Chapter 29: Seedless Plants
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
82 Terms
What is the order of the evolution of land plants?
Green algae --> charophytes --> land plants
What is the link between green algae and land plants?
Charophytes
What issues did plants have to overcome on land?
Water loss and protection from the sun
Who helped colonize the land?
Fungi
What are the two major clades of green algae?
Charophytes and Chlorophytes
What are Charophyte's?
It is green algae that never made it to land
What are Chlorophytes?
Sister to all land plants
Describe land plants.
- Have multicellular haploid and diploid stages
- Trend towards more diploid embryo protection
- Trend toward smaller haploid stage
What adaptation protected plants from desiccation?
A waxy stomata and cuticle
What does stomata do?
Stomata opens and closes to limit water loss
What does an closed stomata mean?
Temperatures are too hot
How do plants move water through the plant?
Through tracheids
What type of plants have tracheids?
Tracheophytes
What are the two types of transport tissues in vascular plants?
Xylem and Phloem
What does the Xylem do?
Transports water and dissolved minerals upward from the roots
What does the Phloem do?
Transports sucrose(food) and hormones throughout the plant.
The shift from a _________ haploid generation to a _________ diploid generation:
Dominant
Are humans diplontic or haplontic?
diplontic
What is the multicellular diploid stage called?
Sporophite
How many haploid spores are after the diploid mother cells undergo meiosis?
4 haploid spores
What is the multicellular haploid stage called?
Gametophyte
How do spores divide in the haploid stage?
Mitosis
When gametes fuse during fertilization, a(n) ________ is produced.
Zygote
Haplodiplontic Life Cycle
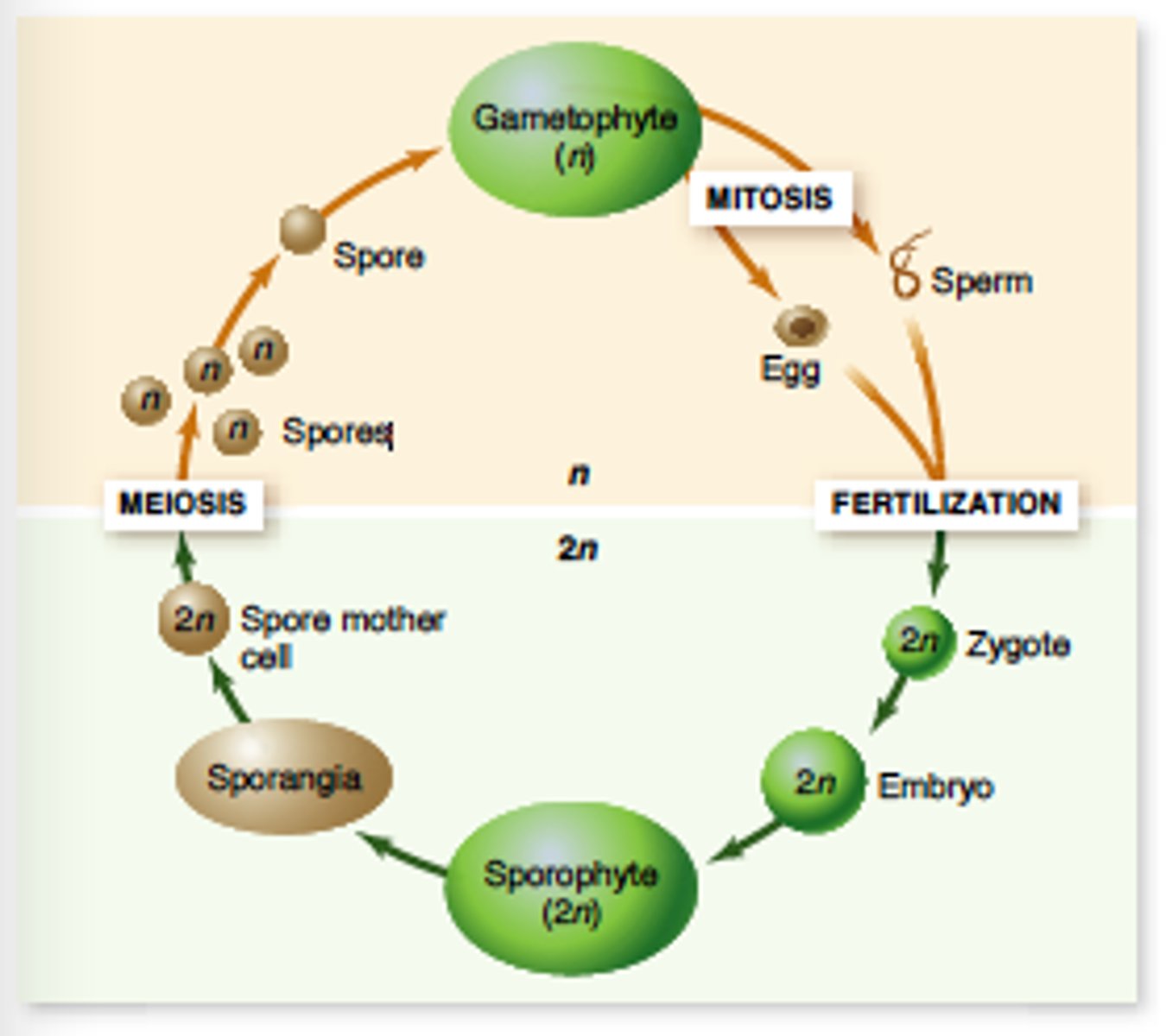
All land plants Haplodiplontic? True or False.
