Three-Dimensional Digital Radiography
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT)
An imaging technique which uses a cone-shaped x-ray beam to acquire information and present it in three dimensions.
DICOM data
Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine. (software)
Field of View
The area captured when performing imaging procedures.
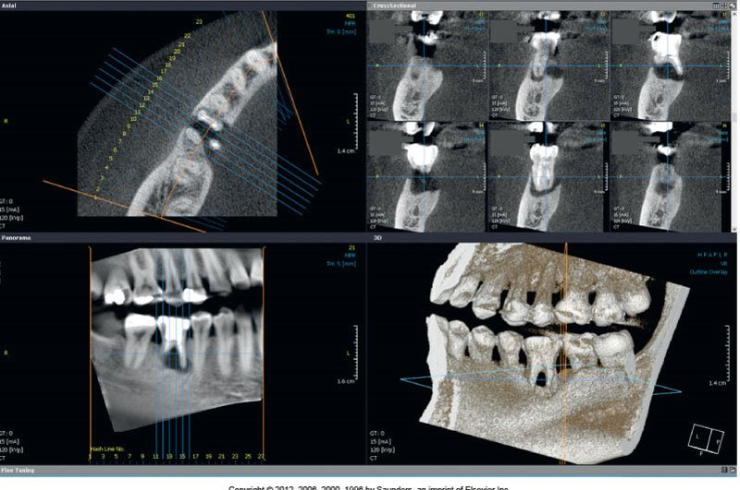
Multiplanar reconstruction (MPR)
the reconstruction of data in a software system creating three anatomic planes of the body.
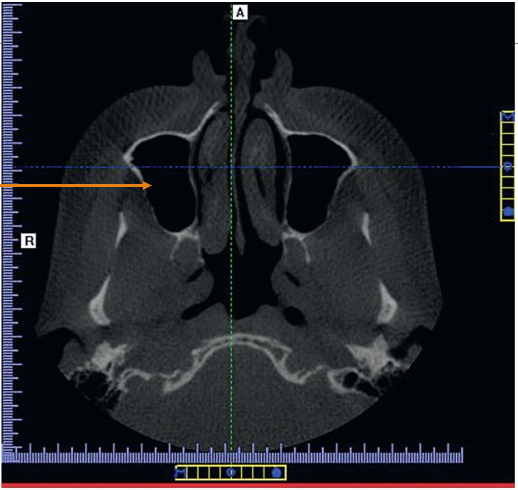
Axial Plane
A horizontal plane that divides the body into superior and inferior parts; runs parallel to the ground.

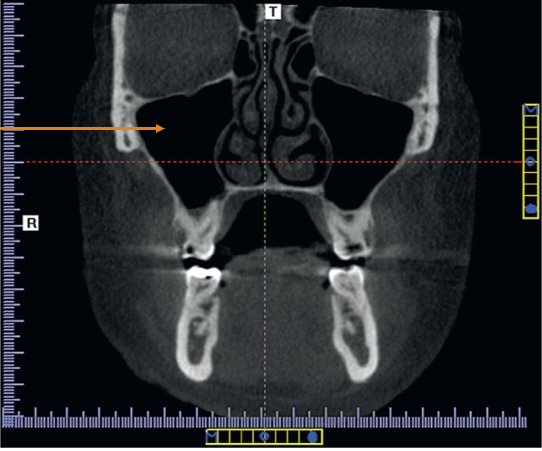
Coronal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into anterior and posterior sides; runs perpendicular to the ground.

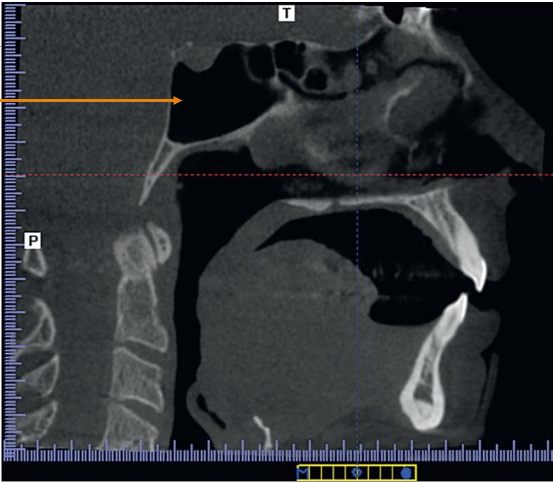
Sagittal Plane
A vertical plane that divides the body into right and left sides; runs perpendicular to the ground.

