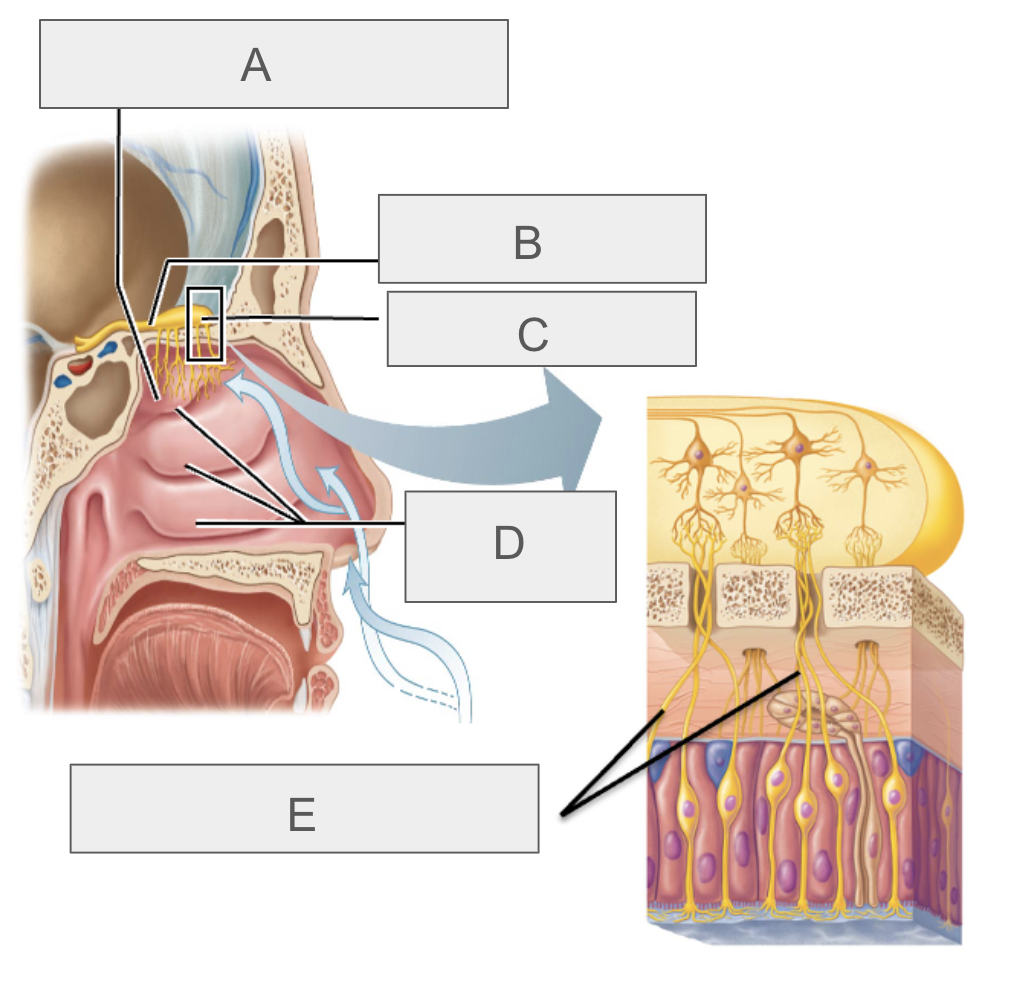
what is E?
olfactory nerves
where is olfactory epithelium found?
in roof of nasal cavity
what does olfactory epithelium cover?
superior nasal conchae
what does the olfactory epithelium contain?
olfactory sensory neurons
what do bundles of nonmyelinated axons of olfactory receptor cells form?
olfactory nerves
what is the structure of Olfactory receptor cells/ sensory neurons?
bipolar neurons with cilia that
what do supporting cells and olfactory glands in the olfactory epithelium do?
produce mucus
what do basal (stem) cells do in the olfactory epithelium?
replace receptor cells every 60 days because they’re mitotic
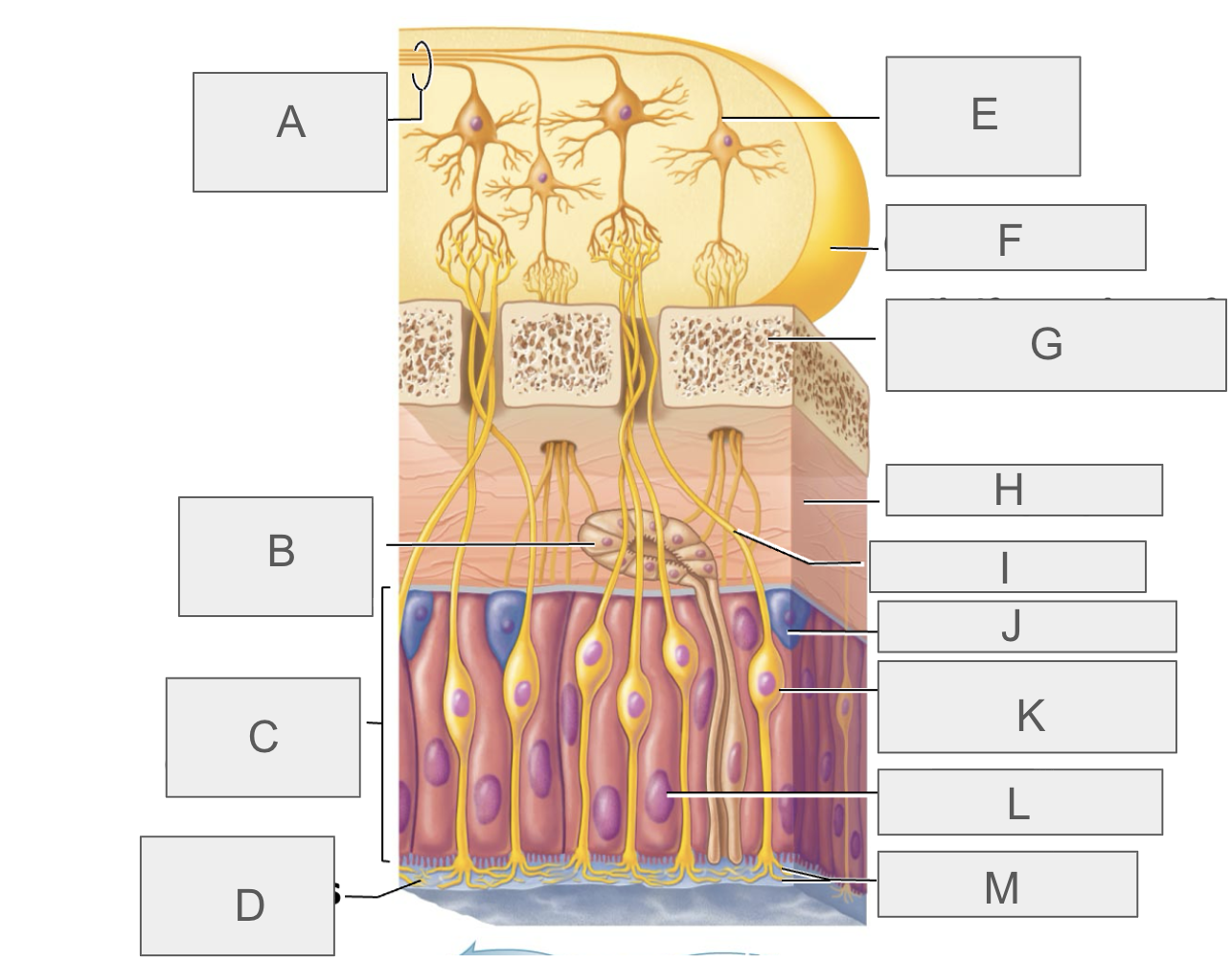
what is A?
olfactory tract
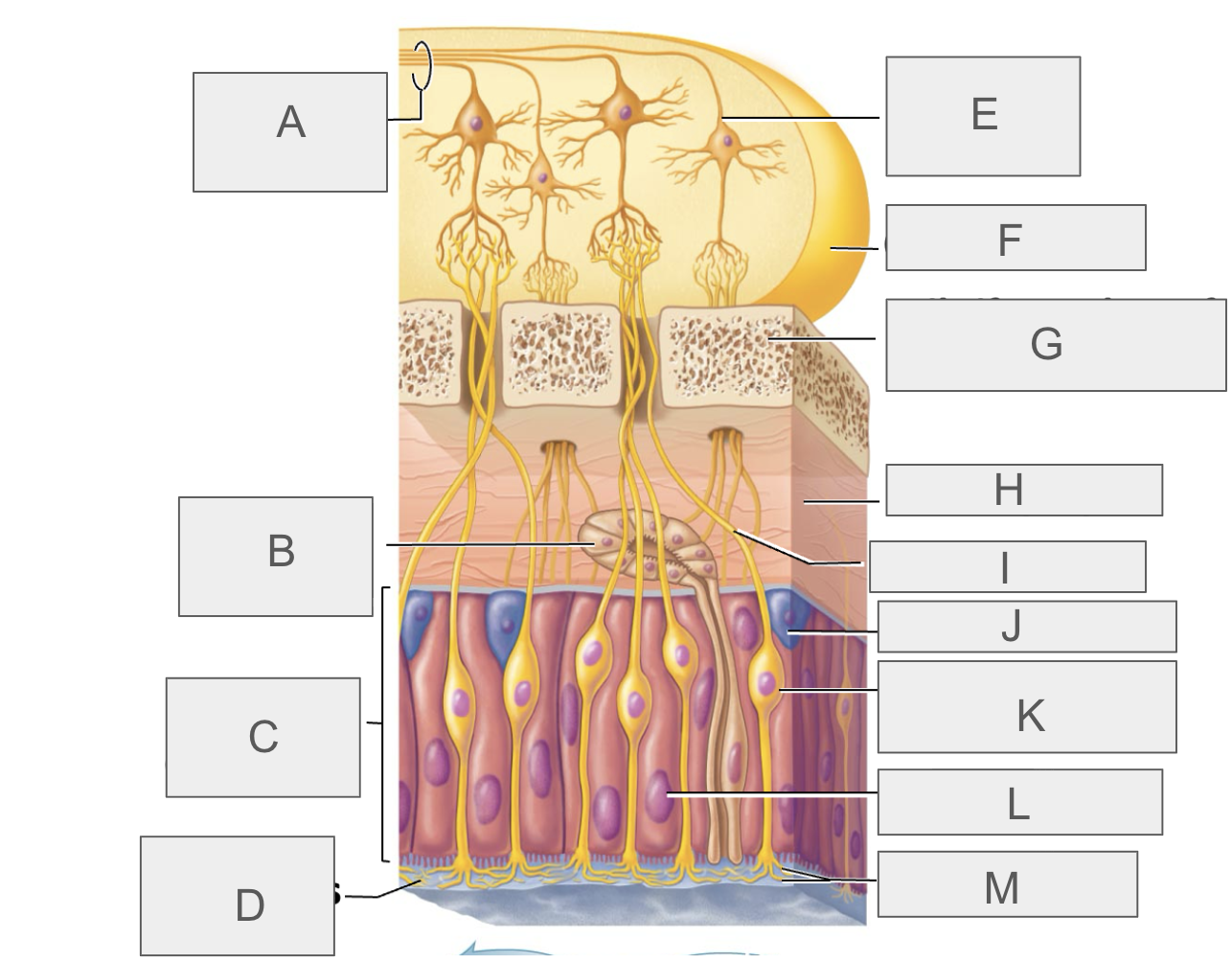
what is B?