True
What are two examples of haplodiplontic land plants?
Moss and Angiosperm
What is an angiosperm?
Any plant that flowers
Describe Moss.
- Large gametophyte
- Small, dependent sporophyte
Describe Angiosperm.
- Small, dependent gametophyte
- Large sporophyte
Who are the closest living descendants of land plants?
Bryophytes
Why are bryophytes call nontracheophytes?
They lack tracheids
What type of relationship do bryophytes have that enhances water uptake?
Mycrorrhizial relationship. (Symbiotic relationship between fungi and plants)
Bryophytes have three clades with approximately _________species.
16,000
What are the three clades of bryophytes?
- Liverworts
- Mosses
- Hornworts
Who dominates in Bryophytes?
Gametophytes
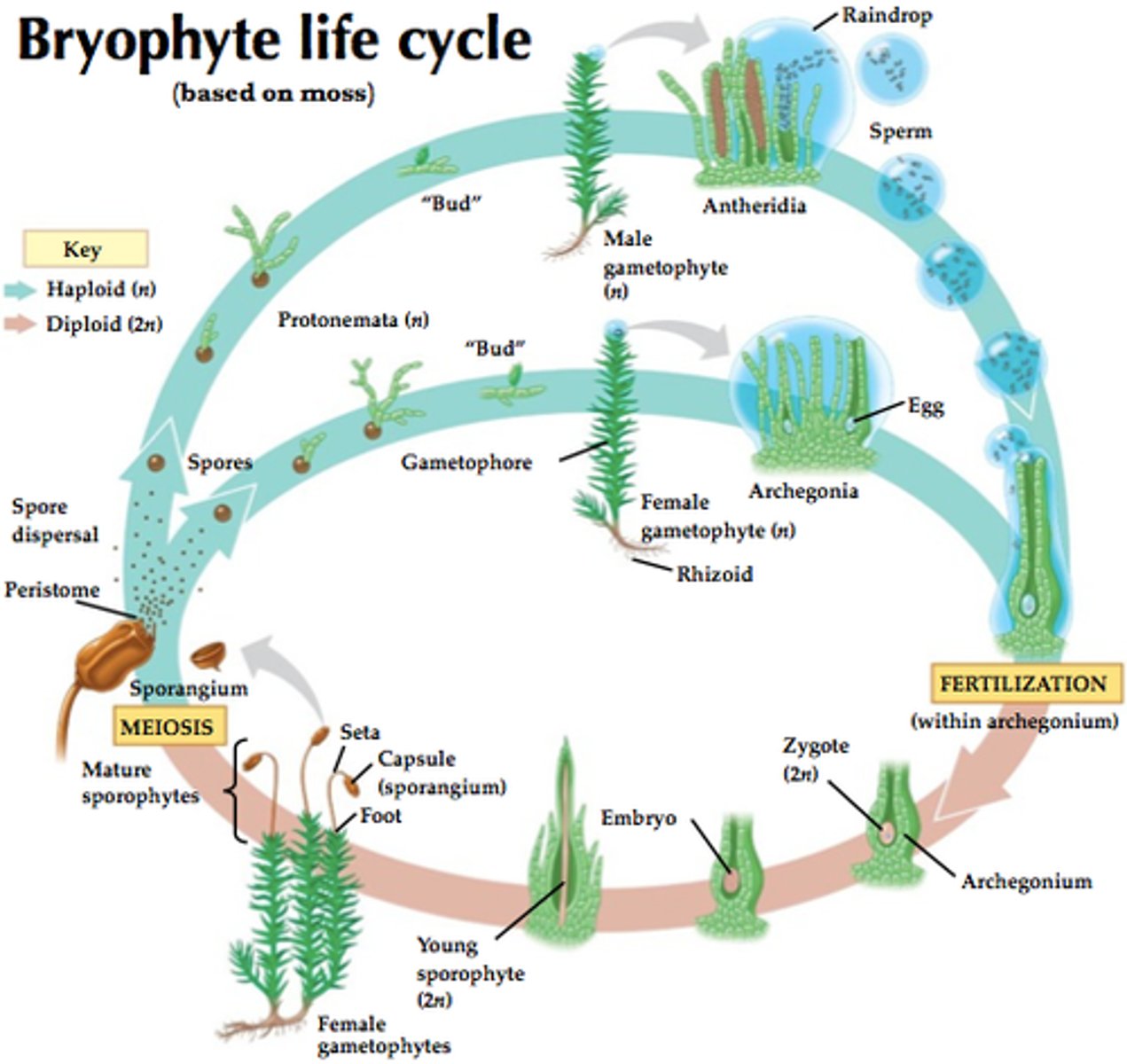
What are the characteristic of the gametophyte and sporophyte of a Bryophyte plant?