Contrast Resolution
The number of gray scale colors available for each pixel in the image.
Spatial Resolution
A measure of pixel size in multiplaner reconstruction.
Three-dimensional Volume Rendering
A three-dimensional shape that is created from two-dimensional images.
Voxel
The smallest element of a three-dimensional image; volume element or three-dimensional pixel.
Three-dimensional digital imaging
A method designed to evaluate the oral-maxillofacial complex
Named because it uses a cone-shaped x-ray beam to acquire three-dimensional information
Source of radiation rotates around the head of the patient.
Field of View
The source of radiation and the digital sensor rotate around the patient and acquire multiple images of the field of view.
Manufacturers use a variety of sizes to accommodate the field of view for diagnostic purposes.
CBCT Machine
Comparable in size to a panoramic machine
Patient sits, stands, or is placed in a supine position.
In one rotation, radiation and receptor capture field of view
Computer
Accepts raw data and converts them into stack of planar images.
Technique is completed during the data reconstruction process.
Viewing Software
Allows dental practitioner to view axial, coronal, and sagittal images along with the three-dimensional renderings.
Purpose and Use of Three-dimensional Digital Radiography
Greatly improve interpretation, diagnosis, and treatment planning of dental care
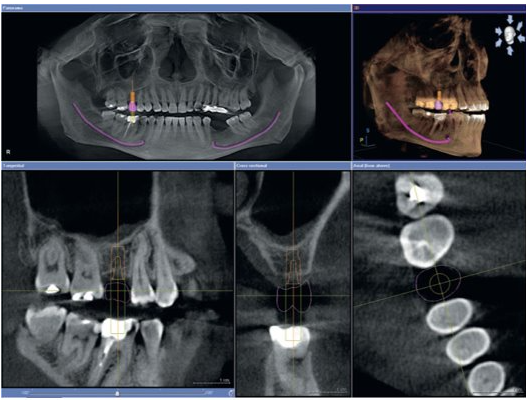
Implant placement
Extraction or exposure of impacted teeth
Definition of anatomic structures
Endodontic assessment
Airway and sinus analysis
Evaluation of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders
Orthodontic evaluation
Pathology evaluation
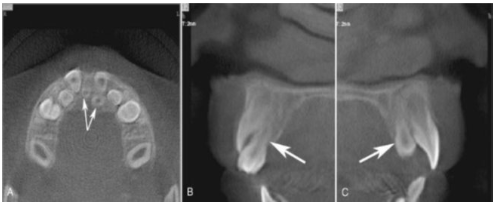
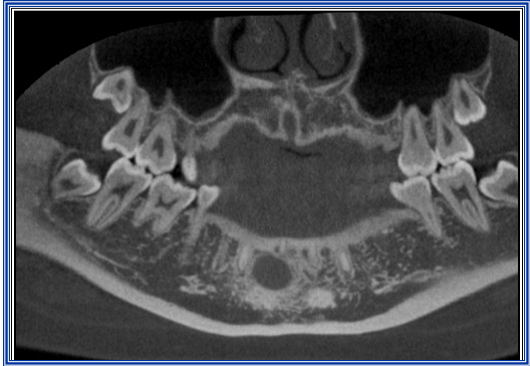
Location of Teeth in Maxilla
Example of how CBCT is used to locate unerupted teeth in the maxillary arch.