olfactory gland
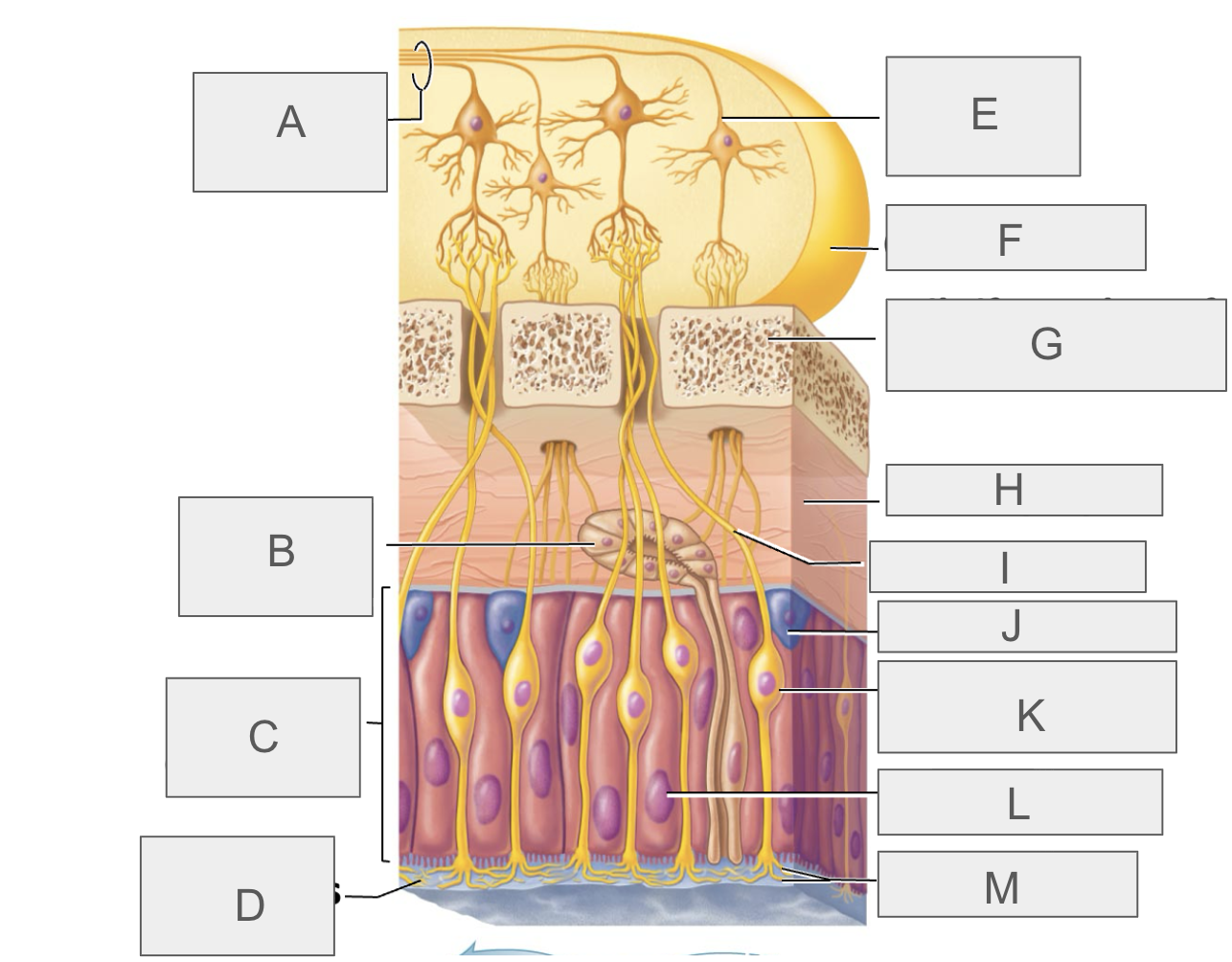
what is C?
olfactory epithelium
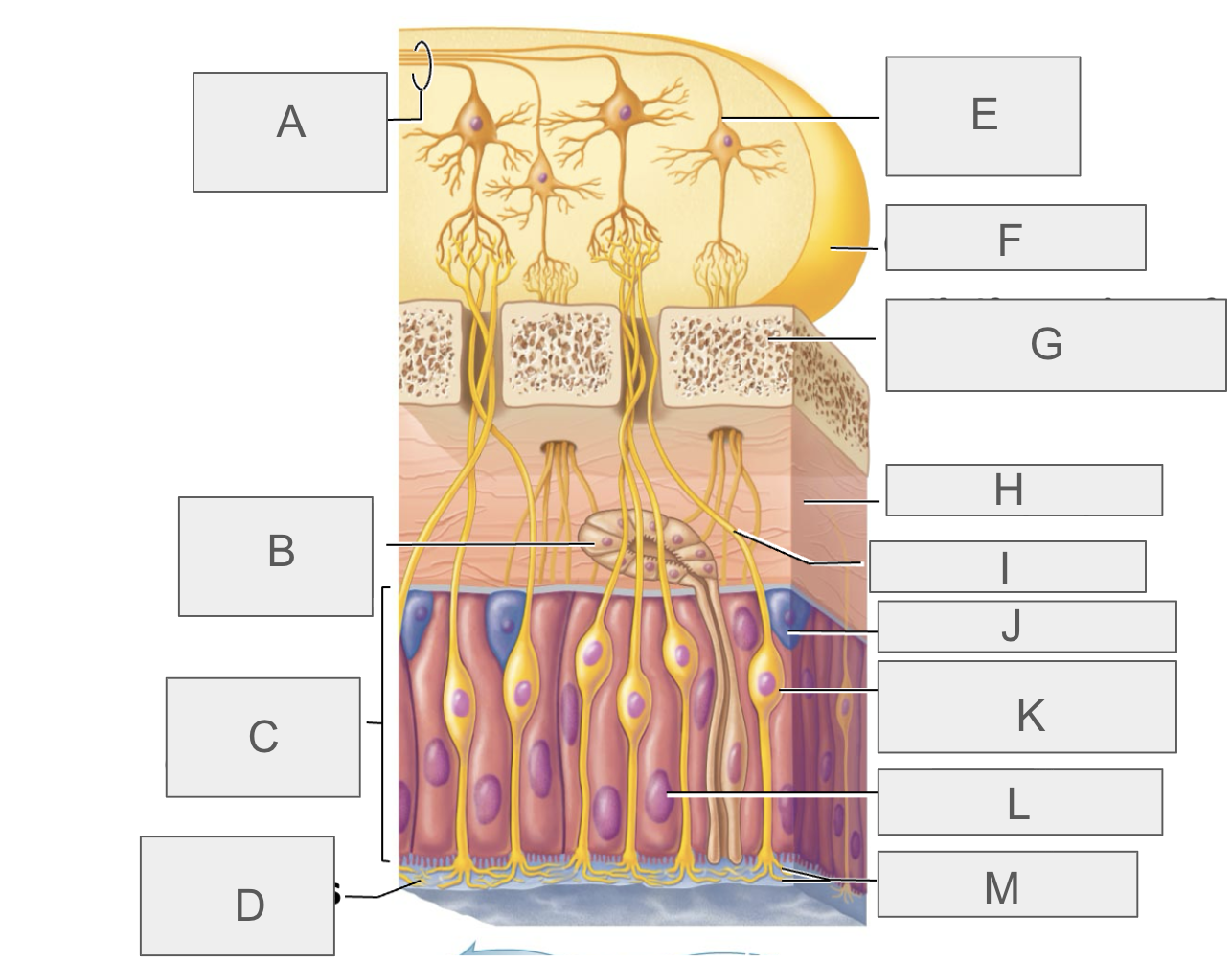
what is D?
mucus
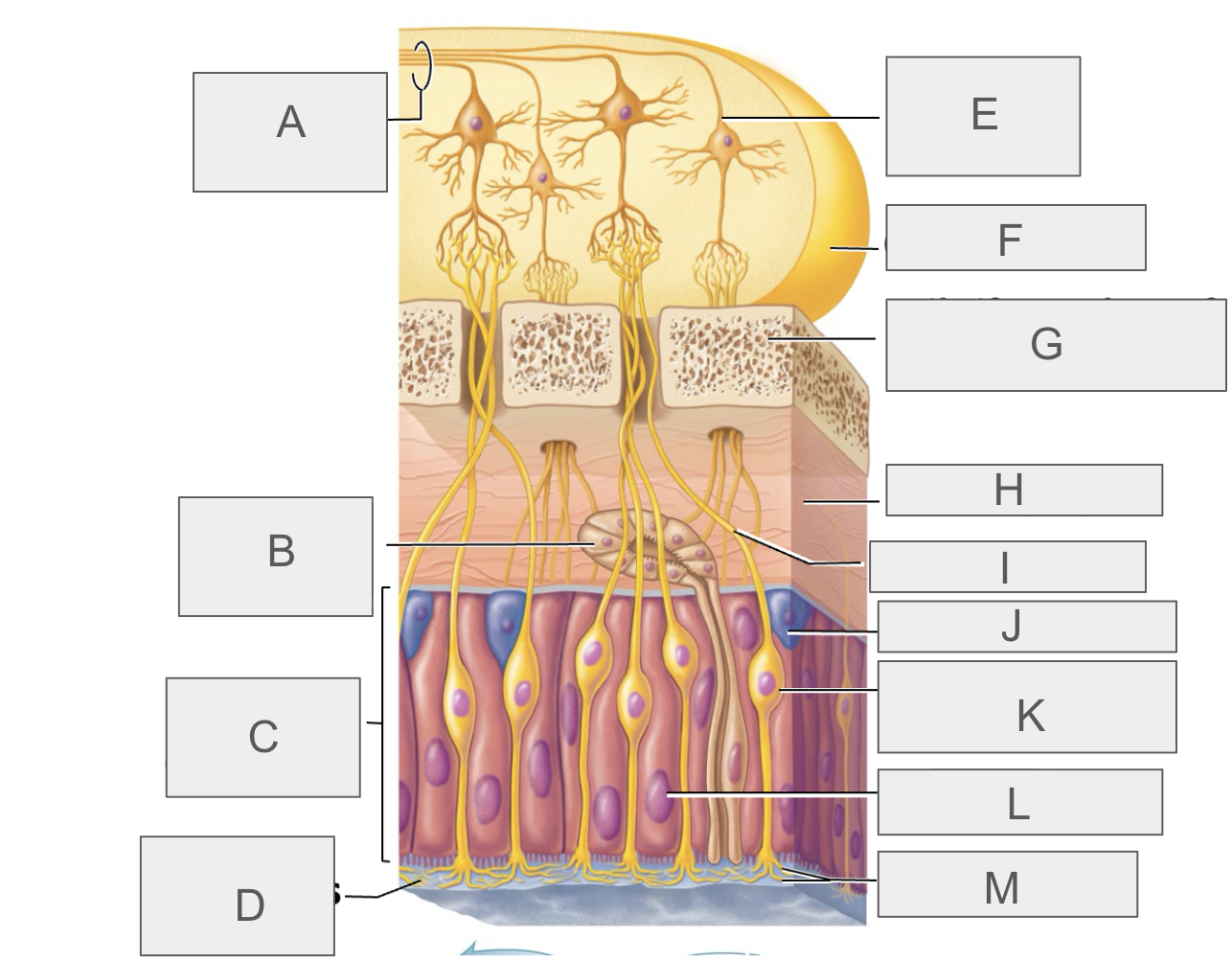
what is E?