Gametophyte - conspicuous and photosynthetic
Sporophytes - small and dependent
Describe Liverworts.
Have flattened gametophytes with liverlike lobes
- 80% look like mosses
Form gametangia in umbrella-shaped structures
Also undergo asexual reproduction
Describe Mosses.
Gametophytes consist of small, leaflike structures, areound a stem-like axis.
- Not true leaves - no vascular tissue
Anchored to substrate by rhizoids
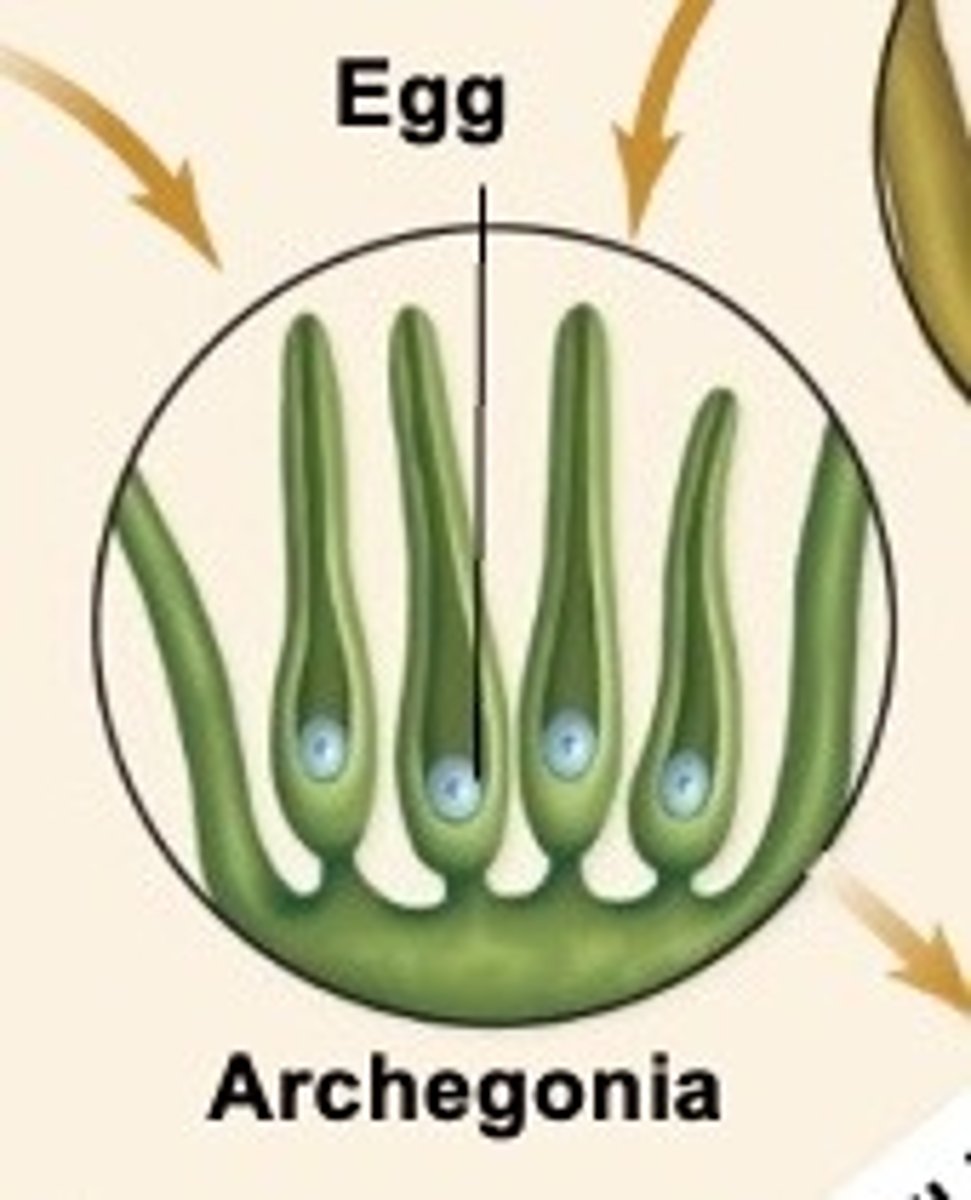
What is a female gametangia called?