Implant Placement
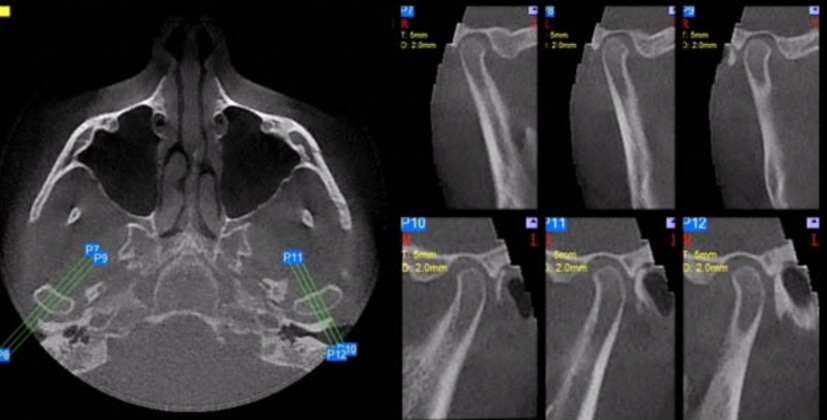
TMJ Projections
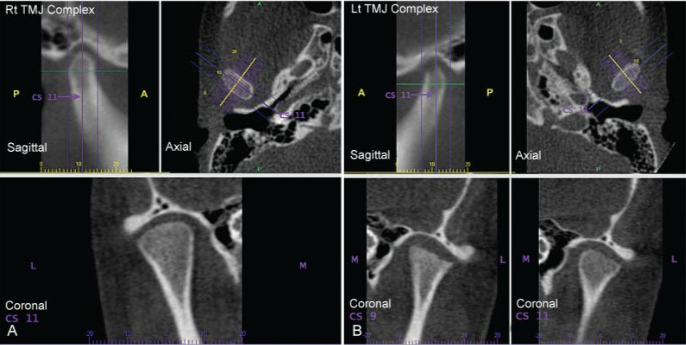
TMJ – Erosion of Left Condyle
Panoramic Style View – Lesion in Bone
Central-Ossifying Fibroma (Pan)
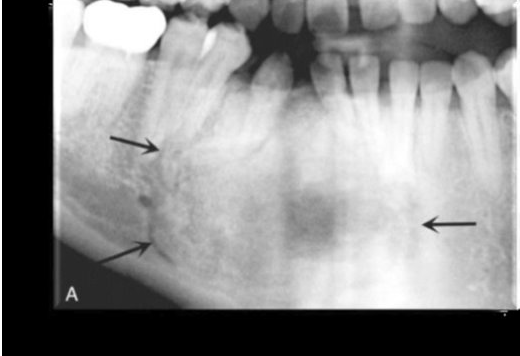
Central-Ossifying Fibroma (CBCT)
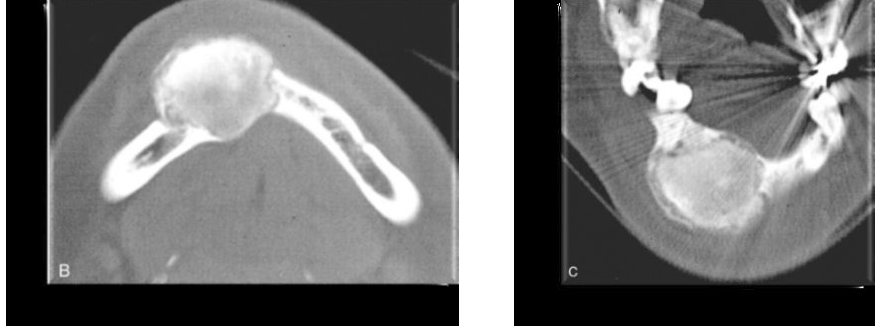
Impacted Tooth
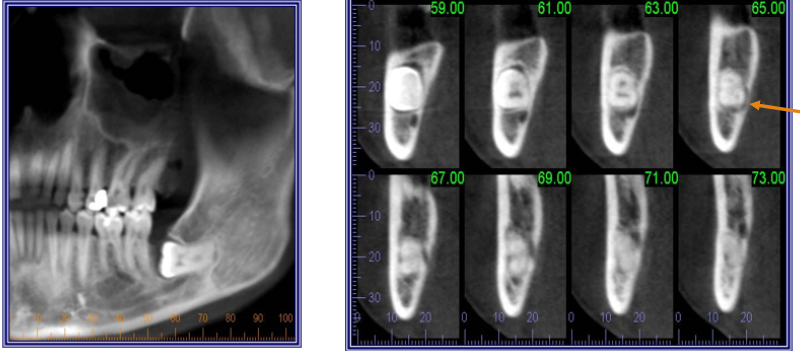
Developmental Abnormalities
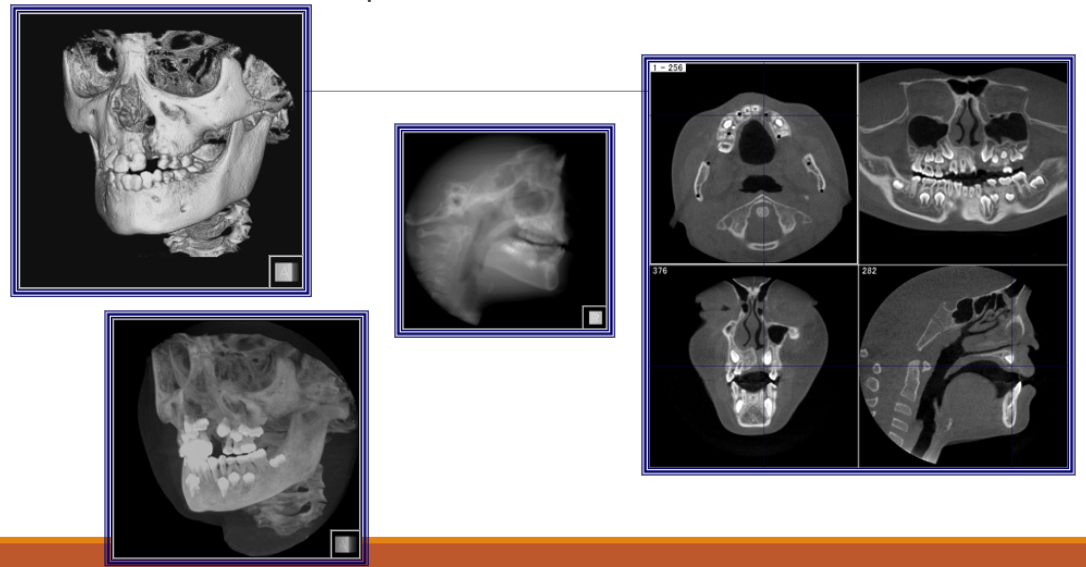
Infection and Bone Loss
Patient Preparation
Patients may be asked to sit or stand or be placed in the supine position during radiation exposure.
Instructions are given to the patient before exposure to remove jewelry, eyeglasses, and removable dental appliances.
A guide may be placed in the patients mouth during the scanning process.
Some specialists may ask that the upper and lower teeth be kept apart.
Patient Positioning
Patient is instructed to remain still.
Scan times vary from 7 to 30 seconds.
Ergonomic head and chin supports have been designed for improved patient comfort.
Laser beams may be installed to help with proper alignment of clinical structures and to ensure correct anatomic positioning.
Advantages
Lower radiation dose – compared to traditional CT scans. (equivalent to three or four full-mouth series of intraoral radiographs)
Brief scanning time
Anatomically accurate images – eliminates the superimposition of structures; little or no magnification of images.
Ability to save and easily transport images – images can be saved to a server or compact disc, printed or emailed.
Disadvantages
Patient movement and artifacts
Size of the field of view – field of view must be appropriate in size to capture the necessary anatomy.
Cost of equipment – CBCT machines range in cost from $150,000. to $300,000. Time and dedication needed to become fully acquainted with the imaging software and correctly interpret and use the images generated.
Lack of training in interpretation of image on data on areas outside the maxilla and the mandible.