mitral cell
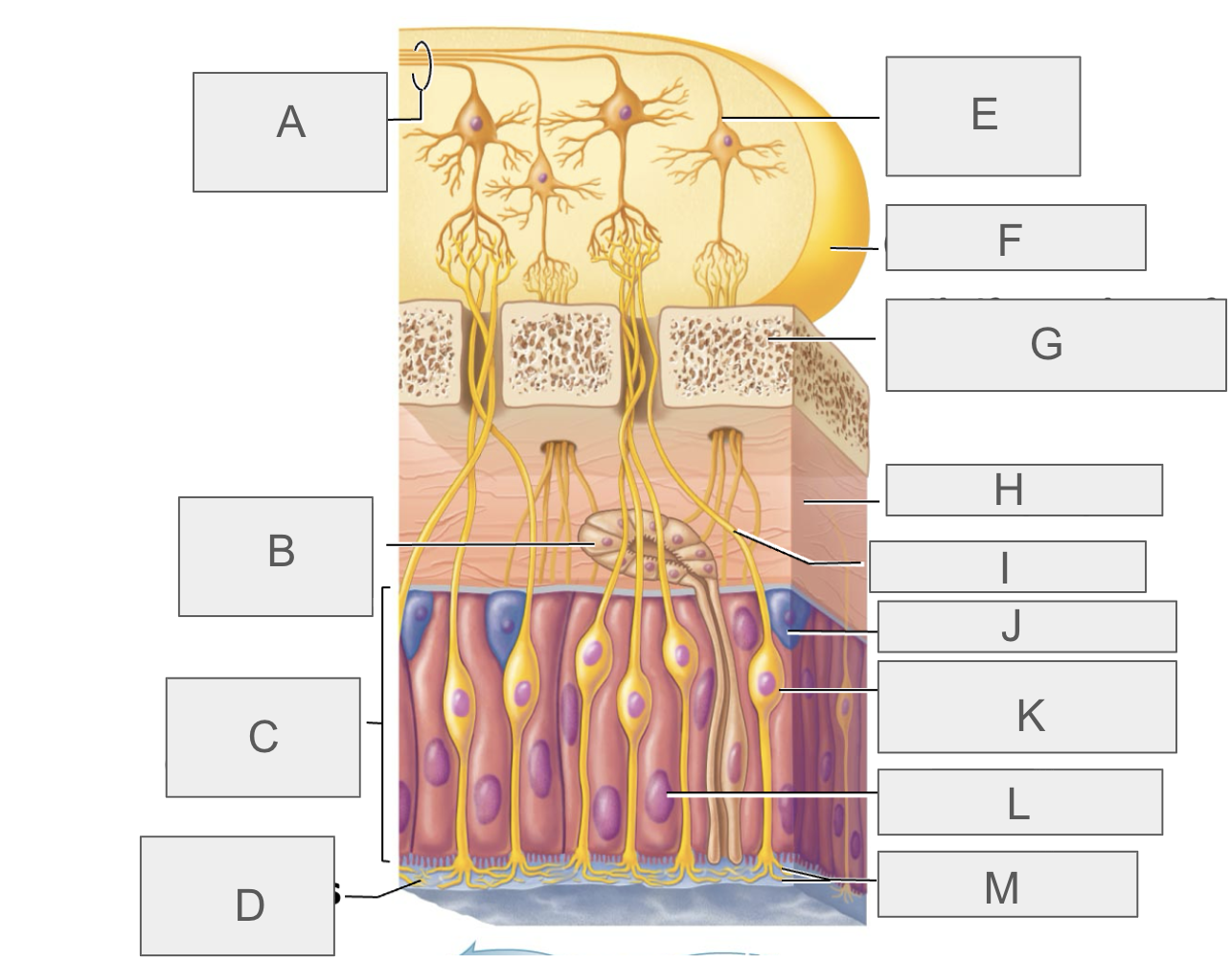
what is F?
olfactory bulb
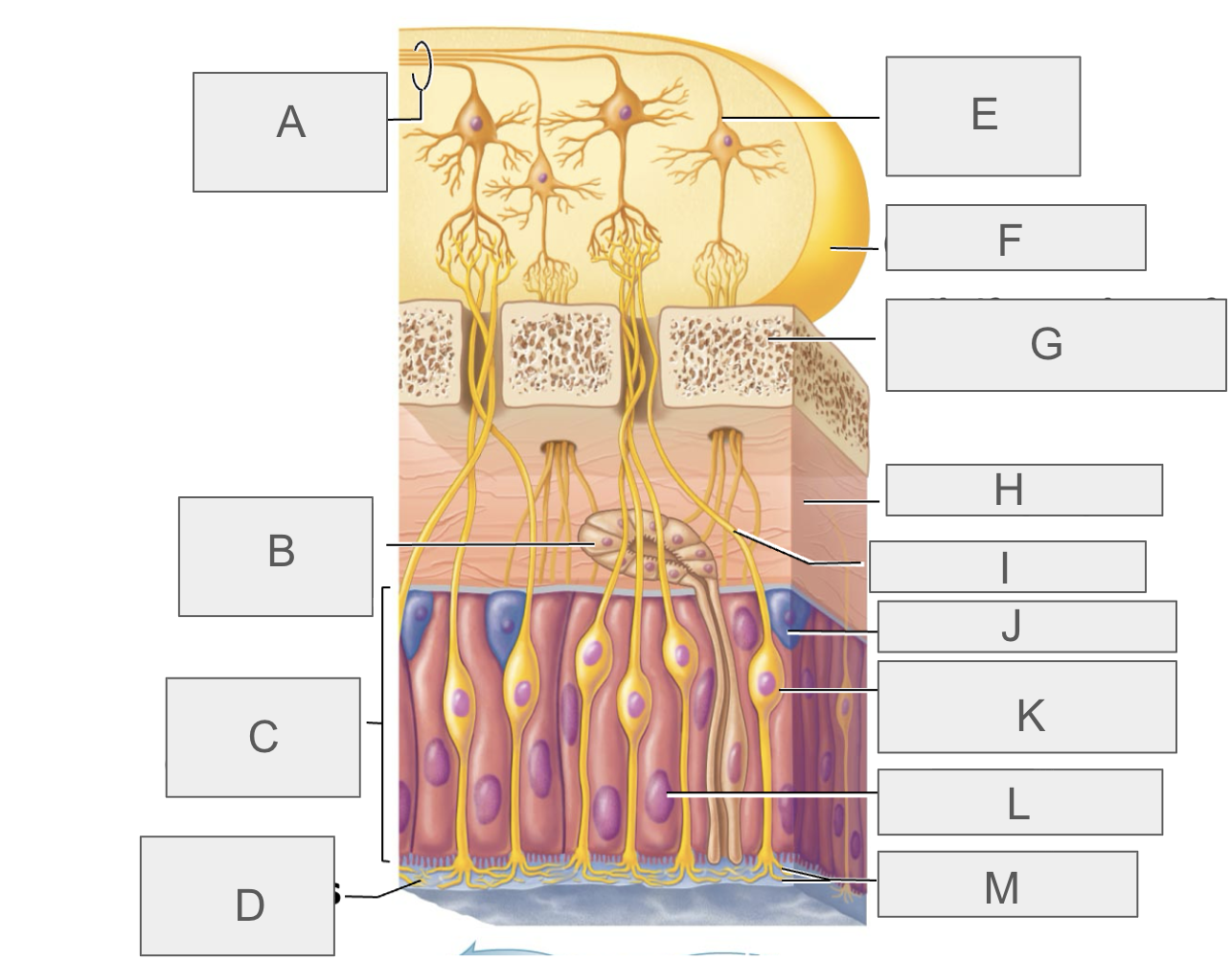
what is G?
cribriform plate of ethmoid bone
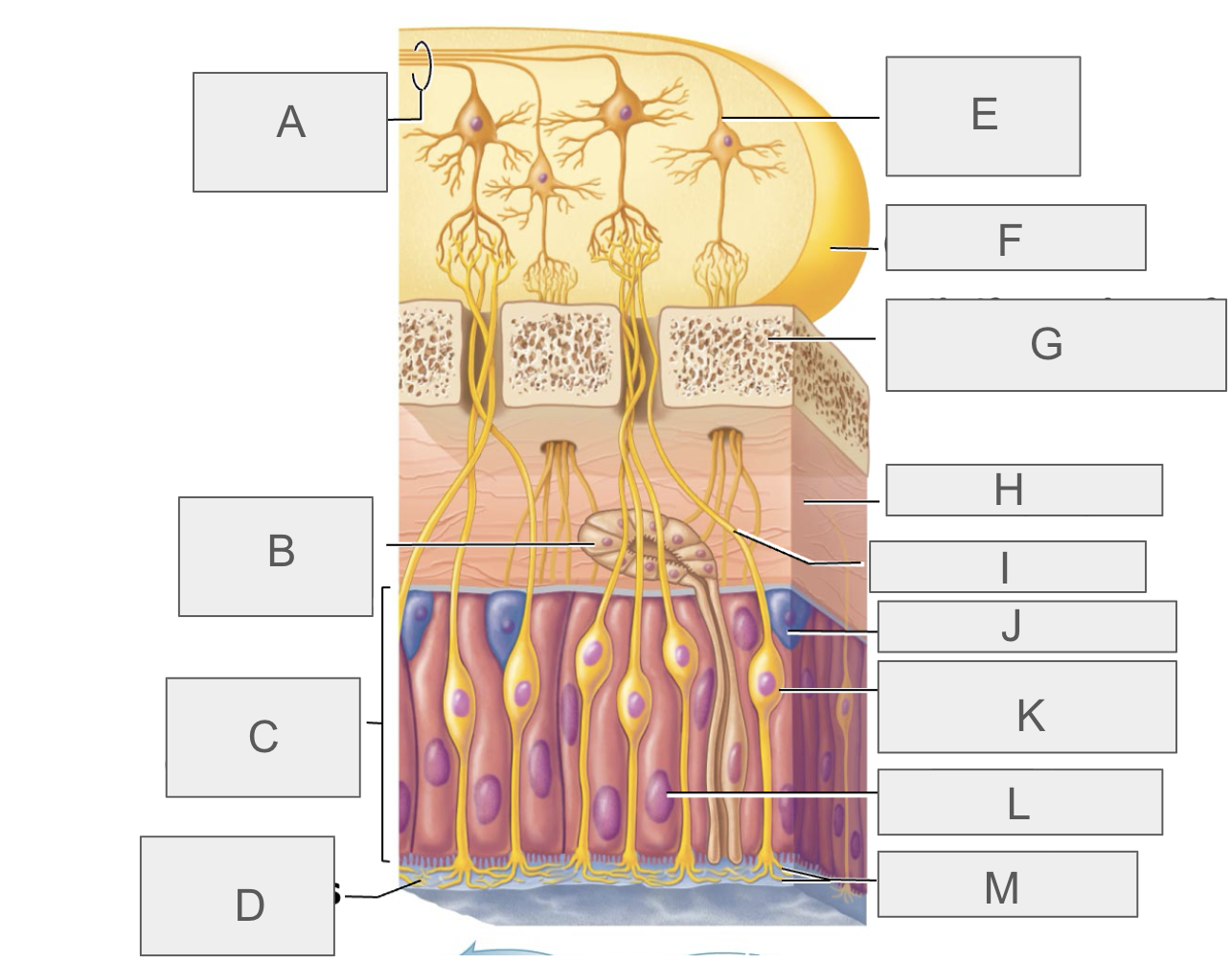
what is H?