Archegonia - contains the egg
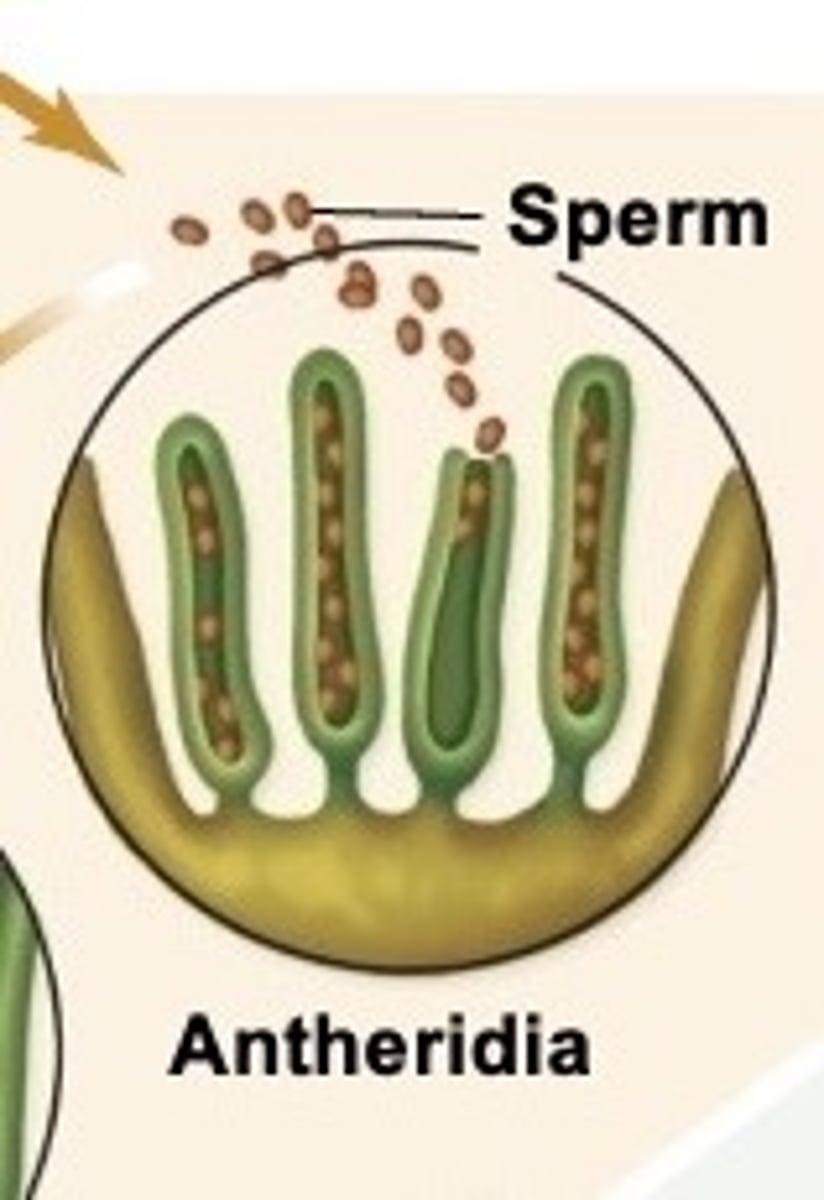
What is a male gametangia called?
Antheridia - contains the sperm
Life Cycle of Moss
Describe Hornworts.
Origin is puzzling - no fossils until Cretaceous
Sporophyte is photosynthetic
Sporophyte embedded in embedded in gametophyte tissue
Cells have a single large chloroplast
What was the first vascular land plant called and when did it appear?
Cooksonia, which appeared about 420 MYA. It had no roots or leaves & was homosporus (only produced one type of spore)
What are tracheophytes?
Vascular plants
What are the three clades of tracheophytes?
- Lycophytes
- Ptetrophytes
- Seed Plants
Describe Stems.
- Early fossils reveal stems but no roots or leaves
- Lack of roots limited early tracheophytes
Describe Roots.
