Physical Science Wave Study Guide
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Concept 1: Nature and Properties of Waves
Definitions:
Wave
a rhythmic disturbance that transfers energy through matter or space
Medium
matter through which a wave travels through, can be solid liquid, or gas
Period
the amount of time it takes one wavelength to pass a point
Frequency
the number of waves that pass a given point in one second
Wavelength
the distance between one point on a wave and the nearest point just like it
Amplitude
the amount of energy carried by a wave
Differentiate between electromagnetic and mechanical waves. Include examples of each.
Mechanical waves travel through a medium, electromagnetic waves travel through electric and magnetic fields. An example of mechanical waves are sound waves and water waves, and an example for electromagnetic waves are microwaves and radio waves.
Differentiate between transverse and longitudinal waves.
The main difference between transverse and longitudinal waves is the direction in which the particles vibrate compared to the direction the energy travels
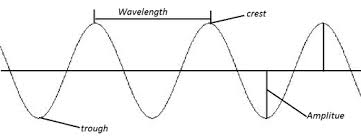
Draw a transverse wave and label a crest, trough, wavelength, and amplitude.
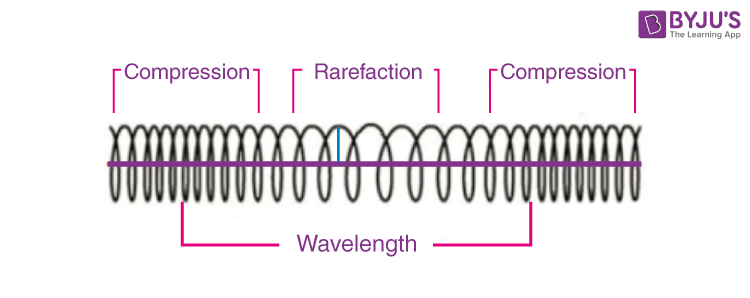
Draw a longitudinal wave and label a compression, rarefaction, and wavelength.
Define amplitude and how it looks different on a transverse and a longitudinal wave.
Amplitude on a transverse wave is perpendicular while amplitude on longitudinal waves are parallel
Explain the two factors that affect wave speed and how these specifically affect sound waves and light waves differently.
Wave speed is primarily affected by the medium's properties for sound, making them faster in solids than gases, and by the medium's refractive index for light, slowing them down in denser materials like glass or water compared to a vacuum
Explain the relationship between loudness, intensity, amplitude, and pitch in relation to sound waves.
amplitude determines Intensity, which our ears perceive as loudness, while frequency determines pitch
A wave has a frequency of 3.2 Hz with a wavelength of 10 m. What is the velocity of the wave?
32 m/s
A wave travels 1.5 m/s with a frequency of 0.45 Hz. What is the wavelength of the wave?
3.33 m
The period of a sound wave is 0.002 seconds. The speed of sound is 344 m/s. Find the frequency and wavelength of the sound wave.
500 Hz and .688 m
Concept 2: Behaviors of Waves
Definitions:
Reflection
when a wave strikes an object and bounces off of it
Refraction
the bending of waves caused by a change in its speed as it moves from one medium through another
Diffraction
when an object causes a wave to change direction and bend around it
Absorption
when a wave strikes an object and goes into it (is absorbed)
Interference
when two or more waves combine to form a new wave
Resonance
process where an object is made to vibrate at its natural frequency by absorbing the energy of another object that is vibrating at the same frequency
List a real-world example of each of the six behaviors of waves listed above.
reflection like an echo, refraction like seeing a straw or pencil bend in water, diffraction like sound spreading around a corner, absorption is like a black shirt getting hot on a sunny day, interference can be noise cancelling headphones, and resonance can be pushing someone on a swing.
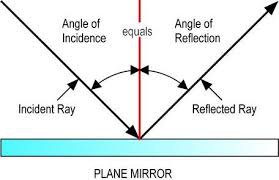
Explain the Law of Reflection. Include a picture of it with the incident ray, reflected ray, angle of incidence, angle of reflection, and normal labeled.
the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection
Explain how a prism works.
by bending light as it passes through its angled, transparent surfaces, using the principle that different colors of light slow down and bend by different amounts, causing white light to split into a spectrum
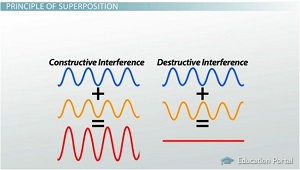
Draw a picture to show the difference between constructive and destructive interference.
Concept 3: Electromagnetic Spectrum
Definitions:
Electromagnetic waves
electric and magnetic waves released by a vibrating electric charge, capable of transferring energy through a vacuum
Electromagnetic Spectrum
the entire range of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation
Write out the electromagnetic spectrum and label the trend of wavelength, frequency, and energy along the spectrum.
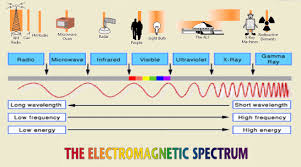
List two uses for each type of wave on the electromagnetic spectrum.
Radio Waves and MRI scans
What is the mnemonic device that we learned in class for the electromagnetic spectrum?
R.aging M.artians I.nvaded V.enus U.sing X.-ray G.uns