lamina propria
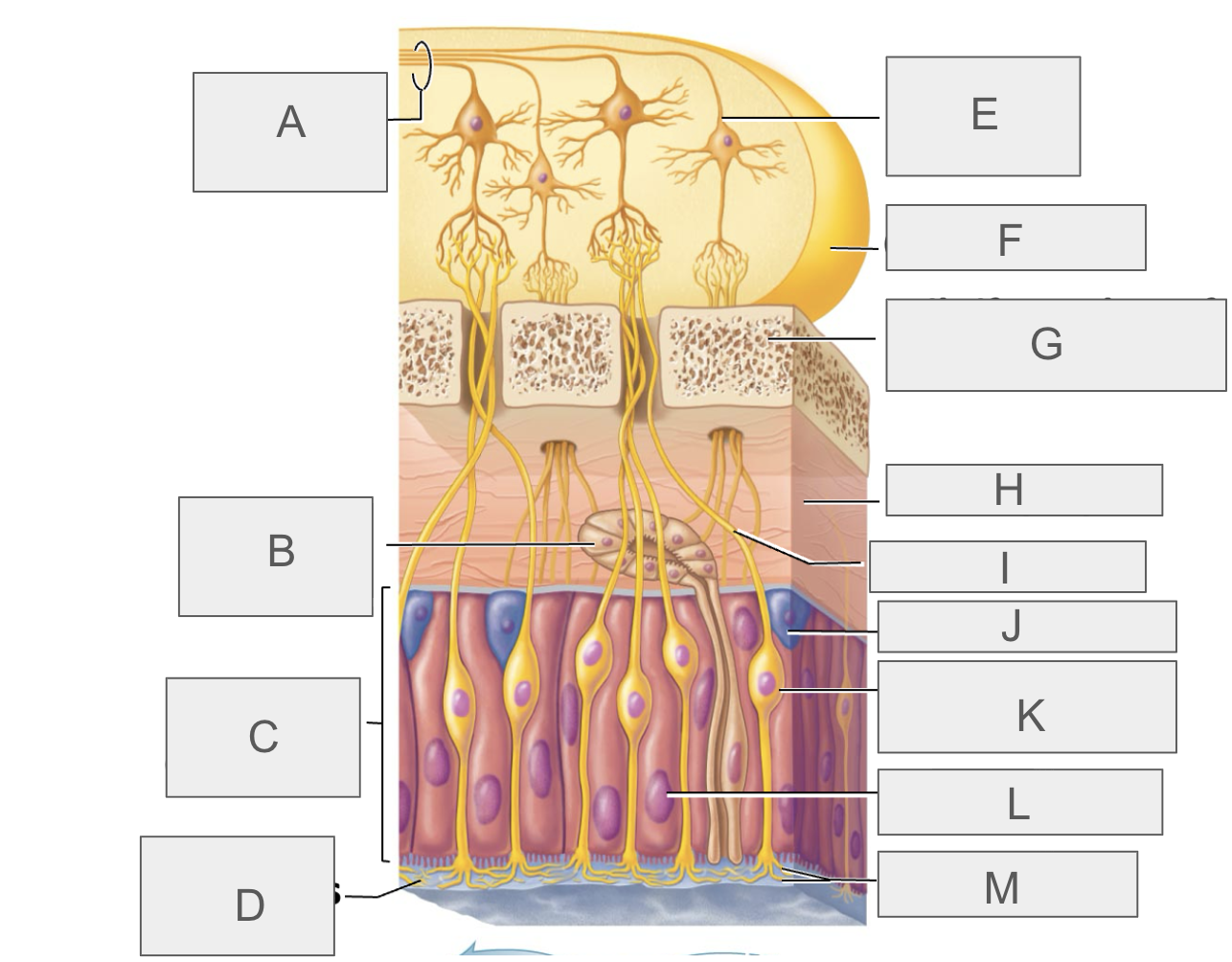
what is I?
olfactory axon
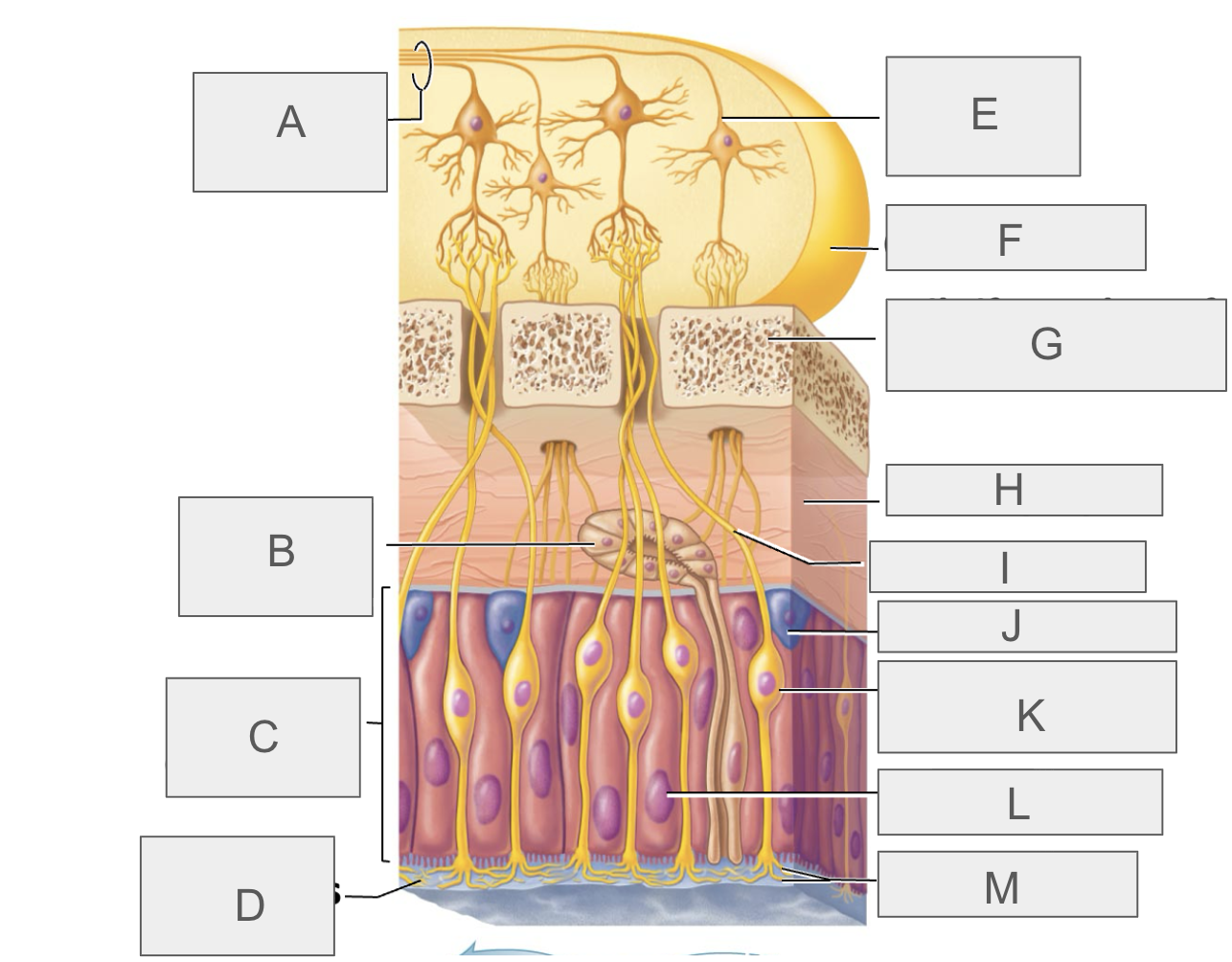
what is J?
basal/stem cell
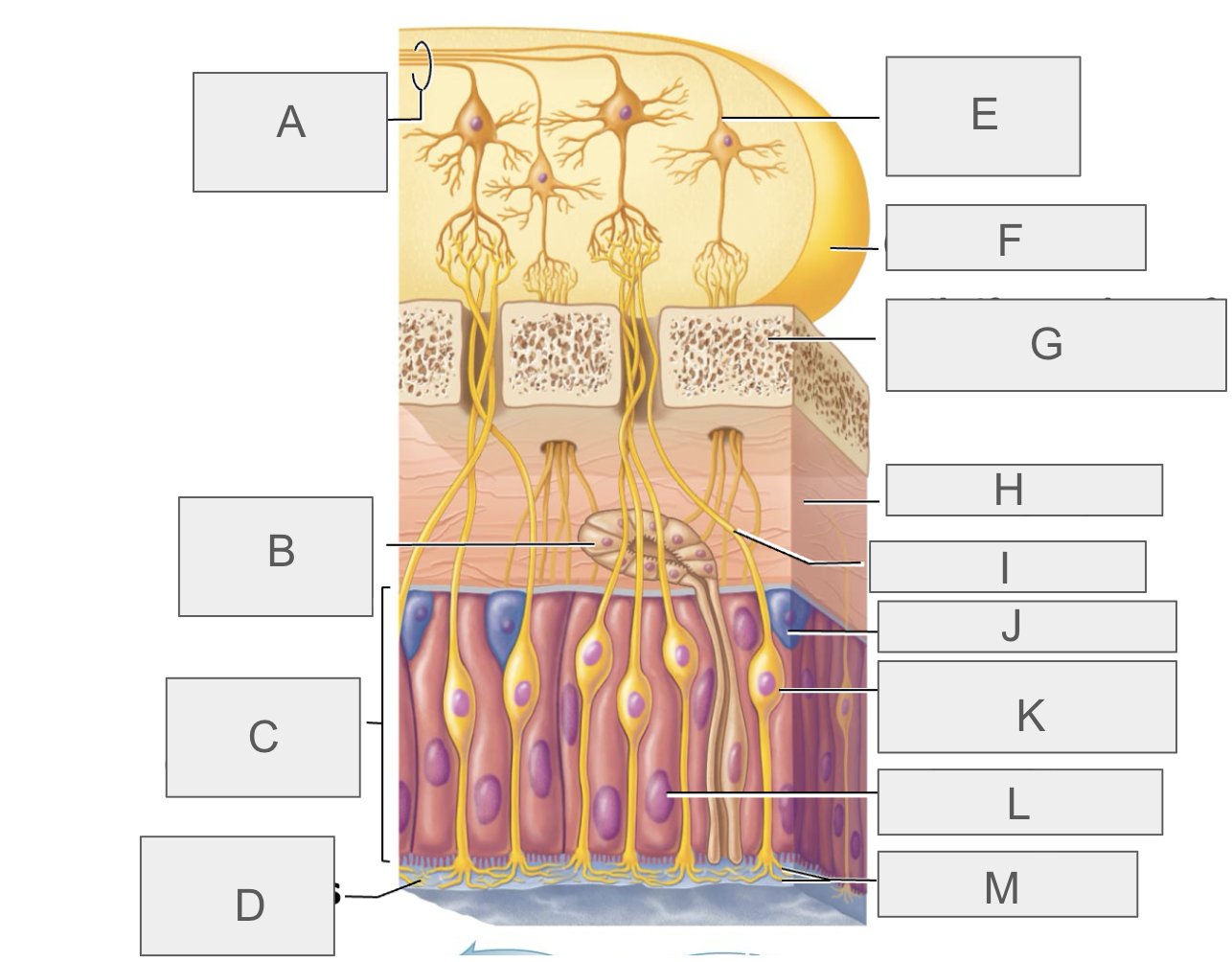
what is K?