-provide transport and support
-lycophytes diverged before true roots appeared
Describe Leaves.
- Increase surface area for photosynthesis
- Evolved twice
What is a Lycophyll?
A singular vein
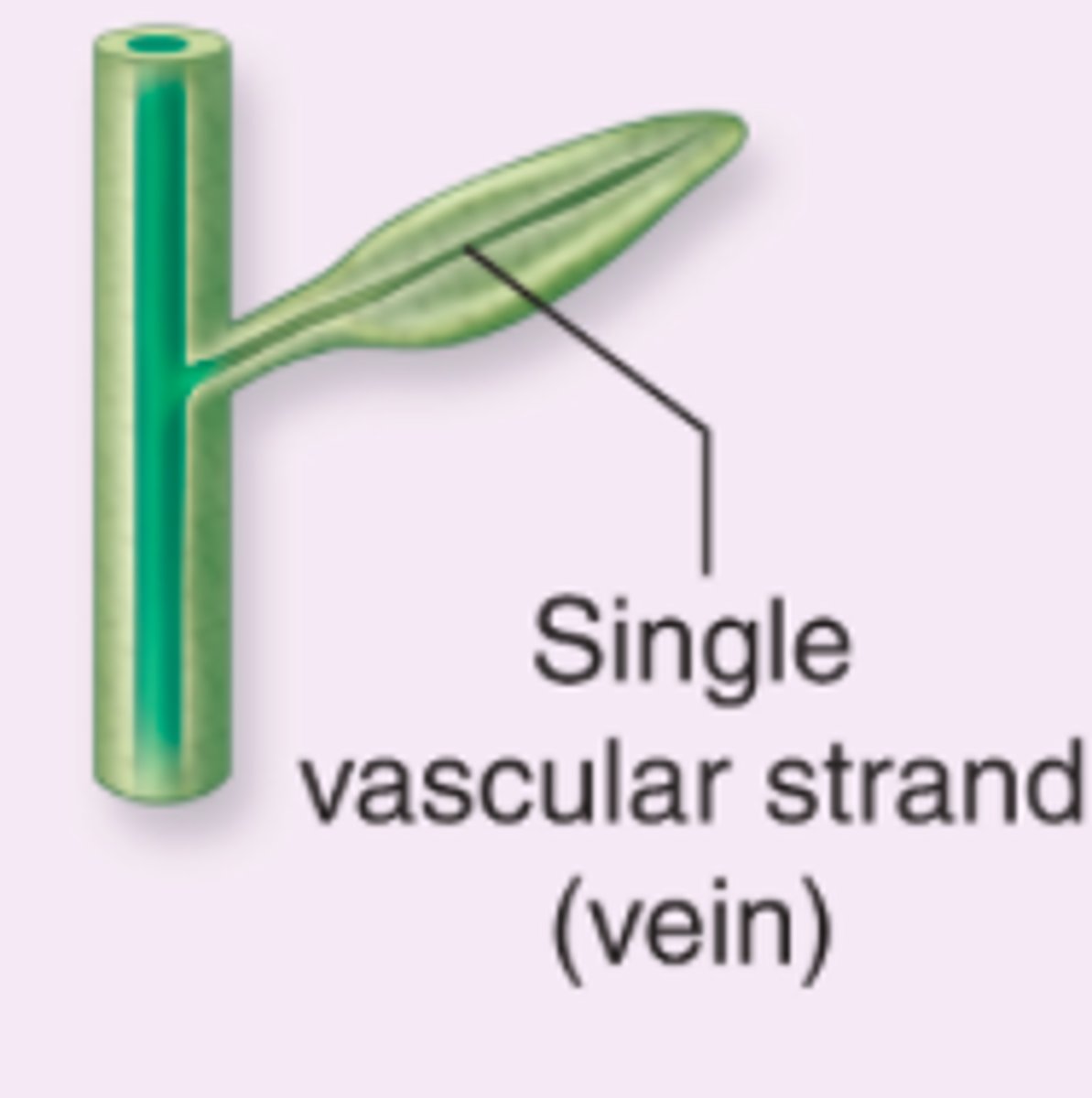
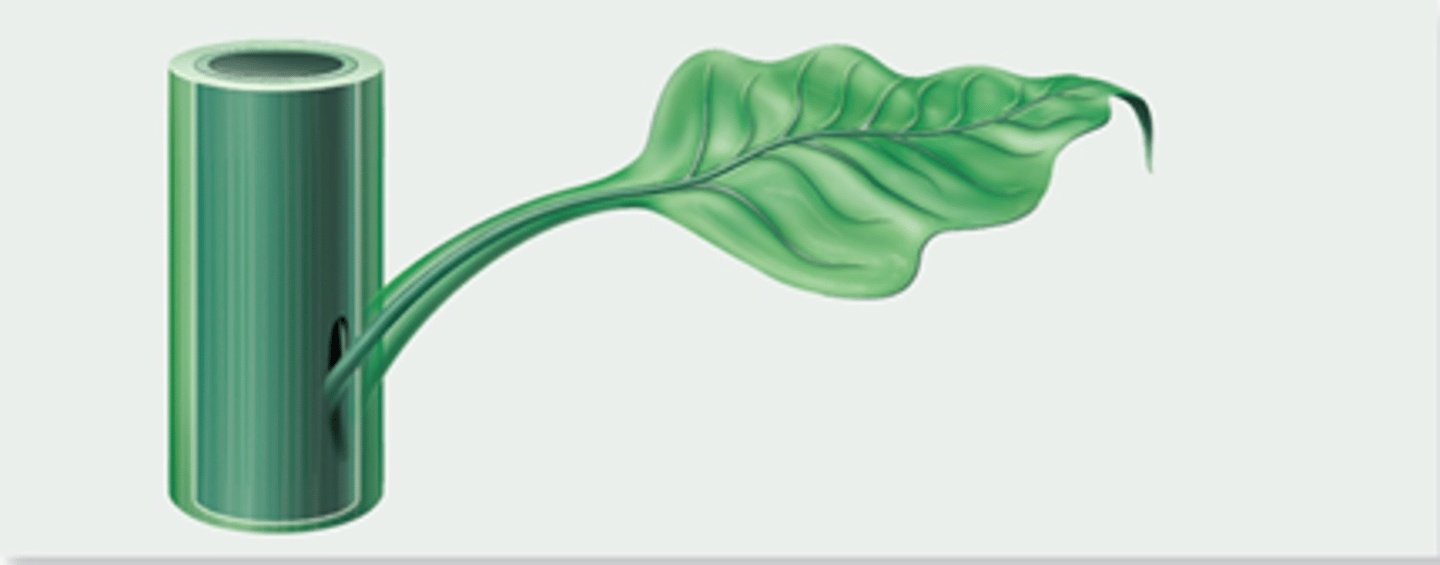
What is a Euphyll?
A branched vein

Describe a Seed?
- Highly resistant
- Contain food supply for young plant
- Lycophytes and Ptetrophytes do not have seeds
- Fruits in the flowering plants(angiosperms) add a layer of protection to seeds and attract animals that assist in seed dispersal, expanding potential range of the species
Describe Lycophytes.
- Worldwide distribution
- Lack seeds
- Superficially resemble true mosses
- Sporophyte dominant
Describe Ptetrophytes.
Phylogenetic relationships among ferns and their relatives is still being sorted out
Common ancestor gave rise to two clades
- whisk ferns and horsetails
All form antheridia and archegonia
All require free water for flagellated sperm
Describe whisk ferns.
Found in tropics
Sporophyte consists of evenly forking green stems without true leaves or roots
Some gametophytes develope elements of vascular tissue
- only one known to do so
Describe Horsetails.
All 15 living species are homosporous
Constitute a single genus, Equisetum
Sporophyte consists of ribbed, jointed photosynthetic stems that arise from branching rhizomes with roots at nodes
Silica deposits in cells -scouring rush
What is the most abundant group of seedless vascular plants?
Ferns with about 11,000 species
Where did coal form and about how many years ago?