olfactory sensory neuron
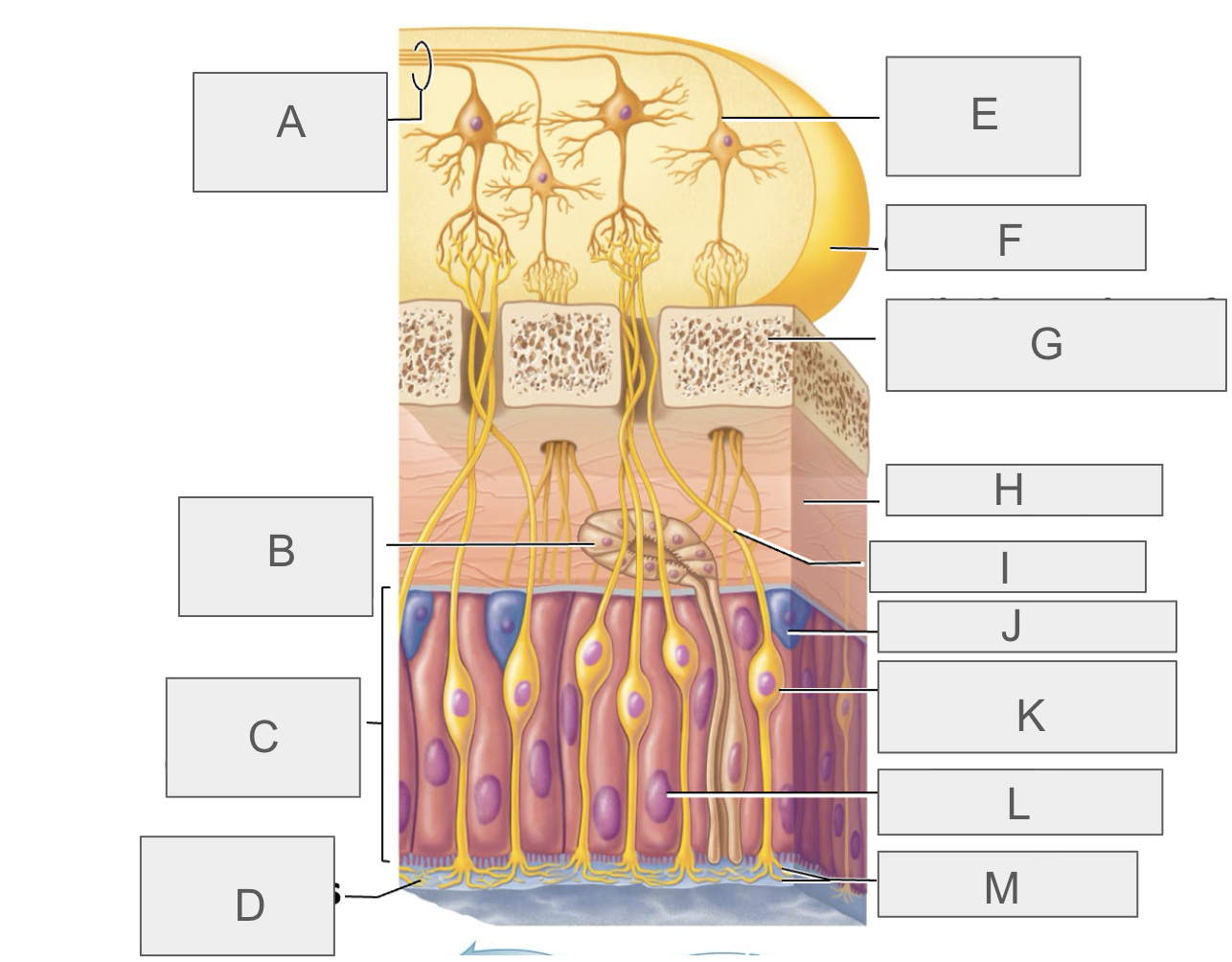
what is L?
supporting cell
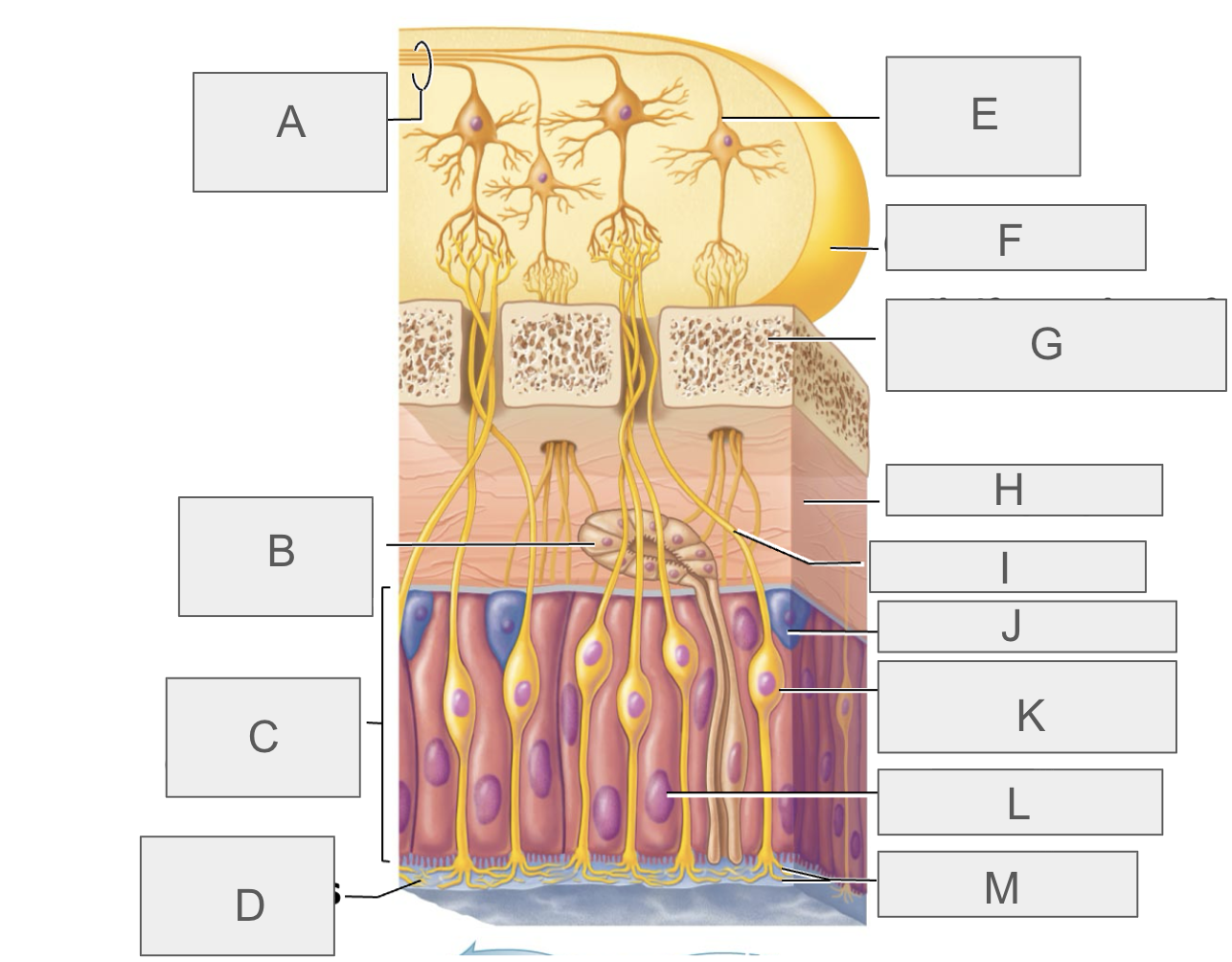
what is M?
olfactory cilia
what is converted during smell transduction?
chemical energy into electrical energy
what is the first step in smell transduction?
chemical in air (odorant) dissolves in mucus
what happens in smell transduction after the odorant is dissolved in mucus?
cilia of dendrite interacts with chemical odorant
what happens in smell transduction after the cilia of a dendrite interacts with the chemical odorant?
odorant binds to receptor
what happens in smell transduction after the odorant binds to the receptor?
secondary messenger system is activated
what does a calcium influx in smell transduction result in?
olfactory adaptation
what is olfactory adaptation?
decreased response to sustained stimulus
describe the adaptation/threshold of olfaction
low threshold, fast adaptation
what does low threshold for olfaction mean?
very small quantity required to perceive as an odor
what do olfactory nerves synapse with and where?
mitral cells in olfactory bulb
what do axons of mitral cells form?
olfactory tract
how do impulses from mitral cells travel to the olfactory cortex?
via olfactory tracts
where do impulses from mitral cells travel to?
the olfactory cortex in the temporal lobe
what is anosmia?
lack of olfaction
what is hyposmia?
reduced olfactory sensitivity
what can cause anosmia?
head injuries that damage neural pathways
what condition develops naturally with aging as fewer olfactory neurons are replaced by basal cells?
hyposmia
what is gustation?
sense of taste
where are gustatory receptors located?
in taste buds
where are taste buds located?
on papillae of tongue
what are the four types of papillae of the tongue?
fungiform, foliate, circumvallate, filiform
what papillae of the tongue is mushroom shaped and scattered over the tongues surface?
fungiform
what papillae of the tongue is located on the posterior sides of the tongue?
foliate
what papillae of the tongue is large, round, and forms a V on the posterior surface?
circumvallate/vallate
what papillae of the tongue is pointed, on the anterior 2/3, and has no taste buds.
filiform
where are most of the taste buds on tongue papillae found?
on tops of fungiform papillae and side walls of foliate and vallate papillae
where are few taste buds found?
soft palate, cheeks, pharynx, epiglottis
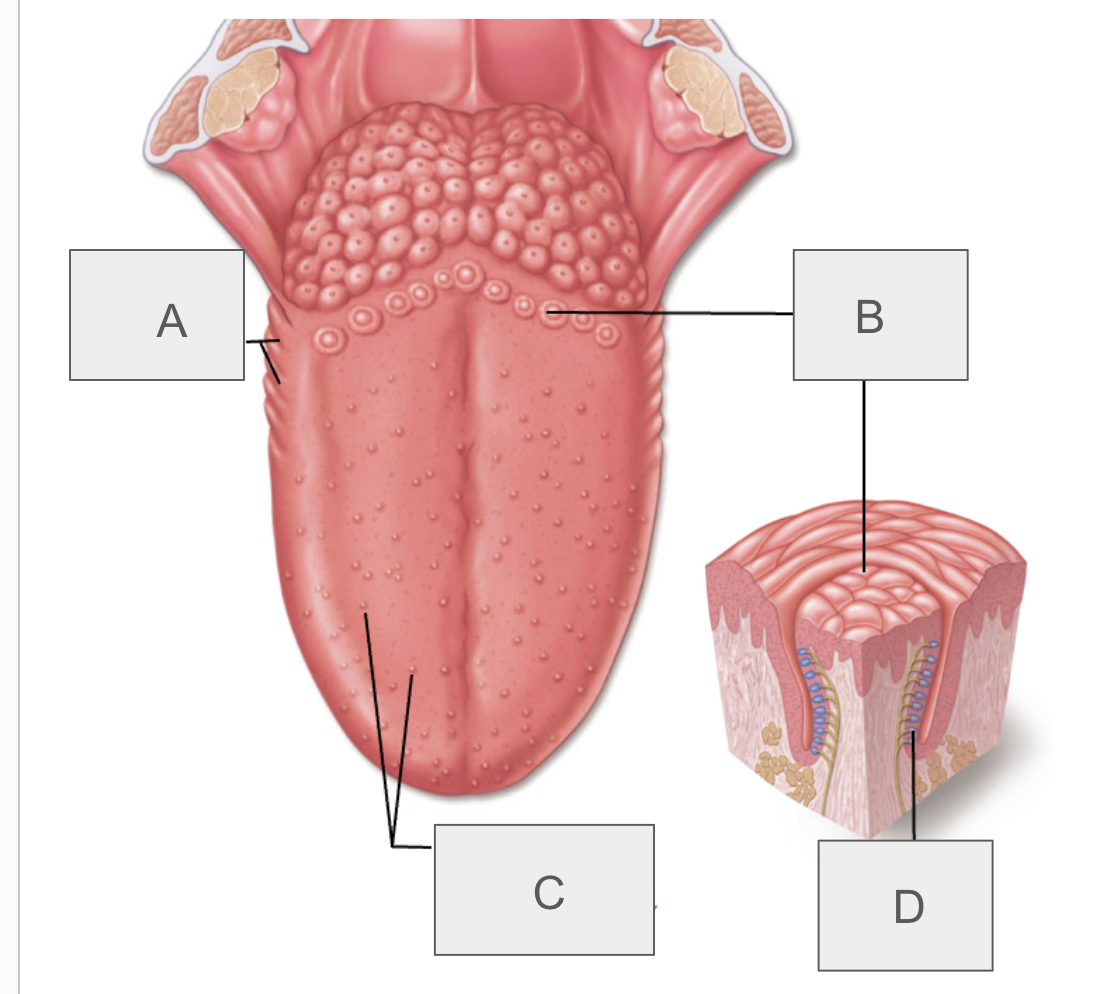
what is A?
foliate papillae
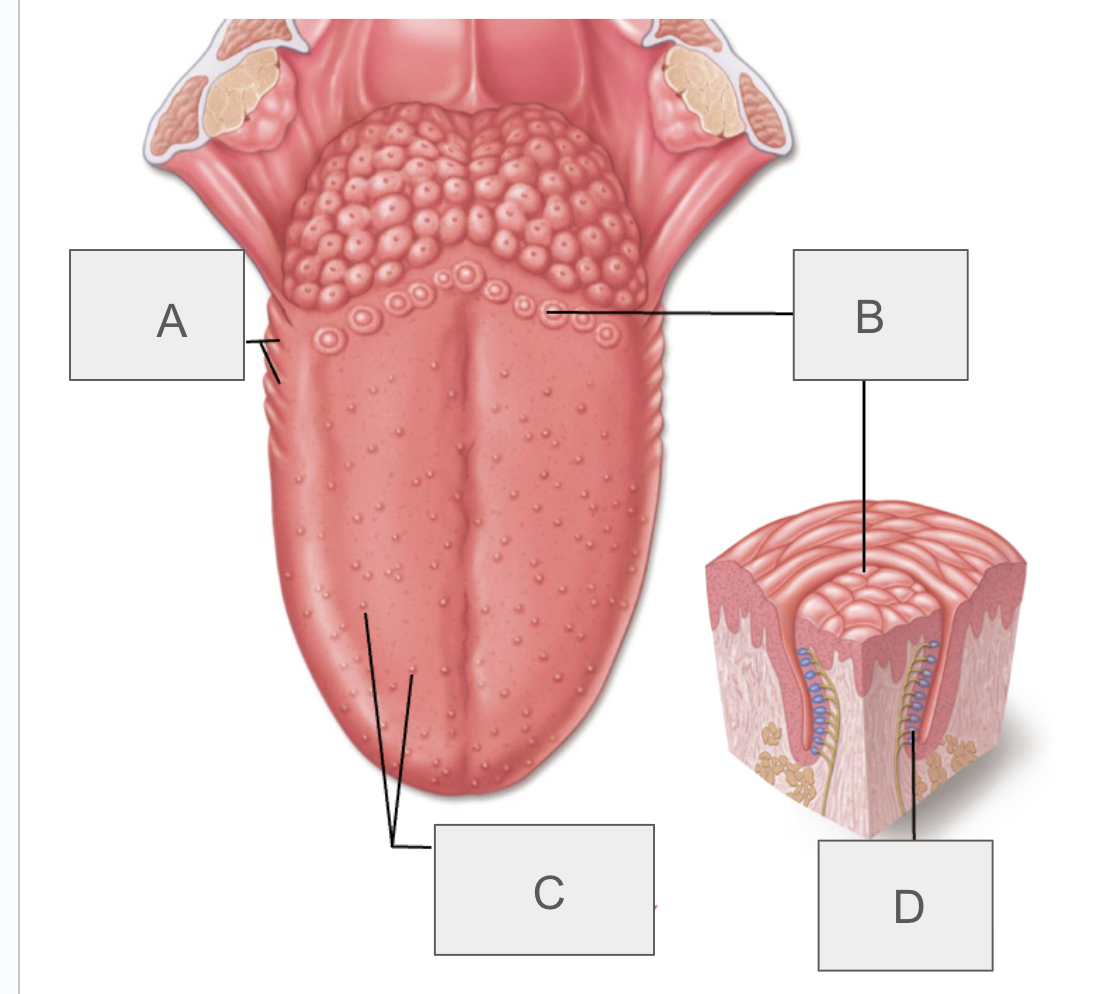
what is B?
vallate papillae
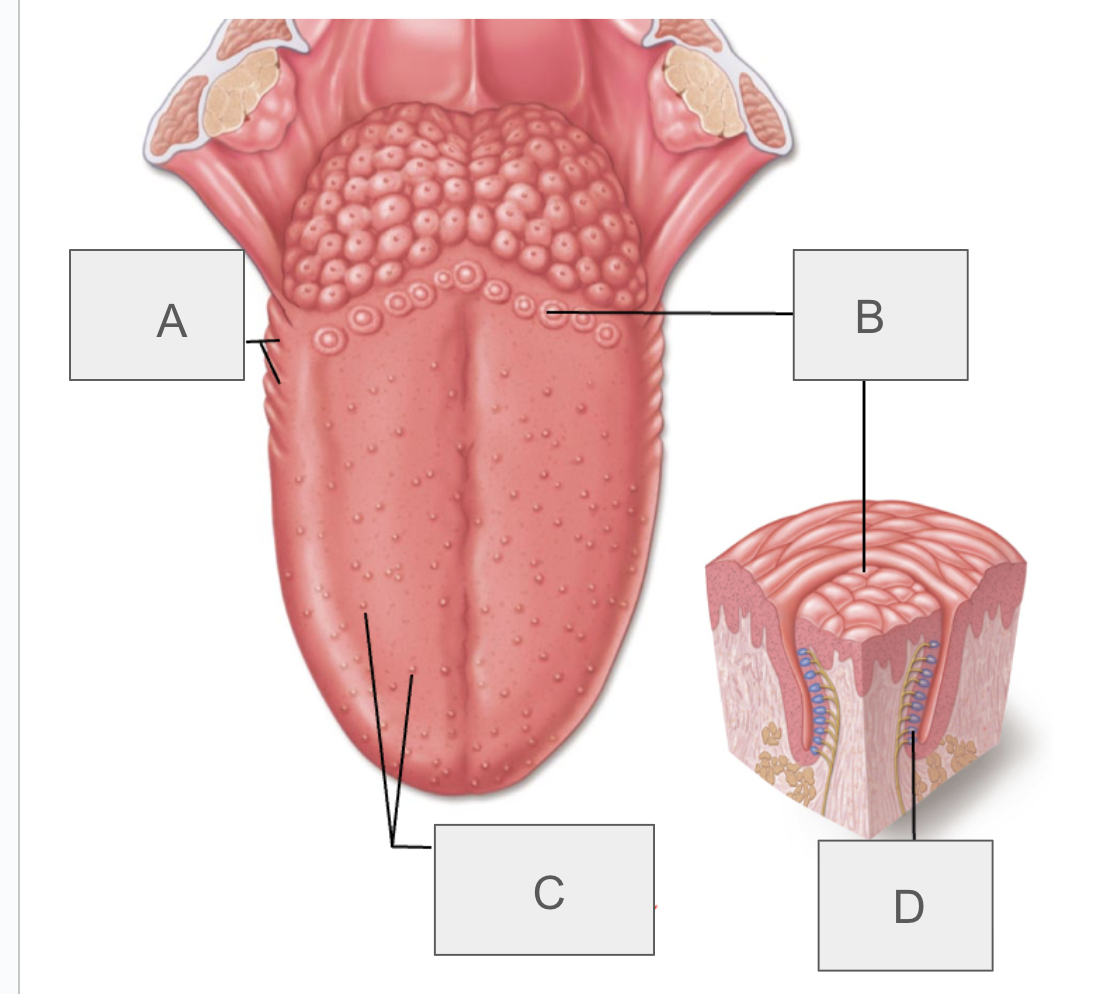
what is C?
fungiform and filiform papillae
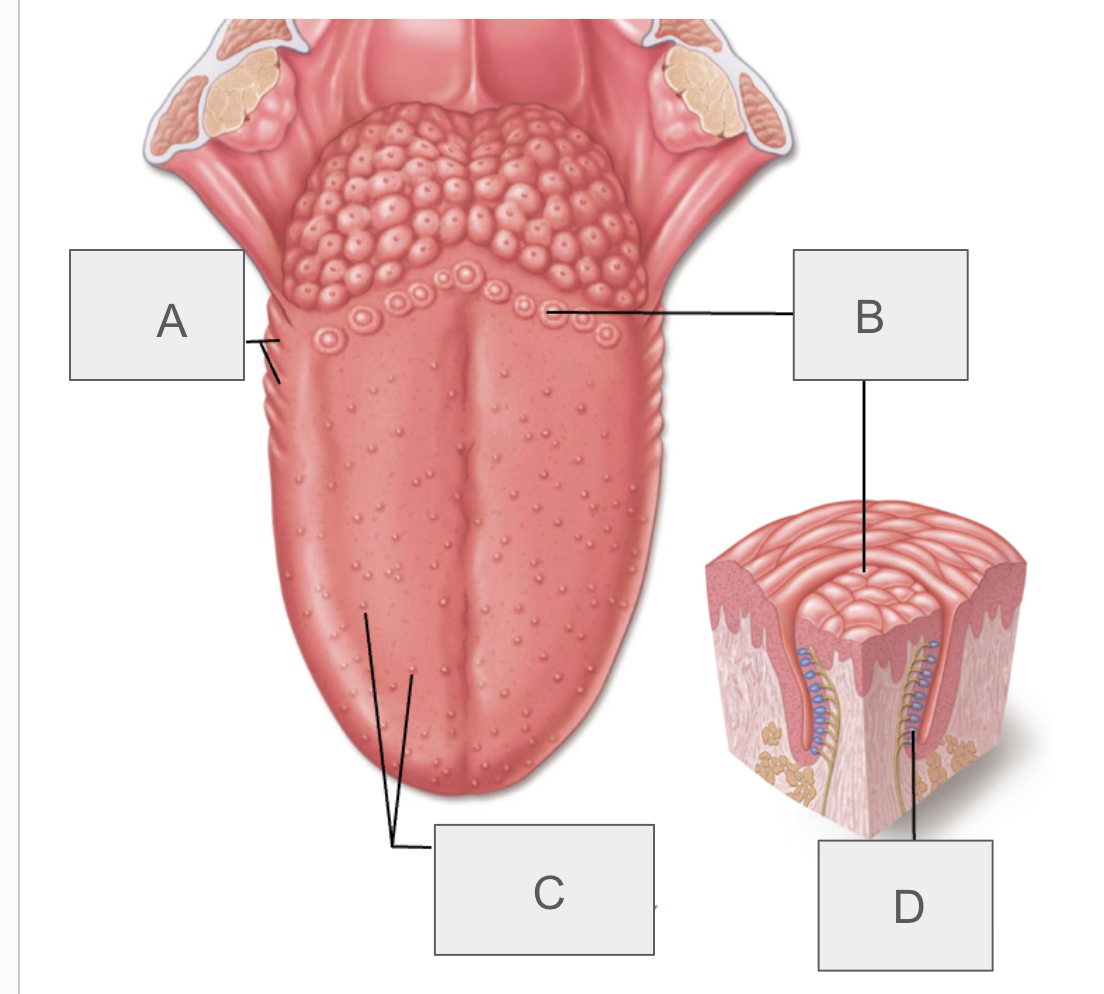
what is D?
taste bud
what are gustatory epithelial cells?
taste receptors
what are gustatory hairs?
microvilli through taste pore
what makes up taste buds?