Formed from forests about 300 MYA
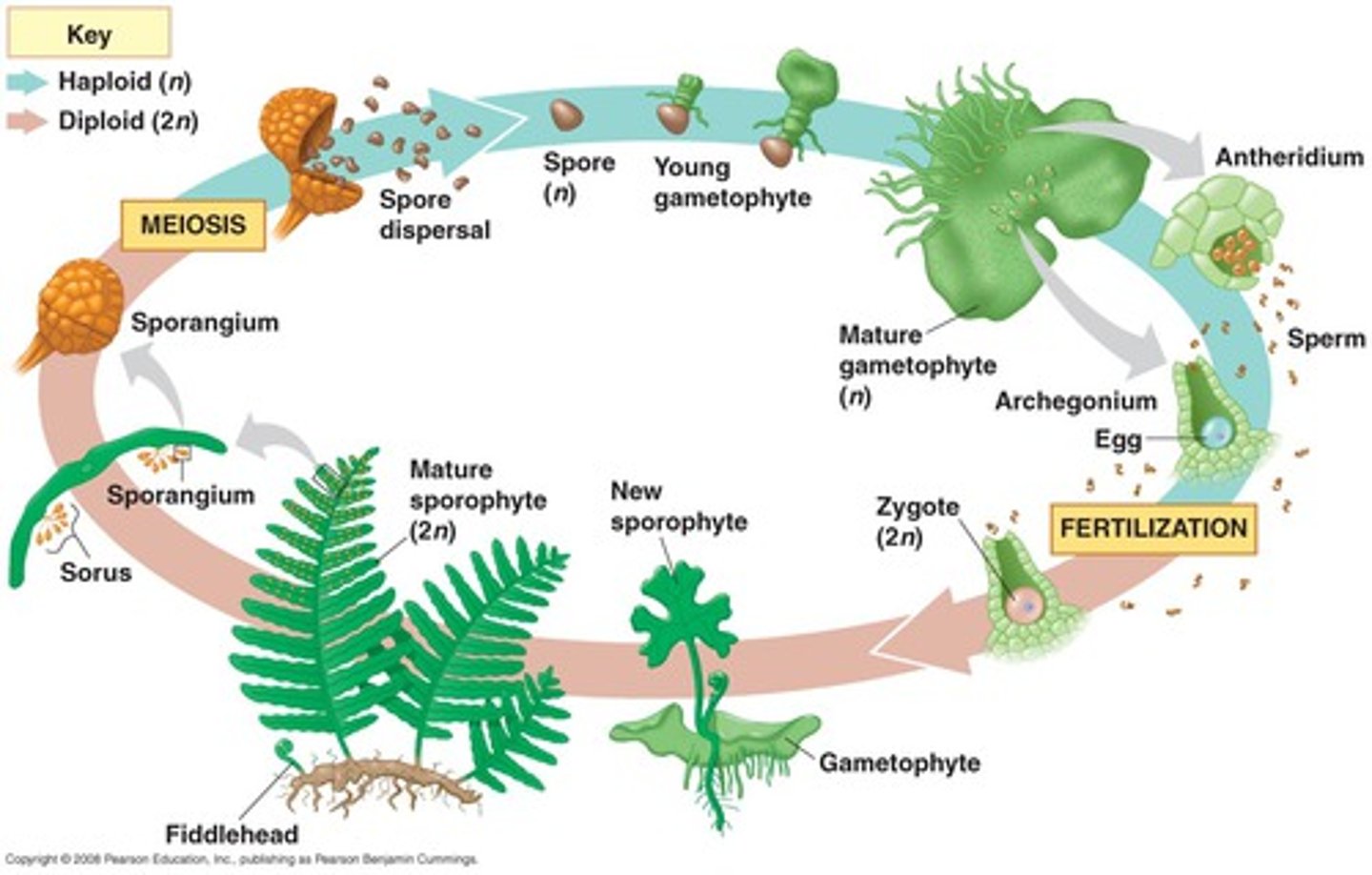
Describe the Sporophyte and gametophyte of Ferns.
Gametophyte - conspicuous and photosynthetic
Sporophytes - small and dependent (FIX)
How is a ferns life cycle different from moss?
- Much greater development, independence, and dominance of the ferns sporophyte.
- Gameophyte lacks vascular tissue
Life cycle of a fern
True or false. Sporophytes do not have rhizomes.
Fasle
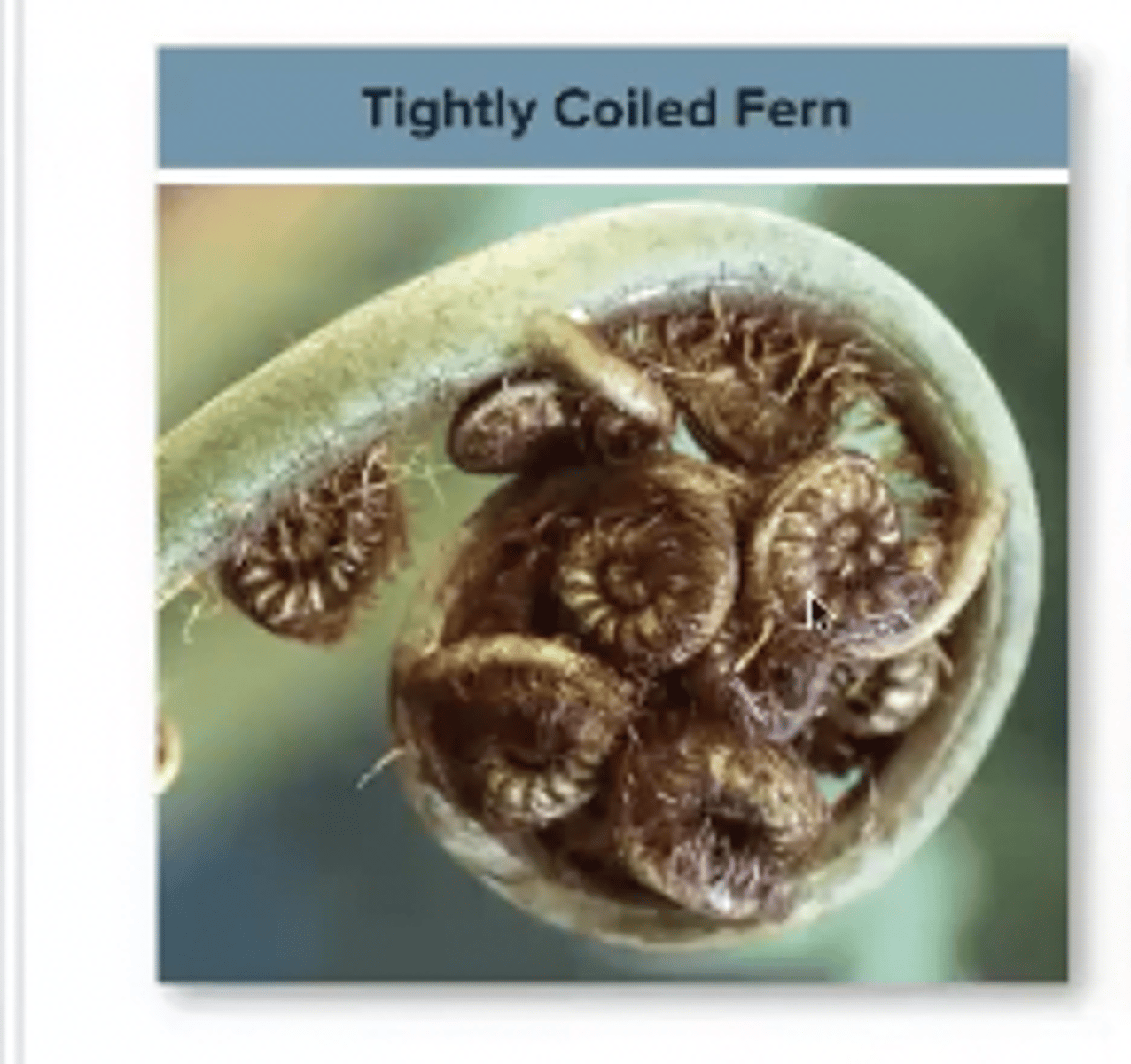
What are fiddleheads?
Fronds(leaves) that are tightly coiled that develop at the tip of the rhizome.
Diploid spore mother cells in sporangia produce haploid spores by meiosis. True or False.
True
Distinctive sporangia in clusters on the back of fronds are clalled?
sori
Today's land plants most likely evolved from a form of _______ called a charophyte.
Green algae
All of the following phyla belong to the Gymnospers except:
A. Cyadophyta
B. Gnetophyta
C. Coniferophyta
D. Ginkophyta
E. Lycophyta
E
Non-vascular plants...
A. Lack roots, stems, and leaves
B. Are tall plants
C. Produce pollen
A
Kingdom Plantae is a clade comprised of bryophytes and what other group?
Tracheophytes
The substance in horsetail stems that makes them suitable for scouring is...
silica
When spores are released from the underside of the fern frond, they fall to the ground where they germinate, growing into:
Haploid Gametophytes
Which of the following is not a characteristic of all plants?
A. They carry out photosynthesis
B. They are eukaryotes
C. They are heterotrophs
D. They are autotrophs
E. They are multicellular organisms
C
Which of the following is not true of fronds?
A. They are synonymous with leaves
B. They number among the largest leaves on the planet
C. They represent the gametophyte generation of ferns
D. They produce sori on their undersides
E. New fronds grow from rhizomes
B
When you see a fern, the large plant you are looking at is the:
A. gametophyte
B. antheridium
C. endosperm
D. sporophyte
E. rhizoid
D
Mosses produce sperm during the _______ stage.
gametophyte
A ______ is an example of a nonvascular plant
A. Maiden hair-fern
B. Liverwort
C. Red Pine
D. Rose
B
The so-called fern allies [relatives of ferns] include several divisions of plants related to ferns. Which of the following belongs to this group?
A. Hornworts
B. Liverworts
C. Club Mosses
D. Lichens
E. Tree Ferns
C
What is the dominant generation in ferns?
Sporophyte
What seedless vascular plant grows in the RGV?
Fern
What does a seed contain?
Embryo, food supply, protective coat
What bryophyte grows in the RGV?
Moss
What is a haplodiplontic life cycle?
Multicellular diploid and haploid phases
What was the trend for the dominant generation in plants?
For sporphytes to dominate