gustatory epithelial cells, gustatory hairs, basal epithelial cells, supporting cells
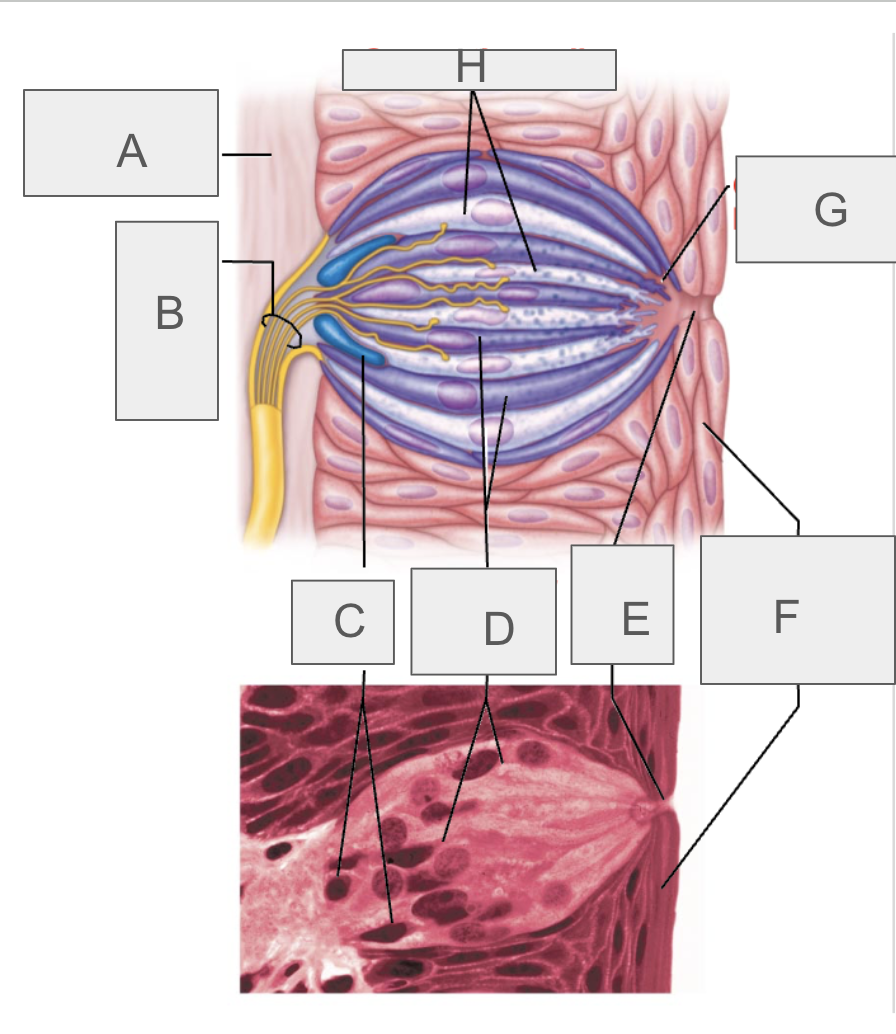
what is A?
connective tissue
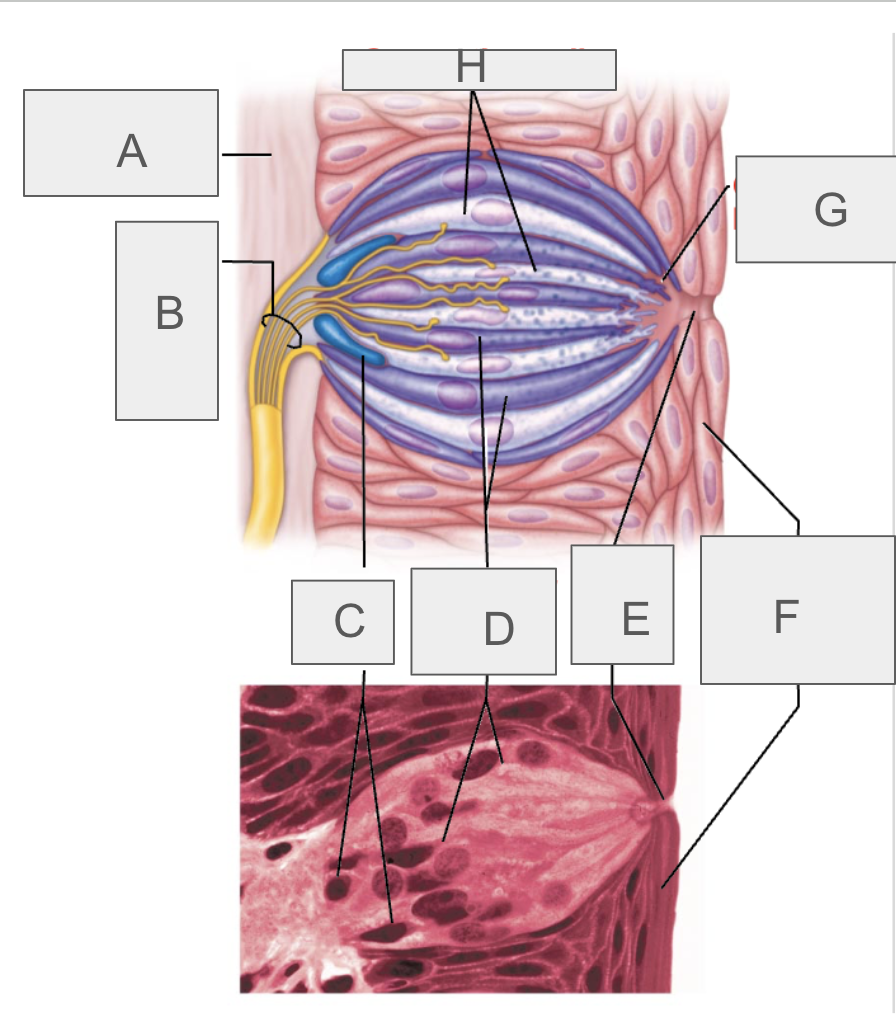
what is B?
taste fibers of cranial nerve
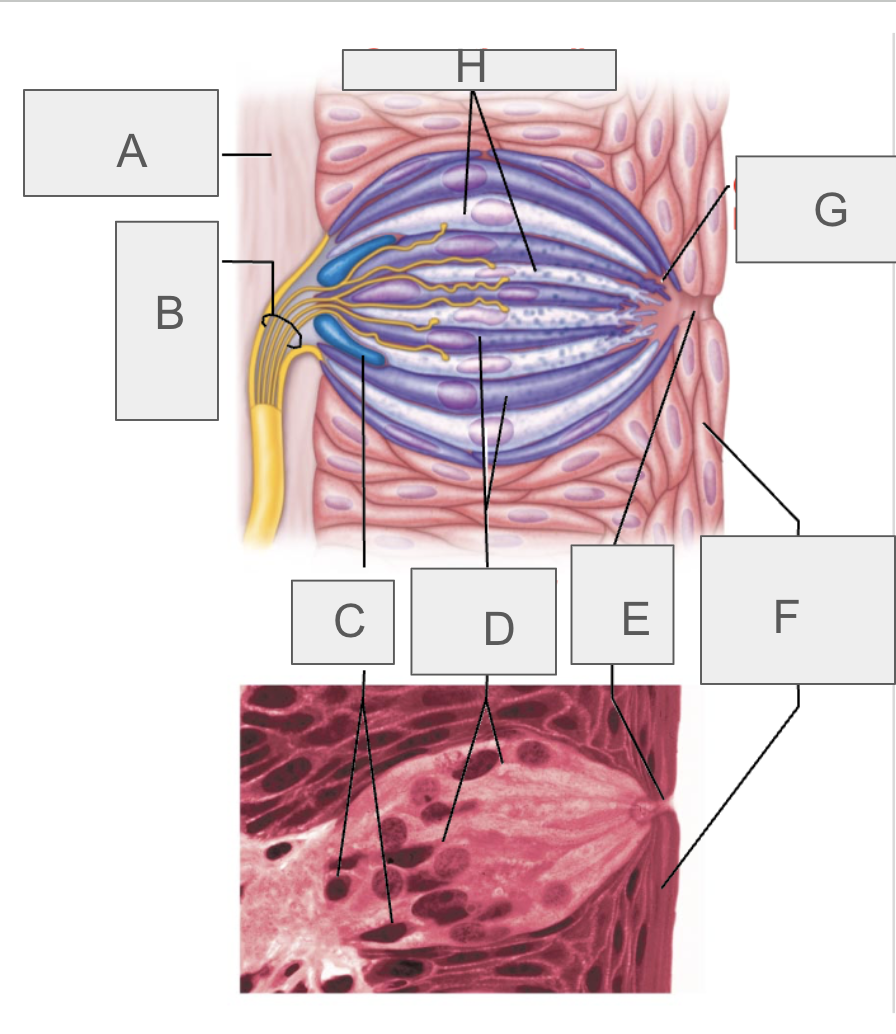
what is C?
basal cells
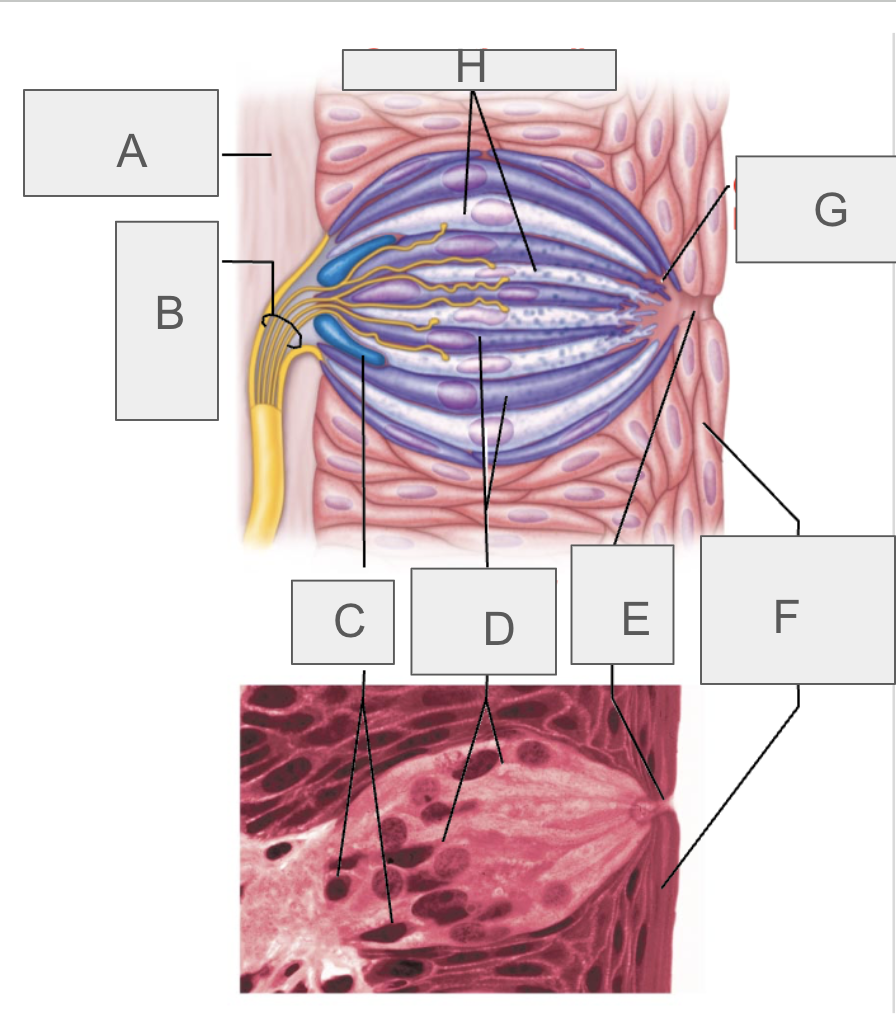
what is D?
gustatory epithelial cells
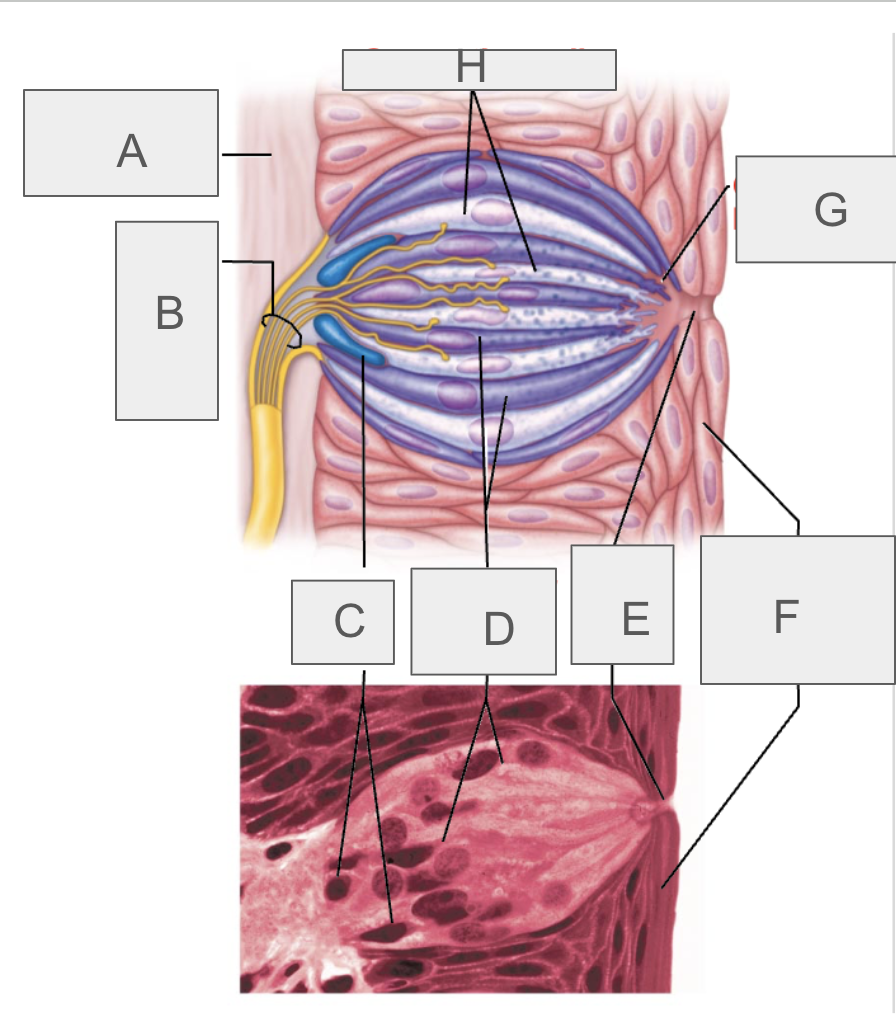
what is E?
taste pore
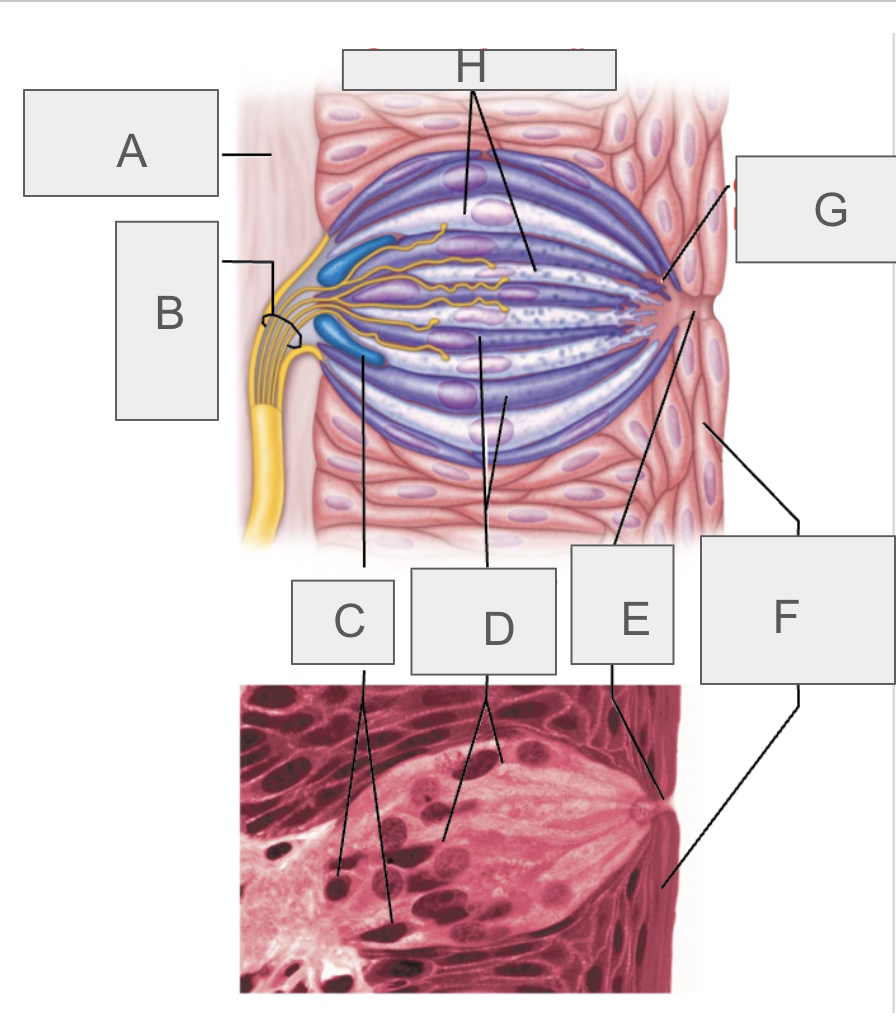
what is F?
stratified squamous epithelium of tongue
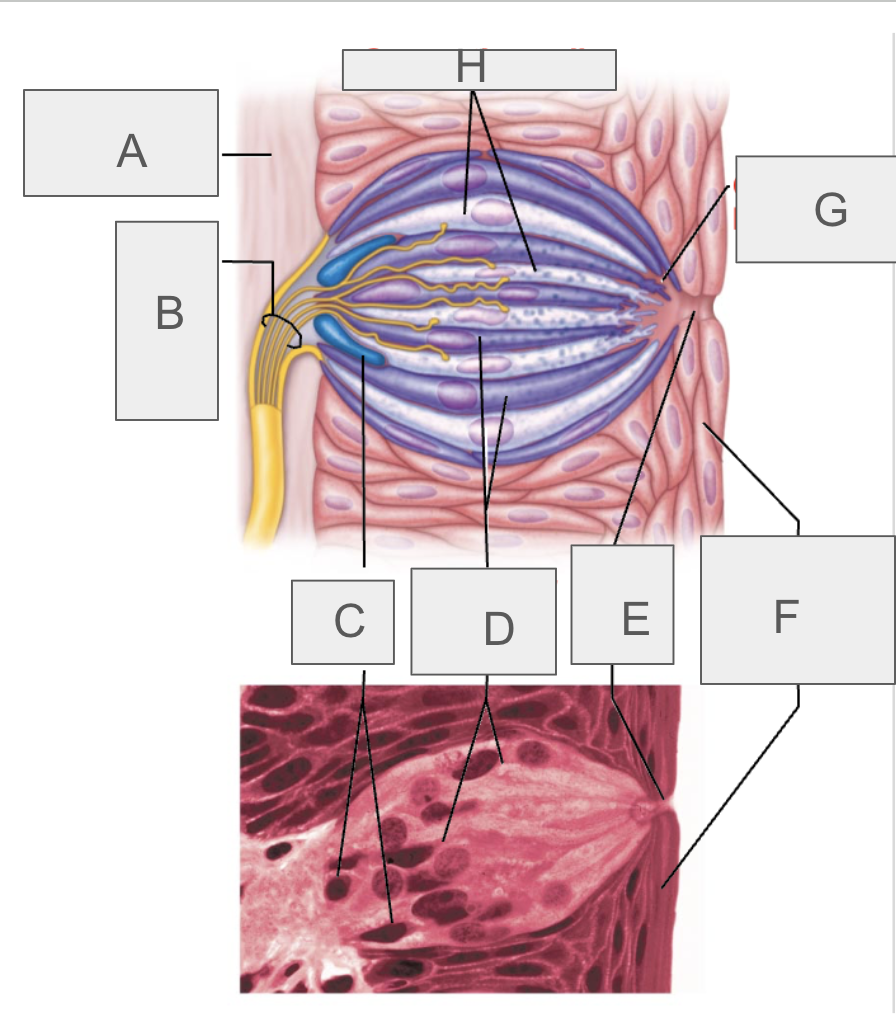
what is G?
gustatory hair
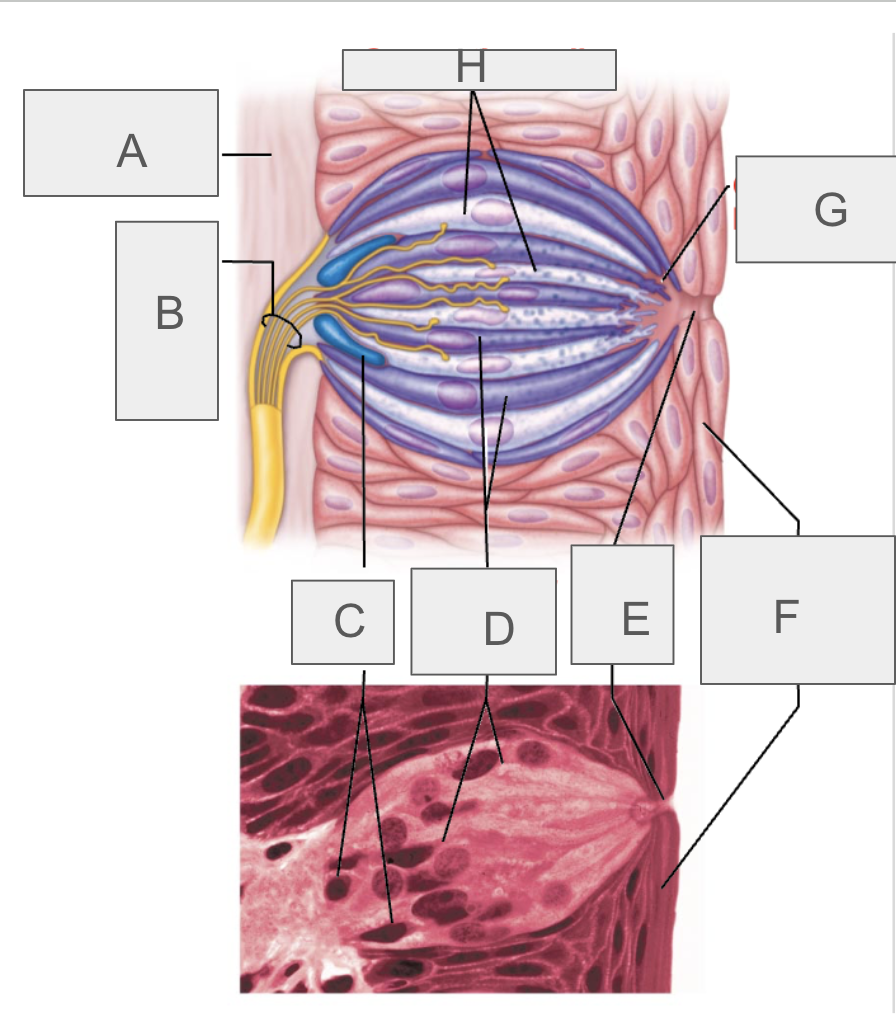
what is H?
supporting cells
what are the five basic taste sensations?
sweet, sour, salty, bitter, umami
what makes things sour?
H+ ions in solution
what makes things salty?
metal ions (inorganic salts)
what makes things bitter?
nitrogen compounds
what makes something umami?
amino acids
what is the first step in taste transduction?
chemicals in food dissolve in saliva
what happens in taste transduction after chemicals in food dissolve in saliva?
chemicals come in contact with gustatory hairs through taste pores
what happens in taste transduction after chemicals come in contact with gustatory hairs through taste pores?
chemicals bind to receptor on hair cells
what happens in taste transduction after chemicals bind to receptors on hair cells?
cation channels open
what happens in taste transduction after cation channels open?
neurotransmitters initiate a graded potential in sensory neurons associated with receptor cells
what does taste trigger?
reflexes involved in digestion
what does taste increase?
secretion of saliva into mouth, and gastric juice into stomach
what are the protective reactions of taste?
gagging, reflexive vomitting
what sense is heavily associated with taste?
smell (olfaction)
what type of receptors influence taste?
thermoreceptors, mechanoreceptors, and nociceptors
what cranial nerves carry impulses from taste buds to the solitary nucleus of medulla?
Facial VII, Glossopharyngeal IX, and Vagus X
where is the gustatory cortex found?
in the insula
what allows for the emotional appreciation of taste?
hypothalamus and limbic system
describe the adaptation and thresholds for gustation
rapid adaptation, variation in thresholds
what are the thresholds in order of lowest to highest in gustation?
bitter, sour and umami, sweet and salty